Assessment of a Novel Adult Mass-Rearing Cage for Aedes albopictus (Skuse) and Anopheles arabiensis (Patton)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mosquito Strains and Rearing Conditions
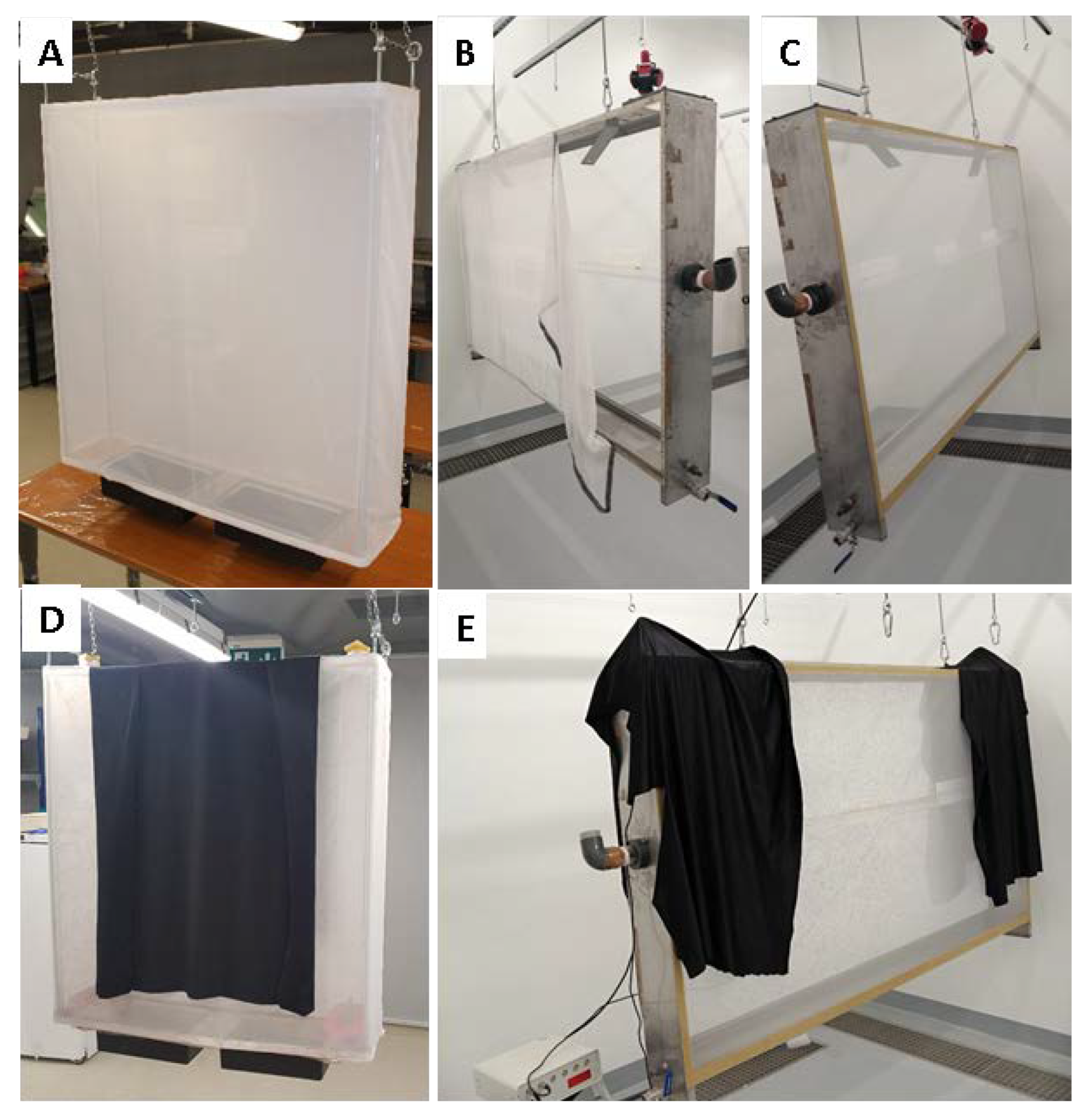
2.2. Experimental Design to Assess the New Mass-Rearing Cage for Ae. albopictus
2.3. Experimental Design to Assess the New Mass-Rearing Cage for Anopheles arabiensis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Egg Production, Floating Eggs, and Egg Hatch Rate for Aedes albopictus
3.2. Adult Aedes albopictus Mortality Rates
3.3. Egg Production in the New Mass-Rearing Cage for Anopheles arabiensis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benedict, M.Q.; Levine, R.S.; Hawley, W.A.; Lounibos, L.P. Spread of The Tiger: Global Risk of Invasion by The Mosquito Aedes albopictus. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2007, 7, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawley, W.A. The biology of Aedes albopictus. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. Suppl. 1988, 1, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levy-Blitchtein, S.; del Valle-Mendoza, J. Zika virus is arriving at the American continent. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 1019–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhatt, S.; Gething, P.W.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Farlow, A.W.; Moyes, C.L.; Drake, J.M.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hoen, A.G.; Sankoh, O.; et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 496, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World-Malaria-Report-2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail/world-malaria-report-2019 (accessed on 18 June 2020).
- WHO. Global Plan for Insecticide Resistance Management in Malaria Vectors. Available online: http://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/gpirm/en/ (accessed on 2 July 2020).
- Moyes, C.L.; Vontas, J.; Martins, A.J.; Ng, L.C.; Koou, S.Y.; Dusfour, I.; Raghavendra, K.; Pinto, J.; Corbel, V.; David, J.-P.; et al. Contemporary status of insecticide resistance in the major Aedes vectors of arboviruses infecting humans. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, P.A.; Hendriks, C.J.M.; Tangena, J.-A.A.; Gibson, H.; Hemingway, J.; Coleman, M.; Gething, P.W.; Cameron, E.; Bhatt, S.; Moyes, C.L. Mapping trends in insecticide resistance phenotypes in African malaria vectors. PLOS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, J.; Yamada, H.; Pereira, R.; Bourtzis, K.; Vreysen, M.J.B. Phased Conditional Approach for Mosquito Management Using Sterile Insect Technique. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO & IAEA. Guidance Framework for Testing the Sterile Insect Technique as a Vector Control Tool against Aedes-Borne Diseases; World Health Organization and the International Atomic Energy Agency: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dyck, V.A.; Hendrichs, J.; Robinson, A.S. (Eds.) Sterile Insect Technique: Principles and Practice in Area-Wide Integrated Pest Management; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrichs, J.; Robinson, A.S.; Cayol, J.P.; Enkerlin, W. Medfly area wide sterile insect technique programmes for prevention, suppression or eradication: The importance of mating behavior studies. Fla. Entomol. 2002, 85, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, M.; Gunay, F.; Puggioli, A.; Balestrino, F.; Oncu, C.; Alten, B.; Bellini, R. Establishment of a satellite rearing facility to support the release of sterile Aedes albopictus males. I. Optimization of mass rearing parameters. Acta Trop. 2016, 159, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiens, D.; Marquereau, L.; Lebon, C.; Le Goff, G.; Gaudillat, B.; Habchi-Hanriot, N.; Gouagna, L.C.; Goff, G.L.; Hanriot, H. Aedes albopictus Adult Medium Mass Rearing for SIT Program Development. Insects 2019, 10, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAO/IAEA. Guidelines for Standardised Mass Rearing of Anopheles Mosquitoes—Version 1.0. 2017, p. 44. Available online: https://www.iaea.org/resources/manual/guidelines-for-standardised-mass-rearing-of-anopheles-mosquitoes-version-10 (accessed on 14 August 2020).
- FAO/IAEA. Spreadsheet for Dimensioning Aedes Mosquito Mass-rearing and Release Facilities; Argilés, R., Cáceres, C., Bouyer, J., Eds.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2019; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- FAO/IAEA. Guidelines for Mass-Rearing of Aedes Mosquitoes; Maiga, H., Mamai, W., Yamada, H., Argilés, R., Bouyer, J., Eds.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2020; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Bellini, R.; Medici, A.; Puggioli, A.; Balestrino, F.; Carrieri, M. Pilot field trials with Aedes albopictus irradiated sterile males in Italian urban areas. J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Wu, Y.; Liang, X.; Liang, Y.; Pan, X.; Hu, L.; Sun, Q.; et al. Incompatible and sterile insect techniques combined eliminate mosquitoes. Nature 2019, 572, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiens, D.; Lebon, C.; Wilkinson, D.A.; Dijoux-Millet, D.; Le Goff, G.; Bheecarry, A.; Gouagna, L.C. Cross-Mating Compatibility and Competitiveness among Aedes albopictus Strains from Distinct Geographic Origins—Implications for Future Application of SIT Programs in the South West Indian Ocean Islands. Bourtzis K, editor. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maïga, H.; Gilles, J.R.L.; Susan Lees, R.; Yamada, H.; Bouyer, J. Demonstration of resistance to satyrization behavior in Aedes aegypti from La Réunion island. Parasite 2020, 27, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iyaloo, D.P.; Damiens, D.; Sunita, F.; Elahee, K.B.; Bheecarry, A. Dispersal and survival of radio-sterilised male Aedes albopictus Skuse (Diptera: Culicidae) and estimation of the wild populations in view of an sterile insect technique programme in Pointe des Lascars, Mauritius. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2019, 39, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, R.; Michaelakis, A.; Petric, D.; Schaffner, F.; Alten, B.; Angelini, P.; Aranda, C.; Becker, N.; Carrieri, M.; Di Luca, M.; et al. Practical management plan for invasive mosquito species in Europe: I. Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus). Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 35, 101691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munhenga, G.; Brooke, B.D.; Gilles, J.R.L.; Slabbert, K.; Kemp, A.; Dandalo, L.C.; Wood, O.R.; Lobb, L.; Govender, D.; Renke, M.; et al. Mating competitiveness of sterile genetic sexing strain males (GAMA) under laboratory and semi-field conditions: Steps towards the use of the Sterile Insect Technique to control the major malaria vector Anopheles arabiensis in South Africa. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knipling, E.F. Sterile-Male Method of Population Control: Successful with some insects, the method may also be effective when applied to other noxious animals. Science 1959, 130, 902–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, J.; Culbert, N.J.; Dicko, A.H.; Pacheco, M.G.; Virginio, J.; Pedrosa, M.C.; Garziera, L.; Pinto, A.T.M.; Klaptocz, A.; Germann, J.; et al. Field performance of sterile male mosquitoes released from an uncrewed aerial vehicle. Sci Robot. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerberg, E.J.; American Mosquito Control Association. Manual for Mosquito Rearing and Experimental Techniques; American Mosquito Control Association: Albany, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Balestrino, F.; Puggioli, A.; Bellini, R.; Petric, D.; Gilles, J.R.L. Mass Production Cage for Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2014, 51, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, D.O.; Nimmo, D.; Naish, N.; McKemey, A.R.; Gray, P.; Wilke, A.B.B.; Marrelli, M.T.; Virginio, J.F.; Alphey, L.; Capurro, M.L. Mass Production of Genetically Modified Aedes aegypti for Field Releases in Brazil. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2014, 83, e3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maiga, H.; Bimbilé-Somda, N.S.; Yamada, H.; Wood, O.; Damiens, D.; Mamai, W.; Balestrino, F.; Lees, R.S.; Dabiré, R.K.; Diabaté, A.; et al. Enhancements to the mass-rearing cage for the malaria vector, Anopheles arabiensis for improved adult longevity and egg production. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2017, 164, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mamai, W.; Bimbile-Somda, N.S.; Maiga, H.; Juarez, J.G.; Muosa, Z.A.I.; Ali, A.B.; Lees, R.S.; Gilles, J.R.L. Optimization of mosquito egg production under mass rearing setting: Effects of cage volume, blood meal source and adult population density for the malaria vector, Anopheles arabiensis. Malar. J. 2017, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zheng, X.; Gilles, J.R.L.; Yamada, H.; Wu, Z.; Xi, Z.; Wu, Y. Establishment of a medium-scale mosquito facility: Tests on mass production cages for Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasit Vectors 2018, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiga, H.; Mamai, W.; Somda, N.S.B.; Konczal, A.; Wallner, T.; Salvador-Herranz, G.; Herrero, R.A.; Yamada, H.; Bouyer, J. Reducing the cost and assessing the performance of a novel adult mass-rearing cage for the dengue, chikungunya, yellow fever and Zika vector, Aedes aegypti (Linnaeus). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestrino, F.; Benedict, M.Q.; Gilles, J.R.L. A New Larval Tray and Rack System for Improved Mosquito Mass Rearing. J. Med. Entomol. 2012, 49, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamai, W.; Somda, N.S.B.; Maiga, H.; Konczal, A.; Wallner, T.; Bakhoum, M.T.; Yamada, H.; Bouyer, J. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae powder as a larval diet ingredient for mass-rearing Aedes mosquitoes. Parasite 2019, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maïga, H.; Damiens, D.; Diabaté, A.; Dabiré, R.K.; Ouédraogo, G.A.; Lees, R.S.; Gilles, J.R.L. Large-scale Anopheles arabiensis egg quantification methods for mass-rearing operations. Malar J. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, M.-L.; Zhang, D.-J.; Damiens, D.D.; Yamada, H.; Gilles, J.R. Standard operating procedures for standardized mass rearing of the dengue and chikungunya vectors Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae)-I-egg quantification. Parasit Vectors 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, M.-L.; Zhang, D.-J.; Damiens, D.D.; Lees, R.S.; Gilles, J.R.L. Standard operating procedures for standardized mass rearing of the dengue and chikungunya vectors Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae)-II-Egg storage and hatching. Parasit Vectors 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Development CORE TEAM R. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2008; Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/doc/manuals/fullrefman.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Chaves, L.F.; Chaves, L.F. An Entomologist Guide to Demystify Pseudoreplication: Data Analysis of Field Studies with Design Constraints. J. Med. Entomol. 2010, 47, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, A.N.; Paterson, G.D. The Analysis of Mortality and Survival Rates in Wild Populations of Mosquitoes. J. Appl. Ecol. 1981, 18, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolker, B. GLMM FAQ: Testing for Overdispersion/Computing Overdispersion Factor. 2020. Available online: https://bbolker.github.io/mixedmodels-misc/glmmFAQ.html#testing-for-overdispersioncomputing-overdispersion-factor (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Kéry, M.; Hatfield, J.S. Normality of Raw Data in General Linear Models: The Most Widespread Myth in Statistics. Bull. Ecol. Soc. Am. 2003, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, M.J. The R Book; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bretz, F.; Hothorn, T.; Westfall, P. Multiple Comparisons Using R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lenth, R. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means. R Package Version 1.2.3. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=emmeans (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Armbruster, P.; Hutchinson, R.A. Pupal Mass and Wing Length as Indicators of Fecundity in Aedes albopictus and Aedes geniculatus (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2002, 39, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blackmore, M.S.; Lord, C.C. The relationship between size and fecundity in Aedes albopictus. J. Vector Ecol. 2000, 25, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Somda, N.S.B.; Maïga, H.; Mamai, W.; Yamada, H.; Ali, A.; Konczal, A.; Gnankiné, O.; Diabaté, A.; Sanon, A.; Dabiré, K.R.; et al. Insects to feed insects—Feeding Aedes mosquitoes with flies for laboratory rearing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesus, C.E.; Reiskind, M.H. The importance of male body size on sperm uptake and usage, and female fecundity in Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Day, J. Mosquito Oviposition Behavior and Vector Control. Insects 2016, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, J.R.; O’Connell, S.M. Oviposition by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus: Influence of congeners and of oviposition site characteristics. J. Vector Ecol. 2014, 39, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserberg, G.; Bailes, N.; Davis, C.; Yeoman, K. Hump-Shaped Density-Dependent Regulation of Mosquito Oviposition Site-Selection by Conspecific Immature Stages: Theory, Field Test with Aedes albopictus, and a Meta-Analysis. Lorenzo MG, editor. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, F.A.; Silva, J.C.; Bretas de Souza Oliveira, J.B.; Santos De Abreu, F.V. Estudo do comportamento de oviposição do Aedes aegypti em dois bairros sob a influência do clima semiárido no município de Salinas. Rev. Patol. Trop. 2015, 44, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madeira, N.; Macharelli, C.; Carvalho, L. Variation of the Oviposition Preferences of Aedes aegypti in Function of Substratum and Humidity. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2002, 97, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richards, S.L.; Anderson, S.L.; Yost, S.A. Effects of blood meal source on the reproduction of Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Vector Ecol. 2012, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gavotte, L.; Mercer, D.R.; Vandyke, R.; Mains, J.W.; Dobson, S.L. Wolbachia Infection and Resource Competition Effects on Immature Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzales, K.K.; Hansen, I.A. Artificial Diets for Mosquitoes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peters, T.M.; Barbosa, P. Influence of Population Density on Size, Fecundity, and Developmental Rate of Insects in Culture. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1977, 22, 431–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delatte, H.; Gimonneau, G.; Triboire, A.; Fontenille, D. Influence of Temperature on Immature Development, Survival, Longevity, Fecundity, and Gonotrophic Cycles of Aedes albopictus, Vector of Chikungunya and Dengue in the Indian Ocean. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisnham, P.T.; Sala, L.M.; Juliano, S.A. Geographic Variation in Adult Survival and Reproductive Tactics of the Mosquito Aedes albopictus. J. Med. Entomol. 2008, 45, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Task/Day | 1 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 9 | 13 | 16 | 20 | 23 | 27 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pupal Loading | x | x | ||||||||
| Blood Feeding | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Egg Papers | x | x | x | x | x | |||||
| Egg Paper Removal | x | x | x | x | x | |||||
| Week of Egg Collection | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||||||
| Task/Day | 1 | 2 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 13 | 14 | 16 | 17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pupal Loading | x | x | |||||||||
| Blood Feeding | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||
| Water | x | x | x | ||||||||
| Egg Collection | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Fixed Factors | Predictors/Fixed Factors | Odds Ratio (±95% CI) | Estimate | Std. Error | Z-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 3.84 (2.17–6.78) | 1.34 | 0.28 | 4.64 | <0.001 | |
| Week of egg collection (3 levels: Weeks 1–3) | Week 2 | 0.51 (0.36–0.73) | −0.65 | 0.17 | −3.65 | <0.001 |
| Week 3 | 0.62 (0.43–0.89) | −0.46 | 0.18 | −2.60 | 0.009 | |
| Egg origin (2 levels: Floating and Paper) | Paper | 1.62 (1.12–2.34) | 0.48 | 0.18 | 2.59 | 0.009 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maïga, H.; Mamai, W.; Bimbilé Somda, N.S.; Wallner, T.; Poda, B.S.; Salvador-Herranz, G.; Argiles-Herrero, R.; Yamada, H.; Bouyer, J. Assessment of a Novel Adult Mass-Rearing Cage for Aedes albopictus (Skuse) and Anopheles arabiensis (Patton). Insects 2020, 11, 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110801
Maïga H, Mamai W, Bimbilé Somda NS, Wallner T, Poda BS, Salvador-Herranz G, Argiles-Herrero R, Yamada H, Bouyer J. Assessment of a Novel Adult Mass-Rearing Cage for Aedes albopictus (Skuse) and Anopheles arabiensis (Patton). Insects. 2020; 11(11):801. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110801
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaïga, Hamidou, Wadaka Mamai, Nanwintoum Séverin Bimbilé Somda, Thomas Wallner, Bèwadéyir Serge Poda, Gustavo Salvador-Herranz, Rafael Argiles-Herrero, Hanano Yamada, and Jérémy Bouyer. 2020. "Assessment of a Novel Adult Mass-Rearing Cage for Aedes albopictus (Skuse) and Anopheles arabiensis (Patton)" Insects 11, no. 11: 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110801
APA StyleMaïga, H., Mamai, W., Bimbilé Somda, N. S., Wallner, T., Poda, B. S., Salvador-Herranz, G., Argiles-Herrero, R., Yamada, H., & Bouyer, J. (2020). Assessment of a Novel Adult Mass-Rearing Cage for Aedes albopictus (Skuse) and Anopheles arabiensis (Patton). Insects, 11(11), 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110801





