Insecticidal Effect of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles against Spodoptera frugiperda under Laboratory Conditions
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
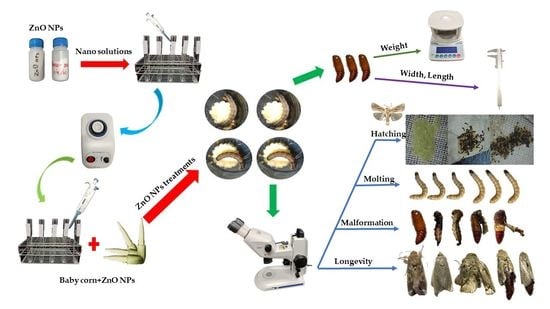
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Area of the Study
2.2. Fall Armyworm Rearing
2.3. Source of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
2.4. Bioassay of Fall Armyworm Reared on Different Concentration ZnO NPs
2.5. Oviposition Preference
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
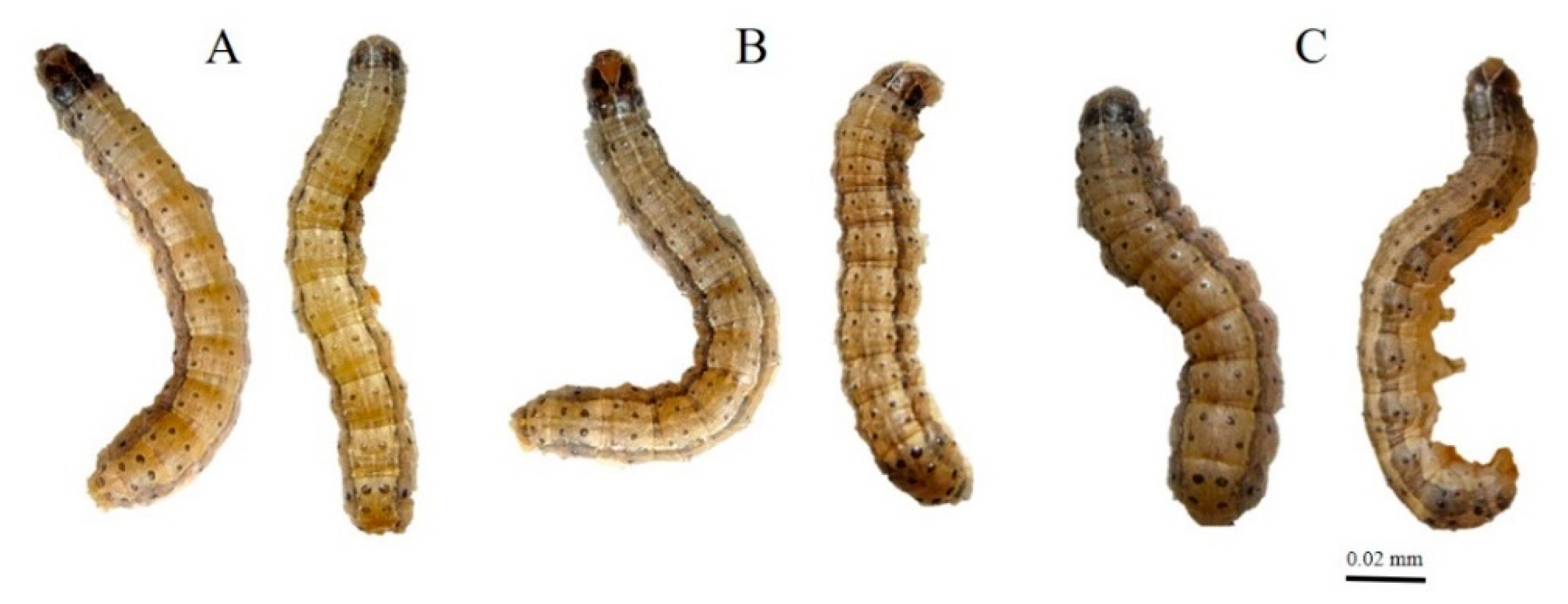
3.1. The Development of FAW Fed on Baby Corn Dipped in Different Concentrations of ZnO Nanoparticles
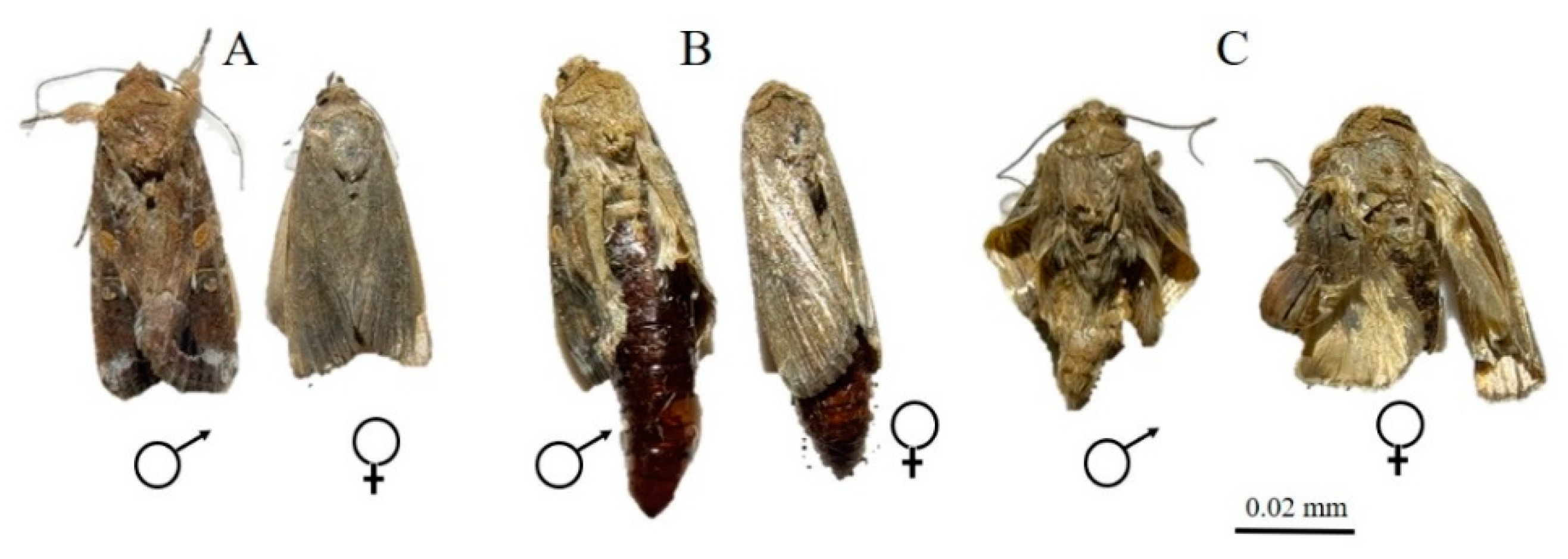
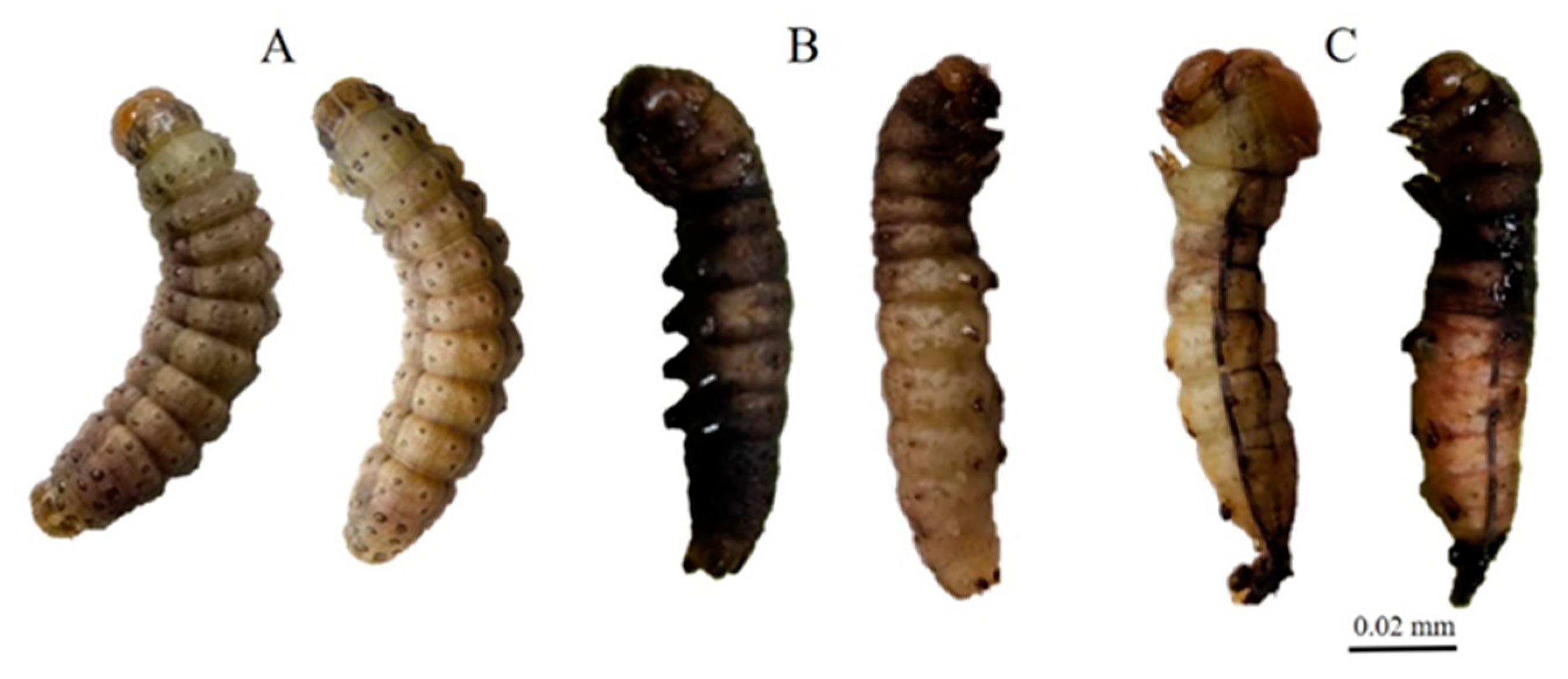
3.2. ZnO NPs Induced Morphological Changes in the Insect
3.3. Mortality of Spodoptera frugiperda Fed on Baby Corn Dipped in ZnO NPs
3.4. Effect of ZnO NPs on Fecundity and Fertility of Spodoptera frugiperda
3.5. Effects of ZnO NPs on the Longevity of Spodoptera frugiperda
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhusal, S.; Chapagain, E. Threats of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) incidence in Nepal and it’s integrated management-A review. J. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2020, 3, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartiami, D.; Harahap, I.S.; Kusumah, Y.M.; Anwar, R. First record of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) in Indonesia and its occurence in three provinces. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 468, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, B.; Babu, A.; Baruah, C.; Barthakur, M. Nanopesticides: A Systematic Review of Their Prospects With Special Reference to Tea Pest Management. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 686131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, C.A.; Scott, M.P. Evaluation of 21 Thailand Maize Germplasms for Resistance to Leaf Feeding Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 2020, 93, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piesik, D.; Rochat, D.; Delaney, K.J.; Marion-Poll, F. Orientation of European corn borer first instar larvae to synthetic green leaf volatiles. J. Appl. Entomol. 2013, 137, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piesik, D.; Wenda-Piesik, A. Sitophilus granarius responses to blends of five groups of cereal kernels and one group of plant volatiles. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2015, 62, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoczek, A.; Piesik, D.; Wenda-Piesik, A.; Buszewski, B.; Bocianowski, J.; Wawrzyniak, M. Volatile organic compounds released by maize following herbivory or insect extract application and communication between plants. J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 141, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitherian, S. Nano and Bio-nanoparticles for Insect Control. Res. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, A.H.; Qamar, A.; Qadir, I.; Naqvi, A.H.; Begum, R. Accumulation and trafficking of zinc oxide nanoparticles in an invertebrate model, Bombyx mori, with insights on their effects on immuno-competent cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, S.; Arshad, M.; Chaudhari, S.K. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for revolutionizing agriculture: Synthesis and applications. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 925494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAO. Fall Armyworm (Faw). 2017. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i7471e/i7471e.pdf (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- Athanassiou, C.G.; Kavallieratos, N.G.; Benelli, G.; Losic, D.; Usha Rani, P.; Desneux, N. Nanoparticles for pest control: Current status and future perspectives. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, T.; Bhaumik, A.; Rani, P.; Mandal, S.; Epidi, T. Nano-particles—A recent approach to insect pest control. Afric. J. Biotechnol. 1995, 9, 3489–3493. [Google Scholar]
- Barik, T.K.; Sahu, B.; Swain, V. Nanosilica—From medicine to pest control. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 103, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabet, A.F.; Boraei, H.A.; Galal, O.A.; El-Samahy, M.F.M.; Mousa, K.M.; Zhang, Y.A.; Tuda, M.; Helmy, E.A.; Wen, J.; Nozaki, T. Silica nanoparticles as pesticide against insects of different feeding types and their non-target attraction of predators. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Pi, J.; Cai, J. The Advancing of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 2018, 1062562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czyżowska, A.; Barbasz, A. A review: Zinc oxide nanoparticles–friends or enemies? Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseer, M.; Aslam, U.; Khalid, B.; Chen, B. Green route to synthesize Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Cassia fistula and Melia azadarach and their antibacterial potential. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.K.; Boruah, F.; Parween, N. Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO Nanoparticles using Leaf Extract of Camellia sinesis and Evaluation of their Antimicrobial Efficacy. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2015, 4, 444–450. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Arasu, M.V. Environmentally-friendly green approach for the production of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their anti-fungal, ovicidal, and larvicidal properties. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Men, L.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Deng, A.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, R. Morphological differences of the reproductive system could be used to predict the optimum Grapholita molesta (Busck) control period. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, M.; Shoeb, M.; Khan, M.T.; Ullah, R.; Mobin, M.; Farooqi, M.K.; Adnan, S.M. Enhanced Insecticidal Activity of Thiamethoxam by Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: A Novel Nanotechnology Approach for Pest Control. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajula, J.; Rahman, A.; Krutmuang, P. Entomopathogenic fungi in Southeast Asia and Africa and their possible adoption in biological control. Biol. Control 2020, 151, 104399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, M.; Samih, M.A.; Kalantari, S. Insecticied effect of silver and zinc nanoparticles against Aphis nerii Boyer of fonscolombe (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 72, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, H.; Chi, D.; Yu, J.; Li, X. A novel photodegradable insecticide: Preparation, characterization and properties evaluation of nano-Imidacloprid. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2008, 92, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khooshe-Bast, Z.; Sahebzadeh, N.; Ghaffari-Moghaddam, M.; Mirshekar, A. Insecticidal effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles and Beauveria bassiana TS11 on Trialeurodes vaporariorum (Westwood, 1856) (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Acta Agric. Slov. 2016, 107, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haroun, S.A.; Elnaggar, M.E.; Zein, D.M.; Gad, R.I. Insecticidal efficiency and safety of zinc oxide and hydrophilic silica nanoparticles against some stored seed insects. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2020, 60, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.S.; Silva, T.M.; Cardoso, J.; de Albuquerque-Júnior, R.L.C.; Zielinska, A.; Souto, E.B.; Severino, P.; da Costa Mendonça, M. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles mediated by entomopathogenic fungi: Antimicrobial resistance, nanopesticides, and toxicity. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaimurugan, D.; Vivekanandhan, P.; Sivasankar, P.; Durairaj, K.; Senthilkumar, P.; Shivakumar, M.S.; Venkatesan, S. Larvicidal Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Pseudomonas fluorescens YPS3 Isolated from the Eastern Ghats of India. J. Clust. Sci. 2019, 30, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekanandhan, P.; Swathy, K.; Thomas, A.; Kweka, E.J.; Rahman, A.; Pittarate, S.; Krutmuang, P. Insecticidal Efficacy of Microbial-Mediated Synthesized Copper Nano-Pesticide against Insect Pests and Non-Target Organisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaikozhundan, B.; Vaseeharan, B.; Vijayakumar, S.; Thangaraj, M.P. Bacillus thuringiensis coated zinc oxide nanoparticle and its biopesticidal effects on the pulse beetle, Callosobruchus maculatus. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 174, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, N.; Ramamoorthy, M.; Lyon, D.; Jones, K.; Duttaroy, A. Mechanism of silver nanoparticles action on insect pigmentation reveals intervention of copper homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
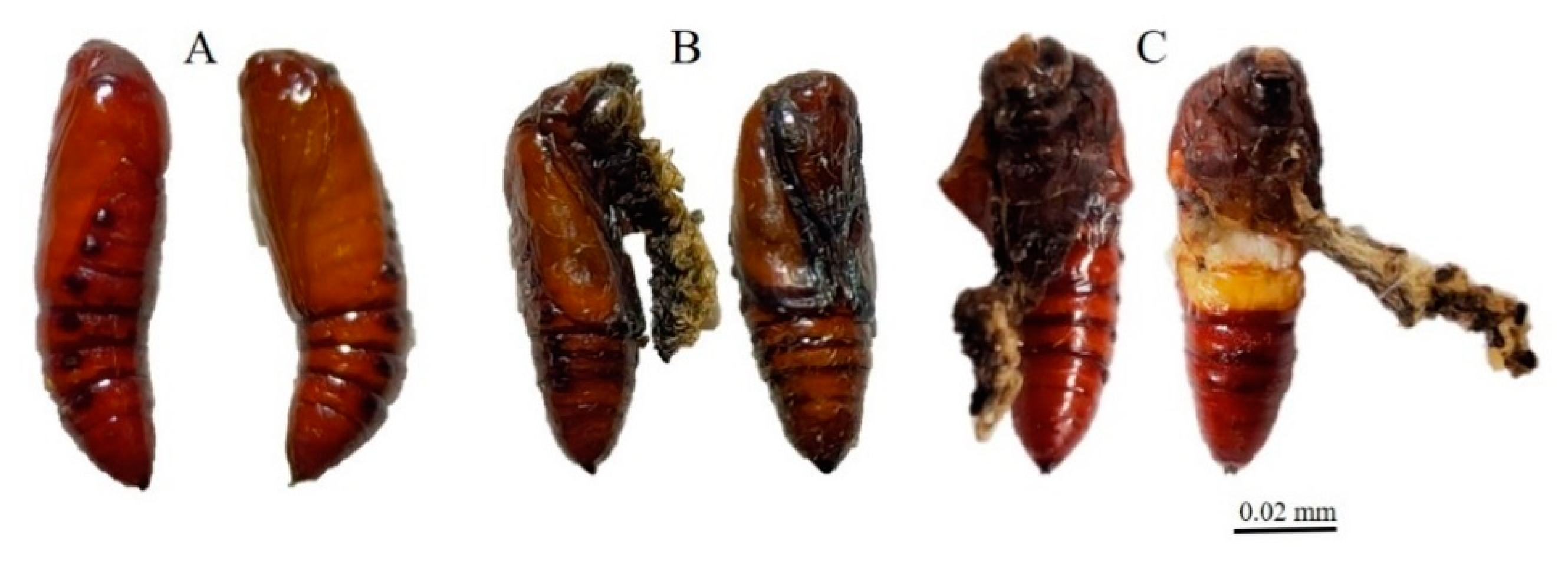





| Parameters | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | Control | df | F | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Days | n | Days | n | Days | n | Days | n | Days | n | Days | |||
| Egg | 80 | 2.50 ± 0.000 | 80 | 2.50 ± 0.000 | 80 | 2.50 ± 0.00 | 80 | 2.50 ± 0.000 | 80 | 2.50 ± 0.000 | 80 | 2.50 ± 0.000 | - | - |
| L1 | 80 | 2.30 ± 0.105 a | 80 | 2.50 ± 0.115 ab | 79 | 2.60 ± 0.112 ab | 80 | 2.65 ± 0.109 ab | 80 | 2.85 ± 0.082 b | 80 | 2.45 ± 0.114 ab | 5 | 3.100 |
| L2 | 80 | 2.15 ± 0.167 a | 80 | 2.25 ± 0.160 a | 79 | 2.30 ± 0.147 a | 80 | 2.35 ± 0.109 a | 80 | 2.55 ± 0.114 a | 80 | 2.00 ±0.126 a | 5 | 1.796 |
| L3 | 80 | 1.60 ± 0.112 a | 80 | 1.60 ± 0.112 a | 76 | 1.95 ± 0.114 ab | 80 | 2.35 ± 0.131 bc | 80 | 2.40 ± 0.134 c | 80 | 1.85 ± 0.109 a | 5 | 8.671 |
| L4 | 73 | 1.50 ± 0.115 a | 77 | 1.55 ± 0.135 a | 73 | 1.55 ± 0.114 a | 76 | 1.75 ± 0.123 ab | 80 | 1.85 ± 0.820 ab | 80 | 2.05 ± 0.135 b | 5 | 3.292 |
| L5 | 61 | 2.25 ± 0.099 ab | 72 | 2.35 ± 0.109 abc | 73 | 2.40 ± 0.169 abc | 75 | 2.60 ± 0.112 bc | 80 | 2.75 ± 0.099 c | 80 | 2.05 ± 0.088 a | 5 | 4.620 |
| L6 | 39 | 2.00 ± 0.126 a | 34 | 1.90 ± 0.176 a | 34 | 2.50 ± 0.154 ab | 37 | 2.80 ± 0.172 bc | 40 | 3.30 ± 0.164 c | 76 | 2.20 ± 0.156 a | 5 | 11.241 |
| Prepupa | 39 | 1.50 ± 0.115 a | 34 | 1.55 ± 0.114 a | 34 | 1.60 ± 0.134 a | 37 | 1.65 ± 0.131 a | 40 | 2.10 ± 0.143 b | 76 | 1.45 ± 0.114 a | 5 | 3.505 |
| Pupa | 39 | 9.15 ± 0.167 bc | 32 | 8.45 ± 0.246 b | 34 | 8.95 ± 170 bc | 36 | 9.70 ± 0.219 c | 40 | 7.30 ± 0.317 a | 76 | 9.55 ± 0.114 c | 5 | 16.701 |
| Adults | 30 | - | 20 | - | 24 | - | 23 | - | 26 | - | 72 | - | - | - |
| Female | 22 | 8.7 ± 0.524 b | 11 | 8.45 ± 0.515 b | 16 | 7.85 ± 0.554 b | 14 | 5.2 ± 0.374 a | 17 | 5.05 ± 0.394 a | 39 | 13.15 ± 0.284 c | 5 | 42.962 |
| Male | 8 | 07.05 ± 0.526 b | 9 | 04.95 ± 0.276 a | 8 | 4.65 ± 2.84 a | 9 | 4.65 ± 2.84 a | 9 | 4.80 ± 0.445 a | 33 | 09.55 ± 0.312 c | 5 | 29.502 |
| Treatments (ZnONPs: ppm) | Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Width | Length | |
| 100 | 0.160 ± 0.007 b | 0.426 ± 0.008 a | 1.397 ± 0.031 a |
| 200 | 0.130 ± 0.005 a | 0.432 ± 0.006 a | 1.416 ± 0.025 a |
| 300 | 0.125 ± 0.005 a | 0.422 ± 0.010 a | 1.376 ± 0.024 a |
| 400 | 0.120 ± 0.006 a | 0.415 ± 0.007 a | 0.415 ± 0.007 a |
| 500 | 0.113 ± 0.006 a | 0.407 ± 0.007 a | 1.407 ± 0.029 a |
| Control | 0.186 ± 0.002 c | 0.438 ± 0.007 a | 1.504 ± 0.015 b |
| df | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| F | 27.288 | 2.112 | 3.457 |
| Parameters | Treatments (ZnONPs: ppm) | df | F | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | Control | |||
| Pupa | ||||||||
| % Normal | 48.75 ± 5.907 a | 40.00 ± 4.564 a | 42.50 ± 3.227 a | 45.00 ± 3.536 a | 50.00 ± 2.041 a | 95.00 ± 2.887 b | 5 | 28.077 |
| % Abnormal | 3.75 ± 1.250 a | 5.00 ± 2.041 a | 7.50 ± 1.443 a | 7.50 ± 1.443 a | 6.25 ± 1.250 a | 2.50 ± 1.443 a | 5 | 1.846 |
| % Dead | 7.50 ± 1.443 ab | 10.00 ± 2.041 b | 5.00 ± 0.000 ab | 8.75 ± 1.250 ab | 11.25 ± 2.394 b | 2.50 ± 1.443 a | 5 | 4.080 |
| Adults | ||||||||
| % Normal | 16.25 ± 2.394 ab | 15.00 ± 2.041 ab | 17.50 ± 1.443 ab | 12.50 ± 1.443 a | 21.25 ± 1.250 b | 87.50 ± 1.443 c | 5 | 287.506 |
| % Abnormal | 21.25 ± 5.154 b | 10.00 ± 2.041 ab | 12.50 ± 2.500 ab | 16.25 ± 3.750 ab | 11.25 ± 3.146 ab | 2.50 ± 1.443 a | 5 | 3.774 |
| Treatments: (ZnONPs: ppm) | Total Females | Reproductive Females | APOP (Days) | TPOP (Days) | Oviposition Period (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 22 | 7 | 2.40 ± 0.152 a | 33.55 ± 0.738 a | 3.55 ± 0.303 a |
| 200 | 11 | 8 | 2.85 ± 0.167 a | 33.45 ± 0.709 a | 3.50 ± 0.366 a |
| 300 | 16 | 9 | 2.85 ± 0.167 a | 34.55 ± 0.766 a | 2.65 ± 0.365 a |
| 400 | 14 | 9 | 2.95 ± 0.185 a | 34.00 ± 0.533 a | 2.85 ± 0.365 a |
| 500 | 17 | 8 | 3.05 ± 0.185 a | 33.20 ± 0.663 a | 2.55 ± 0.444 a |
| Control | 39 | 29 | 2.60 ± 0.152 a | 39.35 ± 0.519 b | 5.30 ± 0.145 b |
| df | - | - | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| F | - | - | 2.035 | 12.452 | 8.826 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pittarate, S.; Rajula, J.; Rahman, A.; Vivekanandhan, P.; Thungrabeab, M.; Mekchay, S.; Krutmuang, P. Insecticidal Effect of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles against Spodoptera frugiperda under Laboratory Conditions. Insects 2021, 12, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12111017
Pittarate S, Rajula J, Rahman A, Vivekanandhan P, Thungrabeab M, Mekchay S, Krutmuang P. Insecticidal Effect of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles against Spodoptera frugiperda under Laboratory Conditions. Insects. 2021; 12(11):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12111017
Chicago/Turabian StylePittarate, Sarayut, Julius Rajula, Afroja Rahman, Perumal Vivekanandhan, Malee Thungrabeab, Supamit Mekchay, and Patcharin Krutmuang. 2021. "Insecticidal Effect of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles against Spodoptera frugiperda under Laboratory Conditions" Insects 12, no. 11: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12111017
APA StylePittarate, S., Rajula, J., Rahman, A., Vivekanandhan, P., Thungrabeab, M., Mekchay, S., & Krutmuang, P. (2021). Insecticidal Effect of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles against Spodoptera frugiperda under Laboratory Conditions. Insects, 12(11), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12111017