Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Immune Competence in Hemolymph of Bombyx mori Pupa Parasitized by Silkworm Maggot Exorista sorbillans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Sample Preparation
2.2. 2-DE and Protein Digestion
2.3. MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS/MS Analysis and Protein Identification
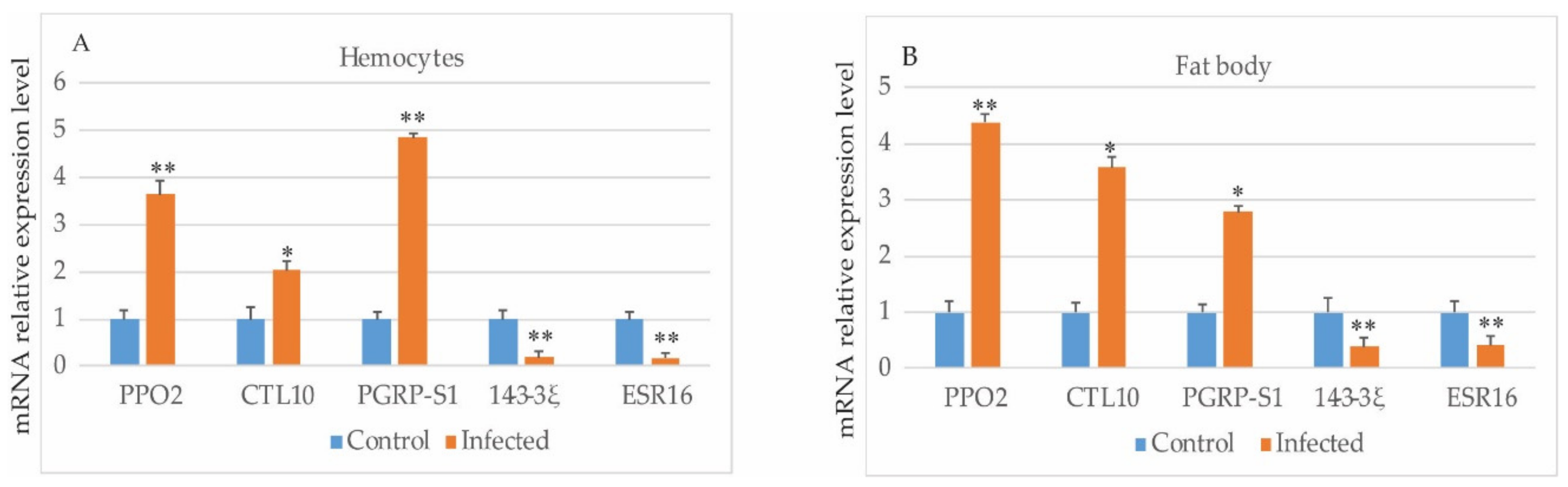
2.4. Quantitative PCR
3. Results
3.1. Identification of DEPs
3.2. GO Annotation and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis of the DEPs
3.3. Verification of Gene Expressions by Quantitative PCR
4. Discussion
4.1. Innate Immune System Enhanced Resistance to E. sorbillans Infestation
4.2. Apoptosis Triggered in Response to E. sorbillans Infestation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffmann, J.A.; Kafatos, F.C.; Janeway, C.A.; Ezekowitz, R.A. Phylogenetic perspectives in innate immunity. Science 1999, 284, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, J.A. The immune response of Drosophila. Nature 2003, 426, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osta, M.A.; Christophides, G.K.; Vlachou, D.; Kafatos, F.C. Innate immunity in the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae: Comparative and functional genomics. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 2551–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Ishibashi, J.; Fujita, K.; Nakajima, Y.; Sagisaka, A.; Tomimoto, K.; Suzuki, N.; Yoshiyama, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Iwasaki, T.; et al. A genome-wide analysis of genes and gene families involved in innate immunity of Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 1087–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Eleftherianos, I. Prolonged Storage Increases Virulence of Steinernema Entomopathogenic Nematodes Toward Drosophila Larvae. J. Parasitol. 2018, 104, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filosa, J.N.; Berry, C.T.; Ruthel, G.; Beverley, S.M.; Warren, W.C.; Tomlinson, C.; Myler, P.J.; Dudkin, E.A.; Povelones, M.L.; Povelones, M. Dramatic changes in gene expression in different forms of Crithidia fasciculata reveal potential mechanisms for insect-specific adhesion in kinetoplastid parasites. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xia, Q.; He, X.; Dai, M.; Ruan, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, G.; Yuan, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, R.; et al. SilkDB: A knowledgebase for silkworm biology and genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D399–D402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, A.N.; Anitha, J.; Awasthi, A.K.; Babu, M.A.; Geetha, M.N.; Arun, H.K.; Chandrashekhar, S.; Rao, G.C.; Vijayaprakash, N.B. Activation of autophagic programmed cell death and innate immune gene expression reveals immuno-competence of integumental epithelium in Bombyx mori infected by a dipteran parasitoid. Cell Tissue Res. 2013, 352, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, A.; Pradeep, A.N.R.; Awasthi, A.K.; Murthy, G.N.; Ponnuvel, K.M.; Sasibhushan, S.; Rao, G.C. Coregulation of host-response genes in integument: Switchover of gene expression correlation pattern and impaired immune responses induced by dipteran parasite infection in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Appl. Genet. 2014, 55, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooja, M.; Pradeep, A.N.R.; Hungund, S.P.; Sagar, C.; Ponnuvel, K.M.; Awasthi, A.K.; Trivedy, K. Oxidative stress and cytotoxicity elicited lipid peroxidation in hemocytes of Bombyx mori larva infested with dipteran parasitoid, Exorista bombycis. Acta Parasitol. 2017, 62, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makwana, P.; Pradeep, A.N.; Hungund, S.P.; Ponnuvel, K.M.; Trivedy, K. The dipteran parasitoid Exorista bombycis induces pro- and anti-oxidative reactions in the silkworm Bombyx mori: Enzymatic and genetic analysis. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, J.; Pradeep, A.R.; Sivaprasad, V. Upregulation of Atg5 and AIF gene expression in synchronization with programmed cellular death events in integumental epithelium of Bombyx mori induced by a dipteran parasitoid infection. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2014, 104, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiba, H.; Uchida, D.; Kobayashi, H.; Natori, M. Involvement of cathepsin B- and L-like proteinases in silk gland histolysis during metamorphosis of Bombyx mori. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 390, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Srivastava, P.; Sirisena, P.; Dubey, S.K.; Kumar, R.; Shrinet, J.; Sunil, S. Mosquito Innate Immunity. Insects 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, A.; Wilm, M.; Vorm, O.; Mann, M. Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Yu, H.Z.; Xu, J.P.; Zhang, S.Z.; Yu, D.; Liu, M.H.; Wang, L.L. Comparative Subcellular Proteomics Analysis of Susceptible and Near-isogenic Resistant Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera) Larval Midgut Response to BmNPV infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevillon, E.; Silventoinen, V.; Pillai, S.; Harte, N.; Mulder, N.; Apweiler, R.; Lopez, R. InterProScan: Protein domains identifier. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W116–W120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotz, S.; Garcia-Gomez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Williams, T.D.; Nagaraj, S.H.; Nueda, M.J.; Robles, M.; Talon, M.; Dopazo, J.; Conesa, A. High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3420–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Sato, Y.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D109–D114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Qin, S.; Xu, P.; Zhang, G. Identifying potential maternal genes of Bombyx mori using digital gene expression profiling. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Dong, Z.; Duan, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Xia, Q. Genome-wide identification and immune response analysis of serine protease inhibitor genes in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, Y.; Kanamori, Y.; Kiuchi, M.; Kamimura, M. Effects of silkworm paralytic peptide on in vitro hematopoiesis and plasmatocyte spreading. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2003, 52, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.G.; Chen, K.P.; Yao, Q.; Gao, G.T.; Xu, J.P.; Chen, H.Q. Cloning and characterization of Bombyx mori PP-BP a gene induced by viral infection. Yi Chuan Xue Bao Acta Genet. Sin. 2006, 33, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.F.; Li, Y.N.; Jia, R.; Cui, W.Z.; Mu, Z.M.; Zhang, Z.F. Alternative splicing of the antitrypsin gene in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 2793–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, D.; Wang, X.; Shang, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Wu, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J. Involvement of a versatile pattern recognition receptor, apolipophorin-III in prophenoloxidase activation and antibacterial defense of the Chinese oak silkworm, Antheraea pernyi. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 65, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Kusakabe, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Miyagawa, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Mon, H.; Nho, S.K.; Koga, K. Molecular cloning and characterization of the translationally controlled tumor protein gene in Bombyx mori. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 139, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Hu, C.; Hua, X.; Song, L.; Xia, Q. Translationally controlled tumor protein, a dual functional protein involved in the immune response of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, T.; Liu, G.; Kang, D.; Ekengren, S.; Steiner, H.; Hultmark, D. A family of peptidoglycan recognition proteins in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13772–13777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royet, J.; Reichhart, J.M.; Hoffmann, J.A. Sensing and signaling during infection in Drosophila. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2005, 17, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, S.; Hoege, C.; Pyrowolakis, G.; Jentsch, S. SUMO, ubiquitin’s mysterious cousin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.P.; Hao, W.; He, D.; Xu, Y.S. Smt3 is required for the immune response of silkworm, Bombyx mori. Biochimie 2010, 92, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaitre, B.; Hoffmann, J. The host defense of Drosophila melanogaster. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 697–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Gregorio, E.; Han, S.J.; Lee, W.J.; Baek, M.J.; Osaki, T.; Kawabata, S.; Lee, B.L.; Iwanaga, S.; Lemaitre, B.; Brey, P.T. An immune-responsive Serpin regulates the melanization cascade in Drosophila. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Q.M.; Yang, B.; Xu, Q.Y.; Li, X.Q.; Lu, Z.Q.; Wang, C.S.; Huang, Y.P.; Soderhall, K.; Ling, E.J. Hindgut Innate Immunity and Regulation of Fecal Microbiota through Melanization in Insects. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 14270–14279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koizumi, N.; Imamura, M.; Kadotani, T.; Yaoi, K.; Iwahana, H.; Sato, R. The lipopolysaccharide-binding protein participating in hemocyte nodule formation in the silkworm Bombyx mori is a novel member of the C-type lectin superfamily with two different tandem carbohydrate-recognition domains. FEBS Lett. 1999, 443, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.Q.; Kanost, M.R. Immulectin-2, a lipopolysaccharide-specific lectin from an insect, Manduca sexta, is induced in response to gram-negative bacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 37373–37381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, A.; Miyazawa, S.; Kitami, M.; Tabunoki, H.; Ueda, K.; Sato, R. Characterization of a novel C-type lectin, Bombyx mori multibinding protein, from the B. mori hemolymph: Mechanism of wide-range microorganism recognition and role in immunity. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4594–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gondi, C.S.; Kandhukuri, N.; Kondraganti, S.; Gujrati, M.; Olivero, W.C.; Dinh, D.H.; Rao, J.S. RNA interference-mediated simultaneous down-regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor and cathepsin B induces caspase-8-mediated apoptosis in SNB19 human glioma cells. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 3197–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Zali, A.; Hashemi, J.; Oraee-Yazdani, S.; Akbari, A. Down-regulation of 14-3-3 zeta sensitizes human glioblastoma cells to apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 2018, 23, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakannan, P.; Eftekharpour, E. Differential redox sensitivity of cathepsin B and L holds the key to autophagy-apoptosis interplay after Thioredoxin reductase inhibition in nutritionally stressed SH-SY5Y cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.M.; Bae, E.; Ahn, S.G.; Pang, K.; Park, Y.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Ooshima, A.; Park, B.; Kim, J.; et al. Co-chaperone BAG2 Determines the Pro-oncogenic Role of Cathepsin B in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 2952–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mackintosh, C. Dynamic interactions between 14-3-3 proteins and phosphoproteins regulate diverse cellular processes. Biochem. J. 2004, 381, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulvila, J.; Vanha-aho, L.M.; Kleino, A.; Vaha-Makila, M.; Vuoksio, M.; Eskelinen, S.; Hultmark, D.; Kocks, C.; Hallman, M.; Parikka, M.; et al. Cofilin regulator 14-3-3zeta is an evolutionarily conserved protein required for phagocytosis and microbial resistance. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.J.; Lee, J.S.; Cui, M.N.; Yun, H.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H. BIS targeting induces cellular senescence through the regulation of 14-3-3 zeta/STAT3/SKP2/p27 in glioblastoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasekara, V.K.; Panek, D.J.; Broadbent, D.G.; Mortenson, J.B.; Mathis, A.D.; Logan, G.N.; Prince, J.T.; Thomson, D.M.; Thompson, J.W.; Andersen, J.L. Metabolic-stress-induced rearrangement of the 14-3-3zeta interactome promotes autophagy via a ULK1- and AMPK-regulated 14-3-3zeta interaction with phosphorylated Atg9. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 34, 4379–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trujillo-Ocampo, A.; Cazares-Raga, F.E.; Del Angel, R.M.; Medina-Ramirez, F.; Santos-Argumedo, L.; Rodriguez, M.H.; Hernandez-Hernandez, F.C. Participation of 14-3-3epsilon and 14-3-3zeta proteins in the phagocytosis, component of cellular immune response, in Aedes mosquito cell lines. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niemantsverdriet, M.; Wagner, K.; Visser, M.; Backendorf, C. Cellular functions of 14-3-3 zeta in apoptosis and cell adhesion emphasize its oncogenic character. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serbielle, C.; Moreau, S.; Veillard, F.; Voldoire, E.; Bezier, A.; Mannucci, M.A.; Volkoff, A.N.; Drezen, J.M.; Lalmanach, G.; Huguet, E. Identification of parasite-responsive cysteine proteases in Manduca sexta. Biol. Chem. 2009, 390, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.D.; Hui, M.; Cui, Z.X.; Liu, Y.; Song, C.W.; Shi, G.H. Comparative transcriptomic analysis provides insights into the molecular basis of the metamorphosis and nutrition metabolism change from zoeae to megalopae in Eriocheir sinensis. Comp. Biochem. Phys. D 2015, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Spot No. | Protein Name | SilkDB Accession No. | NCBI Accession No. | Theoretical (kDa/pI) | Sequence Coverage(%) | Peptides Identified | Fold Change | Signal Peptide | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upregulated | |||||||||
| 1 | phenoloxidase subunit 2 precursor | BGIBMGA013115-PA | gi|112983448 | 80.12/5.62 | 18 | 11 | 3.66 | - | Serine protease involved in melanization |
| 2 | very low-density lipoprotein receptor isoform 1 precursor | BGIBMGA006214-PA | gi|160333138 | 61.54/5.20 | 4 | 3 | 4.53 | - | Chitin metabolic |
| 3 | 60 kDa heat shock protein, mitochondrial-like | BGIBMGA007349-PA | gi|512896628 | 61.06/5.51 | 22 | 8 | 2.61 | - | Protein refolding |
| 4 | paralytic peptide binding protein | BGIBMGA010168-PA | gi|112983896 | 50.01/6.33 | 30 | 11 | 3.17 | - | Extracellular region |
| 5 | uncharacterized protein LOC101739845 | BGIBMGA002604-PA | gi|512931715 | 49.40/5.42 | 15 | 6 | 2.94 | - | Farnesoic acid o-methyltransferase |
| 6 | antitrypsin | BGIBMGA009953-PA | gi|253809709 | 43.43/5.41 | 26 | 8 | 9.88 | - | Peptidase inhibitor activity |
| 7 | failed axon connections isoform X1 | BGIBMGA000552-PA | gi|512921311 | 42.89/5.31 | 11 | 3 | 3.64 | - | N/A |
| 8 | proliferation-associated protein 2G4 | BGIBMGA002493-PA | gi|512926720 | 42.14/7.13 | 33 | 9 | 3.24 | - | Cellular process |
| 9 | DNA supercoiling factor | BGIBMGA001107-PA | gi|347326520 | 38.02/4.48 | 40 | 12 | 2.83 | - | Calcium ion binding |
| 10 | C-type lectin 10 | BGIBMGA006768-PA | gi|148298818 | 36.56/5.53 | 6 | 2 | 3.59 | - | Carbohydrate binding |
| 11 | 32 kDa apolipoprotein precursor | BGIBMGA002703-PA | gi|226501956 | 32.09/4.79 | 7 | 3 | 2.91 | 1 | Pigment binding |
| 12 | spermidine synthase | BGIBMGA005897-PA | gi|512899761 | 32.43/5.54 | 26 | 8 | 3.15 | - | Catalytic activity |
| 13 | small glutamine-rich tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein alpha-like | BGIBMGA010000-PA | gi|827549620 | 31.43/4.88 | 8 | 2 | 5.77 | - | Protein binding |
| 14 | uncharacterized protein LOC778506 isoform X1 | — | gi|827559778 | 30.66/4.31 | 9 | 2 | 4.22 | - | Cell surface glycoprotein |
| 15 | gasp precursor | BGIBMGA007677-PA | gi|114052326 | 29.09/4.82 | 7 | 1 | 24.35 | 1 | Chitin binding |
| 16 | uncharacterized protein LOC778506 isoform X2 | — | gi|827559780 | 28.45/4.25 | 9 | 2 | 4.15 | 1 | N/A |
| 17 | low molecular mass 30 kDa lipoprotein 21G1 isoform X1 | BGIBMGA004395-PA | gi|827538310 | 30.24/6.84 | 33 | 9 | 5.78 | 1 | Extracellular region |
| 18 | low molecular 30 kDa lipoprotein PBMHPC-19-like precursor | BGIBMGA004398-PA | gi|525343846 | 28.50/5.72 | 13 | 3 | 5.77 | 1 | Extracellular region |
| 19 | charged multivesicular body protein 5 | BGIBMGA002470-PA | gi|512926615 | 25.26/4.71 | 16 | 2 | 4.34 | - | Protein transport |
| 20 | Rab7 | BGIBMGA007712-PA | gi|114051368 | 23.42/5.16 | 4 | 1 | 8.85 | - | Small GTPase mediated signal transduction |
| 21 | uncharacterized protein LOC101746349 | BGIBMGA006731-PA | gi|512923633 | 20.06/4.56 | 27 | 4 | 5.38 | 1 | N/A |
| 22 | apolipophorin III | BGIBMGA013108-PA | gi|112983018 | 20.73/9.04 | 29 | 7 | 7.04 | 1 | Defense response |
| 23 | translationallycontrolled tumor protein | BGIBMGA003073-PA | gi|112982880 | 19.86/4.66 | 13 | 2 | 31.59 | - | Pathogen binding |
| 24 | translation initiation factor 5A | BGIBMGA007469-PA | gi|112982832 | 17.52/5.16 | 14 | 2 | 2.93 | - | Translational frameshifting |
| 25 | abnormal wing disc-like protein | BGIBMGA007701-PA | gi|153791847 | 17.31/6.74 | 26 | 5 | 11.04 | - | Nucleoside diphosphate phosphorylation |
| 26 | cyclophilin-like protein | BGIBMGA002429-PA | gi|60592747 | 17.96/7.74 | 17 | 2 | 3.81 | - | Protein peptidyl-prolyl isomerization |
| 27 | peptidoglycan recognition protein | BGIBMGA008038-PA | gi|112983994 | 21.63/6.70 | 33 | 6 | 3.32 | 1 | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase activity |
| 28 | probable pterin-4-alpha-carbinolamine dehydratase | — | gi|512899129 | 17.93/9.94 | 30 | 3 | 18.51 | - | 4-α-hydroxytetrahydrobiopterin dehydratase activity |
| 29 | odorant-binding protein 6 isoform X1 | BGIBMGA008354-PA | gi|827551076 | 15.96/4.94 | 18 | 3 | 3.41 | 1 | Odorant binding |
| 30 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ZNRF2 | BGIBMGA011980-PA | gi|512897556 | 21.91/5.42 | 7 | 1 | 4.56 | - | Zinc ion binding |
| 31 | ribosomal protein S12 | BGIBMGA004374-PA | gi|112982671 | 15.03/5.79 | 24 | 2 | 4.62 | - | Structural constituent of ribosome |
| 32 | chemosensory protein 4 precursor | BGIBMGA004045-PA | gi|112983094 | 14.55/5.17 | 8 | 1 | 2.51 | 1 | Transporters of pheromone/odor molecules |
| 33 | chemosensory protein 7 precursor | BGIBMGA004041-PA | gi|112983052 | 13.52/4.97 | 18 | 3 | 4.77 | - | Transporters of pheromone/odor molecules |
| 34 | FK506-binding protein | BGIBMGA004331-PA | gi|114051243 | 11.82/7.85 | 43 | 4 | 10.66 | - | Isomerase activity |
| 35 | uncharacterized protein LOC101736984 isoform X3 | BGIBMGA007627-PA | gi|512916631 | 11.18/5.02 | 9 | 1 | 3.53 | - | N/A |
| 36 | ubiquitin-like protein SMT3 | BGIBMGA011581-PA | gi|112983974 | 10.31/5.29 | 23 | 3 | 2.73 | - | Protein binding |
| Downregulated | |||||||||
| 37 | heat shock protein 83 | BGIBMGA004612-PA | gi|112983556 | 82.42/4.98 | 3 | 2 | 0.11 | - | Unfolded protein binding |
| 38 | ATP synthase | BGIBMGA001853-PA | gi|114052278 | 59.66/9.21 | 4 | 2 | 0.21 | - | ATP binding |
| 39 | serine proteinase-like protein isoform X1 | BGIBMGA009551-PA | gi|827563139 | 44.88/5.73 | 15 | 6 | 0.01 | 1 | Serine-type endopeptidase activity |
| 40 | ornithine aminotransferase, mitochondrial | BGIBMGA003564-PA | gi|512922127 | 44.70/6.36 | 5 | 2 | 0.21 | - | Pyridoxal phosphate binding |
| 41 | aldose 1-epimerase | BGIBMGA009232-PA | gi|512891308 | 39.71/5.88 | 27 | 7 | 0.28 | - | Transaminase activity |
| 42 | aldo-ketoreductase AKR2E4-like isoform X1 | BGIBMGA001348-PA | gi|512908850 | 38.99/5.82 | 10 | 5 | 0.26 | 1 | Oxidoreductase activity |
| 43 | cathepsin B | BGIBMGA007061-PA | gi|112983908 | 37.56/5.95 | 18 | 5 | 0.17 | - | Regulation of catalytic activity |
| 44 | aldose reductase-like isoform X1 | BGIBMGA012152-PA | gi|512901366 | 35.84/6.10 | 20 | 6 | 0.39 | - | Oxidoreductase activity |
| 45 | 14-3-3 protein zeta | BGIBMGA002644-PA | gi|114050901 | 28.17/4.90 | 6 | 2 | 0.21 | - | Protein domain specific binding |
| 46 | vacuolar ATP synthase subunit E | BGIBMGA010247-PA | gi|114052088 | 26.12/8.98 | 17 | 3 | 0.19 | - | ATP hydrolysis |
| 47 | tyrosine-protein phosphatase Lar | BGIBMGA012106-PA | gi|512933991 | 22.75/6.29 | 7 | 1 | 0.18 | 1 | Protein binding |
| 48 | diapause bioclock protein | BGIBMGA002907-PA | gi|68144076 | 18.29/6.12 | 27 | 3 | 0.15 | 1 | Superoxide dismutase activity |
| 49 | ecdysteroid-regulated 16 kDa protein precursor | BGIBMGA008405-PA | gi|151301100 | 15.82/5.92 | 12 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | Ecdysteroid level regulated |
| 50 | chemosensory protein 5 precursor | BGIBMGA004065-PA | gi|112983054 | 14.26/6.89 | 22 | 3 | 0.23 | 1 | RNA-binding |
| Number | Pathway | Pathway ID | Accession No. | Description | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Galactose metabolism | ko00052 | gi|512891308 | aldose 1-epimerase | 0.28 |
| gi|512908850 | aldehyde reductase | 0.26 | |||
| gi|512901366 | aldehyde reductase | 0.39 | |||
| 2 | Huntington’s disease | ko05016 | gi|60592747 | peptidyl-prolyl isomerase | 3.81 |
| gi|114052278 | ATPase | 0.21 | |||
| gi|68144076 | superoxide dismutase | 0.15 | |||
| 3 | Glycerolipid metabolism | ko00561 | gi|512908850 | aldehyde reductase | 0.26 |
| gi|512901366 | aldehyde reductase | 0.39 | |||
| 4 | Longevity regulating pathway—worm | ko04212 | gi|512896628 | chaperonin | 2.61 |
| gi|114050901 | protein binding | 0.21 | |||
| 5 | Lysosome | ko04142 | gi|112983908 | cathepsin B | 0.17 |
| gi|151301100 | Niemann–Pick C2 protein | 0.01 | |||
| 6 | Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | ko00040 | gi|512908850 | aldehyde reductase | 0.26 |
| gi|512901366 | aldehyde reductase | 0.39 | |||
| 7 | Fructose and mannose metabolism | ko00051 | gi|512908850 | aldehyde reductase | 0.26 |
| gi|512901366 | aldehyde reductase | 0.39 | |||
| 8 | Parkinson’s disease | ko05012 | gi|60592747 | peptidyl-prolyl isomerase | 3.81 |
| gi|114052278 | ATPase | 0.21 | |||
| 9 | Amoebiasis | ko05146 | gi|253809709 | serpin B | 9.88 |
| gi|114051368 | Ras-related protein | 8.85 | |||
| 10 | Oxidative phosphorylation | ko00190 | gi|114052278 | ATPase | 0.21 |
| gi|114052088 | ATPase | 0.19 | |||
| 11 | Tuberculosis | ko05152 | gi|512896628 | chaperonin | 2.61 |
| gi|114051368 | Ras-related protein | 8.85 | |||
| 12 | Antigen processing and presentation | ko04612 | gi|112983556 | molecular chaperone | 0.11 |
| gi|112983908 | cathepsin B | 0.17 | |||
| 13 | Phagosome | ko04145 | gi|114051368 | Ras-related protein | 8.85 |
| gi|114052088 | ATPase | 0.19 | |||
| 14 | Endocytosis | ko04144 | gi|512926615 | charged multivesicular body protein | 4.34 |
| gi|114051368 | Ras-related protein | 8.85 | |||
| 15 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | ko04151 | gi|112983556 | molecular chaperone | 0.11 |
| gi|114050901 | protein binding | 0.21 | |||
| 16 | Arginine and proline metabolism | ko00330 | gi|512899761 | spermidine synthase | 3.15 |
| gi|512922127 | ornithine–oxo-acid transaminase | 0.21 | |||
| 17 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | ko04621 | gi|112983556 | molecular chaperone | 0.11 |
| 18 | Legionellosis | ko05134 | gi|512896628 | chaperonin | 2.61 |
| 19 | Epstein-Barr virus infection | ko05169 | gi|114050901 | protein binding | 0.21 |
| 20 | Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis | ko00010 | gi|512891308 | aldose 1-epimerase | 0.28 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, P.-Z.; Zhang, M.-R.; Gao, L.; Wu, Y.-C.; Qian, H.-Y.; Li, G.; Xu, A.-Y. Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Immune Competence in Hemolymph of Bombyx mori Pupa Parasitized by Silkworm Maggot Exorista sorbillans. Insects 2019, 10, 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10110413
Xu P-Z, Zhang M-R, Gao L, Wu Y-C, Qian H-Y, Li G, Xu A-Y. Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Immune Competence in Hemolymph of Bombyx mori Pupa Parasitized by Silkworm Maggot Exorista sorbillans. Insects. 2019; 10(11):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10110413
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Ping-Zhen, Mei-Rong Zhang, Li Gao, Yang-Chun Wu, He-Ying Qian, Gang Li, and An-Ying Xu. 2019. "Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Immune Competence in Hemolymph of Bombyx mori Pupa Parasitized by Silkworm Maggot Exorista sorbillans" Insects 10, no. 11: 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10110413
APA StyleXu, P.-Z., Zhang, M.-R., Gao, L., Wu, Y.-C., Qian, H.-Y., Li, G., & Xu, A.-Y. (2019). Comparative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Immune Competence in Hemolymph of Bombyx mori Pupa Parasitized by Silkworm Maggot Exorista sorbillans. Insects, 10(11), 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10110413




