Synthesis of Organic and Inorganic Compounds in Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Molecular Synthesis in the Stellar Winds of AGB Stars
3. Synthesis of Complex Organics in Post-AGB Evolution
3.1. Origin of the UIE Bands
3.2. Laboratory Synthesis of Carbonaceous Solids
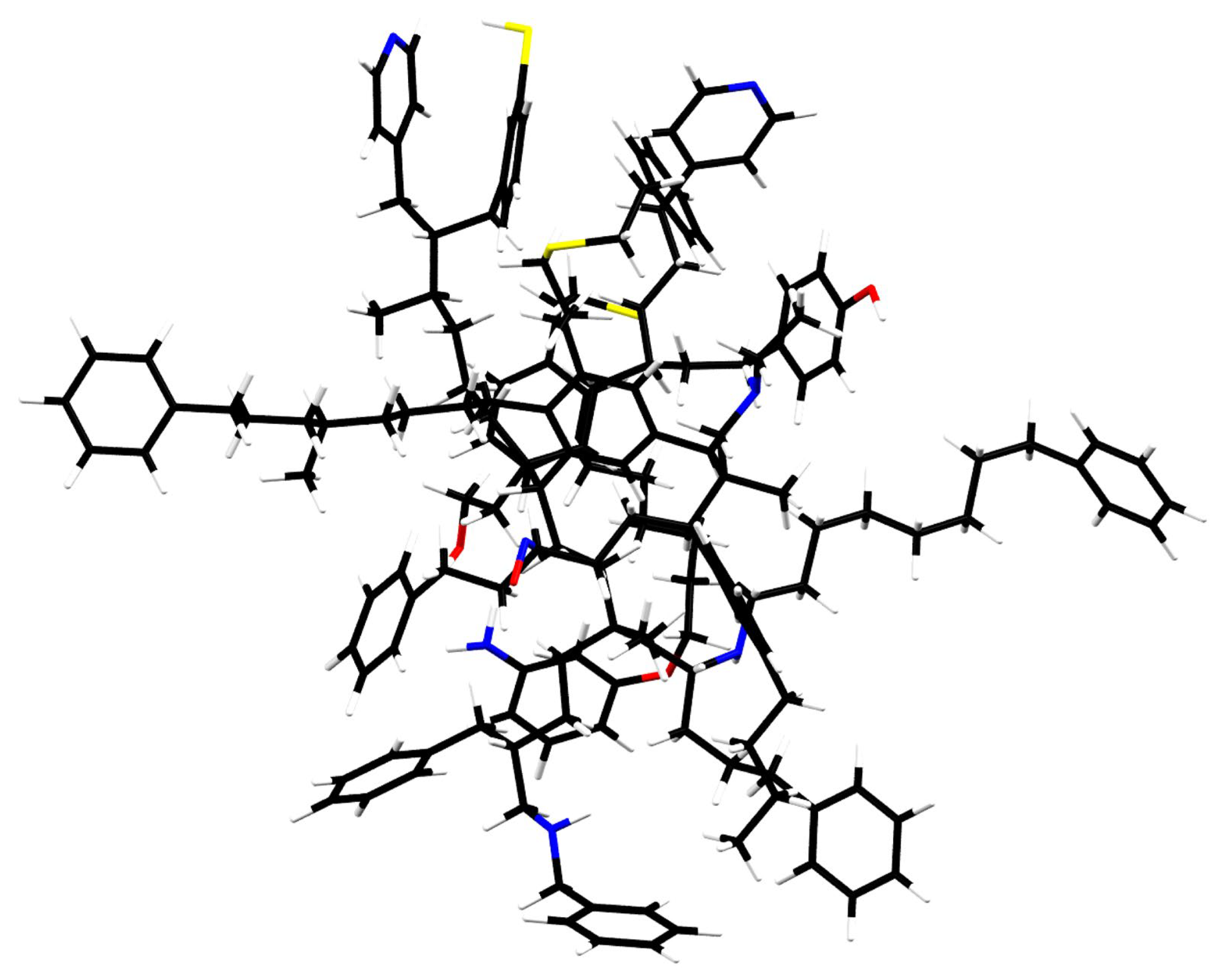
4. Mixed Aromatic/Aliphatic Organic Nanoparticles (MAONs) as Carrier of UIE Bands
5. Circumstellar Chemical Synthesis
6. Summary
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oró, J. Synthesis of adenine from ammonium cyanide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1960, 2, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, R.A.; Ferbis, J.P.; Orgel, L.E. Studies in Prebiodc Synthesis: II. Synthesis of purine precursors and amino acids from aqueous hydrogen cyanide. J. Mol. Biol. 1967, 30, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, J.P.; Sanchez, R.A.; Orgel, L.E. Studies in prebiotic synthesis: III. Synthesis of pyrimidines from cyanoacetylene and cyanate. J. Mol. Biol. 1968, 33, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dow, W.G. Kerogen studies and geological interpretations. J. Geochem. Explor. 1977, 7, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood Lollar, B.; Westgate, T.D.; Ward, J.A.; Slater, G.F.; Lacrampe-Couloume, G. Abiogenic formation of alkanes in the Earth’s crust as a minor source for global hydrocarbon reservoirs. Nature 2002, 416, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. Organic Matter in the Universe; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ziurys, L.M. The chemistry in circumstellar envelopes of evolved stars: Following the origin of the elements to the origin of life. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12274–12279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernicharo, J.; Agúndez, M.; Guélin, M.; Bachiller, R. Spectral Line Surveys of Evolved Stars. In Proceedings of the IAU Symposium 280: The Molecular Universe, Toledo, Spain, 1 December 2011; pp. 237–248. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, S.; Volk, K.; Bidelman, W.P. Classification and Identification of IRAS Sources with Low-Resolution Spectra. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1997, 112, 557–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posch, T.; Kerschbaum, F.; Mutschke, H.; Dorschner, J.; Jäger, C. On the origin of the 19.5 μm feature. Identifying circumstellar Mg-Fe-oxides. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 393, L7–L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Russell, R.W.; Soifer, B.T.; Willner, S.P. The 4 to 8 micron spectrum of NGC 7027. Astrophys. J. 1977, 217, L149–L153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, E. The Infrared Emission Bands. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 2013, 9, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. The mystery of unidentified infrared emission bands. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2022, 367, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, S. The Origin and Evolution of Planetary Nebulae; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. Proto-planetary nebulae. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1993, 31, 63–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrivnak, B.J.; Geballe, T.R.; Kwok, S. A Study of the 3.3 and 3.4 μm Emission Features in Proto-Planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 2007, 662, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kwok, S.; Volk, K.; Bernath, P. On the Origin of Infrared Plateau Features in Proto-Planetary Nebulae. Astrophys. J. 2001, 554, L87–L90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knacke, R.F. Carbonaceous compounds in interstellar dust. Nature 1977, 269, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duley, W.W.; Williams, D.A. The infrared spectrum of interstellar dust—Surface functional groups on carbon. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1981, 196, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagan, C.; Khare, B.N. Tholins—Organic chemistry of interstellar grains and gas. Nature 1979, 277, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S.; Volk, K.; Hrivnak, B.J. Chemical evolution of carbonaceous materials in the last stages of stellar evolution. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 350, L35–L38. [Google Scholar]
- Sellgren, K.; Uchida, K.I.; Werner, M.W. The 15–20 mm Spitzer spectra of interstellar emission features in NGC 7023. Astrophys. J. 2007, 659, 1338–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sturm, E.; Lutz, D.; Tran, D.; Feuchtgruber, H.; Genzel, R.; Kunze, D.; Moorwood, A.F.M.; Thornley, M.D. ISO-SWS spectra of galaxies: Continuum and features. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 358, 481–493. [Google Scholar]
- Allamandola, L.J.; Tielens, A.G.G.M.; Barker, J.R. Interstellar polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: The infrared emission bands, the excitation/emission mechanism and the astrophysical implications. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1989, 71, 733–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puget, J.L.; Léger, A. A new component of the interstellar matter—Small grains and large aromatic molecules. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1989, 27, 161–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tielens, A.G.G.M. Interstellar Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Molecules. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 46, 289–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, A.; Wada, S.; Onaka, T.; Tokunaga, A.T. Quenched carbonaceous composite. III—Comparison to the 3.29 micron interstellar emission feature. Astrophys. J. 1990, 353, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S.; Zhang, Y. Unidentified Infrared Emission Bands: PAHs or MAONs? Astrophys. J. 2013, 771, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Kwok, S. On the Origin of the 11.3 Micron Unidentified Infrared Emission Feature. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leger, A.; Puget, J.L. Identification of the ‘unidentified’ IR emission features of interstellar dust? Astron. Astrophys. 1984, 137, L5–L8. [Google Scholar]
- Hudgins, D.M.; Allamandola, L.J. The Spacing of the Interstellar 6.2 and 7.7 Micron Emission Features as an Indicator of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Size. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1999, 513, L69–L73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Diedenhoven, B.; Peeters, E.; Van Kerckhoven, C.; Hony, S.; Hudgins, D.M.; Allamandola, L.J.; Tielens, A.G.G.M. The Profiles of the 3-12 Micron Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Features. Astrophys. J. 2004, 611, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauschlicher, C.W., Jr. The Infrared Spectra of C96H24, C96H+24, and C96H+25. Astrophys. J. 2002, 564, 782–786. [Google Scholar]
- Hudgins, D.M.; Bauschlicher, C.W., Jr.; Allamandola, L.J. Variations in the Peak Position of the 6.2 μm Interstellar Emission Feature: A Tracer of N in the Interstellar Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Population. Astrophys. J. 2005, 632, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, K.I.; Sellgren, K.; Werner, M.W.; Houdashelt, M.L. Infrared Space Observatory mid-infrared spectra of reflection nebulae. Astrophys. J. 2000, 530, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, G.C.; Gordon, K.D.; Salama, F.; Allamandola, L.J.; Martin, P.G.; Snow, T.P.; Whittet, D.C.B.; Witt, A.N.; Wolff, M.J. The Role of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ultraviolet Extinction. I. Probing Small Molecular Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Astrophys. J. 2003, 592, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, F.; Galazutdinov, G.A.; Krełowski, J.; Biennier, L.; Beletsky, Y.; Song, I.-O. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and the Diffuse Interstellar Bands: A Survey. Astrophys. J. 2011, 728, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gredel, R.; Carpentier, Y.; Rouillé, G.; Steglich, M.; Huisken, F.; Henning, T. Abundances of PAHs in the ISM: Confronting observations with experimental results. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 530, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, B.A.; Loomis, R.A.; Burkhardt, A.M.; Lee, K.L.K.; Shingledecker, C.N.; Charnley, S.B.; Cooke, I.R.; Cordiner, M.A.; Herbst, E.; Kalenskii, S.; et al. Detection of two interstellar polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons via spectral matched filtering. Science 2021, 371, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernicharo, J.; Agúndez, M.; Cabezas, C.; Tercero, B.; Marcelino, N.; Pardo, J.R.; de Vicente, P. Pure hydrocarbon cycles in TMC-1: Discovery of ethynyl cyclopropenylidene, cyclopentadiene, and indene. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 649, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.R.; Kim, H.; Saykally, R.J. Peripherally Hydrogenated Neutral Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons as Carriers of the 3 Micron Interstellar Infrared Emission Complex: Results from Single-Photon Infrared Emission Spectroscopy. Astrophys. J. 2000, 545, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kwok, S. On the Viability of the PAH Model as an Explanation of the Unidentified Infrared Emission Features. Astrophys. J. 2015, 798, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, E.; Mackie, C.; Candian, A.; Tielens, A.G.G.M. A Spectroscopic View on Cosmic PAH Emission. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 1921–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.; O’Reilly, E.P. Electronic and atomic structure of amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 1987, 35, 2946–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, A.; Wada, S.; Onaka, T.; Tokunaga, A.T. Infrared spectrum of quenched carbonaceous composite (QCC). II—A new identification of the 7.7 and 8.6 micron unidentified infrared emission bands. Astrophys. J. 1987, 320, L63–L67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godard, M.; Féraud, G.; Chabot, M.; Carpentier, Y.; Pino, T.; Brunetto, R.; Duprat, J.; Engrand, C.; Bréchignac, P.; D’Hendecourt, L.; et al. Ion irradiation of carbonaceous interstellar analogues. Effects of cosmic rays on the 3.4 μm interstellar absorption band. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 529, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangeli, L.; Mennella, V.; Palumbo, P.; Rotundi, A.; Bussoletti, E. Mass extinction coefficients of various submicron amorphous carbon grains: Tabulated values from 40 NM to 2 mm. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1995, 113, 561. [Google Scholar]
- Mennella, V.; Baratta, G.A.; Esposito, A.; Ferini, G.; Pendleton, Y.J. The Effects of Ion Irradiation on the Evolution of the Carrier of the 3.4 Micron Interstellar Absorption Band. Astrophys. J. 2003, 587, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.; Duley, W.W. Ultraviolet and Infrared Refractive Indices of Amorphous Silicates. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1996, 105, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennella, V.; Brucato, J.R.; Colangeli, L.; Palumbo, P. Activation of the 3.4 Micron Band in Carbon Grains by Exposure to Atomic Hydrogen. Astrophys. J. 1999, 524, L71–L74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, C.; Huisken, F.; Mutschke, H.; Jansa, I.L.; Henning, T.H. Formation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Carbonaceous Solids In Gas-Phase Condensation Experiments. Astrophys. J. 2009, 696, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlin, N.; Bohn, I.; Reynaud, C.; Cauchetier, M.; Galvez, A.; Rouzaud, J.-N. Nanoparticles produced by Laser Pyrolysis of hydrocarbons: Analogy with carbon cosmic dust. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 330, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Dartois, E.; Muñoz Caro, G.M.; Deboffle, D.; d’Hendecourt, L. Diffuse interstellar medium organic polymers. Photoproduction of the 3.4, 6.85 and 7.25 μm features. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 423, L33–L36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, T.; Dartois, E.; Cao, A.-T.; Carpentier, Y.; Chamaillé, T.; Vasquez, R.; Jones, A.P.; D’Hendecourt, L.; Bréchignac, P. The 6.2 μm band position in laboratory and astrophysical spectra: A tracer of the aliphatic to aromatic evolution of interstellar carbonaceous dust. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 490, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, Y.; Féraud, G.; Dartois, E.; Brunetto, R.; Charon, E.; Cao, A.-T.; d’Hendecourt, L.; Bréchignac, P.; Rouzaud, J.-N.; Pino, T. Nanostructuration of carbonaceous dust as seen through the positions of the 6.2 and 7.7 μm AIBs. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 548, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.; Santoro, G.; Merino, P.; Accolla, M.; Lauwaet, K.; Sobrado, J.; Sabbah, H.; Pelaez, R.J.; Herrero, V.J.; Tanarro, I.; et al. Prevalence of non-aromatic carbonaceous molecules in the inner regions of circumstellar envelopes. Nat. Astron. 2020, 4, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, S.; Zhang, Y. Mixed aromatic-aliphatic organic nanoparticles as carriers of unidentified infrared emission features. Nature 2011, 479, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadjadi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Kwok, S. A Theoretical Study on the Vibrational Spectra of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Molecules with Aliphatic Sidegroups. Astrophys. J. 2015, 801, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, C.-H.; Sadjadi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Kwok, S. The 6 μm Feature as a Tracer of Aliphatic Components of Interstellar Carbonaceous Grains. Astrophys. J. 2016, 832, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Kwok, S. On the Origin of the 3.3 μm Unidentified Infrared Emission Feature. Astrophys. J. 2017, 845, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, S.; Kwok, S.; Cataldo, F.; García-Hernández, D.A.; Manchado, A. A theoretical investigation of the possible detection of C24 in space. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2020, 28, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.D.T.; Draine, B.T.; Dale, D.A.; Moustakas, J.; Kennicutt, R.C.; Helou, G.; Armus, L.; Roussel, H.; Sheth, K.; Bendo, G.J.; et al. The mid-infrared spectrum of star-forming galaxies: Global properties of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon emission. Astrophys. J. 2007, 656, 770–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A. Spitzer’s perspective of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in galaxies. Nat. Astron. 2020, 4, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genzel, R.; Lutz, D.; Sturm, E.; Egami, E.; Kunze, D.; Moorwood, A.F.M.; Rigopoulou, D.; Spoon, H.W.W.; Sternberg, A.; Tacconi-Garman, L.E.; et al. What Powers Ultraluminous IRAS Galaxies? Astrophys. J. 1998, 498, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galliano, F.; Madden, S.C.; Tielens, A.G.G.M.; Peeters, E.; Jones, A.P. Variations of the Mid-IR Aromatic Features inside and among Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2008, 679, 310–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. The synthesis of organic and inorganic compounds in evolved stars. Nature 2004, 430, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, K.; Xiong, G.-Z.; Kwok, S. Infrared Space Observatory Spectroscopy of Extreme Carbon Stars. Astrophys. J. 2000, 530, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernicharo, J.; Heras, A.M.; Tielens, A.G.G.M.; Pardo, J.R.; Herpin, F.; Guélin, M.; Waters, L.B.F.M. Infrared Space Observatory’s Discovery of C4H2, C6H2, and Benzene in CRL 618. Astrophys. J. 2001, 546, L123–L126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilker, J.S.; Phadke, K.A.; Aravena, M.; Archipley, M.; Bayliss, M.B.; Birkin, J.E.; Béthermin, M.; Burgoyne, J.; Cathey, J.; Chapman, S.C.; et al. Spatial variations in aromatic hydrocarbon emission in a dust-rich galaxy. Nature 2023, 618, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbidge, E.M.; Burbidge, G.R.; Fowler, W.A.; Hoyle, F. Synthesis of the Elements in Stars. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1957, 29, 547–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallerstein, G.; Iben, I.; Parker, P.; Boesgaard, A.M.; Hale, G.M.; Champagne, A.E.; Barnes, C.A.; Käppeler, F.; Smith, V.V.; Hoffman, R.D.; et al. Synthesis of the elements in stars: Forty years of progress. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1997, 69, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. Organics in the solar system. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 19, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. Delivery of Complex Organic Compounds from Planetary Nebulae to the Solar System. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2009, 8, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. Stardust: The Cosmic Seeds of Life; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwok, S. Synthesis of Organic and Inorganic Compounds in Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars. Galaxies 2024, 12, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12050064
Kwok S. Synthesis of Organic and Inorganic Compounds in Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars. Galaxies. 2024; 12(5):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12050064
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwok, Sun. 2024. "Synthesis of Organic and Inorganic Compounds in Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars" Galaxies 12, no. 5: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12050064
APA StyleKwok, S. (2024). Synthesis of Organic and Inorganic Compounds in Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars. Galaxies, 12(5), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12050064





