Intestinal Bacterial Diversity and Functional Analysis of Three Lepidopteran Corn Ear Worm Larvae
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects and Corn Samples
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. PCR Amplification and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. Statistical and Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of 16S rDNA Sequencing Results
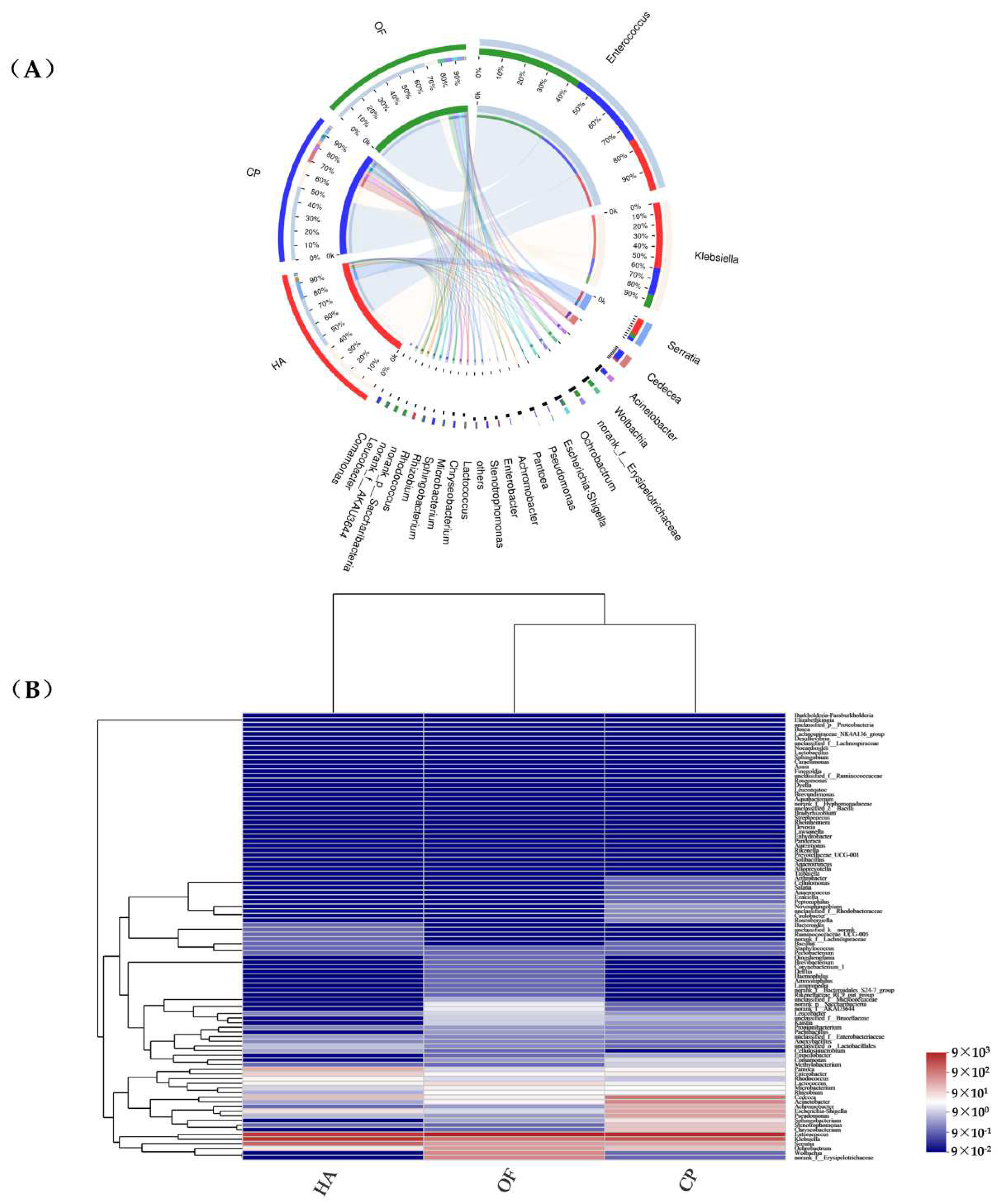
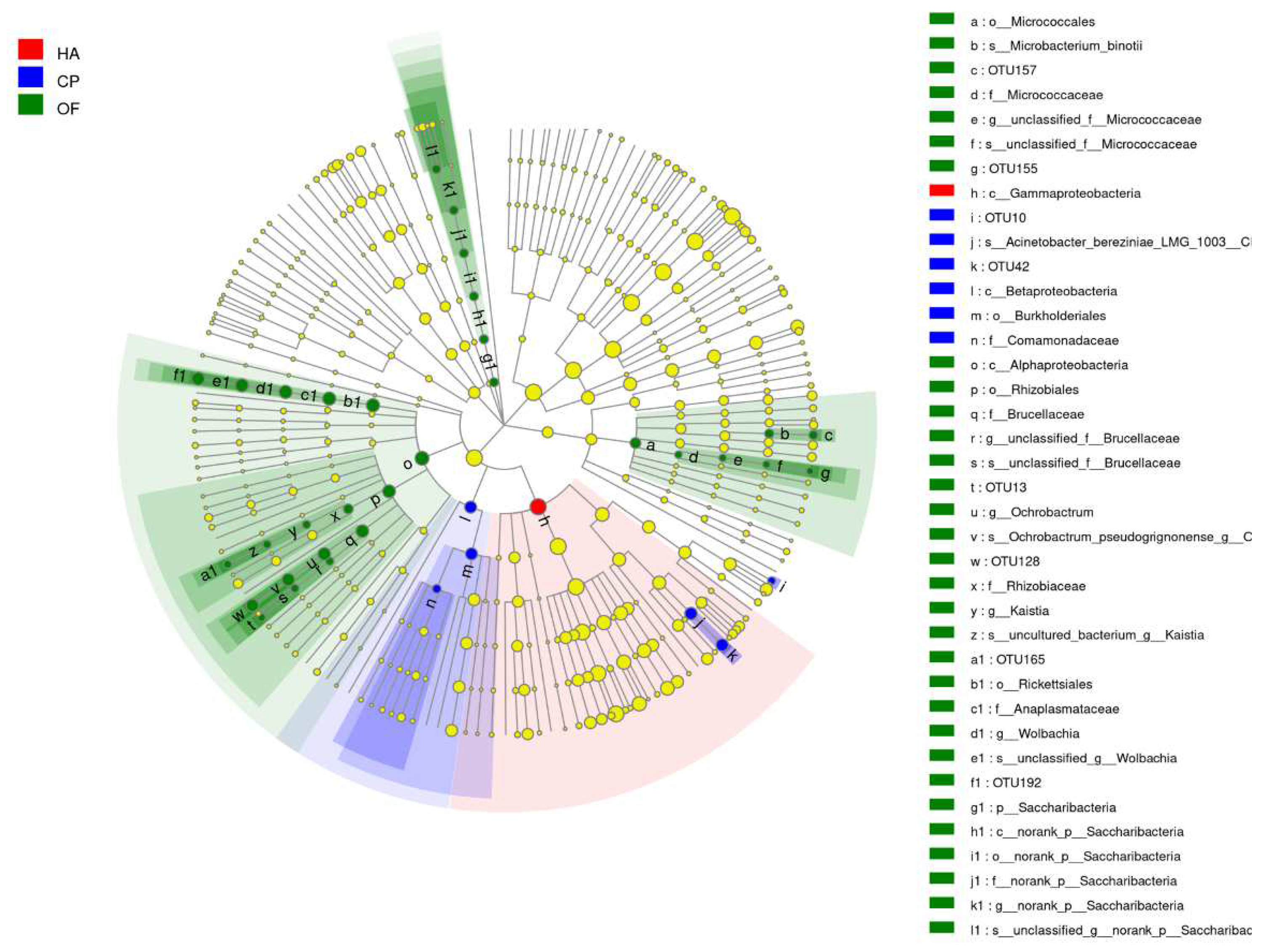
3.2. Comparison of the Gut Microbiota
3.3. Beta Diversity Analysis
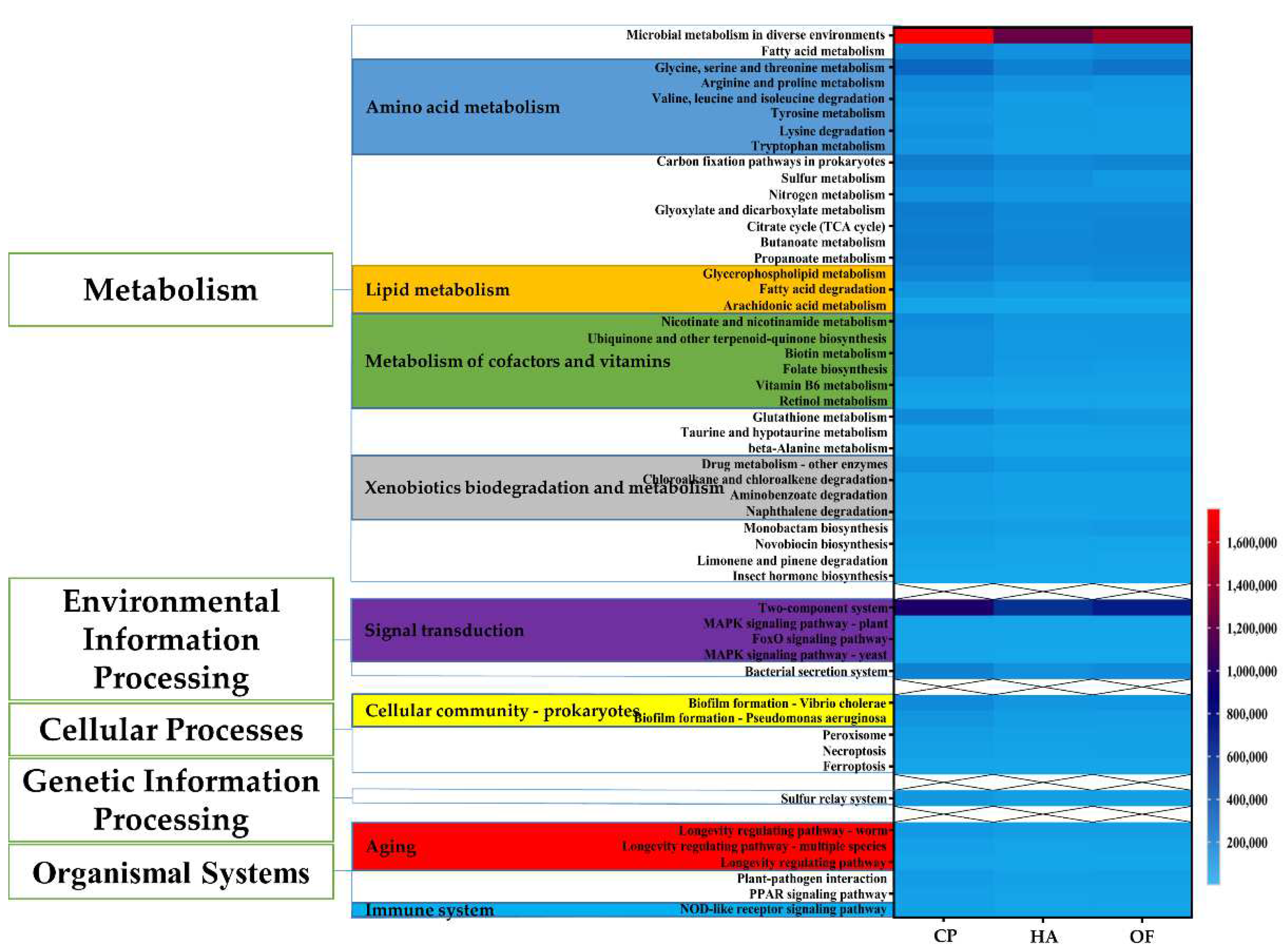
3.4. Functional Prediction of Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shwe, S.M.; Prabu, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.C.; Jing, D.P.; Bai, S.X.; He, K.L.; Wang, Z.Y. Baseline susceptibility and laboratory selection of resistance to Bt Cry1Ab protein of Chinese populations of yellow peach moth, Conogethes punctiferalis (Guenee). Toxins 2021, 13, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.S.; Hallerman, E.; Peng, Y.F.; Li, Y.H. Development of Bt rice and Bt maize in China and their efficacy in target pest control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez-Arias, C.C.; Ligarreto-Moreno, G.A.; Ramirez-Godoy, A.; Restrepo-Diaz, H. Maize responses challenged by drought, elevated daytime temperature and arthropod herbivory stresses: A physiological, biochemical and molecular view. Front. Plant. Sci. 2021, 12, 702841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.P.; Wu, K.M. Commercial strategy of transgenic insect-resistant maize in China. J. Plant Protect. 2022, 49, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Sung, K. Assessment of causality between climate variables and production for whole crop maize using structural equation modeling. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L. Changes and occur rence trend of corn diseases and insect pests in Huang-Huai-Hai summer corn regions. Plant Protect. 2005, 31, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.F.; He, K.L.; Meng, Y.J.; Hellmich, R.L.; Chen, S.J.; Lopez, M.D.; Lauter, N.; Wang, Z.Y. Asian corn borer damage is affected by rind penetration strength of corn stalks in a spatiotemporally dependent manner. Plant Direct 2022, 6, e381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, Y.; Smith, J.L.; Limay-Rios, V.; Schaafsma, A.W. The effect of simulated Lepidopteran ear feeding injury on mycotoxin accumulation in grain corn (Poales: Poaceae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 2187–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, R.; Umer, M.J.; Wang, Y.Z.; He, K.L.; Zhang, T.T.; Bai, S.X.; Zhi, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.Y. Synergistic effect of beauveria bassiana and trichoderma asperellum to induce maize (Zea mays L.) defense against the Asian Corn Borer, Ostrinia furnacalis (Lepidoptera, Crambidae) and larval immune response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.G.; Yang, M.T.; Dong, K.; Zhang, J.B.; Wang, H.L.; Xie, M.J.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, Z.Z. Structural insights into the ligand-binding and -releasing mechanism of Helicoverpa armigera pheromone-binding protein PBP1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Zhang, T.T.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L.; Bai, S.X. Identification of putative chemosensory receptor genes from yellow peach moth Conogethes punctiferalis (Guenée) antennae transcriptome. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L.; Shi, J.; Ma, S.Y. Analysis of the heavily occurrence trend of the yellow peach borer in corn and its management strategy. Plant Protect. 2006, 32, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.F.; Qi, J.F.; He, K.L.; Wu, J.Q.; Bai, S.X.; Zhang, T.T.; Zhao, J.R.; Wang, Z.Y. The Asian corn borer Ostrinia furnacalis feeding increases the direct and indirect defence of mid-whorl stage commercial maize in the field. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.P.; Zhang, F.; Tay, W.T.; Robin, C.; Shi, Y.; Guan, F.; Yang, Y.H.; Wu, Y.D. Population genomics provides insights into lineage divergence and local adaptation within the cotton bollworm. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 10, 13581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berasategui, A.; Shukla, S.; Salem, H.; Kaltenpoth, M. Potential applications of insect symbionts in biotechnology. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2016, 100, 1567–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereghetti, V.; Chouaia, B.; Montagna, M. New insights into the microbiota of moth pests. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.Y.; Dong, Y.L.; Yan, Z.Z.; Lv, D.B.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.P. Comparison of gut bacterial communities of Grapholita molesta (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) reared on different host plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.T.; Luo, S.Q.; Zhou, X. Enterococcus faecium regulates honey Bee developmental genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Ren, F.R.; Yao, Y.L.; Sun, X.; Walling, L.L.; Li, N.N.; Bai, B.; Bao, X.Y.; Xu, X.R.; Luan, J.B. Intracellular symbionts drive sex ratio in the whitefly by facilitating fertilization and provisioning of B vitamins. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2923–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceja-Navarro, J.A.; Vega, F.E.; Karaoz, U.; Hao, Z.; Jenkins, S.; Lim, H.C.; Kosina, P.; Infante, F.; Northen, T.R.; Brodie, E.L. Gut microbiota mediate caffeine detoxification in the primary insect pest of coffee. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.K.; Shu, J.P.; Xue, H.J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.B.; Liu, Y.N.; Fang, L.X.; Wang, Y.D.; Wang, H.J. The gut microbiota in Camellia Weevils are influenced by plant secondary metabolites and contribute to saponin degradation. mSystems 2020, 5, e00692-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skowronek, M.; Sajnaga, E.; Kazimierczak, W.; Lis, M.; Wiater, A. Screening and molecular identification of bacteria from the midgut of Amphimallon solstitiale larvae exhibiting antagonistic activity against bacterial symbionts of entomopathogenic nematodes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skowronek, M.; Sajnaga, E.; Pleszczynska, M.; Kazimierczak, W.; Lis, M.; Wiater, A. Bacteria from the midgut of common cockchafer (Melolontha melolontha L.) larvae exhibiting antagonistic activity against bacterial symbionts of entomopathogenic nematodes: Isolation and molecular identification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, Z.S.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Y.Y.; Cheng, D.F. The divergence in bacterial components associated with Bactrocera dorsalis across developmental stages. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.Q.; Chen, B.S.; Sun, C.; Ishida, K.; Hertweck, C.; Boland, W. Symbiont-derived antimicrobials contribute to the control of the Lepidopteran gut microbiota. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, P.R.; Rolff, J. Host and symbiont jointly control gut microbiota during complete metamorphosis. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Dittmer, J.; Douglas, B.; Huang, L.; Brucker, R.M. Coadaptation between host genome and microbiome under long-term xenobiotic-induced selection. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.F.; Guo, Z.J.; Riegler, M.; Xi, Z.Y.; Liang, G.W.; Xu, Y.J. Gut symbiont enhances insecticide resistance in a significant pest, the oriental fruit fly Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Microbiome 2017, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Cai, T.W.; Ren, Z.J.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, M.J.; Cai, Y.F.; Yu, C.; Shu, R.H.; He, S.; Li, J.H.; et al. Decline in symbiont-dependent host detoxification metabolism contributes to increased insecticide susceptibility of insects under high temperature. ISME J. 2021, 15, 3693–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voirol, L.R.P.; Frago, E.; Kaltenpoth, M.; Hilker, M.; Fatouros, N.E. Bacterial symbionts in Lepidoptera: Their diversity, transmission, and impact on the Host. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Shen, Z.J.; Yu, J.M.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.X.; Xu, H.L. Comparison of gut bacterial communities and their associations with host diets in four fruit borers. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Wei, G.F.; Jia, S.H.; Huang, J.H.; Miao, X.X.; Zhou, Z.H.; Zhao, L.P.; Huang, Y.P. Microbial communities in the larval midgut of laboratory and field populations of cotton bollworm (Helicoverpa armigera). Can. J. Microbiol. 2007, 52, 23–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.P.; Huang, J.R.; Ji, T.J.; Tian, C.H.; Zhao, X.C.; Feng, H.Q. Baseline susceptibility and resistance allele frequency in Ostrinia furnacalis related to Cry1 toxins in the Huanghuaihai summer corn region of China. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 4311–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.X.; Yang, R.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L.; Camara, I.; Dong, X.H.; Liu, Y.Q.; Shi, W.P. Efficacy of Bt maize producing the Cry1Ac protein against two important pests of corn in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 21511–21516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.K.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Li, L.L.; Lu, Z.B.; Li, C.; Ouyang, F.; Tscharntke, T.; Yu, Y.; Men, X.Y. Landscape agricultural simplification correlates positively with the spatial distribution of a specialist yet negatively with a generalist pest. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Du, K.Q.; Sun, C.; Vimalanathan, A.; Liang, X.L.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.H.; Lu, X.M.; Li, L.J.; Shao, Y.Q. Gut bacterial and fungal communities of the domesticated silkworm (Bombyx mori) and wild mulberry-feeding relatives. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2252–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.X.; Xu, H.; Gao, S.S.; Gao, Z.; Wang, N.X. Effects of Different Hosts on Bacterial Communities of Parasitic Wasp Nasonia vitripennis. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Fu, K.H.; Gao, S.G.; Wu, Q.; Fan, L.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Chen, J. Impact on bacterial community in midguts of the Asian corn borer larvae by transgenic Trichoderma strain overexpressing a heterologous chit42 gene with chitin-binding domain. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, D.R.; Toolson, E.C.; Takacs-Vesbach, C.D. Do diet and taxonomy influence insect gut bacterial communities? Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 5124–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.R.; Ni, X.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L. Effects of photoperiod and temperature on diapause induction in Conogethes punctiferalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Insect. Sci. 2014, 21, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Rui, C.H.; Wang, L.; Nahiyoon, S.A.; Huang, W.L.; Zhu, J.S.; Ji, X.J.; Yang, Q.J.; Yuan, H.Z.; Cui, L. Field-evolved resistance to 11 insecticides and the mechanisms involved in Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pest. Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 5086–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.L.; He, J.T.; Zhang, N.; Muhammad, A.; Lu, X.M.; Shao, Y.Q. Probiotic potentials of the silkworm gut symbiont Enterococcus casseliflavus ECB140, a promising L-tryptophan producer living inside the host. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, N.; Siddiqui, R.; Iqbal, M.; Sagathevan, K.; Khan, N.A. Gut bacteria of cockroaches are a potential source of antibacterial compound(s). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 66, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, F.; Wei, L.; Xinyi, T.; Jian, L.; Fang, T. Termicin silencing enhances the toxicity of Serratia marcescens Bizio (SM1) to Odontotermes formosanus (Shiraki). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 185, 105120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymann, K.; Coon, K.L.; Shaffer, Z.; Salisbury, S.; Moran, N.A. Pathogenicity of Serratia marcescens Strains in Honey Bees. Mbio 2018, 9, e01649-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambong, J.T. Phylogeny of bacteria isolated from Rhabditis sp (Nematoda) and identification of novel Entomopathogenic Serratia marcescens Strains. Curr. Microbiol. 2013, 66, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Mustafa, A.M.; Sun, J.Z. Wood-feeding Termites as an obscure yet promising source of bacteria for biodegradation and detoxification of creosote-treated wood along with methane production enhancement. Bioresource. Technol. 2021, 338, 125521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, A.; Rai, S.K.; Chownk, M.; Sangwan, R.S.; Yadav, S.K. Xylanase from Acinetobacter pittii MASK 25 and developed magnetic cross-linked xylanase aggregate produce predominantly xylopentose and xylohexose from agro biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova, C.; Baixeras, J.; Latorre, A.; Porcar, M. The generalist inside the specialist: Gut bacterial communities of two insect species feeding on toxic plants are dominated by Enterococcus sp. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, e21751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.Y.; Hu, Y.Y.; Yu, F.; Lu, X.J.; Zong, Z.Y. Pseudomonas sichuanensis sp. nov., isolated from hospital sewage. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.; Vohra, M.S.; Janjua, H.A. Whole-genome sequence and broad-spectrum antibacterial activity of Chryseobacterium cucumeris strain MW-6 isolated from the Arabian Sea. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.S.; Chu, J.H.; Hong, S.J.; Kwak, Y.; Khan, A.R.; Jung, B.K.; Ullah, I.; Shin, J.H. Complete genome sequence of the caprolactam-degrading bacterium Pseudomonas mosselii SJ10 isolated from wastewater of a nylon 6 production plant. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 192, 263–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladipo, O.G.; Ezeokoli, O.T.; Maboeta, M.S.; Bezuidenhout, J.J.; Tiedt, L.R.; Jordaan, A.; Bezuidenhout, C.C. Tolerance and growth kinetics of bacteria isolated from gold and gemstone mining sites in response to heavy metal concentrations. J. Environ. Manage. 2018, 212, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Deng, S.M.; Liu, M.; Li, Z.; Wu, D.Q.; Wang, T.; Chen, X.M. Study on the aerobic remediation of Ni (II) by Pseudomonas hibiscicola strain L1 interaction with nitrate. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 299, 113641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.N.; Zhao, C.; Gao, X.W.; Wang, L.P.; Tian, Q.Q.; Liu, Y.; Xue, S.W.; Han, Z.; Chen, F.L.; Wang, S.W. Characterization and transcriptome analysis of a long-chain n-alkane-degrading strain Acinetobacter pittii SW-1. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.G.; Pei, D.M.; He, X.R.; Liu, Y.C.; Zhu, P.P.; Yan, X. The operon encoding hydrolytic dehalogenation of 4-chlorobenzoate is transcriptionally regulated by the TetR-Type Repressor FcbR and its ligand 4-chlorobenzoyl coenzyme A. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2021, 87, e02652-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Liang, J.Q.; Yang, S.Y.; Yao, J.B.; Chen, K.; Yang, L.X.; Zheng, W.; Tian, Y. Finding novel chemoreceptors that specifically sense and trigger chemotaxis toward polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Novosphingobium pentaromativorans US6-1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeukens, J.; Freschi, L.; Vincent, A.T.; Emond-Rheault, J.G.; Kukavica-Ibrulj, I.; Charette, S.J.; Levesque, R.C. A Pan-genomic approach to understand the basis of host adaptation in Achromobacter. Genome. Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 1030–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punjabi, K.; Mehta, S.; Chavan, R.; Chitalia, V.; Deogharkar, D.; Deshpande, S. Efficiency of biosynthesized silver and zinc nanoparticles against multi-drug resistant pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iimura, M.; Hayashi, W.; Arai, E.; Natori, T.; Horiuchi, K.; Matsumoto, G.; Tanaka, H.; Soga, E.; Nagano, Y.; Nagano, N. Detection of Acinetobacter pittii ST220 co-producing NDM-1 and OXA-820 carbapenemases from a hospital sink in a non-endemic country of NDM. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 21, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Dong, N.; Xu, C.; Ye, L.W.; Chen, S. Emergence of ST63 Pandrug-Resistant Acinetobacter pittii Isolated from an AECOPD Patient in China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 739211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.H.; Li, S.Z.; Li, Y.L.; Yan, Y.C.; Fang, Y.; Zou, L.F.; Chen, G.Y. Bactericidal effect of Pseudomonas oryziphila sp. nov., a novel pseudomonas species against xanthomonas oryzae reduces disease severity of bacterial leaf streak of rice. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 759536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinsanya, M.A.; Goh, J.K.; Lim, S.P.; Ting, A.S.Y. Diversity, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of culturable bacterial endophyte communities in Aloe vera. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.N.; Aravind, S.R.; Jacob, J.; Gopinath, G.; Lankalapalli, R.S.; Sreelekha, T.T.; Kumar, B.S.D. Pseudopyronine B: A potent antimicrobial and anticancer molecule isolated from a Pseudomonas mosselii. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leneveu-Jenvrin, C.; Madi, A.; Bouffartigues, E.; Biaggini, K.; Feuilloley, M.; Chevalier, S.; Connil, N. Cytotoxicity and inflammatory potential of two Pseudomonas mosselii strains isolated from clinical samples of hospitalized patients. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample\Info | Seq_Num | Base_Num | Mean_Length | Min_Length | Max_Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA_1 | 94,956 | 42,807,665 | 451 | 280 | 452 |
| HA_2 | 97,686 | 43,966,345 | 450 | 274 | 502 |
| HA_3 | 102,225 | 45,948,879 | 449 | 388 | 455 |
| HA_4 | 44,224 | 19,901,174 | 450 | 424 | 499 |
| HA_5 | 42,012 | 18,903,405 | 450 | 362 | 454 |
| CP_1 | 90,727 | 40,862,237 | 450 | 271 | 452 |
| CP_2 | 103,449 | 46,502,122 | 450 | 266 | 471 |
| CP_3 | 95,403 | 42,844,770 | 449 | 243 | 455 |
| CP_4 | 31,459 | 14,157,568 | 450 | 423 | 454 |
| CP_5 | 41,857 | 18,862,255 | 451 | 271 | 487 |
| OF_1 | 100,844 | 45,255,687 | 449 | 274 | 476 |
| OF_2 | 96,632 | 43,290,905 | 448 | 274 | 464 |
| OF_3 | 96,775 | 43,465,463 | 449 | 274 | 499 |
| OF_4 | 96,328 | 42,869,068 | 445 | 308 | 466 |
| OF_5 | 102,951 | 46,293,847 | 450 | 351 | 489 |
| ZM_1 | 110,385 | 47,802,629 | 433 | 379 | 452 |
| ZM_2 | 33,976 | 14,943,705 | 440 | 401 | 494 |
| ZM_3 | 41,486 | 17,993,290 | 434 | 403 | 501 |
| SUM/AVG | 1,423,375 | 636,671,014 | 447 | 326 | 473 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Gao, S.; Zheng, F.; Wang, N. Intestinal Bacterial Diversity and Functional Analysis of Three Lepidopteran Corn Ear Worm Larvae. Insects 2022, 13, 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13080740
Zhang J, Gao S, Zheng F, Wang N. Intestinal Bacterial Diversity and Functional Analysis of Three Lepidopteran Corn Ear Worm Larvae. Insects. 2022; 13(8):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13080740
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiqiang, Shanshan Gao, Fangqiang Zheng, and Ningxin Wang. 2022. "Intestinal Bacterial Diversity and Functional Analysis of Three Lepidopteran Corn Ear Worm Larvae" Insects 13, no. 8: 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13080740
APA StyleZhang, J., Gao, S., Zheng, F., & Wang, N. (2022). Intestinal Bacterial Diversity and Functional Analysis of Three Lepidopteran Corn Ear Worm Larvae. Insects, 13(8), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13080740





