Why Jet Power and Star Formation Are Uncorrelated in Active Galaxies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Star Formation as a Function of Jet Power from Theory
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heckman, T.M.; Kauffmann, G.; Brinchmann, J.; Charlot, S.; Tremonti, C.; White, S.D. Present-day growth of black holes and bulges: The Sloan Digital Sky Survey perspective. Astrophys. J. 2004, 613, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Cresci, G.; Maiolino, R. Observing positive and negative AGN feedback. Nat. Astron. 2018, 2, 179. [Google Scholar]
- Kokorev, V.; Chisholm, J.; Endsley, R.; Finkelstein, S.L.; Greene, J.E.; Akins, H.B.; Bromm, V.; Casey, C.M.; Fujimoto, S.; Labbé, I.; et al. Silencing the Giant: Evidence of Active Galactic Nucleus Feedback and Quenching in a Little Red Dot at z = 4.13. Astrophys. J. 2024, 975, 178. [Google Scholar]
- Kalfountzou, E.; Jarvis, M.J.; Bonfield, D.G.; Hardcastle, M.J. Star formation in high-redshift quasars: Excess [O ii] emission in the radio-loud population. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 427, 2401. [Google Scholar]
- Zinn, P.C.; Middelberg, E.; Norris, R.P.; Dettmar, R.J. Active galactic nucleus feedback works both ways. Astrophys. J. 2013, 774, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Kimmig, L.C.; Remus, R.S.; Seidel, B.; Valenzuela, L.M.; Dolag, K.; Burkert, A. Blowing Out the Candle: How to Quench Galaxies at High Redshift—An Ensemble of Rapid Starbursts, AGN Feedback, and Environment. Astrophys. J. 2025, 979, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo, A.; Faber, S.M.; Binney, J.; Dekel, A.; Kormendy, J.; Mushotzky, R.; Babul, A.; Best, P.N.; Brüggen, M.; Fabian, A.C.; et al. The role of black holes in galaxy formation and evolution. Nature 2009, 460, 213–219. [Google Scholar]
- Fabian, A.C. Observational evidence of active galactic nuclei feedback. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 50, 455. [Google Scholar]
- Fabian, A.C.; Ferland, G.J.; Sanders, J.S.; Russell, H.R.; McNamara, B.R.; Pinto, C.; Hlavacek-Larrondo, J.; Walker, S.A.; Ivey, L.R.; McDonald, M. Hidden cooling flows—IV. More details on Centaurus and the efficiency of AGN feedback in clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 535, 2173. [Google Scholar]
- Silk, J.; Rees, M.J. Quasars and galaxy formation. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 331, L1. [Google Scholar]
- Di Matteo, T.; Springel, V.; Hernquist, L. Energy input from quasars regulates the growth and activity of black holes and their host galaxies. Nature 2005, 433, 604. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Croton, D.J.; Springel, V.; White, S.D.M.; De Lucia, G.; Frenk, C.S.; Gao, L.; Jenkins, A.; Kauffmann, G.; Navarro, J.F.; Yoshida, N. The many lives of active galactic nuclei: Cooling flows, black holes and the luminosities and colours of galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 365, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Nesvadba, N.P.; Lehnert, M.D.; Eisenhauer, F.; Gilbert, A.; Tecza, M.; Abuter, R. Extreme Gas Kinematics in the z = 2.2 Powerful Radio Galaxy MRC 1138–262: Evidence for Efficient Active Galactic Nucleus Feedback in the Early Universe? Astrophys. J. 2006, 650, 693. [Google Scholar]
- Nesvadba, N.P.H.; Boulanger, F.; Salomé, P.; Guillard, P.; Lehnert, M.D.; Ogle, P.; Appleton, P.; Falgarone, E.; Des Forets, G.P. Energetics of the molecular gas in the H2 luminous radio galaxy 3C 326: Evidence for negative AGN feedback. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 521, A65. [Google Scholar]
- Silk, J.; Mamon, G.A. The current status of galaxy formation. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 12, 917. [Google Scholar]
- Magorrian, J.; Tremaine, S.; Richstone, D.; Bender, R.; Bower, G.; Dressler, A.; Faber, S.M.; Gebhardt, K.; Green, R.; Grillmair, C.; et al. The Demography of Massive Dark Objects in Galaxy Centers. Astron. J. 1998, 115, 2285. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrarese, L.; Merritt, D.A. A Fundamental Relation between Supermassive Black Holes and TheirHost Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2000, 539, L9. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, N.; Graham, A.W.; David, B.L. Revealing Hidden Substructures in the MBH–σ Diagram, and Refining the Bend in the L–σ Relation. Astrophys. J. 2019, 887, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, G.; Kauffmann, G.; Best, P.; Shenoy, S.; Malek, K. The host galaxies of radio AGN: New views from combining LoTSS and MaNGA observations. Astron. Astrophys. 2025, 694, A309. [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo, D.; Evans, D.A.; Sambruna, R.M. The evolution of radio-loud active galactic nuclei as a function of black hole spin. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 406, 975–986. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, C.B.; Kulasiri, N.; North, M.; Garofalo, D. The black hole-star formation connection over cosmic time. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2021, 133, 104101. [Google Scholar]
- Comerford, J.M.; Negus, J.; Müller-Sánchez, F.; Eracleous, M.; Wylezalek, D.; Storchi-Bergmann, T.; Greene, J.E.; Barrows, R.S.; Nevin, R.; Roy, N.; et al. A Catalog of 406 AGNs in MaNGA: A Connection between Radio-mode AGNs and Star Formation Quenching. Astrophys. J. 2020, 901, 159. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, C.B.; Williams, M.; Garofalo, D.; Rojas Castillo, L.; Taylor, L.; Harmon, E. Characteristics of Powerful Radio Galaxies. Universe 2024, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M.; Petterson, J.A. The Lense-Thirring Effect and Accretion Disks around Kerr Black Holes. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1975, 195, L65. [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo, D.; Joshi, R.; Yang, X.; Singh, C.B.; North, M.; Hopkins, M. A Unified Framework for X-shaped Radio Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2021, 889, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Gültekin, K.; Richstone, D.O.; Gebhardt, K.; Lauer, T.R.; Tremaine, S.; Aller, M.C.; Bender, R.; Dressler, A.; Faber, S.M.; Filippenko, A.V.; et al. The M–σ and M–L relations in galactic bulges, and determinations of their intrinsic scatter. Astrophys. J. 2009, 698, 198. [Google Scholar]
- Tchekhovskoy, A.; McKinney, J.; Narayan, R. General relativistic modeling of magnetized jets from accreting black holes. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 372, 012040. [Google Scholar]
- Lowell, B.; Jacquemin-Ide, J.; Tchekhovskoy, A.; Duncan, A. Rapid black hole spin-down by thick magnetically arrested disks. Astrophys. J. 2024, 960, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Reines, A.E.; Volonteri, M. Relations between central black hole mass and total galaxy stellar mass in the local universe. Astrophys. J. 2015, 813, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo, D.; Christian, D.J.; Hames, C.; North, M.; Thottam, K.; Nazaroff, S.; Eckelbarger, A. M-σ relations across cosmic time. Open J. Astrophys. 2023, 6, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Neilsen, J.; Lee, J.C. Accretion disk winds as the jet suppression mechanism in the microquasar GRS 1915+105. Nature 2009, 458, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponti, G.; Fender, R.P.; Begelman, M.C.; Dunn RJ, H.; Neilsen, J.; Coriat, M. Ubiquitous equatorial accretion disc winds in black hole soft states. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 422, L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Nagao, T.; Yamashita, T.; Uchiyama, H.; Kubo, M.; Toba, Y.; Harikane, Y.; Ichikawa, K.; Kajisawa, M.; Noboriguchi, A.; et al. A Wide and Deep Exploration of Radio Galaxies with Subaru HSC (WERGS). X. The Massive and Passive Nature of Radio Galaxies at z~4. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.19009v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
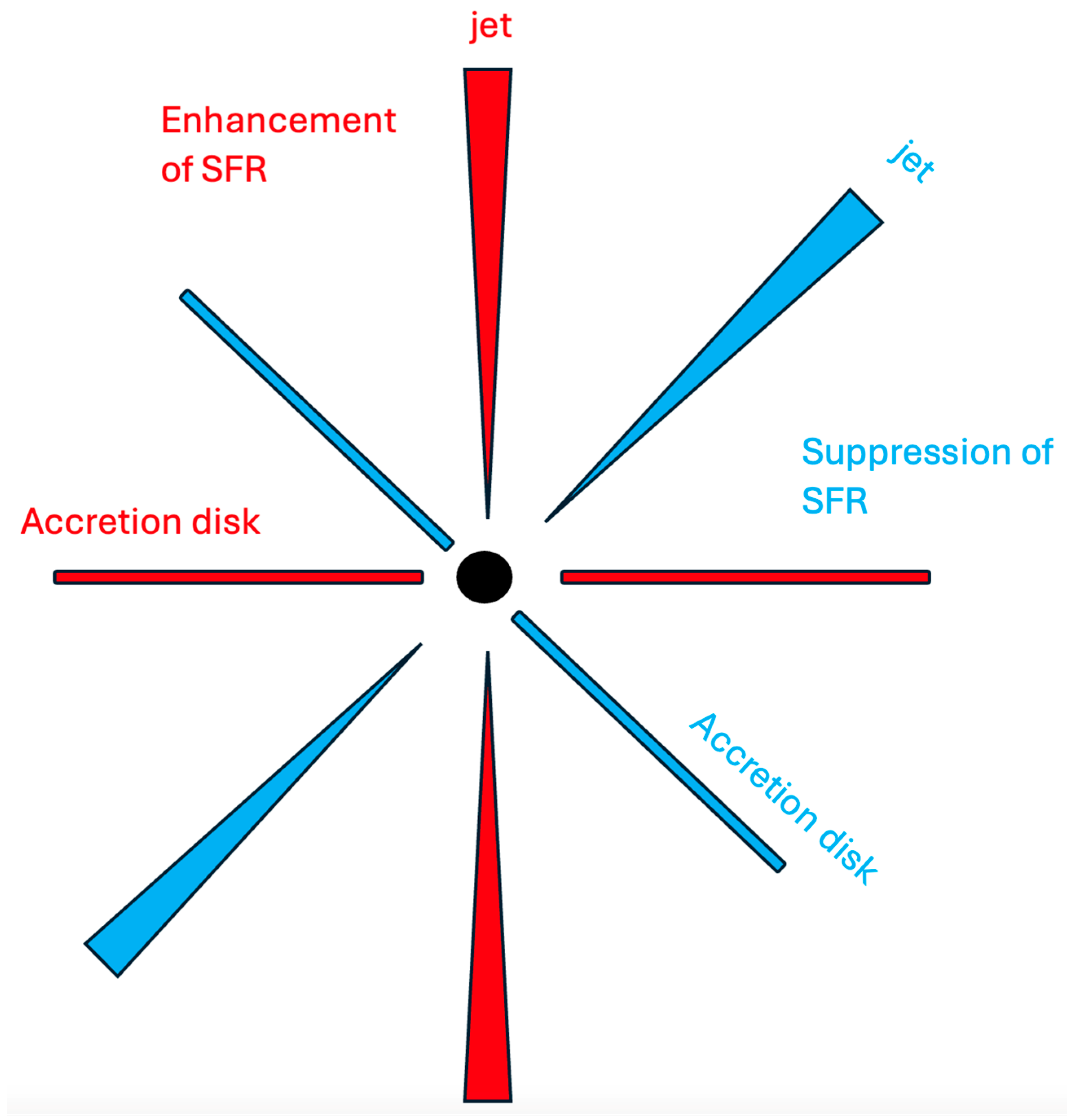
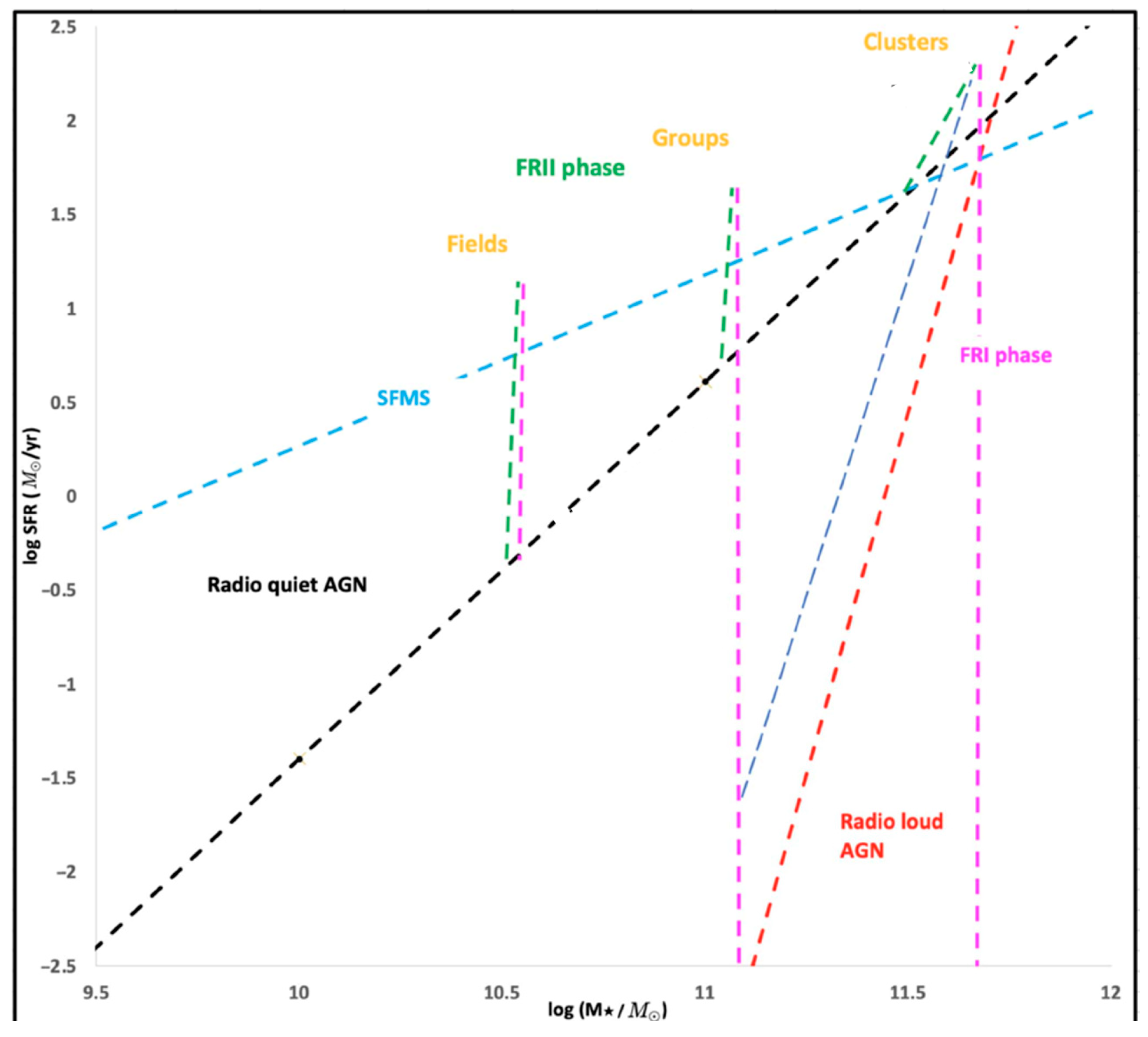

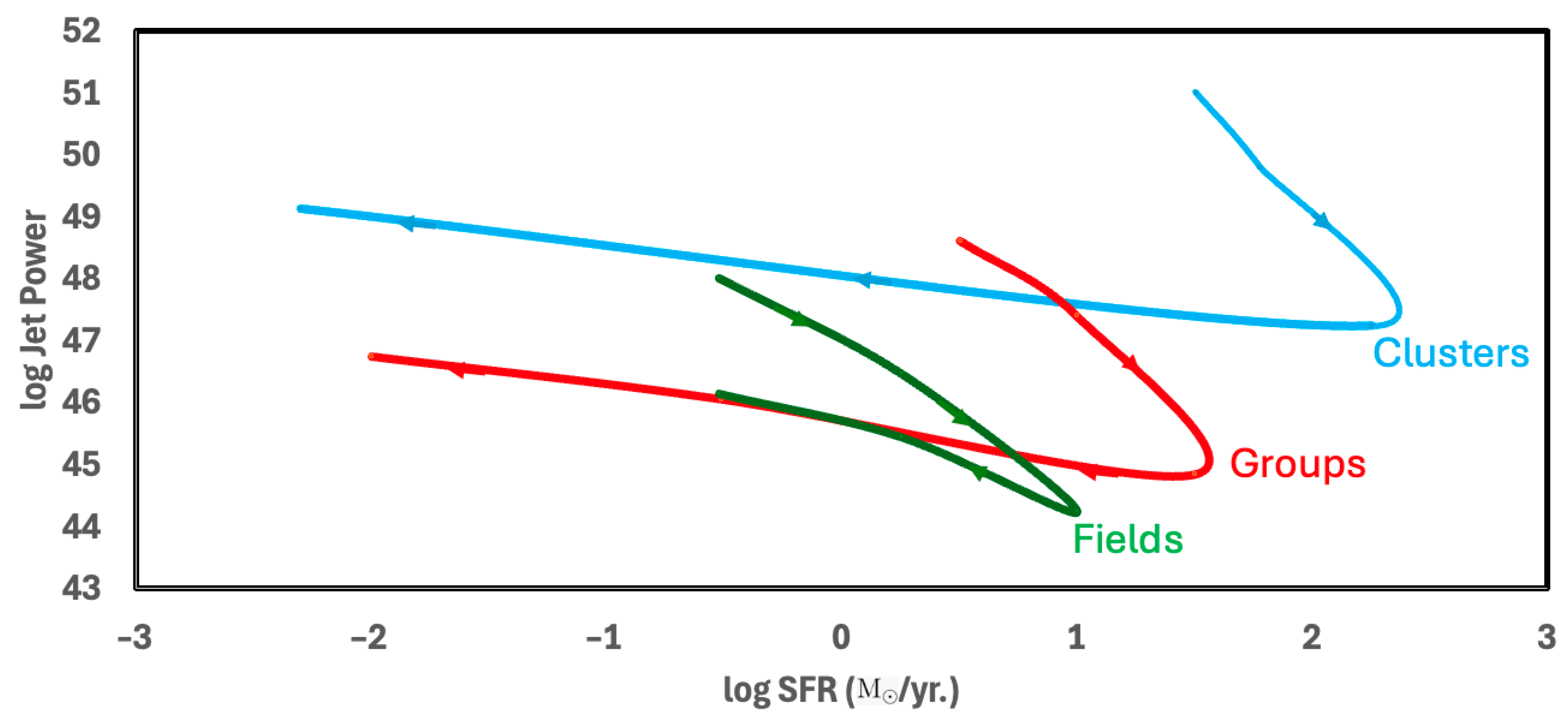
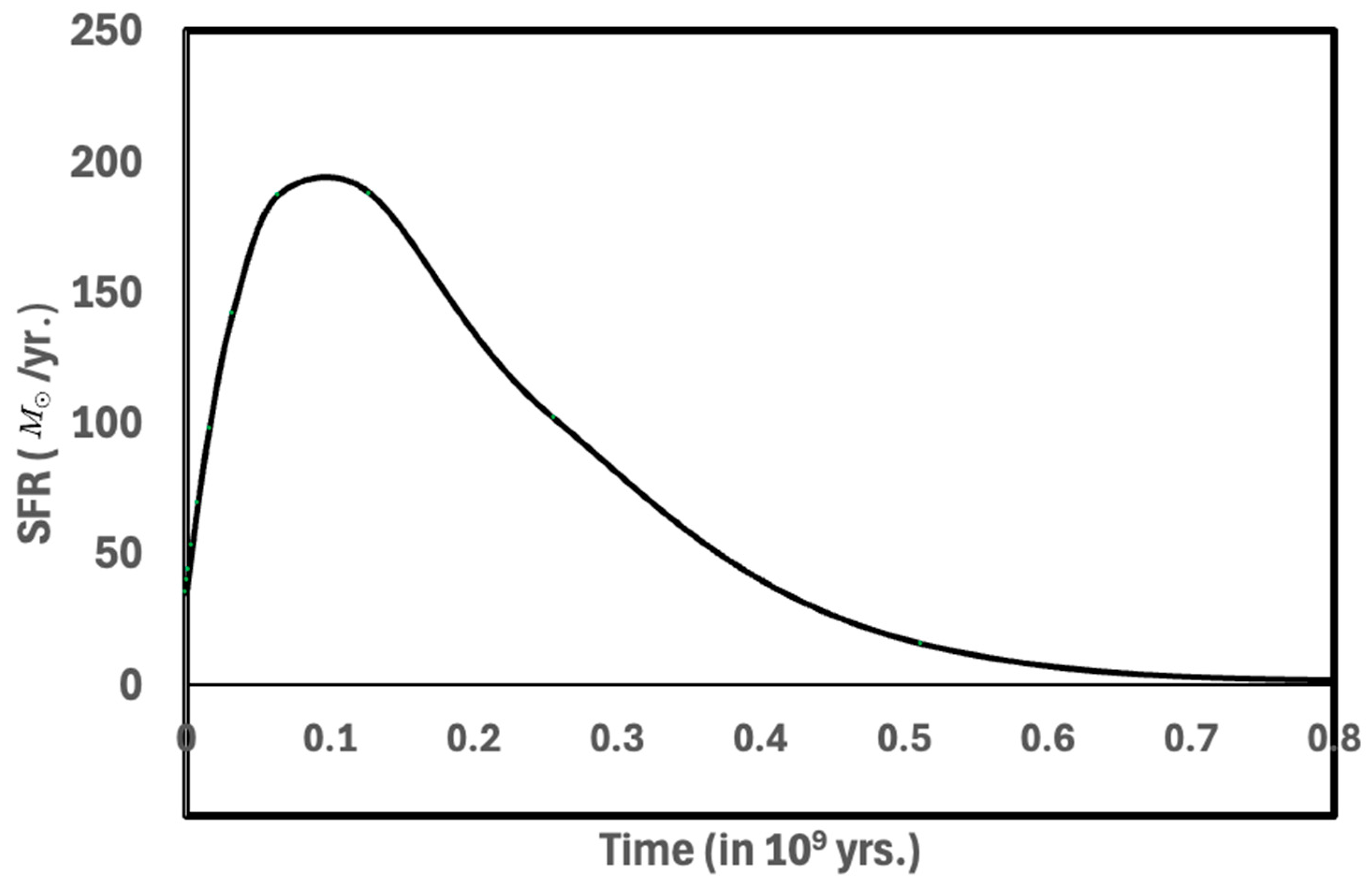
| Environment | Counter-Rotating Phase | Corotating Phase | Stellar Mass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fields | −0.5 < log SFR < 1.0 | −0.5 < log SFR < 1.0 | log (M*/M⊙) = 10.5 |
| Groups | 0.5 < log SFR < 1.6 | −2.1 < log SFR < 1.6 | log (M*/M⊙) = 11.0 |
| Clusters | 1.5 <log SFR < 2.2 | −2.4 < log SFR < 2.2 | log (M*/M⊙) = 11.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garofalo, D.; McDaniel, B.; North, M. Why Jet Power and Star Formation Are Uncorrelated in Active Galaxies. Galaxies 2025, 13, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13020035
Garofalo D, McDaniel B, North M. Why Jet Power and Star Formation Are Uncorrelated in Active Galaxies. Galaxies. 2025; 13(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarofalo, David, Brent McDaniel, and Max North. 2025. "Why Jet Power and Star Formation Are Uncorrelated in Active Galaxies" Galaxies 13, no. 2: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13020035
APA StyleGarofalo, D., McDaniel, B., & North, M. (2025). Why Jet Power and Star Formation Are Uncorrelated in Active Galaxies. Galaxies, 13(2), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13020035






