Alternative Nesting Strategies of Polistine Wasps in a Subtropical Locale
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Do polistine wasps in a subtropical locale initiate nests in both early and late season?
- (2)
- Does colony duration and peak number of adults, pupae (capped cells), and cells differ between early and late season?
- (3)
- Does the proportion of single foundress and multi foundress nests differ between early and late season among species?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
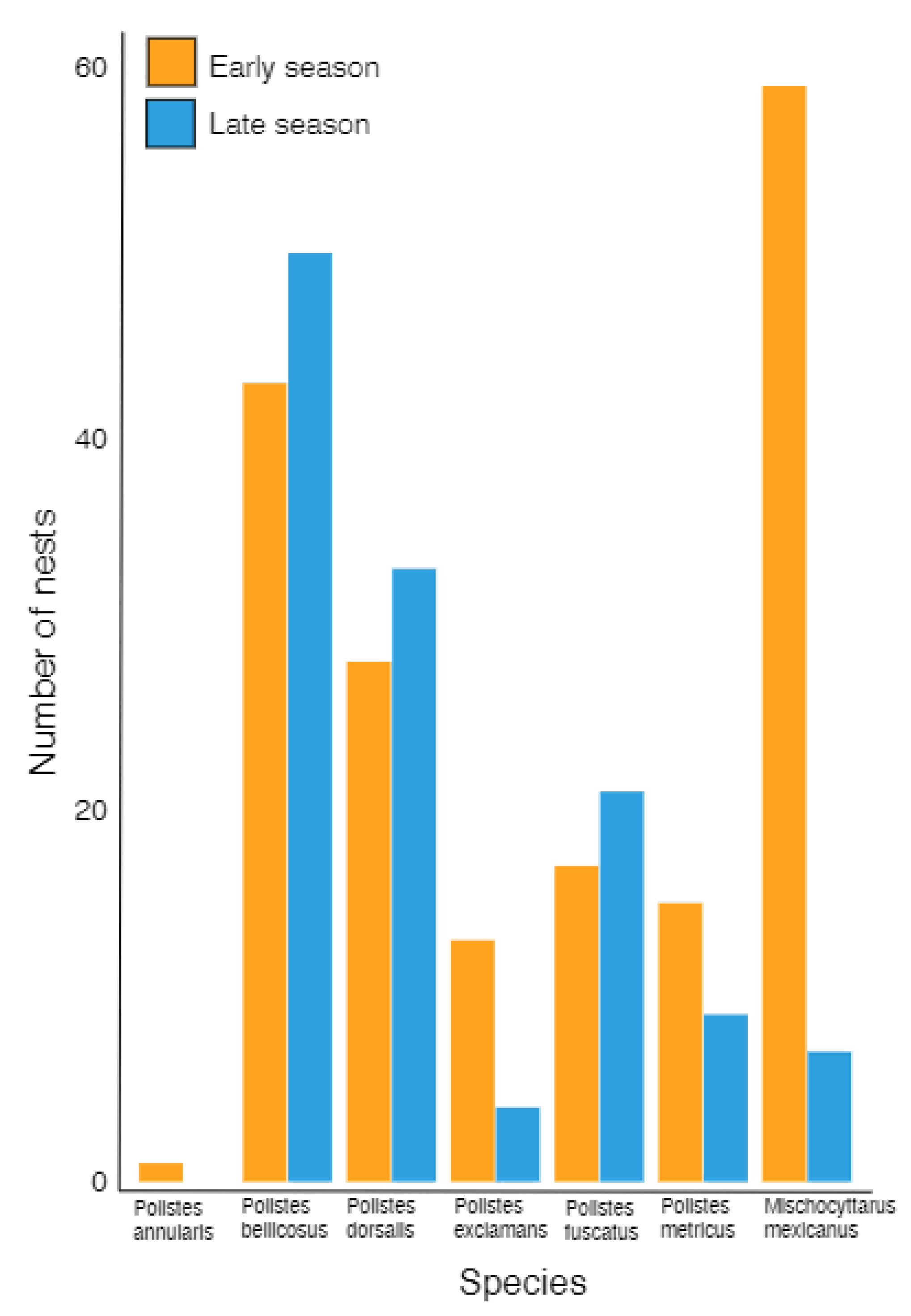
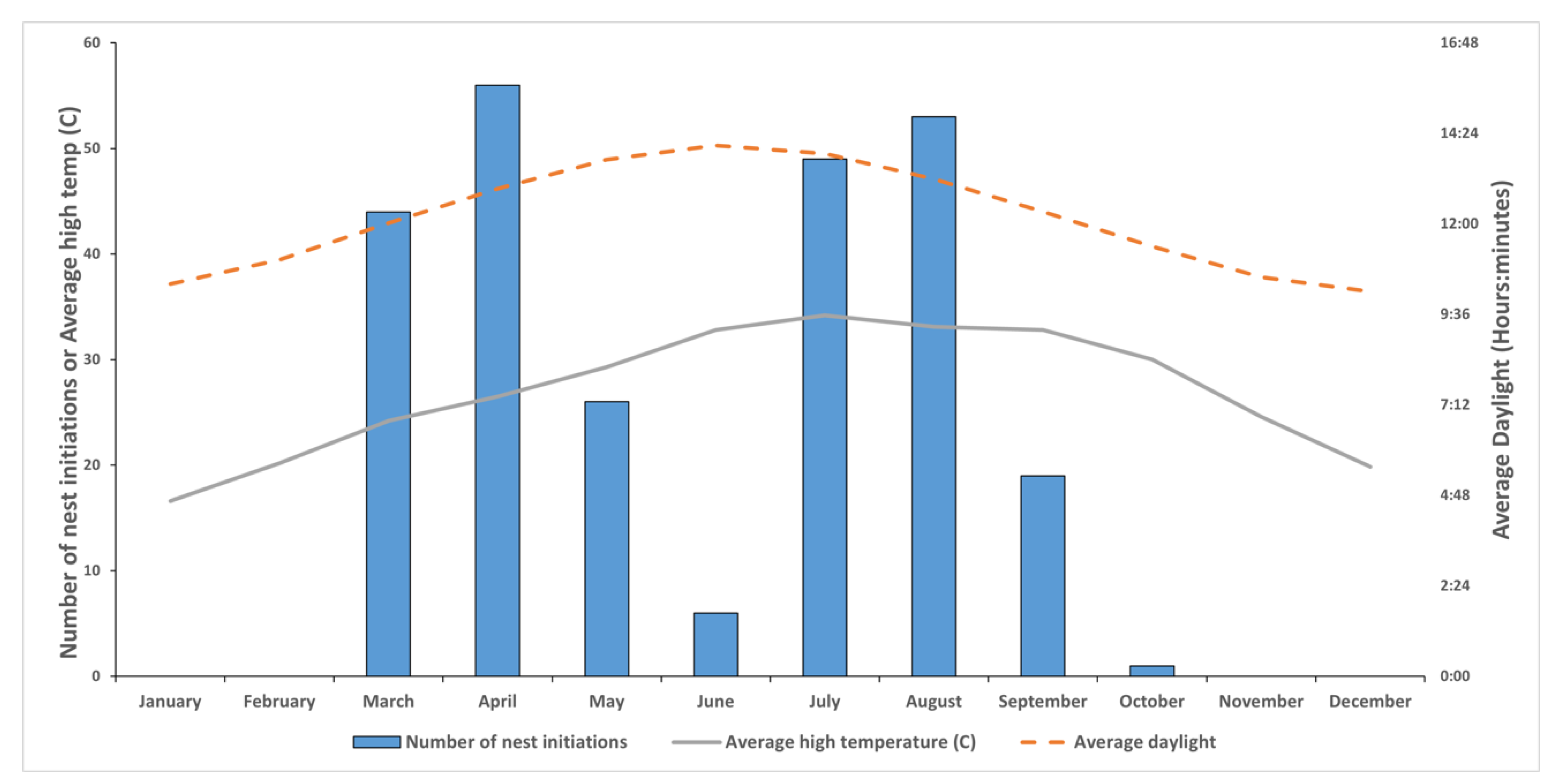
3.1. Species Composition and Periods of Nest Initiation
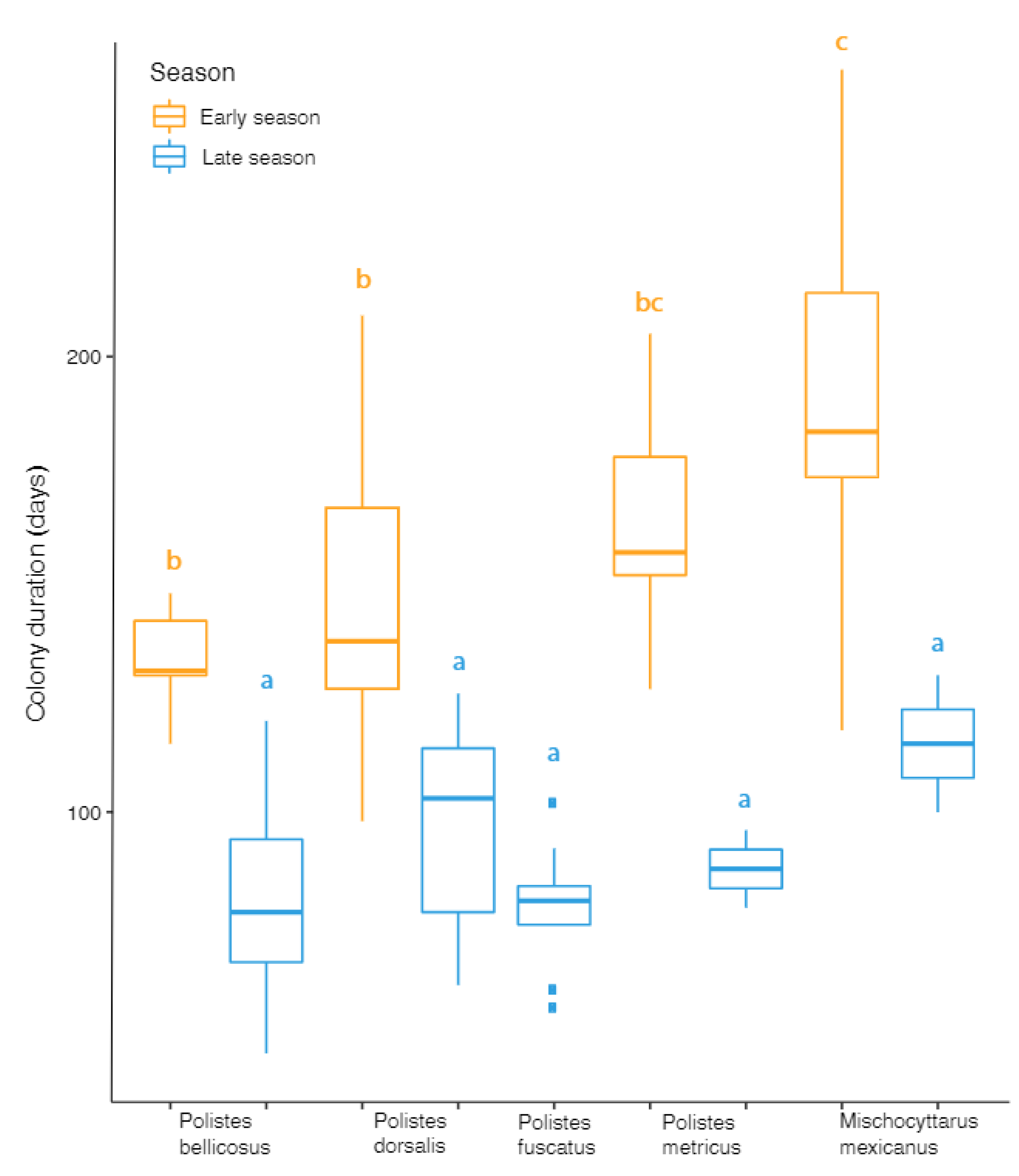
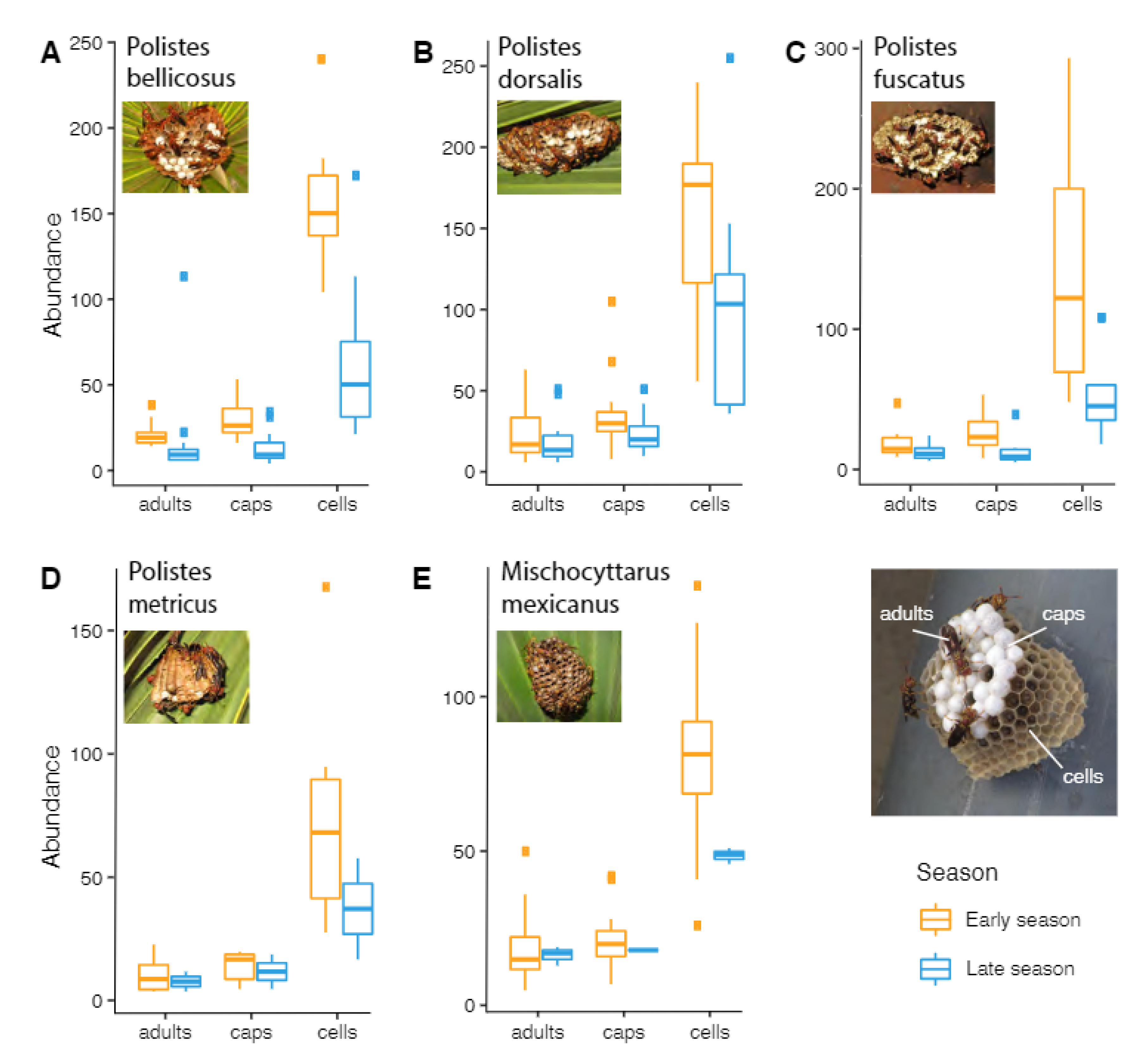
3.2. Colony Duration and Nest Parameters
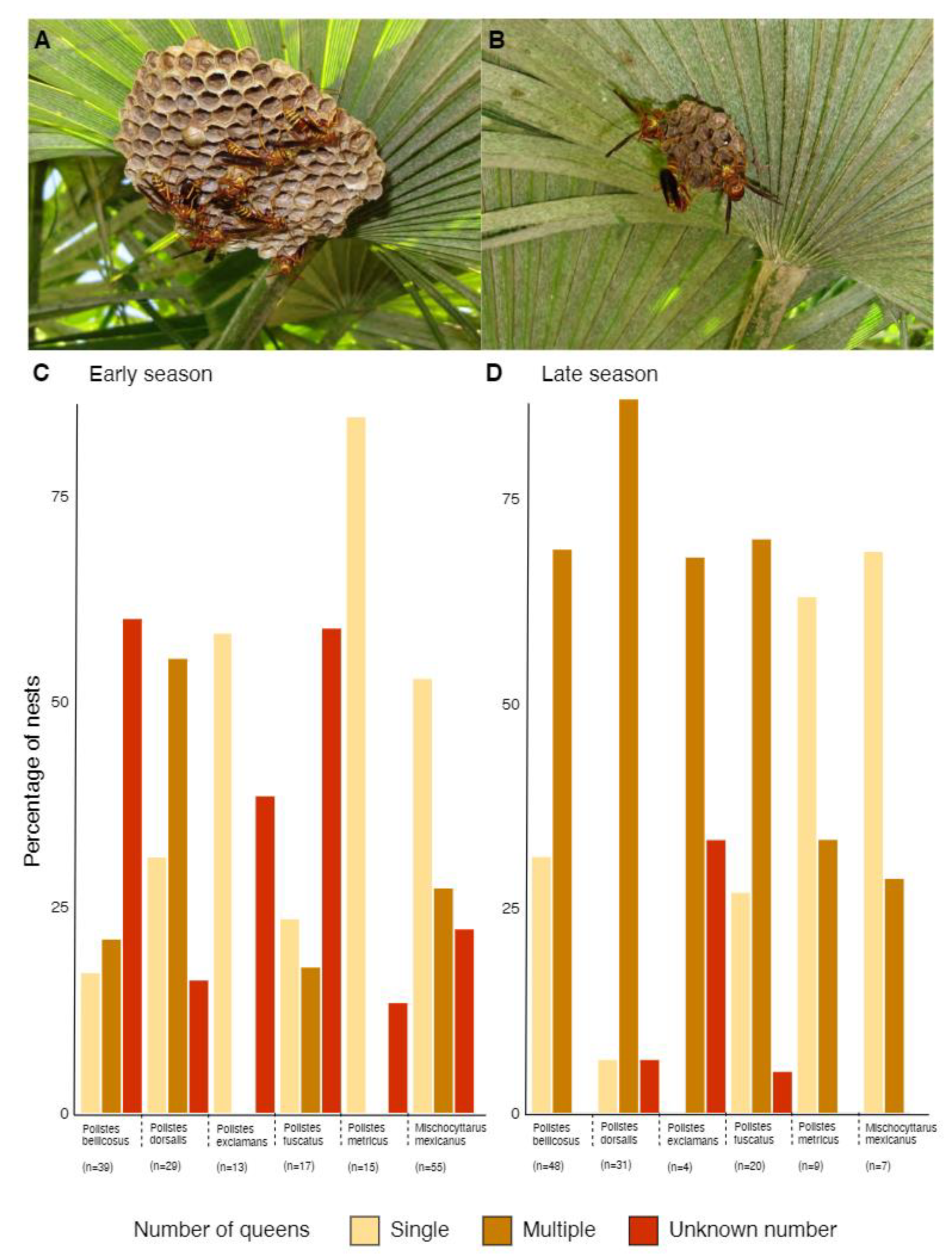
3.3. Polistine Nesting Behavior
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- West-Eberhard, M.J. The Social Biology of Polistine Wasps; Miscellaneous Publications Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan No. 140; University of Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Tauber, M.J.; Tauber, C.A.; Masaki, S. Seasonal Adaptations of Insects; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Forrest, J.R. Complex responses of insect phenology to climate change. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2016, 17, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrest, J.; Miller-Rushing, A.J. Toward a synthetic understanding of the role of phenology in ecology and evolution. Philos. Trans. R Soc. B 2010, 365, 3101–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ovaskainen, O.; Skorokhodova, S.; Yakovleva, M.; Sukhov, A.; Kutenkov, A.; Kutenkova, N.; del Mar Delgado, M. Community-level phenological response to climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13434–13439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boivin, T.; Bouvier, J.C.; Beslay, D.; Sauphanor, B. Variability in diapause propensity within populations of a temperate insect species: Interactions between insecticide resistance genes and photoperiodism. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2004, 83, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macevicz, S.; Oster, G. Modeling social insect populations II: Optimal reproductive strategies in annual eusocial insect colonies. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1976, 1, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.J.; Roff, D.A. Genetic and phenotypic sources of life history variation along a cline in voltinism in the cricket Allonemobius socius. Oecologia 1995, 103, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segev, U.; Burkert, L.; Feldmeyer, B.; Foitzik, S. Pace-of-life in a social insect: Behavioral syndromes in ants shift along a climatic gradient. Behav. Ecol. 2017, 28, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, F.B.; da Silva, M.; Soleman, R.A.; Lopes, R.B.; Grandinete, Y.C.; Almeida, E.A.; Carpenter, J.M. Marimbondos: Systematics, biogeography, and evolution of social behaviour of neotropical swarm-founding wasps (Hymenoptera: Vespidae: Epiponini). Cladistics 2021, 37, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West-Eberhard, M.J. Polygyny and the evolution of social behavior in wasps. J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 1978, 51, 832–856. [Google Scholar]
- Silveira, O.T. Phylogeny of wasps of the genus Mischocyttarus de Saussure (Hymenoptera, Vespidae, Polistinae). Rev. Bras. Entomol. 2008, 52, 510–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altermatt, F. Climatic warming increases voltinism in European butterflies and moths. Proc. R Soc. B 2010, 277, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshimura, H.; Yamada, Y.Y. Caste-fate determination primarily occurs after adult emergence in a primitively eusocial paper wasp: Significance of the photoperiod during the adult stage. Sci. Nat. 2018, 105, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, S.; Cini, A. Paper wasps (Polistes). In Encyclopedia of Social Insects; Starr, C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2021; pp. 697–709. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, J.H.; Amdam, G.V. Bivoltinism as an antecedent to eusociality in the paper wasp genus Polistes. Science 2005, 308, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strassmann, J.E. Evolutionary implications of early male and satellite nest production in Polistes exclamans colony cycles. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1981, 8, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, S.; Okazawa, T. Some biological observations on a paper wasp, Polistes (Megapolistes) tepidus malayanus Cameron (Hymenoptera, Vespidae) in New Guinea. Insects 1977, 45, 283–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, S. Ecological Factors Influencing the colony cycle of Polistes wasps. In Natural History and Evolution of Paper-Wasps; Turillazzi, S., West-Eberhard, M.J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- Gadagkar, R. The Evolution of eusociality, including a review of the social status of Ropalidia marginata. In Natural History and Evolution of Paper-Wasps; Turillazzi, S., West-Eberhard, M.J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 248–271. [Google Scholar]
- Tibbetts, E.A. Dispersal decisions and predispersal behavior in Polistes paper wasp ‘workers’. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2007, 61, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, B.F.; Payne, A.; Pickett, K.M.; Carpenter, J.M. Phylogeny and historical biogeography of the paper wasp genus Polistes (Hymenoptera: Vespidae): Implications for the overwintering hypothesis of social evolution. Cladistics 2015, 31, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate-Data.org. Available online: https://en.climate-data.org/region/943/ (accessed on 2 February 2017).
- Elisei, T.; Guimaraes, D.L.; Junior, C.R.; Melo, A.C.; Grazinoli, D.J.; Lopes, J.F.; Prezoto, F. Influence of environmental factors on the foraging activity of the paper wasp Polistes simillimus (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Sociobiology 2008, 51, 219. [Google Scholar]
- Weiner, S.A.; Noble, K.; Upton, C.T.; Flynn, G.; Woods, W.A.; Starks, P.T. The cost of flight: A role in the Polistes dominulus invasion. Insectes Soc. 2012, 59, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, M.; Marshall, S.A.; Cheung, D.K.B. Identification atlas of the Vespidae (Hymenoptera, Aculeata) of the northeastern nearctic region. Can. J. Arthropod. Identif. 2008, 5, 1–492. [Google Scholar]
- Strassmann, J.E.; Orgren, M.C. Nest architecture and brood development times in the paper wasp, Polistes exclamans (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Psyche 1983, 90, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; v.3.6.1 Computer Software; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D.; R Core Team. nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R Package Version 3.1-153. 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=nlme (accessed on 27 November 2021).
- Lenth, R.V. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means. R Package Version 1.2.1 2018. Available online: https://mran.microsoft.com/snapshot/2018-06-10/web/packages/emmeans/emmeans.pdf (accessed on 27 November 2021).
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. lme4: Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Eigen and S4. R Package Version1 1–23. 2014. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.5823 (accessed on 27 November 2021).
- Zuur, A.; Ieno, E.N.; Walker, N.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R.; Springer Science & Business Media: Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Weather Atlas. Available online: https://www.weather-us.com/en/louisiana-usa/baton-rouge-climate (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- U.S. Climate Data. Available online: https://www.usclimatedata.com/climate/baton-rouge/louisiana/united-states/usla0033 (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Page, R.E., Jr.; Post, D.C.; Metcalf, R.A. Satellite nests, early males, and plasticity of reproductive behavior in a paper wasp. Am. Natural. 1989, 134, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassmann, J.E.; Meyer, D.C. Gerontocracy in the social wasp, Polistes exclamans. Anim. Behav. 1983, 31, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T. Paradox of worker reproduction and worker mating in temperate paper wasps, Polistes chinensis and P. snelleni (Hymenoptera Vespidae). Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 1998, 10, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeve, H.K.; Peters, J.M.; Nonacs, P.; Starks, P.T. Dispersal of first “workers” in social wasps: Causes and implications of an alternative reproductive strategy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13737–13742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gobbi, N.; Noll, F.B.; Penna, M.A. “Winter” aggregations, colony cycle, and seasonal phenotypic change in the paper wasp Polistes versicolor in subtropical Brazil. Naturwissenschaften 2006, 93, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giray, T.; Giovanetti, M.; West-Eberhard, M.J. Juvenile hormone, reproduction, and worker behavior in the neotropical social wasp Polistes canadensis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3330–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denlinger, D.L. Dormancy in tropical insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1986, 31, 239–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, H.C.; Vinson, S.B. Nesting ecology of paper wasps (Polistes) in a Texas urban area (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 1979, 52, 673–689. [Google Scholar]
- Hermann, H.R.; Chao, J.T. Distribution of Mischocyttarus mexicanus cubicola in the United States. Fla. Entomol. 1984, 67, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litte, M. Behavioral Ecology of the Social wasp, Mischocyttarus mexicanus. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1977, 2, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, H.R.; Chao, J.T. Nesting biology and defensive behavior of Mischocyttarus mexicanus cubicola (Vespidae: Polistinae). Psyche 1984, 91, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litte, M. Mischocyttarus flavitarsis in Arizona: Social and nesting biology of a polistine wasp. Z. Tierpsychol. 1979, 50, 282–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, V.O.; Montagna, T.S.; Fernandes, W.D.; Antonialli-Junior, W.F. Colony cycle of the social wasp Mischocyttarus consimilis Zikán (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Rev. Bras. Entomol. 2011, 55, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanne, R.L. Social biology of the neotropical wasp Mischocyttarus drewseni. Bull. Mus. Comp. Zool. Harv. Univ. 1972, 144, 63–150. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nacko, S.; Hall, M.A.; Henderson, G. Alternative Nesting Strategies of Polistine Wasps in a Subtropical Locale. Insects 2022, 13, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010053
Nacko S, Hall MA, Henderson G. Alternative Nesting Strategies of Polistine Wasps in a Subtropical Locale. Insects. 2022; 13(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010053
Chicago/Turabian StyleNacko, Scott, Mark A. Hall, and Gregg Henderson. 2022. "Alternative Nesting Strategies of Polistine Wasps in a Subtropical Locale" Insects 13, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010053
APA StyleNacko, S., Hall, M. A., & Henderson, G. (2022). Alternative Nesting Strategies of Polistine Wasps in a Subtropical Locale. Insects, 13(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010053





