Population Dynamics and Yield Loss Assessment for Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) (Homoptera: Aphididae), on Lentil in Morocco
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Design
2.2. Field Monitoring
2.3. Yield, Avoidable Yield Loss, and Yield Increase over Untreated Control
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Population Dynamics of Pea Aphid
3.1.1. 2016. Cropping
3.1.2. 2017 Cropping
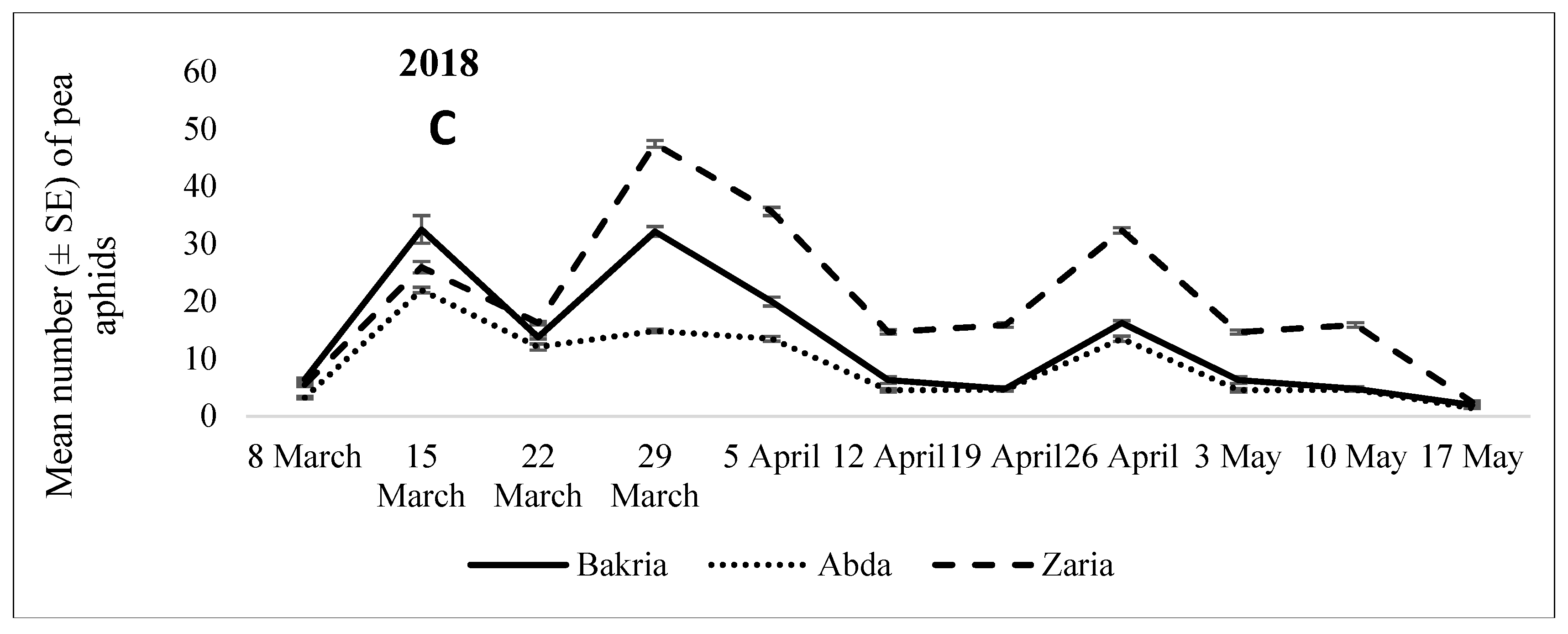
3.1.3. 2018 Cropping
3.2. Yield Loss Caused by Pea Aphid
3.3. Effect of Climatic Factors on Pea Aphid Population
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tullu, A.; Diederichsen, A.; Suvorova, G.; Vandenberg, A. Genetic and genomic resources of lentil: Status, use and prospects. Plant Genet. Res. 2011, 9, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Rajendran, K.; Kumar, J.; Hamwieh, A.; Baum, M. Current knowledge in lentil genomics and its application for crop improvement. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Idrissi, O.; Sakr, B.; Dahan, R.; Houasli, C.; Nsarellah, N.; Udupa, S.M.; Sarker, A. Registration of ‘Chakkouf’ Lentil in Morocco. J. Plant Regist. 2012, 6, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAOStat. Rome, Italy. 2019. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC (accessed on 18 November 2019).
- Hariri, G. Insect and Other Pests. In Lentils; Webs, C., Hawtin, G., Eds.; Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau: Oxfordshire, UK, 1981; pp. 173–189. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, P.C.; Dhillon, M.K.; Sharma, H.C.; El Bouhssini, M. Insect pests of lentil and their management. In Lentil: An Ancient Crop for Modern Times; Yadav, S.S., McNeil, D.L., Stevenson, P.C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 331–348. [Google Scholar]
- Collinge, S.K. Effects of grassland fragmentation on insect species loss, colonization, and movement patterns. Ecology 2000, 81, 2211–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, S.; Bechinski, E.J.; Stokes, B.S.; Pappu, H.R.; Eigenbrode, S.D. Deriving Economic Models for Pea Aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) as a Direct-Pest and a Virus-Vector on Commercial Lentils. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 2225–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andarge, A. Aspects of Bio-Intensive Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) Management on Lentil, Lens culinaris (Medikus). Master’s Thesis, Free State Bloemfontein University, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Peacock, L.; Worner, S.; Sedcole, R. Climate Variables and Their Role in Site Discrimination of Invasive Insect Species Distributions. Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 958–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melesse, T.; Singh, S.K. Effect of climatic factors on pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum Harris (Homoptera: Aphididae) population and its Management through planting dates and biopesticides in field pea (Pisum sativum L.). J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2012, 8, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Wale, M.; Jembere, B.; Seyoum, E. Biology of pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) (Homoptera: Ahididae on cool season legumes. Insect Sci. Appl. 2000, 20, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, R.K. Techniques for assessment of losses due to pests and diseases of rice. J. Agric. Sci. 1977, 47, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, D.G.; Cullis, B.R.; Gilmour, A.R.; Gogel, B.G.; Thompson, R. ASReml-R Reference Manual Version 4; VSN International Ltd.: Hemel Hempstead, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Freund, R.J.; Littell, R.C. SAS System for Regression, 3rd ed.; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, K.; Habtewold, T. Research on insect pests of cool season food legumes. In Proceedings of the First National Cool-Season Food Legumes Review Conference, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 16–20 December 1993; pp. 367–398. [Google Scholar]
- Kemal, A. Population dynamics of Acyrthosiphon pisum (Homoptera: Aphididae) and its natural enemies on Pisum sativum. PMJoE. 1999, 1–2, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wale, M. Population dynamics of the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) (Homoptera: Aphididae) on field pea (Pisum sativum L.) in northern Ethiopia. Insect Sci. Appl. 2002, 22, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, A.; Mackauer, M.; Hughes, R.D. Reproduction and population growth of the pea aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) under laboratory and field conditions. Can. Entomol. 1977, 109, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, W.D.; Hogg, D.B. Demographic statistics for the Pea Aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) in Wisconsin and a comparison with other populations. Environ. Entomol. 1984, 13, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, S.; Balde, M. Influence of temperature on the development and reproduction of pea and oat aphids in field bean and spring barley. Mitt. Dtsch. Ges. Allg. Angew. Entomol. 1993, 8, 591–597. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, J.R.; Barlow, C.A. Survival of the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Homoptera: Aphididae), at extreme temperatures. Can. Entomol. 1973, 105, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensadia, F.; Boudreault, S.; Guay, J.F.; Michaud, D.; Cloutier, C. Aphid clonal resistance to a parasitoid fails under heat stress. J. Insect Physiol. 2006, 52, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, T.; Schmidtberg, H.; Skaljac, M.; Vilcinskas, A. Heat shock protein 83 plays pleiotropic roles in embryogenesis, longevity, and fecundity of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. Dev. Genes Evol. 2017, 227, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Follman, T.T.; Valls, A.; Kral-O’Brien, K.C.; Harmon, J.P. Mechanical stimulation from plant contact and wind negatively impact pea aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae) indirectly through host plants. Can. Entomol. 2019, 151, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ari, M.; Talal, S.; Inbar, M. Anticipatory and Reactive Crouching of Pea Aphids in Response to Environmental Perturbations. Environ. Entomol. 2014, 43, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, R.J.; McArthur, C.; Hochuli, D.F. Exposure to wind alters insect herbivore behaviour in larvae of Uraba lugens (Lepidoptera: Nolidae). Austral Entomol. 2016, 55, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geteneh, M.; Tebkew, D.; Mulatu, W. Category of resistance, antixenosis, antibiosis, and tolerance to Acyrthosiphon pisum (H.) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in selected lentil genotypes (Lens culinaris M.). J. Plant Sci. 2019, 7, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.A.; Jannatul, F.; Salim, M.M.R. Relative abundance and yield loss assessment of lentil aphid, Aphis craccivora Koch in relation to different sowing dates. J. Agric. Rural Dev. 2006, 4, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Regassa, S.; Dadi, L.; Mitiku, D.; Fikre, A.; Aw-Hassan, A. Impact of Research and Technologies in Selected Lentil Growing Areas of Ethiopia; Research Report, No. 67; Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2006; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Mintesnot, W. Efficacy of sowing dates integrated with insecticides against pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) on lentil. Indian J. Entomol. 2017, 79, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Perez Andueza, G.; de los Mozos Pascual, M.; Portillo Rubio, M. Main pests of lentil (Lens culinaris Medikus) in Castilla-la Mancha (central Spain): Crop losses and influence on yield parameters. Bol. San. Veg. Plagas. 2004, 30, 763–772. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, R. Pea enation mosaic virus. In Handbook of Plant Virus Infections and Comparative Diagnosis; Kurstak E, Ed.; Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981; pp. 239–256. [Google Scholar]
- De Zoeten, G.A.; Skaf, J.S. Pea enation mosaic virus and the vagaries of a plant virus. Adv. Virus Res. 2001, 57, 323–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Factors | NumDF | DenDF | F.inc | Pr |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 1 | 2.1 | 6957 | <0.001 |
| Year | 2 | 2.9 | 2.38 | 0.2425 |
| Variety | 2 | 3639.3 | 170.1 | <0.001 |
| Year × Variety | 4 | 2068 | 27.18 | <0.001 |
| Variety × Weeks in 2016 | 21 | 1274.3 | 72.86 | <0.001 |
| Variety × Weeks in 2017 | 27 | 1687.5 | 47.05 | <0.001 |
| Variety × Weeks in 2018 | 30 | 1704 | 117.5 | <0.001 |
| Factors | NumDF | DenDF | F.inc | Pr |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Years | 3 | 4.6 | 3953 | <0.001 |
| Varieties | 2 | 10.6 | 343.1 | <0.001 |
| Years × Varieties | 4 | 13.4 | 33.06 | <0.001 |
| Varieties × Treatment in 2016 | 3 | 10 | 75.26 | <0.001 |
| Varieties × Treatment in 2017 | 3 | 12 | 6.65 | 0.006 |
| Varieties × Treatment in 2018 | 3 | 7.6 | 7.918 | 0.01 |
| Varieties | Seed Weight (kg/ha) | Yield Loss (kg/ha) | Avoidable Yield Loss (%) | Yield Increase Over Control (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015–2016 | 2016–2017 | 2017–2018 | 2015–2016 | 2016–2017 | 2017–2018 | 2015–2016 | 2016–2017 | 2017–2018 | 2015–2016 | 2016–2017 | 2017–2018 | |
| Bakria | 1003 b | 1889 a | 2870 a | 109 | 194 | 649 | ||||||
| Bakria treated | 1112 c | 2083 a | 3519 b | 9.80 | 9.31 | 18.44 | 10.86 | 10.3 | 22.6 | |||
| Zaria | 973 b | 1741 a | 2806 a | 0 | 102 | 601 | ||||||
| Zaria treated | 892 a | 1843 a | 3407 b | 0 | 5.53 | 17.64 | 0 | 5.85 | 21.4 | |||
| Abda | 1086 c | 2880 c | 3880 b | 149 | 0 | 64 | ||||||
| Abda treated | 1235 d | 2380 b | 3944 b | 12.06 | 0 | 1.62 | 13.72 | 0 | 1.64 | |||
| CV (%) | 10.94 | 19.75 | 14.48 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| SEM | 27.00 | 48.80 | 55.70 | |||||||||
| Population | Season | Variety | Grain Yield (kg/ha) | Losses in Grain Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of pea aphids causing yield losses | 2016 | Bakria | −0.998 * | 0.401 * |
| 2017 | −0.124 * | 0.575 * | ||
| 2018 | −0.943 ** | 0.940 * | ||
| 2016 | Abda | −0.922 * | 0.675 * | |
| 2017 | −0.627 ns | |||
| 2018 | −0.953 ns | 0.923 | ||
| 2016 | Zaria | 0.838 ns | ||
| 2017 | −0.014 * | 0.900 * | ||
| 2018 | −0.466 ** | 0.893 ** |
| Abiotic Factors | Mean no. of Pea Aphid per 20 Twigs in the Tested Lentil Varieties | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMW | Date and Month of 2016 | Maximum (°C) | Minimum (°C) | Mean RH (%) | Total Rainfall (mm) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Bakria | Abda | Zaria |
| 12 | 19–25 March | 16.62 | 7.95 | 86.86 | 2.40 | 1.50 | 1.37 | 1.62 | 1.52 |
| 13 | 26 March to 1 April | 19.77 | 7.66 | 84.81 | 2.40 | 0.84 | 2.50 | 2.43 | 2.85 |
| 14 | 2–8 April | 18.86 | 7.80 | 82.20 | 0.51 | 1.34 | 2.55 | 4.55 | 3.46 |
| 15 | 9–15 April | 20.75 | 8.38 | 78.25 | 0.00 | 1.19 | 21.61 | 26.76 | 24.81 |
| 16 | 16–22 April | 22.92 | 10.16 | 71.78 | 1.40 | 1.19 | 24.50 | 27.00 | 27.00 |
| 17 | 23–29 April | 24.34 | 10.09 | 77.09 | 1.20 | 0.83 | 25.00 | 28.8 | 28.00 |
| 18 | 30 April to 6 May | 25.98 | 14.31 | 68.52 | 0.80 | 1.17 | 10.00 | 17.00 | 15.00 |
| 19 | 7–13 May | 19.70 | 11.05 | 81.34 | 0.60 | 2.16 | 8.00 | 9.00 | 9.00 |
| Seasonal mean | 21.12 | 9.68 | 78.86 | 1.16 | 1.28 | 7.68 | 8.91 | 8.44 | |
| Correlation Coefficient (r) between Mean Aphid Population and Abiotic Factors | |||||||||
| Maximum temperature (°C) | 0.62 * | 0.70 * | 0.69 * | ||||||
| Minimum temperature (°C) | 0.24 | 0.35 | 0.33 | ||||||
| Mean relative humidity (%) | −0.61 | −0.70 * | −0.68 * | ||||||
| Total rainfall (mm) | −0.37 | −0.45 | −0.41 | ||||||
| Wind speed (m/s) | −0.38 | −0.36 | −0.37 | ||||||
| Abiotic Factors | Mean no. of Pea Aphid per 20 Twigs in the Tested Lentil Varieties | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMW | Date and Month of 2017 | Maximum (°C) | Minimum (°C) | Mean RH (%) | Total Rainfall (mm) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Bakria | Abda | Zaria |
| 4 | 22–28 January | 14.41 | 4.98 | 84.98 | 15.60 | 1.41 | 1.01 | 2.16 | 2.51 |
| 5 | 29 January to 4 Feb | 18.15 | 6.41 | 87.23 | 0.80 | 0.84 | 5.78 | 6.85 | 6.76 |
| 6 | 5–11 February | 17.99 | 5.59 | 85.60 | 6.20 | 1.39 | 4.00 | 7.66 | 7.43 |
| 7 | 12–18 February | 19.26 | 7.14 | 83.84 | 1.20 | 0.84 | 9.00 | 8.08 | 12.96 |
| 8 | 19–25 February | 14.56 | 9.22 | 98.63 | 0.00 | 0.40 | 6.00 | 9.50 | 14.16 |
| 9 | 26 February to 4 March | 17.62 | 6.76 | 91.14 | 0.00 | 0.66 | 11.00 | 12.45 | 15.53 |
| 10 | 5–11 March | 24.44 | 8.33 | 79.40 | 0.00 | 0.34 | 23.00 | 13.45 | 16.96 |
| 11 | 12–18 March | 18.55 | 6.98 | 85.93 | 0.40 | 0.67 | 12.00 | 14.78 | 20.11 |
| 12 | 19–25 March | 16.65 | 6.36 | 84.74 | 10.60 | 0.94 | 11.00 | 15.06 | 24.70 |
| 13 | 26 March to 1 April | 22.59 | 7.28 | 79.24 | 0.60 | 0.81 | 20.00 | 17.56 | 27.03 |
| 14 | 2–8 April | 26.26 | 6.85 | 61.44 | 0.40 | 0.90 | 24.00 | 6.66 | 20.38 |
| 15 | 9–15 April | 26.96 | 12.00 | 71.47 | 0.00 | 0.76 | 24.50 | 4.43 | 14.56 |
| 16 | 16–22 April | 28.52 | 13.98 | 58.23 | 0.00 | 0.74 | 12.00 | 3.96 | 13.50 |
| 17 | 23–29 April | 24.95 | 12.14 | 75.60 | 0.20 | 1.21 | 5.06 | 3.20 | 6.81 |
| 18 | 30 April to 6 May | 26.49 | 11.88 | 69.05 | 0.00 | 1.06 | 3.00 | 1.83 | 5.36 |
| Seasonal mean | 21.16 | 8.39 | 79.77 | 2.40 | 0.87 | 11.42 | 8.51 | 13.92 | |
| Correlation coefficient (r) between mean aphid population and abiotic factors | |||||||||
| Maximum temperature (°C) | 0.52 * | −0.31 | 0.08 | ||||||
| Minimum temperature (°C) | 0.11 | −0.45 | −0.15 | ||||||
| Mean relative humidity (%) | −0.41 | 0.43 | −0.04 | ||||||
| Total rainfall (mm) | −0.40 | −0.09 | −0.21 | ||||||
| Wind speed (m/s) | −0.53 | −0.50 * | −0.53 * | ||||||
| Abiotic Factors | Mean no. of Pea Aphid per 20 Twigs in the Tested Lentil Varieties | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMW | Date and Month of 2018 | Maximum (°C) | Minimum (°C) | Mean RH (%) | Total Rainfall (mm) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Bakria | Abda | Zaria |
| 10 | 5–11 March | 18.36 | 11.60 | 94.30 | 46.80 | 2.43 | 6.40 | 3.23 | 5.46 |
| 11 | 12–18 March | 16.88 | 8.50 | 90.37 | 23.20 | 1.71 | 32.51 | 21.96 | 25.95 |
| 12 | 19–25 March | 15.13 | 5.66 | 88.94 | 11.60 | 1.21 | 13.78 | 12.05 | 16.23 |
| 13 | 26 March to 1 April | 19.81 | 6.91 | 86.65 | 1.60 | 0.54 | 32.15 | 14.86 | 47.41 |
| 14 | 2–8 April | 19.10 | 8.78 | 88.88 | 8.60 | 0.97 | 19.96 | 13.48 | 19.20 |
| 15 | 9–15 April | 15.85 | 7.72 | 91.73 | 55.00 | 2.04 | 6.30 | 4.53 | 14.66 |
| 16 | 16–22 April | 22.84 | 10.47 | 86.06 | 1.80 | 0.49 | 4.78 | 4.60 | 15.88 |
| 17 | 23–29 April | 19.99 | 11.07 | 92.30 | 46.80 | 0.66 | 16.25 | 13.48 | 32.33 |
| 18 | 30 April to 6 May | 19.35 | 7.68 | 86.38 | 4.80 | 0.67 | 6.30 | 4.53 | 14.65 |
| 19 | 7–13 May | 21.20 | 11.65 | 86.93 | 1.00 | 0.71 | 4.78 | 4.60 | 15.88 |
| 20 | 14–20 May | 24.01 | 11.45 | 79.19 | 1.60 | 0.63 | 1.95 | 1.41 | 2.5 |
| Seasonal mean | 19.32 | 9.23 | 88.34 | 18.44 | 1.10 | 13.20 | 8.98 | 19.10 | |
| Correlation Coefficient (r) between Mean Aphid Population and Abiotic Factors | |||||||||
| Maximum temperature (°C) | −0.35 | −0.43 | −0.14 | ||||||
| Minimum temperature (°C) | −0.46 | −0.44 | −0.39 | ||||||
| Mean relative humidity (%) | 0.24 | 0.31 | 0.18 | ||||||
| Total rainfall (mm) | −0.03 | 0.02 | −0.06 | ||||||
| Wind speed (m/s) | 0.004 | 0.01 | −0.32 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Fakhouri, K.; Sabraoui, A.; Kehel, Z.; El Bouhssini, M. Population Dynamics and Yield Loss Assessment for Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) (Homoptera: Aphididae), on Lentil in Morocco. Insects 2021, 12, 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121080
El Fakhouri K, Sabraoui A, Kehel Z, El Bouhssini M. Population Dynamics and Yield Loss Assessment for Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) (Homoptera: Aphididae), on Lentil in Morocco. Insects. 2021; 12(12):1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121080
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Fakhouri, Karim, Abdelhadi Sabraoui, Zakaria Kehel, and Mustapha El Bouhssini. 2021. "Population Dynamics and Yield Loss Assessment for Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) (Homoptera: Aphididae), on Lentil in Morocco" Insects 12, no. 12: 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121080
APA StyleEl Fakhouri, K., Sabraoui, A., Kehel, Z., & El Bouhssini, M. (2021). Population Dynamics and Yield Loss Assessment for Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) (Homoptera: Aphididae), on Lentil in Morocco. Insects, 12(12), 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121080






