Disruptive Effects of Two Curcuminoids (Demethoxycurcumin and Bisdemethoxycurcumin) on the Larval Development of Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
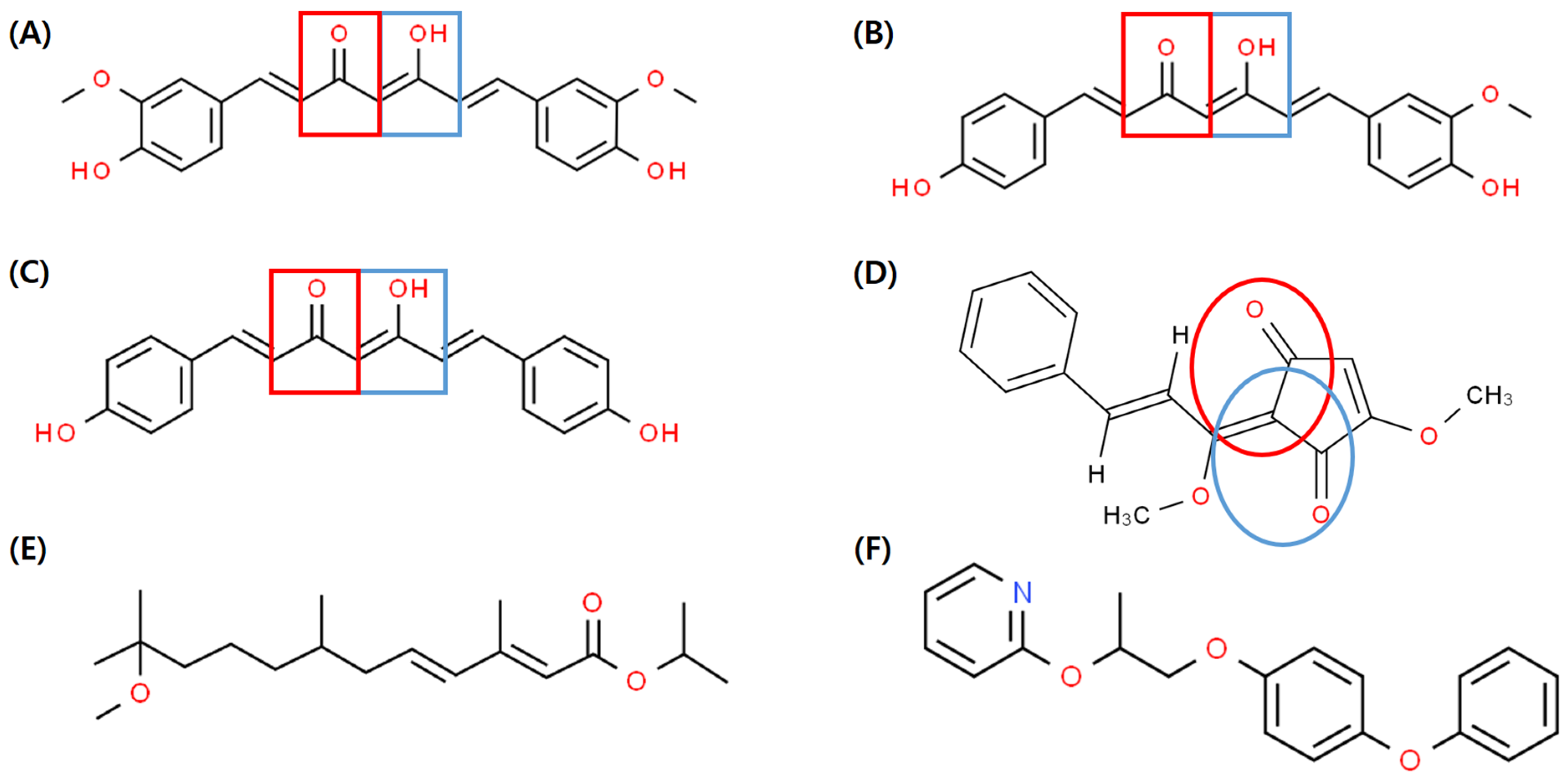
2.1. Chemicals and Insects
2.2. Yeast β–Galactosidase Assay
2.3. Bioassay
2.4. RNA Extraction, Primers, and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
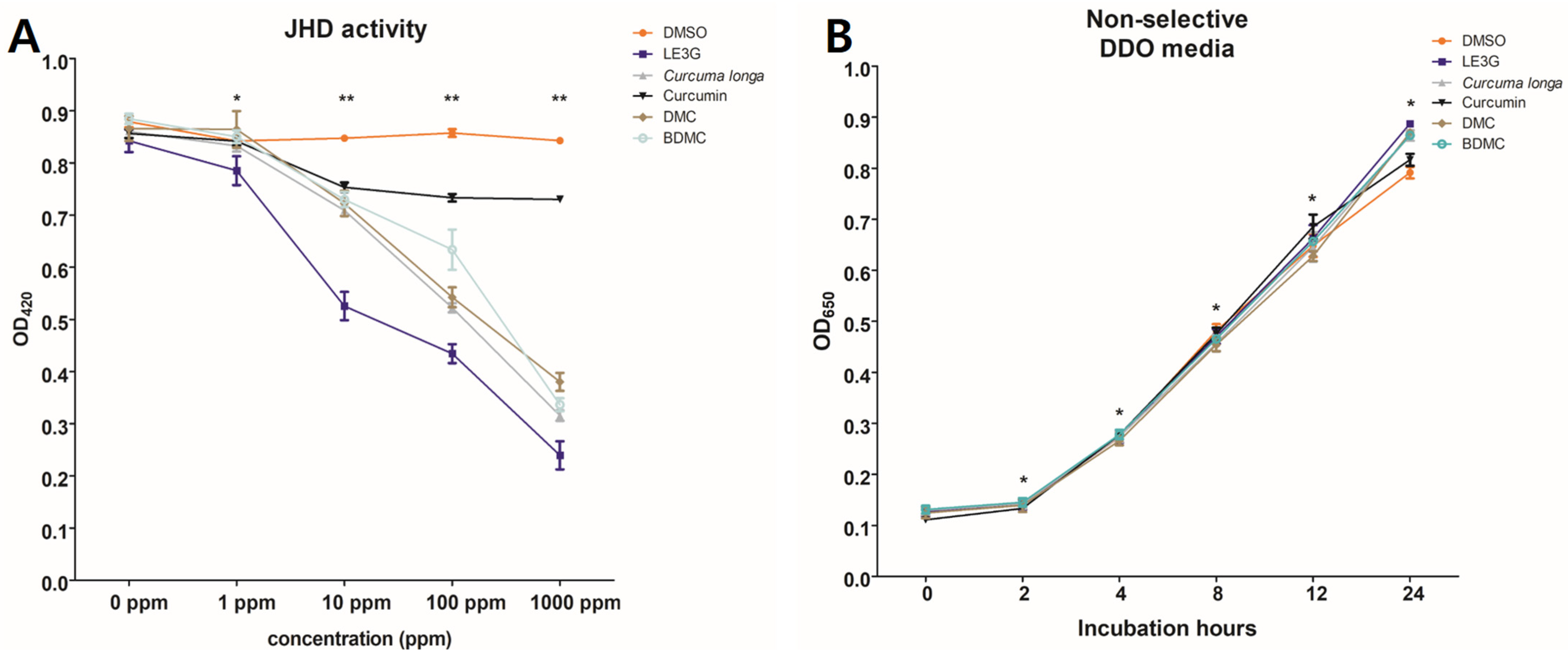
3.1. JHD Activity of Plant Extracts
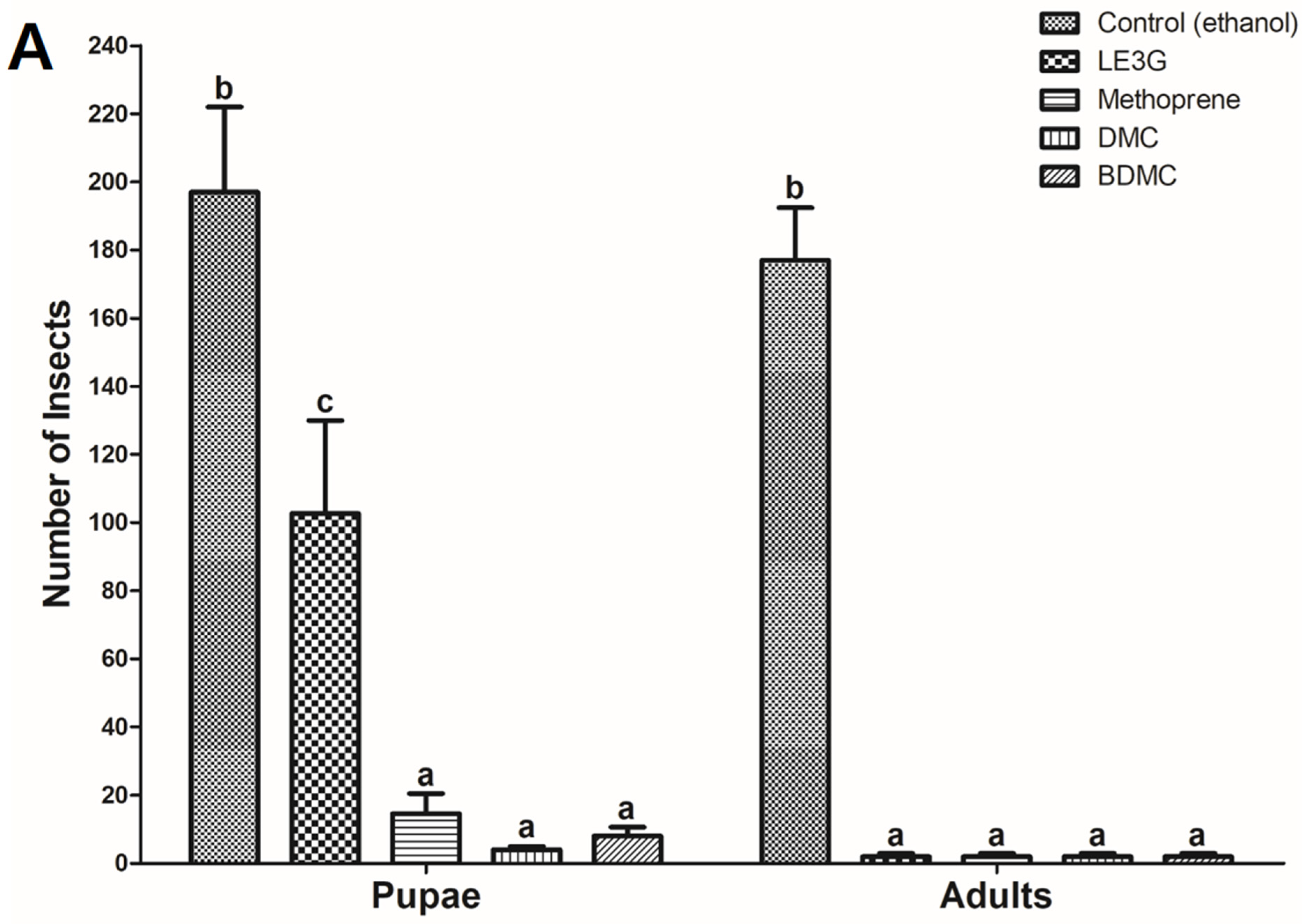
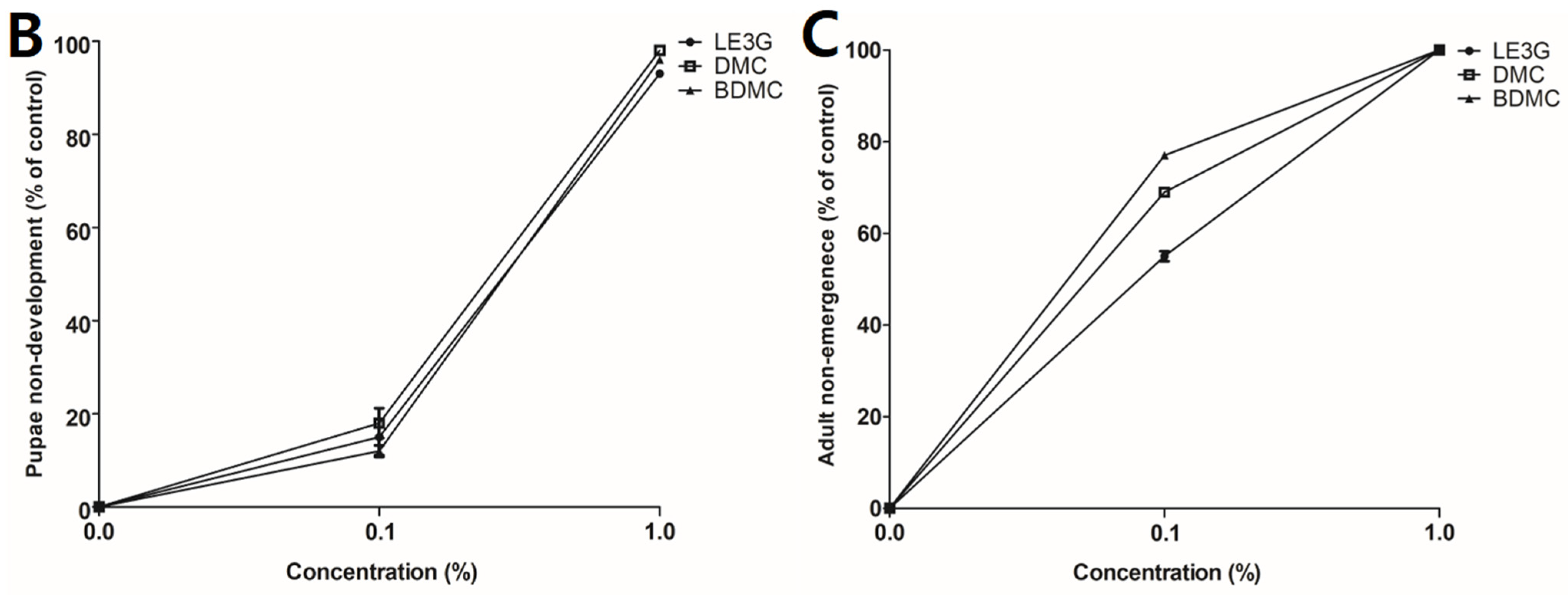
3.2. Changes in the Emergence Rates of D. melanogaster Larvae According to the Diet
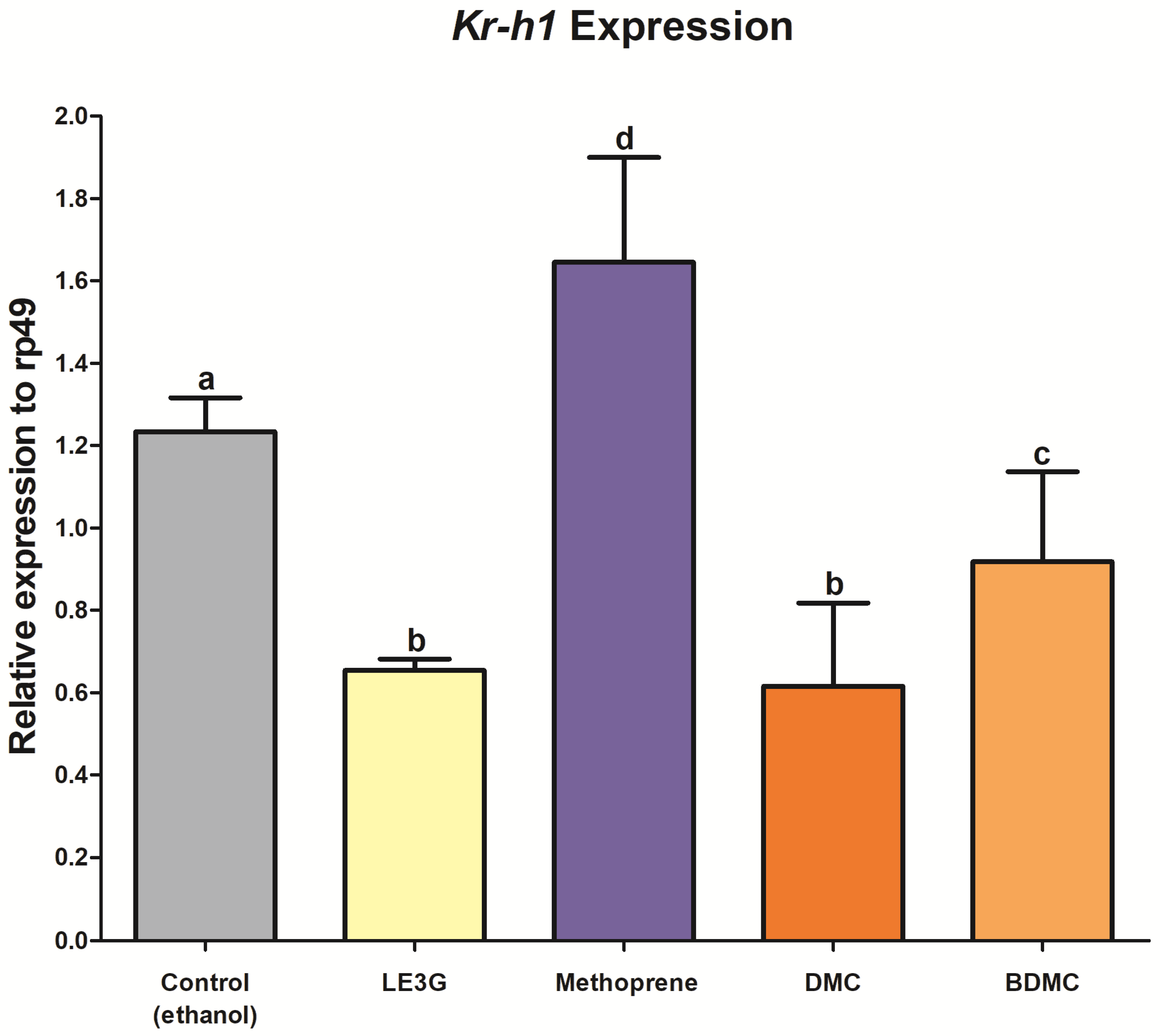
3.3. DMC and BDMC Effects on JH-Dependent Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacey, L.A.; Lacey, C.M. The medical importance of riceland mosquitoes and their control using alternatives to chemical insecticides. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. Suppl. 1990, 2, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Isman, M.B. Botanical insecticides, deterrents, and repellents in modern agriculture and an increasingly regulated world. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattan, R.S. Mechanism of action of insecticidal secondary metabolites of plant origin. Crop Prot. 2010, 29, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalraj, A.; Kuttappan, S.; Matharu, A. Herbs, Spices and Their Roles in Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.A.; Kitts, D.D. Turmeric and its bioactive constituents trigger cell signaling mechanisms that protect against diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 3785–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotha, R.R.; Luthria, D.L. Curcumin: Biological, pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and analytical aspects. Molecules 2019, 24, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, K.M.; Dahlin, J.L.; Bisson, J.; Graham, J.; Pauli, G.F.; Walters, M.A. The essential medicinal chemistry of curcumin: Miniperspective. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1620–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, a component of golden spice: From bedside to bench and back. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esatbeyoglu, T.; Huebbe, P.; Ernst, I.M.; Chin, D.; Wagner, A.E.; Rimbach, G. Curcumin—From molecule to biological function. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5308–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motterlini, R.; Foresti, R.; Bassi, R.; Green, C.J. Curcumin, an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, induces heme oxygenase-1 and protects endothelial cells against oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labban, L. Medicinal and pharmacological properties of Turmeric (Curcuma longa): A review. Int. J. Pharm. Biomed. Sci. 2014, 5, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Durgaprasad, S.; Pai, C.G.; Alvres, J.F. A pilot study of the antioxidant effect of curcumin in tropical pancreatitis. Indian J. Med. Res. 2005, 122, 315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, P.; Babu, K.N.; Sivaraman, K. Turmeric: The Genus Curcuma; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, S.; Sarma, G.C.; Rangan, L. Ethnomedical uses of Zingiberaceous plants of Northeast India. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 132, 286–296. [Google Scholar]
- Solsoloy, A.; Cacayorin, N.; Cano, L. Insecticidal and fungicidal action of some indigenous plant extracts against cotton pests. Cotton Res. J. 1991, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Aurade, R.M.; Jayalakshmi, S.K.; Sreeramulu, K. Modulatory effects of natural curcuminoids on P-glycoprotein ATPase of insecticide-resistant pest Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidopetera: Noctüidae). J. Membr. Biol. 2010, 236, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, G.N.; Chandra, A.; Nair, M.G. Novel bioactivities of Curcuma longa constituents. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiadis, D.; Liggri, P.G.; Kritsi, E.; Tzioumaki, N.; Zoumpoulakis, P.; Papachristos, D.P.; Balatsos, G.; Sagnou, M.; Michaelakis, A. Curcumin derivatives as potential mosquito larvicidal agents against two mosquito vectors, Culex pipiens and Aedes albopictus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.; Goswami, D.; Rawal, R.M. Revealing the molecular interplay of curcumin as Culex pipiens Acetylcholine esterase 1 (AChE1) inhibitor. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Silva, A.S.; Varshney, R.; Chávez-González, M.L.; Singh, P. Curcuma-based botanicals as crop protectors: From knowledge to application in food crops. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2021, 3, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truman, J.W.; Riddiford, L.M. The morphostatic actions of juvenile hormone. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindra, M.; Palli, S.R.; Riddiford, L.M. The juvenile hormone signaling pathway in insect development. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mead, E.A.; Zhu, J. Heterodimer of two bHLH-PAS proteins mediates juvenile hormone-induced gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Oda, M.; Makita, S.; Chinzei, Y. Characterization of the Drosophila Methoprene- tolerant gene product. Juvenile hormone binding and ligand-dependent gene regulation. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, J.P.; Iwema, T.; Epa, V.C.; Takaki, K.; Rynes, J.; Jindra, M. Ligand-binding properties of a juvenile hormone receptor, Methoprene-tolerant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 21128–21133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayukawa, T.; Minakuchi, C.; Namiki, T.; Togawa, T.; Yoshiyama, M.; Kamimura, M.; Mita, K.; Imanishi, S.; Kiuchi, M.; Ishikawa, Y.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of juvenile hormone-mediated induction of Kruppel homolog 1, a repressor of insect metamorphosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11729–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kewley, R.J.; Whitelaw, M.L.; Chapman-Smith, A. The mammalian basic helix–loop–helix/PAS family of transcriptional regulators. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumova, S.; Milacek, M.; Šnajdr, I.; Muthu, M.; Tuma, R.; Reha, D.; Jedlicka, P.; Bittova, L.; Novotna, A.; Majer, P. Unique peptidic agonists of a juvenile hormone receptor with species-specific effects on insect development and reproduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2215541119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Oh, H.W.; Fang, Y.; An, S.B.; Park, D.S.; Song, H.H.; Oh, S.R.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, N.; et al. Identification of plant compounds that disrupt the insect juvenile hormone receptor complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.W.; Yun, C.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, J.A.; Park, D.S.; Ryu, H.W.; Oh, S.R.; Song, H.H.; Shin, Y.; Jung, C.S.; et al. Conifer Diterpene Resin Acids Disrupt Juvenile Hormone-Mediated Endocrine Regulation in the Indian Meal Moth Plodia interpunctella. J. Chem. Ecol. 2017, 43, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.W.; Jeon, J.H.; Jeong, S.A.; Kim, J.A.; Park, D.S.; Shin, Y.; Oh, H.W. A plant diterpene counteracts juvenile hormone-mediated gene regulation during Drosophila melanogaster larval development. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.W.; Jeon, J.H.; Yun, C.S.; Jeong, S.A.; Kim, J.A.; Park, D.S.; Shin, Y.; Oh, H.W. Species-Specific Interactions between Plant Metabolites and Insect Juvenile Hormone Receptors. J. Chem. Ecol. 2018, 44, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wink, M. Plant Secondary Metabolites Modulate Insect Behavior-Steps Toward Addiction? Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khare, S.; Singh, N.; Singh, A.; Hussain, I.; Niharika, K.; Yadav, V.; Bano, C.; Yadav, R.K.; Amist, N. Plant secondary metabolites synthesis and their regulations under biotic and abiotic constraints. J. Plant Biol. 2020, 63, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrid, R.B.; Benmrid, B.; Hafsa, J.; Boukcim, H.; Sobeh, M.; Yasri, A. Secondary metabolites as biostimulant and bioprotectant agents: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divekar, P.A.; Narayana, S.; Divekar, B.A.; Kumar, R.; Gadratagi, B.G.; Ray, A.; Singh, A.K.; Rani, V.; Singh, V.; Singh, A.K. Plant secondary metabolites as defense tools against herbivores for sustainable crop protection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, P.; Dubey, N. Exploitation of natural products as an alternative strategy to control postharvest fungal rotting of fruit and vegetables. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2004, 32, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Sriranjini, V. Plant products as fumigants for stored-product insect control. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2008, 44, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damalas, C.A. Potential uses of turmeric (‘Curcuma longa’) products as alternative means of pest management in crop production. Plant Omics 2011, 4, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Sagnou, M.; Mitsopoulou, K.; Koliopoulos, G.; Pelecanou, M.; Couladouros, E.; Michaelakis, A. Evaluation of naturally occurring curcuminoids and related compounds against mosquito larvae. Acta Trop. 2012, 123, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, H.; Walia, S.; Saxena, V.S. Isolation, characterization and insect growth inhibitory activity of major turmeric constituents and their derivatives against Schistocerca gregaria (Forsk) and Dysdercus koenigii (Walk). Pest Manag. Sci. Former. Pestic. Sci. 2000, 56, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahne, F.; Mohammadi, M.; Najafpour, G.D.; Moghadamnia, A.A. Enzyme-assisted ionic liquid extraction of bioactive compound from turmeric (Curcuma longa L.): Isolation, purification and analysis of curcumin. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 95, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siviero, A.; Gallo, E.; Maggini, V.; Gori, L.; Mugelli, A.; Firenzuoli, F.; Vannacci, A. Curcumin, a golden spice with a low bioavailability. J. Herb. Med. 2015, 5, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sláma, K. The history and current status of juvenoids. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Urban Pests, Hronov, Czech Republic, 19–22 July 1999; pp. 9–25. [Google Scholar]
- Senthil Kumar, K.; Wang, S.-Y. Pharmacological Applications of Lucidone: A Naturally Occurring Cyclopentenedione. In Medicinal Plants—Recent Advances in Research and Development; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 273–295. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.-W.; Jeon, J.-H.; Kim, J.-A.; Park, D.-S.; Shin, Y.-J.; Oh, H.-W. Inducible Expression of Several Drosophila melanogaster Genes Encoding Juvenile Hormone Binding Proteins by a Plant Diterpene Secondary Metabolite, Methyl Lucidone. Insects 2022, 13, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Primer |
|---|---|
| Krüppel homolog 1 | Forward 5′-TCACACATCAAGAAGCCAACT-3′ Reverse 5′-GCTGGTTGGCGGAATAGTAA-3′ |
| Rp49 | Forward 5′-ATGCTAAGCTGTCGCACAAATG-3′ Reverse 5′-GTTCGATCCGTAACCGATGT-3′ |
| Species | Plant Part | Family | JHD Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Curcuma longa L. | Root | Zingiberaceae | 1.217175 |
| Pulsatilla koreana Nakai | Root | Ranunculaceae | 1.101688 |
| Machilus thunbergii Siebold & Zucc. | Trunk-bark | Lauraceae | 1.056931 |
| Echinosophora koreensis Nakai | Root | Fabaceae | 0.960778 |
| Pinus densiflora Siebold & Zucc. | Trunk-bark | Pinaceae | 0.936298 |
| Alpinia officinarum | Root | Zingiberaceae | 0.904591 |
| Smilax sieboldii Miq. | Leaf | Liliaceae | 0.886733 |
| Scutellaria baicalensis | Flower | Labiatae | 0.825496 |
| Portulaca oleracea L. | Whole | Portulacaceae | 0.806894 |
| Magnolia kobus DC | Leaf | Magnoliaceae | 0.785417 |
| Broussonetia papyrifera (L.) L’Hér. ex Vent. | Leaf | Moraceae | 0.768187 |
| Syringa patula (Palib.) Nakai | Leaf | Oleaceae | 0.759335 |
| Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb. | Whole | Rosaceae | 0.750968 |
| Cudrania tricuspidata (Carr.) Bureau ex Lavallée | Fruit | Moraceae | 0.745534 |
| Psoralea corylifolia (Babchi) | Seed | Fabaceae | 0.658419 |
| Phlomis umbrosa Turcz. | Whole | Labiatae | 0.65772 |
| Cudrania tricuspidata (Carr.) Bureau ex Lavallée | Trunk | Moraceae | 0.613586 |
| Zingiber officinale | Root | Zingiberaceae | 0.546682 |
| Myristica fragrans | Seed | Myristicaceae | 0.535624 |
| Saururus chinensis (Lour.) Baill. | Whole | Saururaceae | 0.493735 |
| Glycyrrhiza uralensis | Root | Fabaceae | 0.469728 |
| Picrasma quassioides (D. Don) Benn. | Trunk | Simaroubaceae | 0.433324 |
| Sophora flavescens | Root | Fabaceae | 0.391224 |
| Morus alba L. | Root | Moraceae | 0.390836 |
| Actinostemma lobatum Maxim. | Whole | Cucurbitaceae | 0.381283 |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge | Whole | Labiatae | 0.363577 |
| Cudrania tricuspidata (Carr.) Bureau ex Lavallée | Root | Moraceae | 0.257315 |
| Eclipta prostrata | Whole | Compositae | 0.237714 |
| Magnolia obovata Thunb | Trunk-bark | Lauraceae | 0.176234 |
| Angelica keiskei | Leaf | Apiaceae | 0.134399 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, J.-H.; Jeong, S.-A.; Park, D.-S.; Park, H.-H.; Shin, S.-W.; Oh, H.-W. Disruptive Effects of Two Curcuminoids (Demethoxycurcumin and Bisdemethoxycurcumin) on the Larval Development of Drosophila melanogaster. Insects 2023, 14, 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14120959
Jeon J-H, Jeong S-A, Park D-S, Park H-H, Shin S-W, Oh H-W. Disruptive Effects of Two Curcuminoids (Demethoxycurcumin and Bisdemethoxycurcumin) on the Larval Development of Drosophila melanogaster. Insects. 2023; 14(12):959. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14120959
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Jun-Hyoung, Seon-Ah Jeong, Doo-Sang Park, Hong-Hyun Park, Sang-Woon Shin, and Hyun-Woo Oh. 2023. "Disruptive Effects of Two Curcuminoids (Demethoxycurcumin and Bisdemethoxycurcumin) on the Larval Development of Drosophila melanogaster" Insects 14, no. 12: 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14120959
APA StyleJeon, J.-H., Jeong, S.-A., Park, D.-S., Park, H.-H., Shin, S.-W., & Oh, H.-W. (2023). Disruptive Effects of Two Curcuminoids (Demethoxycurcumin and Bisdemethoxycurcumin) on the Larval Development of Drosophila melanogaster. Insects, 14(12), 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14120959






