Evaluation of the Physiological Host Range for the Parasitoid Ooencyrtus mirus, a Potential Biocontrol Agent of Bagrada hilaris
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Host Sources and Rearing
2.2. Parasitoid Rearing
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Number of O. mirus Eggs (Pedicels) Per Host Egg
3.2. Progeny Emergence
3.3. Survival (Proportion of O. mirus Progeny from Parasitized Host Eggs)
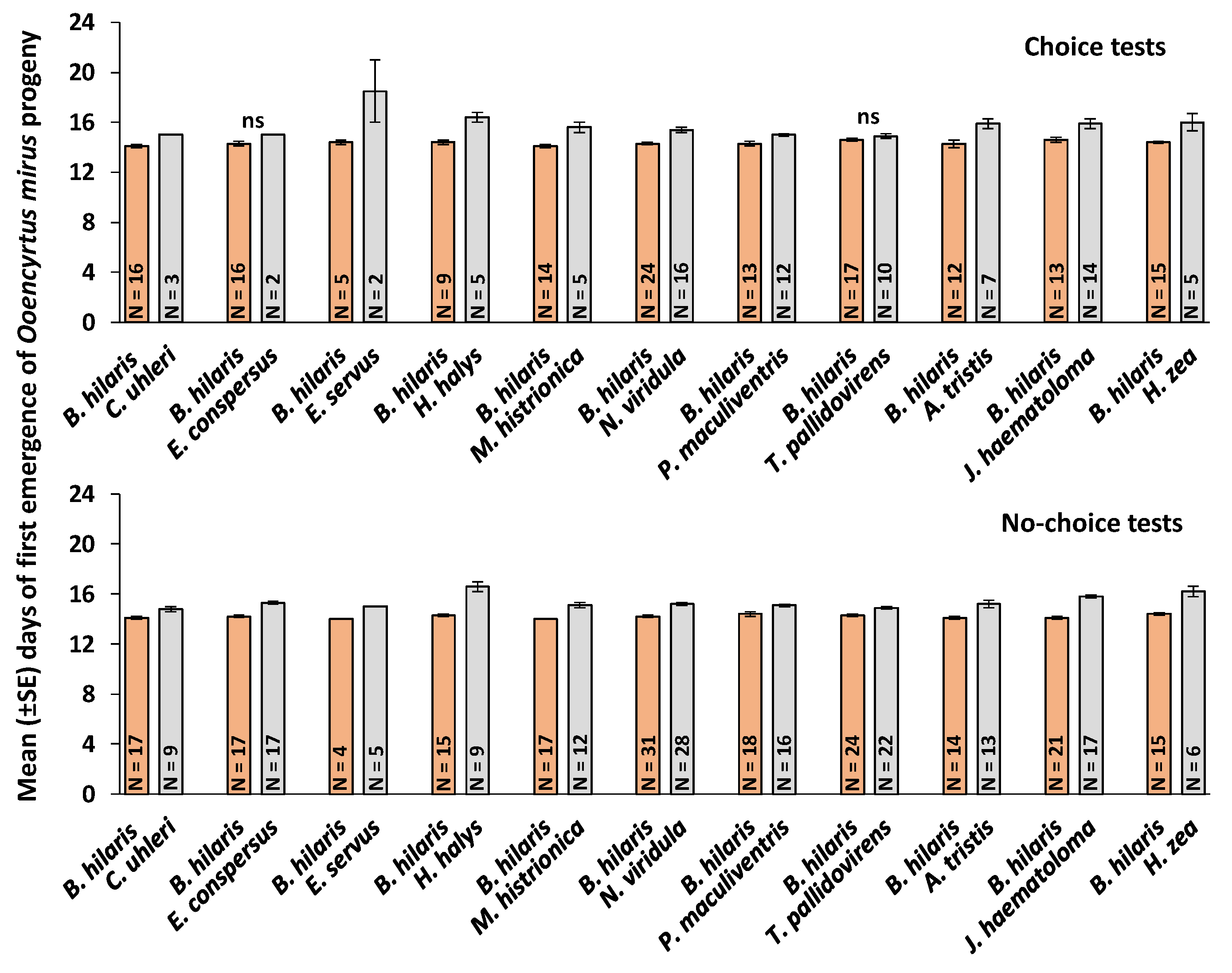
3.4. First Day of Emergence and Developmental Time
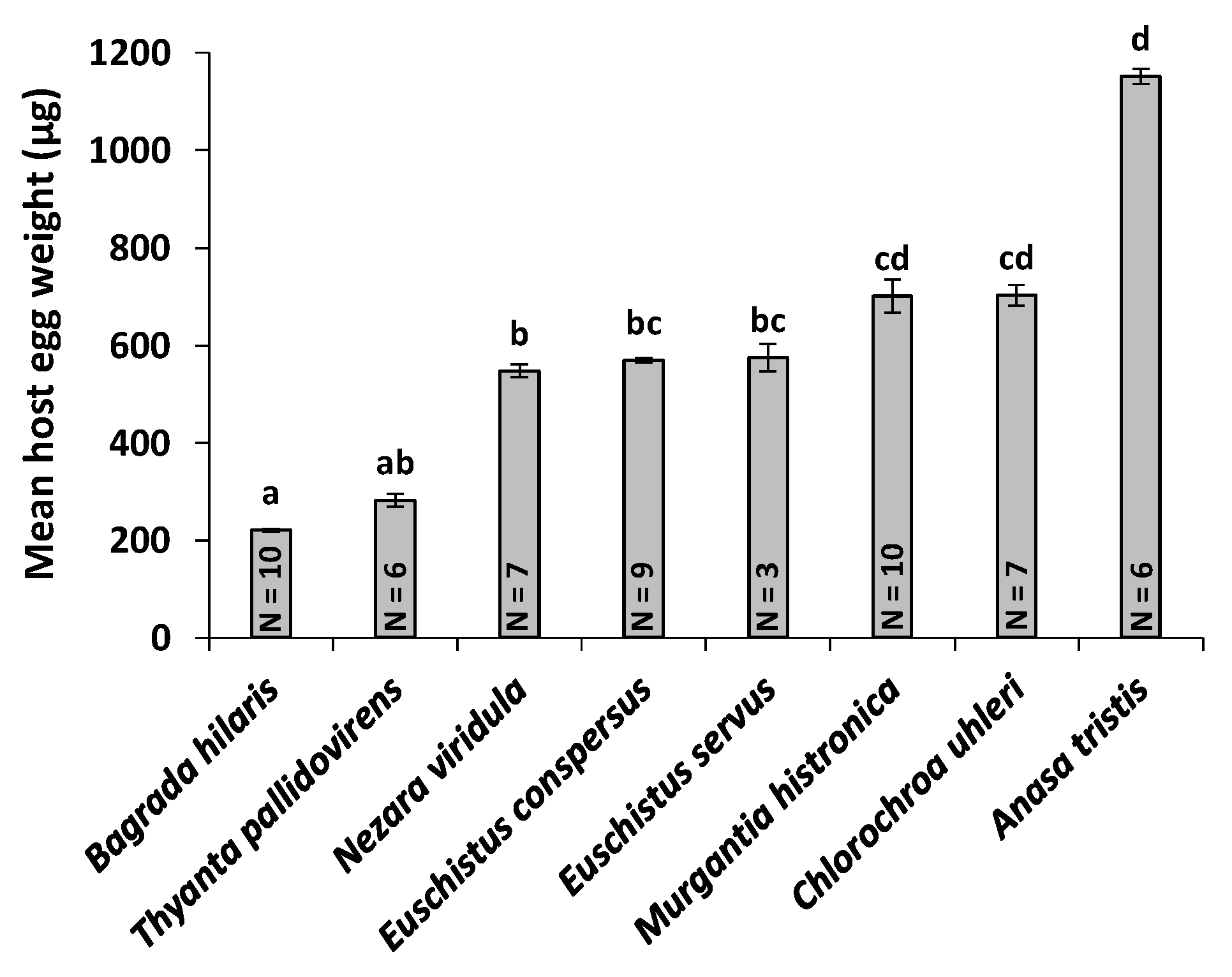
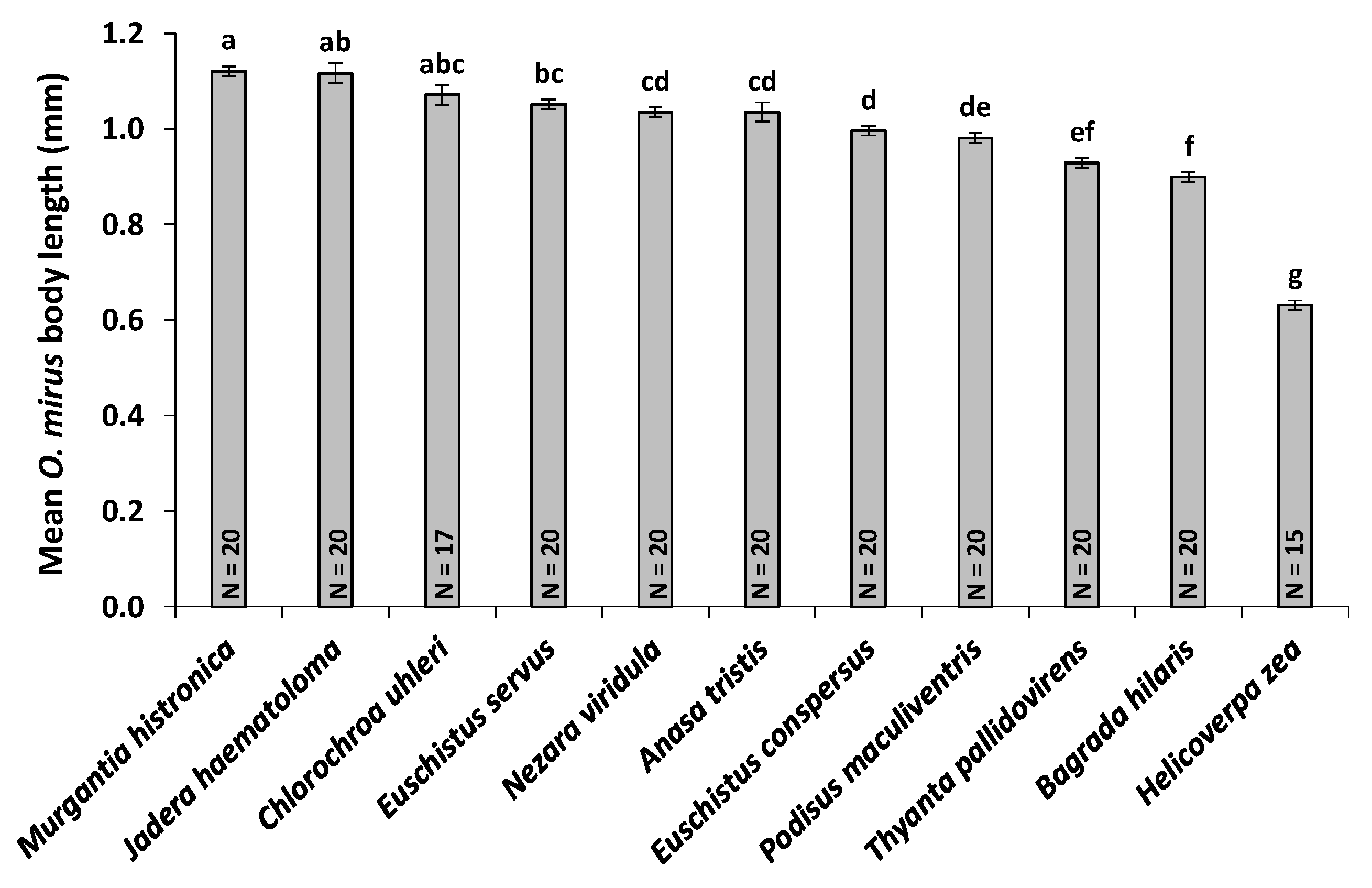
3.5. Host Egg Weight and O. mirus Body Length
3.6. Reproductive Success of O. mirus Emerged from the Alternate Host Eggs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reed, D.A.; Palumbo, J.C.; Perring, T.M.; May, C. Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), an invasive stink bug attacking cole crops in the southwestern United States. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2013, 4, C1–C7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, C.W. The Entomological section: The bagrada bug (Bagrada hilaris). Transvaal Agric. J. 1906, 5, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Husain, M.A. Annual report of the entomologist to government, Punjab, Lyallpur, for the year ending 30 June 1924. Rept. Dept. Agric. Punjab 1923–24 1925, 1, 55–90. [Google Scholar]
- Sachan, G.; Purwar, J. Integrated insect pest management in rapeseed and mustard. In Entomology: Novel Approaches; Jain, P.C., Bhargava, M.C., Eds.; New India Publishing Agency: New Delhi, India, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.K. Biology and Breeding of Crucifers; CRC Press: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bundy, C.S.; Perring, T.M.; Reed, D.A.; Palumbo, J.C.; Grasswitz, T.R.; Jones, W.A. Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister). In Invasive Stink Bugs and Related Species (Pentatomoidea): Biology, Higher Systematics, Semiochemistry, and Management; McPherson, J.E., Ed.; CRC Press: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Colazza, S.; Guarino, S.; Peri, E. Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) a pest of capper in the island of Pantelleria [Capparis spinosa L.; Sicily]. Informatore Fitopatologico 2004, 54, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Arakelian, G. Bagrada Bug (Bagrada hilaris); Los Angeles County Agricultural Commissioner/Weights and Measures Department: Arcadia, CA, USA, 2008.
- Palumbo, J.C.; Natwick, E.T. The bagrada bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae): A new invasive pest of cole crops in Arizona and California. Plant Health Prog. 2010, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, C.S.; Grasswitz, T.R.; Sutherland, C. First report of the invasive stink bug Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) from New Mexico, with notes on its biology. Southwest Entomol. 2012, 37, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitanza, S. Issues in agriculture. Texas A&M Agrilife Ext. Newsl. 2012, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Perring, T.M.; Reed, D.A.; Palumbo, J.C.; Grasswitz, T.; Bundy, C.S.; Jones, W.; Royer, T. National Pest Alert: Bagrada Bug Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister) Family Pentatomidae; USDA-NIFA Regional IPM Centers: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2013. Available online: https://www.ncipmc.org/projects/pest-alerts1/bagrada-bug-bagrada-hilaris-burmeister/ (accessed on 9 July 2020).
- Matsunga, J.N. Bagrada Bug, Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae); State of Hawaii Department of Agriculture, New Pest Advisory: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2014. Available online: https://hdoa.hawaii.gov/pi/files/2013/01/Bagrada-hilaris-NPA4-5-16.pdf (accessed on 9 July 2020).
- Sánchez-Peña, S.R. First record in Mexico of the invasive stink bug Bagrada hilaris, on cultivated crucifers in Saltillo. Southwest Entomol. 2014, 39, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Acosta, R.I.; Sánchez-Peña, S.R. Geographical distribution of Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in Mexico. J. Entomol. Sci. 2016, 51, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faúndez, E.I.; Lüer, A.; Cuevas, Á.G.; Rider, D.A.; Valdebenito, P. First record of the painted bug Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister, 1835) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in South America. Arq. EntomolóXicos 2016, 16, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Guarino, S.; Peri, E.; Colazza, S.; Luchi, N.; Michelozzi, M.; Loreto, F. Impact of the invasive painted bug Bagrada hilaris on physiological traits of its host Brassica oleracea var botrytis. Arthropod-Plant Inte. 2017, 11, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, J.C.; Perring, T.M.; Millar, J.G.; Reed, D.A. Biology, ecology, and management of an invasive stink bug, Bagrada hilaris, in North America. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, J.C.; Carrière, Y. Association between Bagrada hilaris density and feeding damage in broccoli: Implications for pest management. Plant Health Prog. 2015, 16, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, S.; Kemp, D. Insecticides and acaricides: Resistance and environmental impact. Rev. Sci. -Tech.-Off. Int. Des. Epizoot. 1994, 13, 1249–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.E.; Bundy, C.S.; McPherson, J.E. Unusual ovipositional behavior of the stink bug Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2014, 107, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, R.; Jones, W.A.; Bajwa, B.E.; Rashid, K. Egg parasitoids from Pakistan as possible classical biological control agents of the invasive pest Bagrada hilaris (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). J. Entomol. Sci. 2015, 50, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjisaffar, F.; Talamas, E.J.; Bon, M.C.; Gonzalez, L.; Brown, B.V.; Perring, T.M. Trissolcus hyalinipennis Rajmohana & Narendran (Hymenoptera, Scelionidae), a parasitoid of Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister) (Hemiptera, Pentatomidae), emerges in North America. J. Hymenopt. Res. 2018, 65, 111–130. [Google Scholar]
- Martel, G.; Auge, M.; Talamas, E.; Roche, M.; Smith, L.; Sforza, R.F.H. First laboratory evaluation of Gryon gonikopalense (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae), as potential biological control agent of Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Biol. Control 2019, 135, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triapitsyn, S.; Andreason, S.; Power, N.; Ganjisaffar, F.; Fusu, L.; Dominguez, C.; Perring, T.M. Two new species of Ooencyrtus (Hymenoptera, Encyrtidae), egg parasitoids of the bagrada bug Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera, Pentatomidae), with taxonomic notes on Ooencyrtus telenomicida. J. Hymenopt. Res. 2020, 76, 57–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, P.B. Host specificity and biological pest control. BioScience 1996, 46, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Onstand, D.W.; McManus, M.L. Risks of host range expansion by parasites of insects. BioScience 1996, 46, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.P. Contrasts in reproductive ecology between temperate and tropical populations of Jadera haematoloma, a mate-guarding Hemipteran (Rhopalidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1988, 81, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maple, J.D. The Eggs and First Instar Larvae of Encyrtidae and Their Morphological Adaptations for Respiration; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1947. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kavar, T.; Pavlovcic, P.; Susnik, S.; Meglic, V.; Virant-Doberlet, M. Genetic differentiation of geographically separated populations of the southern green stink bug Nezara viridula (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2006, 96, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokkanen, H. Polymorphism, parasites, and the native area of Nezara viridula (Hemiptera, Pentatomidae). Ann. Entomol. Fenn. 1986, 52, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ruckes, H. The taxonomic status and distribution of Thyanta custator (Fabricius) and Thyanta pallido-virens (Stal) (Heteroptera, Pentatomidae). Am. Mus. Novit. 1957, 1824, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Giunti, G.; Canale, A.; Messing, R.; Donati, E.; Stefanini, C.; Michaud, J.; Benelli, G. Parasitoid learning: Current knowledge and implications for biological control. Biol. Control 2015, 90, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobdell, C.E.; Yong, T.H.; Hoffmann, M.P. Host color preferences and short-range searching behavior of the egg parasitoid Trichogramma ostriniae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2005, 116, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchetta, P.; Bernstein, C.; Théry, M.; Lazzari, C.; Desouhant, E. Foraging and associative learning of visual signals in a parasitic wasp. Anim. Cogn. 2008, 11, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.; Rojas, J.C.; Montoya, P.; Liedo, P.; Gonzáles, F.J.; Castillo, A. Size, shape and hue modulate attraction and landing responses of the braconid parasitoid Fopius arisanus to fruit odour-baited visual targets. BioControl 2012, 57, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talamas, E.J.; Johnson, N.F.; Buffington, M. Key to Nearctic species of Trissolcus Ashmead (Hymenoptera, Scelionidae), natural enemies of native and invasive stink bugs (Hemiptera, Pentatomidae). J. Hymenopt. Res. 2015, 43, 45–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, G. Evaluation of Host Specificity in Pentatomid Parasitoids through their Response to the Host Unit. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Perugia, Perugia, Italy, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Samra, S.; Ghanim, M.; Protasov, A.; Mendel, Z. Development, reproduction, host range and geographical distribution of the variegated caper bug Stenozygum coloratum (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2015, 112, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botch, P.S.; Delfosse, E.S. Host-acceptance behavior of Trissolcus japonicus (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) reared on the invasive Halyomorpha halys (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) and nontarget species. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 47, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, L.S.; Liu, H.; Miller, D.; Gould, J. Developing a classical biological control program for Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), an invasive ash pest in North America. Newsl. Mich. Entomol. Soc. 2008, 53, 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Abram, P.K.; Brodeur, J.; Burte, V.; Boivin, G. Parasitoid-induced host egg abortion: An underappreciated component of biological control services provided by egg parasitoids. Biol. Control 2020, 98, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, R.W. Some ichneumonid-sarcophagid interactions in the gypsy moth Porthetria dispar (L.) (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae). Can. Entomol. 1963, 95, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashomb, J.; Krainacker, D.; Jansson, R.; Ng, Y.; Chianese, R. Parasitism of Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Say) eggs by Edovum puttleri Grissell (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae): Effects of host age, parasitoid age, and temperature. Can. Entomol. 1987, 119, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, M.; Ratner, S.; Vinson, S. Maternally induced host regulation by the egg parasitoid Telenomus heliothidis. Physiol. Entomol. 1983, 8, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, S.; Rivers, D.B. Venom proteins from endoparasitoid wasps and their role in host-parasite interactions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, N.; Ganjisaffar, F.; Perring, T.M. Effect of temperature on the survival and developmental rate of immature Ooencyrtus mirus (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
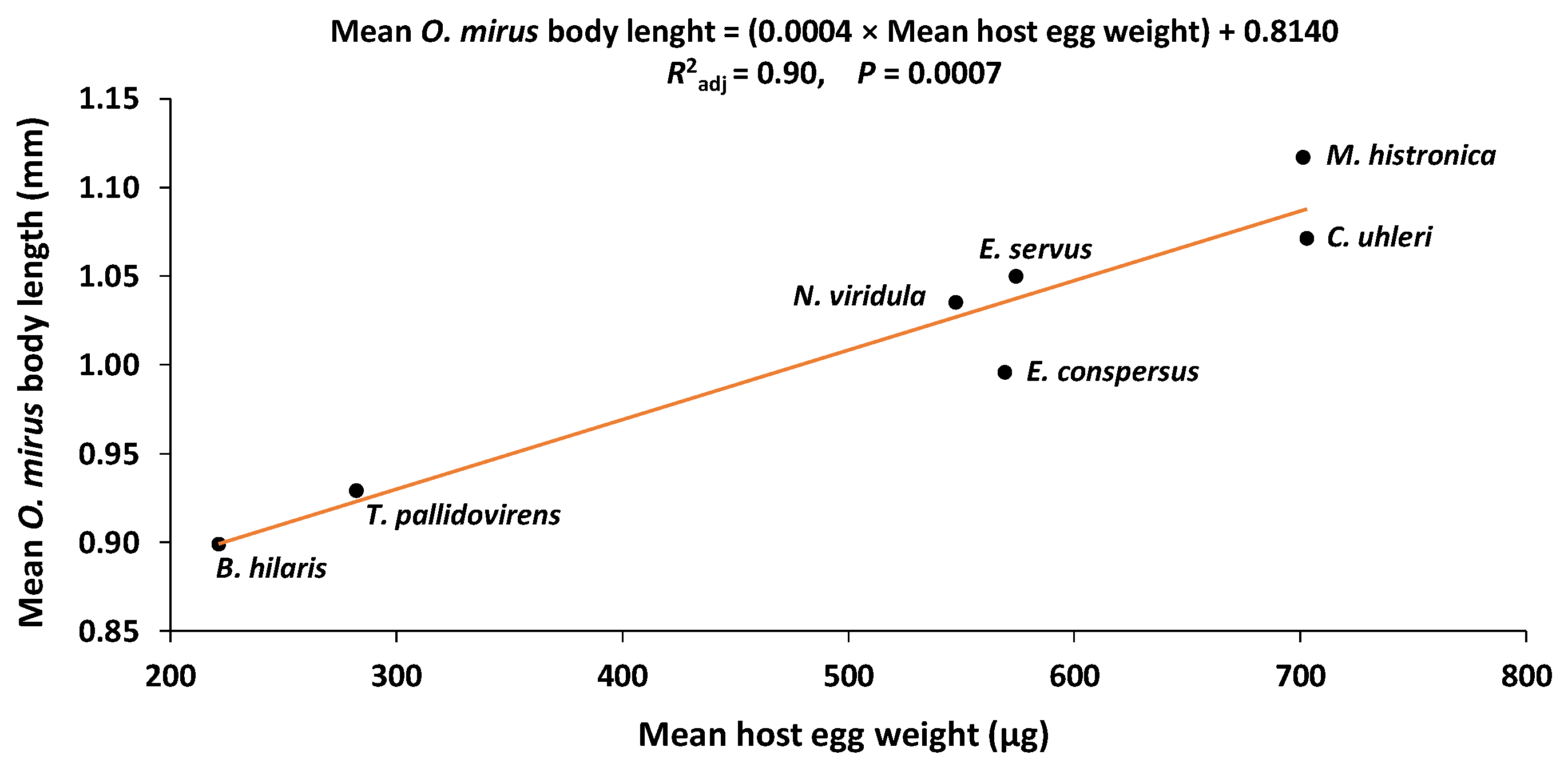
| Alternate Host Species | Diet |
|---|---|
| Anasa tristis | Fruits and fresh leaves of squash, Cucurbita moschata L. variety Black Futsu |
| Chlorochroa uhleri | Fresh green beans, raw peanuts, raw sunflower seeds, and bouquets of Russian thistle, Salsola tragus L., and alfalfa, Medicago sativa L. |
| Ectomyelois ceratoniae | Lab-prepared mixture of soy meal, sugar and water |
| Euschistus conspersus | Alfalfa bouquet, fresh green beans, raw peanuts, raw sunflower seeds, raw pistachio nut meats, and broccoli floret |
| Euschistus servus | Alfalfa bouquet, fresh green beans, raw peanuts, and raw sunflower seeds |
| Halyomorha halys | Apples, avocados, carrots, grapes, fresh green beans, and fresh cuttings of empress tree, Paulownia tomentosa (Thunb.), and butterfly bush, Buddleja davidii Franchet |
| Helicoverpa zea | Lepidoptera Diet—Product “F9772-Tray”, Frontier Agricultural Sciences, Newark, DE, USA |
| Jadera haematoloma | Bouquet of bladderpod, Peritoma arborea (Nutt.) |
| Murgantia histrionica | Bouquet of bladderpod, Peritoma arborea (Nutt.) |
| Nezara viridula | Fresh green beans, raw peanuts, raw sunflower seeds |
| Podisus maculiventris | N/A |
| Thyanta pallidovirens | Fresh green beans, raw peanuts, raw sunflower seeds, and broccoli floret |
| Host Species | Choice | No-Choice | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean ± SE | p | N | Mean ± SE | p | ||
| Pentatomidae | B. hilaris | 19 | 6.5 ± 0.7 | <0.001 | 18 | 6.2 ± 0.6 | <0.001 |
| C. uhleri | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.5 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 17 | 7.2 ± 0.7 | <0.001 | 17 | 7.4 ± 0.4 | 0.294 | |
| E. conspersus | 0.5 ± 0.4 | 7.1 ± 0.6 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 5 | 6.4 ± 1.1 | 0.021 | 5 | 6.6 ± 1.8 | 0.786 | |
| E. servus | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 8.2 ± 0.9 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 15 | 3.9 ± 1.0 | 0.046 | 15 | 7.6 ± 0.4 | <0.001 | |
| H. halys | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 16 | 5.3 ± 0.8 | 0.002 | 16 | 7.1 ± 0.5 | <0.001 | |
| M. histrionica | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 17 | 3.9 ± 0.7 | 0.107 | 17 | 6.5 ± 0.6 | 0.069 | |
| N. viridula | 2.3 ± 0.7 | 5.1 ± 0.7 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 20 | 3.9 ± 0.9 | 0.344 | 20 | 7.8 ± 0.6 | <0.001 | |
| P. maculiventris | 3.3 ± 0.7 | 4.9 ± 0.6 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 13 | 3.8 ± 1.0 | 0.089 | 13 | 6.8 ± 0.5 | 0.857 | |
| T. pallidovirens | 2.2 ± 0.7 | 7.5 ± 0.4 | |||||
| Other Heteroptera | B. hilaris | 16 | 4.9 ± 0.9 | 0.004 | 15 | 7.7 ± 0.4 | <0.001 |
| A. tristis | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 2.3 ± 0.4 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 21 | 3.7 ± 0.8 | 0.255 | 21 | 7.4 ± 0.4 | 0.003 | |
| J. haematoloma | 3.3 ± 0.7 | 5.0 ± 0.7 | |||||
| Lepidoptera | B. hilaris | 15 | 7.6 ± 0.6 | <0.001 | 15 | 7.3 ± 0.5 | <0.001 |
| H. zea | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | |||||
| Host Species | Choice | No-Choice | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | # Progeny Emerged | Mean ± SE | p | N | # Progeny Emerged | Mean ± SE | p | ||
| Pentatomidae | B. hilaris | 19 | 110 | 5.8 ± 0.7 | <0.001 | 19 | 104 | 5.5 ± 0.5 | <0.001 |
| C. uhleri | 5 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 28 | 1.5 ± 0.4 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 17 | 111 | 6.5 ± 0.7 | <0.001 | 17 | 108 | 6.4 ± 0.5 | 0.251 | |
| E. conspersus | 6 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 92 | 5.4 ± 0.5 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 5 | 29 | 5.8 ± 1.0 | 0.043 | 5 | 32 | 6.4 ± 1.7 | 0.325 | |
| E. servus | 2 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 28 | 5.6 ± 0.7 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 15 | 52 | 3.5 ± 0.8 | 0.040 | 15 | 111 | 7.4 ± 0.4 | <0.001 | |
| H. halys | 18 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 24 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 17 | 87 | 5.1 ± 0.7 | 0.002 | 17 | 115 | 6.8 ± 0.5 | <0.001 | |
| M. histrionica | 14 | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 37 | 2.2 ± 0.6 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 31 | 110 | 3.5 ± 0.5 | 0.014 | 31 | 171 | 5.5 ± 0.4 | 0.080 | |
| N. viridula | 44 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 134 | 4.3 ± 0.4 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 20 | 73 | 3.7 ± 0.7 | 0.408 | 20 | 136 | 6.8 ± 0.5 | <0.001 | |
| P. maculiventris | 54 | 2.7 ± 0.6 | 70 | 3.5 ± 0.5 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 23 | 91 | 4.0 ± 0.7 | 0.021 | 24 | 138 | 5.8 ± 0.3 | 0.987 | |
| T. pallidovirens | 40 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 131 | 5.5 ± 0.6 | |||||
| Other Heteroptera | B. hilaris | 16 | 76 | 4.8 ± 0.9 | 0.004 | 15 | 105 | 7.0 ± 0.3 | <0.001 |
| A. tristis | 13 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 34 | 2.3 ± 0.4 | |||||
| B. hilaris | 21 | 72 | 3.4 ± 0.8 | 0.111 | 21 | 149 | 7.1 ± 0.4 | <0.001 | |
| J. haematoloma | 32 | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 60 | 2.9 ± 0.5 | |||||
| Lepidoptera | B. hilaris | 15 | 104 | 6.9 ± 0.6 | <0.001 | 15 | 102 | 6.8 ± 0.5 | <0.001 |
| H. zea | 8 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 14 | 0.9 ± 0.4 | |||||
| Host Species | Choice | No-Choice | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean ± SE | p | N | Mean ± SE | p | ||
| Pentatomidae | B. hilaris | 17 | 0.98 ± 0.02 | 0.169 | 16 | 0.92 ± 0.03 | 0.183 |
| C. uhleri | 3 | 1.33 ± 0.33 | 10 | 1.03 ± 0.17 | |||
| B. hilaris | 16 | 0.98 ± 0.02 | 0.974 | 17 | 0.91 ± 0.03 | 0.085 | |
| E. conspersus | 2 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 17 | 1.01 ± 0.04 | |||
| B. hilaris | 5 | 0.94 ± 0.04 | 0.762 | 4 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.444 | |
| E. servus | 2 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 5 | 0.90 ± 0.06 | |||
| B. hilaris | 9 | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 0.475 | 15 | 0.97 ± 0.02 | 0.001 | |
| H. halys | 7 | 0.83 ± 0.3 | 10 | 1.70 ± 0.31 | |||
| B. hilaris | 14 | 0.95 ± 0.03 | 1.000 | 17 | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 0.470 | |
| M. histrionica | 8 | 0.79 ± 0.18 | 13 | 1.02 ± 0.02 | |||
| B. hilaris | 13 | 0.93 ± 0.03 | 0.084 | 17 | 0.94 ± 0.02 | 0.388 | |
| N. viridula | 11 | 0.73 ± 0.10 | 16 | 0.98 ± 0.06 | |||
| B. hilaris | 13 | 0.98 ± 0.02 | 0.225 | 18 | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 0.803 | |
| P. maculiventris | 13 | 0.85 ± 0.09 | 16 | 0.92 ± 0.05 | |||
| B. hilaris | 9 | 0.83 ± 0.11 | 0.945 | 13 | 0.94 ± 0.02 | 0.852 | |
| T. pallidovirens | 7 | 0.80 ± 0.14 | 13 | 0.94 ± 0.03 | |||
| Other Heteroptera | B. hilaris | 12 | 0.99 ± 0.01 | 1.000 | 16 | 0.98 ± 0.01 | 0.069 |
| A. tristis | 7 | 1.00 ± 0.11 | 14 | 1.07 ± 0.07 | |||
| B. hilaris | 13 | 0.99 ± 0.01 | 0.047 | 21 | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 0.039 | |
| J. haematoloma | 14 | 0.79 ± 0.07 | 18 | 0.77 ± 0.08 | |||
| Lepidoptera | B. hilaris | 15 | 0.97 ± 0.02 | 0.284 | 15 | 0.95 ± 0.03 | 0.772 |
| H. zea | 5 | 0.80 ± 0.12 | 9 | 0.83 ± 0.20 | |||
| Host Species | Choice | No-Choice | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # Progeny Emerged | Mean ± SE | p | # Progeny Emerged | Mean ± SE | p | ||
| Pentatomidae | B. hilaris | 110 | 14.3 ± 0.0 | <0.001 | 104 | 14.3 ± 0.1 | <0.001 |
| C. uhleri | 5 | 15.2 ± 0.2 | 28 | 14.9 ± 0.1 | |||
| B. hilaris | 111 | 14.5 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | 108 | 14.4 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | |
| E. conspersus | 6 | 15.5 ± 0.3 | 92 | 15.7 ± 0.1 | |||
| B. hilaris | 29 | 14.6 ± 0.1 | 0.004 | 32 | 14.4 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | |
| E. servus | 2 | 18.5 ± 2.5 | 28 | 15.5 ± 0.3 | |||
| B. hilaris | 52 | 15.0 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | 111 | 14.5 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | |
| H. halys | 18 | 16.1 ± 0.1 | 24 | 16.0 ± 0.2 | |||
| B. hilaris | 87 | 14.3 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | 115 | 14.3 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | |
| M. histrionica | 8 | 15.4 ± 0.3 | 31 | 15.4 ± 0.1 | |||
| B. hilaris | 110 | 14.7 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | 171 | 14.6 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | |
| N. viridula | 44 | 15.7 ± 0.2 | 134 | 15.4± 0.1 | |||
| B. hilaris | 73 | 14.3 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | 136 | 14.6 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | |
| P. maculiventris | 54 | 15.3 ± 0.1 | 70 | 15.5 ± 0.1 | |||
| B. hilaris | 91 | 14.9 ± 0.1 | 0.020 | 138 | 14.9 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | |
| T. pallidovirens | 40 | 15.1± 0.1 | 131 | 15.2 ± 0.1 | |||
| Other Heteroptera | B. hilaris | 76 | 14.4 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | 105 | 14.3 ± 0.0 | <0.001 |
| A. tristis | 13 | 15.8 ± 0.3 | 34 | 15.2 ± 0.2 | |||
| B. hilaris | 72 | 14.4 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | 149 | 14.4 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | |
| J. haematoloma | 32 | 16.2 ± 0.1 | 60 | 16.2 ± 0.1 | |||
| Lepidoptera | B. hilaris | 104 | 14.9 ± 0.1 | 0.001 | 102 | 14.8 ± 0.1 | <0.001 |
| H. zea | 8 | 16.1 ± 0.4 | 14 | 16.6 ± 0.3 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Power, N.; Ganjisaffar, F.; Perring, T.M. Evaluation of the Physiological Host Range for the Parasitoid Ooencyrtus mirus, a Potential Biocontrol Agent of Bagrada hilaris. Insects 2020, 11, 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11070432
Power N, Ganjisaffar F, Perring TM. Evaluation of the Physiological Host Range for the Parasitoid Ooencyrtus mirus, a Potential Biocontrol Agent of Bagrada hilaris. Insects. 2020; 11(7):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11070432
Chicago/Turabian StylePower, Nancy, Fatemeh Ganjisaffar, and Thomas M. Perring. 2020. "Evaluation of the Physiological Host Range for the Parasitoid Ooencyrtus mirus, a Potential Biocontrol Agent of Bagrada hilaris" Insects 11, no. 7: 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11070432
APA StylePower, N., Ganjisaffar, F., & Perring, T. M. (2020). Evaluation of the Physiological Host Range for the Parasitoid Ooencyrtus mirus, a Potential Biocontrol Agent of Bagrada hilaris. Insects, 11(7), 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11070432






