Precision Machining of Different Metals by Plasma Electrolytic Polishing: A Review for Improving Surface Smoothness and Properties
Abstract
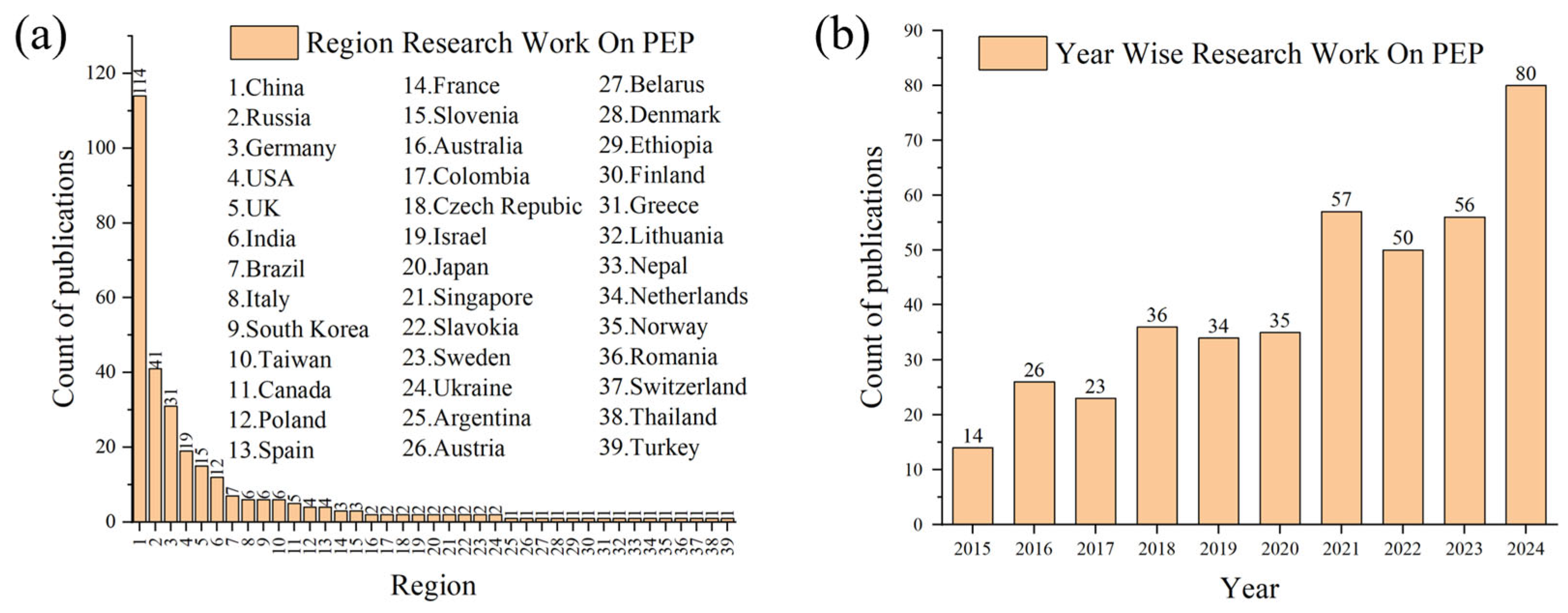
1. Introduction
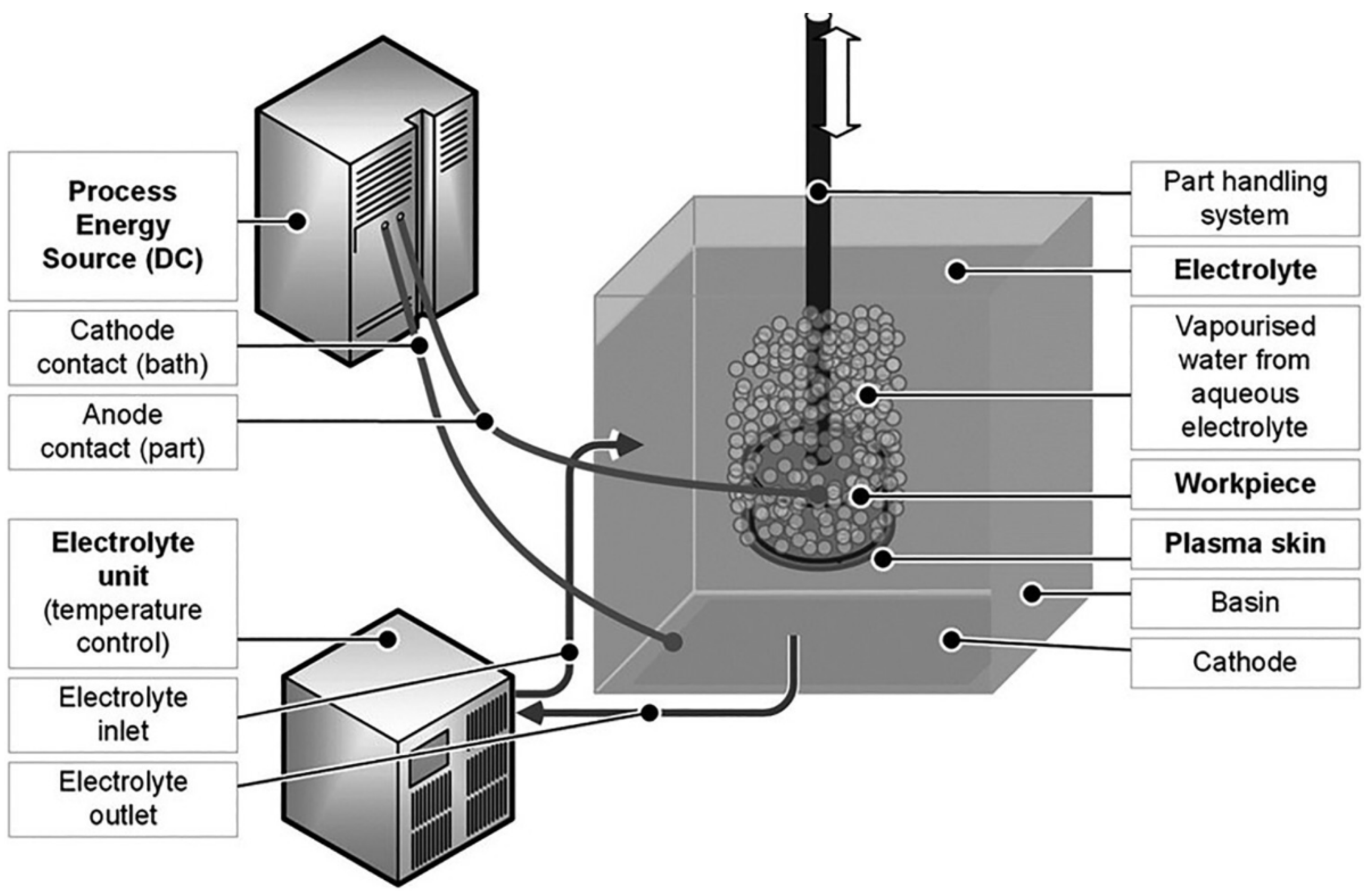
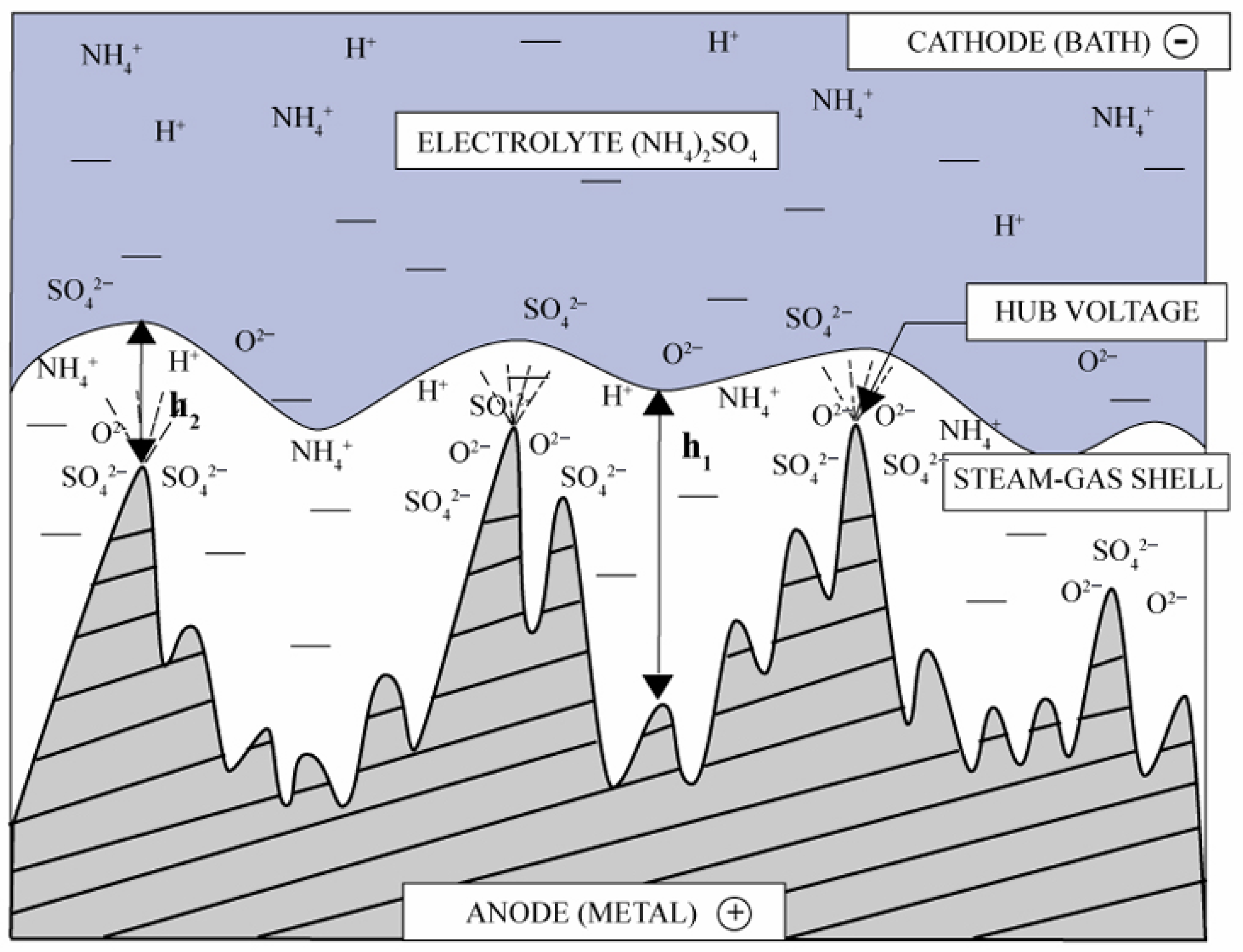
2. Mechanism of Plasma Electrolytic Polishing
2.1. Advantages and Disadvantages of PEP
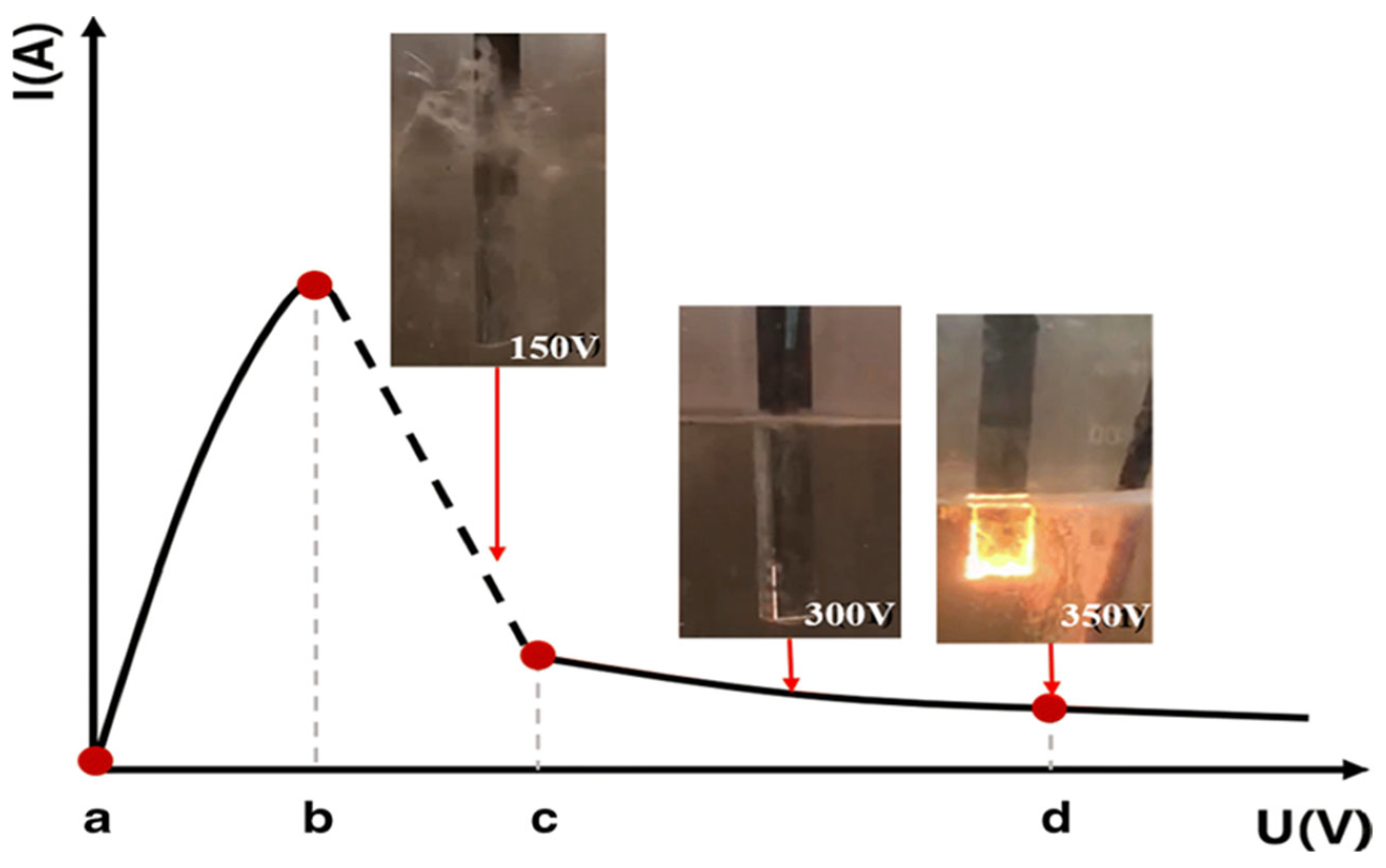
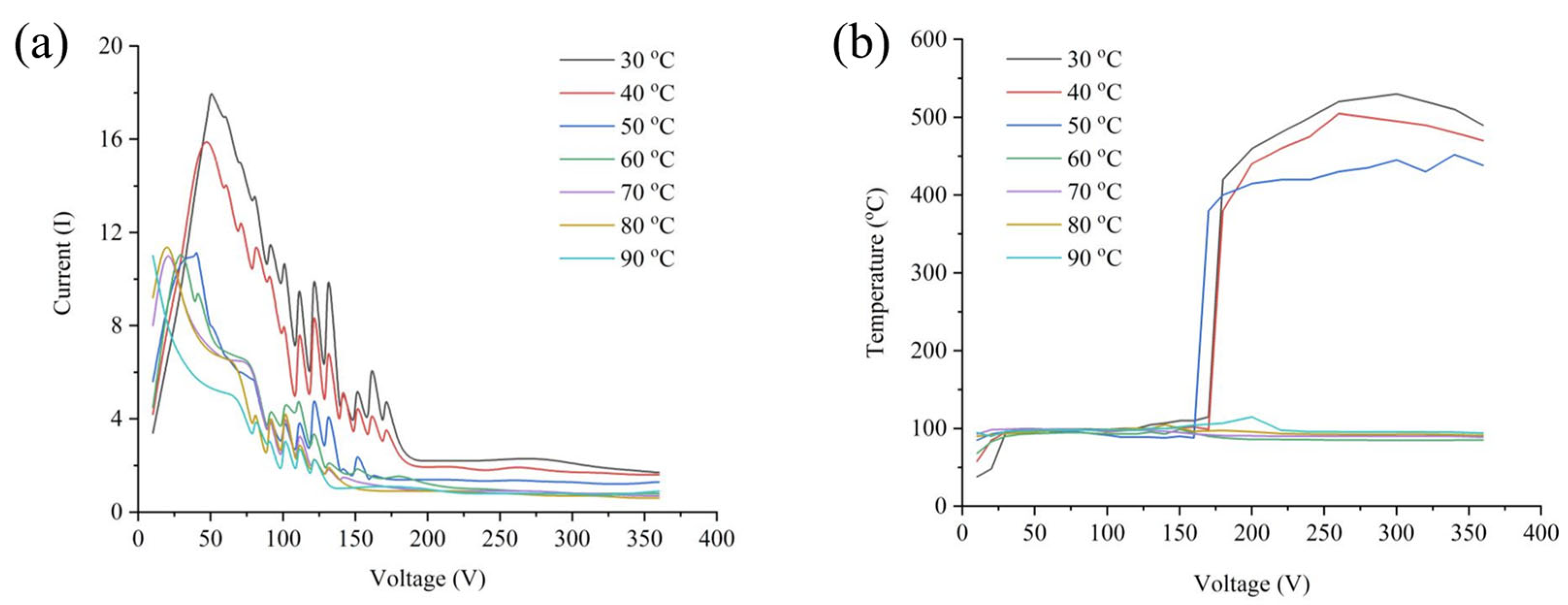
2.2. Voltage-Current Characteristics of PEP
2.3. PEP Discharge Mechanism
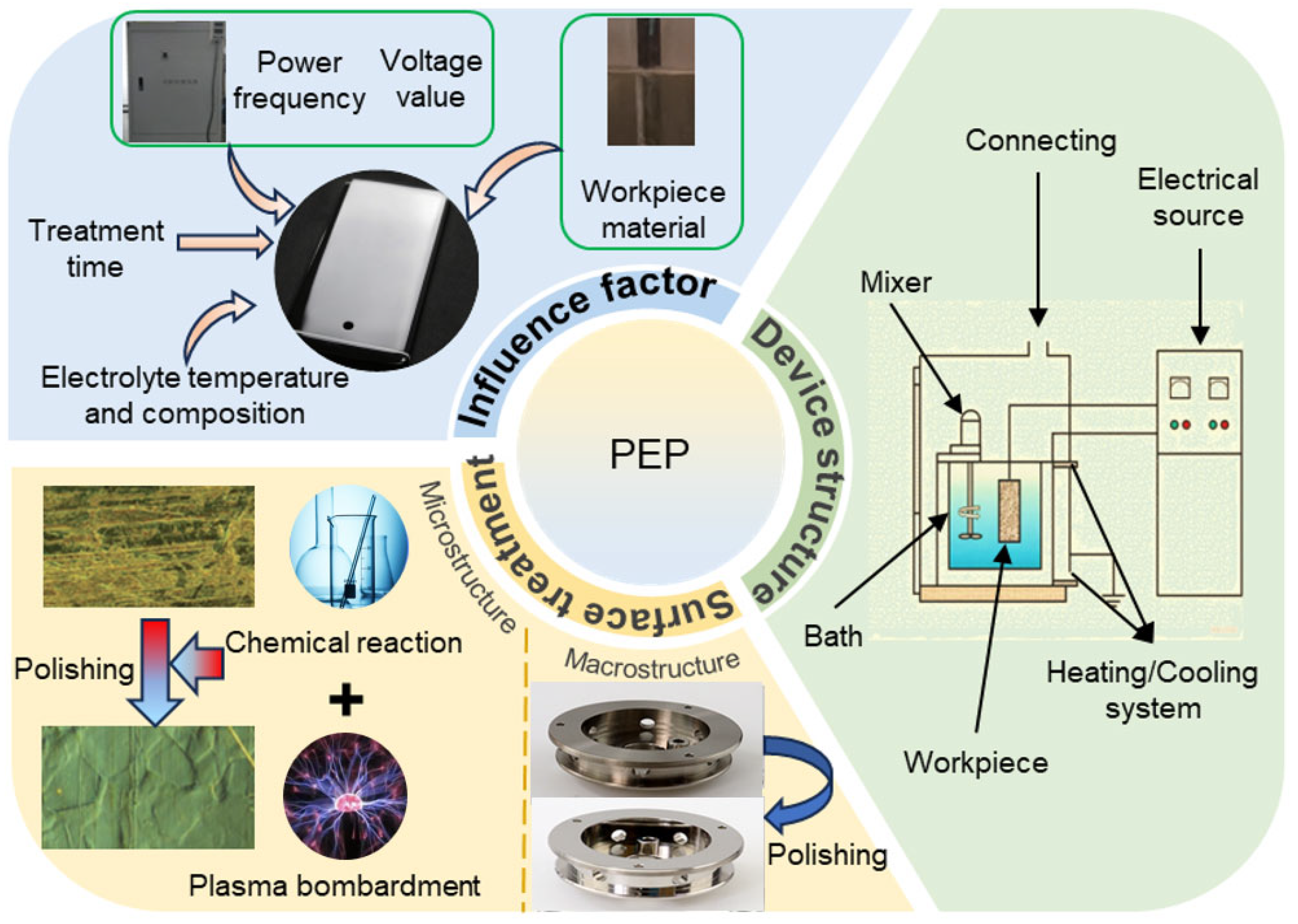
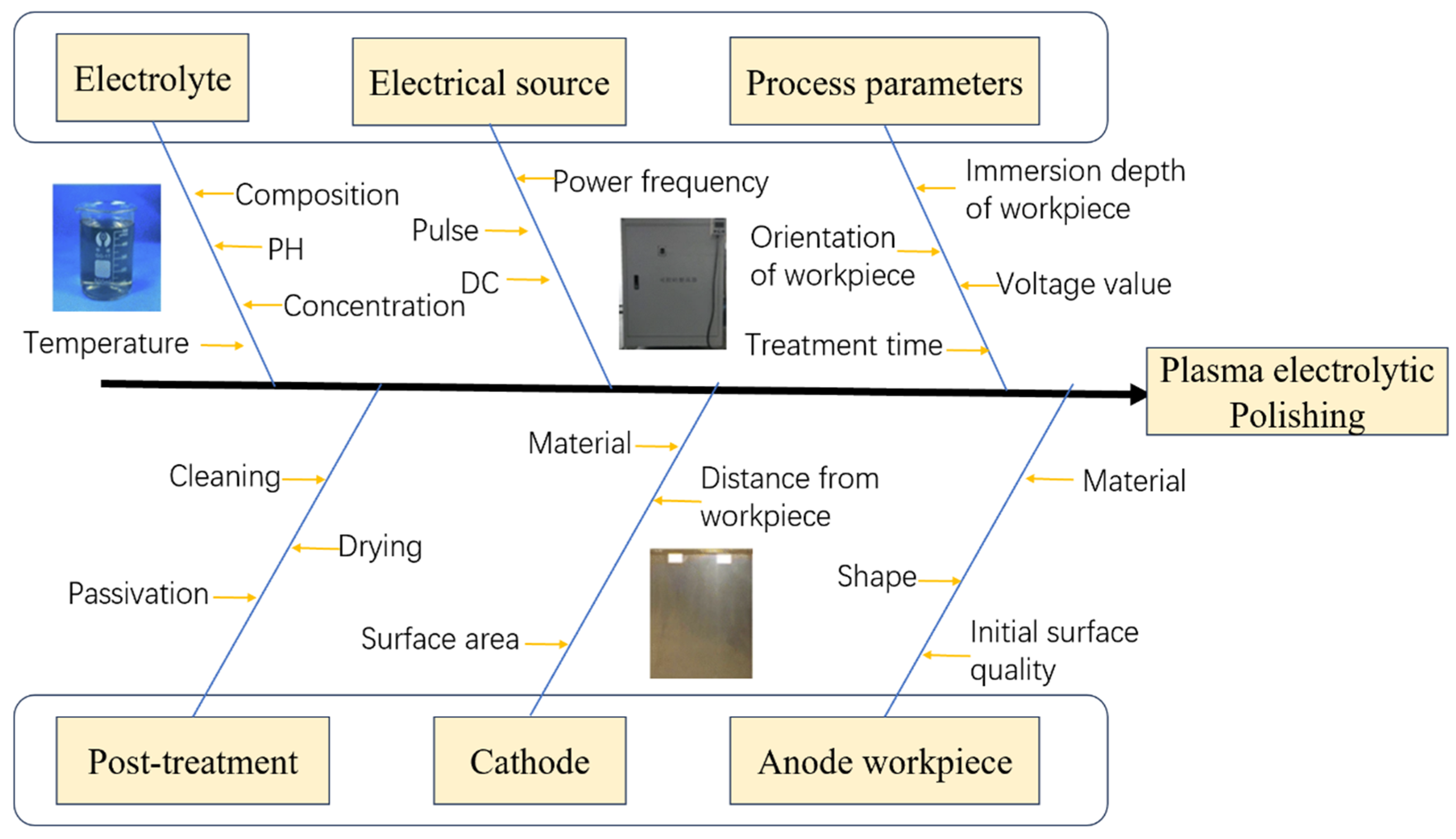
3. Plasma Electrolytic Polishing Process
3.1. Supply Voltage
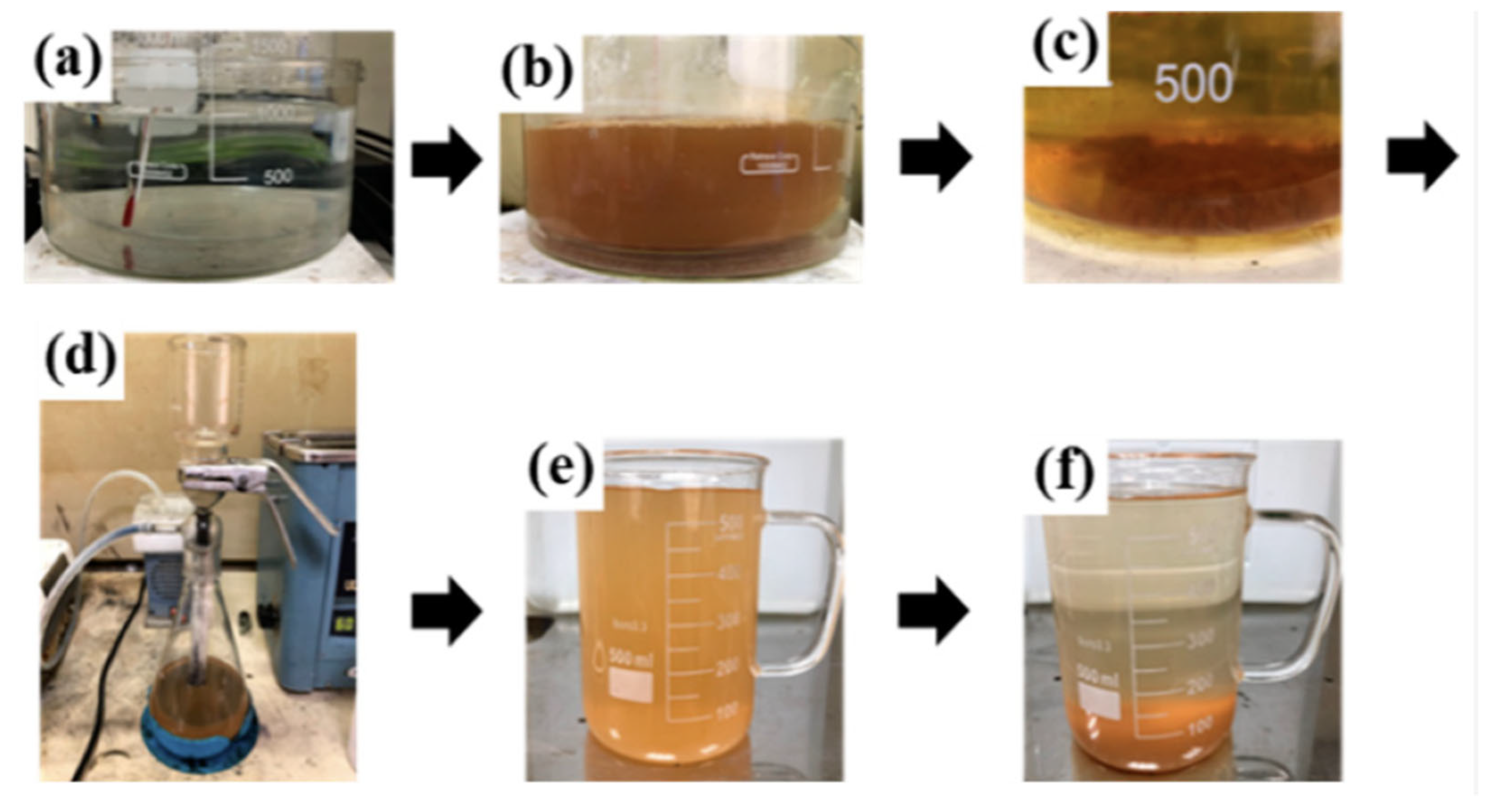
3.2. Electrolyte
3.3. Polishing Time
4. The Application of Plasma Electrolytic Polishing in Various Alloys
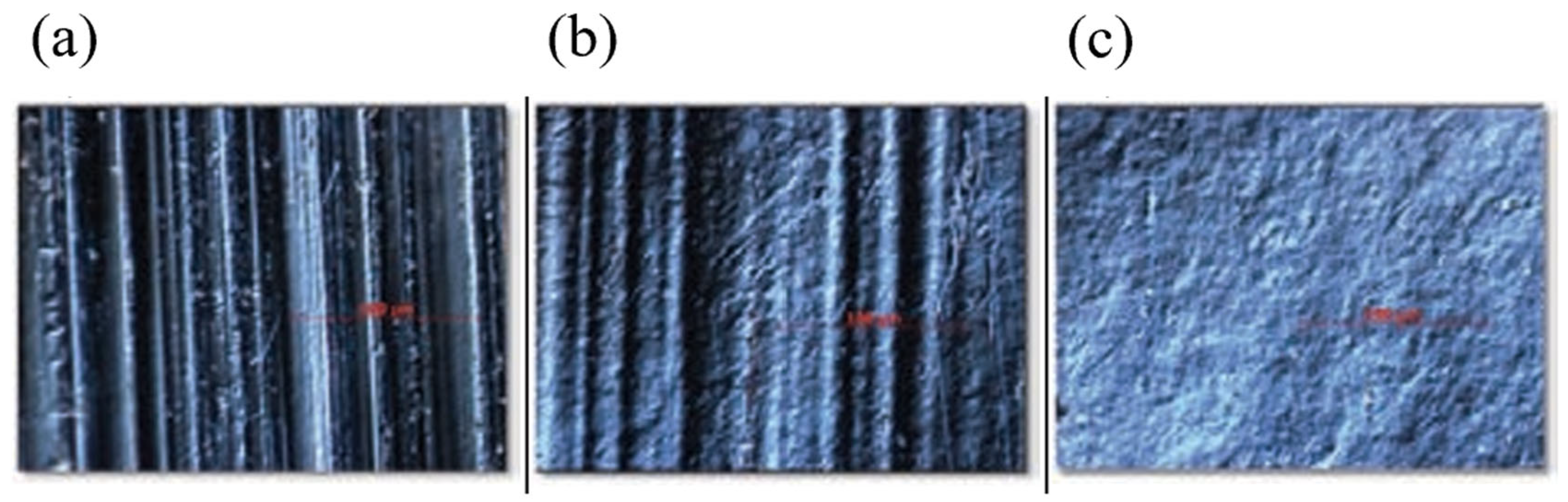
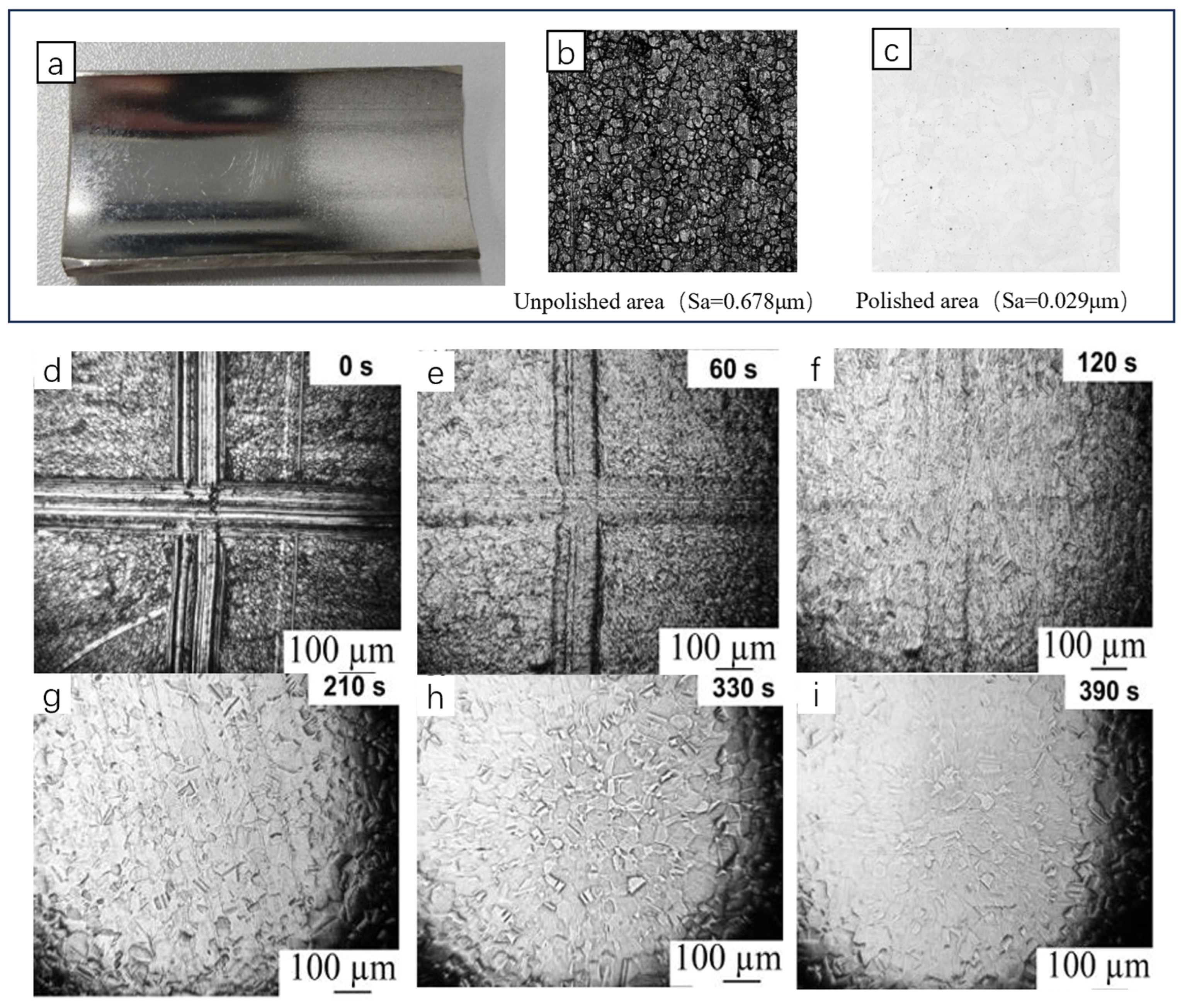
4.1. Stainless Steel
4.2. Aluminum Alloys
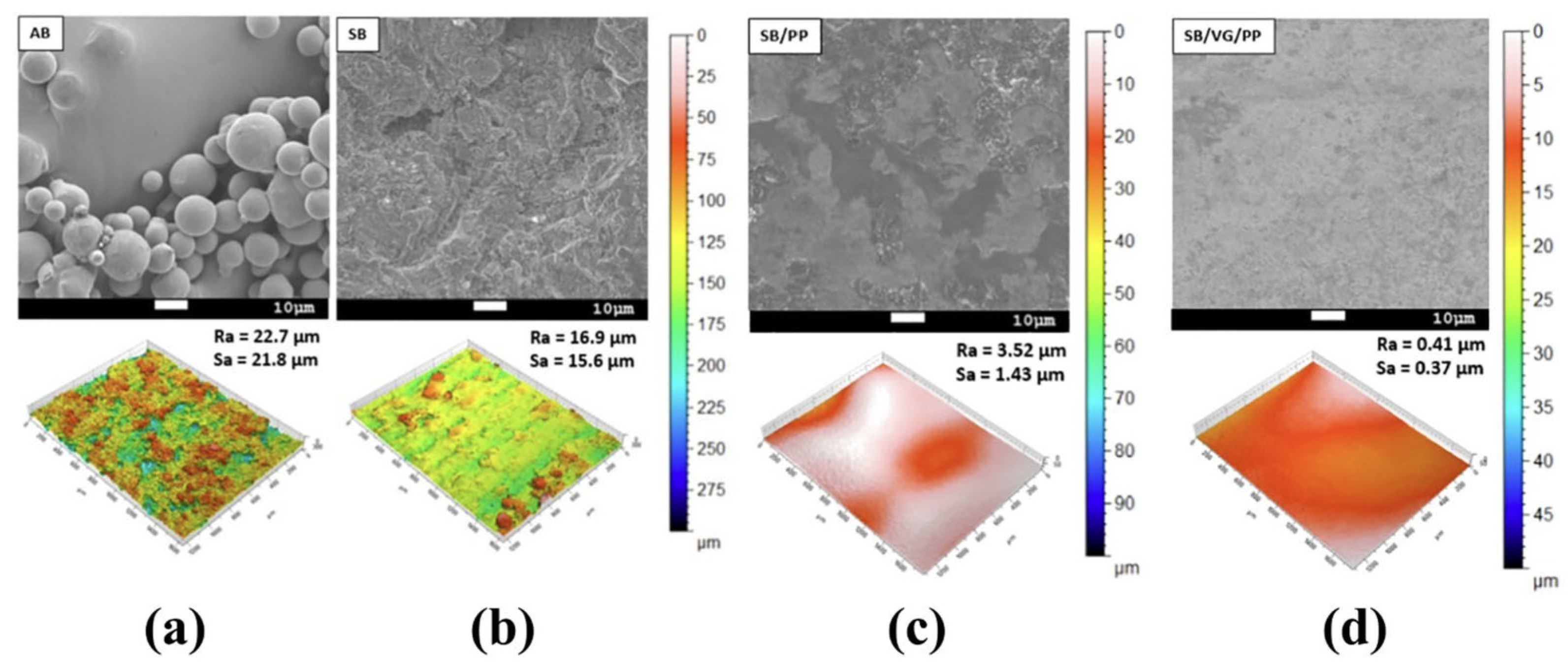
4.3. Titanium Alloy
4.4. Copper Alloys
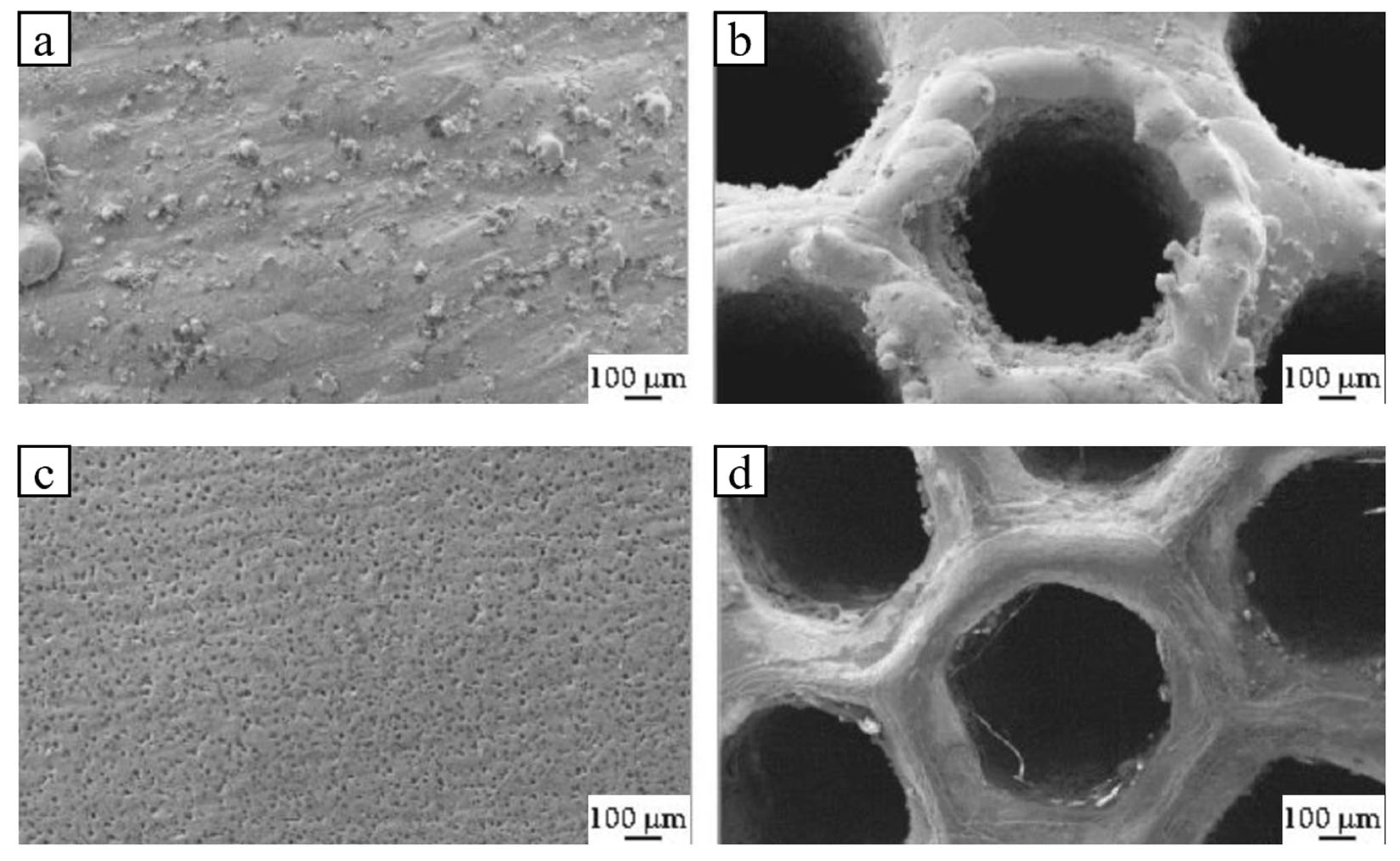
4.5. Cemented Carbide
5. Other Plasma Polishing Processes
5.1. Plasma Electrolytic Polishing Removal Process for Coatings
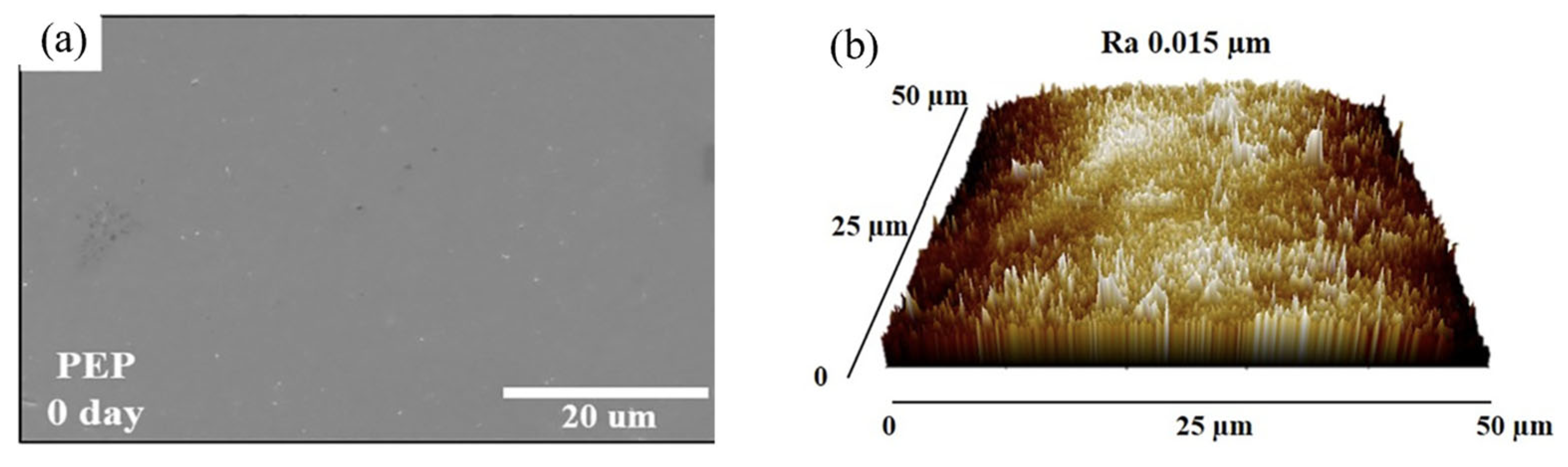
5.2. Plasma Polishing of Non-Metallic Materials
6. Limitations of Plasma Electrolytic Polishing
7. Summary
8. Future Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kusmanov, S.; Tambovskiy, I.; Korableva, S.; Silkin, S.; Naumov, A. Modification of Steel Surface by Anodic Plasma Electrolytic Boriding and Polishing. Trans. Indian. Inst. Met. 2022, 75, 3185–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.Y.; Shih, A.J. Electrochemical machining. chemical machining and chemical mechanical polishing processes. In Analysis of Machining and Machine Tools; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 181–191. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.Q.; Li, J.S. Metal Surface Polishing Technology; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.L. Metal Material Polishing Technology; National Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Duradzhi, V.N.; Bryantsev, I.V.; Tokarov, A.K. Investigation of erosion of the anode under the action of an electrolytic plasma on it. Elektron. Obrab. Mater. 1979, 5, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hans, H.; Eckart, R.; Klaus, R.; Egbert, K.; Jan, P. Method for Highly Glaining Power-Conductive Workstuffs in Anodic Electrolyte Plasma. Patent DD238074A1, 6 August.
- Stanishevsky, V.K.; Parshuto, A.E.; Kosobutsky, A.A.; Semenenko, L.M.; Tikhonovsky, V.N.; Khlebtsevich, V.A.; Velichko, L.S.; Semchenko, A.A.; Slepnev, G.E. Method of Electrochemical Machining of Articles Made of Conducting Materials. U.S. Patent No. 5.028.304, 2 July 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Nestler, K.; Böttger-Hiller, F.; Adamitzki, W.; Glowa, G.; Zeidler, H.; Schubert, A. Plasma electrolytic polishing–an overview of applied technologies and current challenges to extend the polishable material range. Procedia Cirp 2016, 42, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, C.; Ding, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, T.; He, X.; Zheng, L.; Li, N. Principle. process. and application of metal plasma electrolytic polishing: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 114, 1893–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeidler, H.; Böttger-Hiller, F. Plasma-electrolytic polishing as a post-processing technology for additively manufactured parts. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2022, 94, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeidler, H.; Meyer, W.; Loeser, C.; Adamitzki, W.; Nestler, K. Changes on surfaces of electrodes in aqueous electrolytic solutions at high voltages. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Electro Chemical Machining Technology INSECT, Chemnitz, Germany, 12–13 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Parfenov, E.V.; Yerokhin, A.; Nevyantseva, R.R.; Gorbatkov, M.V.; Liang, C.J.; Matthews, A. Towards smart electrolytic plasma technologies: An overview of methodological approaches to process modelling. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 269, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalenchukova, O.V.; Nagula, P.K.; Tretinnikov, D.L. About changes in the chemical composition of the electrolyte in the process of electrolytic-plasma treatment of materials. Mater. Methods Technol. 2015, 9, 404–413. [Google Scholar]
- Yerokhin, A.L.; Nie, X.; Leyland, A.; Matthews, A.; Dowey, S.J. Plasma electrolysis for surface engineering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 122, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickling, A. Electrochemical Processes in Glow Discharge at the Gas Solution Interface. In Modern Aspect of Electrochemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1971; No 6. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, S.K.; Singh, O.P. Contact glow discharge electrolysis: A study of its chemical yields in aqueous inert-type electrolytes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1994, 369, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, B.; Pedeferri, P.; Re, G. Hydrodynamic instabilities in electrolytic gas evolution. Electrochim. Acta 1978, 23, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podhorský, Š. Utilisation of Plasma Discharges in Electrolyte for Surface Finishing of Stainless Steels; Hochsch. Anhalt (FH): Bernburg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann-Lnstitut Fuer Technologieentwicklung, De. Device for Plasma Polishing Using a Liquid Electrolyte. Germany Patent DE202008011646U1, 2 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, G.; Ma, L.; Wu, L. Effect of the gas layer evolution on electrolytic plasma polishing of stainless steel. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenov, E.V.; Mukaeva, V.R.; Farrakhov, R.G. Plasma electrolytic treatments for advanced surface finishing technologies. Mater. Technol. Des. 2019, 1, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg, H.H. Anode effect in aqueous electrolysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1950, 97, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikov, N.V.; Smyslov, A.M.; Timindarov, D.R. To the question of the model of electrolyte-plasma polishing of the surface. Bull. UGATU 2013, 17, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharov, S.V.; Korotkikh, M.T. Electrolyte-Plasma Polishing Ionization Model. In Advances in Mechanical Engineering; Evgrafov, A., Ed.; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelsen, M.; Deutsch, C.; Seitz, H. Electrolytic plasma polishing of pipe inner surfaces. Metals 2017, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Suo, L.C.; Guan, L.L.; Fu, Y.L. Analytical study on mechanism of electrolysisand plasma polishing. J. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 472, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podhorský, Š.; Malík, A. The possibilities of plasma polishing of the steel DIN 1.0570 in electrolyte. In Proceedings of the 19th Conference Metal, Roznov pod Radhostem, Czech Republic, 18–20 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Volenko, A.; Boychenko, O.V.; Chirkunova, N.V. Introduction of technology of electrolytic-plasma polishing of metal goods. Vektor Nauki Tol’yattinskogo Gosudarstvennogo Universiteta. 2016, 1, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, I.; Hackert-Oschätzchen, M.; Schaarschmidt, I.; Zinecker, M.; Schubert, A. Transient simulation of the removal process in plasma electrolytic polishing of stainless steel. In Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference, Lausanne, Switzerland, 22–24 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nevyantseva, R.R.; Gorbatkov, S.A.; Parfenov, E.V.; Bybin, A.A. The influence of vapor–gaseous envelope behavior on plasma electrolytic coating removal. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 148, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeidler, H.; Boettger-Hiller, F.; Edelmann, J.; Schubert, A. Surface finish machining of medical parts using plasma electrolytic polishing. Procedia CIRP 2016, 49, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablyaz, T.R.; Muratov, K.R.; Kochergin, E.U.; Shakirzanov, T. Improving the quality of the surfacesof products obtained by electrical discharge machining using electrolytic-plasma polishing technology. Bull. PNRPU Mech. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2018, 20, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrynin, D.A. Electrolytic-plasma polishing of VT6 and VT8M-1 titanium alloys. Tr. VIAM 2017, 7, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.; Tenhundfeld, G.; Daigle, E.O.; Ryabkov, D. Electrolytic plasma technology: Science and engineering—An overview. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 8746–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapkiv, M.D. State of Electrolytic Plasma in the Process of Synthesis of Oxides Based on Aluminum. Mater. Sci. 1995, 31, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M. Cavitation Erosion. In ASM Handbook; ASM International: Metals Park, OH, USA, 2003; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Su, H.; Qian, N.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J. Characteristics and function of vapour gaseous envelope fluctuation in plasma electrolytic polishing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 7815–7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zong, X.; Liu, J.; Feng, S. Influence of voltage on electrolysis and plasma polishing. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Manufacturing Engineering and Intelligent Materials (ICMEIM 2017), Guangzhou, China, 25–26 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Parfenov, E.V.; Farrakhov, R.G.; Mukaeva, V.R.; Gusarov, A.V.; Nevyantseva, R.R.; Yerokhin, A. Electric field effect on surface layer removal during electrolytic plasma polishing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 307, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, P.N.; Kusmanov, S.A.; Parfenov, E.V. Mechanism and technological opportunity of plasma electrolytic polishing of metals and alloys surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2005, 1, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.B. A Polishing Solution and Polishing Method for Amorphous Alloys. China Patent CN102453444A, 15 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yerokhin, A.; Pilkington, A.; Matthews, A. Pulse current plasma assisted electrolytic cleaning of AISI 4340 steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, I.S.; Vashenko, S.V.; Kamenev, A.Y. Electrolytic Plasma Processing of Materials; Belarusian Science, Republic of Belarus: Minskaja voblasć, Belarus, 2010; ISBN 978-985-08-1215-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kusmanov, S.A.; Tambovskiy, I.V.; Kusmanova, I.A.; Belkin, P.N. Some features of anodic plasma electrolytic processes in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1396, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkevich, Y.V.; Sheleg, V.K.; Yankovsky, I.N. Investigation of metal current efficiency during electropulse polishing of structural carbon steels. Vestn. Baranivichi State. Univ. Ser. Fiz-Math Nauk. 2013, 1, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Suo, L.; Guan, L.; Fu, Y. Optimization of Processing Parameters for Electrolysis and Plasma Polishing. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 217–219, 1368–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podhorský, Š.; Bajčičák, M. Plasma Polishing of Stainless Steels–The Electrolyte Concentration Vs. Gloss. Level. Research Papers Faculty of Materials Science and Technology Slovak. Univ. Technol. 2018, 26, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, A.S.; Zeidler, H.; Schubert, A. Analysis of voltage and current during the plasma electrolytic polishing of stainless steel. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference European Society Precision Engineering Nanotechnology, Hannover, Germany, 29 May–2 June 2017; pp. 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrynin, D. Electrolytic-plasma polishing of titanium alloys VT6 and VT8M-1. Proc. VIAM 2017, 5, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Vaňa, D.; Stefanpodhorsky; Suba, R.; Hurajt, M. The change of surface properties on tested smooth stainless steel surfaces after plasma polishing. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. 2013, 2, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- An, S.; Foest, R.; Fricke, K.; Riemer, H.; Fröhlich, M.; Quade, A.; Schäfer, J.; Weltmann, K.D.; Kersten, H. Pretreatment of cutting tools by plasma electrolytic polishing (PEP) for enhanced adhesion of hard coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 405, 126504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakseyeu, Y.G.; Korolyov, A.Y.; Niss, V.S.; Parshuto, A.E.; Budnitskiy, A.S. Electrolyte-plasma polishing of titanium and niobium alloys. Sci. Tech. 2018, 17, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentinčič, J.; Koroth, J.E.; Zeidler, H. Advancements in surface finish for additive manufacturing of metal parts: A comprehensive review of plasma electrolytic polishing (PEP). Virtual Phys. Prototyping 2024, 19, e2364222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihal, O.V.; Moroz, O.V.; Starovoytov, R.I.; Lytovchenko, S.V.; Mazilin, B.A.; Iliushyn, L.O. Dynamics of the plasma electrolytic polishing process of austenitic steel AISI 304 in a solution of ammonium sulfate. Вoпрoсы атoмнoй науки и техники 2018, 5, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Löber, L.; Flache, C.; Petters, R.; Kühn, U.; Eckert, J. Comparison of different post processing technologies for SLM generated 316 l steel parts. Rapid Prototyp. 2013, 19, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeidler, H.; Aliyev, R.; Gindorf, F. Efficient finishing of laser beam melting additive manufactured parts. Manuf. Mater. Process 2021, 5, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loaldi, D.; Kain, M.; Haahr-Lillevang, L.; Vedel-Smith, N.K.; Tosello, G. Comparison of Selective Laser Melting Post-Processes based on Amplitude and Functional Surface Roughness parameters. In Proceedings of the Joint Special Interest Group Meeting Between Euspen and ASPE Advancing Precision in Additive Manufacturing, Nantes, France, 16–18 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ablyaz, T.R.; Muratov, K.R.; Radkevich, M.M.; Ushomirskaya, L.A.; Zarubin, D.A. Electrolytic plasma surface polishing of complex components produced by selective laser melting. Russ. Eng. Res. 2018, 38, 491–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Laugel, N.; Housden, J.; Espitalier, L.; Matthews, M.; Yerokhin, A. Plasma additive layer manufacture smoothing (PALMS) technology–an industrial prototype machine development and a comparative study on both additive manufactured and conventional machined AISI 316 stainless steel. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 34, 101204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashapov, L.N.; Kashapov, N.F.; Kashapov, R.N.; Denisov, D.G. Plasma electrolytic treatment of products after selective laser melting. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 669, 12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratov, K.R.; Gashev, E.A.; Ablyaz, T.R. Recommendations for electrolytic plasma polishing of chromium and titanium alloys. Russ. Eng. Res. 2022, 42, 829–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navickaite, K.; Nestler, K.; Kain, M.; Guido, T.; Matteo, C.; David, P.; Michael, P.; Falko, B.H.; Zeidler, H. Effective polishing of inner surfaces of additive manufactured inserts for polymer extrusion using Plasma Electrolytic Polishing. In Proceedings of the 18th Rapid. Tech 3D, Erfurt, Germany, 17–19 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sabotin, I.; Jerman, M.; Lebar, A.; Valentinčič, J.; Böttger, T.; Kühnel, L.; Zeidler, H. Effects of plasma electrolytic polishing on SLM printed microfluidic platform. Adv. Technol. Mater. 2022, 47, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, J.; Liu, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wei, D.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Y. Optimization of electrolytic plasma polishing process and surface performance analysis for 6061 aluminum alloy. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 110162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.; Ho, J.Y.; Wong, T.N. Fabrication of heat sinks by Selective Laser Melting for convective heat transfer applications. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2016, 11, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.S.; Galinovsky, A.L.; Martysyuk, D.A. Reducing additive product surface roughness by electrochemical processing methods. proceedings of higher educational institutions. Маchine Build. 2022, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duradji, V.N.; Kaputkin, D.E.; Duradji, A.Y. Aluminum Treatment in the Electrolytic Plasma During the Anodic Process. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Review. 2017, 10, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaysin, A.F.; Gil’mutdinov, A.K.; Mirkhanov, D.N. Electrolytic-plasma treatment of the surface of a part produced with the use of additive technology. Met. Sci. Heat. Treat. 2018, 60, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, S.V.; Korotkikh, M.T. Electrolytic plasma processing of complex products from aluminum alloy D16. Вестник Кoнцерна ВКО Алмаз-Антей 2017, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kui, Q. Research on Optimization and Application of Aluminium Formula Based on the Small Electrolysis Plasma Polishing Machine. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Calin, M.; Zhang, L.-C.; Attar, H.; Eckert, J. Review on manufacture by selective laser melting and properties of titanium based materials for biomedical applications. Mater. Technol. 2016, 31, 66–76. [Google Scholar]
- Singla, A.K.; Banerjee, M.; Sharma, A.; Singh, J.; Bansal, A.; Gupat, M.K.; Khanna, N.; Shahi, A.S.; Goyal, D.K. Selective laser melting of Ti6Al4 V alloy: Process parameters. defects and post-treatments. Manuf. Process 2021, 64, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navickaitė, K.; Nestler, K.; Böttger-Hiller, F.; Matias, C.; Diskin, A.; Golan, O.; Garkun, A.; Strokin, E.; Biletskiy, R.; Safranchik, D.; et al. Efficient polishing of additive manufactured titanium alloys. Proc. CIRP 2022, 108, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, A.; Schneider, J.; Schroeder, A.; Papadopoulous, K.; Lopez, E.; Brückner, F.; Botzenhart, U. Surface conditioning of additively manufactured titanium implants and its influence on materials properties and in vitro biocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 119, 111631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingath, K.; Zeidler, H.; Parshuta, A. Plasma Polishing of Objects Made of Titanium or Titanium Alloys Comprises Applying a Voltage to the Object Positioned in a Warm Aqueous Electrolyte Solution, Followed by Processing Using Plasma Polishing. Germany Patent DE10207632A1, 22 February 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Smyslova, M.K.; Tamindarov, D.R.; Plotnikov, N.V.; Modina, I.M.; Semenova, I.P. Surface electrolytic-plasma polishing of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with ultrafine-grained structure produced by severe plastic deformation. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. IOP Publ. 2018, 461, 012079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenov, E.V.; Neviantseva, R.R.; Gorbatkov, S.A.; Yerokhin, A. Plasma Electrolytic Treatment: Modelling. Diagnostics. Control; Mashinostrojenije: Moscow, Russia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Smyslov, A.M.; Smyslova, M.K.; Mingazhev, A.D.; Selivanov, K.S. Multi-Stage Electrolyte-Plasma Processing of Products from Titanium and Titanium Alloys; Ufa State Aviation Technical University: Moscow, Russia, 2009; pp. 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, U.; Lange, R.; Neumann, H.-G. Micro- and Nanoscaled Titanium Surface Structures Textured by Electrolytic Plasma and Etching Methods. Adv. Mater. Res. 2006, 15–17, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, F.; Böttger-Hiller, F.; Kranhold, C.; Schulze, H.P.; Kröning, O.; Zeidler, H.; Lampke, T. Surface modification for corrosion resistance of electric conductive metal surfaces with plasma electrolytic polishing. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2113, 110009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duradji, V.N.; Kaputkin, D.E. Metal Surface Treatment in Electrolyte Plasma during Anodic Process. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 163, E43–E48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.I.; Khafizov, A.A.; Shakirov, Y.I.; Sushchikova, A.N. Polishing and deburring of machine parts in plasma of glow discharge between solid and liquid electrodes. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 86, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.P. Copper Alloy Electrolyte-Plasma Polishing Method. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Duradji, V.N.; Kaputkin, D.E.; Duradji, A.Y. Method of Plasma Electrolytic Treatment of Metal Surface. Russian Patent 2537346, 10 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bottger-Hiller, F.; Nestler, K.; Zeidler, H.; Glowa, G.; Lampke, T. Plasma Electrolytic Polishing of Metalized Carbon Fibers. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2016, 3, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.R. Mechanism and Process Optimization of Plasma Electropolishing on the Surface of Aluminum, Titanium Alloy and Copper. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bobzin, K. High-performance coatings for cutting tools. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2016, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmersson, U.; Lattemann, M.; Bohlmark, J.; Ehiasarian, A.P.; Gudmundsson, J.T. Ionized physical vapor deposition (IPVD): A review of technology and applications. Thin Solid Film. 2006, 513, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, B.; Park, H.-K.; Park, K.B.; Kang, H.-S.; Park, K. Effect of hydrogen peroxide on Cr oxide formation of additive manufactured CoCr alloys during plasma electrolytic polishing. Mater. Lett. 2021, 294, 129736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagulin, K.Y.; Terent’ev, A.A.; Belov, M.D.; Gil’mutdinov, A.K. Electrolytic-plasma jet polishing of additively manufactured gas turbine engine components. Russ. Aeronaut. 2022, 65, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, B.; Park, H.K.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, W.R.; Park, K. Corrosion behavior of additive manufactured CoCr parts polished with plasma electrolytic polishing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 406, 126640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakseyeu, Y.G.; Korolyov, A.Y.; Niss, V.S. Electrolytic-plasma polishing of cobalt-chromium alloys for medical products. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus. Phys.-Tech. Ser. 2019, 64, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, I.; Hackert-Oschätzchen, M.; Zinecker, M.; Meichsner, G.; Edelmann, J.; Schubert, A. Process understanding of plasma electrolytic polishing through multiphysics simulation and inline metrology. Micromachines 2019, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirkhanova, N.A.; Nevyantseva, R.R.; Belonogov, V.A.; Timergazina, T.M. Russian Patent 2094546, 30 October 1997.
- Parfenov, E.V.; Nevyantseva, R.R.; Gorbatkov, S.A. Process control for plasma electrolytic removal of TiN coatings. Part 1: Duration control. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 199, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenov, E.V.; Nevyantseva, R.R.; Gorbatkov, S.A. Process control for plasma electrolytic removal of TiN coatings: Part 2: Voltage control. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 199, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmi, T.; Miyashita, M.; Itano, M.; Imaoka, T.; Kawanabe, I. Dependence of thin-Oxide films quality on surface microroughness. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 1922, 39, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Yin, X.; Jia, Z.; Liu, F. Combination of Plasma Electrolytic Processing and Mechanical Polishing for Single-Crystal 4H-SiC. Micromachines 2021, 12, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Li, S.; Ma, G.; Jia, Z.; Liu, X. Investigation of oxidation mechanism of SiC single crystal for plasma electrochemical oxidation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 27338–27345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C. Simulation and Experimental Study on Ultrasonic Assisted Electrolyte Plasma Polishing of SiC Single Crystal. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura, K.; Takiguchi, T.; Ueda, M.; Deng, H.; Hattori, A.N.; Zettsu, N. Plasma assisted polishing of single crystal SiC for obtaining atomically flat strain-free surface. CIRP Ann. 2011, 60, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Yamamura, K. XTEM Observation of 4H-SiC (0001) Surfaces Processed by Plasma Assisted Polishing. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 497, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorn, L.; Wilkat, M.; Lommen, J.; Borelli, M.; Muhammad, S.; Rana, M. Plasma Electrolytic Polished Patient-Specific Orbital Implants in Clinical Use-A Technical Note. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navickaitė, K.; Langenhan, S.; Köckritz, J.; Sherstneva, A.; Nestler, K.; Penzel, M.; Wendler, M.; Szlosarek, R.; Hauser, M.; Volkova, O.; et al. Three modes of plasma electrolytic polishing of high-alloy austenitic steel. Results Surf. Interfaces 2024, 17, 100288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelsen, M.; Deutsch, C.; Seitz, H. Influence of the Velocity and the Number of Polishing Passages on the Roughness of Electrolytic Plasma Polished Pipe Inner Surfaces. Metals 2018, 8, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander Küenzi, M.; Goetschi, M.; Nelis, T.; Bessire, C. Jet Application of Plasma Electrolyte Polishing. Procedia CIRP 2022, 113, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Ma, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L. Study of Electrochemical Behavior and a Material Removal Mechanism During Electrolytic Plasma Polishing of 316L Stainless Steel. Materials 2025, 18, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Tang, Z.; Ding, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, X. Plasma Electrolytic Polishing Process for Zr-based Metallic Glasses and Waste Liquor Treatment. China Surf. Eng. 2024, 37, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Yang, H.; Wu, W.; Chen, Y. An Electrolyte Life Indicator for Plasma Electrolytic Polishing Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



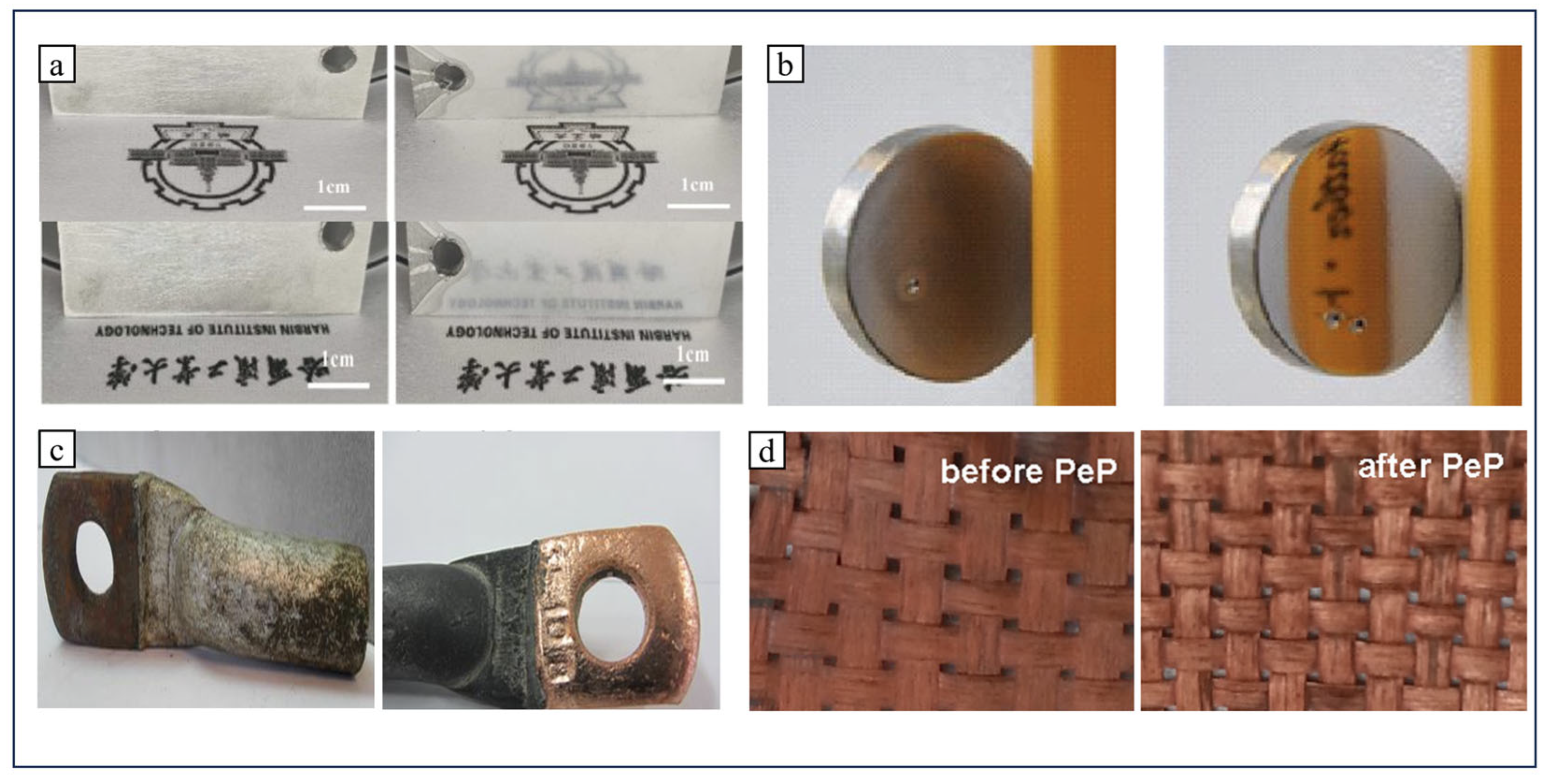
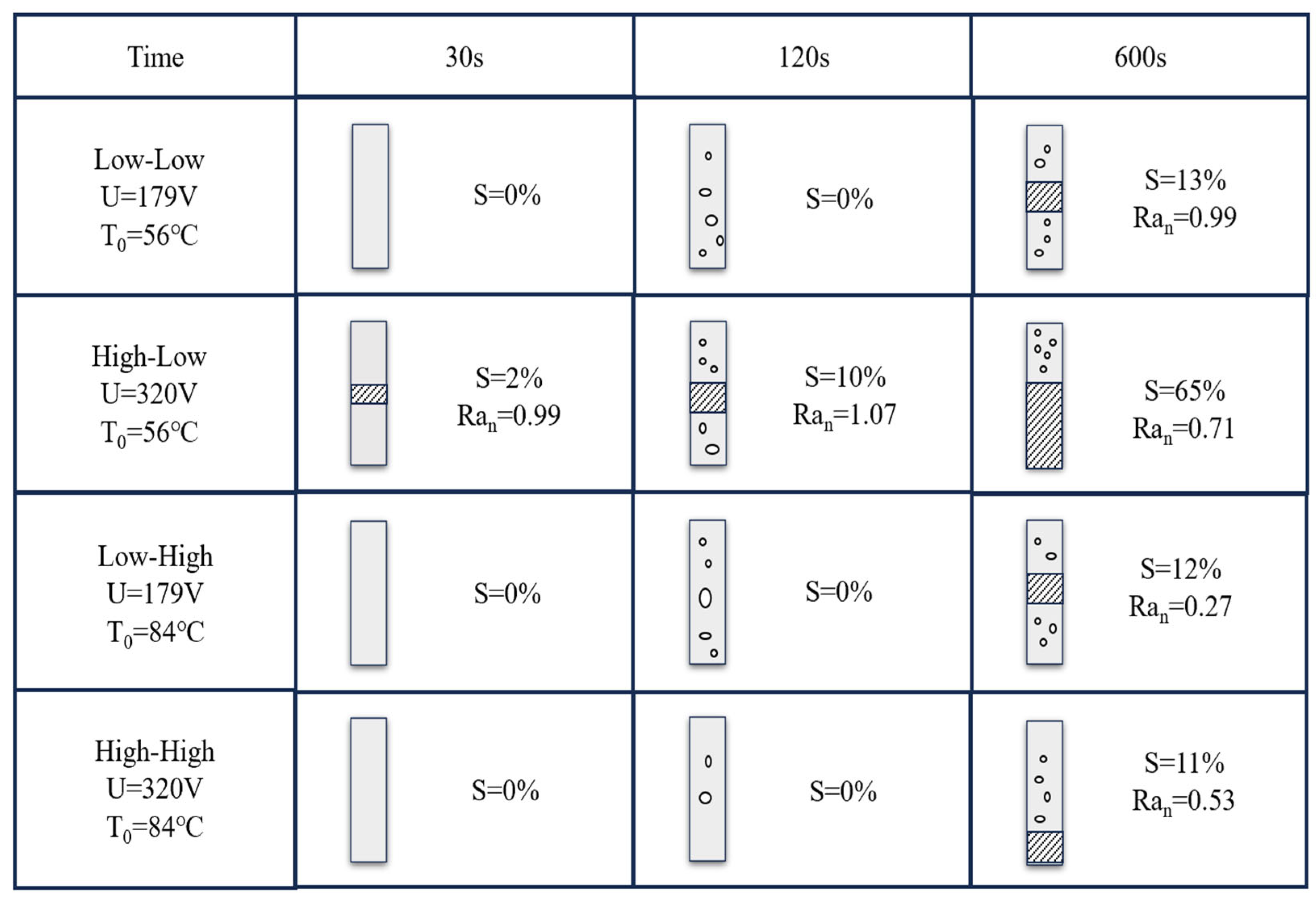

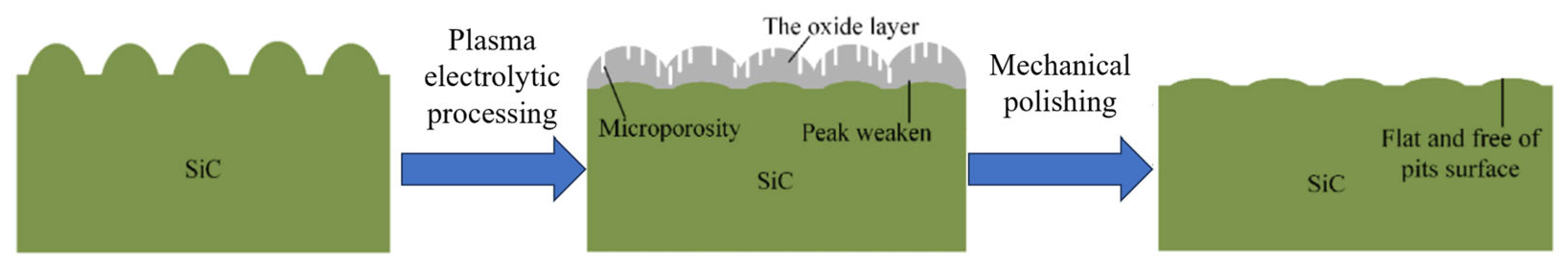
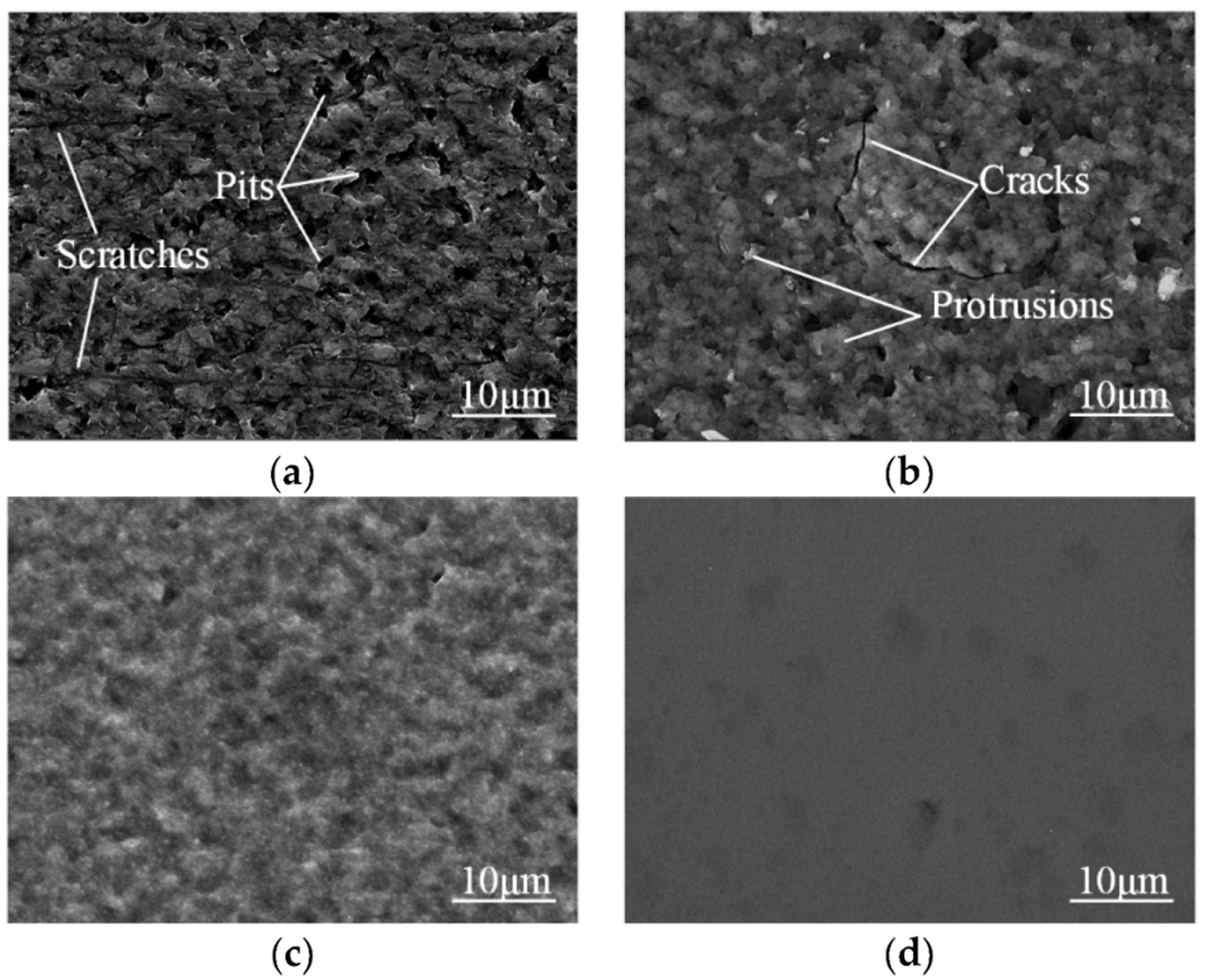
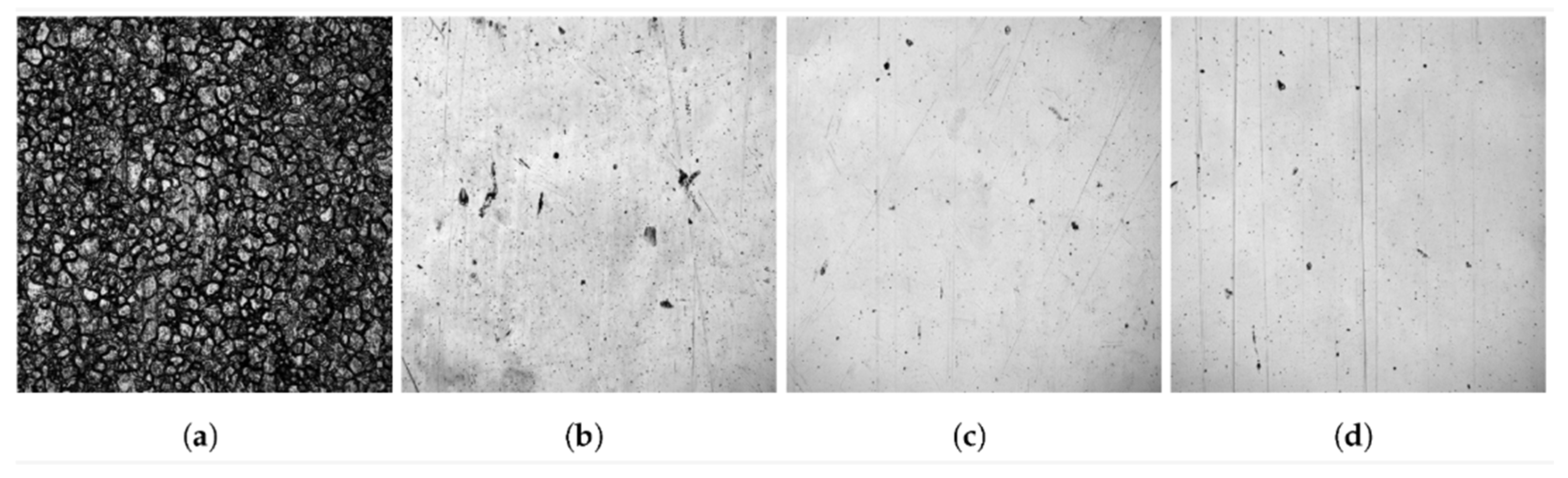

| Method | Mechanism | Efficiency | Machinable Workpiece Shape | Environmental Protection Level | Energy Consumption |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical polishing | Plastic Deformation | Inferior | Simple | Inferior | Medium |
| Chemical polishing | Chemical corrosion | Inferior | Complex | Inferior | Inferior |
| Electrochemical polishing | Electrochemical corrosion | Medium | Complex | Inferior | High |
| Abrasive jet polishing | Erosion, shearing | Inferior | Complex | Medium | Medium |
| Laser Polishing | Remelting | Inferior | Complex | High | High |
| Plasma electrolytic polishing | Plasma bombardment | Plasma bombardment | Complex | High | High |
| Method | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical polishing | Low cost | Low efficiency, high environmental impact |
| Chemical polishing | High efficiency, low cost | Poor roughness, high environmental impact |
| Electrochemical polishing | Good roughness | High environmental impact |
| Plasma electrolytic polishing | Good roughness, low environmental impact | High cost |
| Methodology | Continuous Power | Pulsed Power |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Roughness | Higher Ra | Lower Ra (down to nanometer scale) |
| Material Removal Rate | High | High |
| Thermal Effect | High heat input | Lower average thermal load |
| Energy Consumption | High consumption | Reduced by ~10–30% |
| Suitable Materials | Stainless steels, copper, and stable metals | Titanium alloys, aluminum alloys, difficult-to-machine materials |
| Application Scenarios | Moderate surface finish | High-precision, complex parts |
| Material | Electrolyte Components | U (V) | T (°C) | t (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless steel | 2–6 wt% (NH4)2SO4 | 260–320 | 70–85 | 2–10 |
| Aluminum alloys | 10% NH4Cl + 4% KCl + 3% H2C2O4, 2–4 wt% (NH4)2SO4 | 240–320 | 50–80 | 2–8 |
| Titanium alloy | (NH4)2SO4, NH4F, NaF | 230–330 | 75–95 | 2–10 |
| Copper alloys | 2–5 wt% (NH4)2SO4, NH4F, NH4NO3 | 180–350 | 60–90 | 3–6 |
| Cemented carbide | (NH4)2SO4, NaNO3, Na2CO3 | 220–300 | 70–90 | 2–5 |
| non-metallic materials | 1% NaCl | 150–200 | 20–40 | 15–20 |
| Samples Material | Electrolyte Components | U (V) | T (°C) | t (min) | Ra (μm) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316L | 4% (NH4)2SO4 | 300 | 80 | - | 8.54 | [55] |
| 316L | - | 370 | - | 2–60 | 0.18 | [57] |
| 316L | 4% (NH4)2SO4 and 1% disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate | 330 | 85–90 | 0.5–4 | 1.4 | [58] |
| 316L | - | 350 | 60–90 | 10–90 | 0.1 | [59] |
| 316L | 5% Na2CO3 or NaCl | 130 | - | 1 | - | [60] |
| 316L 304 | 4% (NH4)2SO4 | 220–360 | 80–90 | 5–10 | 0.09 | [61] |
| MS1 | (NH4)2SO4 and C6H8O7 | 330–338 | 70–90 | 10 | 0.53 | [62] |
| MS1 | (NH4)2SO4 | 350 | 80 | 10–20 | 2.6 | [63] |
| Samples Material | Electrolyte Components | U (V) | T (°C) | t (min) | Ra (μm) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 | - | 370 | 80 | 4 | 0.138 | [64] |
| AlSi10Mg | 4% KCl and 2% C2H2O2 | 250 | 70–80 | 2 | 1.6 | [66] |
| Aluminum alloy | 10% NH4Cl, 4% KCl and 3% H2C2O4 | 300 | 60–80 | - | 0.16 | [67] |
| AlSi10Mg | 7% NaCl | 400–500 | 16–90 | 0.5 | 0.68 | [68] |
| D16 | 4–5% KNO3, 2–3% C6H8O7 and 0.5–1% glycerol | 280–320 | - | 2 | 0.2 | [69] |
| Samples Material | Electrolyte Components | U (V) | T (°C) | t (min) | Ra (μm) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC4 | - | 327–337 | 75–90 | 24–32 | <1 | [73] |
| TC4 | 2–5% (NH4)2SO4 | - | 93 | 4 | 0.41 | [74] |
| Titanium alloy | 4% NH4F | 260–300 | 75–95 | 1–5 | 0.1 | [53] |
| Titanium alloy | 1.5–3% NH4Cl and 1.25–2.75% NH4F | - | 80–95 | - | 0.12 | [75] |
| TC4 | 4–6% NH2OH·HCl and 0.7–0.8% KF or NaF | 260–280 | 85–95 | 2–10 | 0.04 | [76] |
| Samples Material | Electrolyte Components | U (V) | T (°C) | t (min) | Ra (μm) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper alloy | C6H8O7 | 180–300 | 120 | 2 | <0.02 | [8] |
| L63 brass | NH4F and C6H5O7(NH4)3 | 290–340 | 60–90 | 10–25 s | 0.05 | [81] |
| Copper | - | 180–300 | 30 | 2 | 6.0 | [81] |
| copper M1 | NaCl, CuSO4, NH4NO3 | 400–550 | 80–120 | 20–35 s | 0.08 | [82] |
| H62 brass | - | - | 80 | 5 | 0.176 | [83] |
| Red copper | - | 260 | 90 | 11 | 0.064 | [84] |
| Samples Material | Electrolyte Components | U (V) | T (°C) | t (min) | Ra (μm) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoCr | (NH4)2SO4 | 350 | 70–80 | 5 | 0.01 | [89] |
| CoCr | 5–15% (NH4)2SO4 | 400 | 80 | - | 1.6 | [90] |
| WC | Na2CO3 | 0–300 | 70 | 40–100 s | 0.08 | [51] |
| CoCr | (NH4)2SO4 | 450 | 75–80 | 8 | 0.02 | [91] |
| CoCr | 4% (NH4)2SO4 | 240–300 | 70–90 | 0.5–2.5 | 0.057 | [92] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, T.; Wang, S.; He, W.; Jin, R.; Zhao, J.; Zou, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Precision Machining of Different Metals by Plasma Electrolytic Polishing: A Review for Improving Surface Smoothness and Properties. Lubricants 2025, 13, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13090412
Yan T, Wang S, He W, Jin R, Zhao J, Zou Y, Ouyang J, Wang Y, Zhou Y. Precision Machining of Different Metals by Plasma Electrolytic Polishing: A Review for Improving Surface Smoothness and Properties. Lubricants. 2025; 13(9):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13090412
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Tongtong, Shuqi Wang, Weidi He, Rui Jin, Jiajun Zhao, Yongchun Zou, Jiahu Ouyang, Yaming Wang, and Yu Zhou. 2025. "Precision Machining of Different Metals by Plasma Electrolytic Polishing: A Review for Improving Surface Smoothness and Properties" Lubricants 13, no. 9: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13090412
APA StyleYan, T., Wang, S., He, W., Jin, R., Zhao, J., Zou, Y., Ouyang, J., Wang, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2025). Precision Machining of Different Metals by Plasma Electrolytic Polishing: A Review for Improving Surface Smoothness and Properties. Lubricants, 13(9), 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13090412






