Exploring Higher-Order Conceptual Learning in an Arthropod with a Large Multisensory Processing Center
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
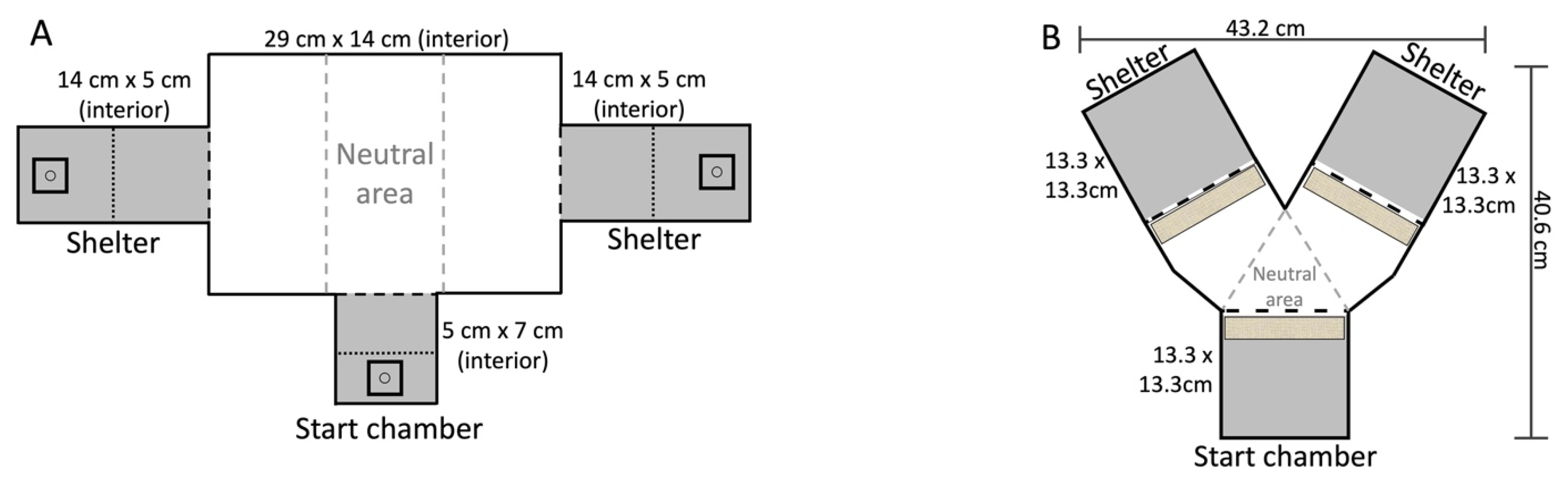
2.1. Experimental Design Overview
2.2. Experiment 1—Within Modality “Sameness” Assay
2.2.1. Study Organism
2.2.2. Initial Training Trials
2.2.3. Trained Odor Test
2.2.4. Reinforcement Training Trials
2.2.5. Novel Odor Test
2.3. Experiment 2—Cross-Modal Same/Different Assay
2.3.1. Study Organism
2.3.2. Training Trials
2.3.3. Test Trials
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Experiment 1—Within Modality ‘Sameness’ Assay
3.2. Experiment 2—Cross-Modal Same/Different Assay
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bayne, T.; Brainard, D.; Byrne, R.W.; Chittka, L.; Clayton, N.; Heyes, C.; Mather, J.; Ölveczky, B.; Shadlen, M.; Suddendorf, T.; et al. What is cognition? Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R608–R615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, J.M. Animal Learning and Cognition An Introduction, 3rd ed.; Psychology Press: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shettleworth, S.J. Cognition, Evolution, and Behavior; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, A.B.; Hebets, E.A.; Cleland, T.A.; Fitzpatrick, C.L.; Hauber, M.E.; Stevens, J.R. Embracing multiple definitions of learning. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamil, A.C.; Gould, K.L. Memory in Food Caching Animals. In Learning and Memory: A Comprehensive Reference, Volume I Learning Theory and Behaviour; Menzel, R., Byrne, J.H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 419–439. [Google Scholar]
- Collett, T.S.; Graham, P.; Harris, R.A.; Hempel-de-Ibarra, N. Navigational Memories in Ants and Bees: Memory Retrieval When Selecting and Following Routes. Adv. Study Behav. 2006, 36, 123–172. [Google Scholar]
- Saverschek, N.; Herz, H.; Wagner, M.; Roces, F. Avoiding plants unsuitable for the symbiotic fungus: Learning and long-term memory in leaf-cutting ants. Anim. Behav. 2010, 79, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, A.S.; Guez, D. Innovation and problem solving: A review of common mechanisms. Behav. Processes 2014, 109, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loukola, O.J.; Perry, C.J.; Coscos, L.; Chittka, L. Bumblebees show cognitive flexibility by improving on an observed complex behavior. Science 2017, 355, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Noser, R.; Hammerschmidt, K. Bioacoustic field research: A primer to acoustic analyses and playback experiments with primates. Am. J. Primatol. 2013, 75, 643–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffer, B.; Walker, S.E. The use of multimodal communication in mate choice decisions by female house crickets, Acheta domesticus. Anim. Behav. 2012, 83, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkart, J.M.; Schubiger, M.N.; Van Schaik, C.P. The evolution of general intelligence. Behav. Brain Sci. 2017, 40, e195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosmides, L.; Tooby, J. Evolutionary psychology: New perspectives on cognition and motivation. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2013, 64, 201–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachman, S.J. Learning is a process: Toward an improved definition of learning. J. Psychol. Interdiscip. Appl. 1997, 131, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J.; Wright, A.A.; Bodily, K.D. Issues in the Comparative Cognition of Abstract-Concept Learning. Comp. Cogn. Behav. Rev. 2007, 2, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Marcus, G.F.; Vijayan, S.; Bandi Rao, S.; Vishton, P.M. Rule learning by seven-month-old infants. Science 1999, 283, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, A.L.; Hagemann, D.; Frischkorn, G.T. Is general intelligence little more than the speed of higher-order processing? J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2017, 146, 1498–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roitberg, E.; Franz, H. Oddity learning by African dwarf goats (Capra hircus). Anim. Cogn. 2004, 7, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, E., III; Killebrew, D.A.; Pack, A.A.; Macha, I.V.B.; Herman, L.M. Generalization of ‘same–different’ classification abilities in bottlenosed dolphins. Behav. Processes 2000, 50, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hille, P.; Dehndardt, G.; Mauck, B. An analysis of visual oddity concept learning in a California sea lion (Zalophus californianus). Learn. Behav. 2006, 34, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wright, A.A.; Shyan, M.R.; Jitsumori, M. Auditory same/different concept learning by monkeys. Anim. Learn. Behav. 1990, 18, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, F.; Burke, D. Conditional same/different concept learning in the short-beaked echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus). J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 2016, 105, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, E. Relational rule learning in the rat. Psychobiology 1993, 21, 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, A.A.; Cook, R.G.; Rivera, J.J.; Sands, S.F.; Delius, J.D. Concept learning by pigeons: Matching-to-sample with trial-unique video picture stimuli. Anim. Learn. Behav. 1988, 16, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, T.A.; Wright, A.A.; Katz, J.S. Abstract-concept learning of difference in pigeons. Anim. Cogn. 2015, 18, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astley, S.L.; Wasserman, E.A. Categorical discrimination and generalization in pigeons: All negative stimuli are not created equal. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 1992, 18, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, A.; Kacelnik, A. Ducklings imprint on the relational concept of “same or different”. Science 2016, 353, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, C.J.; Barron, A.B.; Cheng, K. Invertebrate learning and cognition: Relating phenomena to neural substrate. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Cogn. Sci. 2013, 4, 561–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giurfa, M.; Zhang, S.; Jenett, A.; Menzel, R.; Srinivasan, M.V. The concepts of ‘sameness’ and ‘difference’ in an insect. Nature 2001, 410, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muszynski, N.M.; Couvillon, P.A. Category difference facilitates oddity learning in honeybees (Apis mellifera). J. Comp. Psychol. 2020, 134, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszynski, N.M.; Couvillon, P.A. Relational learning in honeybees (Apis mellifera): Oddity and nonoddity discrimination. Behav. Processes 2015, 115, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortot, M.; Agrillo, C.; Avarguès-Weber, A.; Bisazza, A.; Petrazzini, M.E.M.; Giurfa, M. Honeybees use absolute rather than relative numerosity in number discrimination. Biol. Lett. 2019, 15, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giurfa, M. An Insect’s Sense of Number. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2019, 23, 720–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurfa, M. Honeybees foraging for numbers. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 2019, 205, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strausfeld, N.J. Arthropod Brains: Evolution, Functional Elegance, and Historical Significance; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Strausfeld, N.J.; Sinakevitch, I.; Brown, S.M.; Farris, S.M. Ground plan of the insect mushroom body: Functional and evolutionary implications. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 513, 265–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avarguès-Weber, A.; Giurfa, M. Conceptual learning by miniature brains. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20131907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinakevitch, I.; Long, S.M.; Gronenberg, W. The central nervous system of whip spiders (Amblypygi): Large mushroom bodies receive olfactory and visual input. J. Comp. Neurol. 2020, 529, 1642–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, F.C. The brain of the bee. A preliminary contribution to the morphology of the nervous system of the Arthropoda. J. Comp. Neurol. 1896, 6, 133–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strausfeld, N.J.; Strausfeld, C.M.; Loesel, R.; Rowell, D.; Stowe, S. Arthropod phylogeny: Onychophoran brain organization suggests an archaic relationship with a chelicerate stem lineage. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 1857–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, G.; Harzsch, S.; Hansson, B.S.; Brown, S.; Strausfeld, N. Neuronal organization of the hemiellipsoid body of the land hermit crab, Coenobita clypeatus: Correspondence with the mushroom body ground pattern. J. Comp. Neurol. 2012, 520, 2824–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, G.H.; Strausfeld, N.J. Genealogical correspondence of a forebrain centre implies an executive brain in the protostome-deuterostome bilaterian ancestor. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Belle, J.S.; Heisenberg, M. Associative Odor Learning in Drosophila Abolished by Chemical Ablation of Mushroom Bodies. Science 1994, 263, 692–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zars, T.; Fischer, M.; Schulz, R.; Heisenberg, M. Localization of a short-term memory in Drosophila. Science 2000, 288, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, A.; Préat, T. Localization of long-term memory within the Drosophila mushroom body. Science 2001, 294, 1115–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heisenberg, M. Mushroom body memoir: From maps to models. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cognigni, P.; Felsenberg, J.; Waddell, S. Do the right thing: Neural network mechanisms of memory formation, expression and update in Drosophila. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 49, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guven-Ozkan, T.; Davis, R.L. Functional neuroanatomy of Drosophila olfactory memory formation. Learn. Mem. 2014, 21, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erber, J.; Masuhr, T.H.; Menzel, R. Localization of short-term memory in the brain of the bee, Apis mellifera. Physiol. Entomol. 1980, 5, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, R. Searching for the memory trace in a mini-brain, the honeybee. Learn. Mem. 2001, 8, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaud, J.M.; Papouin, T.; Carcaud, J.; Sandoz, J.C.; Grönewald, B.; Giurfa, M. Neural substrate for higher-order learning in an insect: Mushroom bodies are necessary for configural discriminations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5854–E5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, R.; Giurfa, M. Cognitive architecture of a mini-brain: The honeybee. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2001, 5, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizunami, M.; Weibrecht, J.M.; Strausfeld, N.J. Mushroom bodies of the cockroach: Their participation in place memory. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998, 402, 520–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizunami, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Nishino, H. Olfactory and Visual Learning in Cockroaches and Crickets. In Invertebrate Learning and Memory, Handbook of Behavioral Neuroscience; Menzel, R., Benjamin, P.R., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 22, pp. 549–560. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, L.; Foelix, R.; Gödeke, E.; Kaiser, R. Über die haarsen sillen der geißelspinne Admetus pumilio (Arach., Amblypygi). Naturwissenschaften 1974, 61, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.; Foelix, R.; Gödeke, E.; Kaiser, R. Morphologie, larvalentwicklung und haarsensillen des tastbeinpaares der geißelspinne Heterophrynus longicornis Butler (Arach., Amblypygi). Zoomorphologie 1977, 88, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foelix, R.; Chu-Wang, I.; Beck, L. Fine structure of tarsal sensory organs in the whip spider Admetus pumilio (Amblypygi, Arachnida). Tissue Cell 1975, 7, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foelix, R.F.; Troyer, D. Giant neurons and associated synapses in the peripheral nervous system of whip spiders. J. Neurocytol. 1980, 9, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebets, E.A.; Chapman, R.F. Electrophysiological studies of olfaction in the whip spider Phrynus parvulus (Arachnida, Amblypygi). J. Insect Physiol. 2000, 46, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, R.D.; Hebets, E.A. Agonistic signals received by an arthropod filiform hair allude to the prevalence of near-field sound communication. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 275, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santer, R.D.; Hebets, E.A. Tactile learning by a whip spider, Phrynus marginemaculatus C.L. Koch (Arachnida, Amblypygi). J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 2009, 195, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, R.D.R.D.; Hebets, E.A. Prey capture by the whip spider Phrynus marginemaculatus C. L. Koch. Can. J. Zool. 2009, 37, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, R.D.; Hebets, E.A. The sensory and behavioural biology of whip spiders (Arachnida, Amblypygi). Adv. Insect Phys. 2011, 41, 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Santer, R.D.; Hebets, E.A. Evidence for air movement signals in the agonistic behaviour of a nocturnal arachnid (order amblypygi). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foelix, R.; Hebets, E. Sensory Biology of Whip Spiders (Arachnida, Amblypygi). Andrias 2001, 15, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Spence, A.J.; Hebets, E.A. Anatomy and physiology of giant neurons in the antenniform leg of the amblypygid Phrynus marginemaculatus. J. Arachnol. 2006, 34, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hebets, E.A. Relating the unique sensory system of amblypygids to the ecology and behavior of Phrynus parvulus from Costa Rica (Arachnida, Amblypygi). Can. J. Zool. 2002, 80, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingman, V.P.; Graving, J.M.; Hebets, E.A.; Wiegmann, D.D. Importance of the antenniform legs, but not vision, for homing by the neotropical whip spider Paraphrynus laevifrons. J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebets, E.A.; Gering, E.J.; Bingman, V.P.; Wiegmann, D.D. Nocturnal homing in the tropical amblypygid Phrynus pseudoparvulus (Class Arachnida, Order Amblypygi). Anim. Cogn. 2014, 17, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hebets, E.A.; Aceves-Aparicio, A.; Aguilar-Argüello, S.; Bingman, V.P.; Escalante, I.; Gering, E.J.; Nelsen, D.R.; Rivera, J.; Sánchez-Ruiz, J.Á.; Segura-Hernández, L.; et al. Multimodal sensory reliance in the nocturnal homing of the amblypygid Phrynus pseudoparvulus (Class Arachnida, Order Amblypygi)? Behav. Processes 2014, 108, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegmann, D.D.; Hebets, E.A.; Gronenberg, W.; Graving, J.M.; Bingman, V.P. Amblypygids: Model organisms for the study of arthropod navigation mechanisms in complex environments? Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Escobar, J. Homing in the arachnid taxa Araneae and Amblypygi. Anim. Cogn. 2020, 23, 1189–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffin, D.D.; Curry, C.M. Review: Arachnid navigation-a review of classic and emerging models. J. Arachnol. 2020, 48, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanigan, K.A.S.; Wiegmann, D.D.; Casto, P.; Coppola, V.J.; Flesher, N.R.; Hebets, E.A.; Bingman, V.P. Visual control of refuge recognition in the whip spider Phrynus marginemaculatus. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2021, 207, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanigan, K.A.S.; Wiegmann, D.D.; Hebets, E.A.; Bingman, V.P. Multisensory integration supports configural learning of a home refuge in the whip spider Phrynus marginemaculatus. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 224, jeb238444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casto, P.; Wiegmann, D.D.; Coppola, V.J.; Nardi, D.; Hebets, E.A.; Bingman, V.P. Vertical-surface navigation in the Neotropical whip spider Paraphrynus laevifrons (Arachnida: Amblypygi). Anim. Cogn. 2020, 23, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casto, P.; Gosser, J.; Wiegmann, D.D.; Hebets, E.A.; Bingman, V.P. Self-derived chemical cues support home refuge recognition in the whip spider Phrynus marginemaculatus (Amblypygi: Phrynidae). J. Arachnol. 2019, 47, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegmann, D.D.; Moore, C.H.; Flesher, N.R.; Harper, E.D.; Keto, K.R.; Hebets, E.A.; Bingman, V.P. Nocturnal navigation by whip spiders: Antenniform legs mediate near-distance olfactory localization of a shelter. Anim. Behav. 2019, 149, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, R.E.; Rayor, L.S. Kin discrimination in the amblypygid, Damon diadema. J. Arachnol. 2008, 36, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler-Finn, K.D.; Hebets, E.A. An examination of agonistic interactions in the whip spider Phrynus marginemaculatus (arachnida, amblypygi). J. Arachnol. 2006, 34, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, K.J.; Hebets, E.A. The behavioral ecology of amblypygids. J. Arachnol. 2016, 44, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, D. The Amblypygid Genus Phrynus in the Americas (Amblypygi, Phrynidae). J. Arachnol. 1981, 9, 117–166. [Google Scholar]
- Weygoldt, P. Whip Spiders (Chelicerata: Amblypygi): Their Biology, Morphology, and Systematics; Apollo Books: Stenstrup, Denmark, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mullinex, C.L. Revision of Paraphrynus Moreno (Amblypygida: Phrynidae) for North America and the Antilles. Occas. Pap. Calif. Acad. Sci. San Fr. 1975, 116, 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Corey, T.B.; Hebets, E.A. A characterization of social interactions across age and sex in the amblypygid Paraphrynus laevifrons. J. Arachnol. 2020, 48, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, T.B.; Hebets, E.A. Microhabitat use in the amblypygid Paraphrynus laevifrons. J. Arachnol. 2017, 45, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonferroni, C.E. Teoria statistica delle classi e calcolo delle probabilita. Pubbl. R Ist. Super. Sci. Econ. E Commer. Firenze 1936, 8, 3–62. [Google Scholar]
- Cribari-Neto, F.; Zeileis, A. Beta Regression in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 34, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, M.E.; Kristensen, K.; van Benthem, K.J.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.W.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, H.J.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M. glmmTMB balances speed and flexibility among packages for zero-inflated generalized linear mixed modeling. R J. 2017, 9, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T.M.; Grambsch, P.M. Modeling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 0-387-98784-3. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wilke, C.O. Cowplot: Streamlined Plot Theme and Plot Annotations for “ggplot2”. R Package Version 1.1.1. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=cowplot (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graving, J.M.; Bingman, V.P.; Hebets, E.A.; Wiegmann, D.D. Development of site fidelity in the nocturnal amblypygid, Phrynus marginemaculatus. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2017, 203, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderSal, N.D.; Hebets, E.A. Cross-modal effects on learning: A seismic stimulus improves color discrimination learning in a jumping spider. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 3689–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Newport, C.; Wallis, G.; Siebeck, U.E. Same/different abstract concept learning by archerfish (Toxotes chatareus). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newport, C.; Wallis, G.; Siebeck, U.E. Concept learning and the use of three common psychophysical paradigms in the archerfish (Toxotes chatareus). Front. Neural Circuits 2014, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierszewski, S.; Bleckmann, H.; Schluessel, V. Cognitive Abilities in Malawi Cichlids (Pseudotropheus sp.): Matching-to-Sample and Image/Mirror-Image Discriminations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Model Response Variable | Predictors | Log-Odds/Estimates | SE | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correct First Choice (Y/N) | (Intercept) | 0.20 | 0.32 | 0.525 |
| TrialNo | −0.04 | 0.04 | 0.220 | |
| Observations | 196 | ∆AIC | 0.49 | |
| Success (Y/N) | (Intercept) | 3.68 | 0.93 | <0.001 |
| TrialNo | −0.05 | 0.07 | 0.494 | |
| Observations | 196 | ∆AIC | 1.53 | |
| Proportion of Time Spent on Correct Side | (Intercept) | 0.71 | 0.20 | <0.001 |
| TrialNo | −0.03 | 0.02 | 0.186 | |
| Observations | 195 | ∆AIC | −0.25 |
| Model Response Variable | Predictors | Log-Odds/Estimates | SE | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Success (Y/N) | (Intercept) | 0.62 | 0.71 | 0.384 |
| TrialNo | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.947 | |
| Observations | 120 | ∆AIC | 1.99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lehmann, K.D.S.; Shogren, F.G.; Fallick, M.; Watts, J.C.; Schoenberg, D.; Wiegmann, D.D.; Bingman, V.P.; Hebets, E.A. Exploring Higher-Order Conceptual Learning in an Arthropod with a Large Multisensory Processing Center. Insects 2022, 13, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010081
Lehmann KDS, Shogren FG, Fallick M, Watts JC, Schoenberg D, Wiegmann DD, Bingman VP, Hebets EA. Exploring Higher-Order Conceptual Learning in an Arthropod with a Large Multisensory Processing Center. Insects. 2022; 13(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010081
Chicago/Turabian StyleLehmann, Kenna D. S., Fiona G. Shogren, Mariah Fallick, James Colton Watts, Daniel Schoenberg, Daniel D. Wiegmann, Verner P. Bingman, and Eileen A. Hebets. 2022. "Exploring Higher-Order Conceptual Learning in an Arthropod with a Large Multisensory Processing Center" Insects 13, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010081
APA StyleLehmann, K. D. S., Shogren, F. G., Fallick, M., Watts, J. C., Schoenberg, D., Wiegmann, D. D., Bingman, V. P., & Hebets, E. A. (2022). Exploring Higher-Order Conceptual Learning in an Arthropod with a Large Multisensory Processing Center. Insects, 13(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010081






