Rapid and Simple Species Identification of Cicada Exuviae Using COI-Based SCAR Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and DNA Extraction
2.2. PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.3. Nucleotide Sequence and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.4. SCAR Marker Development and Market-Sample-Authenticity Test
3. Results
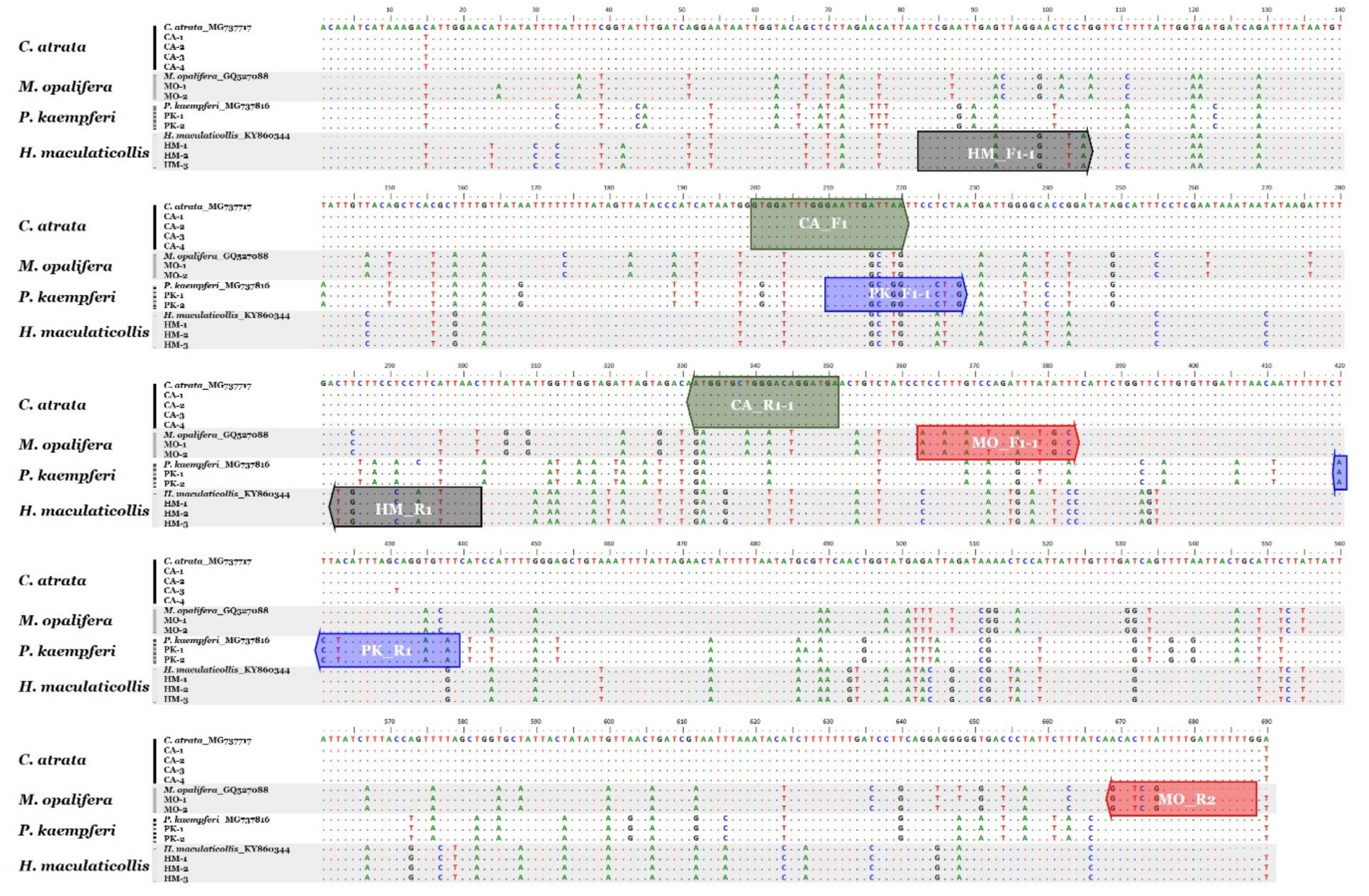
3.1. Nucleotide Sequence and Phylogenetic Analyses
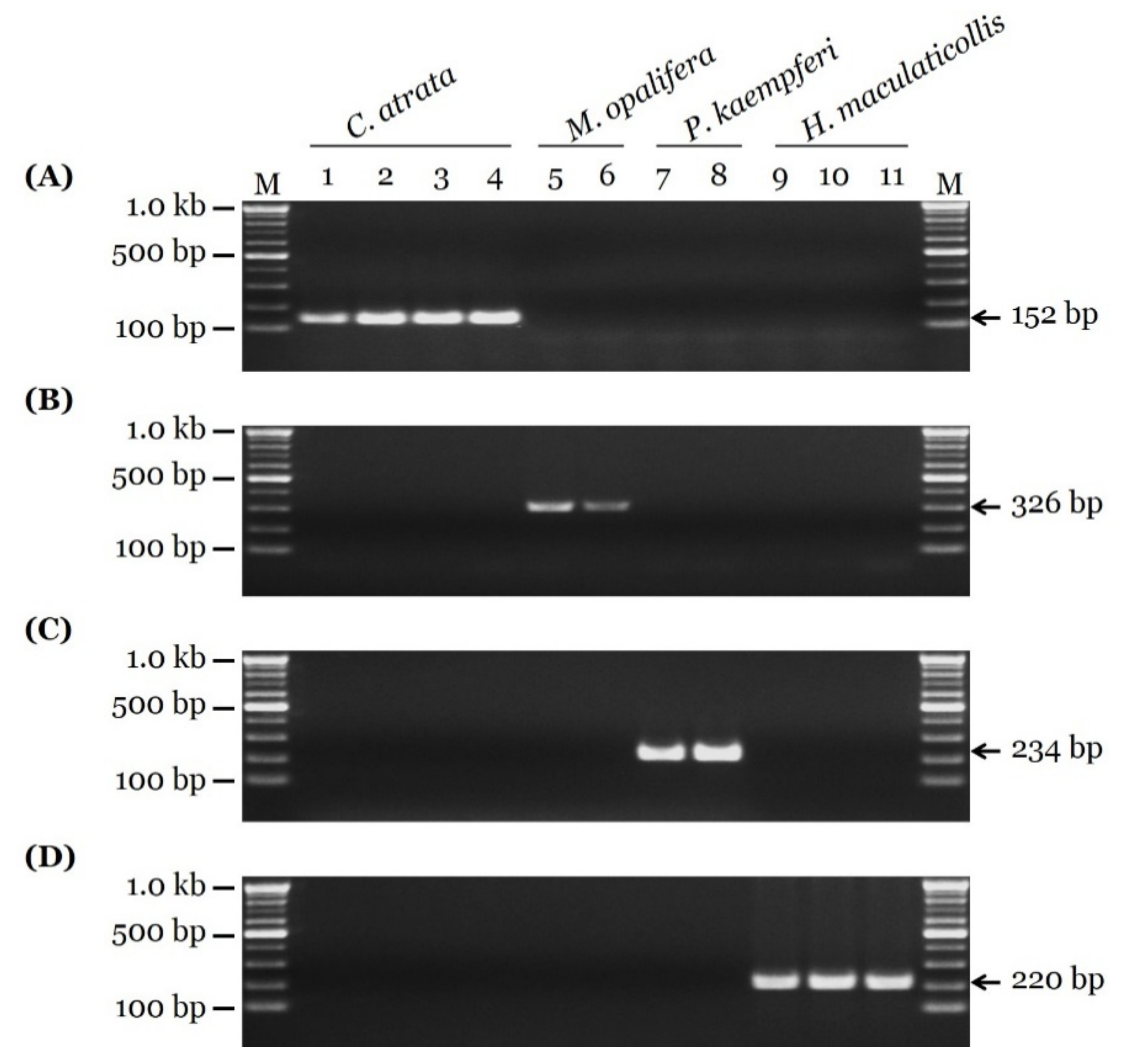
3.2. Development of Species-Specific SCAR Markers
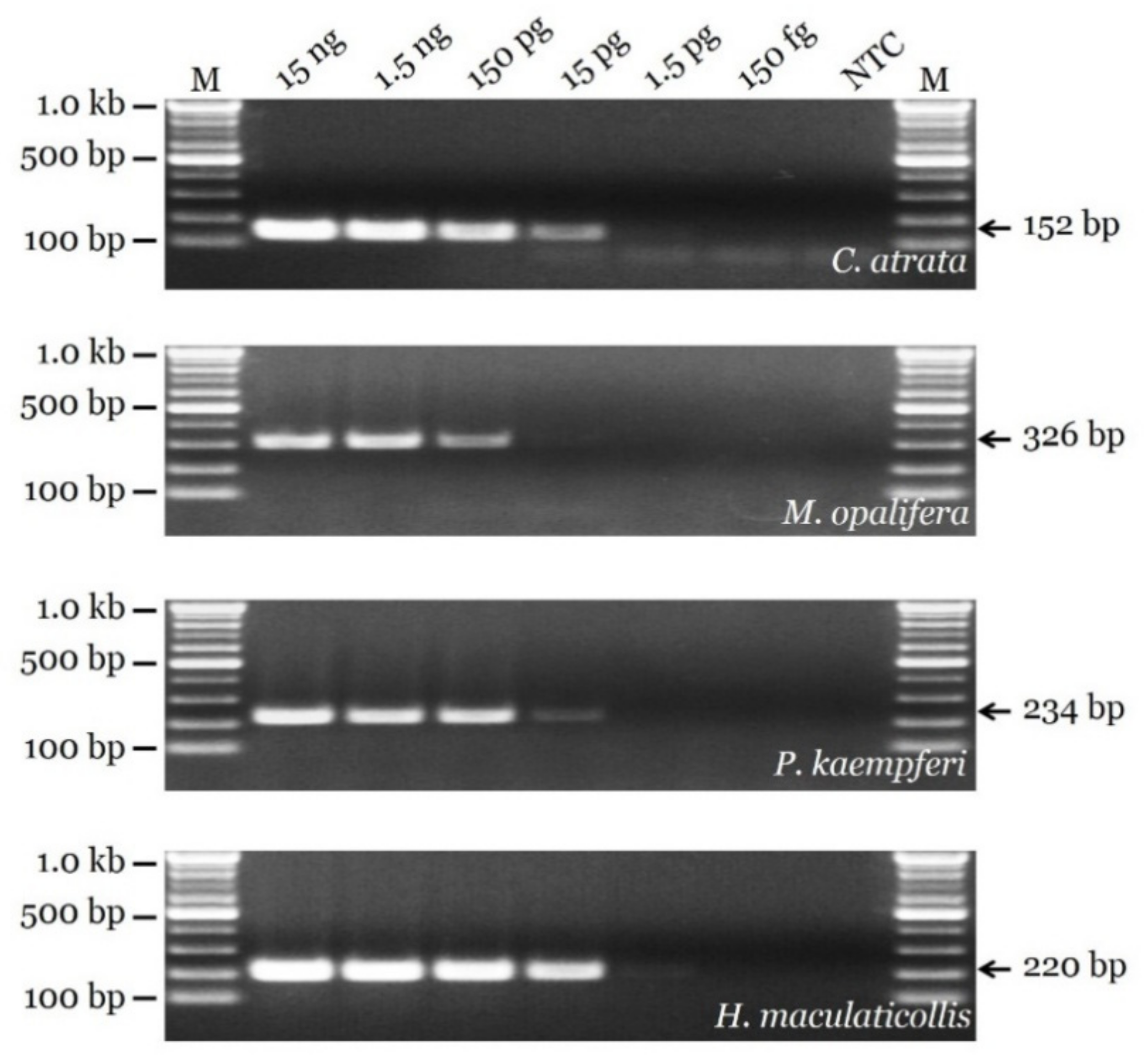
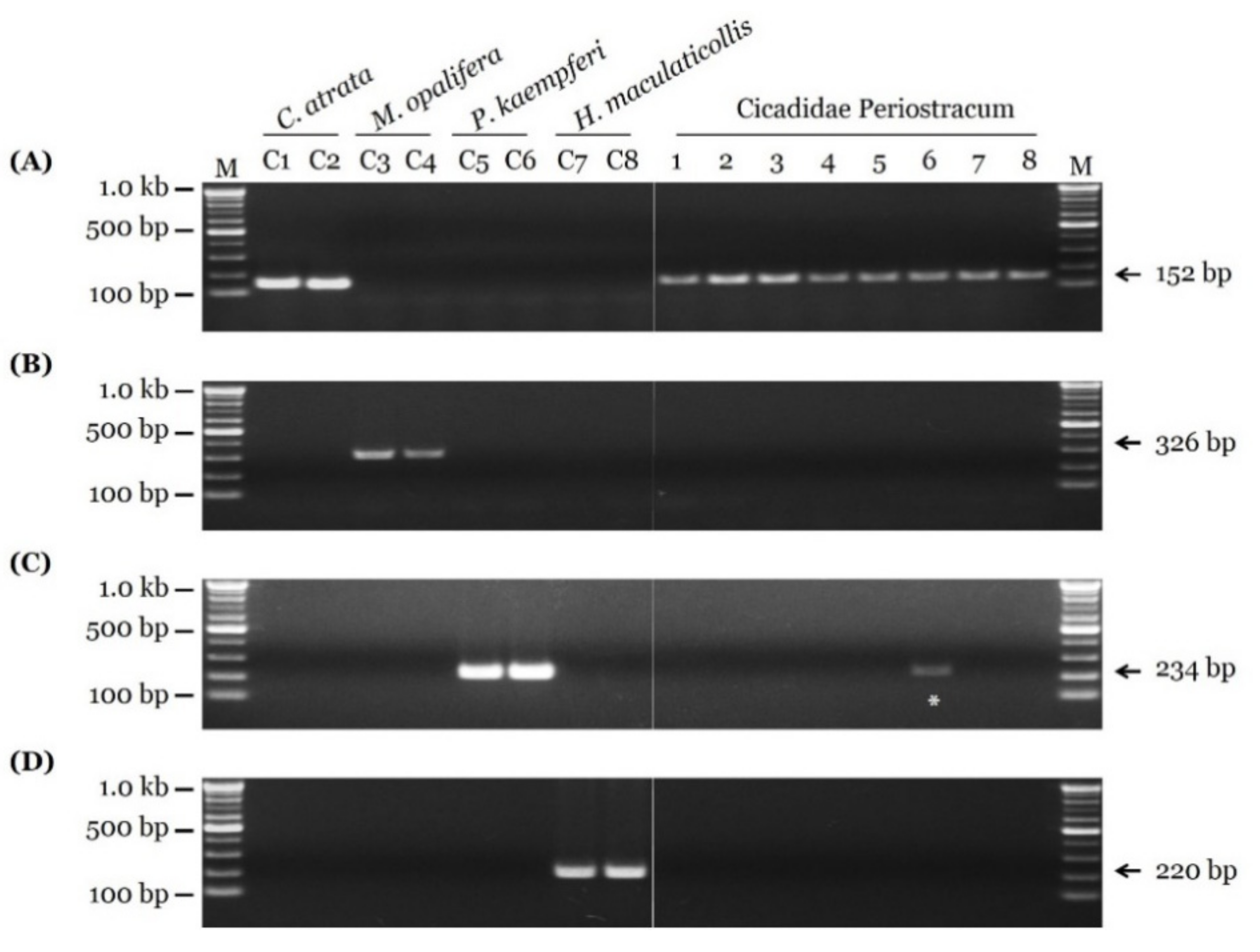
3.3. Sensitivity Test and Authenticity of Market Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, H.; Ma, Q.; Ye, L.; Piao, G. The Traditional Medicine and Modern Medicine from Natural Products. Molecules 2016, 21, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J. Dongui-Bogam: Treasured Mirror of Eastern Medicine; Namsandang Publishers Co.: Seoul, Korea, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Zhao, M.; He, Z.; Chen, Z.; Sun, L. Research and utilization of medicinal insects in China. Entomol. Res. 2009, 39, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Babu, N.; Pandey, H. Traditional insect bioprospecting—As human food and medicine. Indian J. Tradit. Knowl. 2009, 8, 485–494. [Google Scholar]
- Song, B.-K.; Won, J.-H.; Kim, S. Historical medical value of Donguibogam. J. Pharmacopunct. 2016, 19, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. The Korean Herbal Pharmacopoeia, 4th ed.; Ministry of Food and Drug Safety: Osong, Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Defining Dictionary for Medicinal Herbs [Korean, ‘Hanyak Giwon Sajeon’]. Available online: http://boncho.kiom.re.kr/codex/ (accessed on 25 November 2019).
- Park, J.; Choi, G. Review on herbal medicinal materials in the Korean Pharmacopoeia and the Korean Herbal Pharmacopoeia. Korean Herb. Med. Inf. 2016, 4, 9–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-H.; Yang, S.; Kim, W.J.; Moon, B.C. Studies on morphological characteristics of the original species, Cryptotympana atrata as a Cicadidae Periostracum. Korean Herb. Med. Inf. 2019, 7, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Committee on Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy. Taiwan Herbal Pharmacopoeia, 2nd ed.; Ministry of Health and Welfare: Taipei, Taiwan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, H.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Moon, B.C.; Choi, G.; Ryu, S.M.; Lee, J.; Ang, M.J.; Jeon, M.; Moon, C.; Park, G. Cicadidae Periostracum, the Cast-Off Skin of Cicada, Protects Dopaminergic Neurons in a Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5797512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui-hay, B.P.; Hson-mou, C. Pharmacology and Applications of Chinese Materia Medica; World Scientific: Singapore, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, M.T.; Peng, W.H.; Yeh, F.T.; Tsai, H.Y.; Chang, Y.S. Studies on the anticonvulsive, sedative and hypothermic effects of Periostracum Cicadae extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1991, 35, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.Y.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.M. Effect of Cryptotympana atrata extract on compound 48/80-induced anaphylactic reactions. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 66, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-P. Acne-remedy effects of extract mixture of Pulsatillae Radix and Cicadidae Periostracum. J. Physiol. Pathol. Korean Med. 2010, 24, 653–660. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Tian, Q.; Tao, G.; Gao, Q.; Lv, T.; Wang, D. Analyses on ingredients and antibacterial activity of periostracum cicadae. Chin. Bull. Entomol. 2010, 47, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-W.; Cho, H.-B.; Kim, S.-B.; Choe, C.-M.; Seo, Y.-J. The anti-inflammatory effects of Cicadidae Periostracum. J. Orient. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.-Z.; Lee, W.S.; Han, J.-M.; Oh, H.-W.; Park, D.-S.; Tian, G.-R.; Jeong, T.-S.; Park, H.-Y. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of N-acetyldopamine dimers from Periostracum Cicadae. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 7826–7834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.N.R.; Chae, J.W. Effects of Cicadae Periostracum (CP) in allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) induced by DNCB in mice. J. Pediatr. Korean Med. 2015, 29, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.-N.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Wang, Y.-M.; Jin, Y.-R.; Liu, Z.-M. Antitussive, expectorant and antiasthmatic effects of periostracum cicadae. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 2007, 23, 1678. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.E. Anti-Proliferative Activity of Constituent Identified in Cicada Slough on Human Prostate Cancer. Master’s Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.-H.; Kim, W.J.; Cha, J.-M.; Yang, S.; Choi, G.; Moon, B.C. Comparative morphological, ultrastructural, and molecular studies of four cicadinae species using exuvial legs. Insects 2019, 10, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Oh, S.-Y.; Jang, Y. Morphometrics of the final instar exuviae of five cicada species occurring in urban areas of central Korea. J. Asia Pacif. Entomol. 2012, 15, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Li, Q.; Wei, C. Morphology and identification of the final instar nymphs of three cicadas (Hemiptera, Cicadidae) in Guanzhong Plain, China based on comparative morphometrics. ZooKeys 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J. Cicadas of Korea; Geobook: Seoul, Korea, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.J. Revised synonymic list of Cicadidae (Insecta: Hemiptera) from the Korean Peninsula, with the description of a new species and some taxonomic remarks. Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 2008, 121, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Moon, B.C.; Yang, S.; Han, K.S.; Choi, G.; Lee, A.Y. Rapid authentication of the herbal medicine plant species Aralia continentalis Kitag. and Angelica biserrata C.Q. Yuan and R.H. Shan using ITS2 sequences and multiplex-SCAR markers. Molecules 2016, 21, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, P.; Kim, W.J.; Yang, S.; Park, I.; Moon, B.C. Authentication of the herbal medicine Angelicae Dahuricae Radix using an ITS sequence-based multiplex SCAR assay. Molecules 2018, 23, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, B.C.; Kim, W.J.; Han, K.S.; Yang, S.; Kang, Y.; Park, I.; Piao, R. Differentiating authentic Adenophorae Radix from its adulterants in commercially-processed samples using multiplexed ITS sequence-based SCAR markers. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagyawant, S.S. RAPD-SCAR markers: An interface tool for authentication of traits. J. Biosci. Med. 2016, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Long, Y.; Khan, A.; Wei, C.; Fu, S.; Fu, J. Development and significance of RAPD-SCAR markers for the identification of Litchi chinensis Sonn. by improved RAPD amplification and molecular cloning. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 18, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; Dewaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syromyatnikov, M.Y.; Borodachev, A.V.; Kokina, A.V.; Popov, V.N. A molecular method for the identification of honey bee subspecies used by beekeepers in Russia. Insects 2018, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, D.C.; Moulds, M.; Hill, K.B.; Price, B.W.; Wade, E.J.; Owen, C.L.; Goemans, G.; Marathe, K.; Sarkar, V.; Cooley, J.R. A molecular phylogeny of the cicadas (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) with a review of tribe and subfamily classification. Zootaxa 2018, 4424, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Hayashi, M.; Wei, C. Morphological variation, genetic differentiation and phylogeography of the East Asia cicada Hyalessa maculaticollis (Hemiptera: Cicadidae). Syst. Entomol. 2018, 43, 308–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Chen, H.-M.; Yang, J.-X.; Jin, J.-Q.; Jiang, K.; Yuan, Z.-Y.; Murphy, R.W.; Zhang, Y.-P. Universal COI primers for DNA barcoding amphibians. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2012, 12, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Lu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, C.; Yang, J.; Tian, B. Authentication of traditional Chinese medicinal herb “Gusuibu” by DNA-based molecular methods. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2019, 141, 111756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osathanunkul, M.; Osathanunkul, R.; Madesis, P. Species identification approach for both raw materials and end products of herbal supplements from Tinospora species. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Pang, X.; Song, J.; Shi, L.; Yao, H.; Han, J.; Leon, C. A renaissance in herbal medicine identification: From morphology to DNA. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwer, N.; Midgley, J.M.; Timm, A.E.; Villet, M.H. Successful identification of the final instar nymph of Quintilia carinata (Thunberg) (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) by DNA extraction from the exuvium. J. Nat. Hist. 2014, 48, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.-W.; Kuo, L.-Y.; Huang, Y.-M.; Chiou, W.-L.; Wang, C.-N. Tissue-direct PCR, a rapid and extraction-free method for barcoding of ferns. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2010, 10, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yang, Y. Traditional Chinese medicine in the Chinese health care system. Health Policy 2009, 90, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemberton, R.W. Insects and other arthropods used as drugs in Korean traditional medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 65, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.-C.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Xu, J.-D.; Shen, H.; Zhou, S.-S.; Zhu, H.; Kong, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, G.-R.; He, Y. Quality consistency evaluation on four origins of Cicadae Periostracum by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometry analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Collection Site | Collection Date | Voucher Number | Abbrev. | GenBank Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryptotympana atrata | Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, Korea | 16 August 2018 | 2-19-0006 | CA-1 | MN784082 |
| Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, Korea | 16 August 2018 | MBC-KIOM-2018-12 | CA-2 | MN784083 | |
| Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, Korea | 20 August 2018 | MBC-KIOM-2018-14 | CA-3 | MN784084 | |
| Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, Korea | 20 August 2018 | MBC-KIOM-2018-20 | CA-4 | MN784085 | |
| Meimuna opalifera | Idong-myeon, Namhae-gun, Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea | 26 August 2014 | KNAE453746-no.16 | MO-1 | MN784086 |
| Aphae-eup, Sinan-gun, Jeollanam-do, Korea | 29 August 2011 | KNAE301381-no.25 | MO-2 | MN784087 | |
| Platypleura kaempferi | Gyodong-myeon, Ganghwa-gun, Incheon, Korea | 7 July 1998 | KNAE29864-no.19 | PK-1 | MN784088 |
| Soheul-eup, Pocheon-si, Gyeonggi-do, Korea | 3 July 2002 | KNAE43938-no.21 | PK-2 | MN784089 | |
| Hyalessa maculaticollis | Gwangmyeong-si, Gyeonggi-do, Korea | 27 July 2018 | 2-19-0007 | HM-1 | MN784090 |
| Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, Korea | 28 July 2018 | MBC-KIOM-2018-16 | HM-2 | MN784091 | |
| Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul, Korea | 29 July 2018 | MBC-KIOM-2018-18 | HM-3 | MN784092 |
| Target Species | Primer Name 1 | Primer Sequence (5′→3′) | PCR Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cryptotympana atrata | CA_F1 | GTGGATTTGGGAATTGATTAA | 152 bp |
| CA_R1-1 | TCATCCTGTCCCAGCACCAT | ||
| Meimuna opalifera | MO_F1-1 | ACCATTATCTAGAATTTTGTC | 326 bp |
| MO_R2 | CAAAAAATCAAAACAGATGC | ||
| Platypleura kaempferi | PK_F1-1 | GAATTGGCTGGTTCCCTTG | 234 bp |
| PK_R1 | ATACTCCTGCTAAATGAAGT | ||
| Hyalessa maculaticollis | HM_F1-1 | TTCGAATTGAATTAGGGACTTCA | 220 bp |
| HM_R1 | GTTAAAGATGGGGGAAGCAA |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noh, P.; Kim, W.J.; Song, J.-H.; Park, I.; Choi, G.; Moon, B.C. Rapid and Simple Species Identification of Cicada Exuviae Using COI-Based SCAR Assay. Insects 2020, 11, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030168
Noh P, Kim WJ, Song J-H, Park I, Choi G, Moon BC. Rapid and Simple Species Identification of Cicada Exuviae Using COI-Based SCAR Assay. Insects. 2020; 11(3):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030168
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoh, Pureum, Wook Jin Kim, Jun-Ho Song, Inkyu Park, Goya Choi, and Byeong Cheol Moon. 2020. "Rapid and Simple Species Identification of Cicada Exuviae Using COI-Based SCAR Assay" Insects 11, no. 3: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030168
APA StyleNoh, P., Kim, W. J., Song, J.-H., Park, I., Choi, G., & Moon, B. C. (2020). Rapid and Simple Species Identification of Cicada Exuviae Using COI-Based SCAR Assay. Insects, 11(3), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030168







