Aphid Resistance Evaluation and Constitutive Resistance Analysis of Eighteen Lilies
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Preparation
2.2. Aphid Rear
2.3. Aphid Resistance Test
2.3.1. Greenhouse Test
2.3.2. Field Test
2.4. Determination of Biological Parameters of Lily Leaf
2.4.1. Leaf Preparation
2.4.2. Leaf Color
2.4.3. Leaf Stomata
2.4.4. Leaf Anatomical Structure
2.4.5. Leaf Waxy Content
2.4.6. Leaf Water Content
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Aphid Resistance
3.2. Leaf Color
3.3. Leaf Stomata
3.4. Leaf Anatomical Structure
3.5. Leaf Waxy Content
3.6. Leaf Water Content
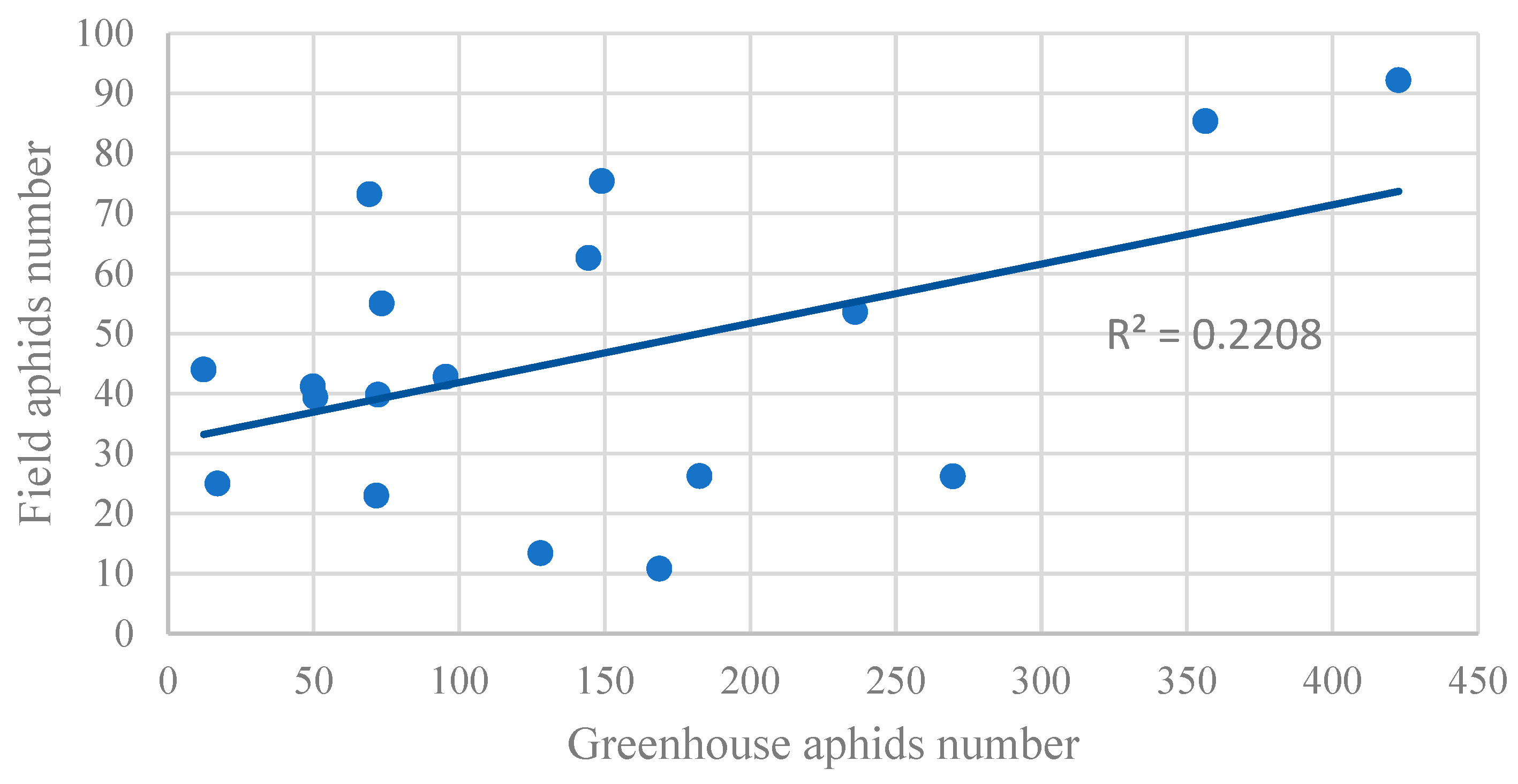
3.7. Correlation between the Aphid Population and Biological Parameters of Lily Leaves
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H. Why are agricultural pests becoming more and more harmful? Agric. Hist. China 2021, 40, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Song, J.; Wu, X.B.; Deng, Q.Q.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Ren, M.J.; Ye, M.; Zeng, R.S. Seed priming with calcium chloride enhances wheat resistance against wheat aphid Schizaphis graminum Rondani. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 4709–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, T.; Liu, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, Z. Identification of aphid resistance in lily. North. Hortic. 2018, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, L.; Guo, X.; Zhao, A.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, X. Combined analysis of metabolome and transcriptome of wheat kernels reveals constitutive defense mechanism against maize weevils. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1147145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, D.A.; Ibrahim, E.S.; Salama, M.R. Effectiveness and persistence of some synthetic insecticides and their nanoformulation against whitefly (Bemisia tabaci) and aphids (Aphis craccivora) on fennel plants and soil. Egypt. J. Chem. 2023, 66, 235–246. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, K.; He, D.; Guo, J.; Li, G.; Li, B.; Chen, X. Molecular advances in breeding for durable resistance against pests and diseases in wheat: Opportunities and challenges. Agronomy 2023, 13, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wumuerhan, P.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, D. Effects of exposure to imidacloprid direct and poisoned cotton aphids Aphis gossypii on ladybird Hippodamia variegata feeding behavior. J. Pestic. Sci. 2020, 45, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Weng, X.; Gao, L.; Chang, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z. Identification and characterization of resistance of three aphid species on contrasting alfalfa cultivars. Insects 2022, 13, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuman, M.C.; Baldwin, I.T. The layers of plant responses to insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 373–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Baldwin, I.T. New insights into plant responses to the attack from insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2010, 44, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.A. Induced responses to herbivory and increased plant performance. Science 1998, 279, 1201–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, I.T. An ecologically motivated analysis of plant-herbivore interactions in native tobacco. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furstenberg-Hagg, J.; Zagrobelny, M.; Bak, S. Plant defense against insect herbivores. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10242–10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cribb, B.W.; Hanan, J.; Zalucki, M.P.; Perkins, L.E. Effects of plant micro-environment on movement of Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) larvae and the relationship to a hierarchy of stimuli. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2010, 4, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triplett, E.; Hayes, C.; Emendack, Y.; Longing, S.; Monclova, C.; Simpson, C.; Laza, H.E. Leaf structural traits mediating pre-existing physical innate resistance to sorghum aphid in sorghum under uninfested conditions. Planta 2023, 258, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, Z.M.; Malik, T.A.; Azhar, F.M.; Ashraf, M. Natural resistance against insect pests in cotton. J Anim. Plant Sci. 2016, 26, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Menzies, I.J.; Youard, L.W.; Lord, J.M.; Carpenter, K.L.; van Klink, J.W.; Perry, N.B.; Schaefer, H.M.; Gould, K.S. Leaf colour polymorphisms: A balance between plant defence and photosynthesis. J. Ecol. 2016, 104, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobożniak, M.; Olczyk, M.; Wójtowicz, T. Relationship between colonization by onion thrips (Thrips tabaci Lind.) and leaf colour measures across eight onion cultivars (Allium cepa L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, L.D.J.; Maciel, O.V.B.; Bücker-Neto, L.; Pilati, L.; Morozini, A.M.; Faria, M.V.; Da-Silva, P.R. A comprehensive analysis of wheat resistance to Rhopalosiphum padi (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in brazilian wheat cultivars. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saska, P.; Skuhrovec, J.; Tylová, E.; Platková, H.; Tuan, S.; Hsu, Y.; Vítámvás, P. Leaf structural traits rather than drought resistance determine aphid performance on spring wheat. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; An, R.; Huang, X. Genus Lilium: A review on traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 270, 113852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Guo, C.; Yan, C.; Sun, R.; Li, Y. Genetic diversity and phylogenetic characteristics of viruses in lily plants in Beijing. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1127235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; He, J.; Wu, J.; Gong, B.; Cao, X.; Seng, S.; Wu, Z.; Wu, C.; Liu, C.; Yi, M. Characterization and functional analysis of transcription factor LoMYB80 related to anther development in lily (Lilium Oriental Hybrids). J. Plant Growth. Regul. 2015, 34, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xin, C.; Li, D.; Sun, M.; Shi, L. Analysis of edible characteristics, antioxidant capacities, and phenolic pigment monomers in Lilium bulbs native to China. Food Res. Int. 2022, 151, 110854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yang, P.; Xu, L.; Ming, J. Identification of resistance to Aphis gossypii Glover and genetic diversity analysis of lily resources. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 2021, 52, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Sochacki, D.; Treder, J. A survey of viruses’ occurrence in polish and imported tulip bulbs. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2017, 16, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Wang, H. Photographic Atlas of Beijing Aphids (Aphidoidea); Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Zhong, T. Economic Insect Fauna of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1983; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, J.; Guo, Y.; Shi, H.; Liang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, M. Volatiles mediated an eco-friendly aphid control strategy of Chrysanthemum genus. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 180, 114734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Su, L.; Li, G.; Huang, Z.; Huang, D.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Y. Expression of Pinellia pedatisecta agglutinin PPA gene in transgenic sugarcane led to stomata patterning change and resistance to sugarcane woolly aphid, Ceratovacuna lanigera Zehntner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wu, L.; Liu, Q.; Luo, B. Correlation between population size of pear Psylla (Cacopsylla chinensis) and leaf structure features in different pear cultivars. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2019, 22, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; He, X.; He, H.; Liu, W. Effects of physical characteristics of Rhododendron leaves on host selection of Stephanitis pyriodes Scott. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 33, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhou, G.; He, Q.; Zhou, L.; Ji, Y.; Lv, X. Capability of leaf water content and its threshold values in reflection of soil–plant water status in maize during prolonged drought. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, S.; Ni, X.; Buntin, G.D.; Toews, M.D. Parasitism of Melanaphis sacchari (Hemiptera: Aphididae) by Lysiphlebus testaceipes (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) in the greenhouse and field. J. Entomol. Sci. 2020, 55, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liang, X.; Wu, C. Trait inheritance in pepper (Capsicum spp.) cultivars identified as resistant to green peach aphid (Myzus persicae). Plant Breed. 2020, 139, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondon, S.I.; Cantliffe, D.J.; Price, J.F. Population dynamics of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii (Homoptera: Aphididae), on strawberries grown under protected structure. Fla. Entomol. 2005, 88, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Darshanee, H.L.C.; Fu, W.; Hu, X.; Fan, Y.; Liu, T. Resistance of seven cabbage cultivars to green peach aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, M.L.; Glinwood, R.; Ignell, R.; Krueger, K. Visual cues and host-plant preference of the bird cherry-oat aphid, Rhopalosiphum padi (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Afr. Entomol. 2014, 22, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doering, T.F.; Chittka, L. Visual ecology of aphids-a critical review on the role of colours in host finding. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2007, 1, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Yao, X.; Luo, C.; Hu, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, H. Biological and morphological features associated with English grain aphid and bird cherry-oat aphid tolerance in winter wheat line XN98-10-35. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 38, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zou, L.; Kuang, R.; He, L. Influence of leaf tissue structure on host feeding selection by pea leafminer Liriomyza Huidobrensis (Diptera: Agromyzidae). Zool. Stud. 2000, 39, 295–300. [Google Scholar]
- Kerstiens, G. Plant cuticles—An integrated functional approach. J. Exp. Bot. 1996, 47, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reifenrath, K.; Riederer, M.; Müller, C. Leaf surface wax layers of Brassicaceae lack feeding stimulants for Phaedon cochleariae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2005, 115, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompon, J.; Quiring, D.; Giordanengo, P.; Pelletier, Y. Role of host-plant selection in resistance of wild Solanum species to Macrosiphum euphorbiae and Myzus persicae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2010, 137, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenbrode, S.D.; Kabalo, N.N. Effects of Brassica oleracea waxblooms on predation and attachment by Hippodamia convergens. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2010, 91, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenbrode, S.D.; White, C.; Rohde, M.; Simon, C.J. Behavior and effectiveness of adult Hippodamia convergens (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) as a predator of Acyrthosiphon pisum (Homoptera: Aphididae) on a wax mutant of Pisum sativum. Environ. Entomol. 1998, 27, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Sun, Y.; Peng, X.; Wang, Q.; Harris, M.; Ge, F. Up-regulation of abscisic acid signaling pathway facilitates aphid xylem absorption and osmoregulation under drought stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Shi, J.; Shi, F.; Xu, H.; He, K.; Wang, Z. Aphid fecundity and defenses in wheat exposed to a combination of heat and drought stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachappa, P.; Culkin, C.T.; Saya, P.M.; Han, J.I.; Nalam, V.J. Water stress modulates soybean aphid performance, feeding behavior, and virus transmission in soybean. Front Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
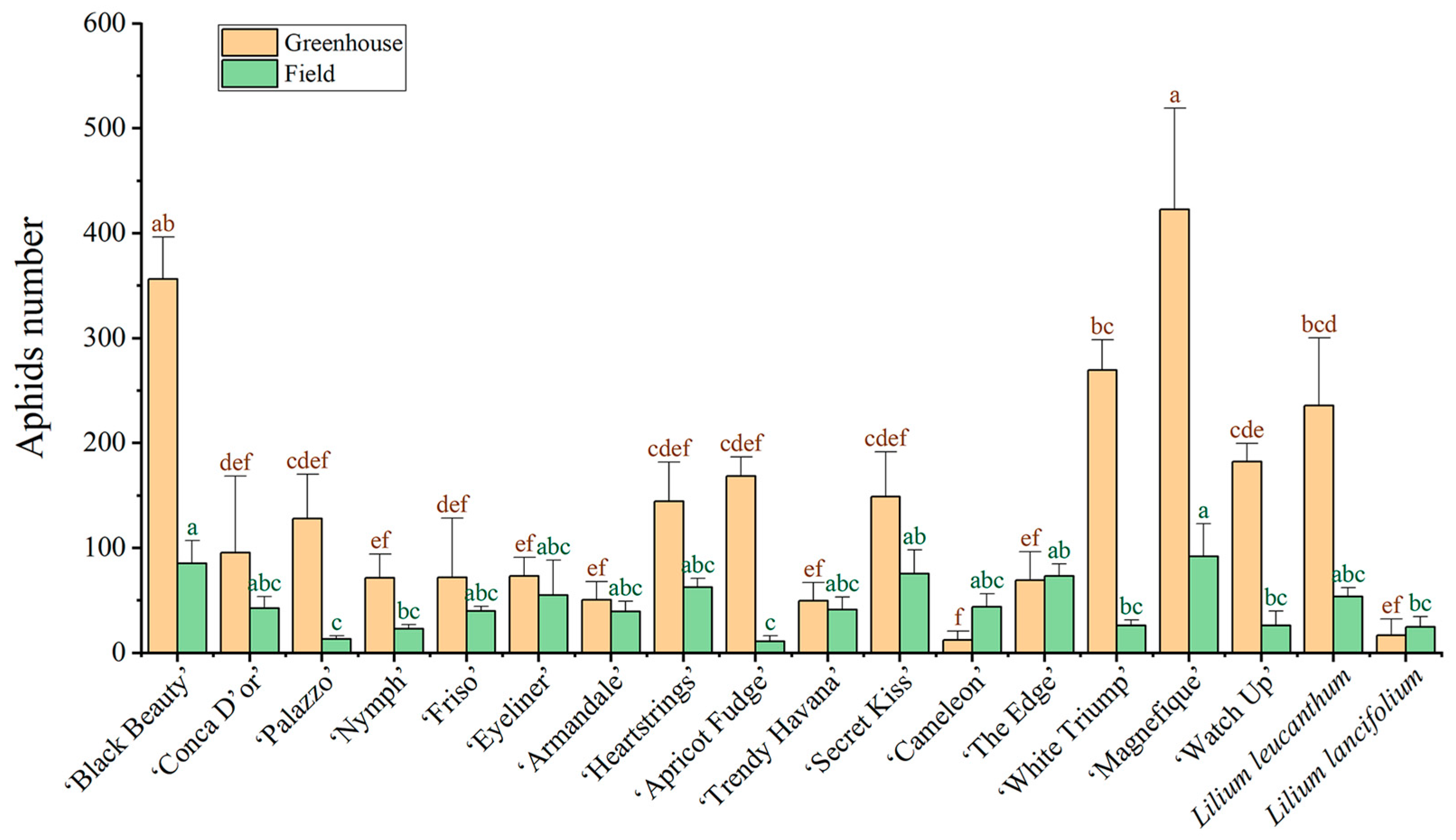




| ID | Cultivars/Species | Germline |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ‘Black Beauty’ | OT |
| 2 | ‘Conca D′or’ | OT |
| 3 | ‘Palazzo’ | OT |
| 4 | ‘Nymph’ | OT |
| 5 | ‘Friso’ | OT |
| 6 | ‘Eyeliner’ | LA |
| 7 | ‘Armandale’ | LA |
| 8 | ‘Heartstrings’ | LA |
| 9 | ‘Apricot Fudge’ | LA |
| 10 | ‘Trendy Havana’ | AA |
| 11 | ‘Secret Kiss’ | AA |
| 12 | ‘Cameleon’ | OO |
| 13 | ‘The Edge’ | OO |
| 14 | ‘White Triumph’ | LO |
| 15 | ‘Magnefique’ | LO |
| 16 | ‘Watch Up’ | LL |
| 17 | Lilium leucanthum | S |
| 18 | Lilium lancifolium | S |
| Cultivars/Species | Colorimetric Characteristics of the Leaf Apaxial Plane | Colorimetric Characteristics of the Leaf Paraxial Plane | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | C* | h* | L* | a* | b* | C* | h* | |
| ‘Black Beauty’ | 37.04 ± 0.81 gh | −18.16 ± 0.79 efg | 23.32 ± 1.29 cde | 29.56 ± 1.5 bc | −0.908 ± 0.008 cd | 48.3 ± 0.71 def | −15.23 ± 0.23 efg | 23.91 ± 0.42 abc | 28.35 ± 0.47 ab | −1.006 ± 0.004 efgh |
| ‘Conca D′or’ | 33.51 ± 0.63 i | −15.31 ± 0.89 bcd | 18.54 ± 1.85 fg | 24.06 ± 2 de | −0.874 ± 0.019 b | 47.23 ± 0.88 ef | −12.37 ± 0.35 ab | 18.67 ± 0.71 gh | 22.4 ± 0.76 gh | −0.984 ± 0.011 abcde |
| ‘Palazzo’ | 35.56 ± 1.13 hi | −18.03 ± 0.36 efg | 24.44 ± 0.89 bcd | 30.37 ± 0.92 bc | −0.934 ± 0.008 def | 48.28 ± 0.62 def | −13.93 ± 0.36 cd | 20.44 ± 0.77 efg | 24.74 ± 0.82 defg | −0.972 ± 0.009 ab |
| ‘Nymph’ | 35.66 ± 1.3 hi | −16.95 ± 0.29 def | 22.28 ± 0.46 def | 28 ± 0.53 cd | −0.92 ± 0.004 de | 46.46 ± 1.02 f | −13.97 ± 0.23 cd | 20.63 ± 0.43 efg | 24.91 ± 0.47 def | −0.976 ± 0.006 abcd |
| ‘Friso’ | 33.19 ± 0.76 i | −15.76 ± 0.42 bcd | 19.1 ± 0.95 fg | 24.77 ± 1 de | −0.878 ± 0.011 b | 47.52 ± 0.4 def | −12.75 ± 0.37 ab | 18.8 ± 0.84 fgh | 22.72 ± 0.9 fgh | −0.972 ± 0.008 ab |
| ‘Eyeliner’ | 40.75 ± 0.23 def | −16.67 ± 0.47 cdef | 21.93 ± 0.76 def | 27.55 ± 0.89 | −0.92 ± 0.005 de | 49.34 ± 0.81 cde | −15.13 ± 0.55 efg | 22.38 ± 1.12 cde | 27.02 ± 1.21 bcd | −0.974 ± 0.011 abc |
| ‘Armandale’ | 45.22 ± 1.14 ab | −18.16 ± 0.53 efg | 23.54 ± 1.24 cde | 29.74 ± 1.31 bc | −0.912 ± 0.011 cd | 52.63 ± 0.51 ab | −14.77 ± 0.25 def | 22.86 ± 0.32 bcd | 27.22 ± 0.39 bc | −0.996 ± 0.004 cdef |
| ‘Heartstrings’ | 46.41 ± 0.49 a | −14.85 ± 0.54 bc | 23.01 ± 0.8 cde | 27.39 ± 0.96 cd | −0.996 ± 0.004 h | 52.7 ± 0.21 ab | −14.61 ± 0.24 de | 20.9 ± 0.5 def | 25.5 ± 0.54 cde | −0.96 ± 0.007 a |
| ‘Apricot Fudge’ | 40.7 ± 1.08 def | −16.27 ± 0.67 bcde | 21.85 ± 1.05 def | 27.24 ± 1.24 cde | −0.932 ± 0.007 def | 53.04 ± 0.36 a | −14.82 ± 0.2 def | 24.51 ± 0.36 abc | 28.64 ± 0.4 ab | −1.026 ± 0.002 h |
| ‘Trendy Havana’ | 41.81 ± 0.45 cde | −19.41 ± 0.55 g | 27.32 ± 1.56 ab | 33.53 ± 1.59 ab | −0.948 ± 0.014 ef | 52.53 ± 0.46 ab | −15.18 ± 0.16 efg | 24.72 ± 0.25 ab | 29.01 ± 0.3 ab | −1.022 ± 0.002 gh |
| ‘Secret Kiss’ | 42.82 ± 0.32 bcd | −19.48 ± 0.93 g | 29.39 ± 2.09 a | 35.27 ± 2.25 a | −0.982 ± 0.013 gh | 50.75 ± 0.52 bc | −16.09 ± 0.31 g | 25.78 ± 0.62 a | 30.39 ± 0.69 a | −1.014 ± 0.002 fgh |
| ‘Cameleon’ | 37.64 ± 1.11 gh | −18.22 ± 0.54 fg | 24.47 ± 1.28 bcd | 30.52 ± 1.35 bc | −0.93 ± 0.011 def | 46.67 ± 0.17 f | −15.14 ± 0.56 efg | 23.7 ± 0.66 abc | 28.12 ± 0.86 ab | −1.006 ± 0.005 efgh |
| ‘The Edge’ | 35.37 ± 0.95 hi | −14.67 ± 0.76 b | 17.96 ± 0.96 g | 23.19 ± 1.23 e | −0.884 ± 0.002 bc | 47.21 ± 0.8 ef | −12.2 ± 0.44 a | 17.81 ± 0.42 h | 21.59 ± 0.58 h | −0.97 ± 0.009 ab |
| ‘White Triumph’ | 35.41 ± 0.54 hi | −12.4 ± 0.68 a | 13.34 ± 0.78 h | 18.21 ± 1.03 f | −0.822 ± 0.008 a | 48.49 ± 0.84 def | −13.38 ± 0.35 bc | 19.55 ± 0.69 fgh | 23.69 ± 0.76 efgh | −0.97 ± 0.007 ab |
| ‘Magnefique’ | 43.79 ± 0.38 bc | −19.01 ± 0.16 g | 26.62 ± 0.43 abc | 32.72 ± 0.44 ab | −0.952 ± 0.005 f | 52.74 ± 0.27 ab | −15.78 ± 0.25 fg | 23.97 ± 0.64 abc | 28.7 ± 0.66 ab | −0.99 ± 0.006 bcde |
| ‘Watch Up’ | 39.1 ± 0.66 fg | −15.24 ± 0.27 bcd | 18.49 ± 0.62 fg | 23.97 ± 0.64 de | −0.878 ± 0.008 b | 49.57 ± 0.97 cd | −13.34 ± 0.4 bc | 20.91 ± 0.59 def | 24.8 ± 0.71 def | −1 ± 0.005 efg |
| Lilium leucanthum | 39.34 ± 0.88 efg | −15.52 ± 0.67 bcd | 22.17 ± 1.47 def | 27.06 ± 1.58 cde | −0.956 ± 0.011 fg | 48.21 ± 1.05 def | −13.21 ± 0.48 abc | 20.53 ± 1.2 efg | 24.42 ± 1.26 efg | −0.998 ± 0.012 def |
| Lilium lancifolium | 38.42 ± 0.66 fg | −14.61 ± 0.49 b | 19.93 ± 0.82 efg | 24.71 ± 0.94 de | −0.936 ± 0.007 def | 51.61 ± 0.45 ab | −13.15 ± 0.33 abc | 18.82 ± 0.72 fgh | 22.96 ± 0.76 fgh | −0.96 ± 0.009 a |
| F | 23.526 | 10.971 | 10.909 | 10.671 | 19.107 | 12.386 | 11.095 | 13.044 | 12.799 | 8.031 |
| df | 17, 72 | 17, 72 | 17, 72 | 17, 72 | 17, 72 | 17, 72 | 17, 72 | 17, 72 | 17, 72 | 17, 72 |
| p value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Cultivars/Species | Stomatal Length (μm) | Stomatal Width (μm) | Stomatal Density (Number/mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Black Beauty’ | 83.86 ± 2.72 g | 56.45 ± 1.35 def | 45.73 ± 2.07 cd |
| ‘Conca D′or’ | 114.24 ± 2.22 b | 70.73 ± 1.51 a | 24.55 ± 0.33 gh |
| ‘Palazzo’ | 113.74 ± 1.72 b | 70.6 ± 1.94 a | 32.93 ± 0.49 f |
| ‘Nymph’ | 92.64 ± 1.53 ef | 59.25 ± 0.57 cd | 47.45 ± 1.64 cd |
| ‘Friso’ | 111.28 ± 2.45 b | 63.44 ± 0.7 bc | 28.92 ± 1.27 fg |
| ‘Eyeliner’ | 107.73 ± 4.5 bc | 65.18 ± 2.29 b | 30.98 ± 0.69 f |
| ‘Armandale’ | 96.58 ± 2.44 de | 59.91 ± 1.76 cd | 39.42 ± 0.66 e |
| ‘Heartstrings’ | 101.25 ± 3.77 cd | 58.37 ± 1.08 de | 47.13 ± 2.53 cd |
| ‘Apricot Fudge’ | 125.98 ± 3.48 a | 69.94 ± 2.13 a | 17.15 ± 0.46 i |
| ‘Trendy Havana’ | 99.34 ± 3.64 de | 70.66 ± 1.8 a | 22.43 ± 0.6 h |
| ‘Secret Kiss’ | 82.33 ± 1.75 g | 53.61 ± 0.8 ef | 45.43 ± 1.76 cd |
| ‘Cameleon’ | 81.87 ± 2.67 g | 59.5 ± 2.3 cd | 70.3 ± 2.47 b |
| ‘The Edge’ | 85.91 ± 1.87 fg | 55.95 ± 1.92 def | 44.87 ± 1.14 d |
| ‘White Triumph’ | 114.96 ± 1.98 b | 58.1 ± 0.96 de | 39.15 ± 0.96 e |
| ‘Magnefique’ | 74.57 ± 1.09 h | 56.02 ± 0.72 def | 50.73 ± 1.07 c |
| ‘Watch Up’ | 72.38 ± 1.54 h | 48.31 ± 0.94 gh | 44.82 ± 1.16 d |
| Lilium leucanthum | 62.98 ± 1.15 i | 47.41 ± 1.24 h | 90.12 ± 4.07 a |
| Lilium lancifolium | 97.76 ± 1.35 de | 52.45 ± 1.19 fg | 49.13 ± 2.18 cd |
| F | 47.17 | 23.90 | 102.18 |
| df | 17, 252 | 17, 252 | 17, 252 |
| p value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Cultivars/Species | Leaf Thickness (μm) | Leaf Epidermis Thickness (μm) | Leaf Palisade Tissue Thickness (μm) | Leaf Spongy Tissue Thickness (μm) | Leaf Lower Epidermis Thickness (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Black Beauty’ | 369.29 ± 9.04 ijk | 48.85 ± 2.08 bcde | 44.56 ± 0.84 cde | 243.25 ± 8.65 efgh | 30.69 ± 0.97 de |
| ‘Conca D′or’ | 465.57 ± 21.8 bcdef | 73.7 ± 0.72 a | 64.67 ± 2.74 abc | 284.56 ± 19.11 defg | 43.33 ± 2.92 abc |
| ‘Palazzo’ | 426.97 ± 21.84 defgh | 44.71 ± 0.89 cde | 42.51 ± 4.95 d | 305.15 ± 22.68 cd | 32.67 ± 1.73 de |
| ‘Nymph’ | 369.43 ± 13.06 ijk | 41.84 ± 4.12 def | 60.81 ± 1.65 abcd | 233.41 ± 10.18 gh | 36.23 ± 3.17 bcde |
| ‘Friso’ | 449.7 ± 20.18 cdefg | 60.46 ± 1.77 b | 68.79 ± 4.26 ab | 289.59 ± 18.36 def | 37.69 ± 1.88 bcd |
| ‘Eyeliner’ | 450.53 ± 23.23 cdefg | 48.56 ± 7.3 bcde | 59.66 ± 3.44 abcd | 303.53 ± 15.98 cd | 33.08 ± 4.06 de |
| ‘Armandale’ | 420.45 ± 25.76 efghi | 46.89 ± 2.82 cde | 66.93 ± 2.57 ab | 275.98 ± 23.24 defg | 31.42 ± 2.83 de |
| ‘Heartstrings’ | 470.6 ± 23.65 bcde | 78.12 ± 6.78 a | 56.42 ± 6.12 bcd | 293.41 ± 27.6 de | 49.74 ± 1.74 a |
| ‘Apricot Fudge’ | 346.5 ± 7.63 jk | 40.49 ± 4.86 ef | 55.88 ± 8.13 bcd | 207.19 ± 19.27 h | 44.03 ± 4.59 ab |
| ‘Trendy Havana’ | 406.85 ± 6.72 ghi | 75.32 ± 3.85 a | 58.64 ± 3.73 bcd | 240.2 ± 16.14 fgh | 44.4 ± 3.81 ab |
| ‘Secret Kiss’ | 326.12 ± 13.87 k | 32.87 ± 1.58 f | 58.01 ± 4.67 bcd | 199.12 ± 11.85 h | 34.03 ± 3.36 cde |
| ‘Cameleon’ | 570.41 ± 8.39 a | 55.92 ± 2.83 bc | 63.9 ± 4.48 abc | 414.58 ± 3.76 a | 34.15 ± 2.19 cde |
| ‘The Edge’ | 380.16 ± 11.72 hij | 50.54 ± 4.43 bcde | 45.62 ± 6.96 cde | 238.26 ± 17.55 fgh | 39.13 ± 4.28 bcd |
| ‘White Triumph’ | 519.18 ± 30.57 b | 53.82 ± 3.61 bcd | 54.37 ± 11.78 bcd | 373.21 ± 13.52 ab | 38.75 ± 1.2 bcd |
| ‘Magnefique’ | 500.19 ± 11.74 bc | 46.61 ± 0.12 cde | 69.4 ± 6.56 ab | 345.27 ± 15.33 bc | 34.13 ± 1.59 cde |
| ‘Watch Up’ | 411.08 ± 9.59 fghi | 43.06 ± 1.29 def | 44.77 ± 3.32 cde | 280.61 ± 8.6 defg | 35.07 ± 1.64 bcde |
| Lilium leucanthum | 478.87 ± 9.07 bcd | 45.33 ± 3.5 cde | 79.73 ± 13.13 a | 321.71 ± 10.18 cd | 29.88 ± 3.09 de |
| Lilium lancifolium | 266.18 ± 5.89 l | 49.68 ± 3.16 bcde | 50.2 ± 4.33 bcd | 142.59 ± 9.62 i | 27.66 ± 2.13 e |
| F | 19.176 | 11.765 | 2.741 | 16.04 | 4.268 |
| df | 17, 36 | 17, 36 | 17, 36 | 17, 36 | 17, 36 |
| p value | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.005 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, H.; Zhong, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Guo, L.; Wang, C.; Tang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Sun, M. Aphid Resistance Evaluation and Constitutive Resistance Analysis of Eighteen Lilies. Insects 2023, 14, 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14120936
Shi H, Zhong J, Liang Y, Zhang P, Guo L, Wang C, Tang Y, Lu Y, Sun M. Aphid Resistance Evaluation and Constitutive Resistance Analysis of Eighteen Lilies. Insects. 2023; 14(12):936. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14120936
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Huajin, Jian Zhong, Yilin Liang, Peng Zhang, Liuyu Guo, Chen Wang, Yuchao Tang, Yufan Lu, and Ming Sun. 2023. "Aphid Resistance Evaluation and Constitutive Resistance Analysis of Eighteen Lilies" Insects 14, no. 12: 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14120936
APA StyleShi, H., Zhong, J., Liang, Y., Zhang, P., Guo, L., Wang, C., Tang, Y., Lu, Y., & Sun, M. (2023). Aphid Resistance Evaluation and Constitutive Resistance Analysis of Eighteen Lilies. Insects, 14(12), 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14120936






