Effects of WC Addition on Microstructure and Properties of Plasma-Cladded AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
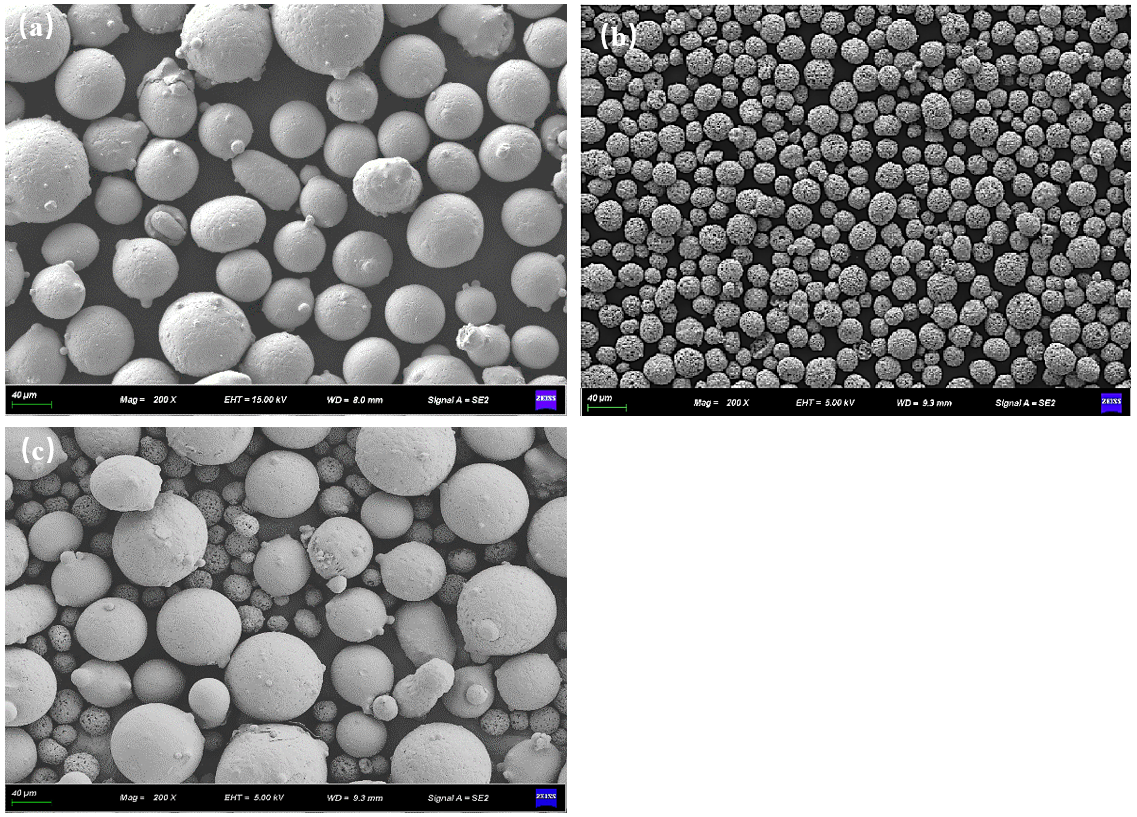
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Process
3. Results and Discussion
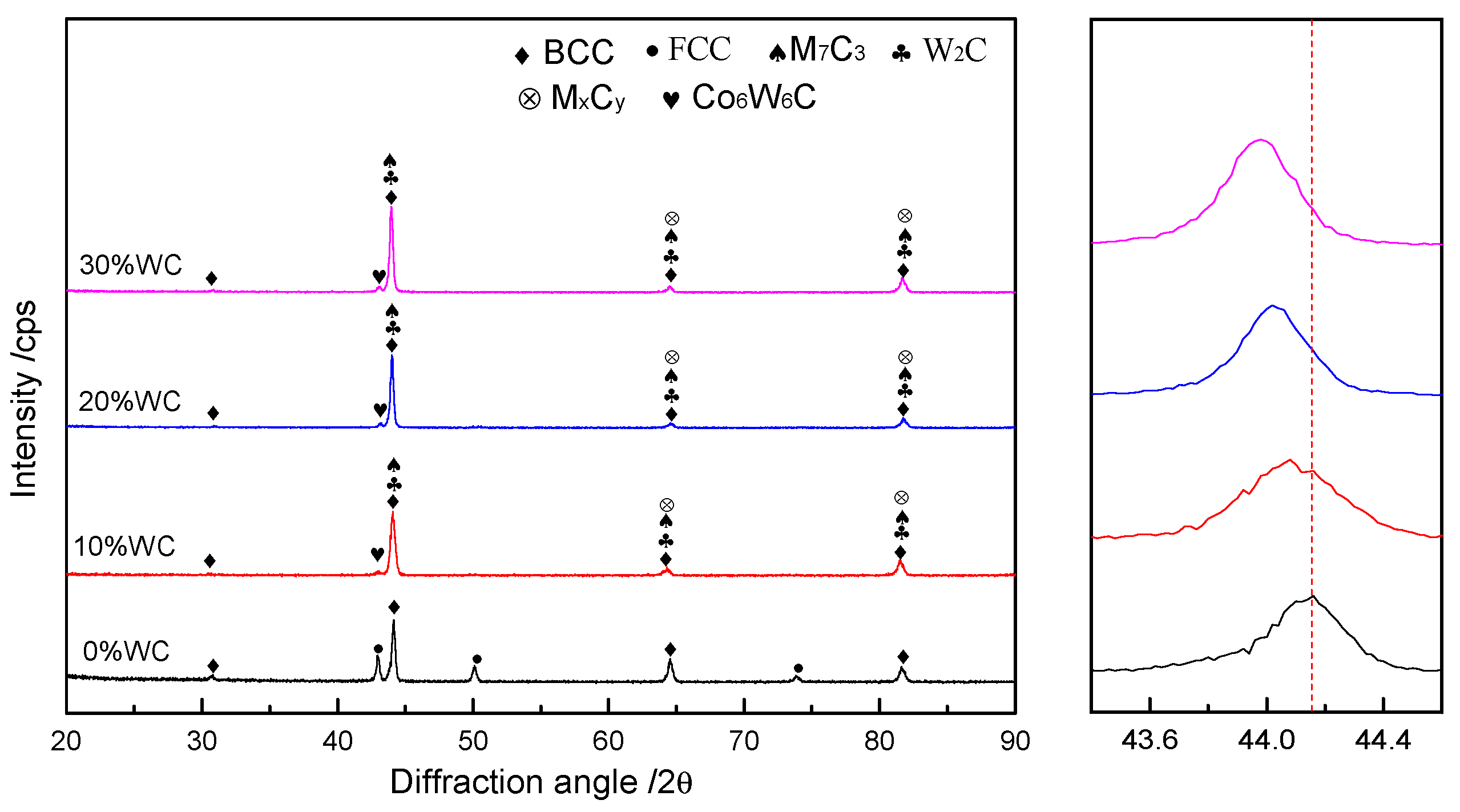
3.1. Phase Analysis of Coating
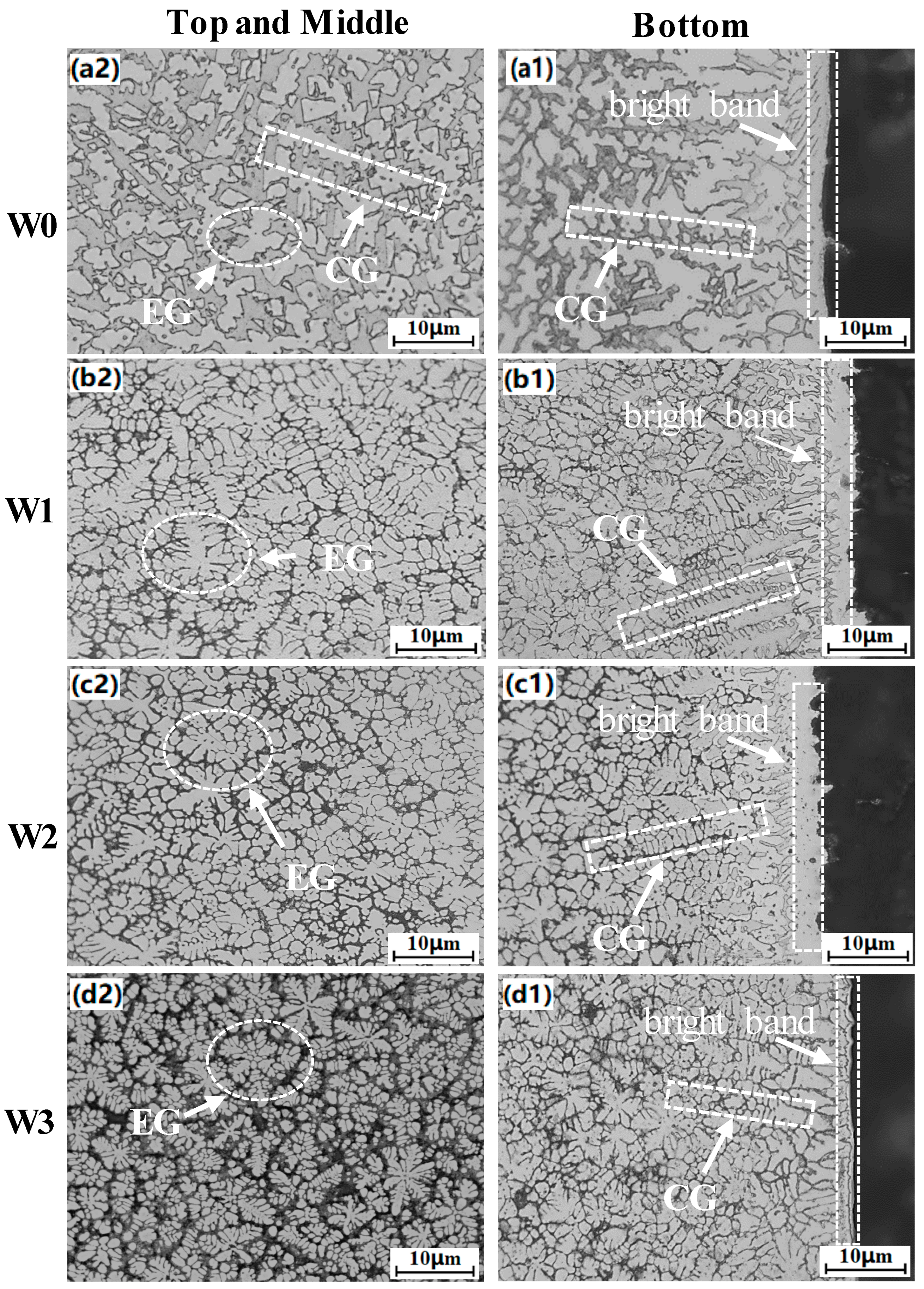
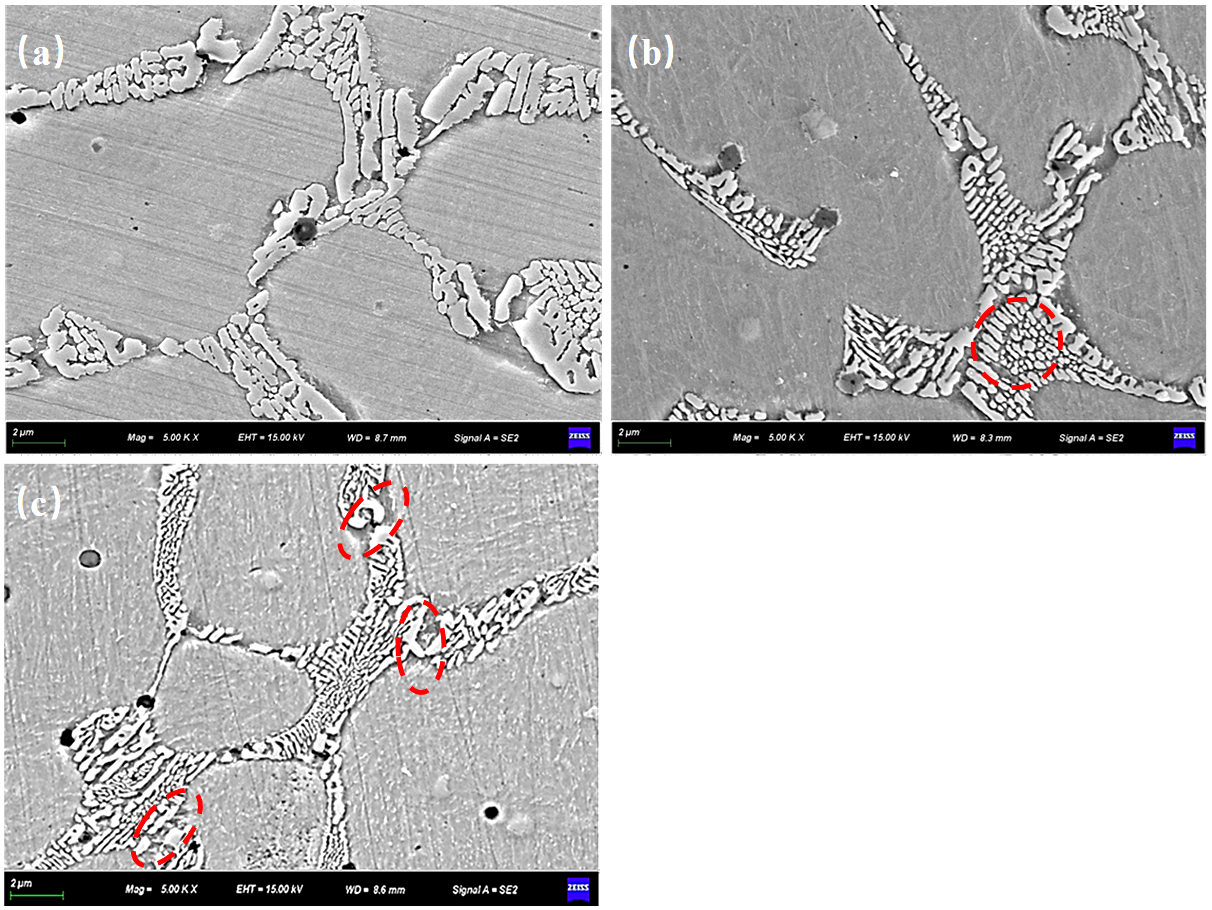
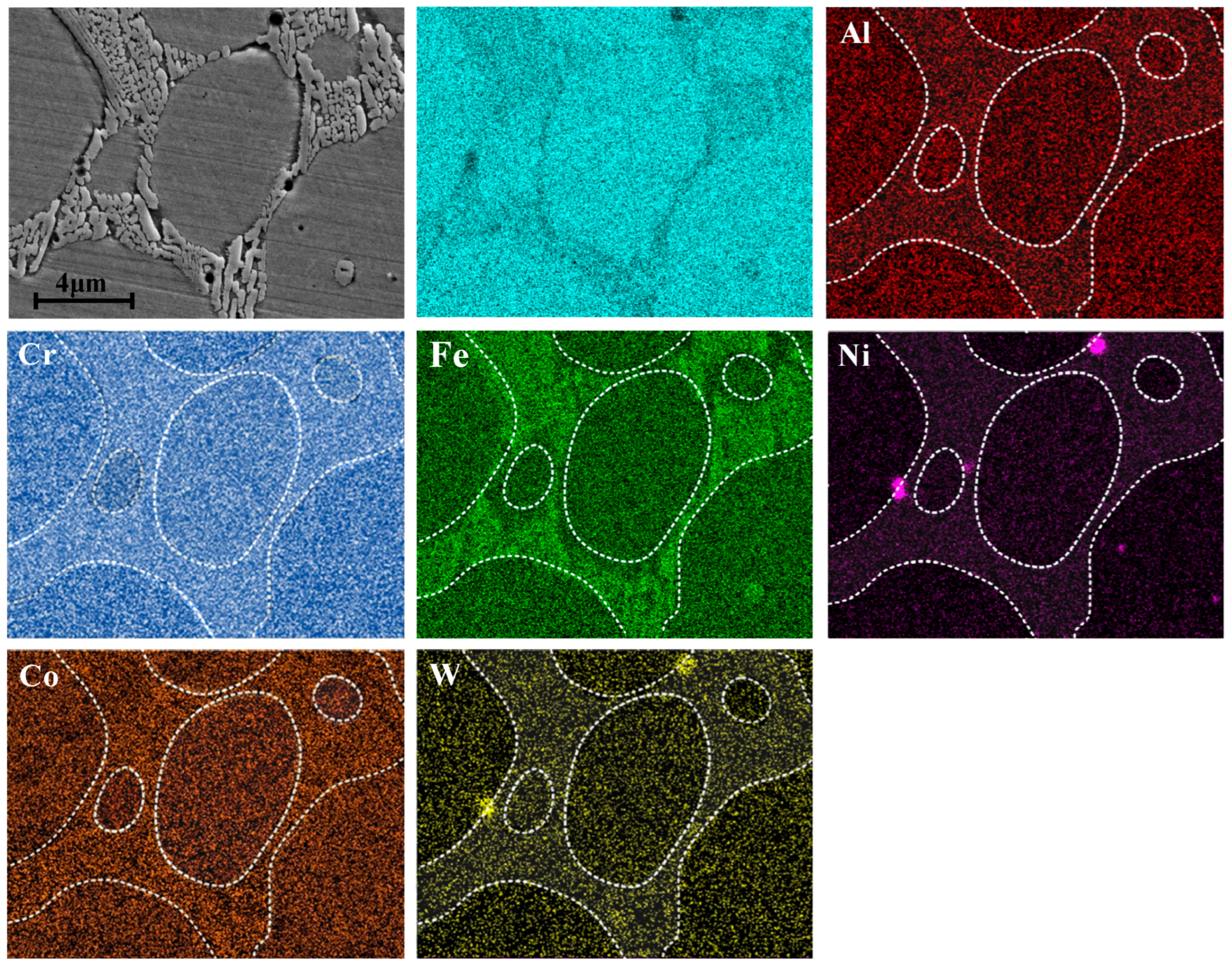
3.2. Microstructure of Coating
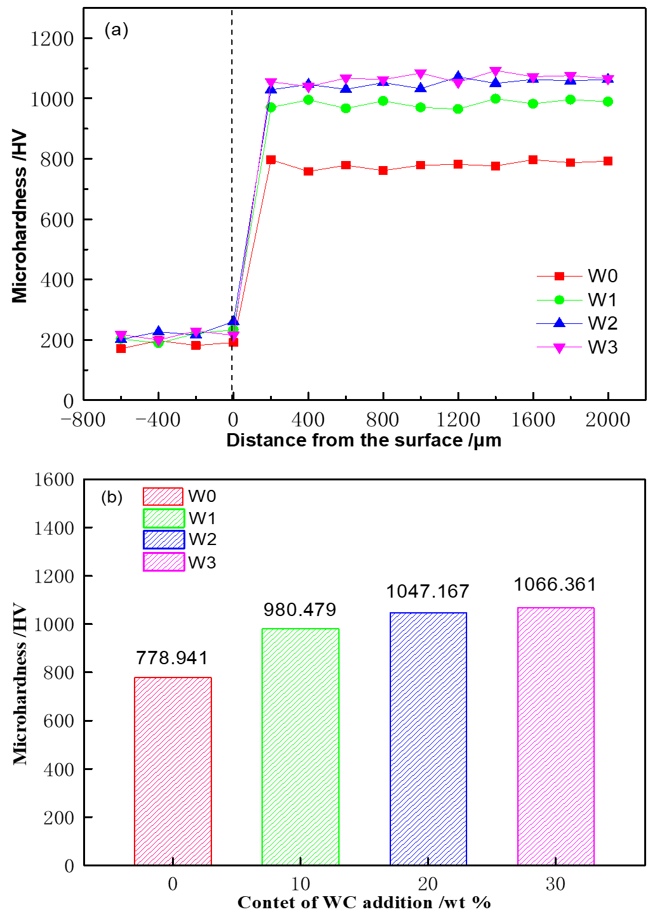
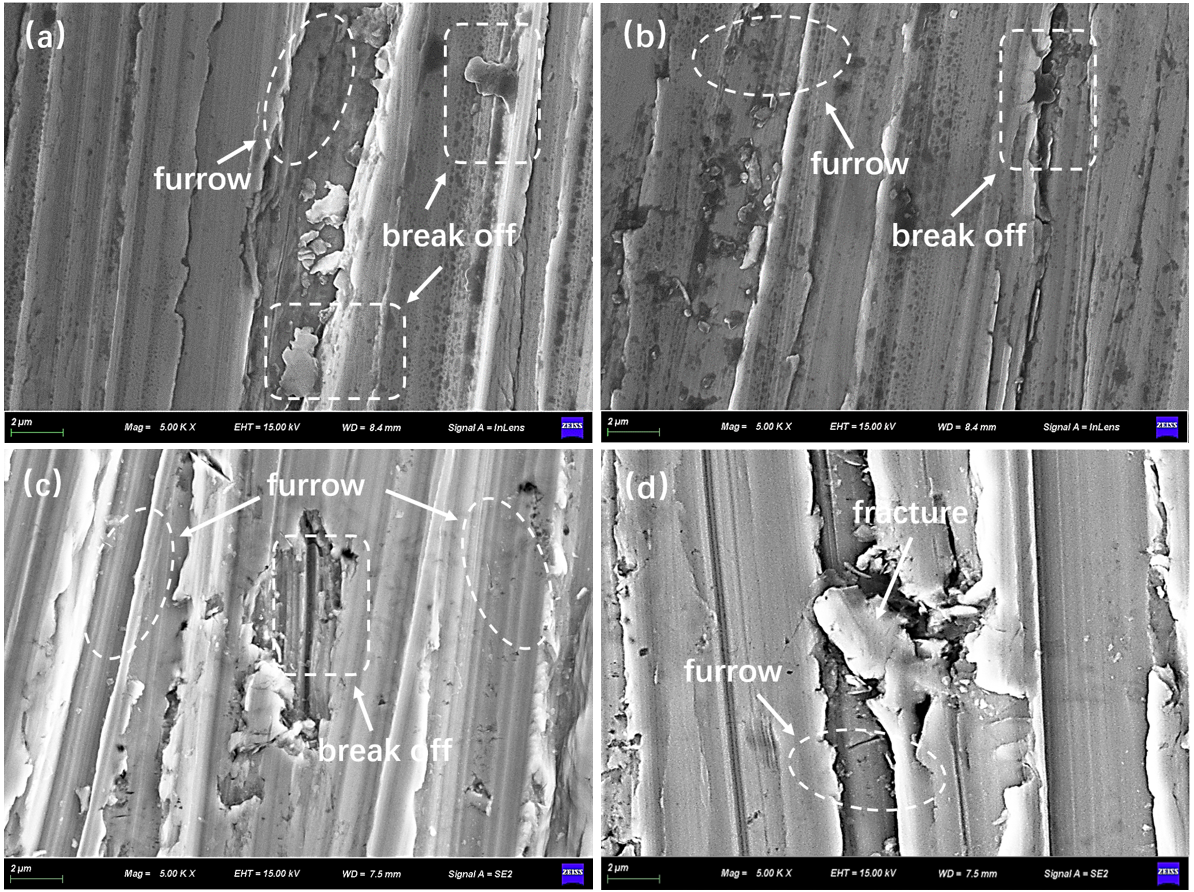
3.3. Hardness and Wear Resistance of Cladding Layers with Different WC Contents
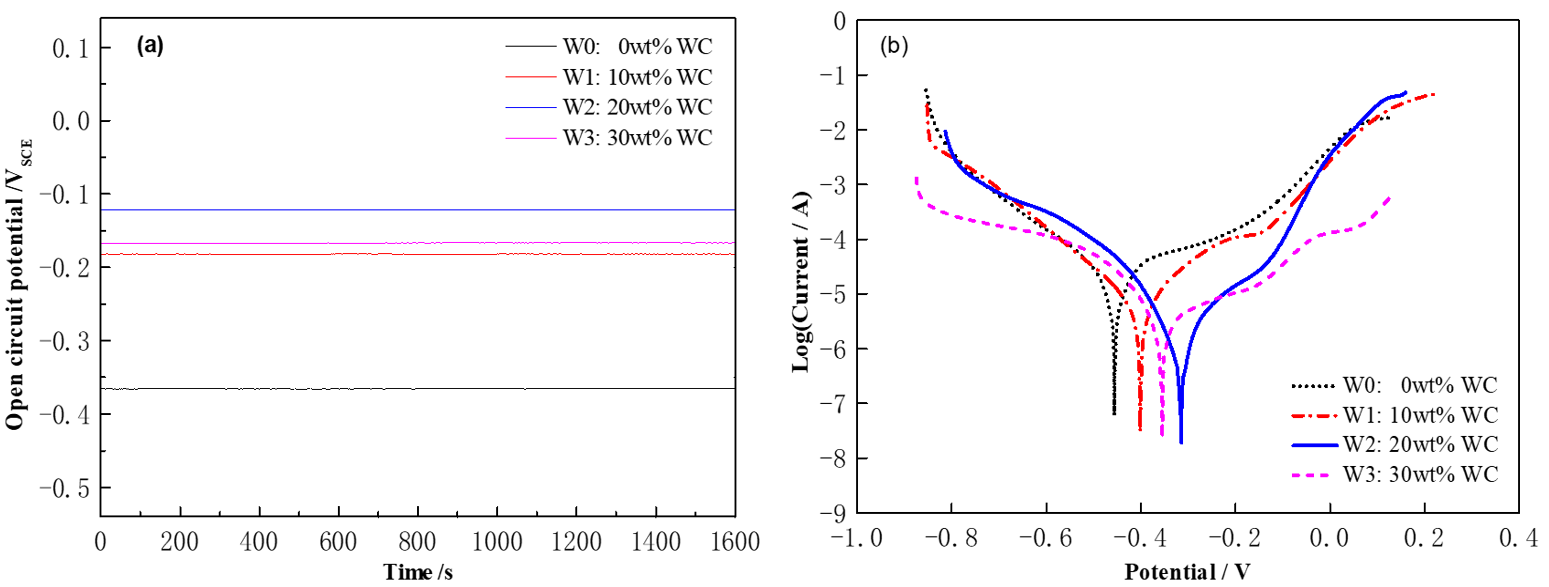
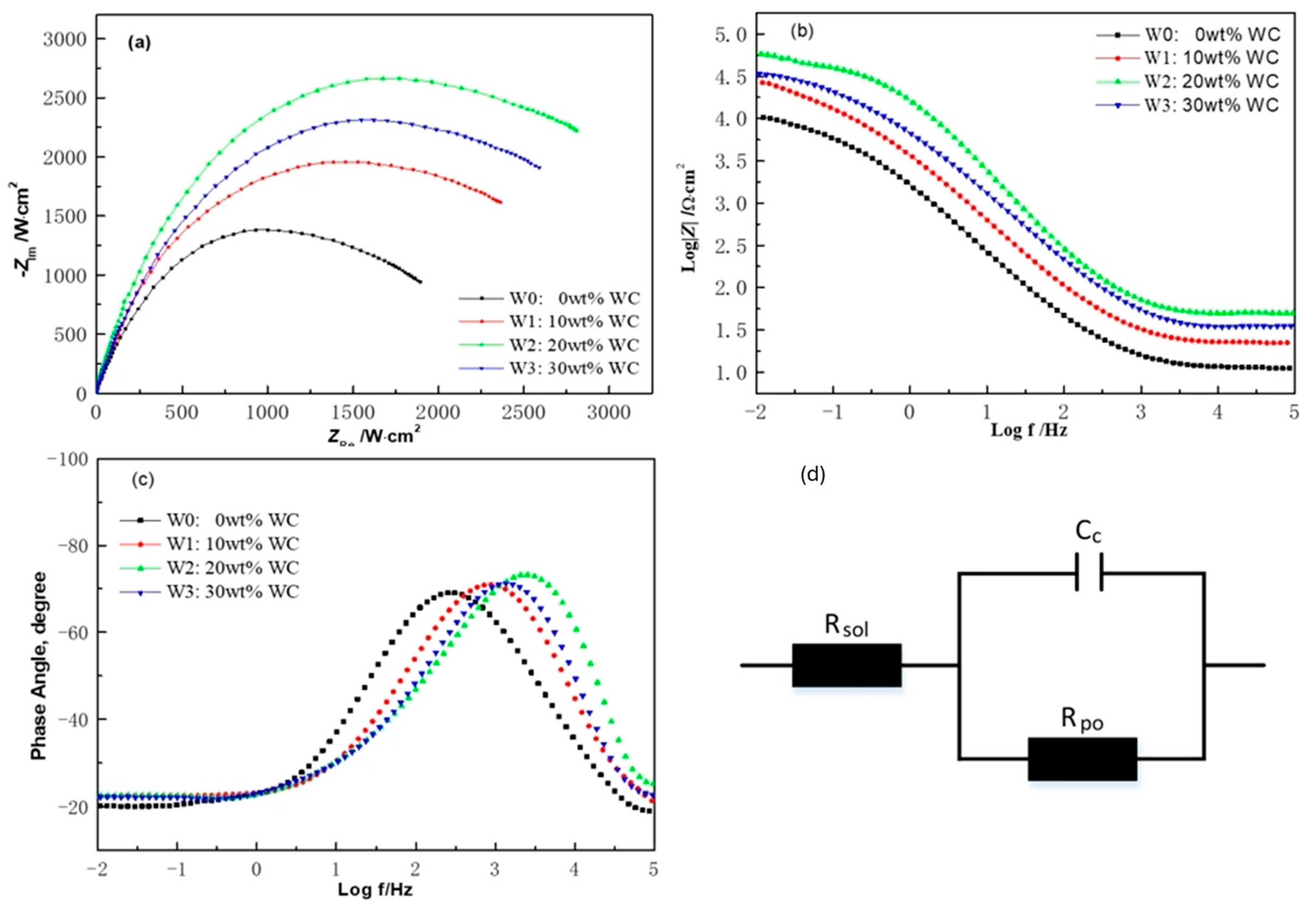
3.4. Analysis of Corrosion Resistance of Cladding Layers with Different WC Content
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coating consists of both BCC (body-centered cubic) and FCC (face-centered cubic) phases. With the addition of WC, the FCC phase gradually disappears, and the coating transforms into a multiphase structure with BCC as the matrix, accompanied by the precipitation of various carbide phases such as W2C, M7C3, MxCγ, and Co6W6C. The carbide phases are primarily distributed at grain boundaries. As the WC content increases, the coating grains are significantly refined, the number of carbides increases, and the coating structure evolves into a combination of equiaxed and columnar grains. Moreover, the coating exhibits excellent metallurgical bonding with the substrate.
- (2)
- The hardness of the coating significantly improves with increasing WC content. However, when the WC content exceeds 20 wt%, the strengthening effect tends to saturate, and the rate of increase slows down noticeably. At 30 wt% WC, the hardness reaches 1066.36 HV. The wear resistance of the coating initially decreases and then increases with higher WC content, reaching its optimal value at 20 wt% WC. At this composition, the friction coefficient is 0.549, and the wear mass loss is only 0.25 mg, representing a reduction of approximately 40% compared to the coating without WC.
- (3)
- During electrochemical corrosion in a 3.5 wt% NaCl solution, the appropriate addition of WC promotes the enrichment of Al and Cr elements at grain boundaries, facilitating the formation of a dense and stable passive film that effectively blocks Cl− ion penetration. However, excessive WC addition increases the density of microstructural defects in the coating, reducing the continuity and protective capability of the passive film and consequently degrading the corrosion resistance. The coating with 20 wt% WC exhibits the best corrosion resistance, with the lowest corrosion current density of 1.349 × 10−6 A·cm−2 and a passive film resistance of 2764 Ω·cm2.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured high entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Zhao, C.; Liang, D.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, S.; Ren, F. Insitu formed heterogeneous grain structure in spark-plasma-sintered CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy overcomes the strength-ductility trade-off. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 771, 138625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Hu, W.; Zhang, X.; Liao, B.; Wan, S.; Kang, L.; Guo, X. Corrosion behavior of the AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic highentropy alloy in chloride-containing sulfuric acid solutions at different temperatures. Materials 2022, 15, 4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santodonato, L.J.; Zhang, Y.; Feygenson, M.; Parish, C.M.; Gao, M.C.; Weber, R.J.; Neuefeind, J.C.; Tang, Z.; Liaw, P.K. Deviation from high-entropy configurations in the atomic distributions of a multiprincipal-element alloy. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Ren, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Huang, A.; Liu, X.; Cai, H.; Shan, X.; Luo, L.; et al. Unraveling the oxidation mechanism of an AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy at 1100 °C. Corros. Sci. 2022, 209, 110736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Dong, T.-S.; Fu, B.-G.; Li, G.-L.; Yang, L.-J. Effect of laser remelting on microstructure and properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coating. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 5728–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xia, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, J.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y. Precipitation behavior of AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys under ion irradiation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parakh, A.; Vaidya, M.; Kumar, N.; Chetty, R.; Murty, B. Effect of crystal structure and grain size on corrosion properties of AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 863, 158056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shockner, R.; Edry, I.; Pinkas, M.; Meshi, L. Systematic study of the effect of Cr on the microstructure, phase content and hardness of the AlCrxFeCoNi alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 940, 168897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.T.; Yang, Y.J.M.T. High-entropy alloy: Challenges and prospects. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Lin, T.; Lian, G.; Chen, C.; Huang, X. Effects of Nb content on the microstructure and properties of CoCrFeMnNiNbx high-entropy alloy coatings by laser cladding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 3835–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.M.; Alfano, J.P.; Martens, R.L.; Weaver, M.L. High-temperature oxidation behavior of Al-Co-Cr-Ni-(Fe or Si) multicomponent high-entropy alloys. JOM 2015, 67, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Jing, C.; Lin, T.; Tu, Y.; Fu, T. Effect of Ti and WC on the microstructure and mechanical properties of laser cladding AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2025, 60, 995–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Sun, W.L.; Yang, K.X.; Xing, X.F.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhou, H.N.; Lu, J. Wear mechanisms and micro-evaluation on WC particles investigation of WC-Fe composite coatings fabricated by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 420, 127341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.Y.; Peng, Y.B. Microstructures and mechanical properties of FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy/WC reinforcing particles composite coatings prepared by laser cladding and plasma cladding. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 84, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Wang, L.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, C.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z. Effect of WC content on the microstructure and wear resistance of laser cladding AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 high-entropy alloy coatings. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 41515–41526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, G.; Gao, W.; Chen, C.; Huang, X.; Feng, M. Review on hard particle reinforced laser cladding high-entropy alloy coatings. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 1366–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Guo, F.; Xiao, P. Y-Hf co-doped AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coating with superior oxidation and spallation resistance at 1100 °C. Corros. Sci. 2021, 182, 109267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, M.; Baker, I.; Yeh, J.; Liu, C.; Nieh, T. An assessment on the future development of high-entropy alloys: Summary from a recent workshop. Intermetallics 2015, 66, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xie, D.; Liu, Y.; Lv, F.; Zhou, K.; Jiao, C.; Gao, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zu, H.; et al. Effect of WC on the microstructure and mechanical properties of laser-clad AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy composite coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 976, 173219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Goyal, D.K.; Kumar, P.; Bansal, A. Influence of laser cladding parameters on slurry erosion performance of NiCrSiBC+50WC claddings. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 105, 105825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-J.; Qiao, J.-W.; Chen, S.-H.; Wang, X.-J.; Wu, Y.-C. Preparation, structures and properties of tungsten-containing refractory high entropy alloys. J. Mech. Eng. 2021, 70, 106201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameh, E.S. A review of basic crystallography and x-ray diffraction applications. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 3289–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, L.; Peng, Y.; Cai, X.; Tian, Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of TiB2-reinforced TiAl-based alloy coatings fabricated by laser melting deposition. Acta Metall. Sin. 2023, 59, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.G.; Li, R.F. Microstructure and property of laser cladding Ni-based alloy coating reinforced by WC particles. China Surf. Eng. 2010, 23, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Z.; Cao, J.; Lu, H.F.; Zhang, L.Y.; Luo, K.Y. Wear properties and microstructural analyses of Fe-based coatings with various WC contents on H13 die steel by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 369, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslarevic, A.; Djukic, M.B.; Rajicic, B.; Bakic, G.M.; Maksimovic, V.; Pavkov, V. Microstructure and wear behavior of MMC coatings deposited by plasma transferred arc welding and thermal flame spraying processes. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2020, 73, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.P.; Ren, X.N.; Ge, C.C. Microstructure and properties of Al0.2CrFeNiCu1.5 high-entropy alloy coating on zirconium alloy surface. At. Energy Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Gu, Y.; Jian, Z.W. Effect of vacuum heat treatment on microstructure and properties of WC-CoCr coatings prepared by HVOF. Mater. Prot. 2022, 55, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Sun, J.; Xiao, Z.; He, J.; Shi, W.; Cui, C. Effect of multi-element microalloying on the structure and properties of high-chromium cast iron. Materials 2023, 16, 3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Nayak, S.K.; Laha, T. Comparative study on wear and corrosion behavior of plasma sprayed Fe73Cr2Si11B11C3 and Fe63Cr9P5B16C7 metallic glass composite coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2022, 31, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, G.; Song, Q.; Lu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Y. Microstructure, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance of SiC reinforced AlxCoCrFeNiTi1-x high-entropy alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 437, 128349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Shen, Y.; Ju, Q.; Zhang, J. Impact toughness and sliding wear behavior of Stellite 6B alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2025, 54, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, K.; Fu, X.; Hua, Z. Effect of WC content on microstructure and properties of CrFeMoNiTi(WC)x high-entropy alloys composite coatings prepared by selective laser melting. Mater. Corros. 2022, 73, 1676–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.K.; Shi, W.Q.; Huang, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of TiC/WC-reinforced AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys prepared by laser cladding. Crystals 2024, 14, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Man, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G.; Xiao, S.; Dong, N. Effect of Nano WC on wear and corrosion resistances of CoCrFeNiTi high entropy alloy coating. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.K.; Huang, F.; Xu, Y.F.; Yuan, W.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, J. Microstructure Evolution and Electrochemical Passivation Behavior of FeCrMn1.3NiAlx High Entropy Alloys. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2022, 42, 218–226. Available online: https://www.jcscp.org/EN/10.11902/1005.4537.2021.080 (accessed on 5 June 2025).




| Element | C | Mn | Si | S | P | Ni | Cr | Cu | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20# | 0.22 | 0.54 | 0.28 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 | Bal. |
| Sample | AlCoCrFeNi Powder | WC Powder |
|---|---|---|
| W0 | 100 | 0 |
| W1 | 90 | 10 |
| W2 | 80 | 20 |
| W3 | 70 | 30 |
| Coatings | OCP (V vs. SCE) | Ecorr (V) | Icorr (A·cm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| W0 | −0.362 | −0.455 | 1.259 × 10−5 |
| W1 | −0.187 | −0.401 | 3.548 × 10−6 |
| W2 | −0.126 | −0.314 | 1.349 × 10−6 |
| W3 | −0.168 | −0.355 | 2.398 × 10−6 |
| Coatings | Rs (Ω·cm2) | CPE-T (Ω−1·sn) | CPE-P | Rp (Ω·cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W0 | 6.378 | 8.326 × 10−4 | 0.786 | 2126 |
| W1 | 6.652 | 3.766 × 10−4 | 0.896 | 2532 |
| W2 | 6.876 | 3.532 × 10−4 | 0.924 | 2764 |
| W3 | 6.674 | 3.985 × 10−4 | 0.877 | 2578 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, T.; Meng, Z.; Qing, J.; Xu, W.; Ouyang, Y.; Zeng, Y. Effects of WC Addition on Microstructure and Properties of Plasma-Cladded AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings. Lubricants 2025, 13, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13090407
Liu X, Zhao J, Li T, Meng Z, Qing J, Xu W, Ouyang Y, Zeng Y. Effects of WC Addition on Microstructure and Properties of Plasma-Cladded AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings. Lubricants. 2025; 13(9):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13090407
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xinbin, Juangang Zhao, Tiansheng Li, Zhengbing Meng, Jinbiao Qing, Wen Xu, Youxuan Ouyang, and Yuanyuan Zeng. 2025. "Effects of WC Addition on Microstructure and Properties of Plasma-Cladded AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings" Lubricants 13, no. 9: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13090407
APA StyleLiu, X., Zhao, J., Li, T., Meng, Z., Qing, J., Xu, W., Ouyang, Y., & Zeng, Y. (2025). Effects of WC Addition on Microstructure and Properties of Plasma-Cladded AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings. Lubricants, 13(9), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13090407




