Factors Guiding the Orientation of Nymphal Spotted Lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
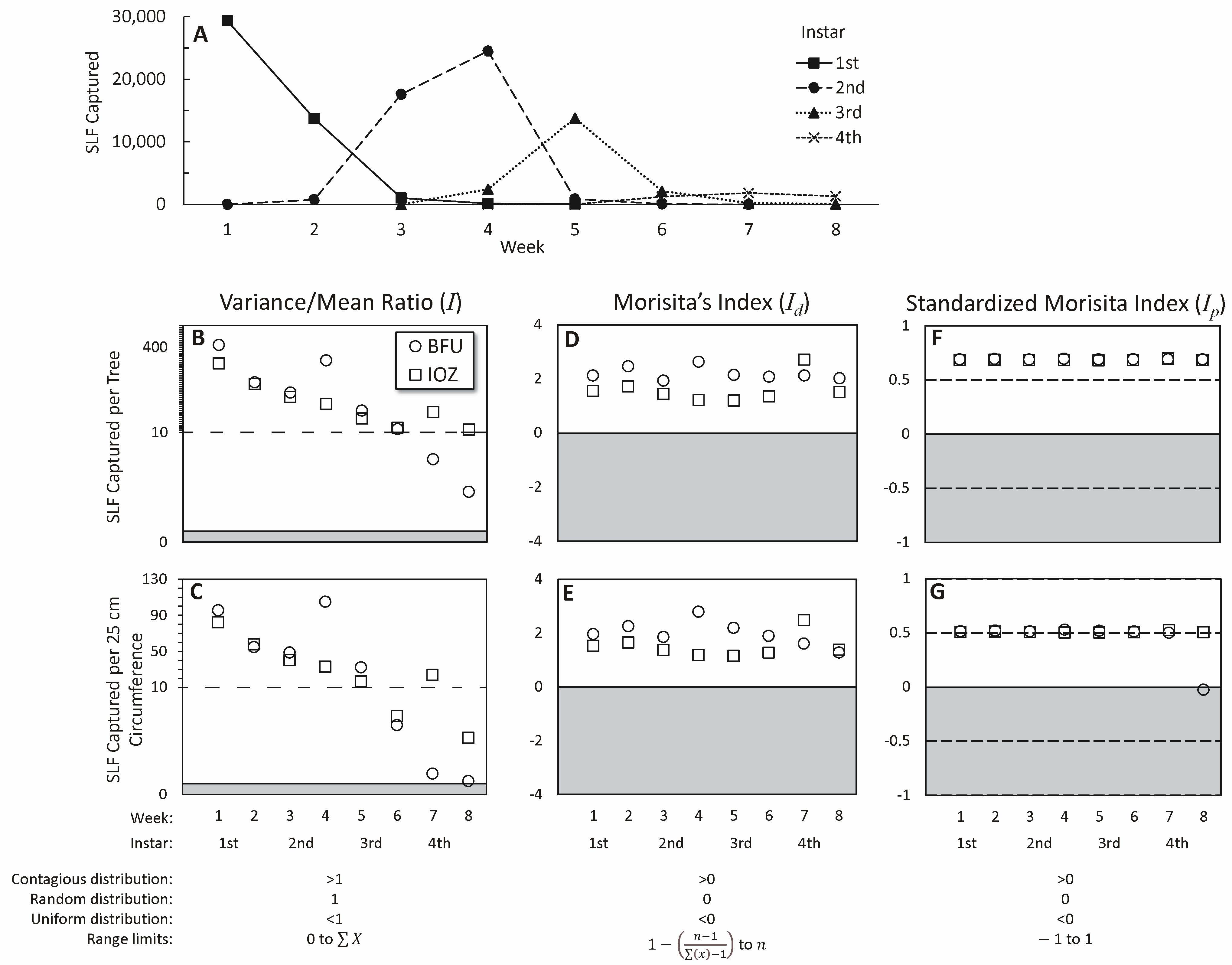
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NYSIPM. New York State Integrated Pest Management: Spotted lanternfly known distribution. Available online: https://nysipm.cornell.edu/environment/invasive-species-exotic-pests/spotted-lanternfly/ (accessed on 17 May 2022).
- Wakie, T.T.; Neven, L.G.; Yee, W.L.; Lu, Z. The establishment risk of Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae) in the United States and globally. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.; Skrip, M.M.; Seliger, B.J.; Jones, S.; Wakie, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Petras, V.; Petrasova, A.; Meentemeyer, R.K. Spotted lanternfly predicted to establish in California by 2033 without preventative management. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G.; Lee, E.-H.; Seo, Y.-M.; Kim, N.-Y. Cyclic behavior of Lycorma delicatula (Insecta: Hemiptera: Fulgoridae) on host plants. J. Insect. Behav. 2011, 24, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Kim, S.; Kwon, S.W.; Lee, S.-I.; Jablonski, P.G. Defense sequestration associated with narrowing of diet and ontogenetic change to aposematic colours in the spotted lanternfly. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barringer, L.E.; Donovall, L.R.; Spichiger, S.-E.; Lynch, D.; Henry, D. The first new world record of Lycorma delicatula (Insecta: Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). Entomol. News 2015, 125, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. Oviposition Substrate Selection, Egg Mass Characteristics, Host Preference, and Life History of the Spotted Lanternfly (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae) in North America. Environ. Entomol. 2019, 48, 1452–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murman, K.; Setliff, G.P.; Pugh, C.V.; Toolan, M.J.; Canlas, I.; Cannon, S.; Abreu, L.; Fetchen, M.; Zhang, L.; Warden, M.L.; et al. Distribution, survival, and development of spotted lanternfly on host plants found in North America. Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 1270–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derstine, N.T.; Meier, L.; Canlas, I.; Murman, K.; Cannon, S.; Carrillo, D.; Wallace, M.; Cooperband, M.F. Plant volatiles help mediate host plant selection and attraction of the spotted lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae): A generalist with a preferred host. Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 1049–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, A.; Kasson, M.; Salom, S.; Davis, D.; Griffin, G.; Kok, L. First report of Verticillium wilt of Ailanthus altissima in Virginia caused by Verticillium nonalfalfae. Plant. Dis. 2013, 97, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barringer, L.; Ciafré, C.M. Worldwide Feeding Host Plants of Spotted Lanternfly, With Significant Additions From North America. Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dara, S.K.; Barringer, L.; Arthurs, S.P. Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae): A new invasive pest in the United States. J. Integr. Pest. Manag. 2015, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooperband, M.F.; Murman, K.; Canlas, I.; Zhang, L.; Wallace, M.S.; Wickham, J.; Swackhamer, E.; Warden, M.L.; Baker, J.; Carrillo, D. Host suitability studies for spotted lanternfly. In Proceedings of the Otis Laboratory 2017 Annual Report; United States Department of Agriculture: Buzzards Bay, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, T.C.; Smyers, E.; Urban, J.; Meng, Z.; Damadaram, K.P.; Myrick, A.J.; Cooperband, M.; Domingue, M. Progression of seasonal activities of adults of the spotted lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula, during the 2017 season of mass flight dispersal behavior in eastern Pennsylvania. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2019, 22, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, J.M. Perspective: Shedding light on spotted lanternfly impacts in the USA. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Tracing the Origin of Korean Invasive Populations of the Spotted Lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). Insects 2021, 12, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Kwon, D.H.; Park, S.; Lee, Y.; Huang, J.; Lee, H.-S.; Hong, K.-J.; Jang, Y.; Lee, S. Molecular comparison of Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae) isolates in Korea, China, and Japan. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2013, 16, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.M.; Hyojoong, K.; Lim, E.J.; Lee, S.; Kwon, Y.-J.; Cho, S. Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Auchenorrhyncha: Fulgoridae: Aphaeninae) finally, but suddenly arrived in Korea. Entomol. Res. 2008, 38, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-E.; Moon, S.-R.; Ahn, H.-G.; Cho, S.-R.; Yang, J.-O.; Yoon, C.; Kim, G.-H. Feeding behavior of Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae) and response on feeding stimulants of some plants. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2009, 48, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-D.; Kim, M.-Y.; Lee, S.-G.; Shin, S.-C.; Kim, J.; Park, I.-K. Biological characteristics of Lycorma delicatula and the control effects of some insecticides. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2009, 48, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Fu, W.; Reardon, R.; Liu, M. Assessing potential biological control of the invasive plant, tree-of-heaven, Ailanthus altissima. Biocontrol. Sci. Technol. 2006, 16, 547–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.K. Damage by Lycorma delicatula and Chemical Control in Vineyards. Master’sThesis, Chunbuk National University, Cheongju, Republic of Korea, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Urban, J.M.; Leach, H. Biology and Management of the Spotted Lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae), in the United States. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2022, 68, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, A.; Leach, H. Characterizing the spatial distributions of spotted lanternfly (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae) in Pennsylvania vineyards. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.J.; Walsh, B.; Keller, J.; Couture, J.J.; Calvin, D.; Urban, J.M. Fidelity and Timing of Spotted Lanternfly (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae) Attack Patterns on Ornamental Trees in the Suburban Landscape. Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooperband, M.F.; Murman, K. Responses of adult spotted lanternflies to artificial aggregations composed of all males or females. Front. Insect. Sci. 2022, 2, 981832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvin, D.D.; Keller, J.; Rost, J.; Walsh, B.; Biddinger, D.; Hoover, K.; Treichler, B.; Johnson, A.; Roush, R.T. Spotted Lanternfly (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae) Nymphal Dispersion Patterns and Their Influence on Field Experiments. Environ. Entomol. 2021, 50, 1490–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faal, H.; Meier, L.R.; Canlas, I.J.; Murman, K.; Wallace, M.S.; Carrillo, D.; Cooperband, M.F. Volatiles from male honeydew excretions attract conspecific male spotted lanternflies, Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). Front. Insect. Sci. 2022, 2, 982965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faal, H.; Canlas, I.; Carrillo, D.; Cooperband, M.F. Evidence of pheromone use in a fulgorid, spotted lanternfly. Forests 2022, 13, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, B.B.; Cooperband, M.F.; Canlas, I.; Mankin, R.W. Evidence of receptivity to vibroacoustic stimuli in the spotted lanternfly. J. Econ. Entomol. 2022, 115, 2116–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.; Myrick, A.; Wolfin, M.; Wang, Y. Visual Responses of Flight-Dispersing Spotted Lanternflies, Lycorma delicatula toward a Tall Vertical Silhouette in a Vineyard. J. Insect. Behav. 2021, 34, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francese, J.A.; Cooperband, M.F.; Murman, K.M.; Cannon, S.L.; Booth, E.G.; Devine, S.M.; Wallace, M.S. Developing traps for the spotted lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooperband, M.F.; Wickham, J.; Cleary, K.; Spichiger, S.-E.; Zhang, L.; Baker, J.; Canlas, I.; Derstine, N.; Carrillo, D. Discovery of three kairomones in relation to trap and lure development for spotted lanternfly (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooperband, M.F.; Canlas, I.; Meier, L.R.; Murman, K.; Cannon, S.; Stella, S.; Jones, T.; Ray, A.M.; Carrillo, D.; Wallace, M.S. Semiochemicals and Behavior of Spotted Lanternfly; United States Department of Agriculture: Buzzards Bay, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Nixon, L.J.; Leach, H.; Barnes, C.; Urban, J.; Kirkpatrick, D.M.; Ludwick, D.C.; Short, B.; Pfeiffer, D.G.; Leskey, T.C. Development of Behaviorally Based Monitoring and Biosurveillance Tools for the Invasive Spotted Lanternfly (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derstine, N.; Canlas, I.; Baker, J.; Carrillo, D.; Cooperband, M.F. Dispersal of spotted lanternfly in a tree of heaven forest habitat. In Proceedings of the Otis Laboratory 2017 Annual Report; United States Department of Agriculture: Buzzards Bay, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M.; Walker, S.C. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, J.F. Biometry, 3rd ed.; W. H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Rohlf, F.J.; Sokal, R.R. Statistical Tables; W. H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Krebs, C.J. Ecological Methodology, 2nd ed.; Addison-Welsey Educational Publishers, Inc.: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 1999; p. 620. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.G.; Barbosa, J.C.; Yamamoto, P.T.; Leal, R.M. Spatial distribution of Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) in citrus orchards. Sci. Agric. 2010, 67, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.H. Measurement of non-randomness in spatial distributions. Res. Popul. Ecol. 1966, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisita, M. Measuring of the dispersion of individuals and analysis of the distributional patterns. Mem. Fac. Sci. Kyushu Univ. Ser. E (Biol.) 1959, 2, 215–235. [Google Scholar]
- Bakus, G.J. Chapter 3: Quantitative methods in field ecology and other useful techniques. In Quantitative Analysis of Marine Biological Communities: Field Biology and Environment; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 123–208. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Hartlieb, R.J. Spatial distribution of Lycorma delicatula (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae) egg masses on tree-of-heaven, black walnut, and Siberian elm in North America. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 1028–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; Rost, J.; Hoover, K.; Urban, J.; Leach, H.; Porras, M.; Walsh, B.; Bosold, M.; Calvin, D. Dispersion patterns and sample size estimates for egg masses of spotted lanternfly (Hemiptera: Fulgoridae). Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 1462–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liang, A.-P. Identification of a self-regulatory pheromone system that controls nymph aggregation behavior of rice spittlebug Callitettix versicolor. Front. Zool. 2015, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, J.R. Chemical ecology of the Heteroptera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1988, 33, 211–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, J.G. Pheromones of true bugs. In The Chemistry of Pheromones and Other Semiochemicals II; Schulz, S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Gaermany, 2005; Volume 240, pp. 37–84. [Google Scholar]
- Nault, L.; Montgomery, M. Aphid pheromones. In Aphids as Virus Vectors; Harris, K.F., Maramorosch, K., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 527–545. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.T.; Maschwitz, U. Sexual pheromone in the Green House Whitefly Trialeurodes vaporariorum Westw. Z. Für Angew. Entomol. 1983, 95, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkens, D.M.; McElfresh, J.S.; Millar, J.G. Identification and synthesis of the sex pheromone of the vine mealybug, Planococcus ficus. Tetrahedron. Lett. 2001, 42, 1619–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenninger, E.J.; Stelinski, L.L.; Hall, D.G. Behavioral evidence for a female-produced sex attractant in Diaphorina citri. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2008, 128, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cooperband, M.F.; Wickham, J.D.; Warden, M.L. Factors Guiding the Orientation of Nymphal Spotted Lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula. Insects 2023, 14, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14030279
Cooperband MF, Wickham JD, Warden ML. Factors Guiding the Orientation of Nymphal Spotted Lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula. Insects. 2023; 14(3):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14030279
Chicago/Turabian StyleCooperband, Miriam F., Jacob D. Wickham, and Melissa L. Warden. 2023. "Factors Guiding the Orientation of Nymphal Spotted Lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula" Insects 14, no. 3: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14030279
APA StyleCooperband, M. F., Wickham, J. D., & Warden, M. L. (2023). Factors Guiding the Orientation of Nymphal Spotted Lanternfly, Lycorma delicatula. Insects, 14(3), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14030279





