Application of Spatio-Temporal Context and Convolution Neural Network (CNN) in Grooming Behavior of Bactrocera minax (Diptera: Trypetidae) Detection and Statistics
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Development Environment
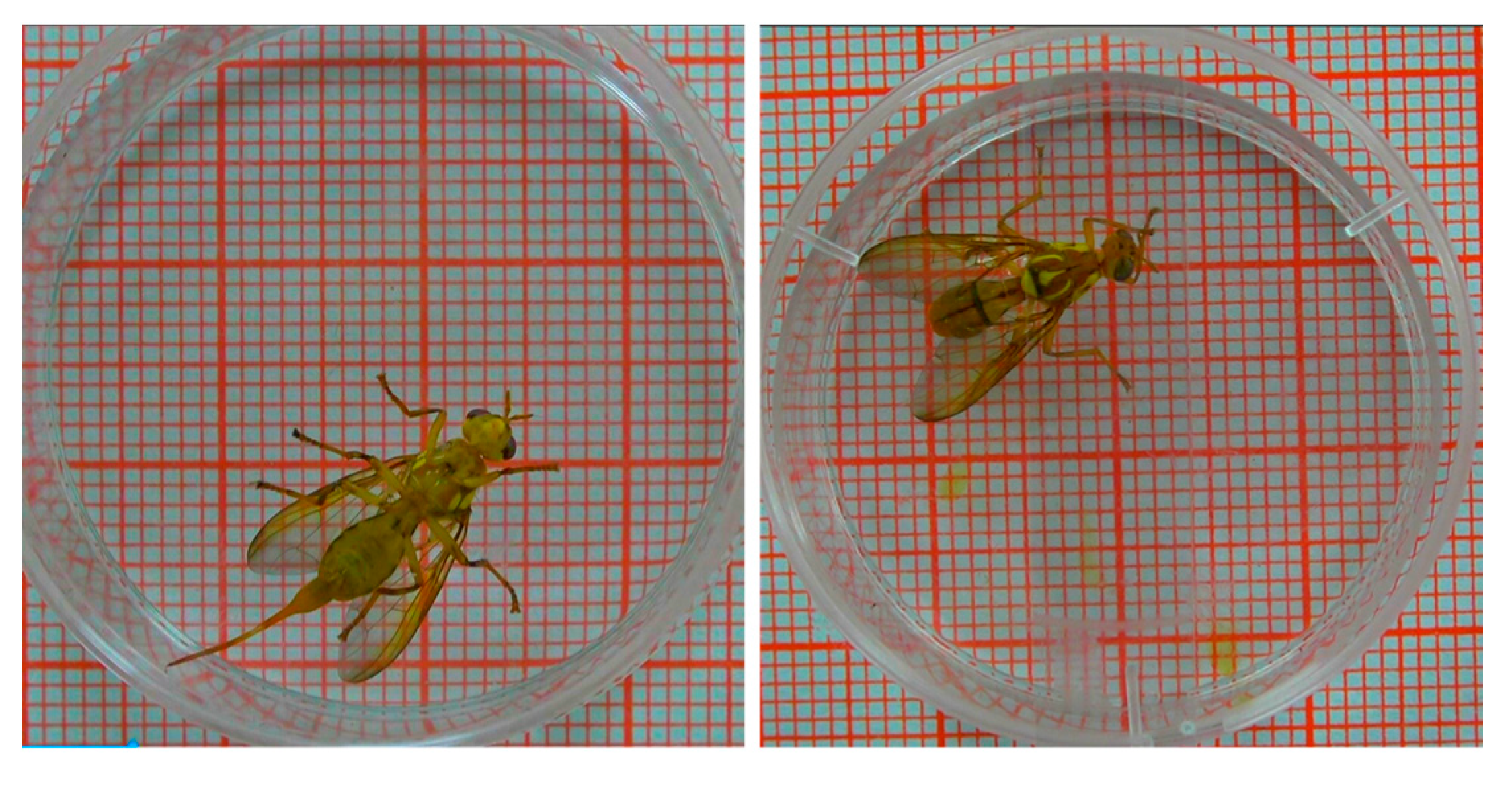
2.1.2. Video Acquisition of Bactrocera minax
2.2. Videos Processing
2.2.1. Color Extraction of Bactrocera minax
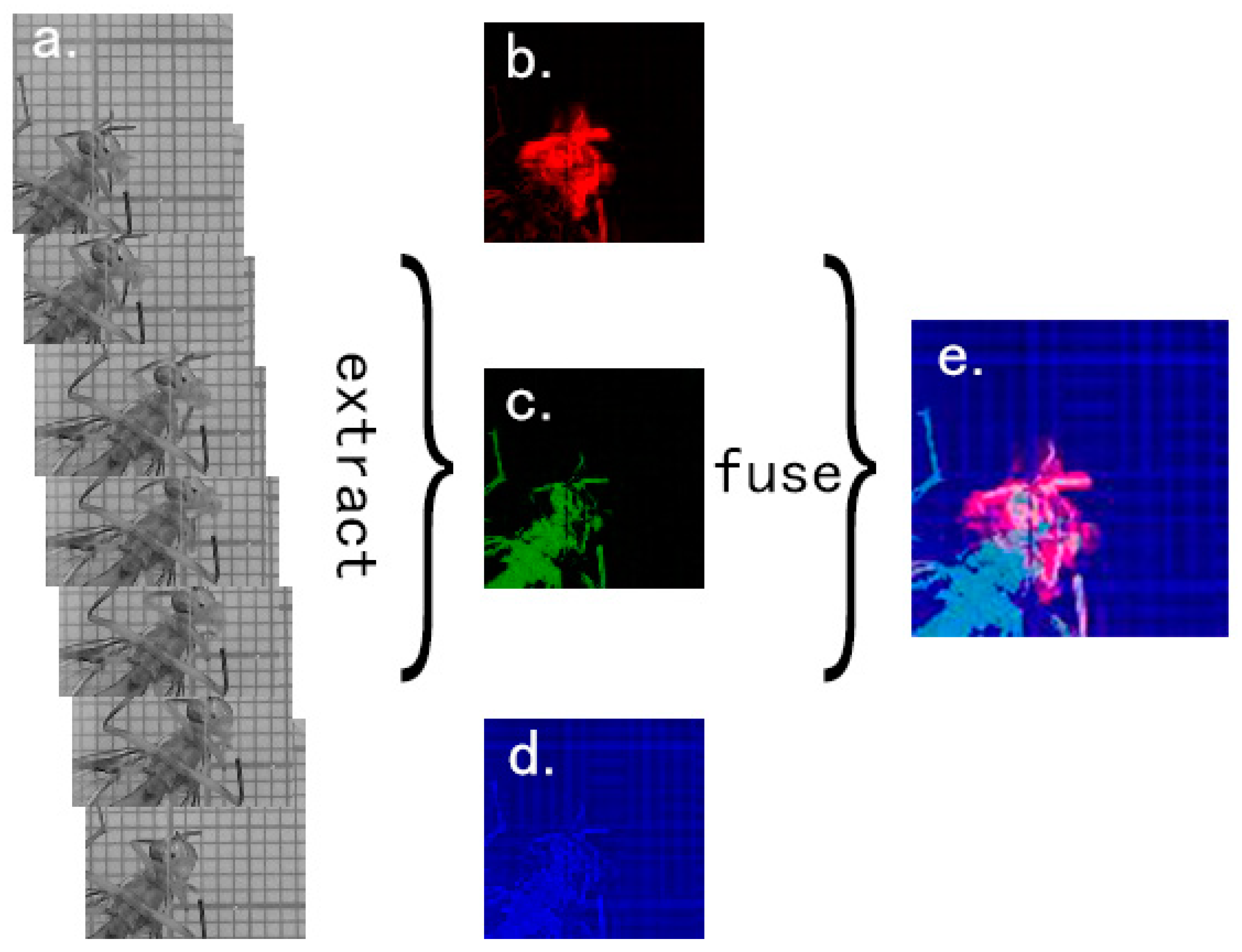
2.2.2. Spatial Information Extracting and Frame Cropping
2.2.3. Temporal Features Extracting
2.2.4. The Combination of Spatial Information and Temporal Features
2.3. Generate the Detection Model
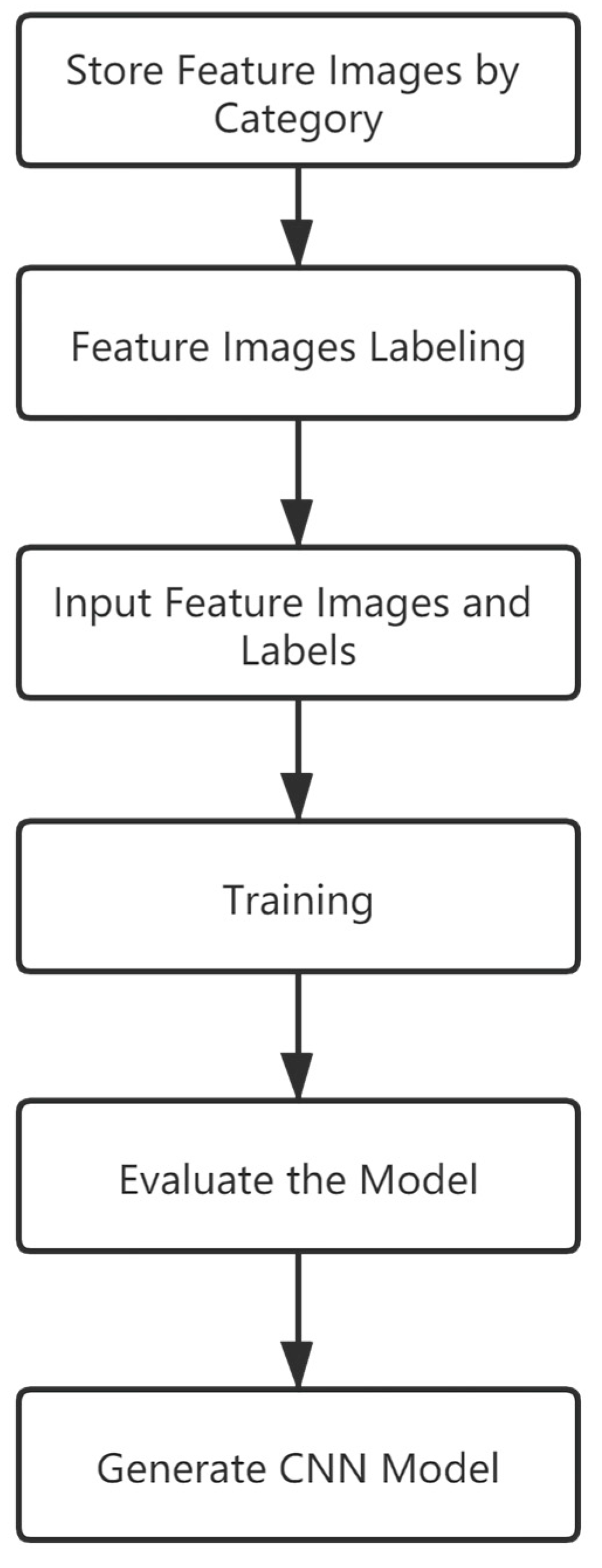
2.3.1. Selecting Feature Images to Create a Training Set
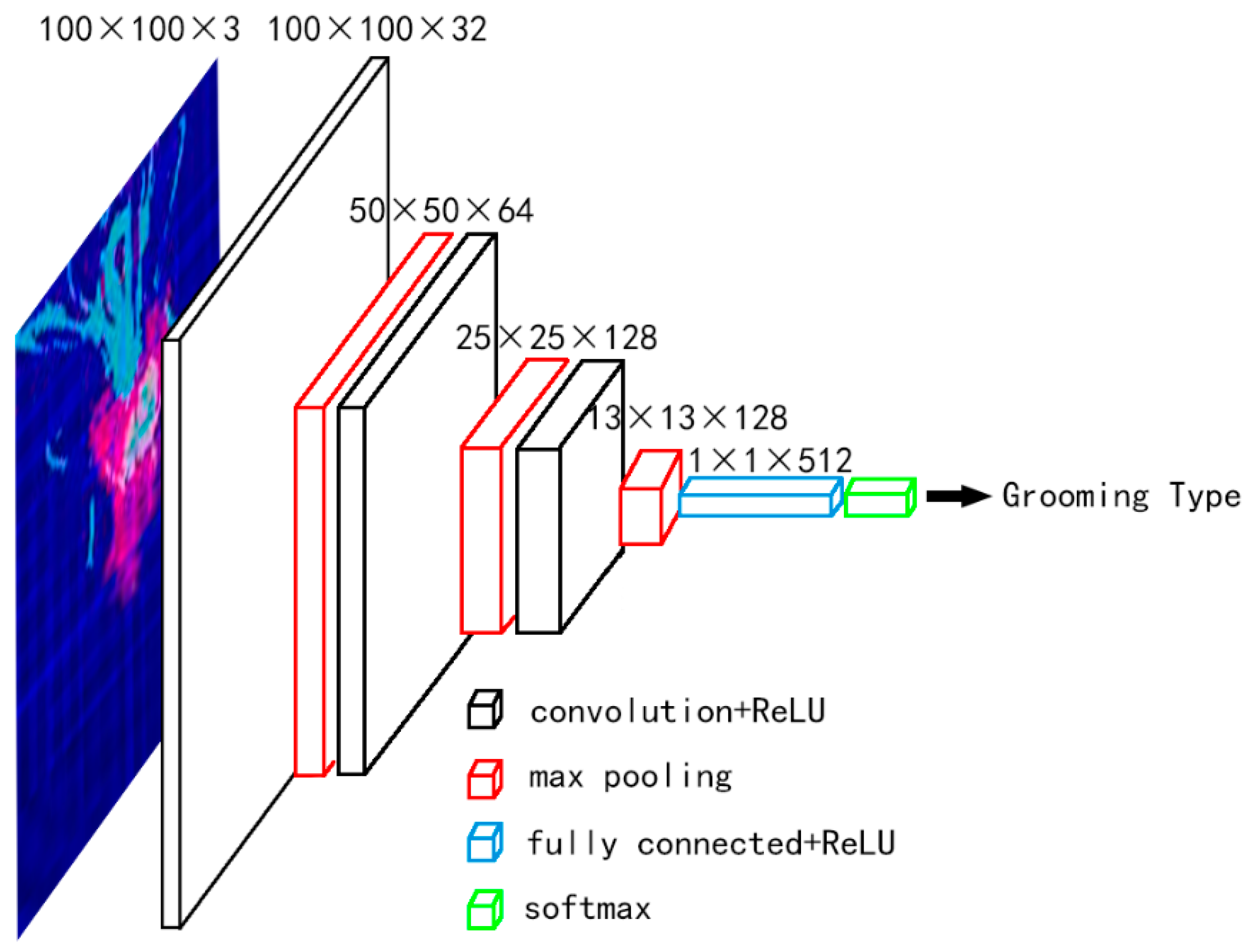
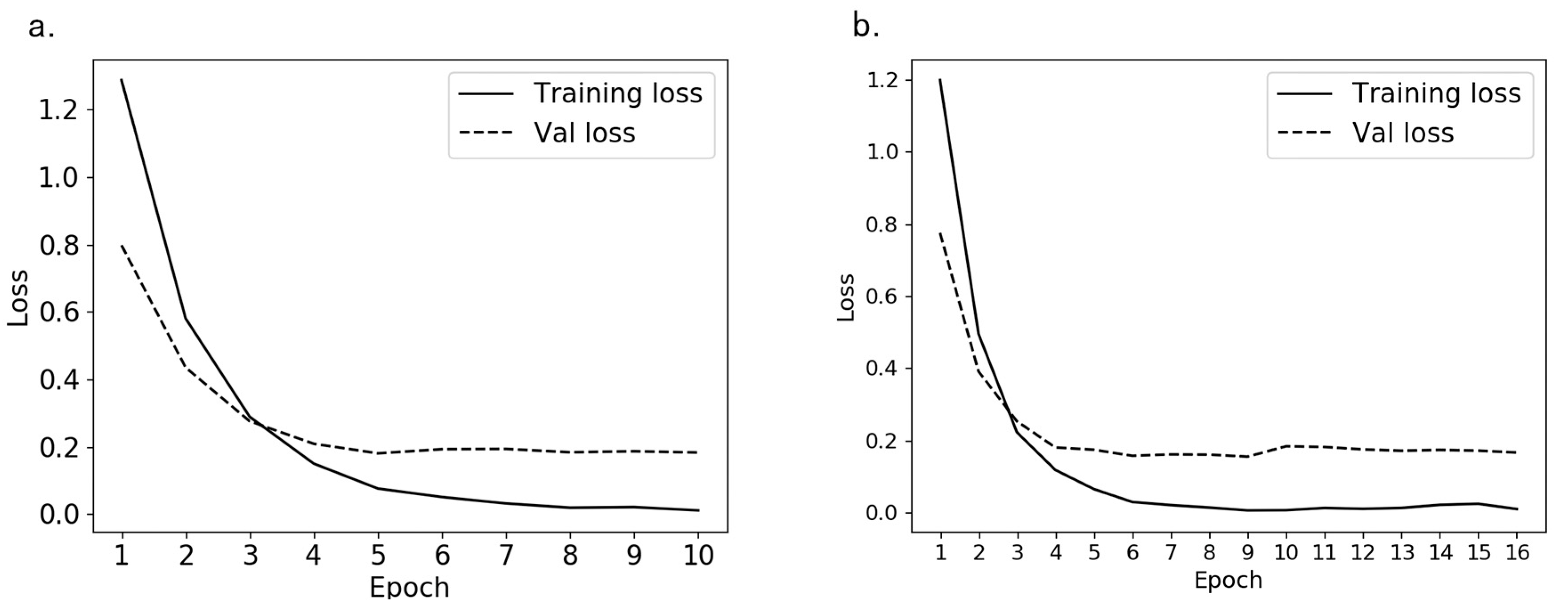
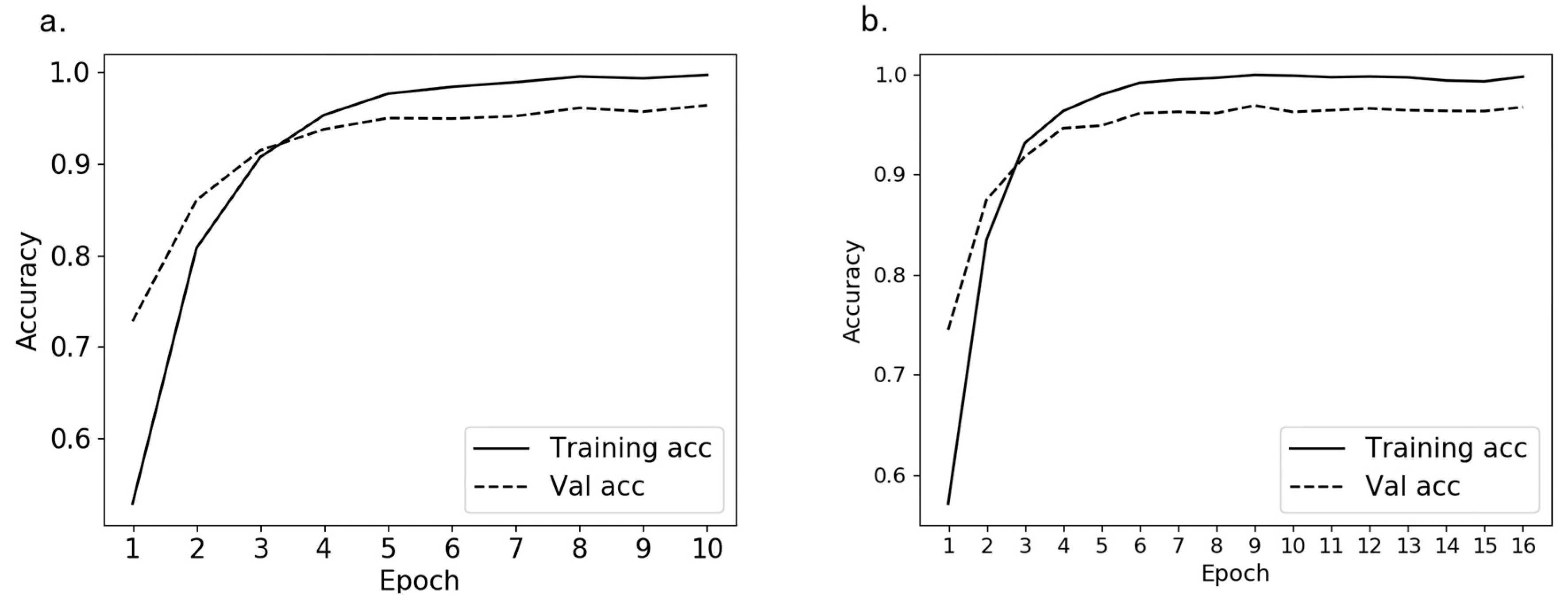
2.3.2. Training Model
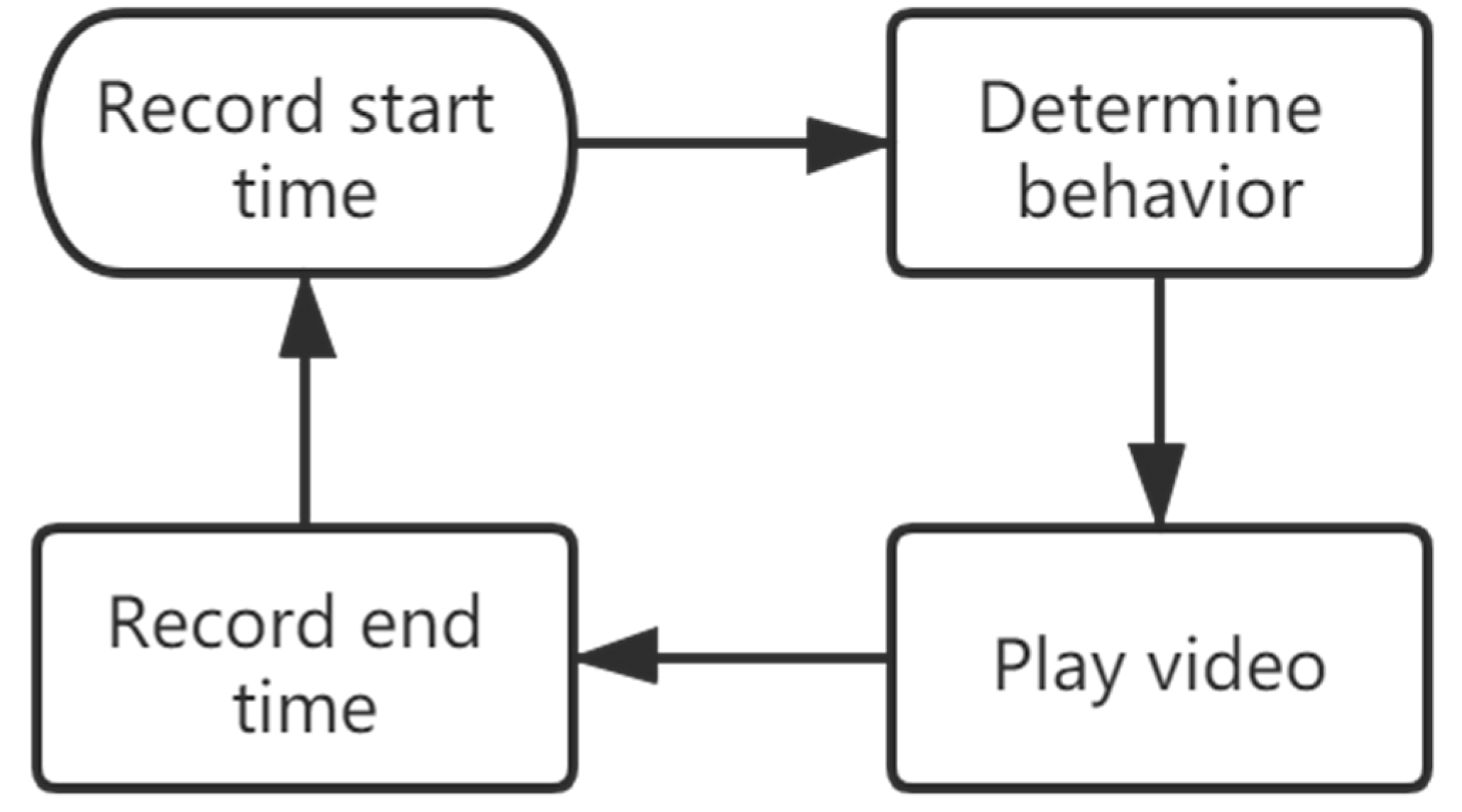
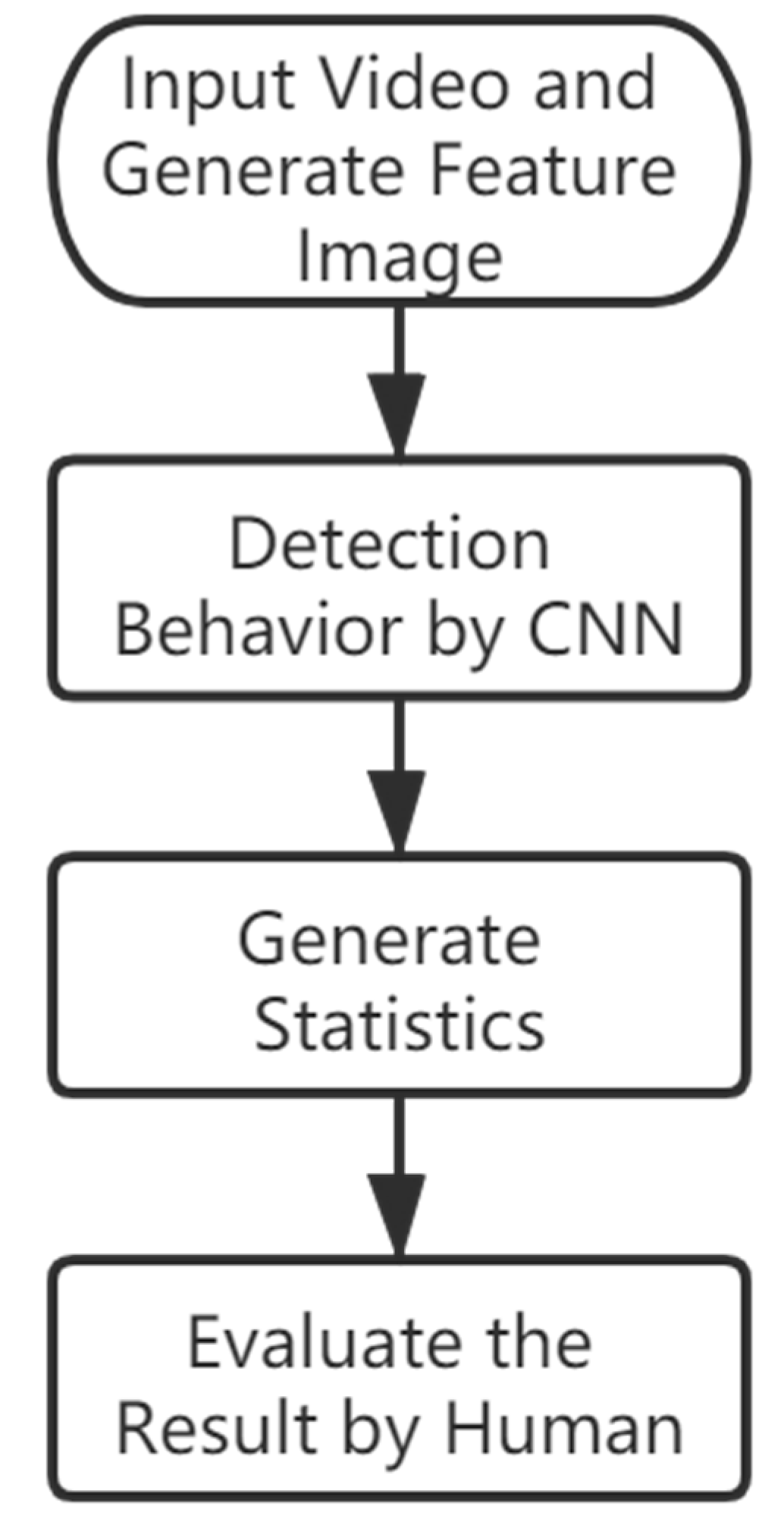
2.4. Analyzing the Detection Result and Generating Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Grooming Behavior of Bactrocera minax Adults
3.2. Detection of the Grooming Behavior
3.3. Statistical Differences
3.4. Comparison of Several Detection Methods
3.5. Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, D.; Ran, L.; Hu, J.; Ye, X.; Xu, D.; Li, J.; Su, H.; Wang, X.; Ren, S.; Keming, L. Mir319a/tcp module and DELLA protein regulate trichome initiation synergistically and improve insect defenses in populus tomentosa. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 867–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, L.Y.; Xiu-Qin, H.; Chuan-Ren, L.; Boiteau, G. Validation of Harmonic Radar Tags to Study Movement of Chinese Citrus Fly. Can. Entomol. 2011, 143, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Q.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, C.R.; Boiteau, G.; Gui, L.Y. Wing loading and extra loading capacity of adults of the Chinese citrus fruit fly, Bactrocera (Tetradacus) minax (Diptera: Tephritidae). Acta Entomologica Sinica 2012, 55, 606–611. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Gui, L.Y.; Wang, F.L. Daily rhythm of flight take off by early emerged adult Chinese citrus fly and their landing locations. J. Environ. Entomol. 2015, 37, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Böröczky, K.; Wadakatsumata, A.; Batchelor, D.; Zhukovskaya, M.; Schal, C. Insects groom their antennae to enhance olfactory acuity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 110, 3615–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukovskaya, M.; Yanagawa, A.; Forschler, B.T. Grooming Behavior as a Mechanism of Insect Disease Defense. Insects 2013, 4, 609–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roode, J.C.; Lefévre, T. Behavioral immunity in insects. Insects 2012, 3, 789–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillis, R.W.; Bramlage, A.T.; Wotus, C.; Whittaker, A.; Gramates, L.S.; Seppala, D.; Farahanchi, F.; Caruccio, P.; Murphey, R.K. Isolation of mutations affecting neural circuitry required for grooming behavior in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1993, 133, 581–592. [Google Scholar]
- Carlin, N.F.; Holldobler, B.; Gladstein, D.S. The kin recognition system of carpenter ants (Camponotus spp.). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1986, 20, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, M.; Wada-Katsumata, A.; Fujikawa, K.; Iwasaki, M.; Yokohari, F.; Satoji, Y.; Nisimura, T.; Yamaoka, R. Ant nestmate and non-nestmate discrimination by a chemosensory sensillum. Science 2005, 309, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, W. Co-Adaptation of Apis cerana Fabr and Varroa jacobsoni Oud. Apidologie 1999, 30, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooring, M.S.; Blumstein, D.T.; Stoner, C.J. The evolution of parasite-defence grooming in ungulates. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2004, 81, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A.E.; Hallett, R.H.; Soroka, J.J. Prefeeding behavior of the crucifer flea beetle, Phyllotreta cruciferae, on host and nonhost crucifers. J. Insect Behav. 2004, 17, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honegger, H.W.; Reif, H.; Müller, W. Sensory mechanisms of eye cleaning behavior in the cricket Gryllus campestris. J. Comp. Physiol. 1979, 129, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryait, H.; Bermudez-Contreras, E.; Harvey, M.; Faraji, J.; Agha, B.M.; Schjetnan, G.P.; Gruber, A.; Doan, J.; Mohajerami, M.; Metz, G.A.S. Data-driven analyses of motor impairments in animal models of neurological disorders. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thelen, E.; Farish, D.J. Analysis of grooming behaviour of wild and mutant strains of Brucon hebefor (Braconidae-Hymenoptera). Behaviour 1977, 62, 70–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoukis, N.C.; Collier, T.C. Computer Vision to Enhance Behavioral Research on Insects. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2019, 112, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Zhan, W.; Yu, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Y. Face Recognition via Convolutional Neural Networks and Siamese Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Automation and Systems (ICICAS), Chongqing, China, 6–8 December 2019; pp. 746–750. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, T.; Yao, A.; Chen, Y.; Sun, F. HyperNet: Towards Accurate Region Proposal Generation and Joint Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Li, Y. Computer vision technology in agricultural automation—A review. Inf. Process. Agric. 2020, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampatzidis, Y.; Partel, V. Uav-based high throughput phenotyping in citrus utilizing multispectral imaging and artificial intelligence. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchetti, R.; Erra, F.; Ricci, N.; Dini, F. Ethogram of aspidisca sedigita. Can. J. Zool. 2003, 81, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, S.M.; Poulin, A. Equid play ethogram. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2002, 78, 263–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuellner, C.T.; Porter, S.D.; Gilbert, L.E. Eclosion, mating, and grooming behavior of the parasitoid fly Pseudacteon curvatus (Diptera: Phoridae). Fla. Entomol. 2002, 85, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Z.; Hua, D.K.; Du, T.H.; Wang, F.L.; Gui, L.Y. Feeding behaviour of Bactrocera minax (Diptera: Trypetidae) on male inflorescence of Castanea mollissima (Fagales: Fagaceae). Acta Entomologica Sinica 2018, 61, 458–467. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, T.D.; Aldarondo, D.E.; Willmore, L.; Willmore, L.; Kislin, M.; Wang, S.S.H.; Murthy, M.; Shaevitz, J.W. Fast animal pose estimation using deep neural networks. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravbar, P.; Branson, K.; Simpson, J.H. An automatic behavior recognition system classifies animal behaviors using movements and their temporal context. J. Neurosci. Meth. 2019, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Ding, M.; Gu, W.; Huang, Y.; Li, S. Study on grooming behavior ethogram and behavior sequence in fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. (Med. Sci.) 2006, 27, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Saffar, A.A.M.; Tao, H.; Talab, M.A. Review of deep convolution neural network in image classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Radar, Antenna, Microwave, Electronics, and Telecommunications (ICRAMET), Jakarta Selatan, Indonesia, 23–24 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rawat, W.; Wang, Z. Deep convolutional neural networks for image classification: A comprehensive review. Neural Comput. 2017, 29, 2352–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhami, B.; Khanali, M.; Akram, A. Combined application of Artificial Neural Networks and life cycle assessment in lentil farming in Iran. Inf. Process. Agric. 2017, 4, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Xu, P.; Denoeux, T. ConvNet and Dempster-Shafer Theory for Object Recognition. In International Conference on Scalable Uncertainty Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 368–381. [Google Scholar]
- Partel, V.; Nunes, L.; Stansly, P.; Ampatzidis, Y. Automated vision-based system for monitoring Asian citrus psyllid in orchards utilizing artificial intelligence. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 162, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flórián, N.; Gránicz, L.; Gergócs, V.; Tóth, F.; Dombos, M. Detecting Soil Microarthropods with a Camera-Supported Trap. Insects 2020, 11, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.-H.; Zhu, F.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, W.-M.; Guo, R.; Liu, W.; Pan, L.; Du, Y. Minor Components Play an Important Role in Interspecific Recognition of Insects: A Basis to Pheromone Based Electronic Monitoring Tools for Rice Pests. Insects 2018, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czyzewski, B.D.; McGraw, B.A. Detection of Listronotus maculicollis (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) Turfgrass Canopy Activity with the Use of a Novel Fluorescent Marking System Suggests Opportunities for Improved Mechanical Control. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 47, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulridha, J.; Ampatzidis, Y.; Kakarla, S.; Roberts, P. Detection of target spot and bacterial spot diseases in tomato using UAV-based and benchtop-based hyperspectral imaging techniques. Precis. Agric. 2019, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.K.; Rath, A.K.; Sethy, P.K. Maturity status classification of papaya fruits based on machine learning and transfer learning approach. Inf. Process. Agric. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Yuan, J.; Song, L.; Liu, X. Recognition of cotton growth period for precise spraying based on convolution neural network. Inf. Process. Agric. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Dorj, U.O.; Lee, M.; Yun, S.S. An yield estimation in citrus orchards via fruit detection and counting using image processing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 140, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, A.; Mamidanna, P.; Cury, K.M.; Abe, T.; Murthy, V.N.; Mathis, M.W.; Bethge, M. Deeplabcut: Markerless pose estimation of user-defined body parts with deep learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hong, T.; Wen, T.; Song, S.; Sun, D.; Li, P.; Zhu, Z. Mature fruit fly identification using machine vision. J. Fruit Sci. 2014, 31, 679–683. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Han, X.; Shen, Z.R.; Huang, D.Z.; Mi, S. Digital classification of noctuid moths (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) base on wings vein characteristics. Environ. Entomol. 2016, 38, 348–353. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Q.; Lu, H.B. Insect classification and retrieval system based on web technology. Environ. Entomol. 2014, 36, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Niederegger, S.; Döge, K.-P.; Peter, M.; Eickhölter, T.; Mall, G. Connecting the Dots: From an Easy Method to Computerized Species Determination. Insects 2017, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, J. Dc-spp-yolo: Dense connection and spatial pyramid pooling based yolo for object detection. Inform. Sci. 2020, 522, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Piotr, D.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.; Tian, Y.; Luo, R.; Zhang, Z.; Lian, J.; Zheng, J. Detection and segmentation of overlapped fruits based on optimized mask r-cnn application in apple harvesting robot. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 172, 105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, T.; Mathis, A.; Chen, A.C.; Patel, A.; Bethge, M.; Mathis, M.W. Using deeplabcut for 3d markerless pose estimation across species and behaviors. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2152–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 28th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lecun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L.D. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreland, K.; Angel, E. The FFT on a GPU. In Proceedings of the ACM Siggraph/Eurographics Conference on Graphics Hardware, San Diego, CA, USA, 26–27 July 2003; pp. 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Naga, K.G.; Brandon, L.; Yuri, D.; Burton, S.; John, M. High performance discrete Fourier transforms on graphics processors. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM/IEEE Conference on Supercomputing, Austin, TX, USA, 15–21 November 2008; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]


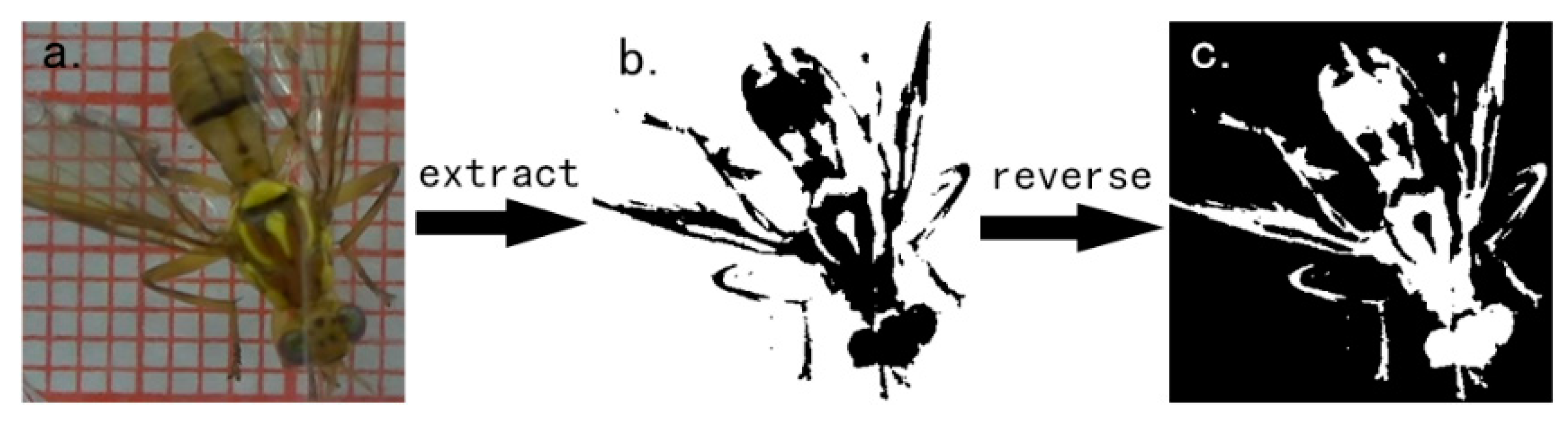
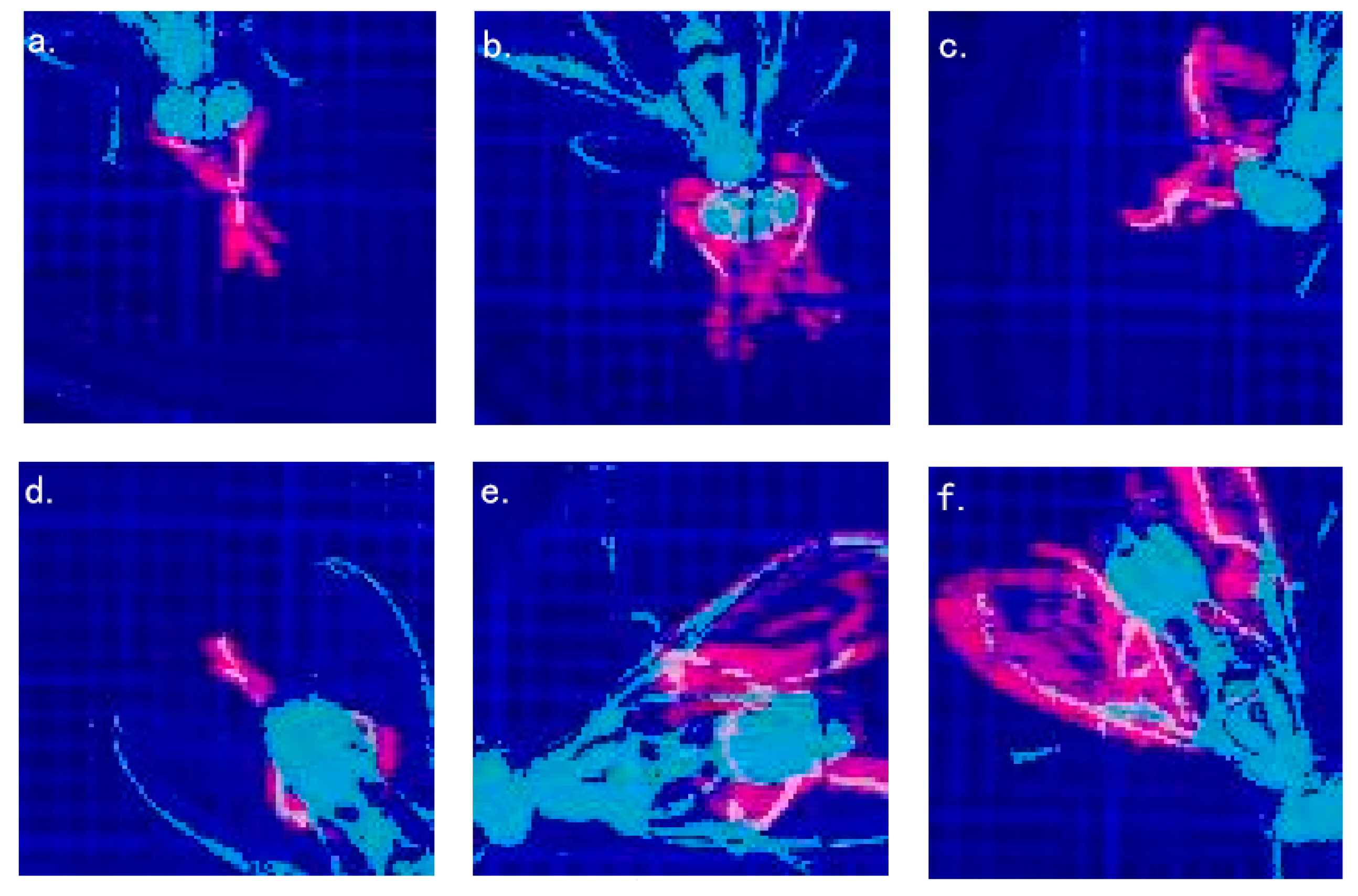
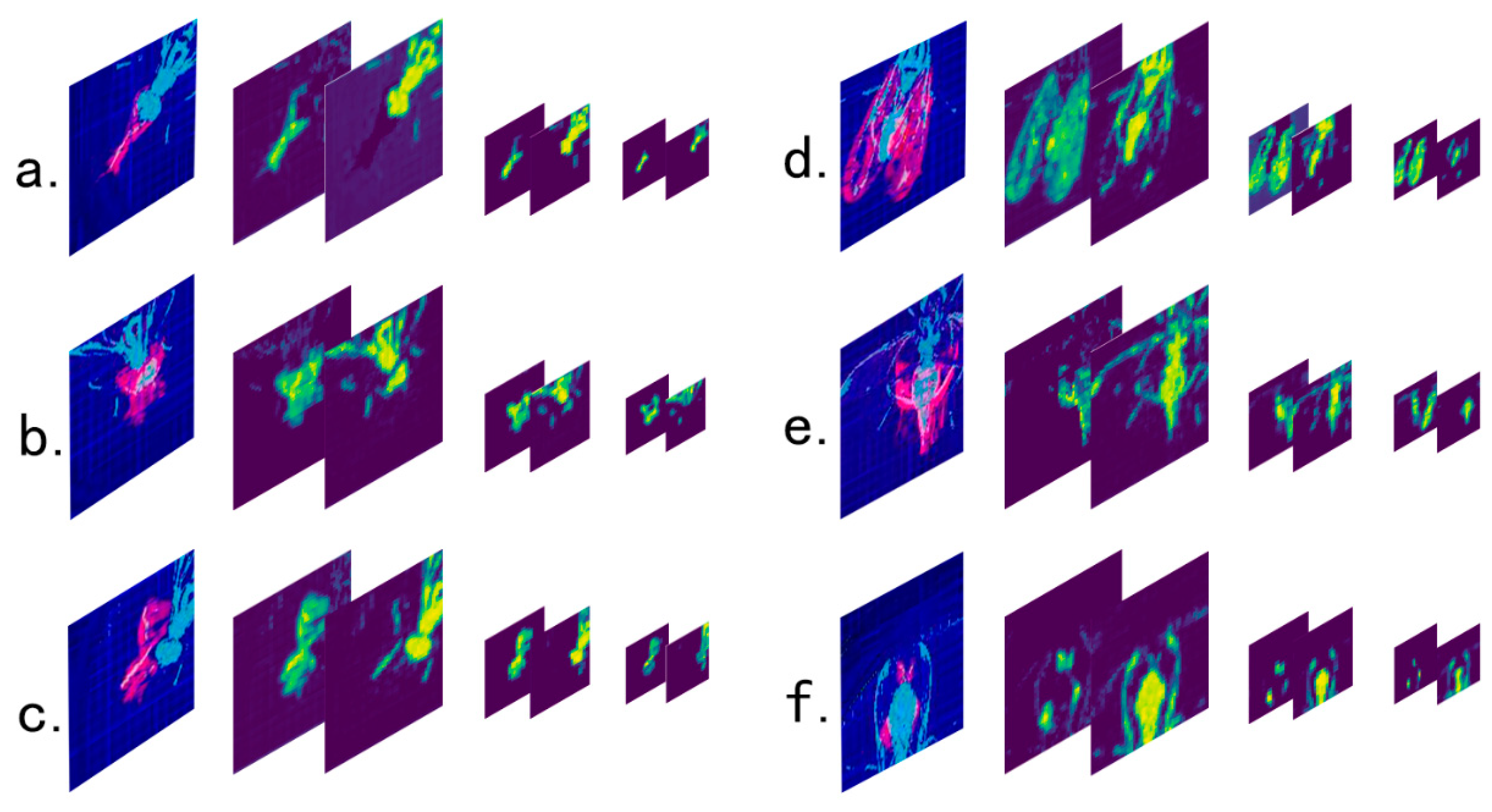
| Behavior Type | Counts | Behavior Type | Counts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foreleg grooming | 5464 | Head grooming | 5202 |
| Mid grooming | 4502 | Abdomen grooming | 3702 |
| Hind leg grooming | 3486 | Wing grooming | 4140 |
| Motionless | 4012 |
| Total Number of Behaviors | Average Accuracy | Standard Error |
|---|---|---|
| 7893 | 95.71% | 2.88% |
| Bactrocera minax Number | Number of Behaviors | Accuracy | Deviance | Bactrocera minax Number | Number of Behaviors | Accuracy | Deviance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 379 | 97.89% | 2.18% | 12 | 417 | 91.37% | −4.34% |
| 2 | 324 | 99.69% | 3.98% | 13 | 237 | 99.16% | 3.45% |
| 3 | 378 | 93.12% | −2.59% | 14 | 406 | 90.89% | −4.82% |
| 4 | 336 | 96.13% | 0.42% | 15 | 218 | 97.71% | 2.00% |
| 5 | 584 | 96.58% | 0.87% | 16 | 558 | 93.73% | −1.98% |
| 6 | 492 | 95.33% | −0.38% | 17 | 53 | 96.23% | 0.52% |
| 7 | 186 | 93.01% | −2.70% | 18 | 397 | 94.71% | −1.00% |
| 8 | 550 | 97.27% | 1.56% | 19 | 328 | 98.78% | 3.07% |
| 9 | 300 | 98.33% | 2.62% | 20 | 121 | 96.69% | 0.98% |
| 10 | 594 | 96.63% | 0.92% | 21 | 247 | 97.17% | 1.46% |
| 11 | 329 | 97.26% | 1.55% | 22 | 459 | 88.02% | −7.69% |
| Video Number | Total Number of Behaviors Counted Manually | Different Number of Results | Difference Degree |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 134 | 20 | 14.93% |
| 2 | 140 | 15 | 10.71% |
| 3 | 50 | 8 | 16.00% |
| 4 | 66 | 6 | 9.09% |
| 5 | 36 | 5 | 13.89% |
| 6 | 94 | 12 | 12.77% |
| 7 | 115 | 13 | 11.30% |
| 8 | 88 | 7 | 7.95% |
| 9 | 79 | 12 | 15.19% |
| 10 | 102 | 11 | 10.78% |
| Detection Methods | Validation Set Accuracy | Convergence Speed on RTX 2070 GPU (s/epoch) |
|---|---|---|
| Method 1 1 | 92.23% | 3.19 |
| Method 2 2 | 95.28% | 7.13 |
| Method 3 3 | 95.30% | 44.75 |
| Method 4 4 | 96.68% | 7.25 |
| Device 1: I7 9700 CPU, RTX 2070 GPU, 16GB RAM | Device 2: I9 9900K CPU, RTX 2080Ti GPU, 32GB RAM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Video Number | Feature Image Generation Rate (fps/s) | Feature Image Detection Time (s) | Video Number | Feature Image Generation Rate (fps/s) | Feature Image Detection Time (s) |
| 1 | 15.16 | 18.74 | 1 | 16.23 | 11.12 |
| 2 | 14.88 | 17.28 | 2 | 15.72 | 10.43 |
| 3 | 14.82 | 17.99 | 3 | 15.69 | 10.03 |
| 4 | 14.87 | 19.15 | 4 | 15.64 | 9.63 |
| 5 | 14.91 | 18.00 | 5 | 16.01 | 8.29 |
| 6 | 14.56 | 18.22 | 6 | 15.52 | 10.25 |
| 7 | 14.65 | 18.67 | 7 | 15.71 | 9.81 |
| 8 | 15.01 | 21.95 | 8 | 15.98 | 9.76 |
| 9 | 14.96 | 15.89 | 9 | 15.92 | 9.72 |
| 10 | 14.89 | 15.29 | 10 | 15.81 | 9.92 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Zhan, W.; He, Z.; Zou, Y. Application of Spatio-Temporal Context and Convolution Neural Network (CNN) in Grooming Behavior of Bactrocera minax (Diptera: Trypetidae) Detection and Statistics. Insects 2020, 11, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11090565
Zhang Z, Zhan W, He Z, Zou Y. Application of Spatio-Temporal Context and Convolution Neural Network (CNN) in Grooming Behavior of Bactrocera minax (Diptera: Trypetidae) Detection and Statistics. Insects. 2020; 11(9):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11090565
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhiliang, Wei Zhan, Zhangzhang He, and Yafeng Zou. 2020. "Application of Spatio-Temporal Context and Convolution Neural Network (CNN) in Grooming Behavior of Bactrocera minax (Diptera: Trypetidae) Detection and Statistics" Insects 11, no. 9: 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11090565
APA StyleZhang, Z., Zhan, W., He, Z., & Zou, Y. (2020). Application of Spatio-Temporal Context and Convolution Neural Network (CNN) in Grooming Behavior of Bactrocera minax (Diptera: Trypetidae) Detection and Statistics. Insects, 11(9), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11090565






