Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Cu40Zn-Ti3AlC2 Composites by Powder Metallurgy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
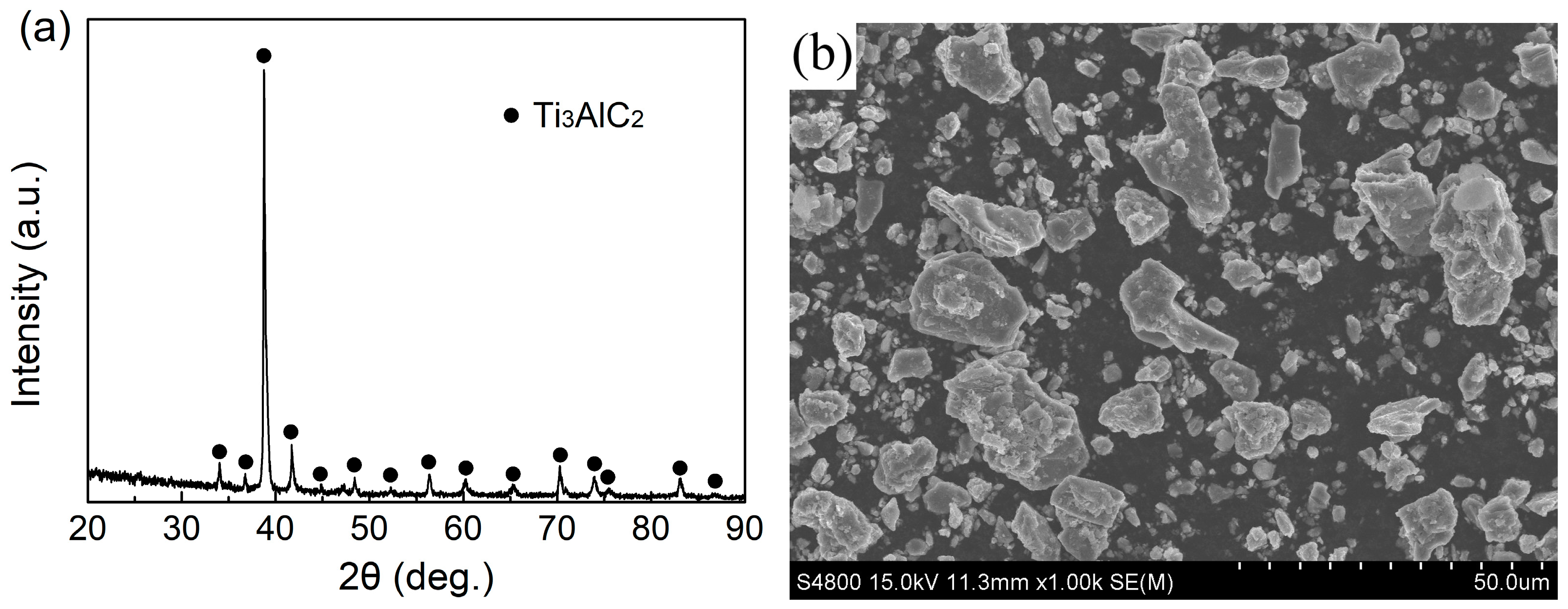
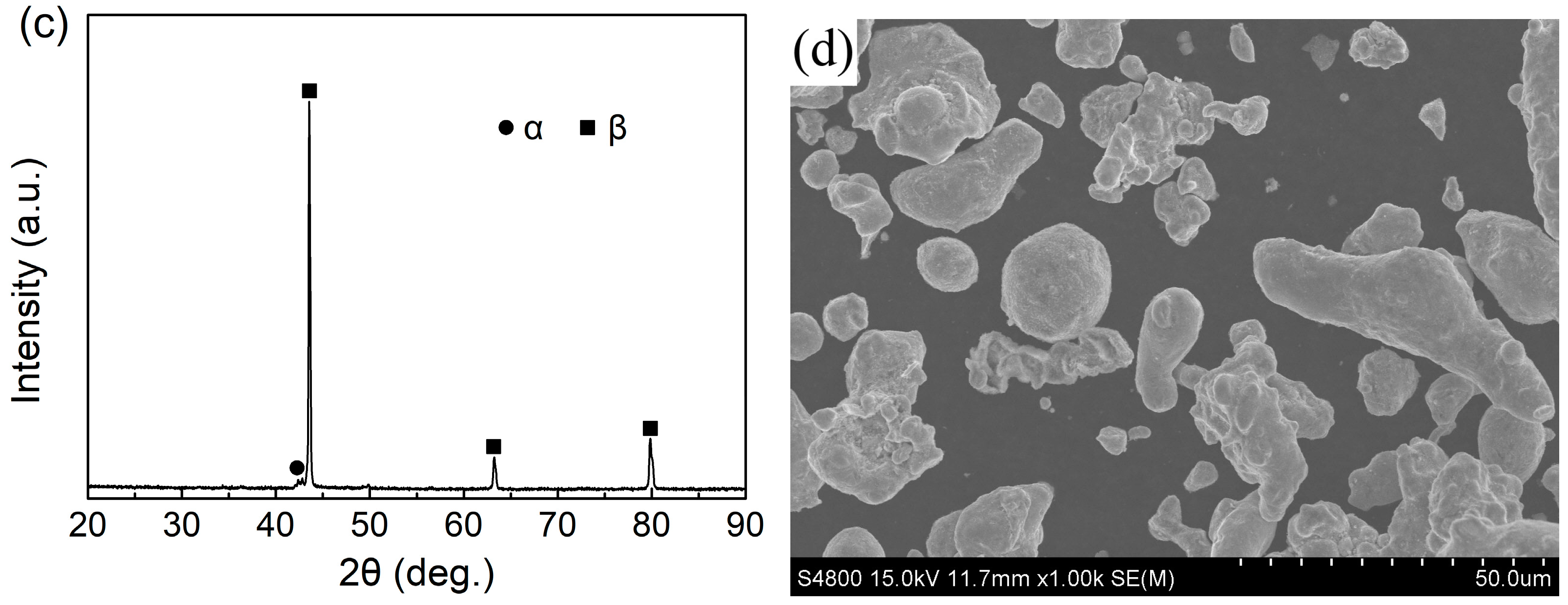
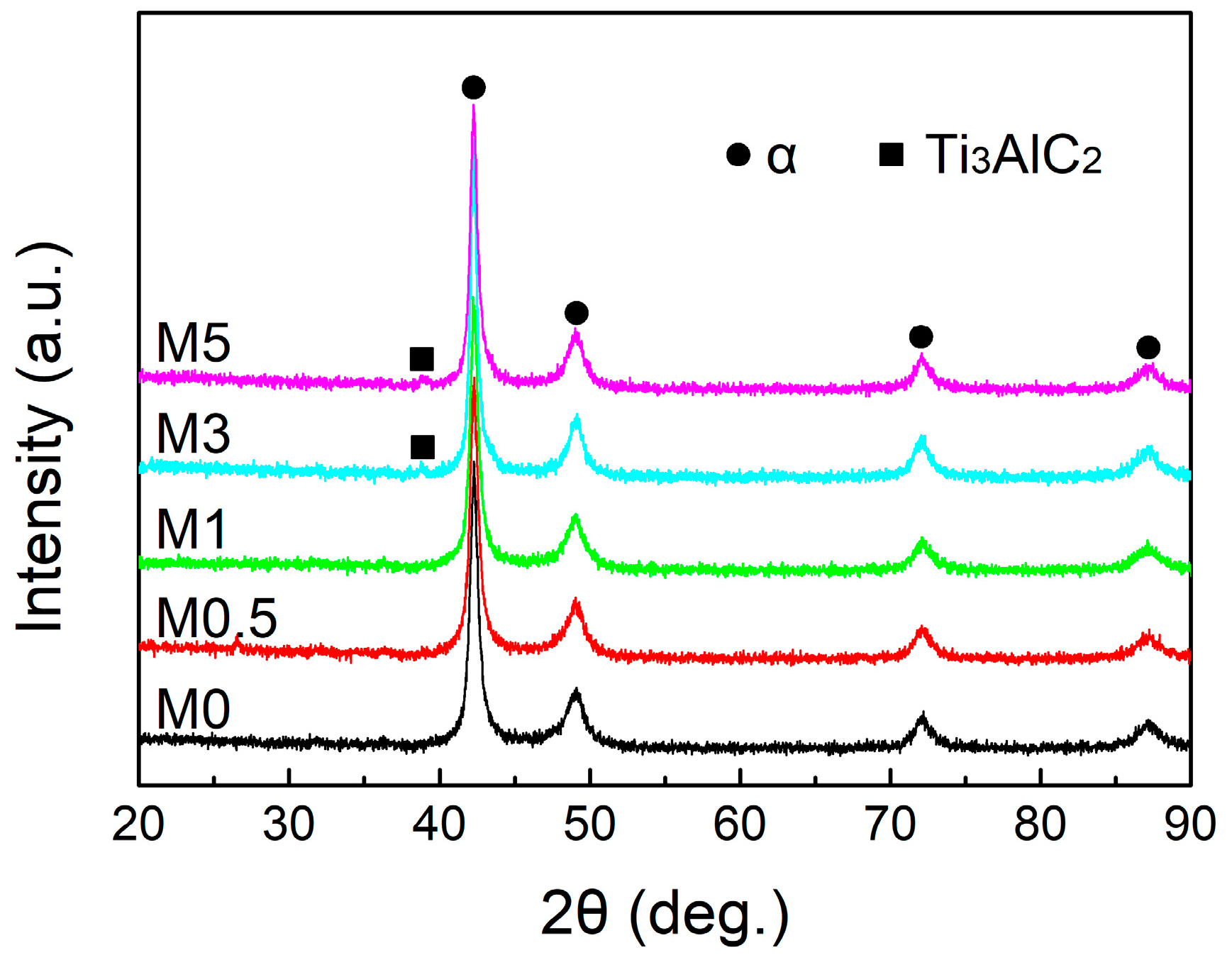
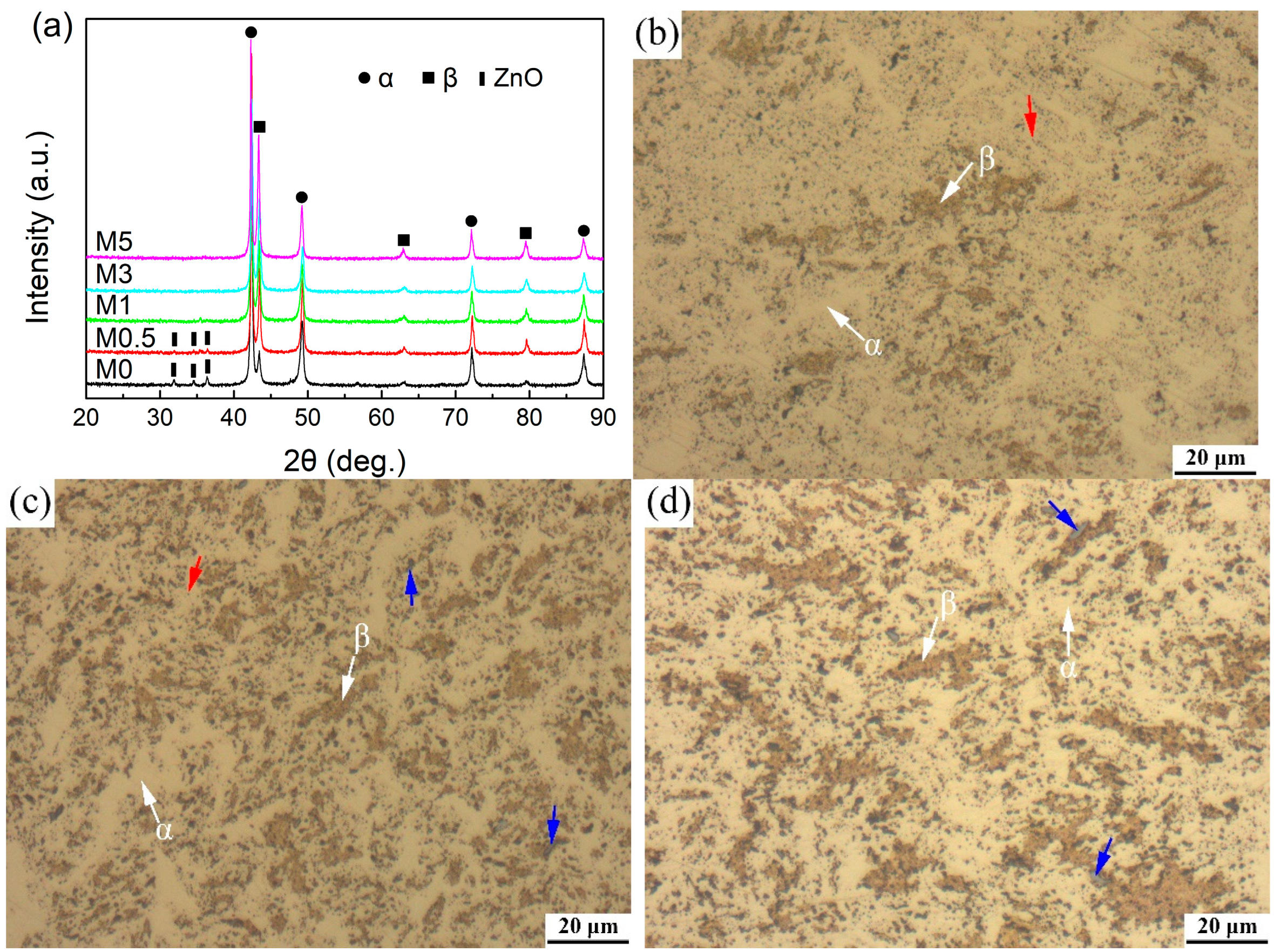
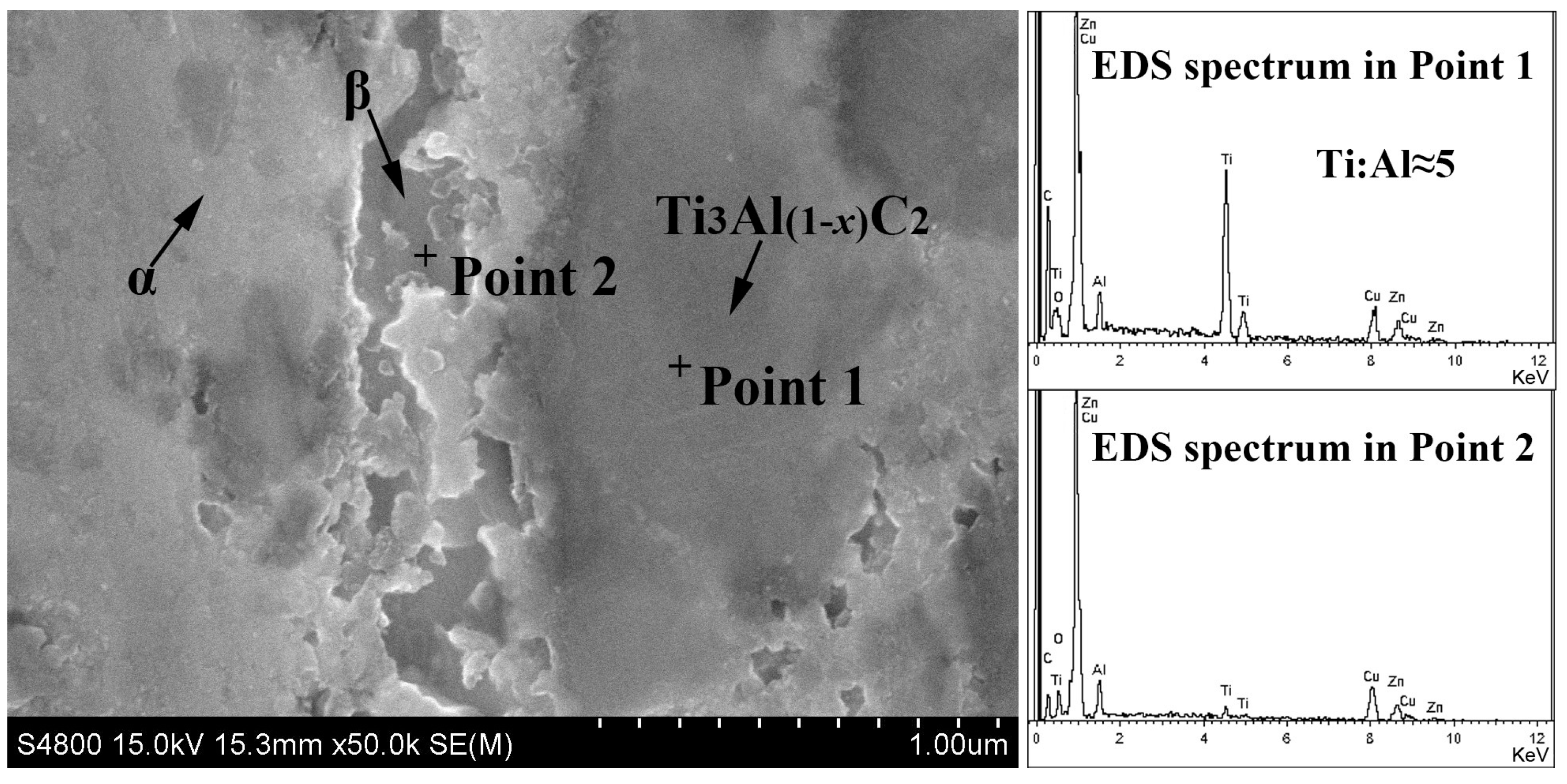
3.1. Microstructural Investigation
3.2. Mechanical Properties
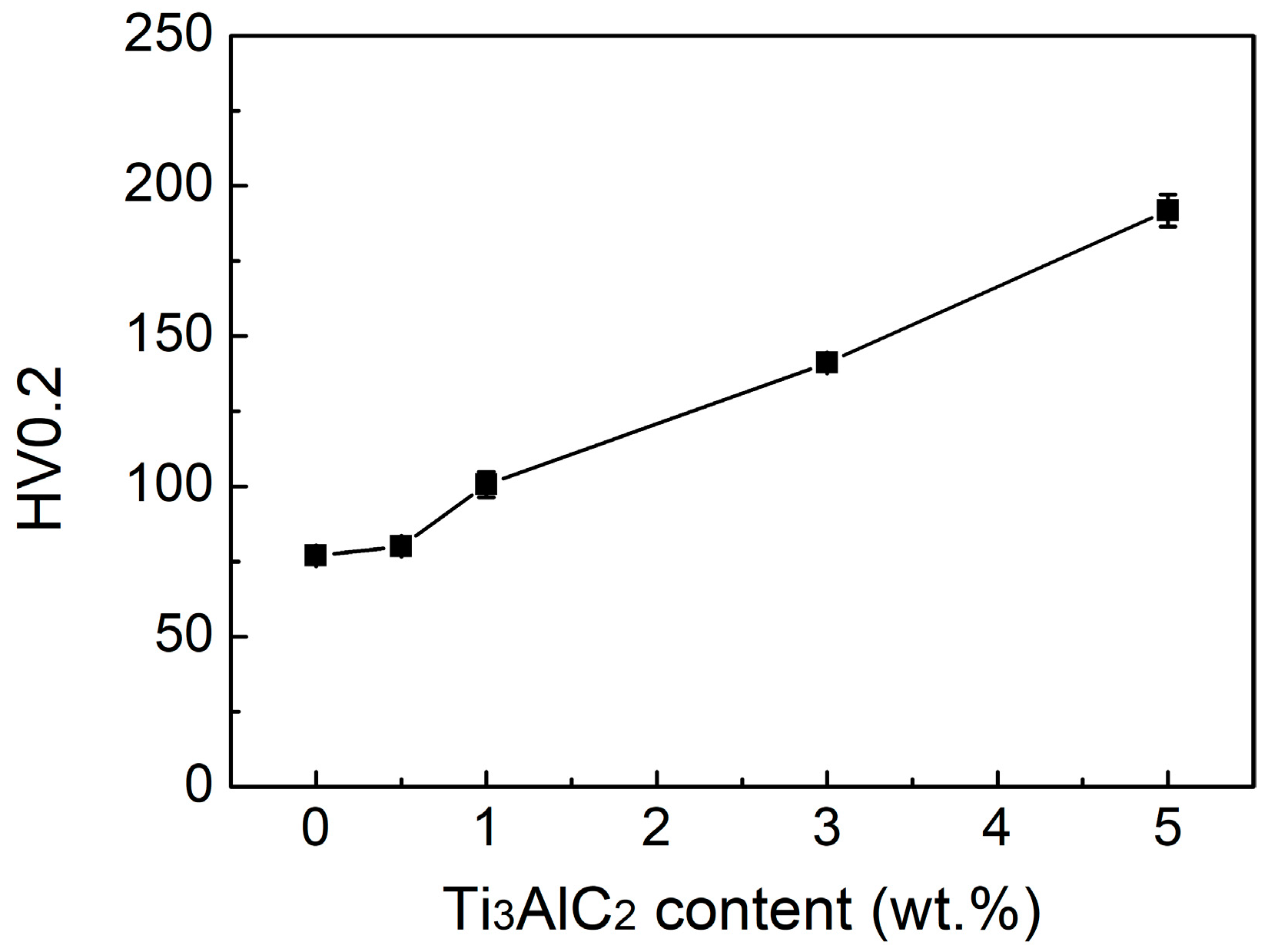
3.2.1. Hardness
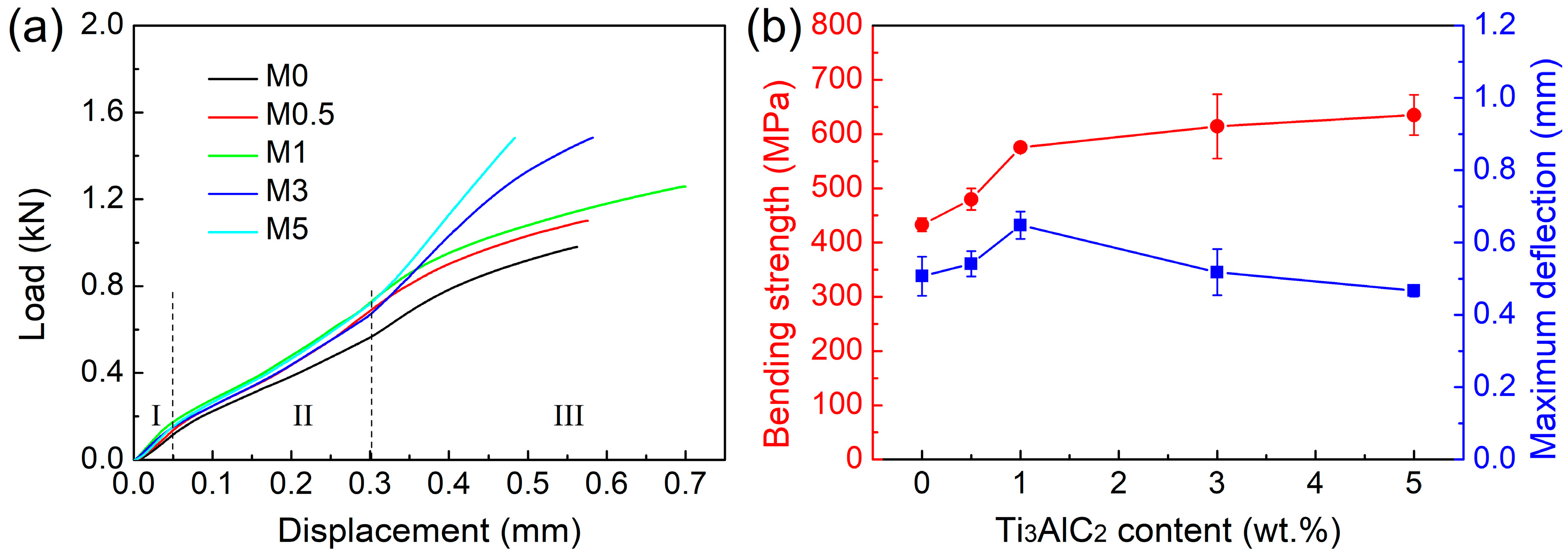
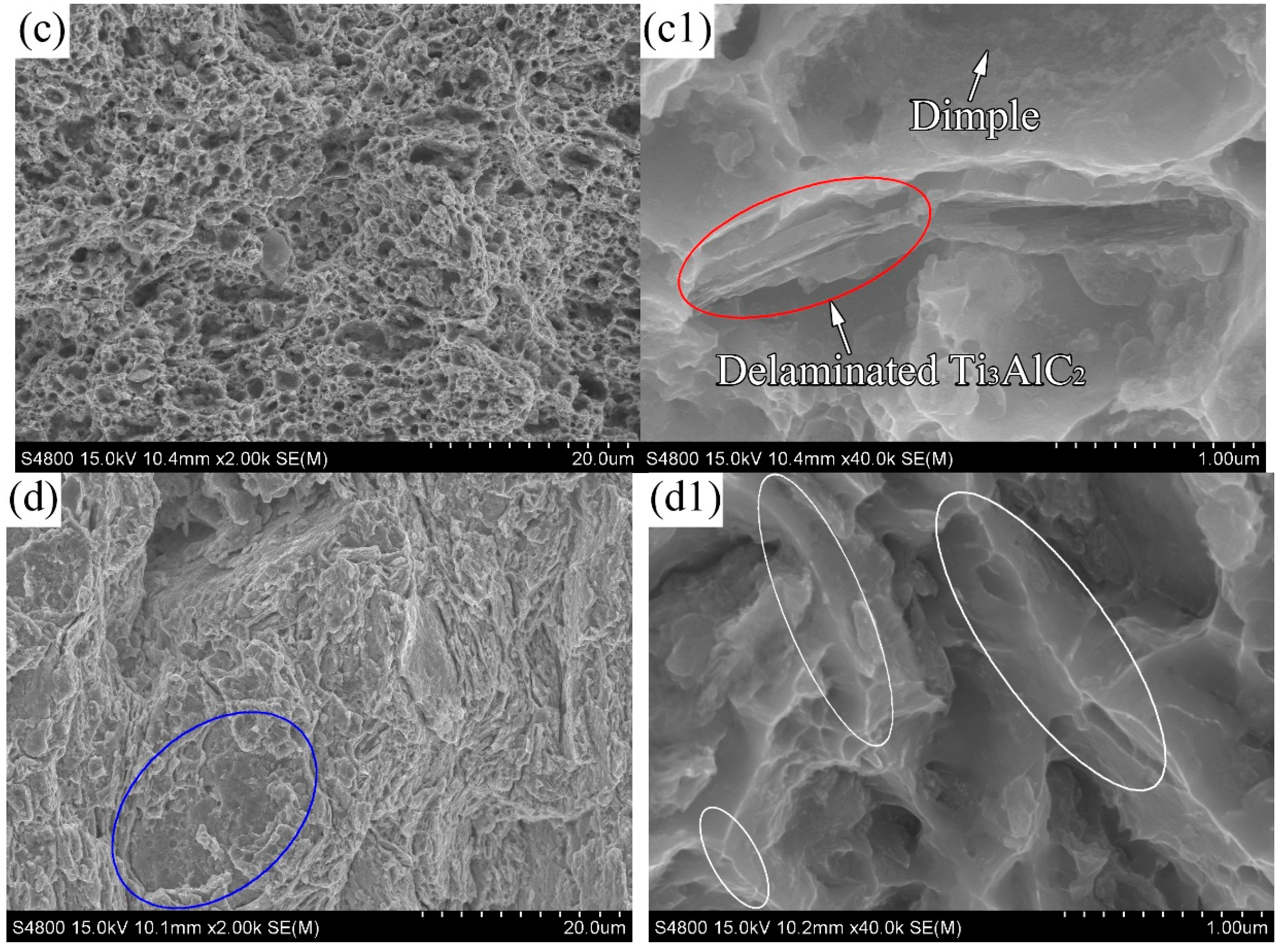
3.2.2. Flexural Properties
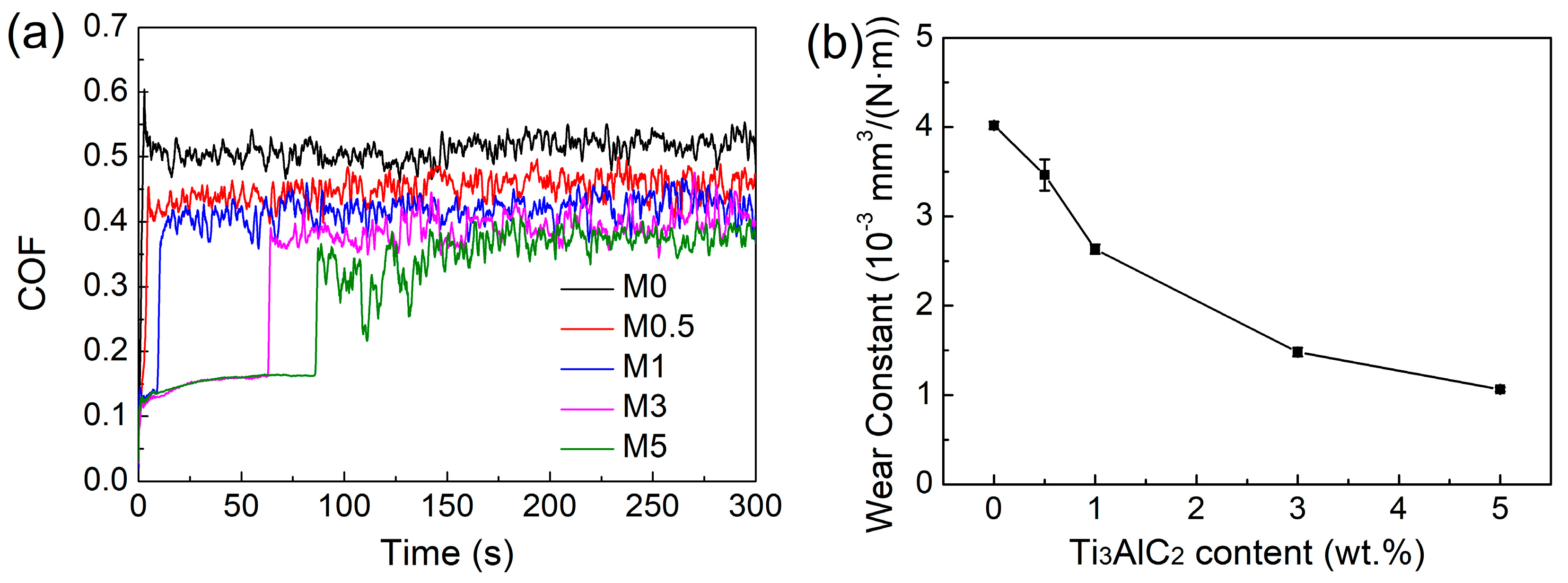
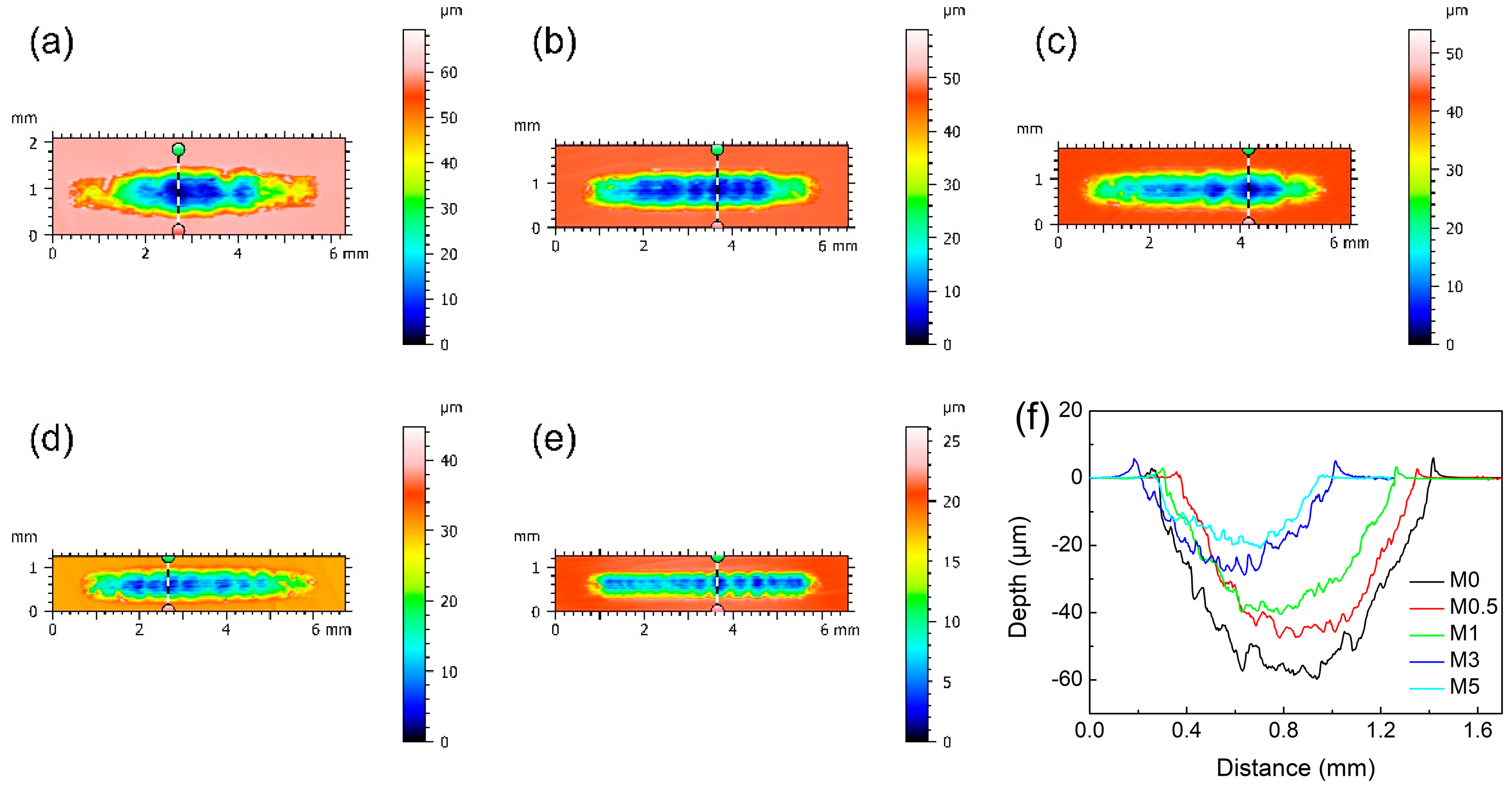
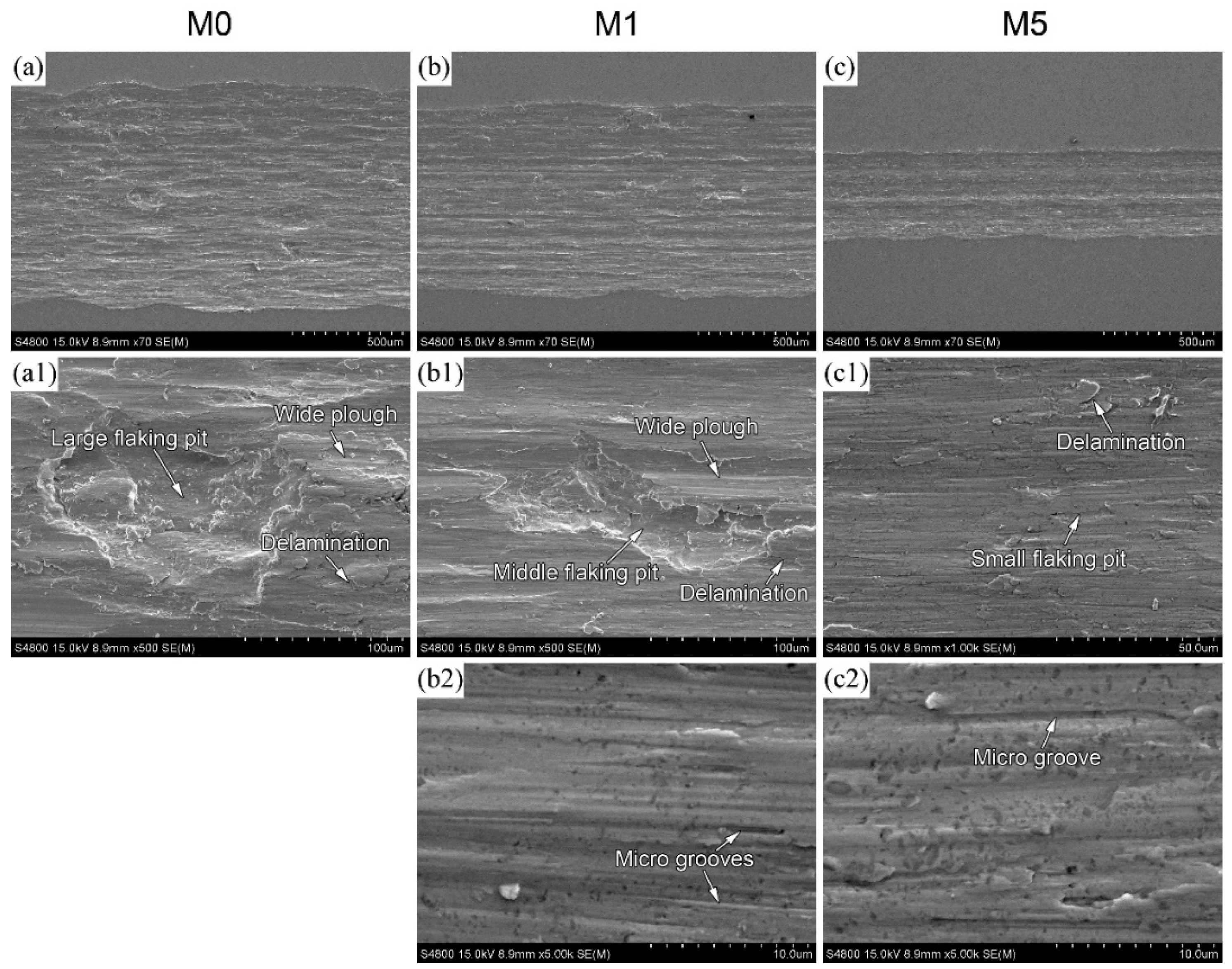
3.3. Tribological Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, J.R. Copper and Copper Alloys; ASM International: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lipowsky, H.; Arpaci, E. Copper in the Automotive Industry; Wiley Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, C.; Li, S.; Pan, D.; Zheng, F. Interface design of lead-free free-cutting titanium reinforced graphite brass composites and its effect on mechanical properties and cutting performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 774, 138909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, J.; Alm, P.; M’Saoubi, R.; Malmberg, P.; Ståhl, J.-E.; Bushlya, V. On the function of lead (Pb) in machining brass alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 7263–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilarinho, C.; Davim, J.P.; Soares, D.; Castro, F.; Barbosa, J. Influence of the chemical composition on the machinability of brasses. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2005, 170, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavroulakis, P.; Toulfatzis, A.I.; Pantazopoulos, G.A.; Paipetis, A.S. Machinable Leaded and Eco-Friendly Brass Alloys for High Performance Manufacturing Processes: A Critical Review. Metals 2022, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-C.; Wang, J.-S.; Wu, P.T.-Y.; Wu, W. Microstructural development of brass alloys with various Bi and Pb additions. Met. Mater. Int. 2013, 19, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Kim, S.; Han, S. Effect of misch metal on elevated temperature tensile ductility of the Cu-Zn-Bi alloy. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, B.; Barbier, F.; Aucouturier, M. Embrittlement of copper by liquid bismuth. Scr. Mater. 1999, 40, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adineh, M.; Doostmohammadi, H. Microstructure, mechanical properties and machinability of Cu–Zn–Mg and Cu–Zn–Sb brass alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1504–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsumi, H.; Imai, H.; Li, S.; Kondoh, K.; Kousaka, Y.; Kojima, A. Fabrication and properties of high-strength extruded brass using elemental mixture of Cu–40% Zn alloy powder and Mg particle. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 135, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostmohammadi, H.; Moridshahi, H. Effects of Si on the microstructure, ordering transformation and properties of the Cu60Zn40 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 640, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ding, Z.; Tao, Q.C.; Liang, L.; Ding, Y.F.; Zhang, W.W.; Zhu, Q.L. High-strength and free-cutting silicon brasses designed via the zinc equivalent rule. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 723, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondoh, K.; Imai, H.; Kosaka, Y.; Kojima, A.; Umeda, J. Machinable Cu-40Zn Composites Containing Graphite Particles by Powder Metallurgy Process. J. Met. 2009, 2009, 853092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, S.; Imai, H.; Umeda, J.; Fu, Y.; Kondoh, K. Investigation of High-strength Lead-free Machinable Cu40Zn Duplex Graphite Brasses by Powder Metallurgy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, H.-C.; Tang, J.-C.; Xue, Y.-Y.; Ye, N. Preparation of lead-free free-cutting graphite brasses by graphitization of cementite. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 3252–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.M. Progress in research and development on MAX phases: A family of layered ternary compounds. Int. Mater. Rev. 2013, 56, 143–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvo, C.; Chicardi, E.; Hernández-Saz, J.; Aguilar, C.; Gnanaprakasam, P.; Mangalaraja, R. Microstructure, electrical and mechanical properties of Ti2AlN MAX phase reinforced copper matrix composites processed by hot pressing. Mater. Charact. 2021, 171, 110812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.C. Microstructure, mechanical, and electrical properties of Cu–Ti3AlC2 and in situ Cu–TiCx composites. J. Mater. Res. 2011, 23, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Feng, Y.; Qian, G.; Huang, X.; Guo, S.; Sun, X. Effect of Ti3AlC2 Content on Electrical Friction and Wear Behaviors of Cu–Ti3AlC2 Composites. Tribol. Lett. 2019, 67, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, P.; Sun, H.; Zhang, P.; Lin, C.; Yang, T.; Wu, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, T.; Lian, Z.; Levchenko, V. Preparation and tribological properties of WS2 solid lubricating coating with dense structure using HiPIMS. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, M.; Spencer, P.J. Thermodynamic reevaluation of the Cu-Zn system. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 1993, 14, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, F.H. Quantitative interpretation of X-ray diffraction patterns of mixtures. II. Adiabatic principle of X-ray diffraction analysis of mixtures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1974, 7, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Structure stability of Ti3AlC2 in Cu and microstructure evolution of Cu–Ti3AlC2 composites. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 4381–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhai, H.; Ai, M.; Huang, Z. Fabrication and properties of Cu-Ti3AlC2 cermet. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2007, 36, 668–670. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, X.-H.; Zhou, S.-F.; Guo, B.-S.; Zhang, Z.-G.; Li, W. Improving mechanical properties of Cu/Ti3AlC2 composites via in-situ decomposed gradient interfaces. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 834, 142615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.P.; Li, X.H. Metallographic Atlas of Processed Copper and Copper Alloy; Central South University Press: Changsha, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Keneshloo, M.; Paidar, M.; Taheri, M. Role of SiC ceramic particles on the physical and mechanical properties of Al–4%Cu metal matrix composite fabricated via mechanical alloying. J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 51, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razazi, H.A.; Paidar, M.; Ojo, O.O. Effect of Mn and Cr on structure and mechanical properties of Al-10%Mg-0.1%Ti alloy. Vacuum 2018, 155, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, F.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, N. A study of the optimization mechanism of solid lubricant concentration in Ni/MoS2 sellf-lubricating composite. Wear 1997, 205, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, W.; Mai, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Jie, X. Fabrication of graphene oxide-Ti3AlC2 synergistically reinforced copper matrix composites with enhanced tribological performance. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 18592–18598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, S.; Cheng, J.; Qiao, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. Microstructural, mechanical and tribological properties of Al matrix composites reinforced with Cu coated Ti3AlC2. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 690, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paidar, M.; Ojo, O.O.; Ezatpour, H.R.; Heidarzadeh, A. Influence of multi-pass FSP on the microstructure, mechanical properties and tribological characterization of Al/B4C composite fabricated by accumulative roll bonding (ARB). Surf. Coatings Technol. 2019, 361, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paidar, M.; Bokov, D.; Mehrez, S.; Ojo, O.O.; Ramalingam, V.V.; Memon, S. Improvement of mechanical and wear behavior by the development of a new tool for the friction stir processing of Mg/B4C composite. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2021, 426, 127797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaheri, Y.; Bahiraei, M.; Jalilvand, M.M.; Ghasemi, S.; Heidarpour, A. Improving mechanical and tribological performances of pure copper matrix surface composites reinforced by Ti2AlC MAX phase and MoS2 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 270, 124790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, F.; Zhou, S.; Yang, T.; Wu, L.; Wu, J.; Ying, P.; Zhang, P.; Lin, C.; Fu, Y.; Tu, Z.; et al. Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Cu40Zn-Ti3AlC2 Composites by Powder Metallurgy. Lubricants 2024, 12, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12090306
Peng F, Zhou S, Yang T, Wu L, Wu J, Ying P, Zhang P, Lin C, Fu Y, Tu Z, et al. Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Cu40Zn-Ti3AlC2 Composites by Powder Metallurgy. Lubricants. 2024; 12(9):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12090306
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Fangdian, Shidong Zhou, Tao Yang, Liwei Wu, Jianbo Wu, Puyou Ying, Ping Zhang, Changhong Lin, Yabo Fu, Zhibiao Tu, and et al. 2024. "Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Cu40Zn-Ti3AlC2 Composites by Powder Metallurgy" Lubricants 12, no. 9: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12090306
APA StylePeng, F., Zhou, S., Yang, T., Wu, L., Wu, J., Ying, P., Zhang, P., Lin, C., Fu, Y., Tu, Z., Wang, T., Zhang, X., Myshkin, N., & Levchenko, V. (2024). Microstructure, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Cu40Zn-Ti3AlC2 Composites by Powder Metallurgy. Lubricants, 12(9), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12090306




