Abstract
The modern era of highly sensitive telescopes is enabling the detection of more and more molecular species in various astronomical environments. Many of these are now being carefully examined for the first time. However, to move beyond detection to more detailed analysis such as radiative transfer modelling, certain molecular properties need to be properly measured and calculated. The importance of contributions from vibrationally excited states or collisional (de-)excitations can vary greatly, depending on the specific molecule and the environment being studied. Here, we discuss the present molecular data needs for detailed radiative transfer modelling of observations of molecular rotational transitions, primarily in the (sub-)millimetre and adjacent regimes, and with a focus on the stellar winds of AGB stars.
1. Introduction
Thanks to advances in telescope technology, more than 200 molecules have been detected in the interstellar medium (ISM) or in circumstellar environments, according to the Cologne Database for Molecular Spectroscopy (CDMS, [1,2,3]). Some of the richest circumstellar environments are the stellar winds of asymptotic giant branch (AGB) stars, with over 90 molecules (excluding isotopologues) detected in these outflows [4]. AGB stars are an evolved form of low- and intermediate-mass stars (with main sequence masses ∼1 to ), which undergo considerable mass loss and end their lives as white dwarfs surrounded by planetary nebulae. They eject a lot of matter which goes on to form molecules and condense into dust in an outwardly expanding stellar wind, also referred to as a circumstellar envelope [5]. These stellar winds are dynamically relatively straightforward systems, typified by smooth acceleration and mainly complicated by pulsation-induced shocks in the regions very close to the stellar surface, and with temperatures ranging from ∼2000 K close to the star to ∼10 K in the outer parts of the circumstellar envelope. Hence, they make ideal laboratories to study molecular emission and chemistry, leading to insights which can be extrapolated to more complex environments such as, for example, protoplanetary discs, high-mass star-forming regions and exoplanet atmospheres.
A common method for understanding the behaviour of AGB stellar winds is using observations of molecular rotational transition lines (commonly found at radio frequencies) to constrain the molecular abundance stratifications via radiative transfer models (e.g., [6,7,8,9]). Such radiative transfer models solve rate equations of the molecule under study. Some molecules, such as CO, are well-known as being good tracers for the temperature and density structure and hence are used to constrain the mass-loss rate of the stellar wind. However, to properly consider radiative excitation effects, these models must take non-local thermodynamic equilibrium (non-LTE) effects into account [10]. This is done by solving (numerically) the statistical equilibrium equations to find the level populations of the molecule being modelled [11]. To do this properly, both radiative and collisional (de-)excitation rates need to be included. Hence, accurate molecular data are required to properly understand the chemistry and dynamics of AGB stellar winds.
Here, we will discuss some of the challenges currently being faced when it comes to radiative transfer modelling of molecular lines. We hope to illustrate the importance of accurate molecular data and highlight some of the gaps that presently exist in molecular measurements and calculations. We also note that our focus is on neutral molecules and their rotational, vibrational, and rovibrational transitions and hence we do not discuss atomic or ionic data here.
While we focus on applications to AGB stellar wind modelling, the molecular data we discuss can be used to study a wide range of environments—any environments where molecules have been detected. This includes protoplanetary discs (e.g., [12]), high-mass star-forming regions, other photon-dominated regions (PDRs) (e.g., [13]), and exoplanet atmospheres (e.g., [14]). Fortney et al. [15] and Tennyson and Yurchenko [16] discuss the similar need for laboratory data (molecular and otherwise) to advance the study of exoplanet atmospheres and Roueff and Lique [17] provide an overview of such data as it relates to the interstellar medium.
2. Required Molecular Data
Detailed radiative transfer modelling of molecular lines involves solving the statistical equations in some way (see [11,18,19,20,21], for example of different methods of solving these equations). The statistical equilibrium system of equations for a transition with upper level u and lower level l is
where and are the populations of levels u and l, respectively, are the rates of spontaneous de-excitation, are the rates of induced de-excitation, are the rates of radiative excitation, are the collisional transition rates (discussed more in Section 2.2), and is the integrated mean intensity averaged over all directions [22]. The A and B parameters are the Einstein coefficients and are related and defined as follows:
and
where is the frequency of the radiation emitted due to the transition, is the transition dipole moment, is the permittivity of free space, , where h is Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light in a vacuum, and is the statistical weight of the u energy level. The collisional excitation and de-excitation rates for upper level u and lower level l are related by
where k is Boltzmann’s constant and is the kinetic temperature.
Radiative transfer modelling of rotational lines from a given molecular species requires energy levels, statistical weights, transition frequencies, Einstein A coefficients (from which the Einstein B coefficients can easily be derived—see Equation (3)), and collisional rate coefficients. Of course, these should cover the full range of energies and temperatures of interest, which often means that vibrationally excited levels also need to be included. For example, stellar winds can reach temperatures of ∼2000 K or higher. When modelling CO in such an environment, at least 40 rotational levels in each of the ground and first excited vibrational state are often included (e.g., as calculated by [23]). Modelling O in a similar environment and taking rotational energy levels from the and vibrational levels into account up to energies of 5000 cm (as calculated by Faure et al. [24]) quickly brings the number of levels considered to more than 800.
2.1. Radiative Rates
There are presently a few useful databases collecting radiative transition data. The previously mentioned CDMS1 [1,2,3] and the JPL spectroscopic database2 [25] provide transition data for a vast number of atomic, molecular, ionic, and isotopic species with 924 listed in CDMS and 401 in JPL. Geared towards the preparation of observations, Splatalogue3 collates and extends data from CDMS, JPL, NIST Recommended Rest Frequencies for Observed Interstellar Molecular Microwave Transitions4, and other databases, boasting over 5.8 million lines in 1038 individual entries. There are also databases such as HITRAN5 and ExoMol6 which have a focus on cool (planetary) atmospheres and go into greater detail for a smaller number of molecules, including listing data for many rarer isotopologues. The molecular data necessary for radiative transfer modelling can be easily obtained or calculated from these databases. However, these databases are not exhaustive and gaps remain that we shall now discuss.
The inclusion of vibrationally excited states is potentially very important to the radiative transfer modelling of some molecules. This is because the star’s light, which for AGB stars peaks around m, can excite some molecules to vibrationally excited levels. The de-excitation follows specific quantum selection rules, yielding level populations that can be quite different to the level population distribution obtained when vibrationally excited states are neglected. This effect is called radiative pumping. For example, Schöier et al. [10] modelled NH with the inclusion of the vibrationally excited state and found a derived fractional abundance about an order of magnitude lower than that found when modelling with only the ground vibrational state. With further study, Schmidt et al. [26] found that the improvement to modelling was negligible for the other vibrationally excited states of NH that they tested their models with. Thus, while not all vibrationally excited states may be significant when modelling low-energy transitions, some are, and ought not to be neglected.
There is also the potential for rotational lines in vibrationally excited states to be detected, especially as telescope sensitivities improve. Historically, vibrationally excited rotational transitions of SiO [27,28] and HCN [29,30,31] have been frequently detected, often thanks to maser activity. These are now joined by a plethora of other molecules in vibrationally excited states such as CO [32], O [33,34], SiS, SO, [35], and others. Of course, the identification of these vibrationally excited lines requires their presence in line lists, which is true of the molecules listed above. It is difficult to gauge to what extent unidentified lines seen in various observations [35,36,37] are due to not yet calculated vibrationally excited rotational transitions of “known” molecules rather than transitions of molecules or isotopologues for which no line lists have been calculated yet.
A final note on vibrationally excited states: while the inclusion of vibrationally excited rotational transitions allows us to identify such lines, to be able to run models—and to include infrared pumping when the model otherwise focuses on the ground vibrational state—the (ro-)vibrational transitions linking the vibrational levels must also be included. Without these, it is not possible to run models that take vibrational levels into account in any way; the level populations cannot converge on a solution if there is no interaction between vibrational levels. While many line lists of vibrationally excited rotational transitions exist, those for (ro-)vibrational transitions are less prevalent.
2.2. Collisional Rates
The most difficult data to obtain for the purposes of radiative transfer modelling are the collisional de-excitation rates (from which the collisional excitation rates can be derived as per Equation (5)). Schöier et al. [38] provides a good overview of the situation and presents the Leiden Atomic and Molecular Database (LAMDA7), which hosts molecular data files with all the required information for radiative transfer modelling. Unlike radiative transitions, which connect levels according to quantum selection rules, collisional transitions result in the transfer of kinetic energy between a collider and the molecule of interest and hence can link any two levels, even those for which radiative transitions are disallowed. This leads to significantly more collisional transitions than radiative transitions linking the same set of energy levels (and can cause modelling efforts to run up against computational limitations).
BASECOL8 [39] is a database focussing on just the collisional rates of various species. It contains collisional rates for 59 species (including deuterated and ionic species) with four possible colliders (electron, H, He, and ), although collisions are generally not listed for all colliders with all species. While collisions with electrons are particularly important in regions with significant electron fractions (≳ [40]), for example in PDRs, collisions with are most important for modelling AGB circumstellar emission. Generally, it is best to consider collisions with both ortho- and para- but when these are not available, a first order approximation can be made by scaling the rates for collisions with He, which tend to be more readily available. Similar approximations can be made when dealing with a species without collisional rates but which is structurally similar to another species for which collisional rates have been measured or calculated. From Schöier et al. [38] we have
where is the collisional rate before taking the number density of the collider into account (such that the collisional rates used in Equation (1) are given by ), and the reduced mass, , is given by
where the mass of component X. This of course results in very approximate collisional rates for the new species and should only be used when better-calculated rates are not available. For example, Daniel et al. [41] shows that there is no simple relationship between O collisions with He, , and H and that therefore each system needs to be computed separately. In the case of isotopologues, substituting the collisional rates from the more abundant isotopologue when modelling the less abundant isotopologue may seem like a reasonable assumption. However, in some cases, there can be significant differences in the collisional rates, particularly when dealing with deuterated species such as DO [42] and ND [43].
In choosing which collisional rates to use, the matter is further complicated by differences arising from different methods of computation. Take, for example, the case of O, one of the most important and abundant molecules found in circumstellar (and many other) environments. Separate sets of recently-calculated collisional rates for O with as the collider exist. The work of [44,45,46,47] calculated the rates using the close coupling method while the work of [48] used quasi-classical trajectory calculations and [24] extended this using an information theory approach. The review of [49] recommends using the rates of [44] at low temperatures (≤20 K), the rates of [48] at intermediate temperatures (∼300 K), and the rates of [24] at high temperatures (≥300 K) since these also include vibrational excitation. Dubernet et al. [45] recommends their own rates up to ∼400 K and those of [48] for higher temperatures. However, it is difficult to gauge which of these rates would be best used for modelling an AGB outflow which can include a wide range of temperatures from ∼2000 K down to ∼10 K.
The matter is further complicated, as noted in [50], when these O collisional rates are used to approximate the collisional rates of other molecules (via Equation (6)) such as S. As well as some discrepancies in the energy ordering of the levels relative to the corresponding quantum numbering, there is the question of how accurate the scaled levels might be when the dipole moments of O and S differ by a factor of ∼2 with 1.8546 D for O [51] and 0.974 D for S [52]. The two different sets of collisional rates employed by [50] produced significantly different results for their S modelling, with very different resultant line intensities for the same circumstellar model depending on the choice of collisional rates. They found the difference in results between sets of collisional rates was more significant than the difference from the inclusion or not of vibrationally excited energy levels and radiative rates. The difference was significant enough that the final S abundance distributions based on their observed data varied significantly depending on the choice of collisional excitation rates, an example of which can be seen in Figure 1.
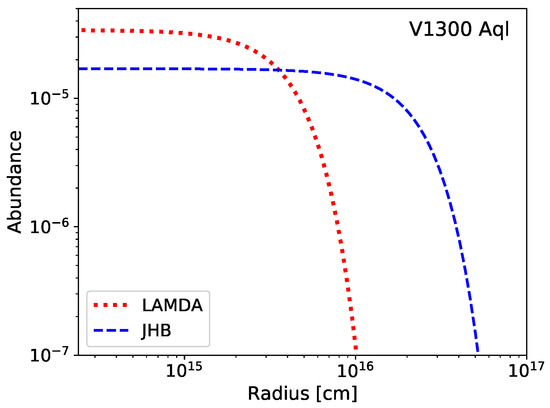
Figure 1.
An example of different abundance profiles for S derived from the same observations based on modelling with different collisional rates with Gaussian abundance distributions. Original modelling and data presented are from [50].
The importance of collisional rates to the S results is most likely due to the fact that S is significantly collisionally excited. That is to say, the collisional rates play a more significant role than the radiative rates, thanks to the relatively small dipole moment of the molecule. Other molecules with small dipole moments are also known to be collisionally excited, such as CO, the cyanopolyynes (HCN), and others. Good collisional rates for HCN and HCN do not exist although they are extremely important for these collisionally excited molecules. Approximate collisional rates can be computed from similar molecules such as HCN and HCN, as shown by Jaber Al-Edhari et al. [53], based on the proportional size of the molecules. A quick test by us indicated that scaling these approximated rates gave different line intensity results for the same circumstellar model, so the accuracy of the chosen rates remains important. Furthermore, these extrapolations can only be done where collisional rates for the smaller molecules involving levels of a given J exist. At similar frequencies, the larger molecules are more likely to be observed at higher J transitions than the smaller molecules [54], and hence observations can quickly move beyond the range for which collisional rates can be easily approximated, prohibiting the radiative transfer modelling of these transitions.
Another aspect that complicates collisional rates from the perspective of radiative transfer modelling is the inclusion of hyperfine structure. A full discussion of this issue is beyond the scope of this paper, but a good overview is provided by Faure et al. [55]. Under an assumption of proportionality following [56], the hyperfine collisional rates can be approximated
where g is the statistical weight of the indicated level. Keto et al. [56] also compare this approximation with a set of exactly calculated hyperfine collisional rates for NH and find minimal differences. Hence, the use of this approximation is a useful shortcut when exactly calculated hyperfine collisional rates are not available.
3. Conclusions
In summary, with growing observational capabilities, the need for molecular data is also growing rapidly. The data required for proper analysis include extensive line lists to facilitate line identification, as well as data describing radiative and collisional transitions, to facilitate radiative transfer modelling. While we have focussed primarily on the molecular stellar winds of AGB stars, most of these molecular data are useable for a range of environments. As such, a close collaboration between astronomy and chemistry will enable us to answer various science questions related to AGB research and, in general, to the field of astrochemistry.
Author Contributions
T.D. wrote the paper; L.D. and M.V.d.S. provided valuable discussion and commented on the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
T.D. acknowledges support from the Fund for Scientific Research (FWO), Flanders, Belgium. L.D. and M.V.d.S. acknowledge support from the ERC consolidator grant 646758 AEROSOL.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AGB | Asymptotic Giant Branch |
| CDMS | Cologne Database for Molecular Spectroscopy |
| HITRAN | High-Resolution Transmission Molecular Absorption Database |
| ISM | Interstellar Medium |
| JPL | Jet Propulsion Laboratory |
| LAMDA | Leiden Atomic and Molecular Database |
| LTE | Local Thermodynamic Equilibrium |
| NIST | National Institute of Standards and Technology |
| NRAO | National Radio Astronomy Observatory |
| PDR | Photon Dominated Region |
References
- Endres, C.P.; Schlemmer, S.; Schilke, P.; Stutzki, J.; Müller, H.S.P. The Cologne Database for Molecular Spectroscopy, CDMS, in the Virtual Atomic and Molecular Data Centre, VAMDC. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 2016, 327, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.S.P.; Thorwirth, S.; Roth, D.A.; Winnewisser, G. The Cologne Database for Molecular Spectroscopy, CDMS. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 370, L49–L52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.S.P.; Schlöder, F.; Stutzki, J.; Winnewisser, G. The Cologne Database for Molecular Spectroscopy, CDMS: a useful tool for astronomers and spectroscopists. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 742, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfner, S.; Olofsson, H. Mass loss of stars on the asymptotic giant branch. Mechanisms, models and measurements. Astron. Astrophys. Res. 2018, 26, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habing, H.J.; Olofsson, H. (Eds.) Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Schöier, F.L.; Ramstedt, S.; Olofsson, H.; Lindqvist, M.; Bieging, J.H.; Marvel, K.B. The abundance of HCN in circumstellar envelopes of AGB stars of different chemical type. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 550, A78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilovich, T.; Bergman, P.; Justtanont, K.; Lombaert, R.; Maercker, M.; Olofsson, H.; Ramstedt, S.; Royer, P. Detailed modelling of the circumstellar molecular line emission of the S-type AGB star W Aquilae. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 569, A76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramstedt, S.; Olofsson, H. The 12CO/13CO ratio in AGB stars of different chemical type. Connection to the 12C/13C ratio and the evolution along the AGB. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 566, A145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decin, L.; Richards, A.M.S.; Waters, L.B.F.M.; Danilovich, T.; Gobrecht, D.; Khouri, T.; Homan, W.; Bakker, J.M.; Van de Sande, M.; Nuth, J.A.; et al. Study of the aluminium content in AGB winds using ALMA. Indications for the presence of gas-phase (Al2O3)n clusters. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 608, A55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöier, F.L.; Maercker, M.; Justtanont, K.; Olofsson, H.; Black, J.H.; Decin, L.; de Koter, A.; Waters, R. A chemical inventory of the S-type AGB star χ Cygni based on Herschel/HIFI observations of circumstellar line emission. The importance of non-LTE chemical processes in a dynamical region. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 530, A83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöier, F.L.; Olofsson, H. Models of circumstellar molecular radio line emission. Mass loss rates for a sample of bright carbon stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 368, 969–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punzi, K.M.; Hily-Blant, P.; Kastner, J.H.; Sacco, G.G.; Forveille, T. An Unbiased 1.3 mm Emission Line Survey of the Protoplanetary Disk Orbiting LkCa 15. Astrophys. J. 2015, 805, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Z.; Choi, Y.; Ossenkopf-Okada, V.; van der Tak, F.F.S.; Bergin, E.A.; Gerin, M.; Joblin, C.; Röllig, M.; Simon, R.; Stutzki, J. Herschel/HIFI spectral line survey of the Orion Bar. Temperature and density differentiation near the PDR surface. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 599, A22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, T.S.; Konopacky, Q.M.; Macintosh, B.; Marois, C. Simultaneous Detection of Water, Methane, and Carbon Monoxide in the Atmosphere of Exoplanet HR8799b. Astrophys. J. 2015, 804, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortney, J.J.; Robinson, T.D.; Domagal-Goldman, S.; Skålid Amundsen, D.; Brogi, M.; Claire, M.; Crisp, D.; Hebrard, E.; Imanaka, H.; de Kok, R.; et al. The Need for Laboratory Work to Aid in The Understanding of Exoplanetary Atmospheres. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:astro-ph.EP/1602.06305. [Google Scholar]
- Tennyson, J.; Yurchenko, S.N. Laboratory spectra of hot molecules: Data needs for hot super-Earth exoplanets. Mol. Astrophys. 2017, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roueff, E.; Lique, F. Molecular Excitation in the Interstellar Medium: Recent Advances in Collisional, Radiative, and Chemical Processes. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 8906–8938. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rybicki, G.B.; Hummer, D.G. An accelerated lambda iteration method for multilevel radiative transfer. I-Non-overlapping lines with background continuum. Astron. Astrophys. 1991, 245, 171–181. [Google Scholar]
- Van Zadelhoff, G.J.; Dullemond, C.P.; van der Tak, F.F.S.; Yates, J.A.; Doty, S.D.; Ossenkopf, V.; Hogerheijde, M.R.; Juvela, M.; Wiesemeyer, H.; Schöier, F.L. Numerical methods for non-LTE line radiative transfer: Performance and convergence characteristics. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 395, 373–384. [Google Scholar]
- Decin, L.; Hony, S.; de Koter, A.; Justtanont, K.; Tielens, A.G.G.M.; Waters, L.B.F.M. Probing the mass-loss history of AGB and red supergiant stars from CO rotational line profiles. I. Theoretical model-Mass-loss history unravelled in VY CMa. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 456, 549–563. [Google Scholar]
- Ferland, G.J.; Porter, R.L.; van Hoof, P.A.M.; Williams, R.J.R.; Abel, N.P.; Lykins, M.L.; Shaw, G.; Henney, W.J.; Stancil, P.C. The 2013 Release of Cloudy. Rev. Mexi. Astron. Astrofísica 2013, 49, 137–163. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalas, D.; Kunasz, P.B.; Hummer, D.G. Solution of the comoving frame equation of transfer in spherically symmetric flows. I - Computational method for equivalent-two-level-atom source functions. Astrophys. J. 1975, 202, 465–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Stancil, P.C.; Balakrishnan, N.; Forrey, R.C. Rotational Quenching of CO due to H2 Collisions. Astrophys. J. 2010, 718, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, A.; Josselin, E. Collisional excitation of water in warm astrophysical media. I. Rate coefficients for rovibrationally excited states. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 492, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, H.M.; Poynter, R.L.; Cohen, E.A.; Delitsky, M.L.; Pearson, J.C.; Müller, H.S.P. Submillimeter, millimeter and microwave spectral line catalog. J. Q. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1998, 60, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.R.; He, J.H.; Szczerba, R.; Bujarrabal, V.; Alcolea, J.; Cernicharo, J.; Decin, L.; Justtanont, K.; Teyssier, D.; Menten, K.M.; et al. Herschel/HIFI observations of the circumstellar ammonia lines in IRC+10216. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 592, A131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhl, D.; Snyder, L.E.; Lovas, F.J.; Johnson, D.R. Silicon Monoxide: Detection of Maser Emission from the Second Vibrationally Excited State. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1974, 192, L97–L100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmurs, J.F.; Bujarrabal, V.; Lindqvist, M.; Alcolea, J.; Soria-Ruiz, R.; Bergman, P. SiO masers from AGB stars in the vibrationally excited v = 1, v = 2, and v = 3 states. In Proceedings of the 12th European VLBI Network Symposium and Users Meeting (EVN 2014), Cagliari, Italy, 7–10 October 2014; p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Ziurys, L.M.; Turner, B.E. Detection of interstellar vibrationally excited HCN. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1986, 300, L19–L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieging, J.H. Discovery of Two New HCN Maser Lines in Five Carbon Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2001, 549, L125–L129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menten, K.M.; Wyrowski, F.; Keller, D.; Kamiński, T. Widespread HCN maser emission in carbon-rich evolved stars. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1803.00943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouri, T.; Vlemmings, W.H.T.; Ramstedt, S.; Lombaert, R.; Maercker, M.; De Beck, E. ALMA observations of the vibrationally excited rotational CO transition v = 1, J = 3 − 2 towards five AGB stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 463, L74–L78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justtanont, K.; Khouri, T.; Maercker, M.; Alcolea, J.; Decin, L.; Olofsson, H.; Schöier, F.L.; Bujarrabal, V.; Marston, A.P.; Teyssier, D.; et al. Herschel/HIFI observations of O-rich AGB stars: molecular inventory. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 537, A144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, A.; Humphreys, E.M.L.; Herpin, F.; Torstensson, K.; Vlemmings, W.H.T.; Richards, A.M.S.; Gray, M.D.; De Breuck, C.; Olberg, M. Vibrationally excited water emission at 658 GHz from evolved stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 609, A25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decin, L.; Richards, A.M.S.; Danilovich, T.; Homan, W.; Nuth, J.A. ALMA spectral line and imaging survey of a low and a high mass-loss rate AGB star between 335 and 362 GHz. Astron. Astrophys. 2018. forthcoming. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velilla Prieto, L.; Sánchez Contreras, C.; Cernicharo, J.; Agúndez, M.; Quintana-Lacaci, G.; Bujarrabal, V.; Alcolea, J.; Balança, C.; Herpin, F.; Menten, K.M.; et al. The millimeter IRAM-30 m line survey toward IK Tauri. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 597, A25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernicharo, J.; Daniel, F.; Castro-Carrizo, A.; Agundez, M.; Marcelino, N.; Joblin, C.; Goicoechea, J.R.; Guélin, M. Unveiling the Dust Nucleation Zone of IRC+10216 with ALMA. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2013, 778, L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöier, F.L.; van der Tak, F.F.S.; van Dishoeck, E.F.; Black, J.H. An atomic and molecular database for analysis of submillimetre line observations. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 432, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubernet, M.L.; Alexander, M.H.; Ba, Y.A.; Balakrishnan, N.; Balança, C.; Ceccarelli, C.; Cernicharo, J.; Daniel, F.; Dayou, F.; Doronin, M.; et al. BASECOL2012: A collisional database repository and web service within the Virtual Atomic and Molecular Data Centre (VAMDC). Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 553, A50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, A.; Varambhia, H.N.; Stoecklin, T.; Tennyson, J. Electron-impact rotational and hyperfine excitation of HCN, HNC, DCN and DNC. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 382, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, F.; Faure, A.; Dagdigian, P.J.; Dubernet, M.L.; Lique, F.; Forêts, G.P.d. Collisional excitation of water by hydrogen atoms. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 446, 2312–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribano, Y.; Faure, A.; Wiesenfeld, L. Communication: Rotational excitation of interstellar heavy water by hydrogen molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 133, 231105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumouchel, F.; Kłos, J.; Toboła, R.; Bacmann, A.; Maret, S.; Hily-Blant, P.; Faure, A.; Lique, F. Fine and hyperfine excitation of NH and ND by He: On the importance of calculating rate coefficients of isotopologues. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 114306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubernet, M.L.; Daniel, F.; Grosjean, A.; Faure, A.; Valiron, P.; Wernli, M.; Wiesenfeld, L.; Rist, C.; Noga, J.; Tennyson, J. Influence of a new potential energy surface on the rotational (de)excitation of H2O by H2 at low temperature. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 460, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubernet, M.L.; Daniel, F.; Grosjean, A.; Lin, C.Y. Rotational excitation of ortho-H2O by para-H2 (j2 = 0, 2, 4, 6, 8) at high temperature. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 497, 911–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, F.; Dubernet, M.L.; Pacaud, F.; Grosjean, A. Rotational excitation of 20 levels of para-H2O by ortho-H2 (j2 = 1, 3, 5, 7) at high temperature. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 517, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, F.; Dubernet, M.L.; Grosjean, A. Rotational excitation of 45 levels of ortho/para-H2O by excited ortho/para-H2 from 5 K to 1500 K: state-to-state, effective, and thermalized rate coefficients. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 536, A76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, A.; Crimier, N.; Ceccarelli, C.; Valiron, P.; Wiesenfeld, L.; Dubernet, M.L. Quasi-classical rate coefficient calculations for the rotational (de)excitation of H2O by H2. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 472, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Tak, F. Radiative Transfer and Molecular Data for Astrochemistry. In The Molecular Universe (IAU S280); Cernicharo, J., Bachiller, R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; Volume 280, pp. 449–460. [Google Scholar]
- Danilovich, T.; Van de Sande, M.; De Beck, E.; Decin, L.; Olofsson, H.; Ramstedt, S.; Millar, T.J. Sulphur-bearing molecules in AGB stars. I. The occurrence of hydrogen sulphide. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 606, A124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 84th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, R.; Dyke, T.R. Electric dipole moments and nuclear hyperfine interactions for H2S, HDS, and D2S. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 1984, 103, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber Al-Edhari, A.; Ceccarelli, C.; Kahane, C.; Viti, S.; Balucani, N.; Caux, E.; Faure, A.; Lefloch, B.; Lique, F.; Mendoza, E.; et al. History of the solar-type protostar IRAS 16293-2422 as told by the cyanopolyynes. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 597, A40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agúndez, M.; Cernicharo, J.; Quintana-Lacaci, G.; Castro-Carrizo, A.; Velilla Prieto, L.; Marcelino, N.; Guélin, M.; Joblin, C.; Martín-Gago, J.A.; Gottlieb, C.A.; et al. Growth of carbon chains in IRC +10216 mapped with ALMA. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 601, A4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure, A.; Lique, F. The impact of collisional rate coefficients on molecular hyperfine selective excitation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 425, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keto, E.; Rybicki, G. Modeling Molecular Hyperfine Line Emission. Astrophys. J. 2010, 716, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | The NRAO Spectral Line Catalog: www.splatalogue.net. |
| 4 | Lovas/National Institute of Standards and Technology: http://physics.nist.gov/restfreq. |
| 5 | The high-resolution transmission molecular absorption database: http://hitran.org. |
| 6 | High temperature molecular line lists for modelling exoplanet atmospheres: http://exomol.com. |
| 7 | |
| 8 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).