Gene Characterization and Enzymatic Activities Related to Trehalose Metabolism of In Vitro Reared Trichogramma dendrolimi Matsumura (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) under Sustained Cold Stress
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Preparation of Artificial Medium and Insect Rearing
2.3. Experimental Set-Up, Sample Collection, and Biological Parameters Assessment
- –
- Pupation rate (%) = (number of pupae/total number of larvae observed per egg card) × 100.
- –
- Emergence rate (%) = (number of adults/(number of adults + dead pupae + dead larvae)) × 100.
- –
- Number of normal adults = total number of normal adults observed to emerge from three replicates (egg cards)/3.
- –
- Female proportion (%) = (total number of adults observed − number of male adults observed)/total number of adults observed × 100.
2.4. Total RNA Extraction and Cloning of the Full-Length cDNA
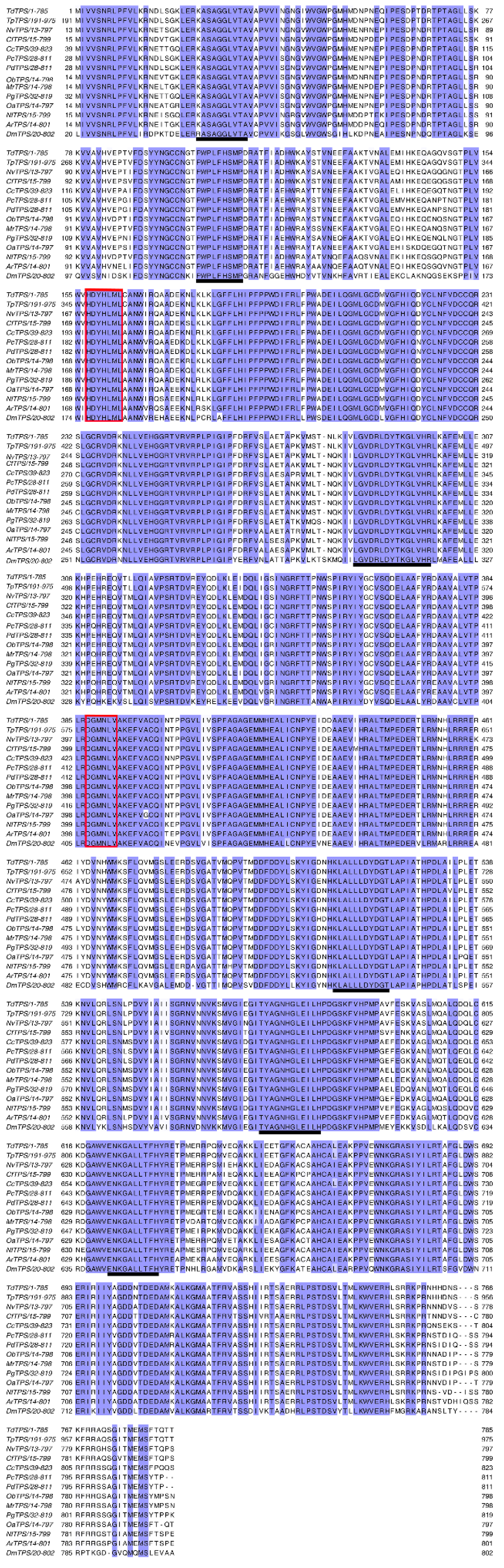
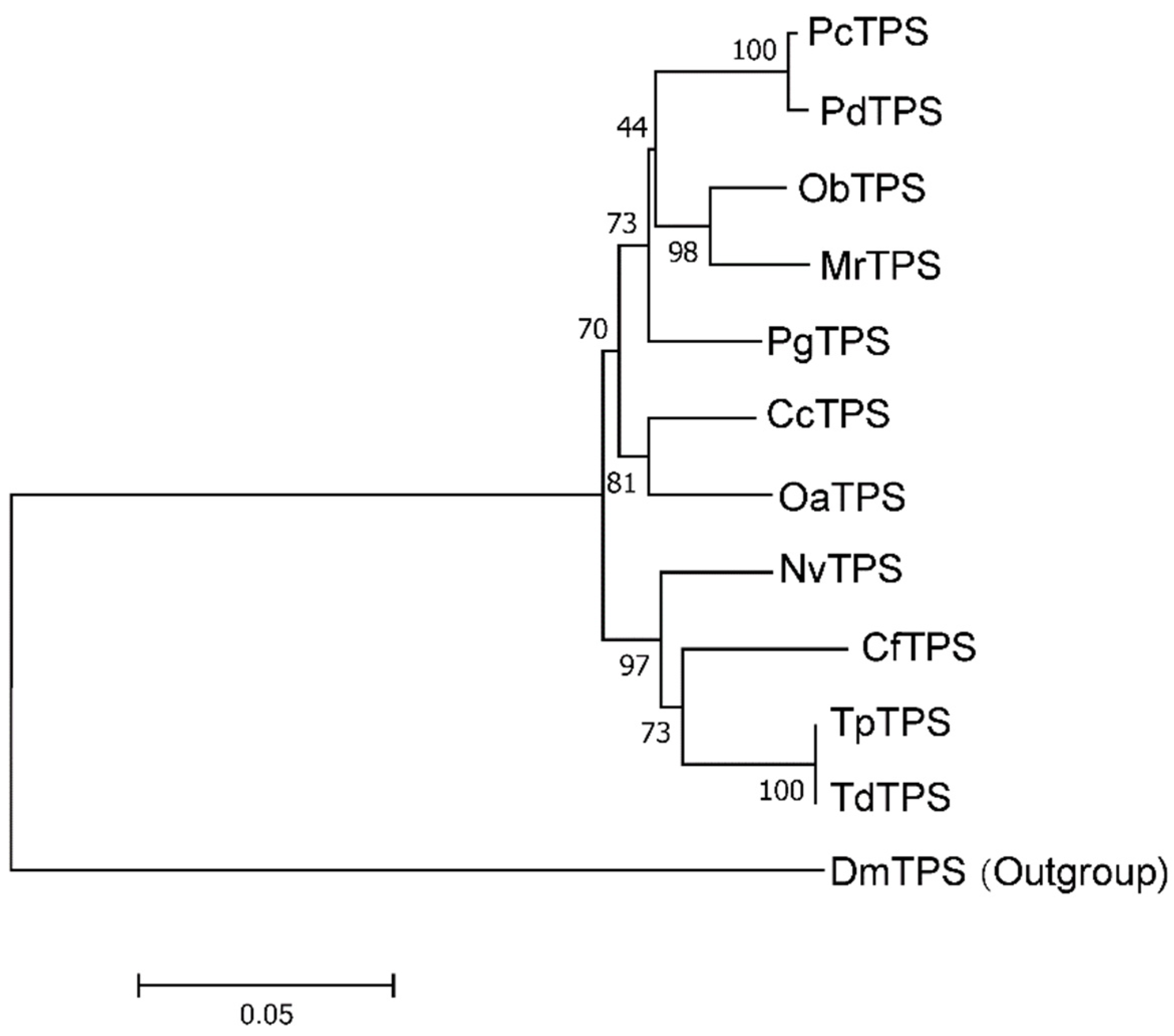
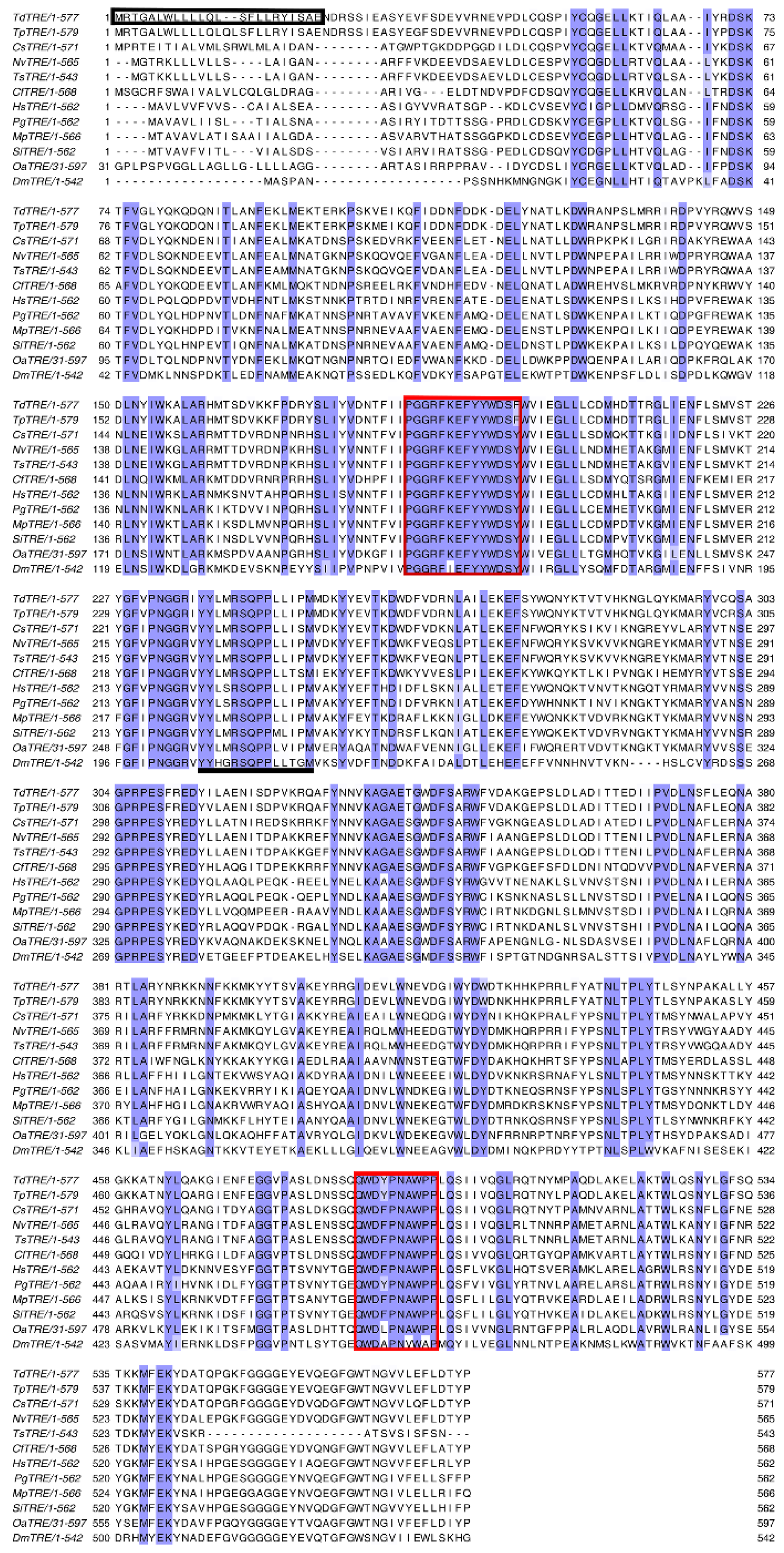
2.5. Sequence Analysis
2.6. Expression of TdTPS and TdTRE
2.7. Enzyme Activity Measurements
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Cloning and Characterization of Full-Length TdTPS and TdTRE cDNAs
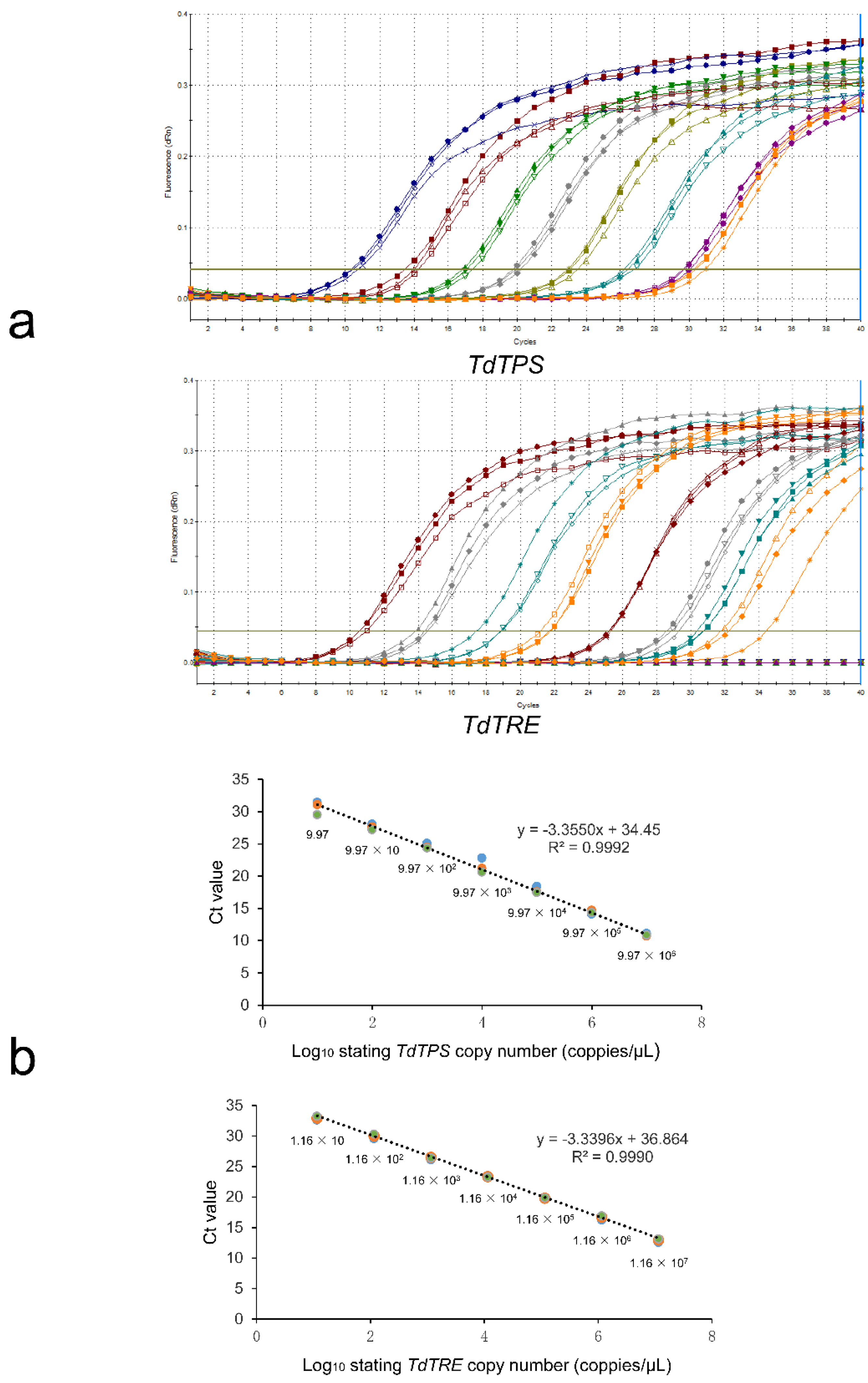
3.2. Standard Curve
3.3. Effect of Temperature on the Expression of TdTPS and TdTRE during Development
3.4. Changes in Enzyme Activities
3.5. In Vitro Rearing at Different Temperatures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rivero, A.; Casas, J. Incorporating physiology into parasitoid behavioral ecology: The allocation of nutritional resources. Res. Popul. Ecol. 1999, 41, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.N. Trehalose—The insect ‘blood’ sugar. Adv. Insect Physiol. 2003, 31, 203–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.B.; Hiszczynska-Sawicka, E.; Iline, I.I.; Novoselov, M.; Jiao, J.; Richards, N.K.; Hardwick, S. A modified enzymatic method for measuring insect sugars and the effect of storing samples in ethanol on subsequent trehalose measurements. Biol. Control 2008, 126, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Ruan, C.C.; Zang, L.S.; Shao, X.W.; Shi, S.S. Technological improvements for mass production of Trichogramma and current status of their applications for biological control on agricultural pests in China. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2015, 31, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, X.; Zang, L.S.; Du, W.M.; Hou, Y.Y.; Ruan, C.C.; Desneux, N. Advantages of diapause in Trichogramma dendrolimi mass production via eggs of the Chinese silkworm, Antheraea Pernyi. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cônsoli, F.L.; Grenier, S. In vitro Rearing of Egg Parasitoids. In Egg Parasitoids in Agroecosystems with Emphasis on Trichogramma; Cônsoli, F.L., Parra, J.R.P., Zucchi, R.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 293–313. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.Y.; Han, S.C.; Lü, X. Mass rearing Trichogramma on Artificial Media in China. In Biological Control of Pests Using Trichogramma: Current Status and Perspectives; Vinson, S.B., Greenberg, S.M., Liu, T.X., Rao, A., Volosciuc, L.F., Eds.; Northwest A & F University Press: Yangling, China, 2015; pp. 32–57. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, X.; Han, S.C.; Li, L.Y.; Grenier, S.; De Clercq, P. The potential of trehalose to replace insect hemolymph in artificial media for Trichogramma dendrolimi Matsumura (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Insect Sci. 2013, 20, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, X.; Han, S.C.; De Clercq, P.; Dai, J.Q.; Li, L.Y. Orthogonal array design for optimization of an artificial medium for In vitro rearing of Trichogramma dendrolimi. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2014, 152, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Han, S.C.; Li, Z.G.; Li, L.Y. Biological characters of Trichogramma dendrolimi (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) reared in vitro versus in vivo for thirty generations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lü, X.; Han, S.-C.; Li, L.-Y. Biochemical analyses of Trichogramma dendrolimi (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) In vitro and in vivo rearing for 10 generations. Fla. Entomol. 2015, 98, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Han, S.C.; Li, J.; Liu, J.S.; Li, Z.G. Effects of cold storage on the quality of Trichogramma dendrolimi Matsumura (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) reared on artificial medium. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, R.H. Influence of temperature on the growth and development of Trichogramma spp. on interspecific and intraspecific levels. Nat. Enemies Insects 1983, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.H.; Liu, S.S. The influence of temperature and humidity on the population increase of Trichogramma dendrolimi. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1993, 13, 328–333. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.L.; Wang, H.X.; Wang, Y.A.; Lu, H. Studies on the relationship of temperature and development of Trichogramma dendrolimi Matsumura. Zool. Res. 1981, 2, 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, G.H.; Zhou, S.X.; Chang, X.; Ding, Y. Difference of development characters of two Trichogramma Species at various temperatures. J. Northeast Agr. Sci. 2017, 42, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Chino, H. Temperature-dependent activation or inactivation of glycogen phosphorylase and synthase of fat body of the silkworm, Philosamia cynthia: The possible mechanism of the temperature-dependent interconversion between glycogen and trehalose. Insect Biochem. 1982, 12, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khani, A.; Moharramipour, S.; Barzegar, M. Cold tolerance and trehalose accumulation in overwintering larvae of the codling moth, Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2007, 104, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, B.; Qin, Z.; Shi, Z.K.; Wang, S.; Guo, X.J.; Wang, S.G.; Zhang, F. Trehalase in Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): Effects on beetle locomotory activity and the correlation with trehalose metabolism under starvation conditions. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2014, 49, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Hao, Y.J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Ren, S.; Si, F.L.; Chen, B. Gene cloning, characterization and expression and enzymatic activities related to trehalose metabolism during diapause of the onion maggot Delia antiqua (Diptera: Anthomyiidae). Gene 2015, 565, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Wei, P.; Zhao, L.N.; Shi, Z.K.; Shen, Q.D.; Yang, M.M.; Xie, G.Q.; Wang, S.G. Knockdown of five trehalase genes using RNA interference regulates the gene expression of the chitin biosynthesis pathways in Tribolium castaneum. BMC Biotechnol. 2016, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wingler, A. The function of trehalose biosynthesis in plants. Phytochemistry 2002, 60, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbein, A.D.; Pan, Y.T.; Pastuszak, I.; Carroll, D. New insights on trehalose: A multifunctional molecule. Glycobiology 2003, 13, 17R–27R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimpel, G.E.; Rosenheim, J.A.; Kattari, D. Adult feeding and lifetime reproductive success in the parasitoid Aphytis melinus. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1997, 83, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olson, D.; Andow, D. Larval crowding and adult nutrition effects on longevity and fecundity of female Trichogramma nubilale Ertle & Davis (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Environ. Entomol. 1998, 27, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, G.R. The biochemistry of sugars and polysaccharides in insects. Adv. Insect Physiol. 1967, 43, 287–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, J.; Hayward, S. Insect overwintering in a changing climate. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 980–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araj, S.E.; Wratten, S.; Lister, A.; Buckley, H.; Ghabeish, I. Searching behavior of an aphid parasitoid and its hyperparasitoid with and without floral nectar. Biol. Control 2011, 57, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsumasu, K.; Azuma, M.; Niimi, T.; Yamashita, O.; Yaginuma, T. Membrane-penetrating trehalase from silkworm Bombyx mori: Molecular cloning and localization in larval midgut. Insect Mol. Biol. 2005, 14, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Alves-Bezerra, M.; Rosas-Oliveira, R.; Majerowicz, D.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R.; Gondim, K.C. Gene identification and enzymatic properties of a membrane bound trehalase from the ovary of Rhodnius prolixus. Arch. Insect Biochem. 2012, 81, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.D.; Yang, M.M.; Xie, G.Q.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, L.Y.; Wang, S.G.; Tang, B. Excess trehalose and glucose affects chitin metabolism in brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens). J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindo, M.L.; Grenier, S. Production of Dipteran Parasitoids. In Mass Production of Beneficial Organisms: Invertebrates and Entomopathogens; Morales-Ramos, J.A., Guadalupe Rojas, M., Shapiro-Ilan, D.I., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2014; pp. 101–143. [Google Scholar]
- Dindo, M.L.; Stangolini, L.; Marchetti, E. A simplified artificial medium for the In vitro rearing of Exorista larvarum (Diptera: Tachinidae). Biocont. Sci. Tech. 2010, 20, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ma, E.; Behar, K.L.; Xu, T.; Haddad, G.G. Role of trehalose phosphate synthase in anoxia tolerance and development in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 3274–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, J.S. A trehalose 6-phosphate synthase gene of the hemocytes of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus: Cloning, the expression, its enzyme activity and relationship to hemolymph trehalose levels. Saline Syst. 2008, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, J.A.; Davies, G.J.; Bulone, V.; Henrissat, B.V. A classification of nucleotide-diphospho-sugar glycosyltransferases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem. J. 1997, 326, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.Y.; Merzendorfer, H.; Zhang, W.Q.; Zhang, J.Z.; Muthukrishnan, S. Biosynthesis, turnover, and functions of chitin in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 61, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, S.; Wei, P.; Xu, C.D.; Tang, B.; Zhang, F. Molecular cloning and expression in cold induction of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene in Harmonia axyridis (Pallas). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2012, 55, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bao, B.; Zhang, Z.F.; Yi, Y.Z.; Xu, W.H. Identification of a novel gene encoding the trehalose phosphate synthase in the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, B.; Chen, J.; Yao, Q.; Pan, Z.Q.; Xu, W.H.; Wang, S.G.; Zhang, W.Q. Characterization of a trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene from Spodoptera exigua and its function identification through RNA interference. J. Insect Physiol. 2010, 56, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Zheng, H.Z.; Xu, Q.; Zou, Q.; Wang, G.J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.G.; Zhang, Z.H. Cloning and pattern of expression of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase cDNA from Catantops pinguis (Orthoptera: Catantopidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2011, 108, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, C.; Wolf, C.; Bender, F.; Berger, M.; Noack, S.; Schmalz, S.; Ilg, T. Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase from the cat flea Ctenocephalides felis and Drosophila melanogaster: Gene identification, cloning, heterologous functional expression and identification of inhibitors by high throughput screening. Insect Mol. Biol. 2012, 21, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Tian, H.; Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W. Characterization and expression patterns of a membrane-bound trehalase from Spodoptera exigua. BMC Mol. Biol. 2008, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tatun, N.; Singtripop, T.; Tungjitwitayakul, J.; Sakurai, S. Regulation of soluble and membrane-bound trehalase activity and expression of the enzyme in the larval midgut of the bamboo borer Omphisa fuscidentalis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of putative soluble and membrane-bound trehalases in a hemipteran insect, Nilaparvata lugens. J. Insect Physiol. 2009, 55, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Wei, P.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.G.; Zhang, W.Q. Progress in gene features and functions of insect trehalases. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2012, 55, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, N.M.; Conyers, C.M.; Keen, J.N.; MacNicoll, A.D.; Smith, I.; Weaver, R.J. cDNAs encoding large venom proteins from the parasitoid wasp Pimpla hypochondriaca identified by random sequence analysis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 134, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, D.G.; Bleasby, A.J.; Fuchs, R. CLUSTAL V: Improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1992, 8, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julie, D.T.; Arnaud, M.; Andrew, W.; Jim, P.; Geoffrey, J.B.; Frédéric, P.; Olivier, P. MACSIMS: Multiple alignment of complete sequences information management system. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 2, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naruya, S.; Masatoshi, N. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.B.; Zhang, H.; Miranda, L.; Lin, S.J. Serious overestimation in quantitative PCR by circular (Supercoiled) plasmid standard: Microalgal pcna as the model gene. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godornes, C.; Leader, B.T.; Molini, B.J.; Centurion-Lara, A.; Lukehart, S.A. Quantitation of rabbit cytokine mRNA by Real-Time RT-PCR. Cytokine 2007, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, F.; Gao, Y.H.; Yuan, J.G. Research on activity measurement of trehalose synthase. Food Drug 2008, 10, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.S. Experiment no. 4A: Glucose Assay by Dinitrosalicylic Colorimetric Method. 2004. Available online: http://www.eng.umd.edu/~nsw/ench485/lab4a.htm (accessed on 27 January 2015).
- Su, Z.H.; Ikeda, M.; Sato, Y.; Saito, H.; Imai, K.; Isobe, M.; Yamashita, O. Molecular characterization of ovary trehalase of the silkworm, Bombyx mori and its transcriptional activation by diapause hormone. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1218, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Schlöder, P.; Steele, J.; Wegener, G. The regulation of trehalose metabolism in insects. Experientia 1996, 52, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.K.; Liu, X.J.; Xu, Q.Y.; Qin, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.G.; Tang, B. Two novel soluble trehalase genes cloned from Harmonia axyridis and regulation of the enzyme in a rapid changing temperature. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 198, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| TdTPS | 5Race-R | TTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTVN | |
| UPM-long | CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT | ||
| UPM-short | CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC | ||
| BD SMART II™ A Oligonucleotide | AAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGTACGCGGG | First full length cDNA synthesis for 5′cDNA amplification | |
| 3’NUP-R | AAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT | ||
| 3Race-R | AAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGTACT(30)VN | First full length cDNA synthesis for 3′cDNA or CDS amplification | |
| 5r-TPS-1R | AGTGGTCCGCGATGAAGGTCGC | ||
| 5r-TPS-2R | CCCAGATGCCATTTCCATTGATGAC | 5′ cDNA amplification | |
| cTPS-F | TCGGGCAGYATGATYGTCGT | ||
| cTPS-R | TGCCTCTCKACCCAYTTGAGCAT | ||
| cTPS-1R | TGTCTGTTACGTGGTCTGGGTGA | cds amplification | |
| 3r-TPS-R | CCACCACGACAACTCCTCGA | 3′ cDNA amplification | |
| qTPS-F | AATGGAAATGGCATCTGGGTC | ||
| qTPS-R | AGCAGCCGTTGTAGTACGAGTC | qRT-PCR | |
| TdTRE | 5r-TRE-1R | GTACAGCTCGTCCTTGTCATCG | |
| 5r-TRE-2R | CGCTAATTGTATCGTCTTTAGTAGTTCG | 5′ cDNA amplification | |
| cTRE-F | TTCCTGAAACAGTAGTMTTTAGTCG | ||
| cTRE-R | CTCAAAAGTACGTTGTCCAAATAGAT | cds amplification | |
| 3r-TRE-R | GTTGATATCAAGAAACCAACGAACG | 3′ cDNA amplification | |
| qTRE-F | AAGCGAAAGCCAAGCAAGGT | ||
| qTRE-R | TGATACACGGGGTCACGAATAC | qRT-PCR |
| Genes | Insects | GenBank Number | Identity |
|---|---|---|---|
| TdTPS | Trichogramma pretiosum | XP_014221069 | 100% |
| Nasonia vitripennis | XP_016837588 | 94.78% | |
| Copidosoma floridanum | XP_014213166 | 93.89% | |
| Cephus cinctus | XP_015588847 | 92.87% | |
| Osmia bicornis | XP_029055554 | 92.45%, | |
| Megachile rotundata | XP_003702415 | 92.32% | |
| Polistes canadensis | XP_014609582 | 92.21% | |
| Polistes dominula | XP_015172546 | 92.08% | |
| Orussus abietinus | XP_012281922 | 91.96% | |
| Pseudomyrmex gracilis | XP_020289281 | 91.85% | |
| Neodiprion lecontei | XP_015522281 | 91.30% | |
| Athalia rosae | XP_012252443 | 90.83% | |
| TdTRE | Trichogramma pretiosum | XP_014236786 | 97.61% |
| Trichomalopsis sarcophagae | OXU30694 | 67.52% | |
| Ceratosolen solmsi marchali | XP_011497766 | 67.18% | |
| Nasonia vitripennis | XP_008215783 | 65.94% | |
| Copidosoma floridanum | XP_014216724 | 60.41% | |
| Harpegnathos saltator | XP_011144292 | 57.38% | |
| Solenopsis invicta | XP_011170317 | 56.69% | |
| Monomorium pharaonic | XP_028048276 | 56.42% | |
| Pseudomyrmex gracilis | XP_020280302 | 56.31% | |
| Orussus abietinus | XP_012271873 | 55.95% |
| Parameters | Factors | df | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute expression of TdTPS | A | 2 | 2348.95 | <0.001 |
| B | 3 | 107.13 | <0.001 | |
| A × B | 6 | 29.89 | <0.001 | |
| Absolute expression of TdTRE | A | 2 | 462.30 | <0.001 |
| B | 3 | 337.41 | <0.001 | |
| A × B | 6 | 8.25 | <0.001 | |
| Activity of TdTPS | A | 2 | 25.24 | <0.001 |
| B | 3 | 18.12 | <0.001 | |
| A × B | 6 | 1.41 | 0.252 | |
| Activity of TdTRE | A | 2 | 7.10 | <0.001 |
| B | 3 | 39.86 | <0.001 | |
| A × B | 6 | 46.64 | <0.001 |
| Gene | Developmental Stage | Gene Absolute Expression (Copy Number (Coppies/μL)) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 °C | 16 °C | 27 °C | ||
| TdTPS | Larva | 46175.06 ± 6494.615 A c | 1419.43 ± 109.256 B b | 1082.30 ± 53.480 B b |
| Prepupa | 221227.25 ± 8108.441 A a | 9516.15 ± 473.110 B a | 1809.35 ± 72.933 B a | |
| Pupa | 84851.80 ± 5186.980 A b | 4581.10 ± 1153.243 B b | 859.34 ± 20.148 B bc | |
| Adult | 66806.48 ± 1349.493 A bc | 9716.46 ± 799.299 B a | 774.88 ± 37.565 C c | |
| TdTRE | Larva | 8.36 ± 0.933 A c | 9.72 ± 0.758 A b | 2.41 ± 0.566 B c |
| Prepupa | 126.08 ± 7.207 A b | 158.51 ± 10.949 A a | 17.78 ± 1.506 B a | |
| Pupa | 122.12 ± 4.192 A b | 136.25 ± 7.018 A a | 11.48 ± 2.241 B ab | |
| Adult | 162.04 ± 12.807 A a | 129.57 ± 3.250 A a | 11.19 ± 0.886 B b | |
| Enzymes | Developmental Stage | Activity [μg/mL (Extract/min)] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 °C | 16 °C | 27 °C | ||
| TdTPS | Larva | 0.15 ± 0.009 A ab | 0.14 ± 0.012 A b | 0.09 ± 0.014 A a |
| Prepupa | 0.12 ± 0.005 A b | 0.11 ± 0.009 A b | 0.08 ± 0.021 A a | |
| Pupa | 0.12 ± 0.015 A b | 0.11 ± 0.006 A b | 0.09 ± 0.006 A a | |
| Adult | 0.20 ± 0.014 A a | 0.19 ± 0.008 A a | 0.11 ± 0.010 B a | |
| TdTRE | Larva | 0.52 ± 0.032 A a | 0.44 ± 0.028 A a | 0.28 ± 0.022 B b |
| Prepupa | 0.22 ± 0.032 B b | 0.18 ± 0.016 B b | 0.49 ± 0.021 A a | |
| Pupa | 0.47 ± 0.019 A a | 0.50 ± 0.031 A a | 0.50 ± 0.012 A a | |
| Adult | 0.50 ± 0.013 A a | 0.50 ± 0.002 A a | 0.22 ± 0.012 B b | |
| Temperature | Developmental Duration (D) | Biological Parameters | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Egg | Larva | Prepupa | Pupa | Total Duration | Pupation Rate (%) | Emergence Rate (%) | Female Proportion (%) | Number of Normal Adults | |
| 27 °C | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 96.77 ± 0.391 a | 77.44 ± 1.451 a | 88.16 ± 0.555 a | 876.00 ± 48.03 a |
| 23 °C | 3 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 13 | 96.44 ± 0.441 ab | 75.16 ± 1.326 a | 87.50 ± 0.620 a | 805.33 ± 35.044 a |
| 20 °C | 4 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 18 | 96.48 ± 0.395 ab | 76.59 ± 0.728 a | 87.62 ± 0.949 a | 814.67 ± 13.119 a |
| 16 °C | 5 | 9 | 4 | 9 | 27 | 94.88 ± 1.35 ab | 75.86 ± 2.499 a | 88.00 ± 0.392 a | 904.00 ±72.746 a |
| 13 °C | 6 | 9 | 7 | 9 | 31 | 92.81 ± 1.041 b | 36.03 ± 1.159 b | 85.55 ± 0.724 a | 92.67 ± 5.897 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lü, X.; Han, S.-c.; Li, Z.-g.; Li, L.-y.; Li, J. Gene Characterization and Enzymatic Activities Related to Trehalose Metabolism of In Vitro Reared Trichogramma dendrolimi Matsumura (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) under Sustained Cold Stress. Insects 2020, 11, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110767
Lü X, Han S-c, Li Z-g, Li L-y, Li J. Gene Characterization and Enzymatic Activities Related to Trehalose Metabolism of In Vitro Reared Trichogramma dendrolimi Matsumura (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) under Sustained Cold Stress. Insects. 2020; 11(11):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110767
Chicago/Turabian StyleLü, Xin, Shi-chou Han, Zhi-gang Li, Li-ying Li, and Jun Li. 2020. "Gene Characterization and Enzymatic Activities Related to Trehalose Metabolism of In Vitro Reared Trichogramma dendrolimi Matsumura (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) under Sustained Cold Stress" Insects 11, no. 11: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110767
APA StyleLü, X., Han, S.-c., Li, Z.-g., Li, L.-y., & Li, J. (2020). Gene Characterization and Enzymatic Activities Related to Trehalose Metabolism of In Vitro Reared Trichogramma dendrolimi Matsumura (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) under Sustained Cold Stress. Insects, 11(11), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110767





