X-ray Polarization from Magnetar Sources
Abstract
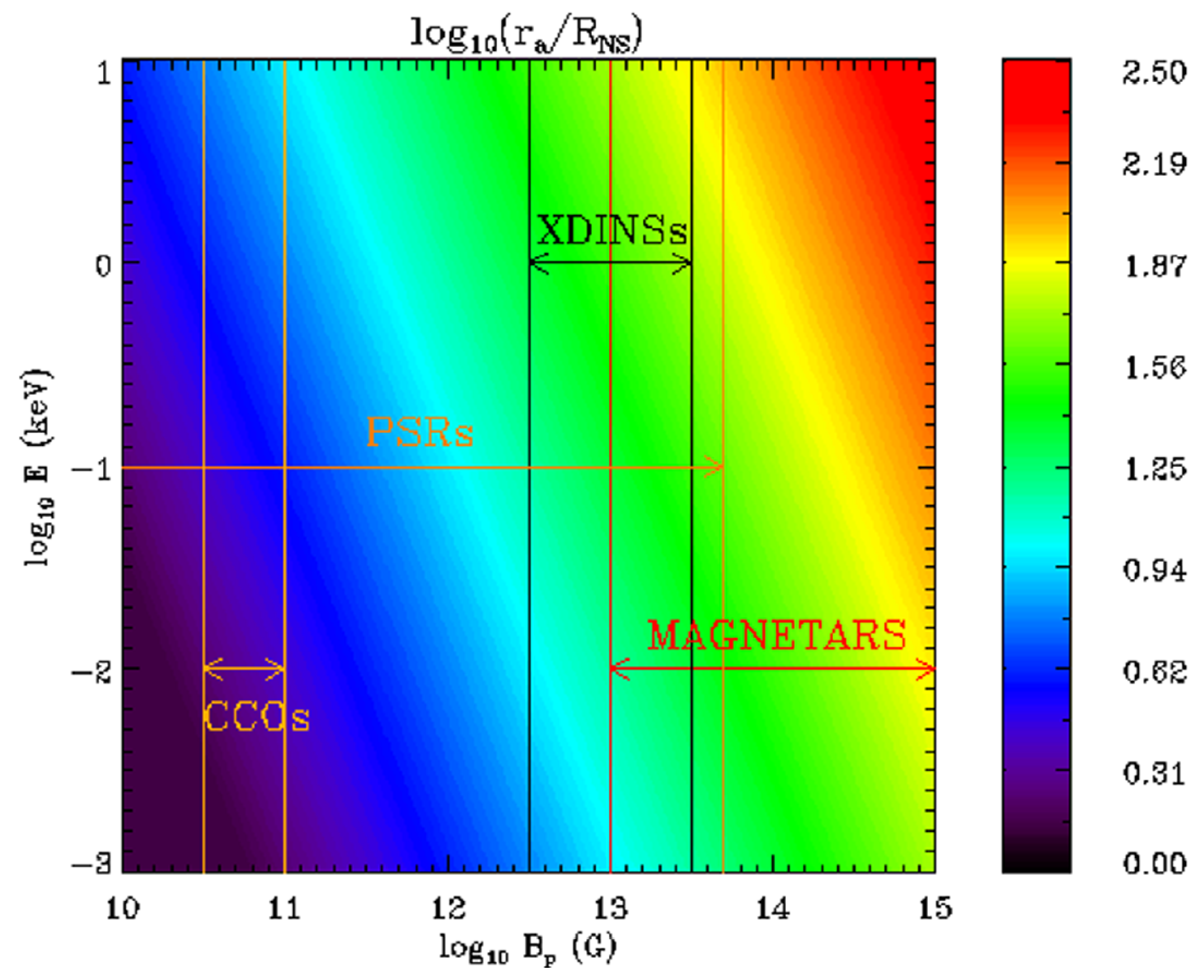
1. Introduction
2. Polarization in Strong Magnetic Fields
2.1. Polarization Properties of the Magnetized Vacuum and Plasma
2.2. Polarization Modes in Strong Magnetic Fields and Vacuum Resonance
2.3. Polarization Transport in Highly Magnetized Media
3. Polarization Properties of Magnetar X-ray Emission
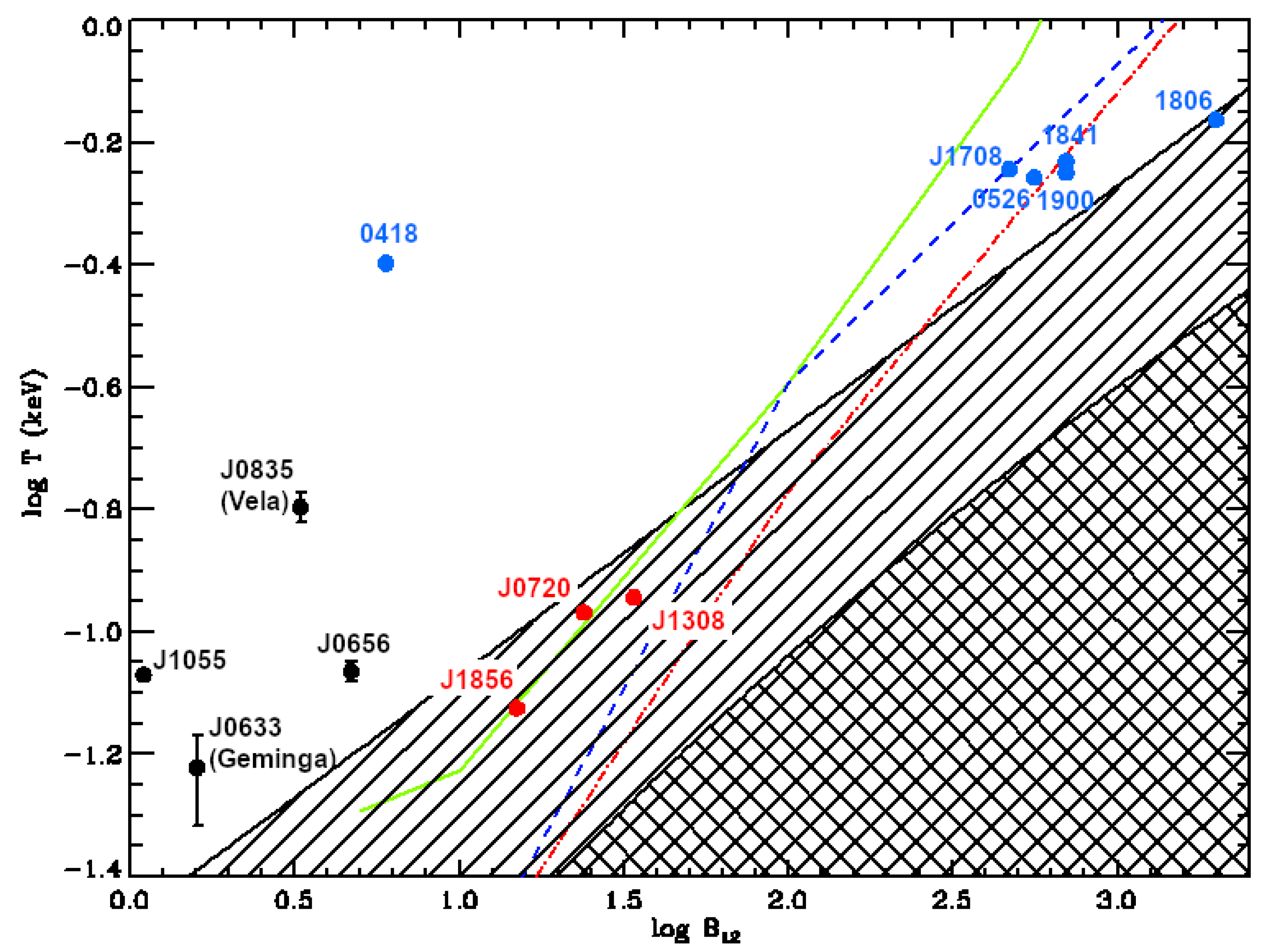
3.1. Magnetized Atmosphere
3.2. Condensed Surface
- Fixed-ions, in which only the electrons may freely respond to incoming electromagnetic waves, while ions are considered to be fixed in the lattice;
- Free-ions, in which both electron and ion motions in response to an incoming electromagnetic wave are considered.
3.3. Resonant Compton Scattering in Magnetar Magnetospheres
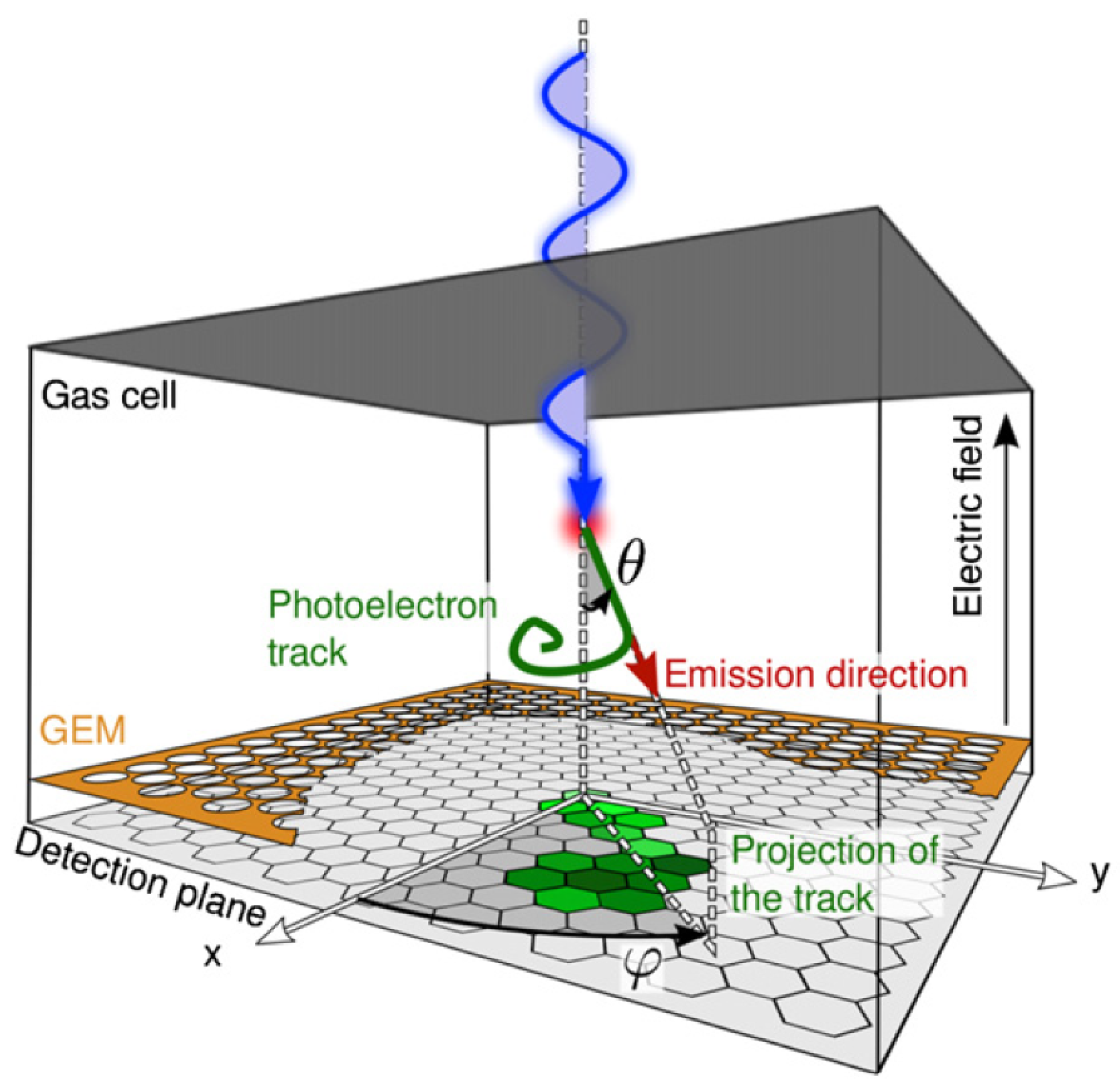
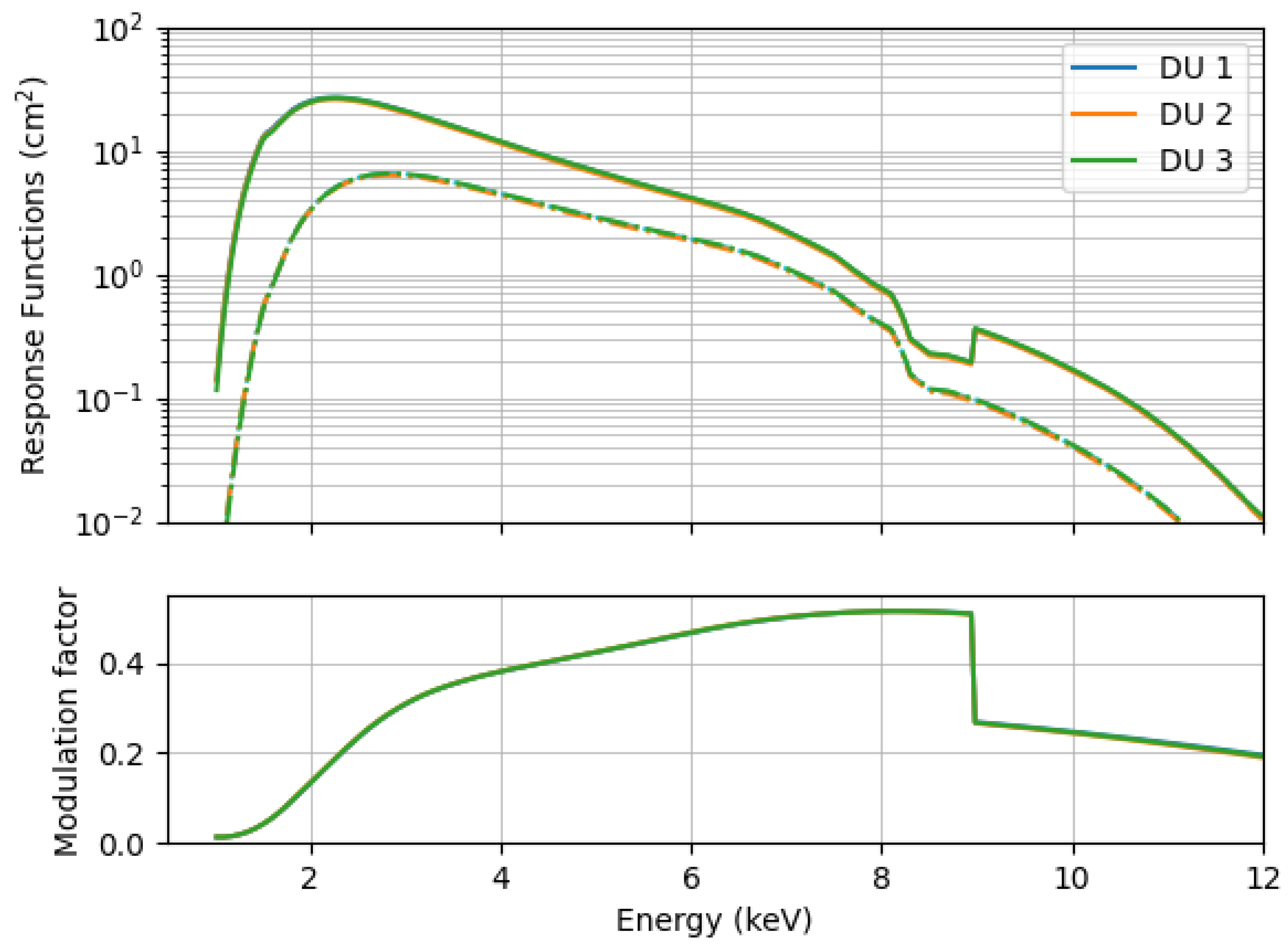
4. X-ray Polarimetry with IXPE
5. IXPE Magnetar Observations
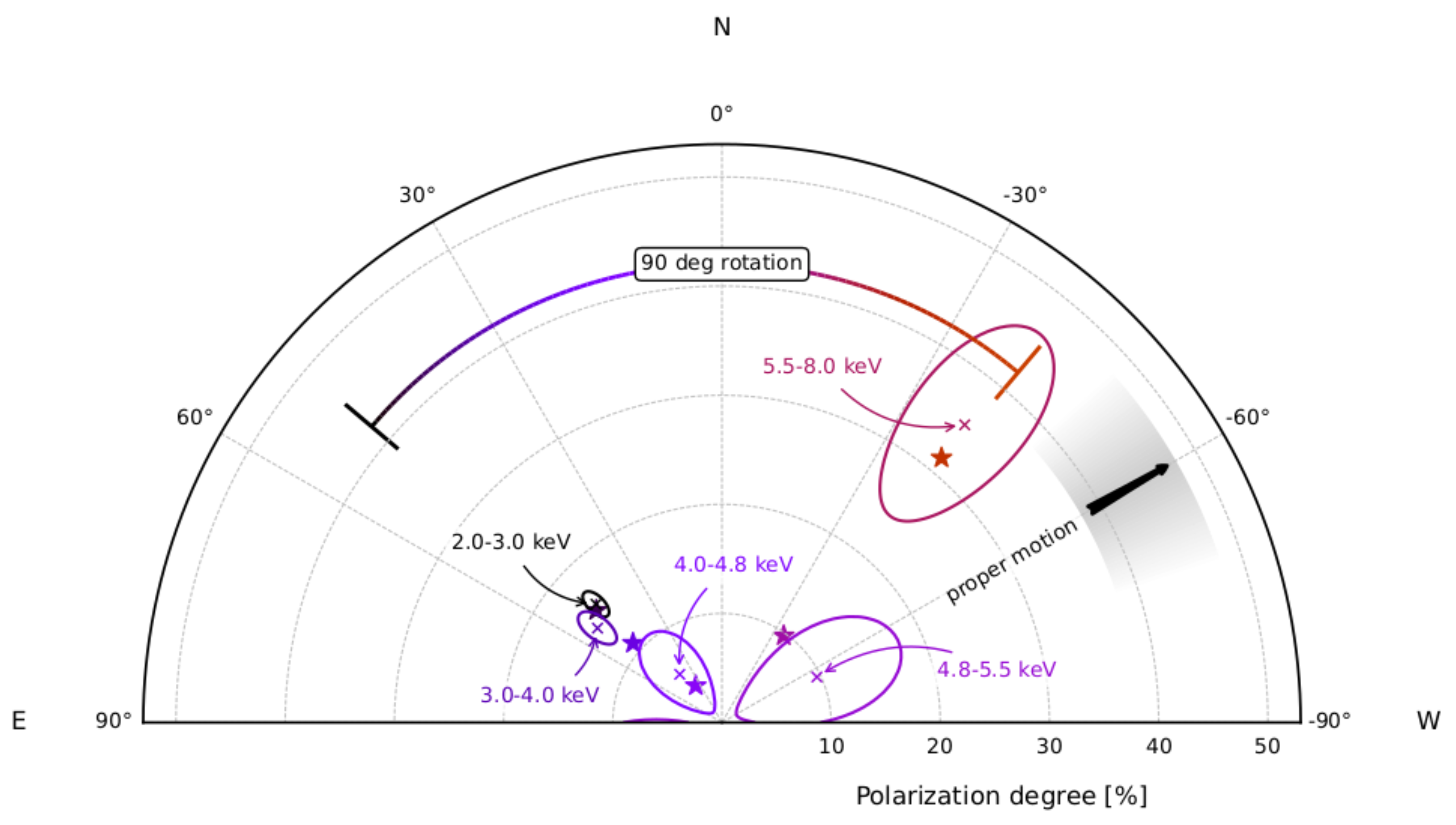
5.1. AXP 4U 0142+61
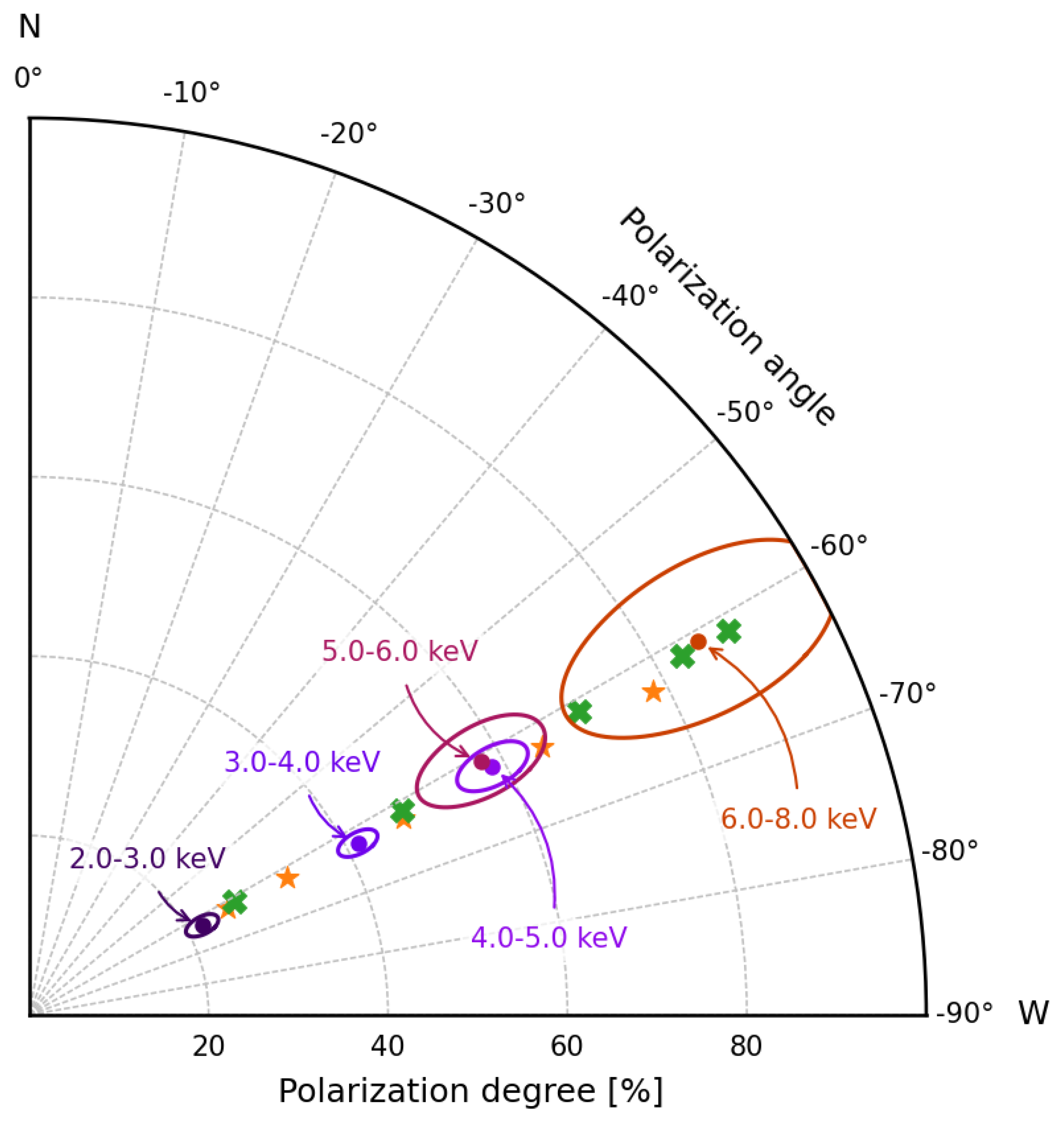
5.2. AXP 1RXS J170849.0−4009100
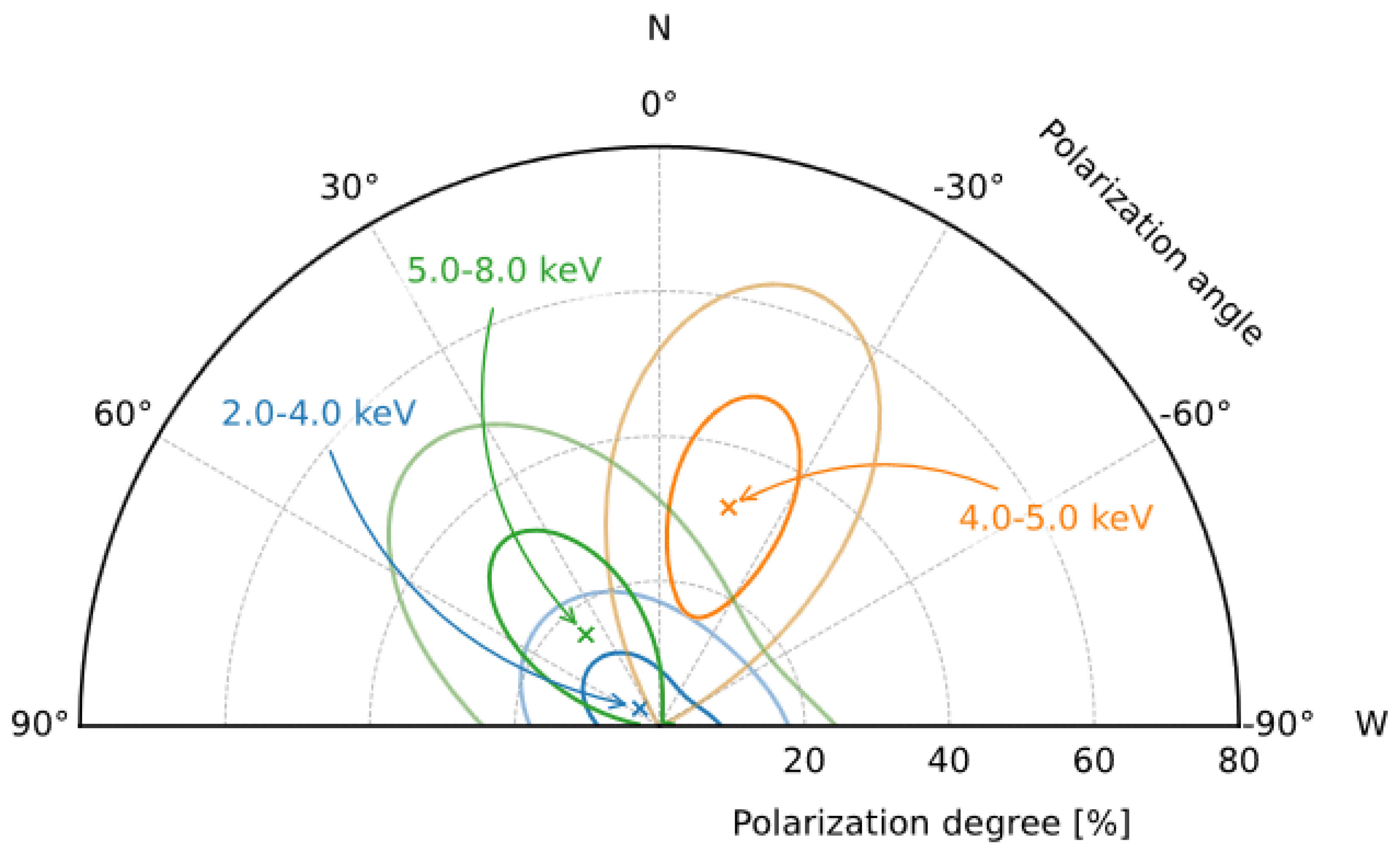
5.3. SGR 1806−20
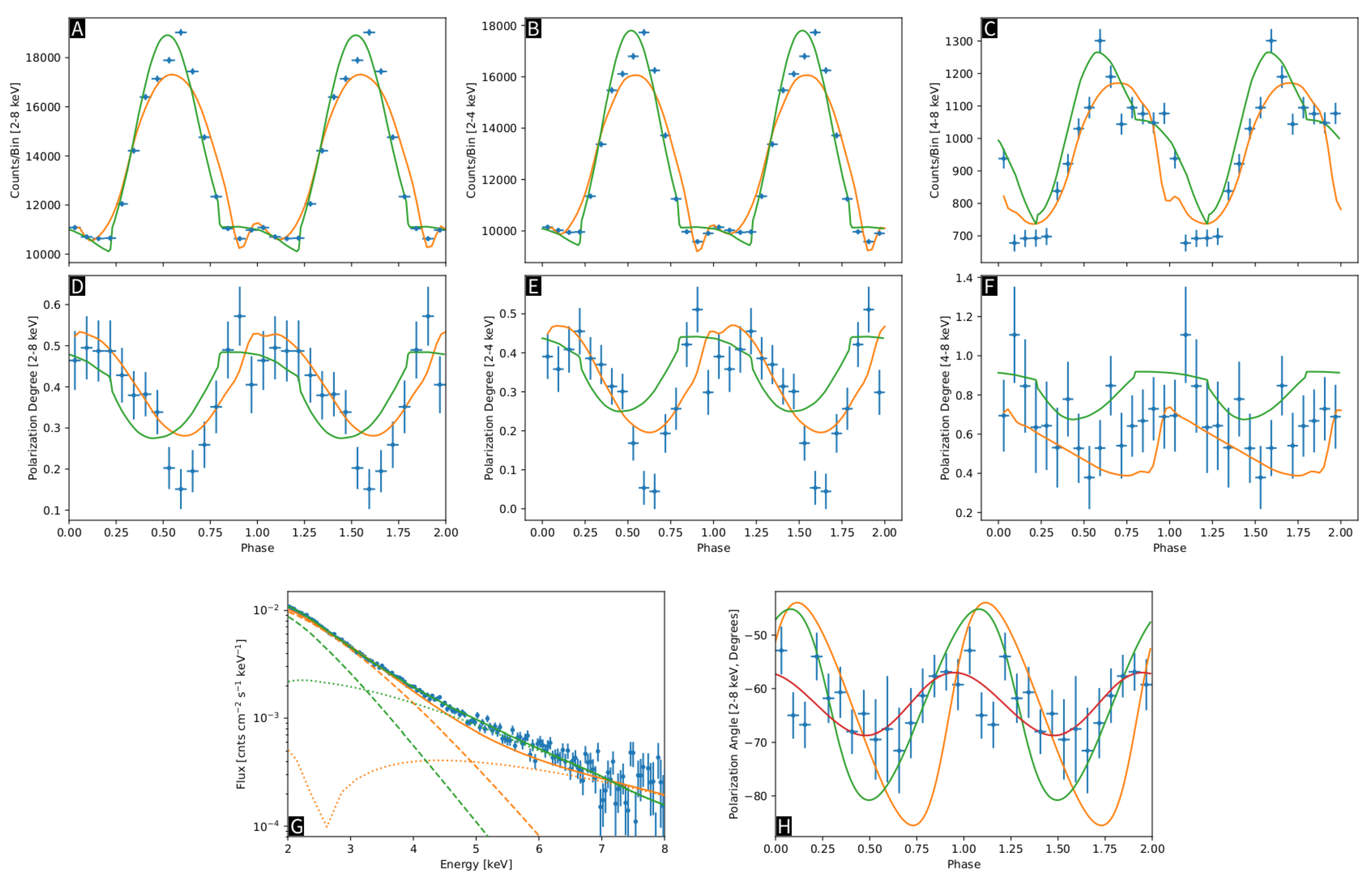
5.4. AXP 1E 2259+586
6. Discussion and Conclusions
- As expected for sources endowed with ultra-strong magnetic fields, magnetar emission turns out to be strongly polarized. The polarization degree observed in the four objects ranges from ≈15– at low energies (2–) to more than in the higher end of the IXPE band.
- Despite the similarities in spectral shape shared by the four magnetars, the different polarization patterns indicate that the thermal emission may have different origins. It may come directly from regions where the condensed surface is exposed or being reprocessed in a geometrically-thin, magnetized atmosphere above the crust. In this respect, polarimetry can indeed provide a way to disentangle different emission models, removing the degeneracy of spectral analysis alone.
- The peculiar swing of the polarization angle detected in the AXP 4U 0142+61 can be naturally explained in terms of photons polarized in two normal modes, the ordinary and extraordinary ones. Since such pattern is expected if radiation propagates in magnetic fields , this can be regarded as indirect proof that magnetar magnetic fields are indeed ultra-strong. Moreover, the limited value of the polarization degree detected at high energies (≈30–) argues in favor of the canonical twisted magnetosphere scenario, according to which resonantly up-scattered photons dominate the high-energy part of the soft X-ray spectrum.
- Even if the phase- and energy-integrated measurements did not yield a polarization degree high enough to validate the presence of vacuum birefringence (≳, see [55]), the detected phase-dependent behavior of the polarization degree and angle (with the PD following the flux pulse profile and the PA modulated according to the RVM) is indeed what one expects if vacuum birefringence is at work. This can be considered as a first step towards testing QED effects in the ultra-magnetized vacuum.
- Phase-resolved polarimetry can be a powerful tool in understanding star magnetic field topology. As in the case of the AXP 1E 2259+586, if a sufficiently high number of photons is collected, the variation of the polarization degree and angle with rotational phase can help in confirming the existence of plasma loops, responsible for the occurrence of phase-dependent absorption lines in the spectrum. In this respect, an important contribution in improving spectro-polarimetric, phase-dependent analysis may come from forthcoming X-ray missions, like HEX-p [108] and eXTP [109].
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mereghetti, S. The strongest cosmic magnets: Soft gamma-ray repeaters and anomalous X-ray pulsars. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2008, 15, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turolla, R.; Zane, S.; Watts, A.L. Magnetars: The physics behind the observations. A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2015, 78, 116091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaspi, V.M.; Beloborodov, A.M. Magnetars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 55, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burderi, L.; Di Salvo, T.; Robba, N.R.; La Bardera, A.; Guainazzi, M. The 0.1–100 keV Spectrum of Centaurus X-3: Pulse Phase Spectroscopy of the Cyclotron Line and Magnetic Field Structure. Astrophys. J. 2000, 530, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereghetti, S. X-ray emission from isolated neutron stars, High-Energy Emission from Pulsars and their Systems. In Astrophysics and Space Science Proceedings; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; p. 345. ISBN 978-4-642-17250-2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.H.; Lin, L.C.; Dai, S.; Takata, J.; Li, K.L.; Hu, C.P.; Hou, X. A Multiwavelength Study of PSR J1119-6127 after 2016 Outburst. Astrophys. J. 2020, 902, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olausen, S.A.; Kaspi, V.M. The McGill Magnetar Catalog. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2014, 212, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, G.L.; Romano, P.; Mangano, V.; Dall’Osso, S.; Chincarini, G.; Stella, L.; Campana, S.; Belloni, T.; Tagliaferri, G.; Blustin, A.J.; et al. A Swift Gaze into the 2006 March 29 Burst Forest of SGR 1900+14. Astrophys. J. 2008, 685, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazets, E.P.; Golentskii, S.V.; Ilinskii, V.N.; Aptekar, R.L.; Guryan, I.A. Observations of a flaring X-ray pulsar in Dorado. Nature 1979, 282, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, K.; Cline, T.; Mazets, E.; Barthelmy, S.; Butterworth, P.; Marshall, F.; Palmer, D.; Aptekar, R.; Golenetskii, S.; Il’Inskii, V.; et al. A giant periodic flare from the soft γ-ray repeater SGR1900+14. Nature 1999, 397, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, D.M.; Barthelmy, S.; Gehrels, N.; Kippen, R.M.; Cayton, T.; Kouveliotou, C.; Eichler, D.; Wijers, R.A.; Woods, P.M.; Granot, J.; et al. A giant γ-ray flare from the magnetar SGR 1806–20. Nature 2005, 434, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, R.C.; Thompson, C. Formation of Very Strongly Magnetized Neutron Stars: Implications for Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1992, 392, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.; Duncan, R.C. The soft gamma repeaters as very strongly magnetized neutron stars—I. Radiative mechanism for outbursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1995, 275, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyed, R.; Leahy, D.; Niebergal, B. Quark-nova remnants. I. The leftover debris with applications to SGRs, AXPs, and XDINs. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 473, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwazaki, A. Color ferromagnetism of quark matter: A possible origin of a strong magnetic field in magnetars. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 114003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.; Duncan, R.C. The Giant Flare of 1998 August 27 from SGR 1900+14. II. Radiative Mechanism and Physical Constraints on the Source. Astrophys. J. 2001, 561, 980. [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite, J. Axisymmetric magnetic fields in stars: Relative strengths of poloidal and toroidal components. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 397, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, R.; Pons, J.A. A Unified Model of the Magnetar and Radio Pulsar Bursting Phenomenology. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 727, L51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.; Lyutikov, M.; Kulkarni, S.R. Electrodynamics of Magnetars: Implication for the Persistent X-Ray Emission and Spin-down of the Soft Gamma Repeaters and Anomalous X-ray Pulsars. Astrophys. J. 2002, 574, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloborodov, A.M.; Thompson, C. Corona of Magnetars. Astrophys. J. 2007, 657, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, L.; Turolla, S.; Zane, S. X-ray spectra from magnetar candidates—I. Monte Carlo simulations in the non-relativistic regime. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 386, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Davis, S.W. The X-ray Polarization Signature of Quiescent Magnetars: Effect of Magnetospheric Scattering and Vacuum Polarization. Astrophys. J. 2011, 730, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverna, R.; Muleri, F.; Turolla, R.; Soffitta, P.; Fabiani, S.; Nobili, L. Probing magnetar magnetosphere through X-ray polarization measurements. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 438, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnedin, Y.N.; Pavlov, G.G. The trasfer equations for normal waves and radiation polarization in an anisotropic medium. Sov. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 1974, 38, 903. [Google Scholar]
- Herold, H. Compton and Thomson scattering in strong magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. D 1979, 19, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, J. Scattering of light in a strongly magnetized plasma. Phys. Rev. D 1979, 19, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mészáros, P. High-Energy Radiation from Magnetized Neutron Stars; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Heisenberg, W.; Euler, H. Folgerungen aus der Diracschen Theorie des Positrons. Z. Phys. 1936, 98, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyl, J.S.; Shaviv, N.J. Polarization evolution in strong magnetic fields. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2000, 311, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyl, J.S.; Shaviv, N.J. QED and high polarization of the thermal radiation from neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 023002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyl, J.S.; Shaviv, N.J.; Lloyd, D. The high-energy polarization-limiting radius of neutron star magnetospheres—I. Slowly rotating neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 342, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.C.; Cohen, G.G.; Kestenbaum, H.L.; Long, K.S.; Novick, R.; Wolff, R.S. Measurement of the X-ray polarization of the Crab nebula. Astrophys. J. 1978, 208, L125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.C.; Silver, E.H.; Kestenbaum, H.L.; Long, K.S.; Novick, R. A precision measurement of the X-ray polarization of the Crab Nebula without pulsar contamination. Astrophys. J. 1978, 220, L117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.C.; Soffitta, P.; Baldini, L.; Ramsey, B.D.; O’Dell, S.L.; Romani, R.W.; Matt, G.; Dininger, W.D.; Baumgartner, W.H.; Bellazzini, R.; et al. The Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE): Pre-Launch. J. Astron. Telesc. Instrum. Syst. 2022, 8, 026002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Ho, W.C.G. Resonant Conversion of Photon Modes Due to Vacuum Polarization in a Magnetized Plasma; Implications for X-ray Emission from Magnetars. Astrophys. J. 2002, 566, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ho, W.C.G.; Lai, D. Atmospheres and spectra of strongly magnetized neutron stars—II. The effect of vacuum polarization. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 338, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, A.K.; Lai, D. Physics of strongly magnetized neutron stars. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2006, 69, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.J.; Nigam, B.P. Dichroism of the Vacuum. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, S.L. Photon splitting and photon dispersion in a strong magnetic field. Ann. Phys. 1971, 67, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, G.G.; Shibanov, I.A. Influence of vacuum polarization by a magnetic field on the propagation of electromagnetic waves in plasmas. Zhurnal Eksperimentalnoi Teor. Fiz. 1979, 76, 1457. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, D.; Ho, W.C.G. Transfer of Polarized Radiation in Strongly Magnetized Plasmas and Thermal Emission from Magnetars: Effect of Vacuum Polarization. Astrophys. J. 2003, 588, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.M.E.; Zane, S.; Turolla, R.; Taverna, R. X-ray Polarisation in Magnetar Atmospheres—Effects of Mode Conversion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Zheleznyakov, V.V. (Ed.) Radiation in Astrophysical Plasmas; Astrophysics & Space Science Library: Toledo, Spain, 1996; p. 204. [Google Scholar]
- Rybicki, G.B.; Lightman, A.P. Radiative Processes in Astrophysics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Taverna, R.; Turolla, R.; González-Caniulef, D.; Zane, S.; Muleri, F.; Soffitta, P. Polarization of neutron star surface emission: A systematic analysis. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 454, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, R.W. Model Atmospheres for Cooling Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. 1987, 313, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibanov, I.A.; Zavlin, V.E.; Pavlov, G.G.; Ventura, J. Model atmospheres and radiation of magnetic neutron stars. I—The fully ionized case. Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 266, 313. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov, G.G.; Shibanov, Y.A.; Ventura, J.; Zavlin, V.E. Model atmospheres and radiation of magnetic neutron stars: Anisotropic thermal emission. Astron. Astrophys. 1994, 289, 837. [Google Scholar]
- Suleimanov, V.; Potekhin, A.Y.; Werner, K. Models of magnetized neutron star atmospheres: Thin atmospheres and partially ionized hydrogen atmospheres with vacuum polarization. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 500, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Adelsberg, M.; Lai, D. Atmosphere models of magnetized neutron stars: QED effects, radiation spectra and polarization signals. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 373, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, D.A. Model atmospheres and thermal spectra of magnetized neutron stars. arXiv 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekhin, A.Y.; Lai, D.; Chabrier, G.; Ho, W.C.G. Electromagnetic Polarization in Partially Ionized Plasmas with Strong Magnetic Fields and Neutron Star Atmosphere Models. Astrophys. J. 2004, 612, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekhin, A.Y.; Chabrier, G.; Ho, W.C.G. Opacities and spectra of hydrogen atmospheres of moderately magnetized neutron stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 572, A69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- González-Caniulef, D.; Zane, S.; Taverna, R.; Turolla, R.; Wu, K. Polarized thermal emission from X-ray dim isolated neutron stars: The case of RX J1856.5–3754. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 459, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverna, R.; Turolla, R.; Suleimanov, V.; Potekhin, A.Y.; Zane, S. X-ray spectra and polarization from magnetar candidates. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 492, 5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, W. Thermal radiation from highly magnetized neutron stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1980, 82, 352. [Google Scholar]
- Turolla, R.; Zane, S.; Drake, J.J. Bare Quark Stars or Naked Neutron Stars? The Case of RX J1856.5–3754. Astrophys. J. 2004, 603, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Azorin, J.F.; Miralles, J.A.; Pons, J.A. Thermal radiation from magnetic neutron star surfaces. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 433, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van Adelsberg, M.; Lai, D.; Potekhin, A.Y.; Arras, P. Radiation from Condensed Surface of Magnetic Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. 2005, 628, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekhin, A.Y.; Suleimanov, V.F.; van Adelsberg, M.; Werner, K. Radiative properties of magnetic neutron stars with metallic surfaces and thin atmospheres. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 546, A121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D. Matter in strong magnetic fields. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2001, 73, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medin, Z.; Lai, D. Density-functional-theory calculations of matter in strong magnetic fields. II. Infinite chains and condensed matter. Phys. Rev. A 2006, 74, 062508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medin, Z.; Lai, D. Condensed surfaces of magnetic neutron stars, thermal surface emission, and particle acceleration above pulsar polar caps. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 382, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Medin, Z.; Lai, D. Density-functional-theory calculations of matter in strong magnetic fields. I. Atoms and molecules. Phys. Rev. A 2006, 74, 062507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turolla, R. Isolated Neutron Stars: The Challenge of Simplicity. In Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Becker, W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; Volume 357, p. 141. [Google Scholar]
- Beloborodov, A.M. Untwisting Magnetospheres of Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. 2009, 703, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczynski, H.; Taverna, R.; Turolla, R.; Mereghetti, S.; Rigoselli, M. Fitting XMM-Newton observations of the AXP 1RXS 170849.0–400910 with four magnetar surface emission models, and predictions for X-ray polarization observations with IXPE. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 658, A161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Thompson, C. Resonant Cyclotron Scattering in Three Dimensions and the Quiescent Nonthermal X-ray Emission of Magnetars. Astrophys. J. 2007, 660, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, L.; Turolla, R.; Zane, S.; Nobili, L. Topology of magnetars external field—I. Axially symmetric fields. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 395, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.C.; Cohen, G.G.; Kestenbaum, H.L.; Novick, R.; Wolff, R.S.; Landecker, P.B. The X-ray polarization experiment on the OSO-8. In X-ray Binaries, Proceedings of a Symposium; NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Muleri, F. On the Operation of X-Ray Polarimeters with a Large Field of View. Astrophys. J. 2014, 782, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.; Soffitta, P.; Bellazzini, R.; Brez, A.; Lumb, N.; Spandre, G. An efficient photoelectric X-ray polarimeter for the study of black holes and neutron stars. Nature 2001, 411, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellazzini, R.; Baldini, L.; Brez, A.; Costa, E.; Latronico, L.; Omodei, N.; Soffitta, P.; Spandre, G. A photoelectric polarimeter based on a Micropattern Gas Detector for X-ray astronomy. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2003, 510, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitler, W. Quantum Theory of Radiation, 3rd ed.; International Series of Monographs on Physics; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Weisskopf, M.C.; Elsner, R.F.; O’Dell, S.L. On understanding the figures of merit for detection and measurement of X-ray polarization. Proc. SPIE 2010, 7732, 77320E. [Google Scholar]
- Strohmayer, T.E.; Kallman, T.R. On the Statistical Analysis of X-ray Polarization Measurements. Astrophys. J. 2013, 773, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, N.; Nichelli, E.; Israel, G.L.; Perna, R.; Oosterbroek, T.; Parmar, A.N.; Turolla, R.; Campana, S.; Stella, L.; Zane, S.; et al. Very deep X-ray observations of the anomalous X-ray pulsar 4U0142+614. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 381, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverna, R.; Turolla, R.; Muleri, F.; Heyl, J.; Zane, S.; Baldini, L.; González-Caniulef, D.; Bachetti, M.; Rankin, J.; Caiazzo, I.; et al. Polarized X-rays from a magnetar. Science 2022, 378, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, L.; Bucciantini, N.; Di Lalla, N.; Ehlert, S.; Manfreda, A.; Negro, M.; Omodei, N.; Pesce-Rollins, M.; Sgro, C.; Silvestri, S. ixpeobssim: A simulation and analysis framework for the imaging X-ray polarimetry explorer. SoftwareX 2022, 19, 101194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, A.; Soffitta, P.; Costa, E.; Ferrazzoli, R.; La Monaca, F.; Rankin, J.; Ratheesh, A.; Xie, F.; Baldini, L.; Del Monte, E.; et al. Handling the Background in IXPE Polarimetric Data. Astron. J. 2023, 165, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib, R.; Kaspi, V.M. 16 yr of RXTE Monitoring of Fiva Anomalous X-Ray Pulsars. Astrophys. J. 2014, 784, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, K.A. XSPEC: The First Ten Years. Astron. Data Anal. Softw. Syst. V 1996, 101, 17. [Google Scholar]
- den Hartog, P.R.; Kuiper, L.; Hermsen, W.; Kaspi, V.M.; Dib, R.; Knödlseder, J.; Gavriil, F.P. Detailed high-energy characteristics of AXP 4U 0142+61. Multi-year observations with INTEGRAL, RXTE, XMM-Newton, and ASCA. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 489, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tendulkar, S.P.; Hascöet, R.; Yang, C.; Kaspi, V.M.; Beloborodov, A.M.; An, H.; Bachetti, M.; Boggs, S.E.; Christensen, F.E.; Craig, W.W.; et al. Phase-resolved NuSTAR and Swift-XRT Observations of Magnetar 4U 0142+61. Astrophys. J. 2015, 808, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D. IXPE detection of polarized X-rays from magnetars and photon mode conversion at QED vacuum resonance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janka, H.-T.; Wongwathanarat, A.; Michael, K. Supernova Fallback as Origin of Neutron Star Spins and Spin-kick Alignment. Astrophys. J. 2022, 926, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Colpi, M.; Wasserman, I. Formation of an Evanescent Proto-Neutron Star Binary and the Origin of Pulsar Kicks. Astrophys. J. 2002, 581, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, V.; Cooke, D.J. Magnetic poles and the polarization structure of pulsar radiation. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1969, 3, 225. [Google Scholar]
- Poutanen, J. Relativistic rotating vector model for X-ray millisecond pulsars. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Caniulef, D.; Caiazzo, I.; Heyl, J.S. Unbinned likelihood analysis for X-ray polarization. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 519, 5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zane, S.; Taverna, R.; González–Caniulef, D.; Muleri, F.; Turolla, R.; Heyl, J.; Uchiyama, K.; Ng, M.; Tamagawa, T.; Caiazzo, I.; et al. A Strong X-Ray Polarization Signal from the Magnetar 1RXS J170849.0–400910. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 944, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, N.; Israel, G.L.; Oosterbroek, T.; Campana, S.; Zane, S.; Turolla, R.; Testa, V.; Méndez, M.; Stella, L. X-ray intensity-hardness correlation and deep IR observations of the anomalous X-ray pulsar 1RXS J170849–400910. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2007, 308, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, G.L.; Covino, S.; Stella, L.; Campana, S.; Haberl, F.; Mereghetti, S. Further Evidence that 1RXS J170849.0–400910 Is an Anomalous X-Ray Pulsar. Astrophys. J. 1999, 518, L107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, D.N.; Hill, J.E.; Nousek, J.A.; Kennea, J.A.; Wells, A.; Osborne, J.P.; Abbey, A.F.; Beardmore, A.; Mukerjee, K.; Short, A.D.T.; et al. The Swift X-Ray Telescope. Space Sci. Rev. 2005, 120, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzoumanian, Z.; Gendreau, K.C.; Baker, C.L.; Cazeau, T.; Hestnes, P.; Kellogg, J.W.; Kenyon, S.J.; Kozon, R.P.; Liu, K.-C.; Manthripragada, S.S.; et al. The neutron star interior composition explorer (NICER): Mission definition. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9144, 914420. [Google Scholar]
- Potekhin, A.Y.; Pons, J.A.; Page, D. Neutron Stars–Cooling and Transport. Space Sci. Rev. 2015, 191, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloborodov, A.M. On the Mechanism of Hard X-Ray Emission from Magnetars. Astrophys. J. 2013, 762, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hascoët, R.; Beloborodov, A.M.; den Hartog, P.R. Phase-Resolved X-ray Spectra of Mangetars and the COronal Outflow Model. Astrophys. J. 2014, 786, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibby, J.L.; Crowther, P.A.; Furness, J.P.; Clark, J.S. A downward revision to the distance of the 1806–20 cluster and associated magnetar from Gemini Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 386, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, F.; Lumb, D.; Altieri, B.; Clavel, J.; Ehle, M.; Erd, C.; Gabriel, C.; Guainazzi, M.; Gondoin, P.; Much, R.; et al. XMM-Newton observatory. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 365, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turolla, R.; Taverna, R.; Israel, G.L.; Muleri, F.; Zane, S.; Bachetti, M.; Heyl, J.; Di Marco, A.; Gau, E.; Krawczynski, H.; et al. IXPE and XMM-Newton Observations of the SOft Gamma Repeater SGR 1806–20. Astrophys. J. 2023, 954, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, G.; Baring, M.G.; Kouveliotou, C.; Harding, A.; Donovan, S.; Göǧüş, E.; Kaspi, V.M.; Granot, J. The Sleeping Monster: NuSTAR Observations of SGR 1806–20. 11 Years after the Giant Flare. Astrophys. J. 2017, 851, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothes, R.; Foster, T. A Thorough Investigation of the Distance to the Supernova Remnant CTB109 and Its Pulsar AXP J2301+5852. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2012, 746, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyl, J.S.; Taverna, R.; Turolla, R.; Israel, G.L.; Ng, M.; Kırmızıbayrak, D.; González-Caniulef, D.; Caiazzo, I.; Zane, S.; Ehlert, S.R.; et al. The detection of polarized x-ray emission from the magnetar 1E 2259+586. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 527, 12219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Kaspi, V.M.; Dim, R.; Woods, P.M.; Gavriil, F.P.; Archibald, A.M. The Long-Term Radiative Evolution of Anomalous X-Ray Pulsar 1E 2259+586 After Its 2002 Outburst. Astrophys. J. 2008, 686, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzocaro, D.; Tiengo, A.; Mereghetti, S.; Turolla, R.; Esposito, P.; Stella, L.; Zane, S.; Rea, N.; Zelati, F.C.; Israel, G. Detailed X-ray spectroscopy of the magnetar 1E 2259+586. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 626, A39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiengo, A.; Esposito, P.; Mereghetti, S.; Turolla, R.; Nobili, L.; Gastaldello, F.; Götz, D.; Israel, G.L.; Rea, N.; Stella, L.; et al. A variable absoprtion feature in the X-ray spectrum of a magnetar. Nature 2013, 500, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, J.A.J.; Younes, G.A.; Wadiasingh, Z.; Abdelmaguid, M.; An, H.; Bachetti, M.; Baring, M.G.; Beloborodov, A.; Chen, A.Y.; Enoto, T.; et al. The high energy X-ray probe (HEX-P): Magnetars and other isolated neutron stars. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2024, 10, 1294449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.N.; Feroci, M.; Santangelo, A.; Dong, Y.W.; Feng, H.; Lu, F.J.; Nandra, K.; Wang, Z.S.; Bozzo, E.; Brandt, S.; et al. eXTP: Enhanced X-ray Timing and Polarization mission. Proc. SPIE 2016, 9905, 99051Q. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taverna , R.; Turolla , R. X-ray Polarization from Magnetar Sources. Galaxies 2024, 12, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12010006
Taverna R, Turolla R. X-ray Polarization from Magnetar Sources. Galaxies. 2024; 12(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaverna , Roberto, and Roberto Turolla . 2024. "X-ray Polarization from Magnetar Sources" Galaxies 12, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12010006
APA StyleTaverna , R., & Turolla , R. (2024). X-ray Polarization from Magnetar Sources. Galaxies, 12(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12010006





