How Clumpy Star Formation Affects Globular Cluster Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
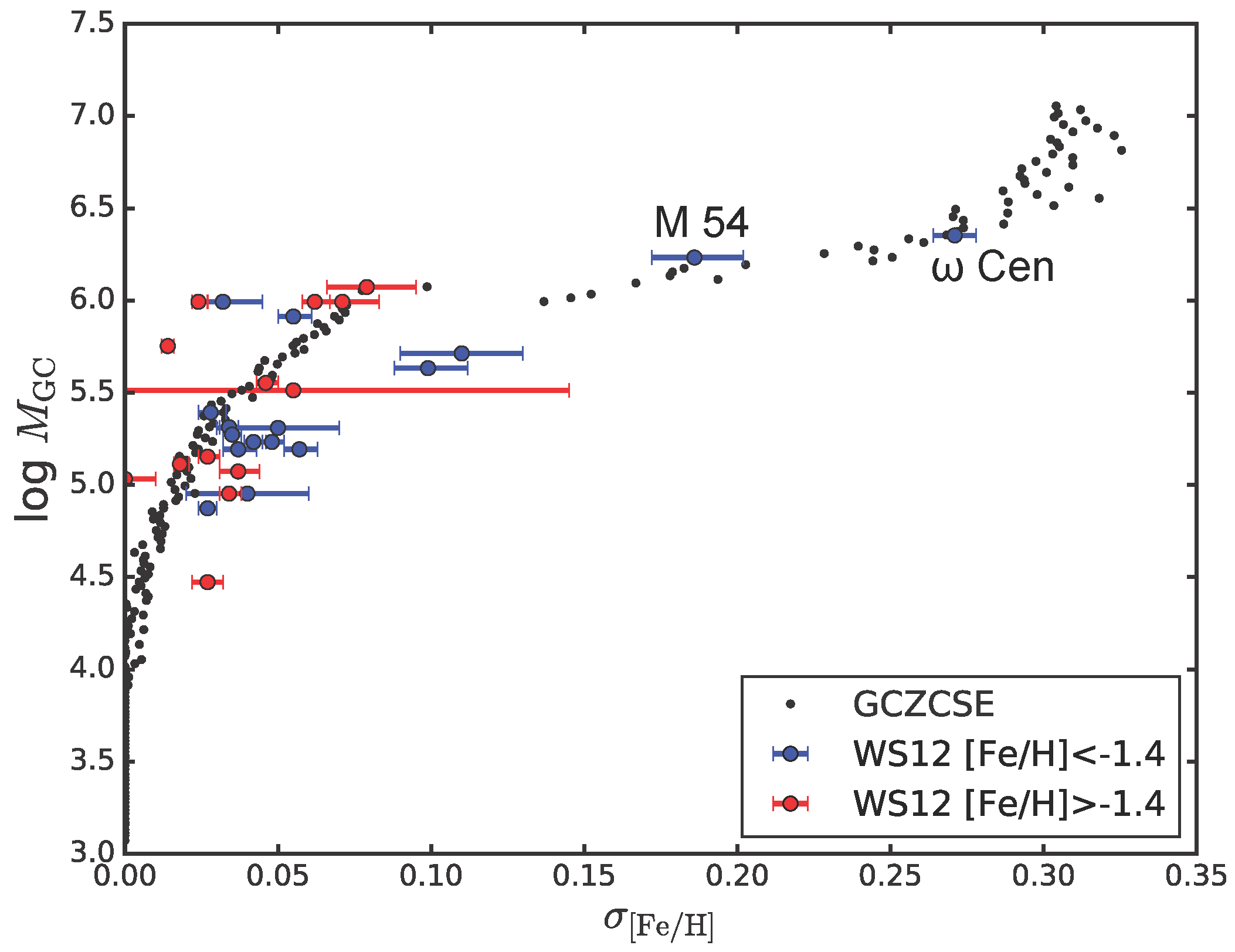
3. Results
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GC | Globular Cluster |
References
- Harris, W.E.; Whitmore, B.C.; Karakla, D.; Okon, W.; Baum, W.A.; Hanes, D.A.; Kavelaars, J.J. Globular Cluster Systems in Brightest Cluster Galaxies: Bimodal Metallicity Distributions and the Nature of the High-Luminosity Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2006, 636, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotto, G.; Bedin, L.R.; Anderson, J.; King, I.R.; Cassisi, S.; Milone, A.P.; Villanova, S.; Pietrinferni, A.; Renzini, A. A Triple Main Sequence in the Globular Cluster NGC 2808. Astrophys. J. 2007, 661, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailin, J.; Harris, W.E. Stochastic Self-Enrichment, Pre-Enrichment, and the Formation of Globular Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2009, 695, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieske, S.; Jordan, A.; Cote, P.; Peng, E.; Ferrarese, L.; Blakeslee, J.; Mei, S.; Baumgardt, H.; Tonry, J.; Infante, L.; et al. The ACS Fornax Cluster Survey. IX. The Color-Magnitude Relation of Globular Cluster Systems. Astrophys. J. 2010, 710, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudfrooij, P.; Kruijssen, J.M.D. Color-Magnitude Relations within Globular Cluster Systems of Giant Elliptical Galaxies: The Effects of Globular Cluster Mass Loss and the Stellar Initial Mass Function. Astrophys. J. 2014, 780, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.B. Turbulence and star formation in molecular clouds. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1981, 194, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, A.J.; Heyer, M.H. The Dense Gas Mass Fraction of Molecular Clouds in the Milky Way. Astrophys. J. 2014, 780, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellsworth-Bowers, T.P.; Glenn, J.; Riley, A.; Rosolowsky, E.; Ginsburg, A.; Evans, N.J., II; Bally, J.; Battersby, C.; Shirley, Y.L.; Merello, M. The Bolocam Galactic Plane Survey. XIII. Physical Properties and Mass Functions of Dense Molecular Cloud Structures. Astrophys. J. 2015, 805, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailin, J. A Model for Clumpy Self-Enrichment in Globular Clusters. 2017; in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Willman, B.; Strader, J. “Galaxy,” Defined. Astron. J. 2012, 144, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbinot, E.; Gieles, M. The devil is in the tails: the role of globular cluster mass evolution on stream properties. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1702.02543. [Google Scholar]
| 1. | We are not arguing that these objects are necessarily GCs, simply that other evidence must be used to make the argument. |
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bailin, J. How Clumpy Star Formation Affects Globular Cluster Systems. Galaxies 2017, 5, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies5030036
Bailin J. How Clumpy Star Formation Affects Globular Cluster Systems. Galaxies. 2017; 5(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies5030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleBailin, Jeremy. 2017. "How Clumpy Star Formation Affects Globular Cluster Systems" Galaxies 5, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies5030036
APA StyleBailin, J. (2017). How Clumpy Star Formation Affects Globular Cluster Systems. Galaxies, 5(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies5030036