Geometric Morphometric Analysis and Molecular Identification of Coconut Mite, Aceria guerreronis Keifer (Acari: Eriophyidae) Collected from Thailand
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
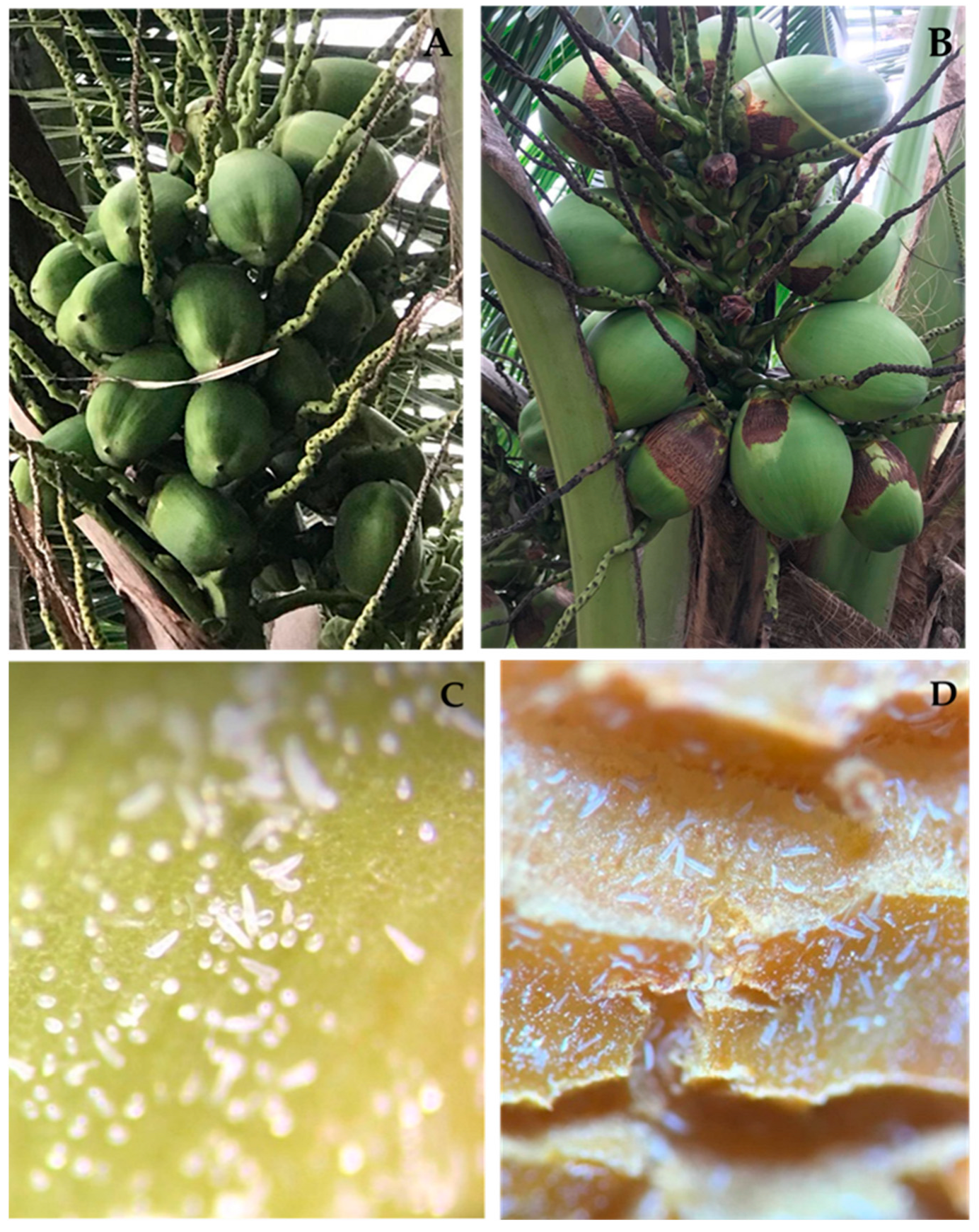
2.1. Coconut Mite Sampling and Identification
2.2. Molecular Identification
2.2.1. Sample Collection
2.2.2. Total DNA Isolation
2.2.3. PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Coconut Mite Sampling and Identification
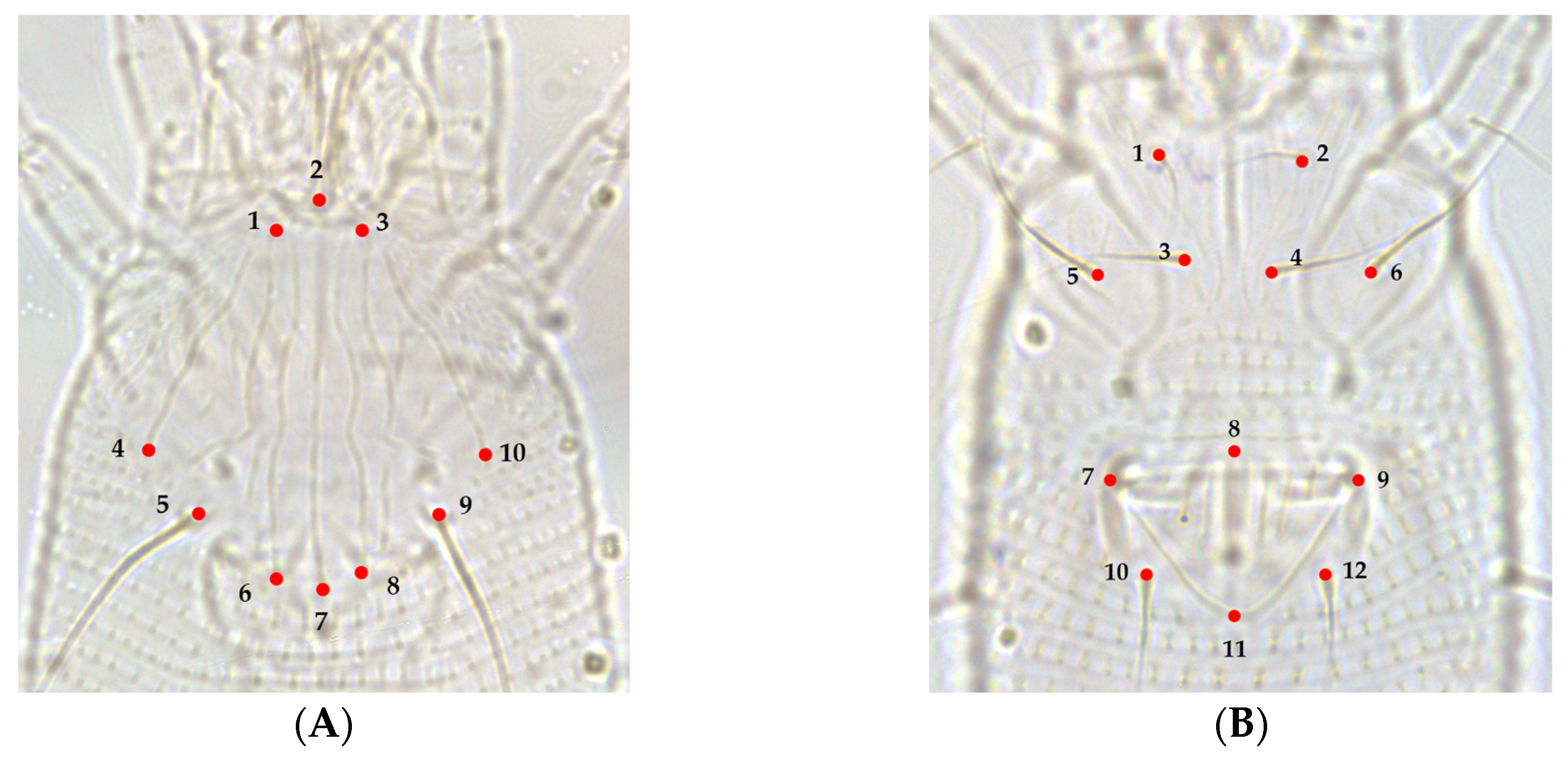
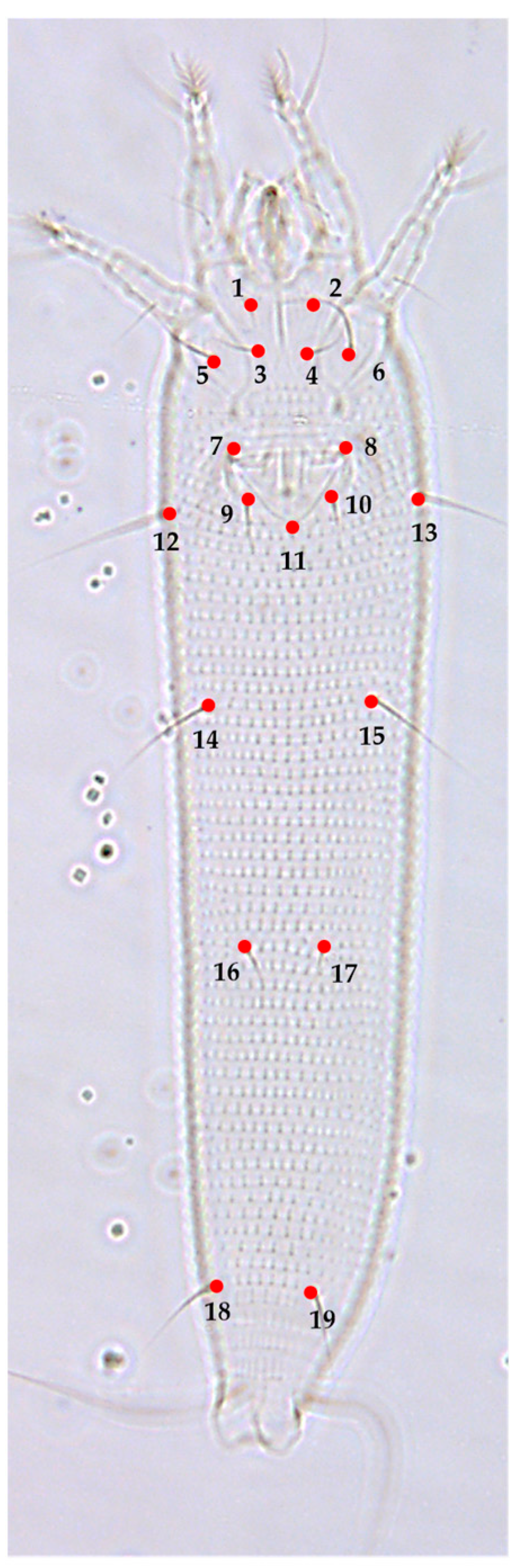
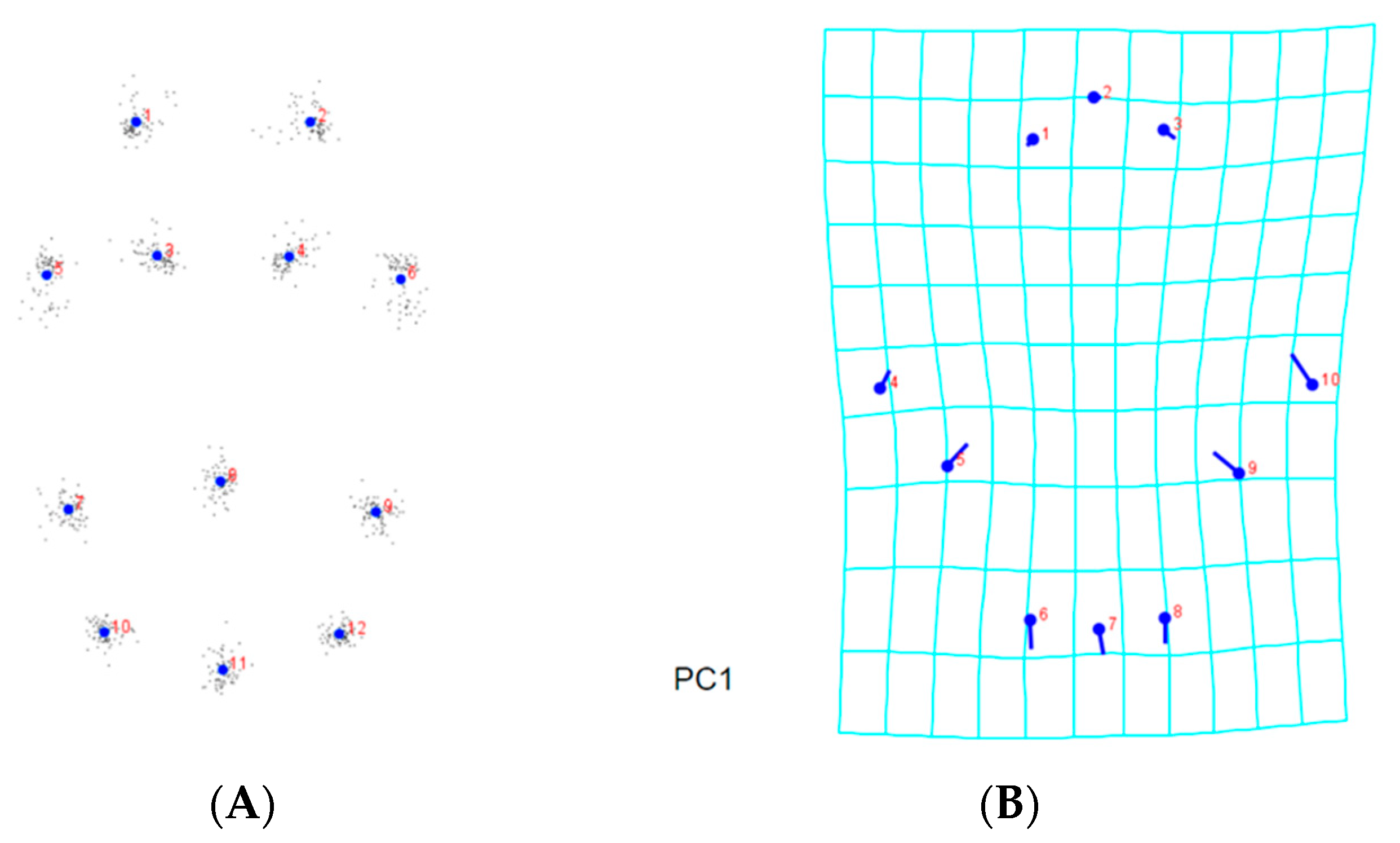
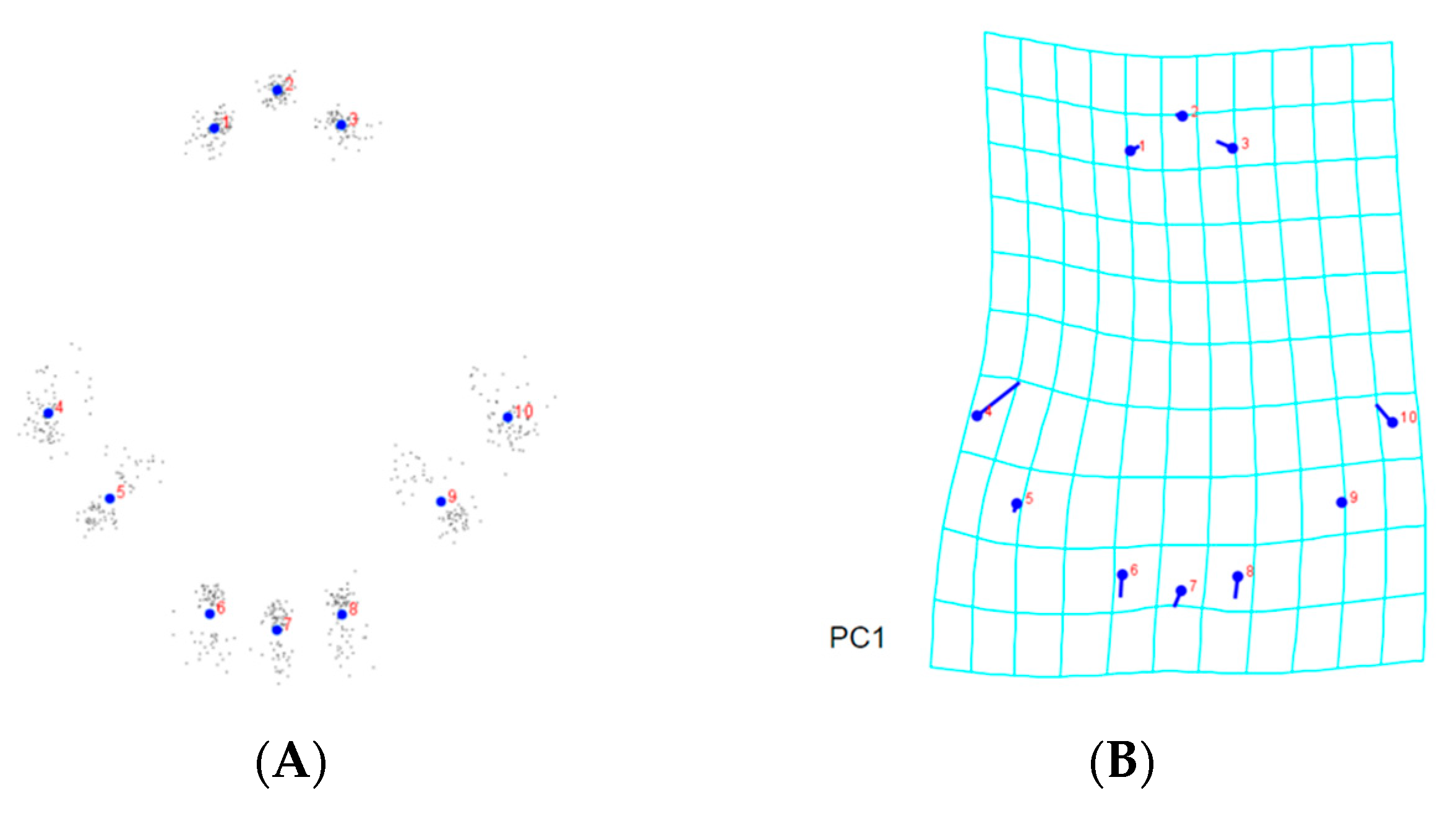
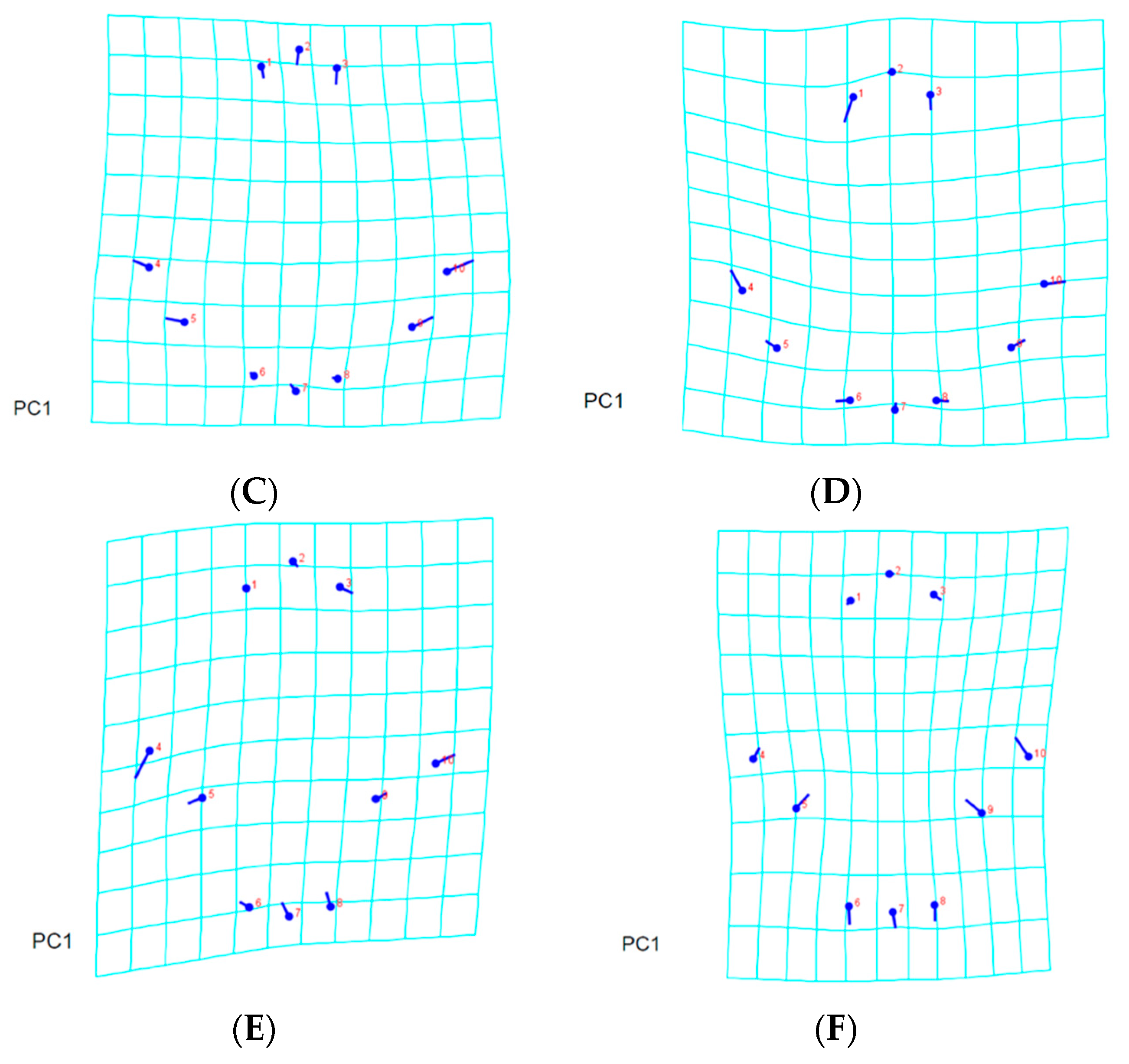
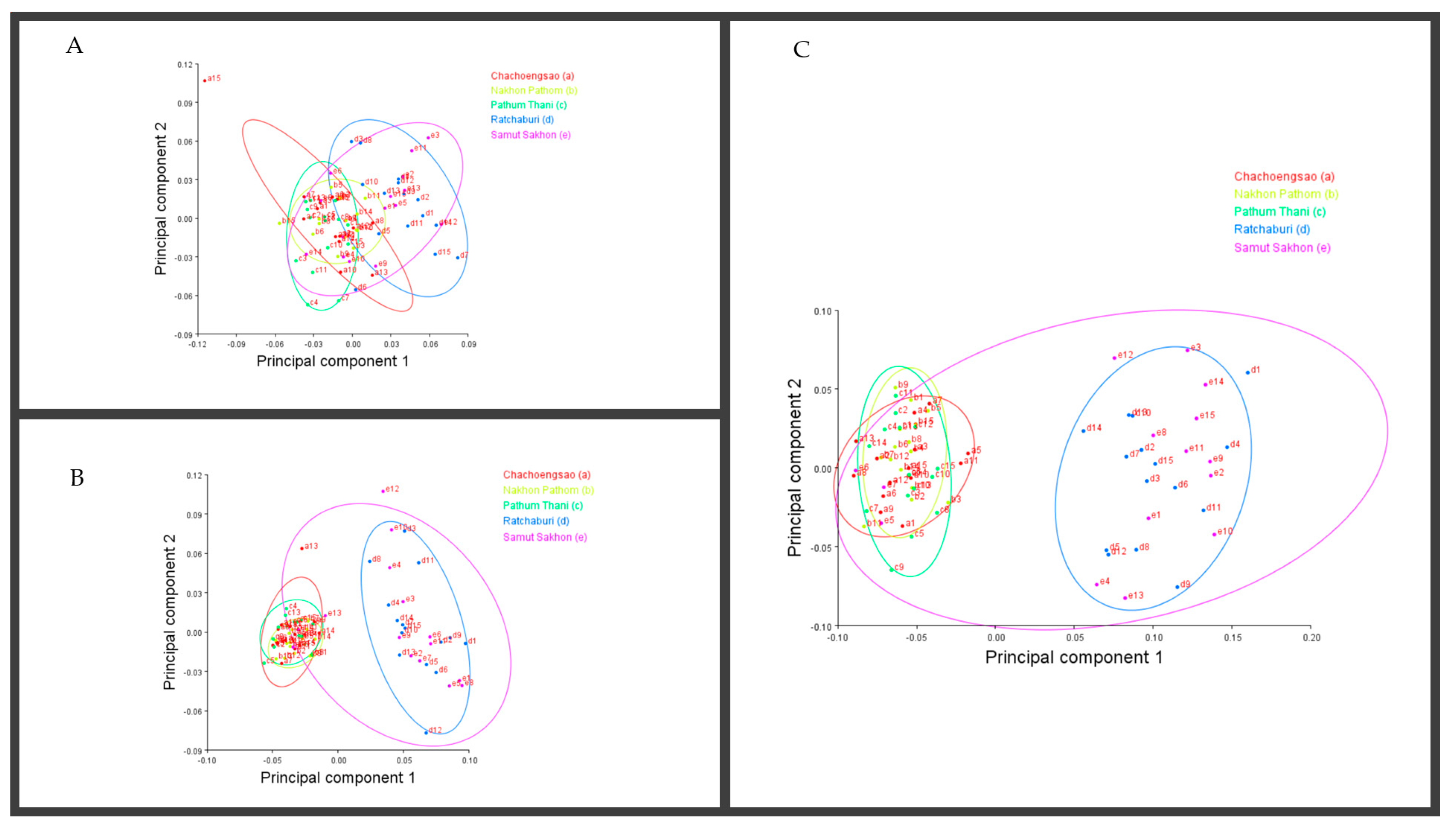
3.2. Landmark-Based Morphometric Methods
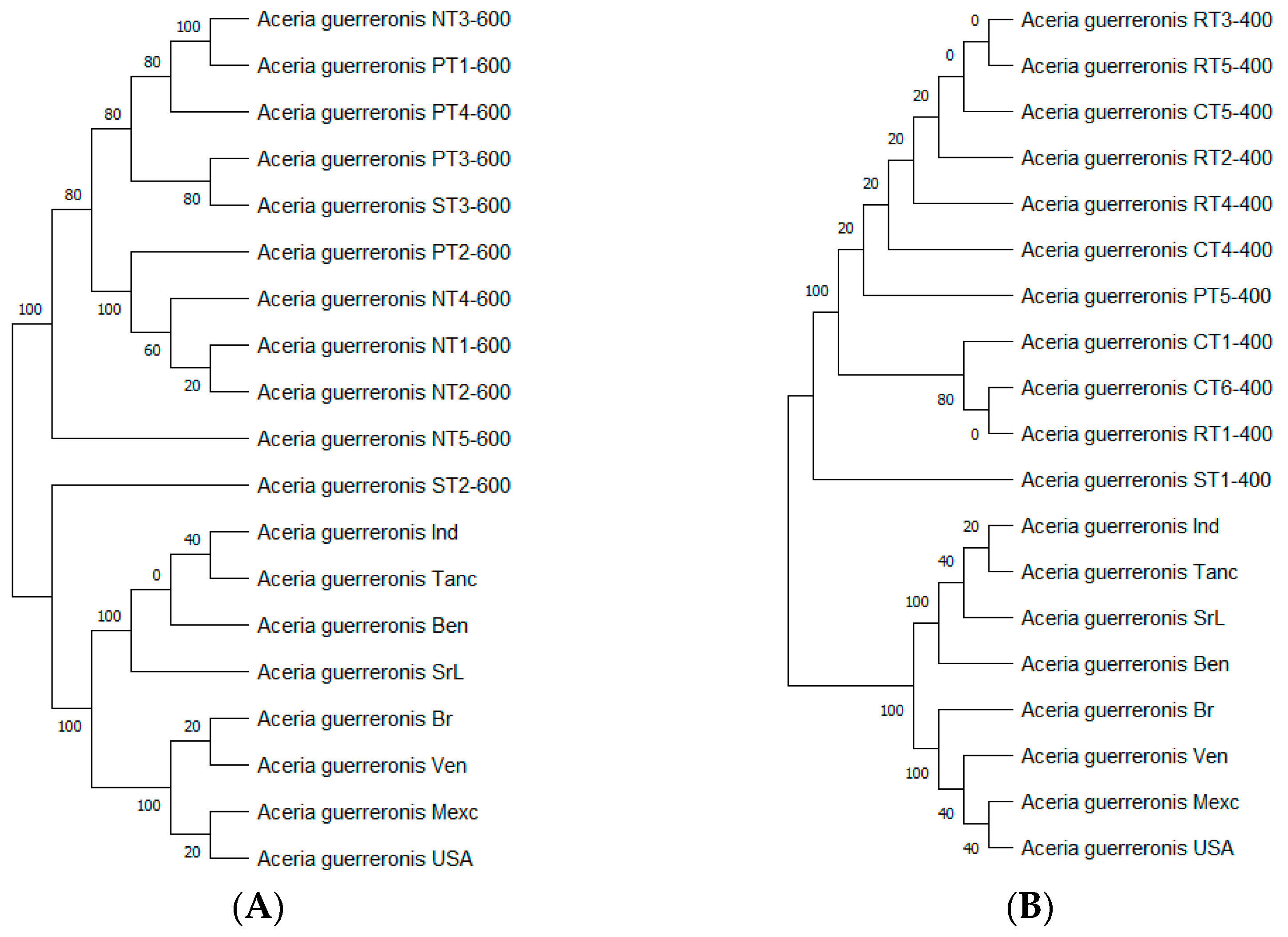
3.3. Molecular Identification
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galvão, A.S.; Gondim, M.G., Jr.; de Moraes, G.J.; Melo, J.W. Distribution of Aceria guerreronis and Neoseiulus baraki among and within coconut bunches in northeast Brazil. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2011, 54, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navia, D.; Gondim, M.G., Jr.; Aratchige, N.S.; de Moraes, G.J. A review of the status of the coconut mite, Aceria guerreronis (Acari: Eriophyidae), a major tropical mite pest. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2013, 59, 67–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, D.C.; de Moraes, G.J.; Dias, C.T.S. Status of Aceria guerreronis Keifer (Acari: Eriophyidae) as a Pest of Coconut in the State of Sao Paulo, Southeastern Brazil. Neotrop. Entomol. 2012, 41, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Keifer, H. Eriophyid studies B-14 Sacramento California Department of Agriculture. Bur. Entomol. 1965, 1–20. Available online: https://www.cdfa.ca.gov/plant/ppd/publications/eriophyid_studies.html (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Teodoro, A.V.; Silva, M.D.J.D.S.; Filho, J.G.D.S.; Oliveira, E.E.D.; Galvão, A.S.; Silva, S.S. Bioactivity of cottonseed oil against the coconut mite Aceria guerreronis (Acari: Eriophyidae) and side effects on Typhlodromus ornatus (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2017, 22, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, V.B.; Lima, D.B.; Gondim, M.G., Jr.; Siqueira, H.A. Residual bioassay to assess the toxicity of acaricides against Aceria guerreronis (Acari: Eriophyidae) under laboratory conditions. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, D.B.; Melo, J.W.D.S.; Gondim, M.G.C.; de Moraes, G.J. Limitations of Neoseiulus baraki and Proctolaelaps bickleyi as control agents of Aceria guerreronis. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2012, 56, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M. Coconut destiny after the invasion of Aceria guerreronis (Acari: Eriophyidae) in India. Zoosymposia 2011, 6, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, N.N.F.C.; Galvão, A.S.; Amaral, E.A.; Santos, A.W.O.; Sena-Filho, J.G.; Oliveira, E.E.; Teodoro, A.V. Toxicity of vegetable oils to the coconut mite Aceria guerreronis and selectivity against the predator Neoseiulus baraki. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2017, 72, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, D.; Melo, J.W.S.; Oliveira, J.E.M.; Gondim, M.G.C. Estimated crop loss due to coconut mite and financial analysis of controlling the pest using the acaricide abamectin. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2016, 69, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, S.; Foale, M.; Samosir, Y. Coconut Revival: New Possibilities for the ‘Tree of Life’. In Proceedings of the International Coconut Forum, Cairns, Australia, 22–24 November 2005; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/102.100.100/177590?index=1 (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Sunpapao, A.; Suwannarach, N.; Kumla, J.; Dumhai, R.; Riangwong, K.; Sanguansub, S.; Wanchana, S.; Arikit, S. Morphological and Molecular Identification of Plant Pathogenic Fungi Associated with Dirty Panicle Disease in Coconuts (Cocos nucifera) in Thailand. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, R.V.; Narita, J.P.Z.; Vichitbandha, P.; Chandrapatya, A.; Konvipasruang, P.; Kongchuensin, M.; Moraes, G.J.D. Prospection for predatory mites to control coconut pest mites in Thailand, with taxonomic descriptions of collected Mesostigmata (Acari). J. Nat. Hist. 2014, 48, 699–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumhai, R.; Wanchana, S.; Saensuk, C.; Choowongkomon, K.; Mahatheeranont, S.; Kraithong, T.; Toojinda, T.; Vanavichit, A.; Arikit, S. Discovery of a novel CnAMADH2 allele associated with higher levels of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline (2AP) in yellow dwarf coconut (Cocos nucifera L.). Sci. Hortic. 2019, 243, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saensuk, C.; Wanchana, S.; Choowongkomon, K.; Wongpornchai, S.; Kraithong, T.; Imsabai, W.; Chaichoompu, E.; Ruanjaichon, V.; Toojinda, T.; Vanavichit, A.; et al. De novo transcriptome assembly and identification of the gene conferring a “pandan-like” aroma in coconut (Cocos nucifera L.). Plant Sci. 2016, 252, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, F.W.; Giblin-Davis, R.; Moore, D.; Abad, R. Insects on Palms; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, L.; Wickramananda, I.; Aratchige, N. Status of coconut mite, Aceria guerreronis in Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Coconut Mite, Lunuwila, Sri Lanka, 6–8 January 2000; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson-Balagbo, L.; Gondim, M.; de Moraes, G.; Hanna, R.; Schausberger, P. Exploration of the acarine fauna on coconut palm in Brazil with emphasis on Aceria guerreronis (Acari: Eriophyidae) and its natural enemies. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2008, 98, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konvipasruang, P.; Kongchuensin, M.C.P.; Chotiwong, W.; Prasoetphon, A. Study of Eriophyid mite pest in Thailand. Thai Agric. Res. J. 2016, 34, 218–229. [Google Scholar]
- Briones, M.L.; Sill, W.H., Jr. Habitat, Gross Morphology and Geographical Distribution of Four New Species of Eriophyid Mites from Coconuts in the Philippines. FAO Plant Prot. Bull. 1963, 11, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Amrine, J., Jr.; Manson, D. 1.6. 3 Preparation, mounting and descriptive study of eriophyoid mites. In: Lindquist, E.E.; Sabelis; M.W.; Bruin, J. (Eds) Eriophyoid Mites. ®Their Biology, Natural Enemies and Control. World Crop Pests 1996, 6, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, E.E.; Bruin, J.; Sabelis, M.W. Eriophyoid Mites: Their Biology, Natural Enemies and Control; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Amrine, J., Jr.; Stasny, T.A.; Flechtmann, C.H. Revised Keys to World Genera of Eriophyoidea (Acari: Prostigmata); Indira Publishing House: Bhopal, India, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein, F.L. Morphometrics in Evolutionary Biology: The Geometry of Size and Shape Change, with Examples from Fishes; Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1985; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Navia, D.; de Moraes, G.J.; Querino, R.B. Geographic pattern of morphological variation of the coconut mite, Aceria guerreronis Keifer (Acari: Eriophyidae), using multivariate morphometry. Braz. J. Biol. 2009, 69, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rohlf, F. Morphometrics at Suny Stony Brook. 2003. Available online: https://www.sbmorphometrics.org/index.html (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Rohlf, F.; Slice, D. Systematic Zoology. Ext. Procrustes Method Optim. Superimpos. Landmarks 1990, 39, 40–59. [Google Scholar]
- Klingenberg, C.P. MorphoJ: An integrated software package for geometric morphometrics. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, Ş.; Altun, A.; Ayyildiz, N.; Kence, A. Morphometric analysis of oppiid mites (Acari, Oribatida) collected from Turkey. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2011, 54, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navia, D.; Ferreira, C.B.S.; Reis, A.C.; Gondim, M.G.C. Traditional and geometric morphometrics supporting the differentiation of two new Retracrus (Phytoptidae) species associated with heliconias. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 67, 87–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Ali, Z.; Boursot, P.; Said, K.; Lagnel, J.; Chatti, N.; Navajas, M. Comparison of Ribosomal ITS Regions Among Androctonus spp. Scorpions (Scorpionida: Buthidae) from Tunisia. J. Med. Entomol. 2000, 37, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, C.; Frati, F.; Beckenbach, A.; Crespi, B.; Liu, H.; Flook, P. Evolution, Weighting, and Phylogenetic Utility of Mitochondrial Gene Sequences and a Compilation of Conserved Polymerase Chain Reaction Primers. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1994, 87, 651–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions when there are strong transition-transversion and G+ C-content biases. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1992, 9, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracka, A.; Kuczynski, L.; Magowski, W. Morphological variation in different host populations of Abacarus hystrix (Acari: Prostigmata: Eriophyoidea). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2002, 26, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracka, A.; Kuczyński, L.; de Mendonça, R.S.; Dabert, M.; Szydło, W.; Knihinicki, D.; Truol, G.; Navia, D. Cryptic species within the wheat curl mite Aceria tosichella (Keifer)(Acari: Eriophyoidea), revealed by mitochondrial, nuclear and morphometric data. Invertebr. Syst. 2012, 26, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidović, B.; Stanisavljević, L.; Petanović, R. Phenotypic variability in five Aceria spp. (Acari: Prostigmata: Eriophyoidea) inhabiting Cirsium species (Asteraceae) in Serbia. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2010, 52, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidović, B.; Cvrković, T.; Marić, I.; Chetverikov, P.E.; Cristofaro, M.; Rector, B.G.; Petanović, R. A New Metaculus Species (Acari: Eriophyoidea) on Diplotaxis tenuifolia (Brassicaceae) From Serbia: A Combined Description Using Morphology and DNA Barcode Data. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2015, 108, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetverikov, P.E. Phytoptus atherodes n. sp.(Acari: Eriophyoidea: Phytoptidae) and a supplementary description of Phytoptus hirtae Roivainen 1950 from sedges (Cyperaceae). Zootaxa 2011, 3045, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, M.; Skoracka, A.; Szydło, W.; Kozak, M.; Druciarek, T.; Griffiths, D.A. Genetic and morphological diversity of Trisetacus species (Eriophyoidea: Phytoptidae) associated with coniferous trees in Poland: Phylogeny, barcoding, host and habitat specialization. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2014, 63, 497–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzano, D.; Tumminello, M.T.; Gualandri, V.; de Lillo, E. Morphological and molecular characterization of the Colomerus vitis erineum strain (Trombidiformes: Eriophyidae) from grapevine erinea and buds. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2020, 80, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi Khederi, S.; Khanjani, M.; Bahman; Fayaz, A. Resistance of three grapevine cultivars to Grape Erineum Mite, Colomerus vitis (Acari: Eriophyidae), in field conditions. Persian J. Acarol. 2014, 3, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczek, J.; Zawadzki, W.; Davis, R. Some morphological and biological differences in Aculus fockeui (Nalepa and Trouessart) (Acari: Eriophyidae) on various host plants. Int. J. Acarol. 1984, 10, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiamma, B.; Nair, C.P.R.; Koshy, P.K. Outbreak of a nut infesting eriophyid mite Eriophyes guerreronis (K.) in coconut plantations in India. Indian Coconut J. 1998, 29, 1–3. Available online: https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/19981111449 (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Fernando, L.; Aratchige, N. Status of coconut mite Aceria guerreronis and biological control research in Sri Lanka. Trends Acarol. 2010, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navia, D.; de Moraes, G.J.; Roderick, G.; Navajas, M. The invasive coconut mite Aceria guerreronis (Acari: Eriophyidae): Origin and invasion sources inferred from mitochondrial (16S) and nuclear (ITS) sequences. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2005, 95, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
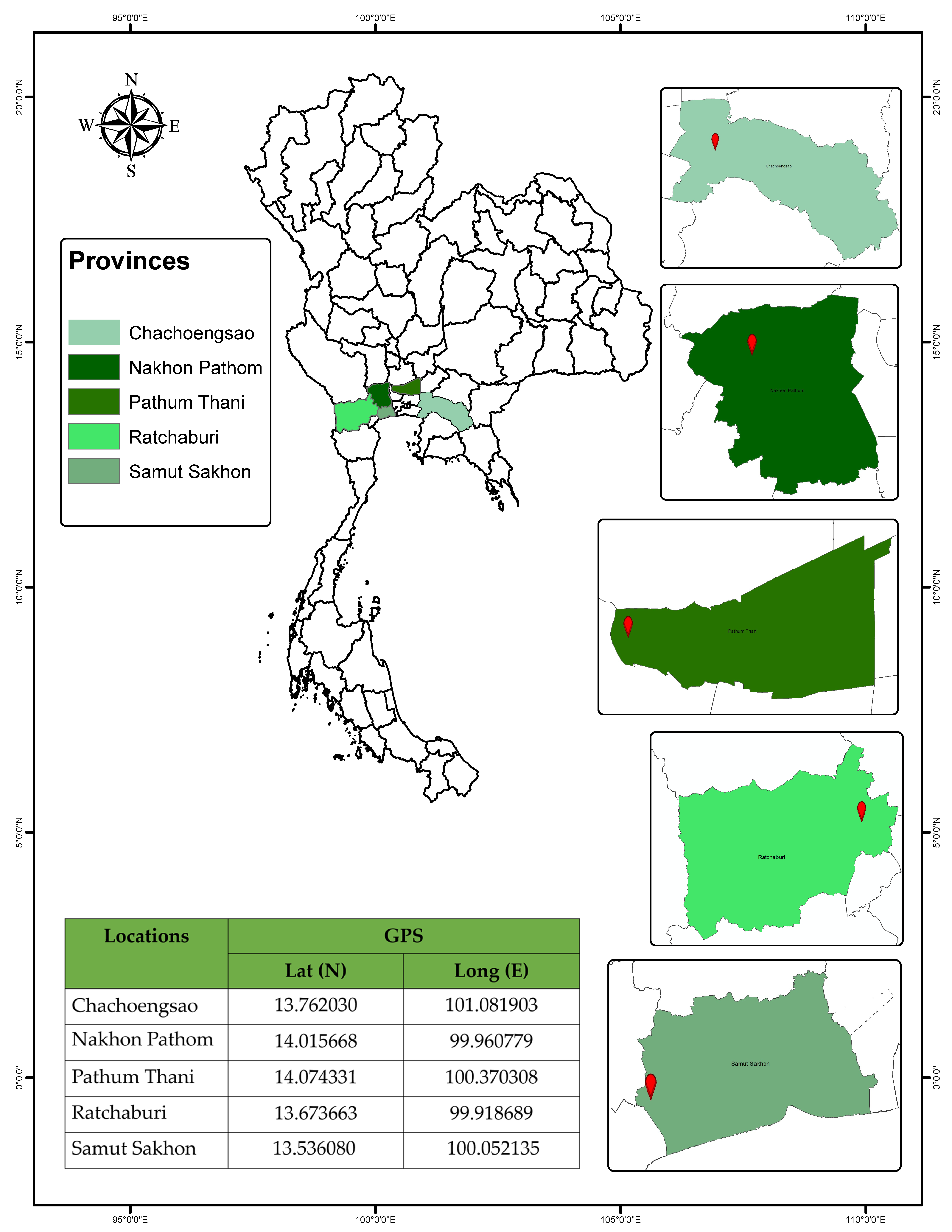






| Continent | Country | Locality | Code | Number of Females |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asia | Thailand | Chachoengsao | a | 15 |
| Nakhon Pathom | b | 15 | ||
| Pathum Thani | c | 15 | ||
| Ratchaburi | d | 15 | ||
| Samut Sakhon | e | 15 |
| Samples | Total Coconut Mite Samples |
|---|---|
| Chachoengsao (C) | CT1, CT2, CT3, CT4, CT5, CT6 (6 samples) |
| Nakhon Pathom (N) | NT1, NT2, NT3, NT4, NT5 (5 samples) |
| Pathum Thani (P) | PT1, PT2, PT3, PT4, PT5 (5 samples) |
| Ratchaburi (R) | RT1, RT2, RT3, RT4, RT5, RT6 (6 samples) |
| Samut Sakhon (S) | ST1, ST2, ST3 (3 samples) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buttachon, S.; Arikit, S.; Nuchchanart, W.; Puangmalee, T.; Duanchay, T.; Jampameung, N.; Sanguansub, S. Geometric Morphometric Analysis and Molecular Identification of Coconut Mite, Aceria guerreronis Keifer (Acari: Eriophyidae) Collected from Thailand. Insects 2022, 13, 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13111022
Buttachon S, Arikit S, Nuchchanart W, Puangmalee T, Duanchay T, Jampameung N, Sanguansub S. Geometric Morphometric Analysis and Molecular Identification of Coconut Mite, Aceria guerreronis Keifer (Acari: Eriophyidae) Collected from Thailand. Insects. 2022; 13(11):1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13111022
Chicago/Turabian StyleButtachon, Suradet, Siwaret Arikit, Wirawan Nuchchanart, Thanapol Puangmalee, Tidapa Duanchay, Nattaya Jampameung, and Sunisa Sanguansub. 2022. "Geometric Morphometric Analysis and Molecular Identification of Coconut Mite, Aceria guerreronis Keifer (Acari: Eriophyidae) Collected from Thailand" Insects 13, no. 11: 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13111022
APA StyleButtachon, S., Arikit, S., Nuchchanart, W., Puangmalee, T., Duanchay, T., Jampameung, N., & Sanguansub, S. (2022). Geometric Morphometric Analysis and Molecular Identification of Coconut Mite, Aceria guerreronis Keifer (Acari: Eriophyidae) Collected from Thailand. Insects, 13(11), 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13111022








