Bombyx mori Nucleopolyhedrovirus (BmNPV) Induces G2/M Arrest to Promote Viral Multiplication by Depleting BmCDK1
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Virus Infection
2.2. Plasmid Construction and Transfection
2.3. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.4. MTS Assay
2.5. Immunofluorescence
2.6. BrdU or EdU Incorporation
2.7. Cell Synchronization
2.8. TCID50
2.9. Quantitative Real Time-PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.10. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
2.11. Co-Immunoprecipitation and LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
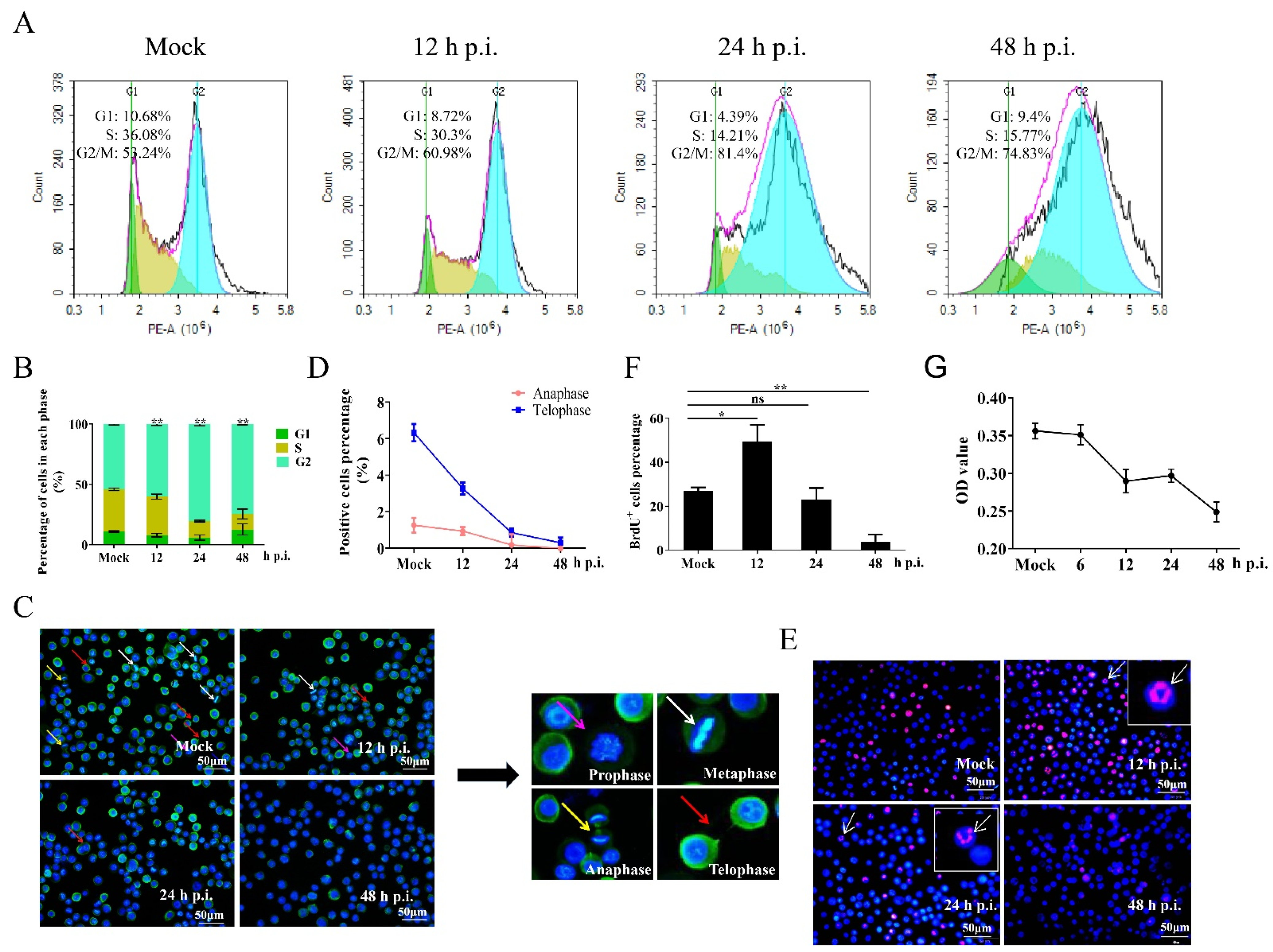
3.1. Regulation of the Cell Cycle in BmNPV-Infected Cells
3.2. Cells in G2/M Phase Create a Favorable Environment for BmNPV Multiplication
3.3. G2/M Arrest by BmCDK1 and BmCyclin B Enhances BmNPV Proliferation
3.4. BmNPV IAP1 Interacts with BmCDK1
3.5. BmNPV iap1 Regulates the Cell Cycle via BmCDK1
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kvansakul, M.; Caria, S.; Hinds, M.G. The Bcl-2 Family in Host-Virus Interactions. Viruses 2017, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vassilaki, N.; Frakolaki, E. Virus-host interactions under hypoxia. Microbes Infect. 2017, 19, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarouf, M.; Rai, K.R.; Goraya, M.U.; Chen, J.L. Immune Ecosystem of Virus-Infected Host Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cruz, L.; Buchkovich, N.J. Rerouting the traffic from a virus perspective. Front. Biosci. 2017, 22, 1845–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flemington, E.K. Herpesvirus lytic replication and the cell cycle: Arresting new developments. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 4475–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Shan, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, J.; Cong, Y. G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis induced by SARS-CoV 3b protein in transfected cells. Virol. J. 2005, 2, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.J.; Makino, S. Murine coronavirus replication induces cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 5658–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinson, T.; Henno, L.; Toots, M.; Ustav, M., Jr.; Ustav, M. The Cell Cycle Timing of Human Papillomavirus DNA Replication. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, J.A.; Mymryk, J.S.; Egan, C.; Branton, P.E.; Bayley, S.T. Retinoblastoma growth suppressor and a 300-kDa protein appear to regulate cellular DNA synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 5883–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dove, B.; Brooks, G.; Bicknell, K.; Wurm, T.; Hiscox, J.A. Cell cycle perturbations induced by infection with the coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus and their effect on virus replication. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4147–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohkawa, T.; Volkman, L.E.; Welch, M.D. Actin-based motility drives baculovirus transit to the nucleus and cell surface. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 190, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Kang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Hou, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T. The Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus NSs Protein Interacts with CDK1 To Induce G2 Cell Cycle Arrest and Positively Regulate Viral Replication. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01575-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boulikas, T. Phosphorylation of transcription factors and control of the cell cycle. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 1995, 5, 1–77. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, J.P.; Siu, W.Y.; Ho, H.T.; Ma, K.H.; Ho, C.C.; Poon, R.Y. Differential contribution of inhibitory phosphorylation of CDC2 and CDK2 for unperturbed cell cycle control and DNA integrity checkpoints. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 40815–40828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.G.; Norbury, C.J.; Spurr, N.K.; Nurse, P. Regulated expression and phosphorylation of a possible mammalian cell-cycle control protein. Nature 1988, 333, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnerch, D.; Yalcintepe, J.; Schmidts, A.; Becker, H.; Follo, M.; Engelhardt, M.; Wasch, R. Cell cycle control in acute myeloid leukemia. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2012, 2, 508–528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhong, A.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J.; Shen, J.; Deng, M.; Chen, M.; Lu, R.; Guo, L. MUS81 Inhibition Increases the Sensitivity to Therapy Effect in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer via Regulating CyclinB Pathway. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 2276–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pines, J. Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: Theme and variations. Am. J. Cancer Res. 1995, 66, 181–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoncini, L.; Lazzi, S.; Bellan, C.; Tosi, P. Cell kinetics and cell cycle regulation in lymphomas. J. Clin. Pathol. 2002, 55, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowan, C.H.; Russell, P. Human Wee1 kinase inhibits cell division by phosphorylating p34cdc2 exclusively on Tyr15. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, S.; Hayles, J.; Nurse, P. Regulation of p34cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis. Cell 1989, 58, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigg, E.A.; Gallant, P.; Krek, W. Regulation of p34cdc2 protein kinase activity by phosphorylation and cyclin binding. Ciba Found. Symp. 1992, 170, 72–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, D.H. Human cytomegalovirus riding the cell cycle. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 204, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Sanyal, S.; Bruzzone, R. Breaking Bad: How Viruses Subvert the Cell Cycle. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherji, A.; Janbandhu, V.C.; Kumar, V. HBx-dependent cell cycle deregulation involves interaction with cyclin E/A-cdk2 complex and destabilization of p27Kip1. Biochem. J. 2007, 401, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benn, J.; Schneider, R.J. Hepatitis B virus HBx protein deregulates cell cycle checkpoint controls. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 11215–11219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Mok, C.K.; Chan, M.C.; Zhang, Y.; Nal, B.; Kien, F.; Bruzzone, R.; Sanyal, S. Cell Cycle-independent Role of Cyclin D3 in Host Restriction of Influenza Virus Infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 5070–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fickenscher, H.; Fleckenstein, B. Herpesvirus saimiri. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. of Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 356, 545–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virgin, H.W.t.; Latreille, P.; Wamsley, P.; Hallsworth, K.; Weck, K.E.; Dal Canto, A.J.; Speck, S.H. Complete sequence and genomic analysis of murine gammaherpesvirus 68. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 5894–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brewster, C.D.; Birkenheuer, C.H.; Vogt, M.B.; Quackenbush, S.L.; Rovnak, J. The retroviral cyclin of walleye dermal sarcoma virus binds cyclin-dependent kinases 3 and 8. Virology 2011, 409, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mo, M.; Fleming, S.B.; Mercer, A.A. Cell cycle deregulation by a poxvirus partial mimic of anaphase-promoting complex subunit 11. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19527–19532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, M.; Kobayashi, M. Cell-cycle perturbation in Sf9 cells infected with Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus. Virology 1999, 258, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, R.; Yu, Z.H.; Li, X.Q.; Jia, F.; Wu, J.H.; Chen, X. Heliocoverpa armigera single nucleocapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus induces Hz-AM1 cell cycle arrest at the G2 phase with accumulation of cyclin B1. Virus Res. 2004, 105, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluchamy, S.; Gopinathan, K.P. Characterization of a cyclin homolog from Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus. Virus Res. 2005, 108, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prikhod’ko, E.A.; Miller, L.K. Role of baculovirus IE2 and its RING finger in cell cycle arrest. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belyavskyi, M.; Braunagel, S.C.; Summers, M.D. The structural protein ODV-EC27 of Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus is a multifunctional viral cyclin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11205–11210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Zhou, K.; Zhao, G.; Qian, H.; Xu, A. Transcriptome-wide analysis of the difference of alternative splicing in susceptible and resistant silkworm strains after BmNPV infection. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.H.; Cai, X.J.; Liu, M.; Lv, J.; Tang, H.; Tan, J.; Lu, C. Establishment and characterization of an ovarian cell line of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Tissue Cell 2010, 42, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; He, Q.; Zhang, C.D.; Chen, X.Y.; Chen, X.M.; Dong, Z.Q.; Li, N.; Kuang, X.X.; Cao, M.Y.; Lu, C.; et al. Inhibition of BmNPV replication in silkworm cells using inducible and regulated artificial microRNA precursors targeting the essential viral gene lef-11. Antivir. Res. 2014, 104, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.T.; Tan, L.R.; Hu, N.; Dong, Z.Q.; Hu, Z.G.; Jiang, Y.M.; Chen, P.; Pan, M.H.; Lu, C. C-lysozyme contributes to antiviral immunity in Bombyx mori against nucleopolyhedrovirus infection. J. Insect Physiol. 2018, 108, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.F.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, C.D.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, T.H.; Zhou, X.L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, P.; Lu, C.; et al. Two Geminin homologs regulate DNA replication in silkworm, Bombyx mori. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiao, Q.; Zhou, X.L.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, Z.Q.; Chen, P.; Pan, M.H.; Lu, C. Bombyx mori Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus (BmNPV) Induces Host Cell Autophagy to Benefit Infection. Viruses 2017, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.L.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, Z.Q.; Chen, P.; Lu, C.; Pan, M.H. BmAtg13 promotes the replication and proliferation of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 157, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Tu, Z.; Xu, G.; Hu, J.L.; Cai, X.F.; Zhan, X.X.; Wang, Y.W.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, A.L. S-phase arrest after vincristine treatment may promote hepatitis B virus replication. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, W.; Liu, H.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y. RGNNV-induced cell cycle arrest at G1/S phase enhanced viral replication via p53-dependent pathway in GS cells. Virus Res. 2018, 256, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressy, C.; Droby, G.N.; Maldonado, B.D.; Steuerwald, N.; Grdzelishvili, V.Z. Cell Cycle Arrest in G2/M Phase Enhances Replication of Interferon-Sensitive Cytoplasmic RNA Viruses via Inhibition of Antiviral Gene Expression. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01885-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okano, K.; Mikhailov, V.S.; Maeda, S. Colocalization of baculovirus IE-1 and two DNA-binding proteins, DBP and LEF-3, to viral replication factories. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mainz, D.; Quadt, I.; Knebel-Morsdorf, D. Nuclear IE2 structures are related to viral DNA replication sites during baculovirus infection. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 5198–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ono, C.; Kamagata, T.; Taka, H.; Sahara, K.; Asano, S.; Bando, H. Phenotypic grouping of 141 BmNPVs lacking viral gene sequences. Virus Res. 2012, 165, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, J.; Qiao, N.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, R.L.; Zhang, X.Q.; Bao, Y.Y.; Xu, Y.P.; Gu, L.Z.; Han, J.D.; Zhang, C.X. Dynamic interactions between Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus and its host cells revealed by transcriptome analysis. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7345–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, G.; Pan, X.; Kormelink, R.; Vlak, J.M. Functional entry of baculovirus into insect and mammalian cells is dependent on clathrin-mediated endocytosis. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8830–8833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llamazares, S.; Moreira, A.; Tavares, A.; Girdham, C.; Spruce, B.A.; Gonzalez, C.; Karess, R.E.; Glover, D.M.; Sunkel, C.E. polo encodes a protein kinase homolog required for mitosis in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991, 5, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lens, S.M.; Vader, G.; Medema, R.H. The case for Survivin as mitotic regulator. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2006, 18, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, D.C. Survivin, versatile modulation of cell division and apoptosis in cancer. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8581–8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Song, C.; Zhan, Y.; Tan, L.; Liao, Y.; Meng, C.; Qiu, X.; et al. Newcastle disease virus induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in asynchronously growing cells. Virology 2018, 520, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, P.; Hu, C.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, A.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, L.; Gong, C.; Guo, K.; Zhang, X.; et al. Classical swine fever virus Shimen infection increases p53 signaling to promote cell cycle arrest in porcine alveolar macrophages. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 55938–55949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, P.; Cheng, Y.; Song, S.; Qiu, J.; Yi, L.; Cao, Z.; Li, J.; Cheng, S.; Wang, J. Viral Nonstructural Protein 1 Induces Mitochondrion-Mediated Apoptosis in Mink Enteritis Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01249-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, M.; Cheng, A.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; et al. Duck Plague Virus Promotes DEF Cell Apoptosis by Activating Caspases, Increasing Intracellular ROS Levels and Inducing Cell Cycle S-Phase Arrest. Viruses 2019, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trapp-Fragnet, L.; Bencherit, D.; Chabanne-Vautherot, D.; Le Vern, Y.; Remy, S.; Boutet-Robinet, E.; Mirey, G.; Vautherot, J.F.; Denesvre, C. Cell cycle modulation by Marek’s disease virus: The tegument protein VP22 triggers S-phase arrest and DNA damage in proliferating cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, X.; Xing, L.; Yue, W.; Yin, H.; He, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, J. HBV infection potentiates resistance to S-phase arrest-inducing chemotherapeutics by inhibiting CHK2 pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Li, X.; Qiu, Z.; Li, A.; Liang, W.; Chen, H.; Cai, X.; Chen, X.; Duan, X.; et al. Zika Virus Envelope Protein induces G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis via an Intrinsic Cell Death Signaling Pathway in Neuroendocrine PC12 Cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrmann, G.F. Baculovirus Molecular Biology, 4th ed.; National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2013.
- Nobiron, I.; O’Reilly, D.R.; Olszewski, J.A. Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus infection of Spodoptera frugiperda cells: A global analysis of host gene regulation during infection, using a differential display approach. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 3029–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, Q.; Chan, L.C.; Nielsen, L.K.; Reid, S. Genome scale analysis of differential mRNA expression of Helicoverpa zea insect cells infected with a H. armigera baculovirus. Virology 2013, 444, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leisy, D.J.; Rasmussen, C.; Owusu, E.O.; Rohrmann, G.F. A mechanism for negative gene regulation in Autographa californica multinucleocapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 5088–5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakai, K.; Barnitz, R.A.; Chaigne-Delalande, B.; Bidere, N.; Lenardo, M.J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vif causes dysfunction of Cdk1 and CyclinB1: Implications for cell cycle arrest. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Portugal, R.; Leitao, A.; Martins, C. Characterization of African swine fever virus IAP homologue expression in porcine macrophages infected with different virulence isolates. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 139, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nogal, M.L.; Gonzalez de Buitrago, G.; Rodriguez, C.; Cubelos, B.; Carrascosa, A.L.; Salas, M.L.; Revilla, Y. African swine fever virus IAP homologue inhibits caspase activation and promotes cell survival in mammalian cells. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 2535–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ince, I.A.; Westenberg, M.; Vlak, J.M.; Demirbag, Z.; Nalcacioglu, R.; van Oers, M.M. Open reading frame 193R of Chilo iridescent virus encodes a functional inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP). Virology 2008, 376, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.W.; Means, J.C.; Penabaz, T.; Clem, R.J. The baculovirus anti-apoptotic protein Op-IAP does not inhibit Drosophila caspases or apoptosis in Drosophila S2 cells and instead sensitizes S2 cells to virus-induced apoptosis. Virology 2005, 335, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.M.; Lin, T.K.; Tseng, Y.Y.; Tu, C.H.; Lui, T.N.; Huang, S.F.; Hsieh, L.L.; Li, Y.Y. Targeting inhibitors of apoptosis proteins suppresses medulloblastoma cell proliferation via G2/M phase arrest and attenuated neddylation of p21. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 3988–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Lin, F.; Gao, P.; Cheng, S.Y.; Zhang, H.Z. Inhibiting XIAP expression by RNAi to inhibit proliferation and enhance radiosensitivity in laryngeal cancer cell line. Auris Nasus Larynx 2009, 36, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.Q.; Chen, T.T.; Zhang, J.; Hu, N.; Cao, M.Y.; Dong, F.F.; Jiang, Y.M.; Chen, P.; Lu, C.; Pan, M.H. Establishment of a highly efficient virus-inducible CRISPR/Cas9 system in insect cells. Antivir. Res. 2016, 130, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandergaast, R.; Mitchell, J.K.; Byers, N.M.; Friesen, P.D. Insect inhibitor-of-apoptosis (IAP) proteins are negatively regulated by signal-induced N-terminal degrons absent within viral IAP proteins. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4481–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerio, R.J.; Vandergaast, R.; Friesen, P.D. Host insect inhibitor-of-apoptosis SfIAP functionally replaces baculovirus IAP but is differentially regulated by Its N-terminal leader. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11448–11460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Primers for Clone | Sequence |
|---|---|
| >BmCDK1Flag-F | F:ATTTGCGGCCGCATGGATTACAAGGATGACGACGATAAGGATGATTTCTTAAAGATAGAAAAGATCG |
| >BmCDK1Flag-R | R:TGCTCTAGATTACTTATCGTCGTCATCCTTGTAATCTACACTTTGAACAGAATCCGTGTC |
| >BmNPV iapHA-F | CGCGGATCCATGTACCCATACGATGTTCCAGATTACGCTAACGAGGACACTCCTCCGT |
| >BmNPV iapHA-R | TGCTCTAGACACCACAAATATTTTTATAAAATCG |
| >SgBmNPV iap1-F | AAGTGTGAAGCAGAAATAAAAAAT |
| >SgBmNPV iap1-R | AAACATTTTTTATTTCTGCTTCAC |
| Primers for qRT-PCR | Sequence |
| >BmCyclin B | F: TGTCAAAAATGTTATTCAGCC; R: TTTCCGTAAAGAGTCAGTTCC. |
| >BmCDK1 | F: AGGGCTCCTGAGGTCTTACT; R: TGTTGGCGTTCTTAGCATTCT. |
| >ie-1 | F: AAGAAGGAGGACGGCAGCAT; R: ATCTCGCCAGAAATCCAATAAAAC. |
| >vp39 | F: CTAATGCCCGTGGGTATGG R: TTGATGAGGTGGCTGTTGC |
| >gp64 | F: CACCATCGTGGAGACGGACTA R: CCTCGCACTGCTGCCTGA |
| >p10 | F: TAGACGCCATTGCGGAAA F: CGGGCAAACCGTCCAAA |
| >gp41 | F: ATGTTGATGTGCGGAAAGC; R: GTGGCGGAATCGGTGA. |
| >sw22934 | F: TTCGTACTGGCTCTTCTCGT; R: CAAAGTTGATAGCAATTCCCT. |
| Primers for RNAi | Sequence |
| BmCyclin B-miRNA1 | AATGTGCACATTCAACGCGGAA TTCGCGTTGAACTTGCACATT |
| BmCyclin B-miRNA2 | GTTGCCGGCACAACTGCTGGAA TTCAGCAGTTGTAACGGCAAC |
| BmCyclin B-miRNA3 | GCGTAGTGTGAAGCAACTAGTA TATAGTTGCTTCGTACTACGC |
| BmCDK1-miRNA1 | TAAACGACACCGTAAGTACCT AGGTACTCGCGGTGTCGTTGTA |
| BmCDK1-miRNA1 | CCCTTGGCGCTGGAAAGTTGCA TGAACTTTCCAGAACCAAGGG |
| BmCDK1-miRNA1 | TCAACAACTCCATCTTGTAGCT AGTACAAGATGGCATTGTTGA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Q.; Dong, Z.-Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; Xiao, M.; Chen, P.; Lu, C.; Pan, M.-H. Bombyx mori Nucleopolyhedrovirus (BmNPV) Induces G2/M Arrest to Promote Viral Multiplication by Depleting BmCDK1. Insects 2021, 12, 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121098
Xiao Q, Dong Z-Q, Zhu Y, Zhang Q, Yang X, Xiao M, Chen P, Lu C, Pan M-H. Bombyx mori Nucleopolyhedrovirus (BmNPV) Induces G2/M Arrest to Promote Viral Multiplication by Depleting BmCDK1. Insects. 2021; 12(12):1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121098
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Qin, Zhan-Qi Dong, Yan Zhu, Qian Zhang, Xiu Yang, Miao Xiao, Peng Chen, Cheng Lu, and Min-Hui Pan. 2021. "Bombyx mori Nucleopolyhedrovirus (BmNPV) Induces G2/M Arrest to Promote Viral Multiplication by Depleting BmCDK1" Insects 12, no. 12: 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121098
APA StyleXiao, Q., Dong, Z.-Q., Zhu, Y., Zhang, Q., Yang, X., Xiao, M., Chen, P., Lu, C., & Pan, M.-H. (2021). Bombyx mori Nucleopolyhedrovirus (BmNPV) Induces G2/M Arrest to Promote Viral Multiplication by Depleting BmCDK1. Insects, 12(12), 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121098






