Changes in Shape, Texture and Airflow Improve Efficiency of Monitoring Traps for Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
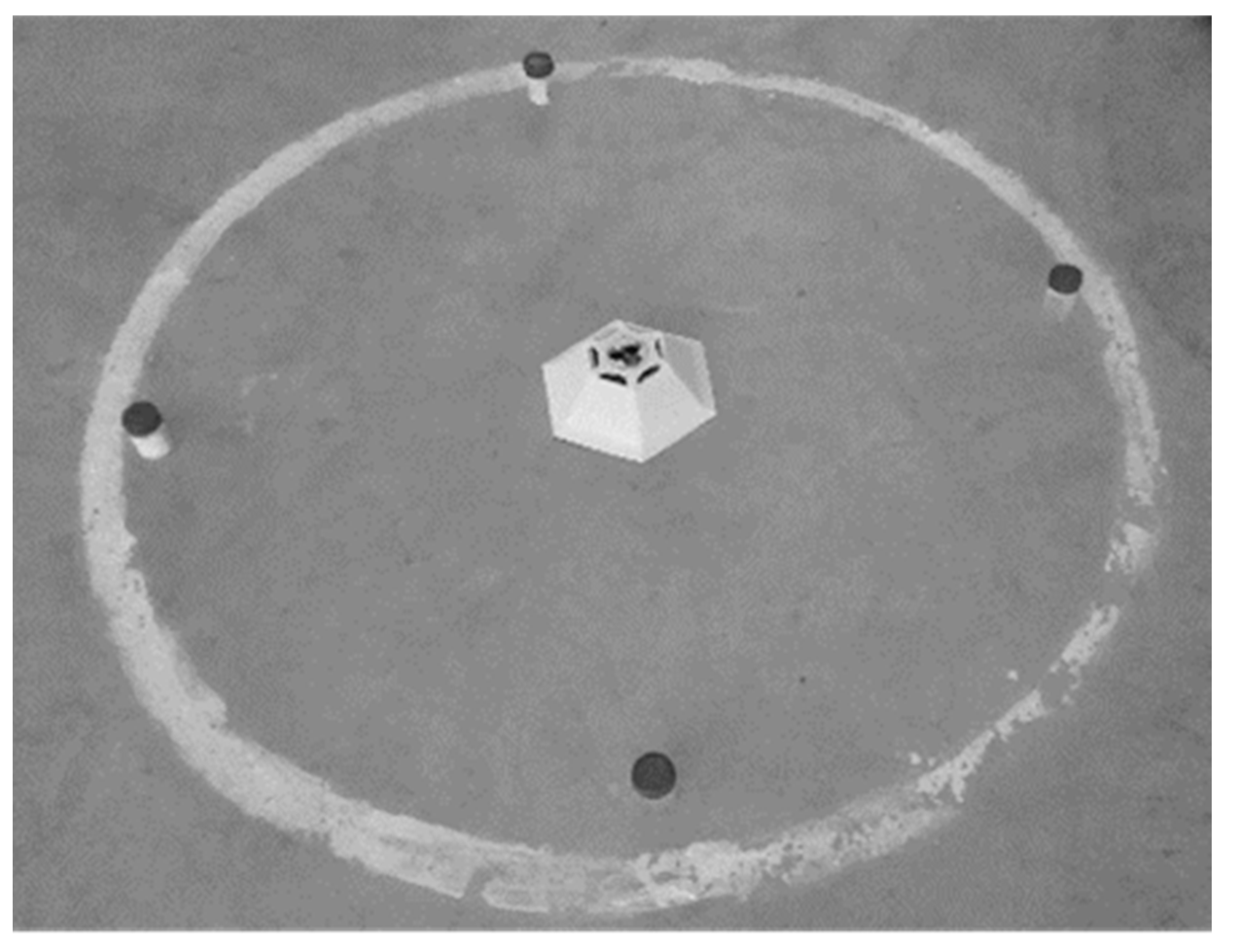
2.2. Commercial Trap
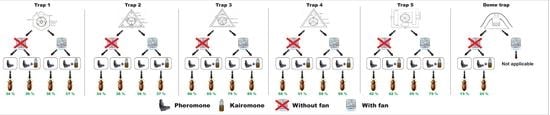
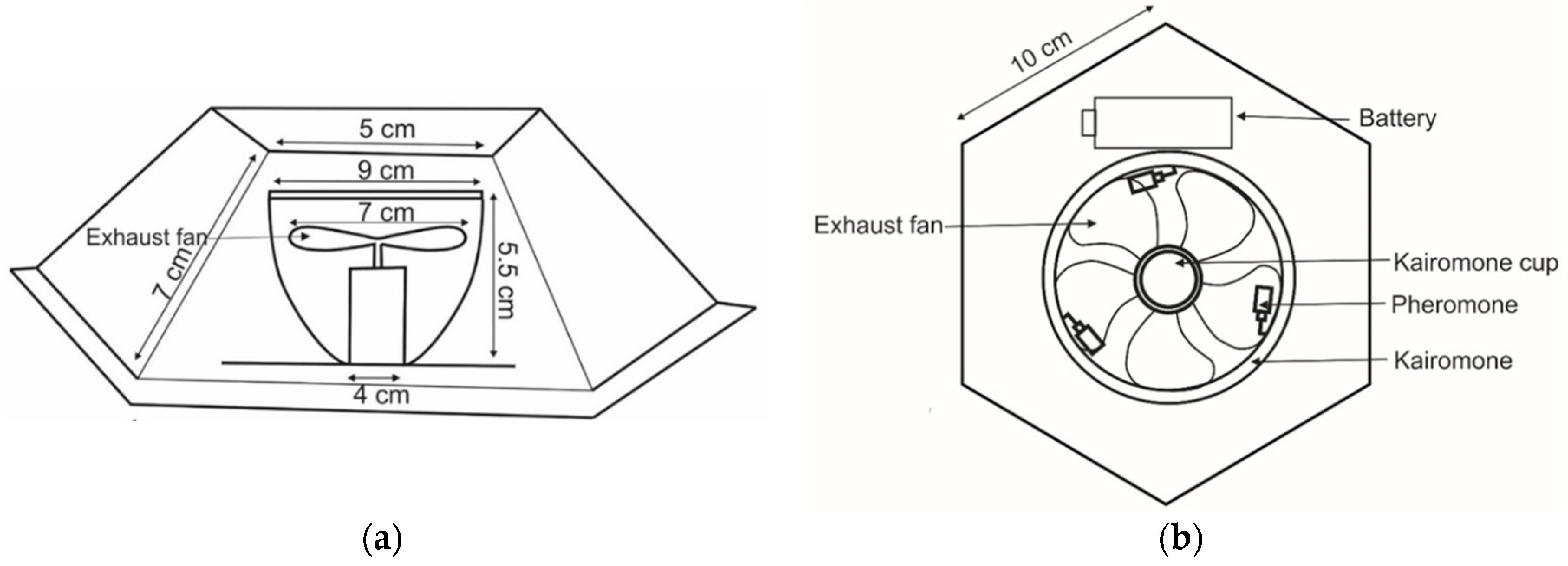
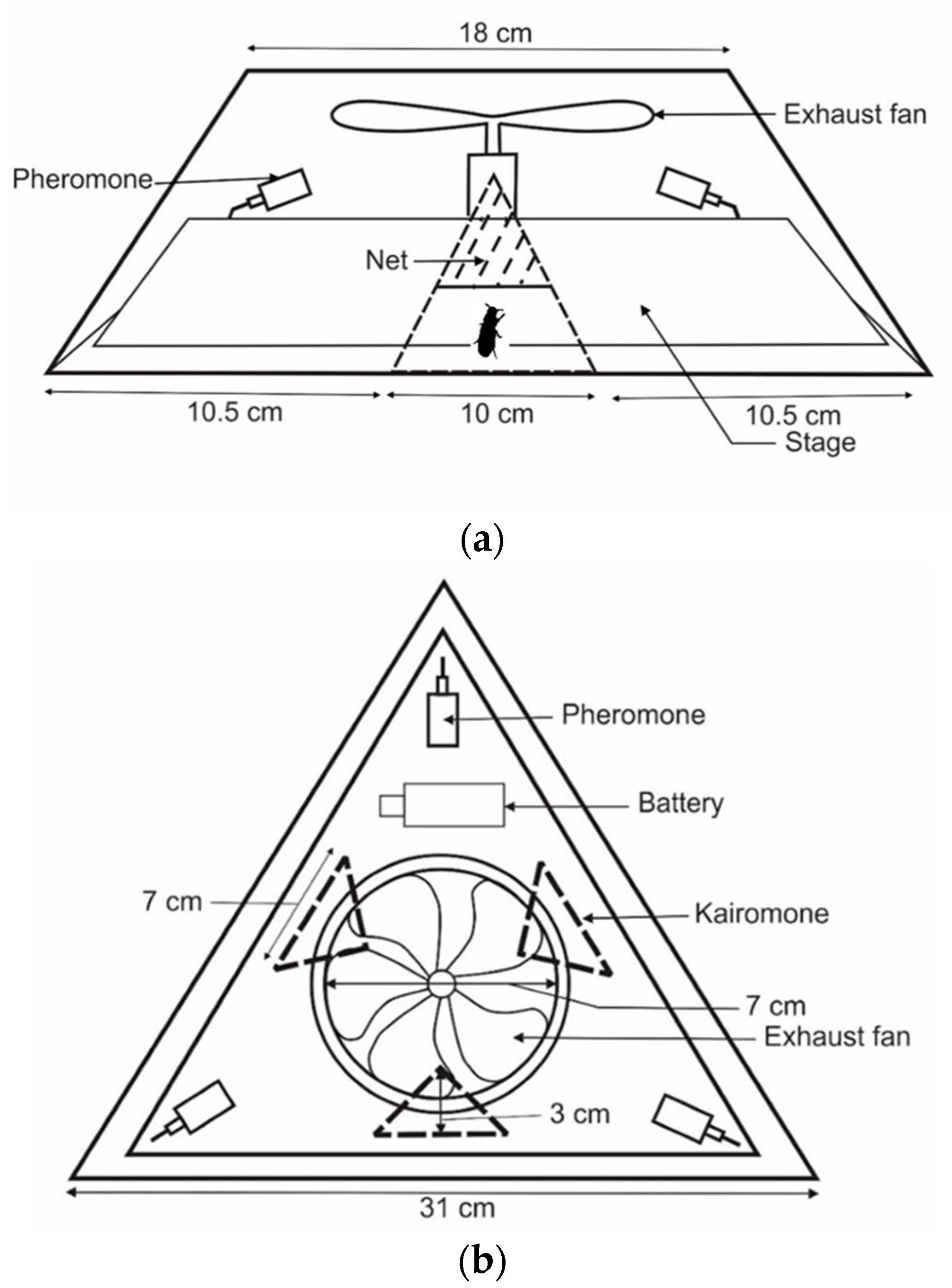
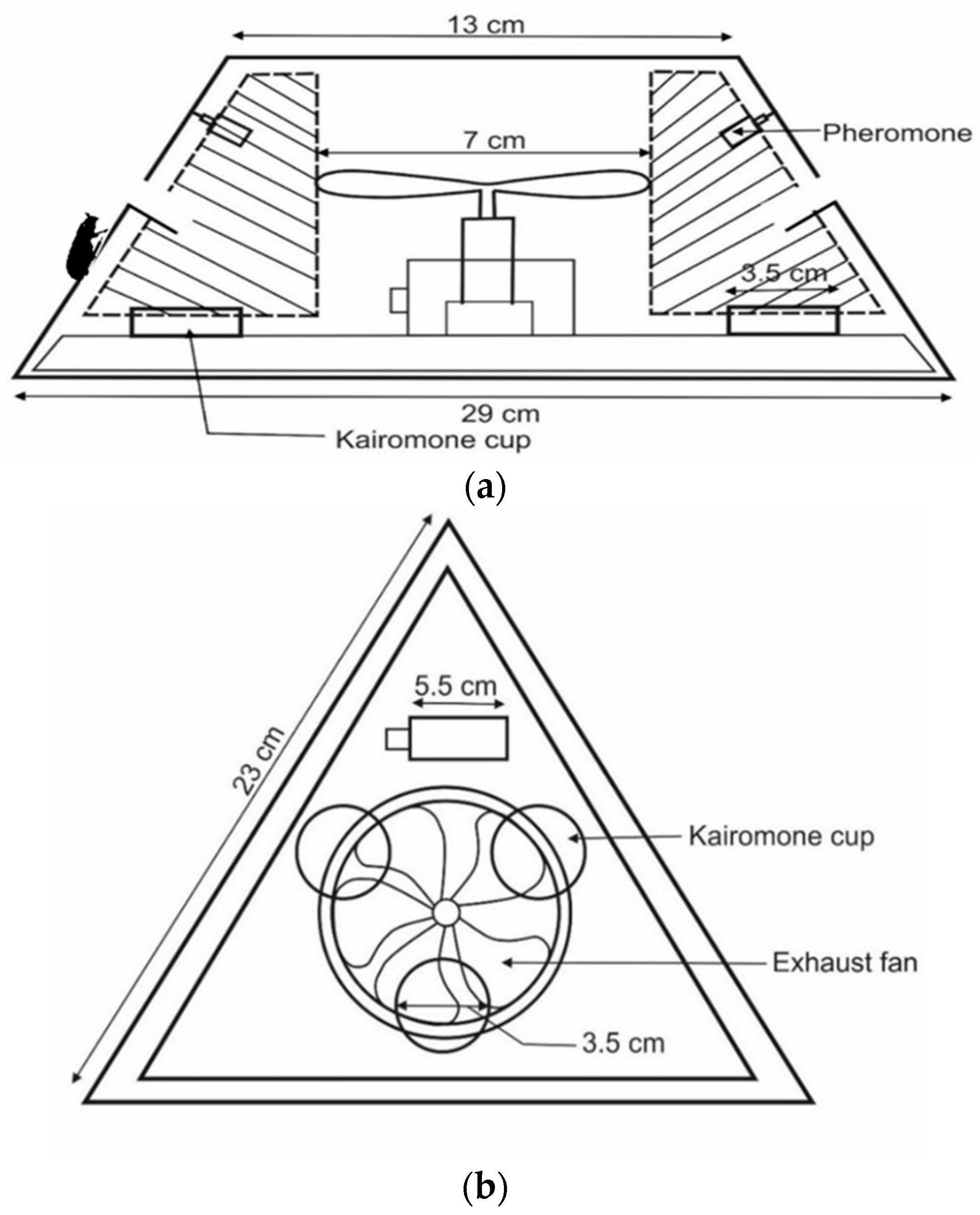
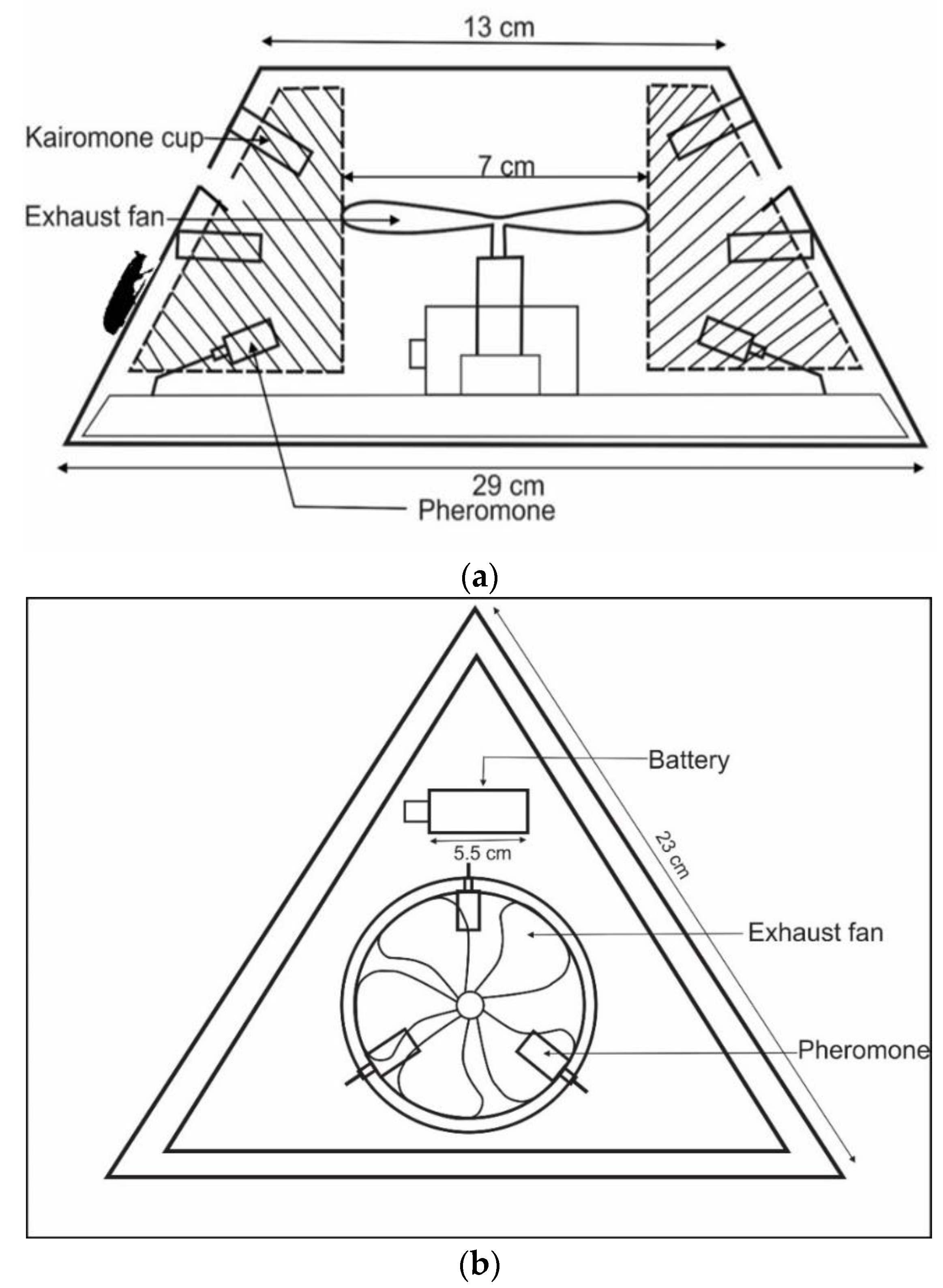
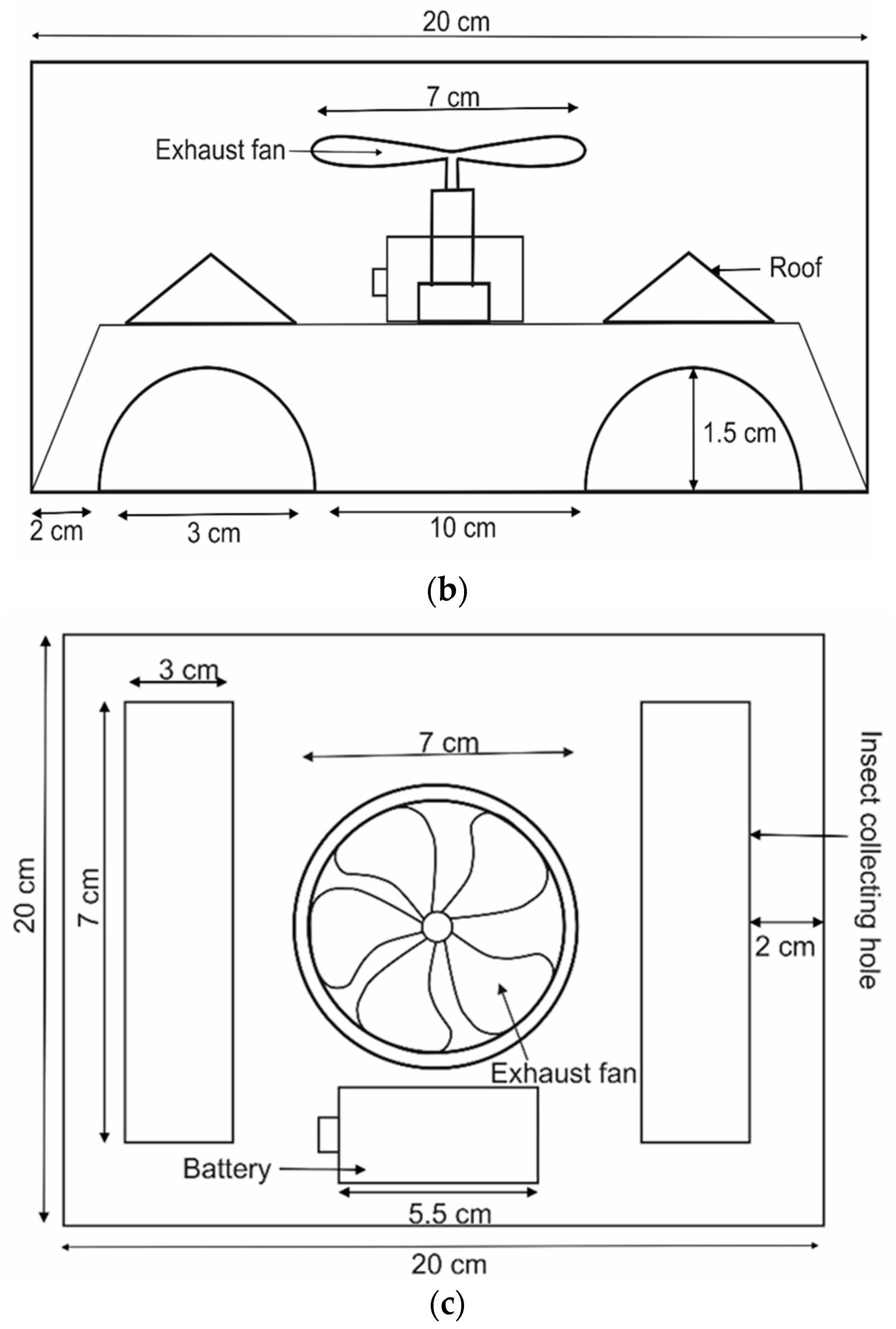
2.3. Development of New Traps
2.4. Pheromone and Kairomone
2.5. Experimental Design
2.6. Experiments
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Trapping Efficiency without the Fan
3.1.1. Trapping Efficiency with Pheromone Alone
3.1.2. Trapping Efficiency with Both Pheromone and Kairomone
3.1.3. Pheromone Alone vs. Both Pheromone and Kairomone
3.2. Trapping Efficiency with the Fan
3.2.1. Trapping Efficiency with Pheromone Alone
3.2.2. Trapping Efficiency with Pheromone and Kairomone
3.2.3. Pheromone Alone vs. Pheromone and Kairomone
3.3. Trapping Efficiency with and without the Fan in Operation
3.4. Differences in Trapping T. castaneum among Traps
- i.
- The newly developed traps are triangular, square shaped or hexagonal in shape in contrast to the circular-shaped commercially available dome trap. The shape of the trap affects dispersal of the pheromone (+kairomone) from inside the trap to outside and subsequently the rate of pheromone diffusion.
- ii.
- The new traps were developed using abrasive type papers. The commercial trap is made of plastic material. This difference in the surface material on which insect moves would have assisted the stability of its movement into the new traps than the commercial trap.
- iii.
- In the commercial traps, the plane of the surface through which the insects move in is curved (not straight) in contrast to the straight surfaces in the new traps. This aids the insect’s stability on the surface during its orientation towards the pheromone/kairomone inside the trap.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, D.S. Types of damage. In Pests of Stored Products and Their Control; Belhaven Press: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayaratne, L.K.W.; Arthur, F.H.; Whyard, S. Methoprene and control of stored-product insects. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2018, 76, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayaratne, L.K.W.; Fernando, M.D.; Palipane, K.B. Control of insect pests under ware-house conditions using smoke generated from partial combustion of rice (paddy) husk. J. Natl. Sci. Found. 2009, 37, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagstrum, D.W.; Phillips, T.W.; Cuperus, G. Stored Product Protection; Kansas State Research and Extension: Kansas, MO, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cogburn, R.R. Stored-product insect populations in boxcars delivering flour and rice to Gulf coast ports. Environ. Entomol. 1973, 2, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, Y. Beetles Associated with Stored Products in Canada: An Identification Guide; Canadian Government Publishing Centre: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Trematerra, P.; Gentile, P.; Brunetti, A.; Collins, L.E.; Chambers, J. Spatio-temporal analysis of trap catches of Tribolium confusum du Val in a semolina-mill, with a comparison of female and male distributions. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2007, 43, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagstrum, D.W.; Subramanyam, B. Fundamentals of Stored-Product Entomology; AACC International: St Paul, MN, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hagstrum, D.W.; Subramanyam, B. Stored-Product Insect Resource; AACC International Inc.: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Edde, P.A.; Eaton, M.; Kells, S.A.; Phillips, T.W. Biology, Behavior, and Ecology of Pests in Other Durable Commodities. In Stored Product Protection; Hagstrum, D.W., Phillips, T.W., Cuperus, G., Eds.; Kansas State Research and Extension: Kansas, MO, USA, 2012; pp. 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sajeewani, P.A.H.; Dissanayaka, D.M.S.K.; Wijayaratne, L.K.W. Progeny production by Stegobium paniceum in different spices. In Proceedings of the 12th International Working Conference on Stored Product Protection, Berlin, Germany, 7–11 October 2018; Adler, C.S., Opit, G., Furstenau, B., Muller-Blenkle, C., Kern, P., Arthur, F.H., Athanassiou, C.G., Bartosik, R., Campbell, J., Carvalho, M.O., et al., Eds.; Julius Kühn-Institut: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 203–205. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayaratne, L.K.W.; Dissanayaka, D.M.S.K.; Sammani, A.M.P. Variation in Rhyzopertha dominica (F.) (Coleoptera: Bostrychidae) progeny adult emergence in different animal feed stored under ventilated and non-ventilated conditions. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2019, 84, 101516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, P.; Nelson, H.D. Insects on dried fruits. In Agriculture Handbook 464; United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Burks, C.S.; Johnson, J.A. Biology, Behavior, and Ecology of Stored Fruit and Nut Insects. In Stored Product Protection; Hagstrum, D.W., Phillips, T.W., Cuperus, G., Eds.; Kansas State Research and Extension: Kansas, MO, USA, 2012; pp. 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Barak, A.V.; Burkholder, W.E.; Faustini, D.L. Factors affecting the design of traps for stored-products insects. J. Kansas Entomol. Soc. 1990, 63, 466–485. [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder, W.E. Practical use of pheromones and other attractants for stored-product insects. In Behavior-modifying Chemicals for Insect Management: Applications of Pheromones and Other Attractants; Ridgway, R.L., Silverstein, R.M., Inscoe, M.N., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 497–516. [Google Scholar]
- Buckman, K.A.; Campbell, J.F. How varying pest and trap densities affect Tribolium castaneum capture in pheromone traps? Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2013, 146, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trematerra, P.; Sciarretta, A. Spatial distribution of some beetles infesting a feed mill with spatio-temporal dynamics of Oryzaephilus surinamensis, Tribolium castaneum and Tribolium confusum. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2004, 40, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbogast, R.T.; Chini, S.R.; McGovern, J.E. Plodia interpunctella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae): Spatial relationship between trap catch and distance from a source of emerging adults. J. Econ. Entomol. 2005, 98, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciarretta, A.; Trematerra, P. Geostatistical characterization of the spatial distribution of Grapholita molesta and Anarsia lineatella males in an agricultural landscape. J. Appl. Entomol. 2006, 130, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, M.A. Development of a pheromone trap for monitoring Tribolium castaneum. J. Stored Prod. Res. 1992, 28, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.H.; Fan, L.; Boon, K.S. Development of a pc-based automatic monitoring system for Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) in a rice warehouse. J. Stored Prod. Res. 1997, 33, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedina, T.Y.; Lewis, S.M. Effect of Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) nutritional environment, sex, and mating status on response to commercial pheromone traps. J. Econ. Entomol. 2007, 100, 1924–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.F.; Toews, M.D.; Arthur, F.H.; Arbogast, R.T. Long-term monitoring of Tribolium castaneum in two flourmills: Seasonal patterns and impact of fumigation. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkin, K.; Stanbridge, D.M.; Fields, P.G. Sampling Tribolium confusum and Tribolium castaneum in mill and laboratory settings: Differences between strains and species. Can. Ent. 2011, 143, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayaka, D.M.S.K.; Sammani, A.M.P.; Wijayaratne, L.K.W. Aggregation pheromone 4,8-dimethyldecanal and kairomone affect the orientation of Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) adults. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2018, 79, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, B.L.; Goyer, R.A. Effect of silhouette color on trap catches of Dendroctonus frontalis (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2001, 94, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sieminska, E.; Ryne, C.; Lofstedt, C.; Anderbrant, O. Long-term pheromone-mediated mating disruption of the Mediterranean flour moth, Ephestia kuehniella, in a flour mill. Ent. Exp. Appl. 2009, 131, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagstrum, D.W.; Flinn, P.W. Comparison of acoustical detection of several species of stored-grain beetles (Coleoptera: Curculionidae, Tenebrionidae, Bostrichidae, Cucujidae) over a range of temperatures. J. Econ. Entomol. 1993, 86, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagstrum, D.W.; Flinn, P.W.; Shuman, D. Automated monitoring using acoustical sensors for insects in farm stored wheat. J. Econ. Entomol. 1996, 89, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeao, A.A.; Campbell, J.F.; Whitworth, R.J.; Sloderbecks, P.E. Influence of environmental and physical factors on capture of Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) in a flour mill. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 686–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Semeao, A.A.; Campbell, J.F.; Whitworth, R.J.; Sloderbeck, P.E. Response of Tribolium castaneum and Tribolium confusum adults to vertical black shapes and its potential to improve trap capture. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2011, 47, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dissanayaka, D.M.S.K.; Sammani, A.M.P.; Wijayaratne, L.K.W. Food oils as kairomones for trapping Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) adults. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2018, 79, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T. 4,8-Dimethyldecanal: The aggregation pheromone of the flour beetles, Tribolium castaneum and T. confusum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Agric. Biol. Chem. 1980, 44, 2519–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Kozaki, J.; Sugawara, R.; Mori, K. Biological activities of the analogs of the aggregation pheromone of Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Appl. Ent. Zool. 1984, 19, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chambers, J. Overview on Stored-Product Insect Pheromones and Food Attractants. J. Kansas Entomol. Soc. 1990, 63, 490–499. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.F. Attraction of walking Tribolium castaneum adults to traps. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2012, 51, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayaka, D.M.S.K.; Sammani, A.M.P.; Wijayaratne, L.K.W. Orientation of Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) adults at various distances to different concentrations of aggregation pheromone 4,8-dimethyldecanal. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2020, 87, 101631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayaka, D.M.S.K.; Sammani, A.M.P.; Wijayaratne, L.K.W. Response of different population sizes to traps and effect of spinosad on the trap catch and progeny adult emergence in Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2020, 86, 101576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijerathne, K.B.T.T.; Karunarathne, E.V.U.P.; Dissanayaka, D.M.S.K.; Wijayaratne, L.K.W. New food medium for rearing Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Rajarata Univ. J. 2020, 5, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Mullen, M.A.; Highland, H.A.; Taggart, R.E.; Lingren, B.W. Insect Monitoring System. U.S. Patent 5,090,153, 25 February 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Barak, A.V.; Burkholder, W.E. A versatile and effective trap for detecting and monitoring stored-product Coleoptera. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1985, 12, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkin, K.J. Monitoring Populations of the Flour Beetles Tribolium Castaneum Jacquelin du Val and Tribolium Confusum (Herbst) in Flour Mills and in Laboratory Settings. Master’s Thesis, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- SAS Institute. The SAS System for Windows, Release 9.1; Statistical Analysis System Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- McNeil, J.N. Behavioral ecology of pheromone-mediated communication in moths and its importance in the use of pheromone traps. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1991, 36, 407–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Philips, T.W.; AliNiazee, M.T. Pheromone biology and factors affecting its production in Tribolium castaneum. In Proceedings of the 6th International Working Conference on Stored-Product Protection, Wallingford, UK, 17–23 April 1994; Highley, E., Wright, E.J., Banks, H.J., Champ, B.R., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1994; pp. 406–409. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, T.W.; Jiang, X.L.; Burkholder, W.E.; Phillips, J.K.; Tran, H.Q. Behavioral responses to food volatiles by two species of stored-product coleoptera Sitophilus oryzae (Curculionidae) and Tribolium castaneum (Tenebrionidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 1993, 19, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, A.V.; Burkholder, W.E. Trapping studies with dermestid sex pheromones. Environ. Ent. 1976, 5, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, A.D.; Thomas, W.P.; Michael, D.T. Responses of Rhyzopertha dominica (Coleoptera: Bostrichidae) to its aggregation pheromone as influenced by Trap design, trap height and habitat. Environ. Ent. 2005, 34, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar]
- Arbogast, R.T.; Kendra, P.E.; Chini, S.R. Lasioderma serricorne (Coleoptera: Anobiidae): Spatial relationship between trap catch and distance from an infested product. Fla. Entomol. 2003, 86, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material | Trap 1 | Trap 2 | Trap 3 | Trap 4 | Trap 5 | Cost of Materials |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A small motor | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.162 |
| 1.5 V battery | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.189 |
| Abrasive paper | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.405 |
| Exhaust fan | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.108 |
| Electric wire | 20 cm | 20 cm | 20 cm | 20 cm | 20 cm | 0.021 |
| Plastic vial | - | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0.216 |
| Nylon net | - | 100 cm | - | - | 150 cm | 0.108 |
| Plastic funnel | 1 | - | - | - | - | 0.108 |
| Trap Design | % Trapped (Mean ± SE) 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Fan | Fan | |||
| Pheromone | Pheromone + Kairomones | Pheromone | Pheromone + Kairomones | |
| Commercial Trap | 12.6 ± 1.9 eB | 23.6 ± 0.6 eA | na | na |
| Trap 1 | 34.4 ± 0.9 dA | 36.0 ± 0.9 dA | 36.1 ± 0.8 eA | 37.0 ± 3.1 eA |
| Trap 2 | 33.75 ± 2.3 dB | 33.88 ± 2.0 dB | 47.5 ± 1.9 dA | 49.25 ± 1.5 dA |
| Trap 3 | 60.0 ± 1.4 aC | 65.75 ± 1.9 aC | 75.0 ± 1.3 aB | 85.13 ± 1.5 aA |
| Trap 4 | 49.75 ± 1.0 bB | 50.5 ± 0.7 bB | 58.0 ± 0.4 cA | 59.13 ± 1.3 cA |
| Trap 5 | 42.0 ± 0.4 cC | 42.5 ± 1.3 cC | 65.38 ± 1.2 bB | 75.0 ± 1.7 bA |
| Trap | Species | Trapped (%) | Duration of Exposure (days) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storgard trap | Oryzaephilus surinamensis | 64 | 0.7 | [42] |
| Storgard trap | Tribolium confusum | 95 | 0.7 | [42] |
| Pitfall traps | Lasioderma serricorne | 30 | 2 | [50] |
| Sticky traps | Plodia interpunctella | 20 | 3 | [50] |
| Dome trap | T. confusum | 2 | 10 | [25] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sajeewani, P.A.H.; Dissanayaka, D.M.S.K.; Wijayaratne, L.K.W.; Burks, C.S. Changes in Shape, Texture and Airflow Improve Efficiency of Monitoring Traps for Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Insects 2020, 11, 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110778
Sajeewani PAH, Dissanayaka DMSK, Wijayaratne LKW, Burks CS. Changes in Shape, Texture and Airflow Improve Efficiency of Monitoring Traps for Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Insects. 2020; 11(11):778. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110778
Chicago/Turabian StyleSajeewani, Panamulla A. H., Dissanayaka M. S. K. Dissanayaka, Leanage K. W. Wijayaratne, and Charles S. Burks. 2020. "Changes in Shape, Texture and Airflow Improve Efficiency of Monitoring Traps for Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae)" Insects 11, no. 11: 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110778
APA StyleSajeewani, P. A. H., Dissanayaka, D. M. S. K., Wijayaratne, L. K. W., & Burks, C. S. (2020). Changes in Shape, Texture and Airflow Improve Efficiency of Monitoring Traps for Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Insects, 11(11), 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110778