Parasitism of Locally Recruited Egg Parasitoids of the Fall Armyworm in Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Environment
2.2. Insect Cultures for Bioassays
2.3. Assessment of FAW Egg Parasitism by T. remus and Trichogrammatoidea sp. in the Laboratory
2.4. Assessment of Field Performance of Telenomus remus Following Augmentative Releases
2.4.1. Preparation of the T. remus Cards for On-Station Field Releases
2.4.2. On-Station Releases
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
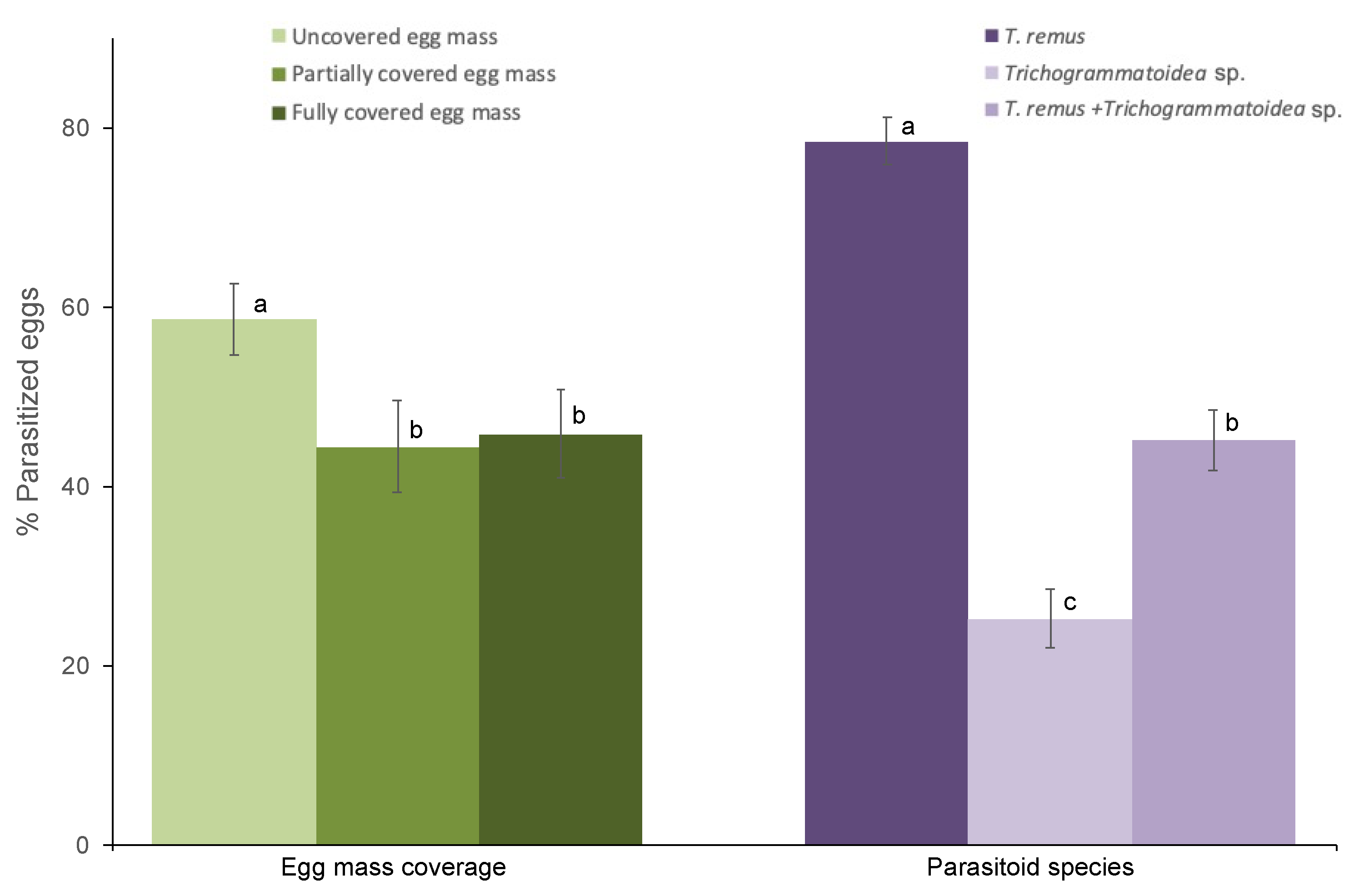
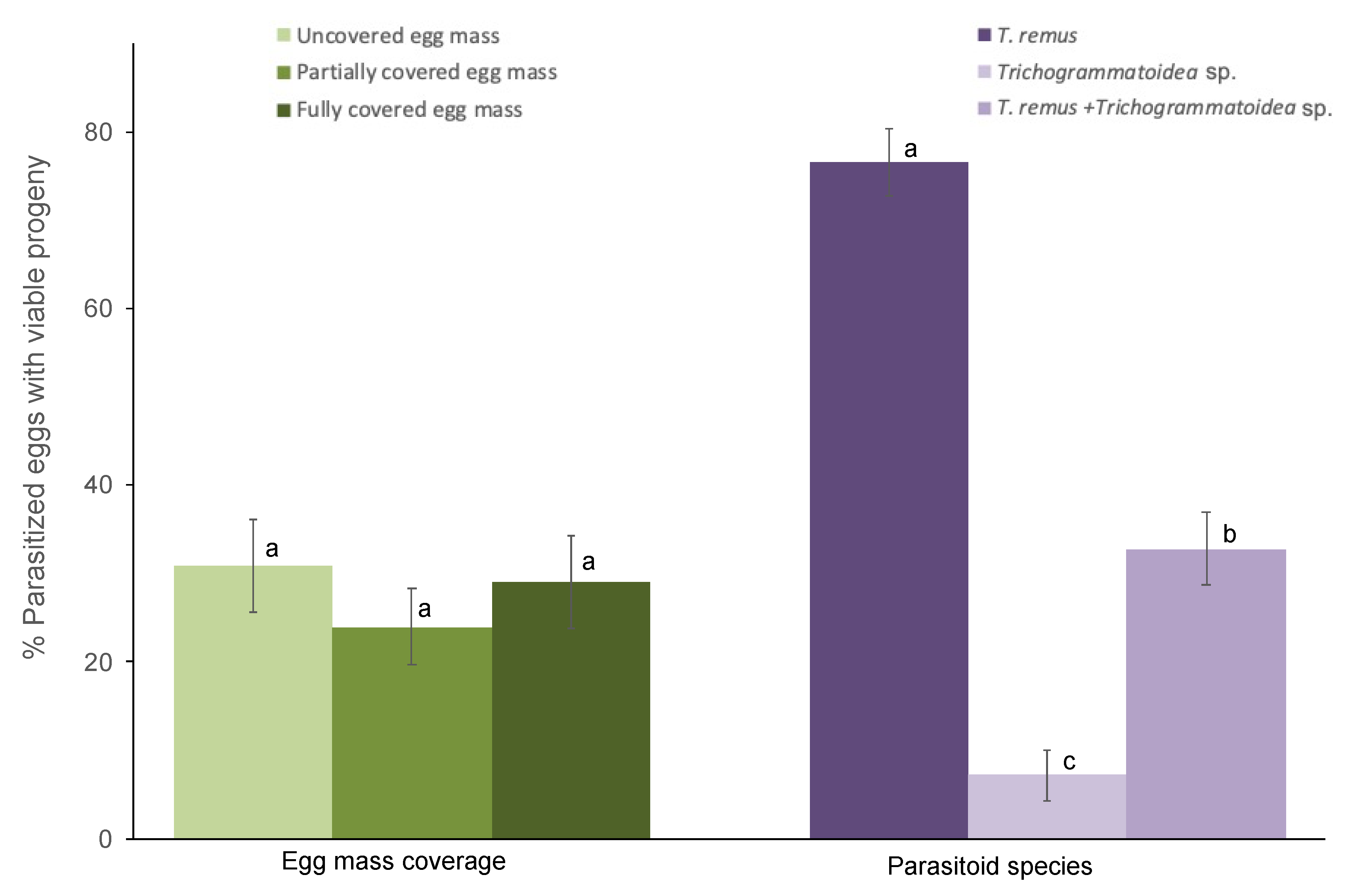
3.1. Parasitism of FAW Eggs by T. remus and Trichogrammatoidea sp. in the Laboratory
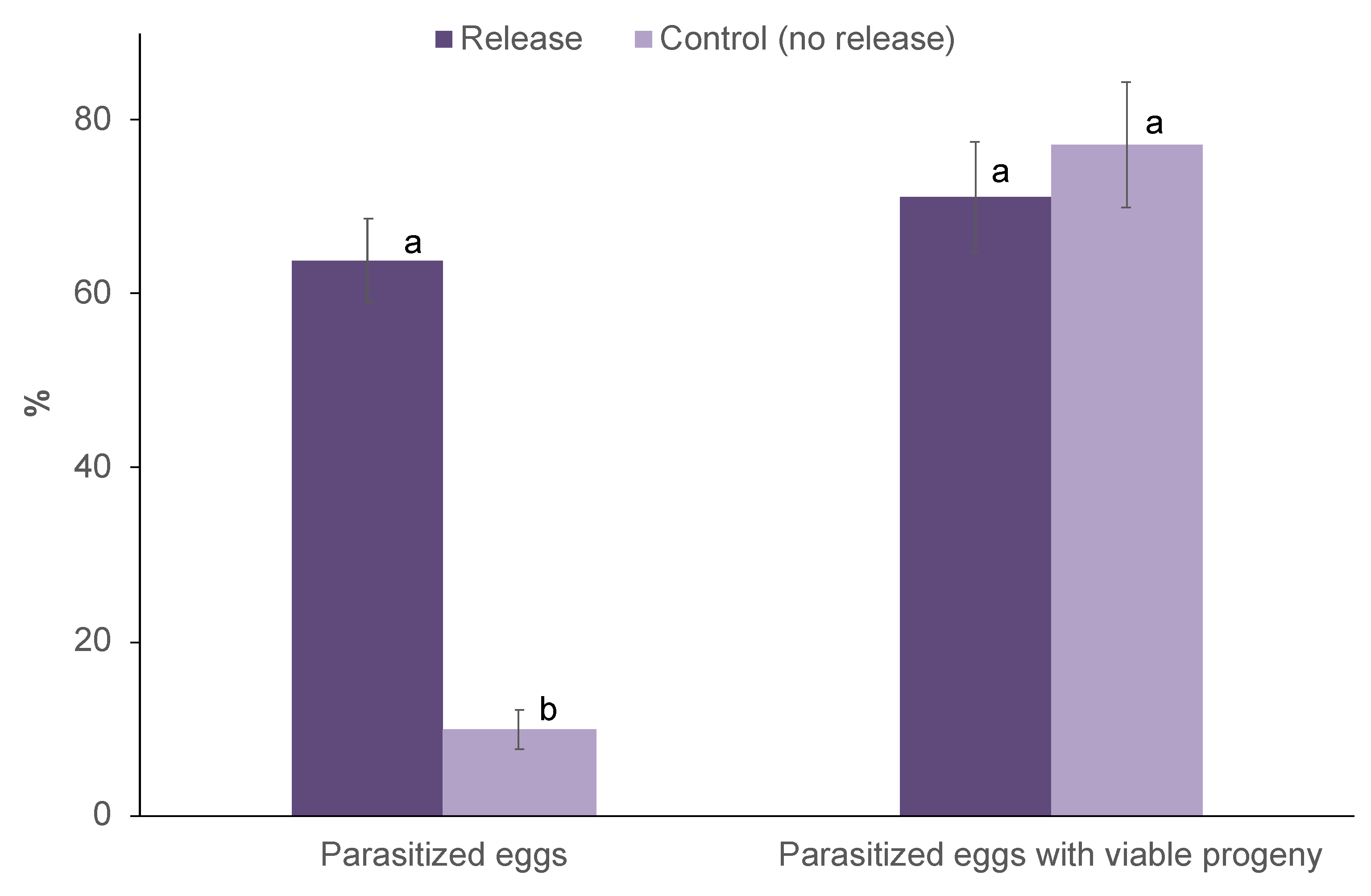
3.2. Parasitism of T. remus Following on-Station Releases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goergen, G.; Kumar, P.L.; Sankung, S.B.; Togola, A.; Tamò, M. First report of outbreaks of the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith) (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae), a new alien invasive pest in West and Central Africa. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, R.; Abrahams, P.; Bateman, M.; Beale, T.; Clottey, V.; Cock, M.; Colmenarez, Y.; Corniani, N.; Early, R.; Godwin, J.; et al. Fall armyworm: Impacts and implications for Africa. Outlooks Pest Manag. 2017, 28, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, P.; Bateman, M.; Beale, T.; Clottey, V.; Cock, M.; Colmenarez, Y.; Corniani, N.; Day, R.; Early, R.; Godwin, J.; et al. Fall Armyworm: Impacts and Implications for Africa; CABI Evidence Note (2); Report to DFID.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2017; Available online: https://www.cabi.org/ISC/FullTextPDF/2018/20187200428.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- Maiga, I.; Ndiaye, M.; Gagare, S.; Oumarou, G.; Oumarou, S. La chenille d’automne Spodoptera frugiperda, nouveau ravageur du maïs en Afrique de l’Ouest, a atteint le Niger; Centre Régional AGRHYMET: Niamey, Niger, 2017; Available online: http://www.reca-niger.org/IMG/pdf/Bulletin_special_Chenille.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- Hruska, J.A. Fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) management by smallholders. CAB Rev. 2019, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CABI. Spodoptera frugiperda. In Invasive Species Compendium; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2020; Available online: www.cabi.org/isc (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Kumela, T.; Simiyu, J.; Sisay, B.; Likhayo, P.; Mendesil, E.; Gohole, L.; Tefera, T. Farmers’ knowledge, perceptions, and management practices of the new invasive pest, fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) in Ethiopia and Kenya. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2019, 65, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, B.M.; Huesing, J.E.; Eddy, R.; Peschke, V.M. Fall Armyworm in Africa: A Guide for Integrated Pest Management, 1st ed.; CIMMYT: Mexico City, Mexico, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sisay, B.; Tefera, T.; Wakgari, M.; Ayalew, G.; Mendesil, E. The efficacy of selected synthetic insecticides and botanicals against fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda, in Maize. Insects 2019, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phambala, K.; Tembo, Y.; Kasambala, T.; Kabambe, V.H.; Stevenson, P.C.; Belmain, S.R. Bioactivity of common pesticidal plants on fall armyworm larvae (Spodoptera frugiperda). Plants 2020, 9, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioba, N.B.; Stevenson, P.C. Opportunities and scope for botanical extracts and products for the management of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) for smallholders in Africa. Plants 2020, 9, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, G.; Niassy, S.; Khan, Z.R.; Ochatum, N.; Subramanian, S. Maize-legume intercropping and Push-pull for management of fall armyworm, stemborers and striga in Uganda. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midega, C.A.O.; Pittchar, J.; Pickett, J.A.; Hailu, G.; Khan, Z.R. A climate-adapted push-pull system effectively controls fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith), in maize in East Africa. Crop Prot. 2018, 105, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisay, B.; Simiyu, J.; Malusi, P.; Likhayo, P.; Mendesil, E.; Elibariki, N.; Wakgari, M.; Ayalew, G.; Tefera, T. First report of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), natural enemies from Africa. J. Appl. Entomol. 2018, 142, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisay, B.; Simiyu, J.; Mendesil, E.; Likhayo, P.; Ayalew, G.; Mohamed, S.; Subramanian, S.; Tefera, T. Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda infestations in East Africa: Assessment of damage and parasitism. Insects 2019, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agboyi, L.K.; Goergen, G.; Beseh, P.; Mensah, S.A.; Clottey, V.A.; Glikpo, R.; Buddie, A.; Cafà, G.; Offord, L.; Day, R.; et al. Parasitoid complex of fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda, in Ghana and Benin. Insects 2020, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, V.H.P.; van Lenteren, J.C. The popularity of augmentative biological control in Latin America: History and state of affairs. In Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Biological Control of Arthropods, Honolulu, HI, USA, 14–18 January 2002; International Organization of Biological Control: Antibes, France, 2002; pp. 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Molina-Ochoa, J.; Carpenter, J.E.; Heinrichs, E.A.; Foster, J.E. Parasitoids and parasites of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in the Americas and Caribbean basin: An inventory. Fla. Entomol. 2003, 86, 254–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, M.D.L.C.; Cruz, I.; da Silva, R.B.; Foster, J.E. Biological control with Trichogramma pretiosum increases organic maize productivity by 19.4%. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaraleño-Teniente, J.; Lomeli-Flores, J.R.; Rodríguez-Leyva, E.; Bujanos-Muñiz, R.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, S.E. Egg parasitoids survey of Spodoptera frugiperda (Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in maize and sorghum in Central Mexico. Insects 2020, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, P. Biological control in Nicaragua. In Biological Control in Latin America and the Caribbean: Its Rich History and Bright Future; van Lenteren, J.C., Bueno, V.H.P., Luna, M.G., Colmenarez, Y., Eds.; CAB International: Boston, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 336–344. [Google Scholar]
- Kenis, M.; du Plessis, H.; Van den Berg, J.; Ba, M.N.; Goergen, G.; Kwadjo, K.E.; Baoua, I.; Buddie, A.; Cafà, G.; Offord, L.; et al. Telenomus remus, a candidate parasitoid for the biological control of Spodoptera frugiperda in Africa, is already present on the continent. Insects 2019, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koffi, D.; Kyerematen, R.; Eziah, V.Y.; Agboka, K.; Adom, M.; Goergen, G.; Meagher, R.L., Jr. Natural enemies of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Ghana. Fla. Entomol. 2020, 103, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadou, L.; Baoua, I.; Ba, M.N.; Karimoune, L.; Muniappan, R. Native parasitoids recruited by the invaded fall armyworm in Niger. Indian J. Entomol. 2018, 80, 1253–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cave, R.D. Biology, ecology and use in pest management of Telenomus remus. Biocontrol News Inf. 2000, 21, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer, F. Biological of agricultural insect pest in Venezuela: Advances, achievements, and future perspectives. Biocontrol News Inf. 2001, 22, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Parra, J.R.P. Egg parasitoids commercialization in the New World. In Egg Parasitoids in Agroecosystems with Emphasis on Trichogramma; Cônsoli, F.L., Parra, J.R.P., Zucchi, R.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 373–388. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, M.D.L.C.; Della Lucia, T.M.C.; Cruz, I. Effect of Telenomus remus Nixon (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) density on control of Spodoptera frugiperda (Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) egg masses upon release in a maize field. Rev. Bras. Milho Sorgo 2002, 1, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, B.M.; Bruce, A.; Winter, S.; Otim, M.; Asea, G.; Sevgan, S.; Ba, M. Host plant resistance to fall armyworm. In Fall Armyworm in Africa: A Guide for Integrated Pest Management, 1st ed.; Prasanna, B.M., Huesing, J.E., Eddy, R., Peschke, V.M., Eds.; CIMMYT: Mexico City, Mexico, 2018; pp. 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, M.N.; Baoua, I.B.; Kaboré, A.; Amadou, L.; Oumarou, N.; Dabire-Binso, C.; Sanon, A. Augmentative on-farm delivery methods for the parasitoid Habrobracon hebetor Say (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) to control the millet head miner Heliocheilus albipunctella (de Joannis) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Burkina Faso and Niger. BioControl 2014, 59, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimoune, L.; Ba, N.M.; Baoua, I.B.; Muniappan, R. The parasitoid Trichogrammatoidea armigera Nagaraja (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) is a potential candidate for biological control of the millet head miner Heliocheilus albipunctella (de Joannis) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in the Sahel. Biol. Control 2018, 127, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefera, T.; Goftishu, M.; Ba, M.; Muniappan, R. A Guide to Biological Control of Fall Armyworm in Africa Using Egg Parasitoids, 1st ed.; ICIPE: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019; Available online: https://ipmil.cired.vt.edu/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/A-Guide-to-Biological-Control-of-FAW_Final-updated.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2020).
- Karimoune, L.; Ba, N.M.; Baoua, I.B.; Muniappan, R. Field performance of the parasitoid wasp, Trichogrammatoidea armigera (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) following releases against the millet head miner, Heliocheilus albipunctella (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in the Sahel. BioControl 2020, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, C.S.B.; Vieira, J.M.; Loiácono, M.; Margaría, C.; Parra, J.R.P. Evidence of exploitative competition among egg parasitoids of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in maize. Rev. Colomb. Entomol. 2015, 41, 184–186. [Google Scholar]
- Queiroz, A.P.; Bueno, A.F.; Pomari-Fernandes, A.; Bortolotto, O.C.; Mikami, A.Y.; Olive, L. Influence of host preference, mating, and release density on the parasitism of Telenomus remus (Nixon) (Hymenoptera, Platygastridae). Rev. Bras. Entomol. 2017, 61, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS. SAS version 9.1 for Windows; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cave, R.D.; Acosta, N.M. Telenomus remus Nixon: Un parasitoide en el control biológico del gusano cogollero, Spodoptera frugiperda (Smith). Ceiba 1999, 40, 215–227. [Google Scholar]
- Pomari, A.F.; Bueno, A.D.F.; Bueno, R.C.O.D.F.; Menezes, A.D.O. Biological characteristics and thermal requirements of the biological control agent Telenomus remus (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae) reared on eggs of different species of the genus Spodoptera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2012, 105, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Wakamura, S.; Arakaki, N.; Yamagishi, K. Parasitism, development and adult longevity of the egg parasitoid Telenomus nawai (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) on the eggs of Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Bull Entomol. Res. 2007, 97, 185–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, R.C.O.D.F.; Carneiro, T.R.; Pratissoli, D.; Bueno, A.D.F.; Fernandes, O.A. Biology and thermal requirements of Telenomus remus reared on fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda eggs. Ciência Rural 2008, 38, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, R.C.O.D.F.; Carneiro, T.R.; Bueno, A.D.F.; Pratissoli, D.; Fernandes, O.A.; Vieira, S.S. Parasitism capacity of Telenomus remus Nixon (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) on Spodoptera frugiperda (Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) eggs. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2010, 53, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, R.C.O.D.F.; Bueno, A.D.F.; Xavier, M.F.D.C.; Carvalho, M.M. Telenomus remus (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae) parasitism on eggs of Anticarsia gemmatalis (Lepidoptera: Eribidae) compared with its natural host Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2014, 107, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomari-Fernandes, A.; Queiroz, A.D.P.; Bueno, A.D.F.; Sanzovo, A.W.; Bortoli, S.D.A. The importance of relative humidity for Telenomus remus (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae) parasitism and development on Corcyra cephalonica (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) and Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) eggs. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2015, 108, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.S.; Gallardo, J.S.V.; Vásquez, C.; Ríos, Y. Respuesta funcional de Telenomus remus (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) a los huevos de Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Bioagro 2001, 13, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Beserra, E.B.; Parra, J.R.P. Impact of the number of Spodoptera frugiperda egg layers on parasitism by Trichogramma atopovirilia. Scientia Agricola 2005, 62, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goulart, M.M.P.; Bueno, A.D.F.; Bueno, R.C.O.D.F.; Vieira, S.S. Interaction between Telenomus remus and Trichogramma pretiosum in the management of Spodoptera spp. Rev. Bras. Entomol. 2011, 55, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, T.R.; Odair, A.; Fernandes, O.A. Interspecific interaction between Telenomus remus (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae) and Trichogramma pretiosum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) on Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) eggs. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências 2012, 84, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, L.; Pham-Delegue, M.H.; Masson, C. Behavioural study of plasticity in host preferences of Trichogramma maidis (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Physiol. Entomol. 1989, 14, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supoyo, N.; Cribb, B.W.; Gordh, G. Experience acquisition by Trichogramma australicum Girault (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Aust. Entomol. 1999, 38, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Giunti, G.; Canale, A.; Messing, R.H.; Donati, E.; Stefanini, C.; Michaud, J.P.; Benelli, G. Parasitoid learning: Current knowledge and implications for biological control. Biol. Control 2015, 90, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cônsoli, F.L.; Kitajima, E.W.; Parra, J.R.P. Ultrastructure of the natural and factitious host eggs of Trichogramma galho Zucchi and Trichogramma pretiosum Riley (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Int. J. Insect Morphol. Embryol. 1999, 28, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigler, F.; Meyer, A.; Bosshart, S. Quality assessment in Trichogramma maidis Pintureau et Voegelé reared from eggs of the factitious hosts Ephestia kuehniella Zell. and Sitotroga cerealella (Olivier). J. Appl. Entomol. 1987, 104, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bergeijk, K.E.; Bigler, F.; Kaashoek, N.K.; Pak, G.A. Changes in host acceptance and host suitability as an effect of rearing Trichogramma maidis on a factitious host. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1989, 52, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Luck, R.F.; Forster, L.; Stephens, B.; Janssen, J.A.M. The effect of host size on quality attributes of the egg parasitoid, Trichogramma pretiosum. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1992, 64, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, S.M.; Norlund, D.A.; Wu, Z. Influence of rearing host on adult size and ovipositional behavior of mass produced female Trichogramma minutum Riley and Trichogramma pretiosum Riley (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Biol. Control 1998, 11, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, J.Y.; Luck, R.F. Interactions between host attributes and wasp size: A laboratory evaluation of Trichogramma platneri as an augmentative biological control agent for two avocado pests. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2001, 100, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerling, D. The development biology of Telenomus remus Nixon (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 1972, 61, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, C.J.; Latto, J. Interactions between the egg and larval parasitoids of a gall forming midge and their impact on the host. Ecol. Entomol. 2001, 26, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, D.L.; Denno, R.F. Predator diversity and the functioning of ecosystems: The role of intraguild predation in dampening trophic cascades. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieshop, M.J.; Flinn, P.W.; Nechols, J.R. Biological control of Indianmeal moth (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) on finished stored products using egg and larval parasitoids. J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, D.; Henderson, R.; Corley, L.S.; Iwabuchi, K. Intrinsic, inter-specific competition between egg, egg–larval, and larval parasitoids of plusiine loopers. Ecol. Entomol. 2007, 32, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigler, F.; Babendreier, D.; van Lenteren, J.C. Risk assessment and non-target effects of egg parasitoids in biological control. In Egg Parasitoids in Agroecosystems with Emphasis on Trichogramma; Cônsoli, F.L., Parra, J.R.P., Zucchi, R.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 413–442. [Google Scholar]
- Strand, M.R.; Vinson, S.B. Facultative hyperparasitism by the egg parasitoid Trichogramma pretiosum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1984, 77, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfir, R.; van Hamburg, H. Interpecific competition between Telenomus ullyetti (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) and Trichogrammatoidea lutea (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) parasitizing eggs of the cotton bollworm Heliothis armigera in the laboratory. Environ. Entomol. 1988, 17, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomari, A.F.; Bueno, A.D.F.; Bueno, R.C.O.D.F.; Menezes-Junior, A.D.O.; Fonseca, A.C.P.F. Releasing number of Telenomus remus (Nixon) (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae) against Spodoptera frugiperda Smith (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in corn, cotton and soybean. Ciência Rural 2013, 43, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, D.E.; Duan, J.J.; Larson, K.M.; Ito, J.P.L.; Shrewsbury, P.M. Evaluating a new method for monitoring the field establishment and parasitism of Oobius agrili (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae), an egg parasitoid of emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). Fla. Entomol. 2014, 97, 1263–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelius, M.L.; Dieckhoff, C.; Vinyard, B.T.; Hoelmer, K.A. Parasitism and predation on sentinel egg masses of the brown marmorated stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in three vegetable crops: Importance of dissections for evaluating the impact of native parasitoids on an exotic pest. Environ. Entomol. 2016, 45, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.L.; Jennings, D.E.; Cerruti, R.R.H.; Shrewsbury, P.M. Sentinel eggs underestimate rates of parasitism of the exotic brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys. Biol. Control 2014, 78, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordlund, D.A.; Strand, M.R.; Lewis, W.J.; Vinson, S.B. Role of kairomones from host accessory gland secretion in host recognition by Telenomus remus and Trichogramma pretiosum, with partial characterization. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1987, 44, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.J.; Nordlund, D.A. Semiochemicals influencing fall armyworm parasitoid behavior: Implications for behavioral manipulation. Fla. Entomol. 1984, 67, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penaflor, M.F.G.V.; Erb, M.; Miranda, L.A.; Werneburg, A.G.; Bento, J.M.S. Herbivore-induced plant volatiles can serve as host location cues for a generalist and a specialist egg parasitoid. J. Chem. Ecol. 2011, 37, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballal, C.R.; Jalali, S.K.; Kumar, P. Plant effects on host- parasitoid relations between Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) and Telenomus remus Nixon. Indian J. Plant Prot. 1989, 17, 97–99. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez-Martinez, A.; Tolon-Becerra, A.; Lastra-Bravo, X.B. Biological control of Spodoptera frugiperda eggs using Telenomus remus Nixon in maize-bean-squash polyculture. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2012, 7, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, K.W. Effects of height and habitat type on egg parasitism by Trichogramma minutum and T. pretiosum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1985, 12, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andow, D.A.; Prokrym, D.R. Plant structural complexity and host finding by a parasitoid. Oecologia 1990, 82, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCravy, K.W.; Berisford, C.W. Parasitism by Trichogramma spp. (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) in relation to Nantucket pine tip moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) egg density and location. Environ. Entomol. 1998, 27, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeis, J.; Shanower, T.G.; Zebitz, C.P.W. Physical and chemical plant characters inhibiting the searching behaviour of Trichogramma chilonis. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1998, 87, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingras, D.; Dutilleul, P.; Boivin, G. Effect of plant structure on searching strategy and searching efficiency of Trichogramma turkestanica. J. Insect Sci. 2008, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomari, A.F.; Bueno, A.F.; Bueno, R.C.O.F.; Menezes, A.O., Jr. Telenomus remus Nixon egg parasitization of three species of Spodoptera under different temperatures. Neotrop. Entomol. 2013, 42, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.F.; Pomari-Fernandes, A.; Lemes, A.A.F.; Vacari, A.M.; De Bortoli, S.A.; Bueno, A.D.F. Cost of production of Telenomus remus (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae) grown in natural and alternative hosts. J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 2724–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laminou, S.A.; Ba, M.N.; Karimoune, L.; Doumma, A.; Muniappan, R. Parasitism of Locally Recruited Egg Parasitoids of the Fall Armyworm in Africa. Insects 2020, 11, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11070430
Laminou SA, Ba MN, Karimoune L, Doumma A, Muniappan R. Parasitism of Locally Recruited Egg Parasitoids of the Fall Armyworm in Africa. Insects. 2020; 11(7):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11070430
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaminou, Saidou A., Malick Niango Ba, Laouali Karimoune, Ali Doumma, and Rangaswamy Muniappan. 2020. "Parasitism of Locally Recruited Egg Parasitoids of the Fall Armyworm in Africa" Insects 11, no. 7: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11070430
APA StyleLaminou, S. A., Ba, M. N., Karimoune, L., Doumma, A., & Muniappan, R. (2020). Parasitism of Locally Recruited Egg Parasitoids of the Fall Armyworm in Africa. Insects, 11(7), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11070430




