Big and Young Supermassive Black Holes in the Early Universe
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Finding High-Redshift Blazars
2.1. All-Sky Surveys
2.2. Candidate Selection
3. Discussion
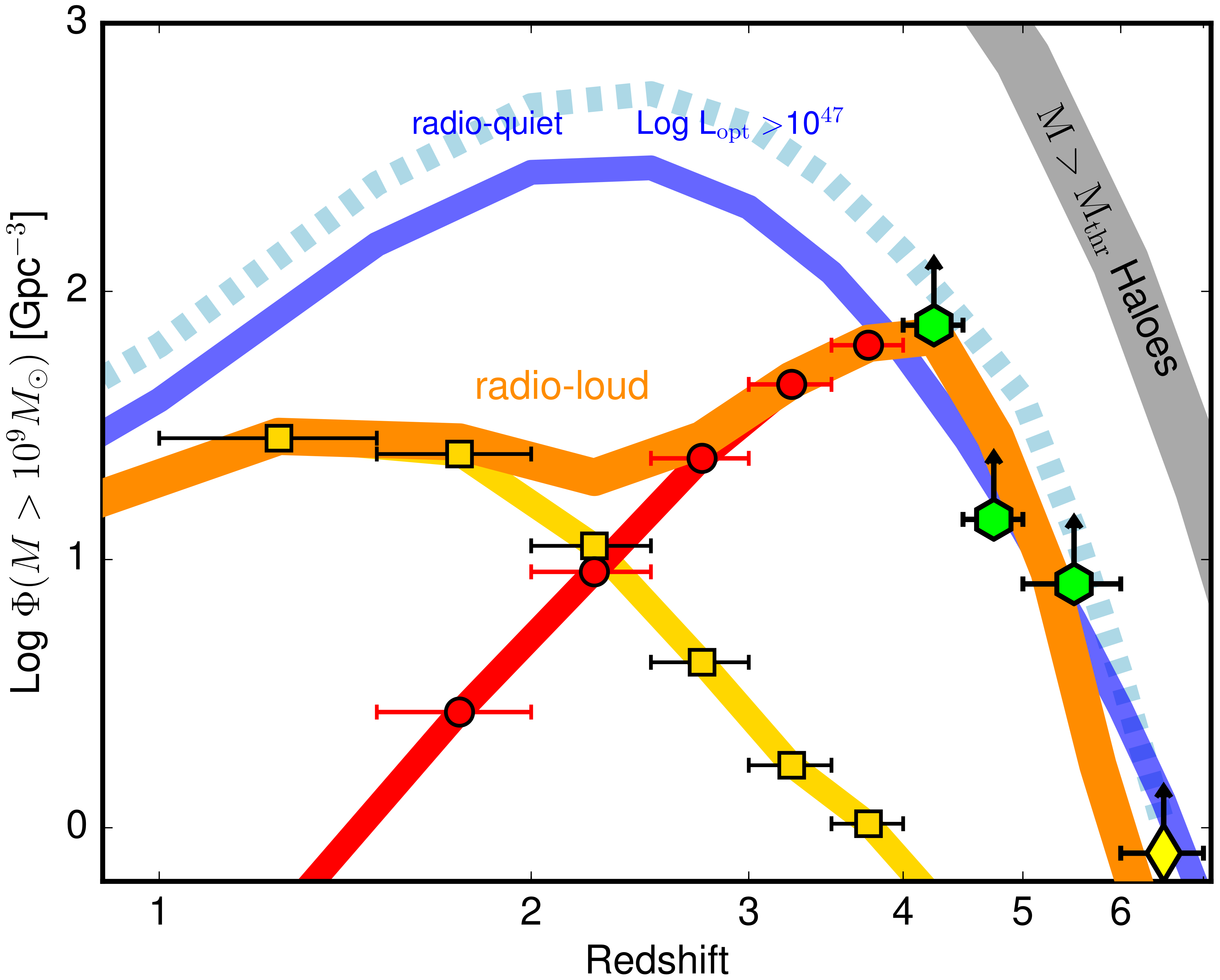
3.1. How Many Jetted AGNs at High-z?
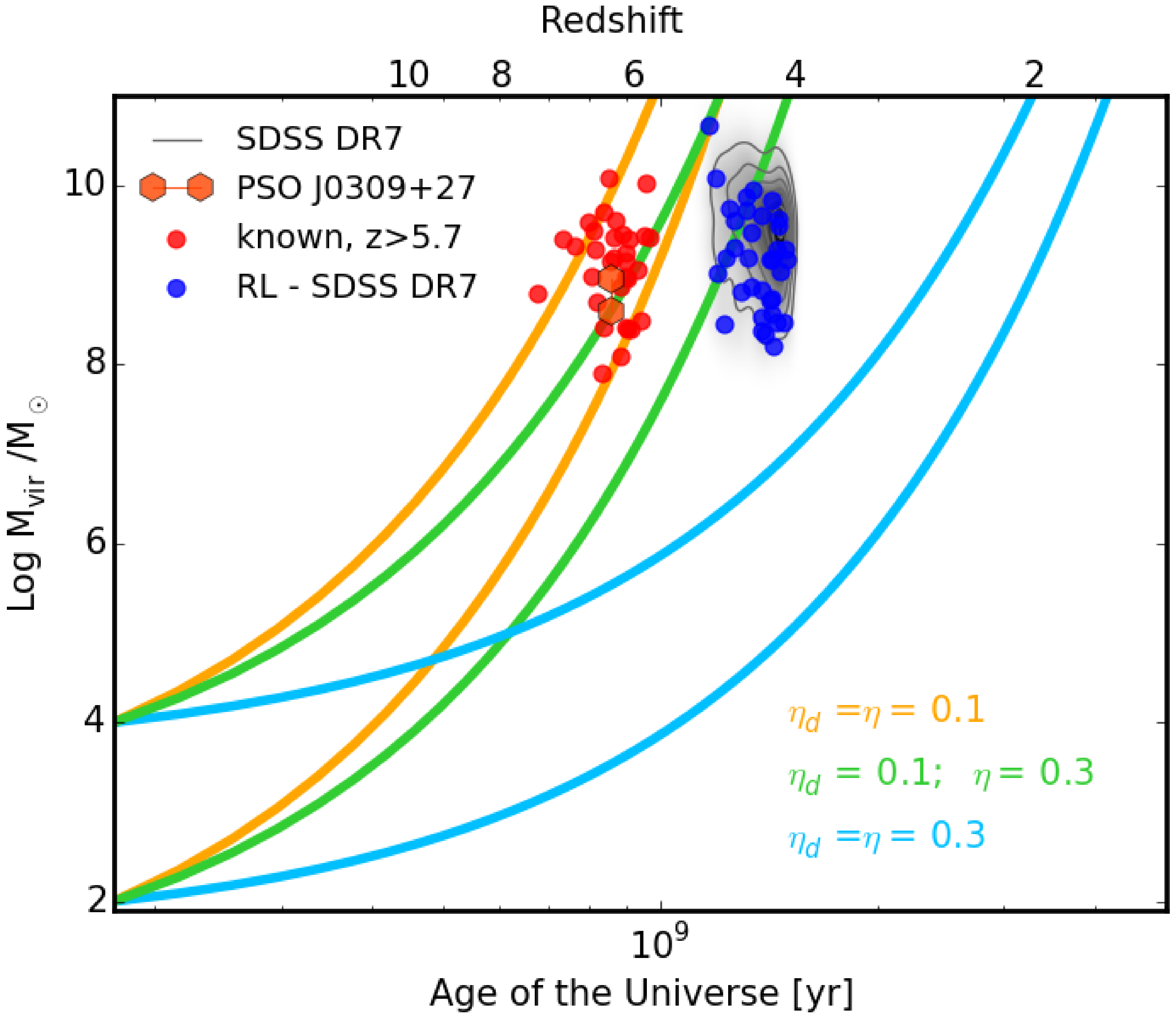
3.2. Early Quasar Evolution
4. Open Issues
4.1. Missing Jetted Sources
4.2. Where Does the Jet Point?
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGN | Active galactic nucleus |
| BL Lac | BL Lacertae object |
| Fermi/LAT | The Large Area Telescope onboard the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope |
| FIRST | Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-Centimeters |
| FRSQ | Flat spectrum radio quasars |
| SDSS | Sloan Digital Sky Survey |
| Swift/BAT | Burst Alert Telescope onboard the Niel Gehrels Swift Observatory |
| VLA | Very Large Array |
| VLBI | Very-long-baseline interferometry |
References
- Urry, C.M.; Padovani, P. Unified Schemes for Radio-Loud Active Galactic Nuclei. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1995, 107, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanaroff, B.L.; Riley, J.M. The morphology of extragalactic radio sources of high and low luminosity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1974, 167, 31P–36P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, P.; Alexander, D.M.; Assef, R.J.; De Marco, B.; Giommi, P.; Hickox, R.C.; Richards, G.T.; Smolčić, V.; Hatziminaoglou, E.; Mainieri, V.; et al. Active galactic nuclei: What’s in a name? Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2017, 25, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicki, G.B.; Lightman, A.P. Radiative Processes in Astrophysics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F. Canonical high-power blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 397, 985–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, R.W.; Sowards-Emmerd, D.; Greenhill, L.; Michelson, P. Q0906+6930: The Highest Redshift Blazar. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2004, 610, L9–L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, R.W. The Spectral Energy Distribution of the High-z Blazar Q0906+6930. Astron. J. 2006, 132, 1959–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bassett, L.C.; Brandt, W.N.; Schneider, D.P.; Vignali, C.; Chartas, G.; Garmire, G.P. Chandra Observations of Radio-Loud Quasars at z>4: X-rays from the Radio Beacons of the Early Universe. Astron. J. 2004, 128, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemmer, O.; Brandt, W.N.; Vignali, C.; Schneider, D.P.; Fan, X.; Richards, G.T.; Strauss, M.A. The X-ray Spectral Properties and Variability of Luminous High-Redshift Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2005, 630, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.; Elvis, M.; Risaliti, G. The Fifth Data Release Sloan Digital Sky Survey/XMM-Newton Quasar Survey. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2009, 183, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Atwood, W.B.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Becerra Gonzalez, J.; Bellazzini, R.; Bissaldi, E.; et al. The Third Catalog of Active Galactic Nuclei Detected by the Fermi Large Area Telescope. Astrophys. J. 2015, 810, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossati, G.; Maraschi, L.; Celotti, A.; Comastri, A.; Ghisellini, G. A unifying view of the spectral energy distributions of blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1998, 299, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Righi, C.; Costamante, L.; Tavecchio, F. The Fermi blazar sequence. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 469, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrels, N.; Chincarini, G.; Giommi, P.; Mason, K.O.; Nousek, J.A.; Wells, A.A.; White, N.E.; Barthelmy, S.D.; Burrows, D.N.; Cominsky, L.R.; et al. The Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission. Astrophys. J. 2004, 611, 1005–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Becerra Gonzalez, J.; Bellazzini, R.; Bissaldi, E.; Blandford, R.D.; et al. Gamma-Ray Blazars within the First 2 Billion Years. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 837, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belladitta, S.; Moretti, A.; Caccianiga, A.; Spingola, C.; Severgnini, P.; Della Ceca, R.; Ghisellini, G.; Dallacasa, D.; Sbarrato, T.; Cicone, C.; et al. The first blazar observed at z > 6. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 635, L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Hopkins, P.F.; Faucher-Giguère, C.A.; Alexander, D.M.; Richards, G.T.; Ross, N.P.; Hickox, R.C. The bolometric quasar luminosity function at z = 0–7. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 495, 3252–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajello, M.; Shaw, M.S.; Romani, R.W.; Dermer, C.D.; Costamante, L.; King, O.G.; Max-Moerbeck, W.; Readhead, A.; Reimer, A.; Richards, J.L.; et al. The Luminosity Function of Fermi-detected Flat-spectrum Radio Quasars. Astrophys. J. 2012, 751, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajello, M.; Costamante, L.; Sambruna, R.M.; Gehrels, N.; Chiang, J.; Rau, A.; Escala, A.; Greiner, J.; Tueller, J.; Wall, J.V.; et al. The Evolution of Swift/BAT Blazars and the Origin of the MeV Background. Astrophys. J. 2009, 699, 603–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Della Ceca, R.; Volonteri, M.; Ghirlanda, G.; Tavecchio, F.; Foschini, L.; Tagliaferri, G.; Haardt, F.; Pareschi, G.; Grindlay, J. Chasing the heaviest black holes of jetted active galactic nuclei. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 405, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Haardt, F.; Della Ceca, R.; Volonteri, M.; Sbarrato, T. The role of relativistic jets in the heaviest and most active supermassive black holes at high redshift. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 432, 2818–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, P.F.; Richards, G.T.; Hernquist, L. An Observational Determination of the Bolometric Quasar Luminosity Function. Astrophys. J. 2007, 654, 731–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.D.; Znajek, R.L. Electromagnetic extraction of energy from Kerr black holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1977, 179, 433–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchekhovskoy, A.; Narayan, R.; McKinney, J.C. Efficient generation of jets from magnetically arrested accretion on a rapidly spinning black hole. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 418, L79–L83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, K.S. Disk-Accretion onto a Black Hole. II. Evolution of the Hole. Astrophys. J. 1974, 191, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salpeter, E.E. Accretion of Interstellar Matter by Massive Objects. Astrophys. J. 1964, 140, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucchelli, C.; Bañados, E.; Venemans, B.P.; Decarli, R.; Farina, E.P.; Walter, F.; Eilers, A.C.; Rix, H.W.; Simcoe, R.; Stern, D.; et al. Physical Properties of 15 Quasars at z ≳ 6.5. Astrophys. J. 2017, 849, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbarrato, T.; Ghisellini, G.; Nardini, M.; Tagliaferri, G.; Greiner, J.; Rau, A.; Schady, P. Blazar candidates beyond redshift 4 observed with GROND. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 433, 2182–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Sbarrato, T. Dark bubbles around high-redshift radio-loud active galactic nucleus. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 461, L21–L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Celotti, A.; Tavecchio, F.; Haardt, F.; Sbarrato, T. Radio-loud active galactic nuclei at high redshifts and the cosmic microwave background. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 438, 2694–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Fabian, A.C.; Celotti, A.; Jonker, P.G. Extended X-ray emission in the high-redshift quasar GB 1508+5714 at z = 4.3. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 346, L7–L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortlock, D.J.; Warren, S.J.; Venemans, B.P.; Patel, M.; Hewett, P.C.; McMahon, R.G.; Simpson, C.; Theuns, T.; Gonzáles-Solares, E.A.; Adamson, A.; et al. A luminous quasar at a redshift of z = 7.085. Nature 2011, 474, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Chen, W.; An, T.; Xie, F.G.; Han, Y.; Knudsen, K.K.; Yang, J. The Hyperluminous, Dust-obscured Quasar W2246-0526 at z = 4.6: Detection of Parsec-scale Radio Activity. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 905, L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S.; Paragi, Z.; Fogasy, J.O.; Gurvits, L.I. The first estimate of radio jet proper motion at z > 5. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 446, 2921–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.M.; Frey, S.; Gabányi, K.É.; Paragi, Z.; Yang, J.; Cseh, D.; Hong, X.Y.; An, T. VLBI observations of four radio quasars at z > 4: Blazars or not? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 467, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spingola, C.; Dallacasa, D.; Belladitta, S.; Caccianiga, A.; Giroletti, M.; Moretti, A.; Orienti, M. Parsec-scale properties of the radio brightest jetted AGN at z > 6. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 643, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sbarrato, T. Big and Young Supermassive Black Holes in the Early Universe. Galaxies 2021, 9, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9020023
Sbarrato T. Big and Young Supermassive Black Holes in the Early Universe. Galaxies. 2021; 9(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleSbarrato, Tullia. 2021. "Big and Young Supermassive Black Holes in the Early Universe" Galaxies 9, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9020023
APA StyleSbarrato, T. (2021). Big and Young Supermassive Black Holes in the Early Universe. Galaxies, 9(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9020023





