Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulations to Personalize Nasal Irrigations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Guidelines
2.3. Patient Selection
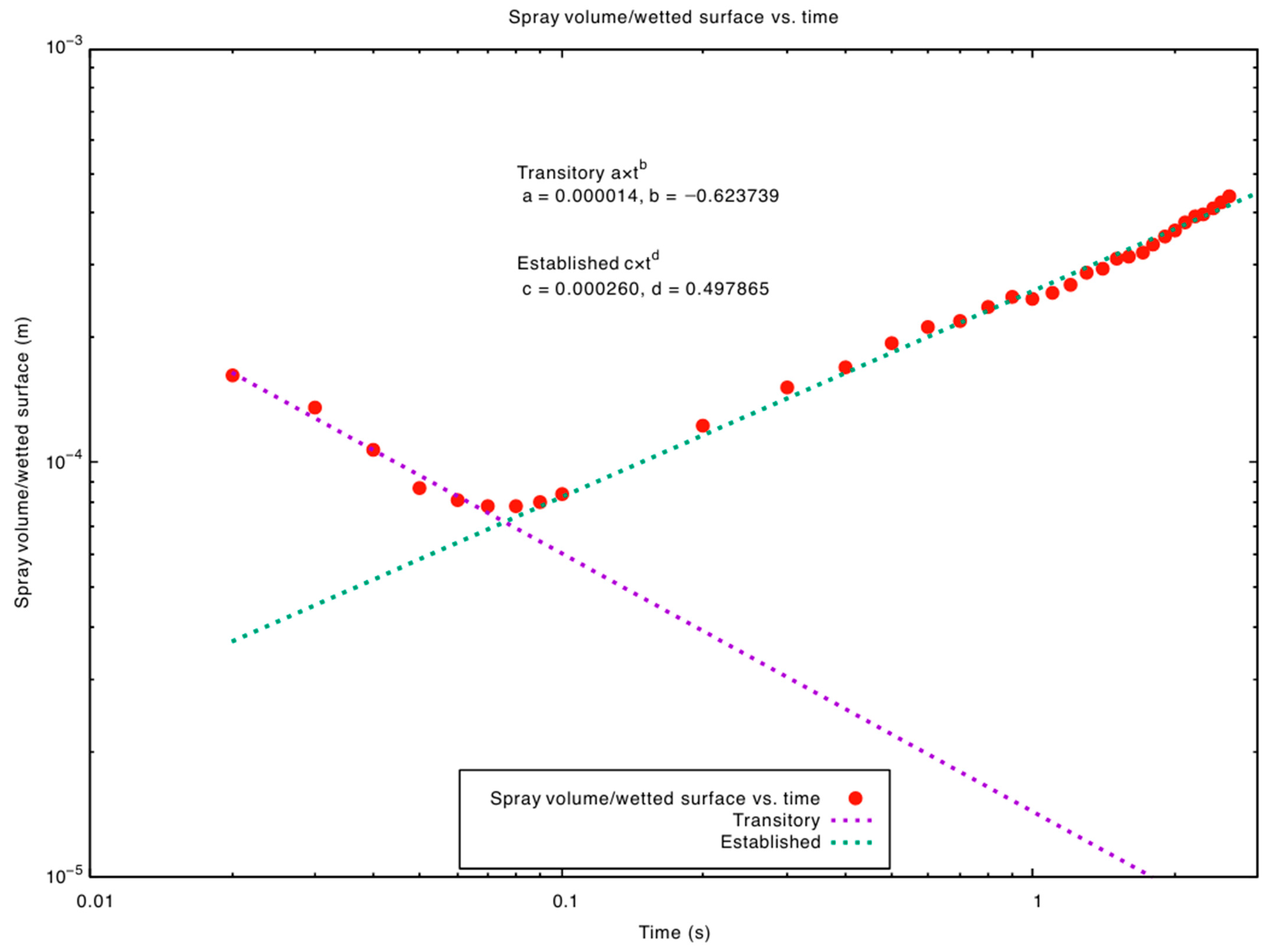
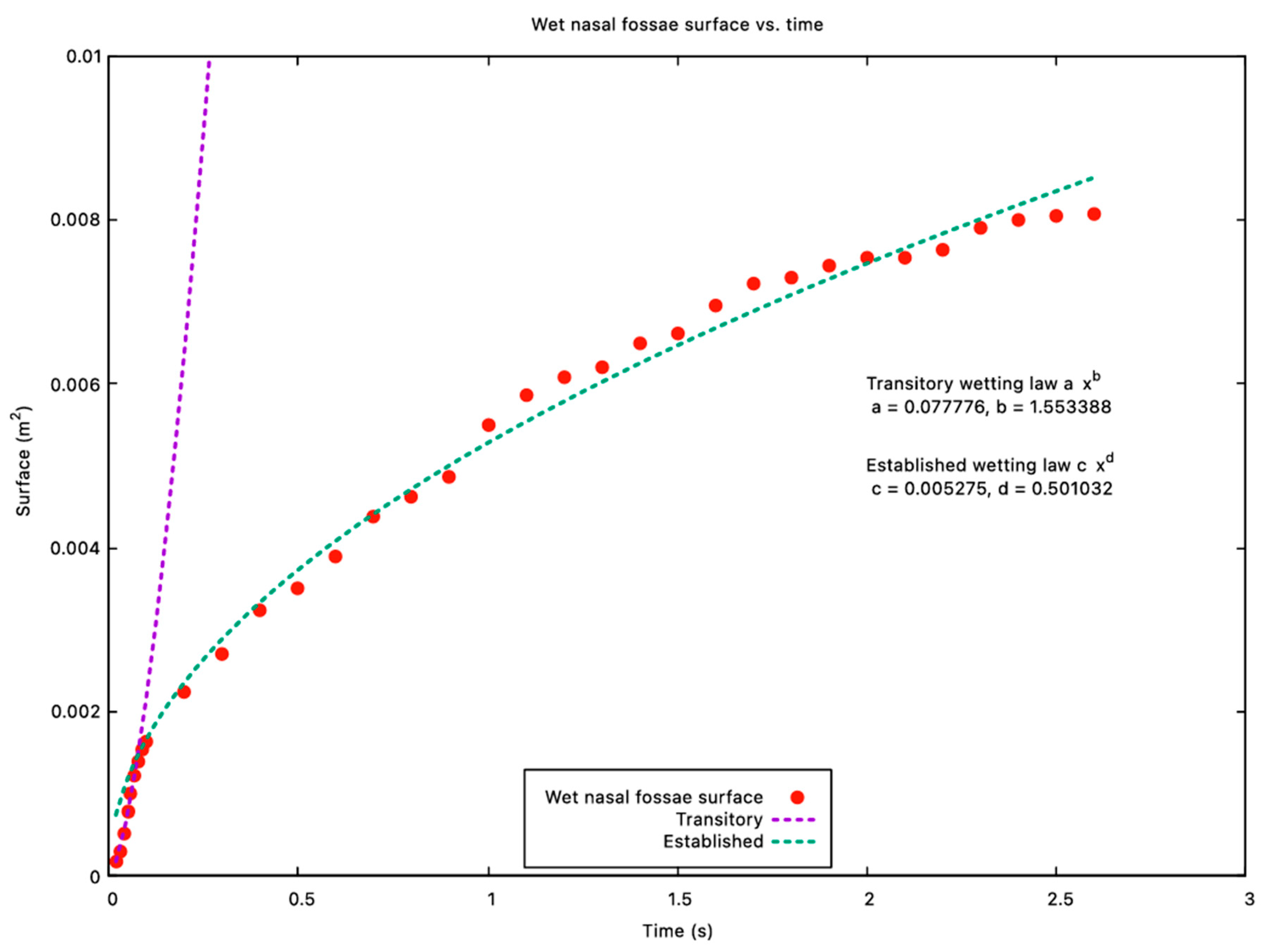
2.4. CFD Protocol
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Interest of CFD
4.2. Impact of Head Position for Nasal Lavages
4.3. Limits
4.4. Future Development
- -
- Post-Operative Anatomies: Surgeries like septoplasty, turbinoplasty, or functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) often modify the geometry of the nasal cavity, altering flow patterns. Personalized CFD can help tailor post-operative irrigation protocols to ensure optimal healing and reduce the risk of adhesions or bacterial colonization.
- -
- Pathological Conditions: Patients with nasal polyposis, chronic rhinosinusitis, or allergic rhinitis may present with inflamed, thickened mucosa that restricts airflow. CFD simulations could quantify how these inflammatory changes impact fluid spread, guiding more effective irrigation protocols.
- -
- Drug Formulation Studies: Beyond saline solutions, medicated sprays (e.g., steroids, antibiotics) vary in viscosity and surface tension. Patient-specific CFD might identify the ideal droplet size or concentration for enhanced mucosal residence time, particularly for areas prone to infection or inflammation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| FESS | Functional endoscopic sinus surgery |
References
- Radulesco, T.; Meister, L.; Bouchet, G.; Varoquaux, A.; Giordano, J.; Mancini, J.; Dessi, P.; Perrier, P.; Michel, J. Correlations between computational fluid dynamics and clinical evaluation of nasal airway obstruction due to septal deviation: An observational study. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2019, 44, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salati, H.; Singh, N.; Khamooshi, M.; Vahaji, S.; Fletcher, D.F.; Inthavong, K. Nasal Irrigation Delivery in Three Post-FESS Models From a Squeeze-bottle Using CFD. Pharm. Res. 2022, 39, 2569–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Craig, J.R.; Cohen, N.A.; Adappa, N.D.; Khalili, S.; Palmer, J.N. Sinus irrigations before and after surgery—Visualization through computational fluid dynamics simulations. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, E90–E96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, K.; Wong, E.; Salati, H.; Fletcher, D.F.; Singh, N.; Inthavong, K. Liquid volume and squeeze force effects on nasal irrigation using Volume of Fluid modelling. Exp. Comput. Multiph. Flow 2022, 4, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiaee, M.; Wachtel, H.; Noga, M.L.; Martin, A.R.; Finlay, W.H. Regional deposition of nasal sprays in adults: A wide ranging computational study. Numer. Methods Biomed Eng. 2018, 34, e2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiller, V.L. Uber die grundlegenden Berechnungen bei der Schwerkraftaufbereitung. Z. Vereines Dtsch. Inge. 1933, 77, 318–321. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.; Gosman, A.D. Development of methodology for spray impingement simulation. SAE Trans. 1995, 104, 550–568. [Google Scholar]
- Bleier, B.S.; Preena, D.; Schlosser, R.J.; Harvey, R.J. Dose quantification of topical drug delivery to the paranasal sinuses by fluorescein luminosity calculation. Int. Forum. Allergy Rhinol. 2012, 2, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, D.; Weitzel, E.K.; Lin, E.; Feldt, B.; Kriete, B.; McMains, K.C.; Thwin, M.; Wormald, P. Effect of head position and surgical dissection on sinus irrigant penetration in cadavers. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 2528–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundoor, V.; Dalby, R.N. Effect of Formulation- and Administration-Related Variables on Deposition Pattern of Nasal Spray Pumps Evaluated Using a Nasal Cast. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechien, J.R.; Radulesco, T.; Calvo-Henriquez, C.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Hans, S.; Barillari, M.R.; Cammaroto, G.; Descamps, G.; Hsieh, J.; Vaira, L.; et al. ACE2 & TMPRSS2 Expressions in Head & Neck Tissues: A Systematic Review. Head Neck Pathol. 2021, 15, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
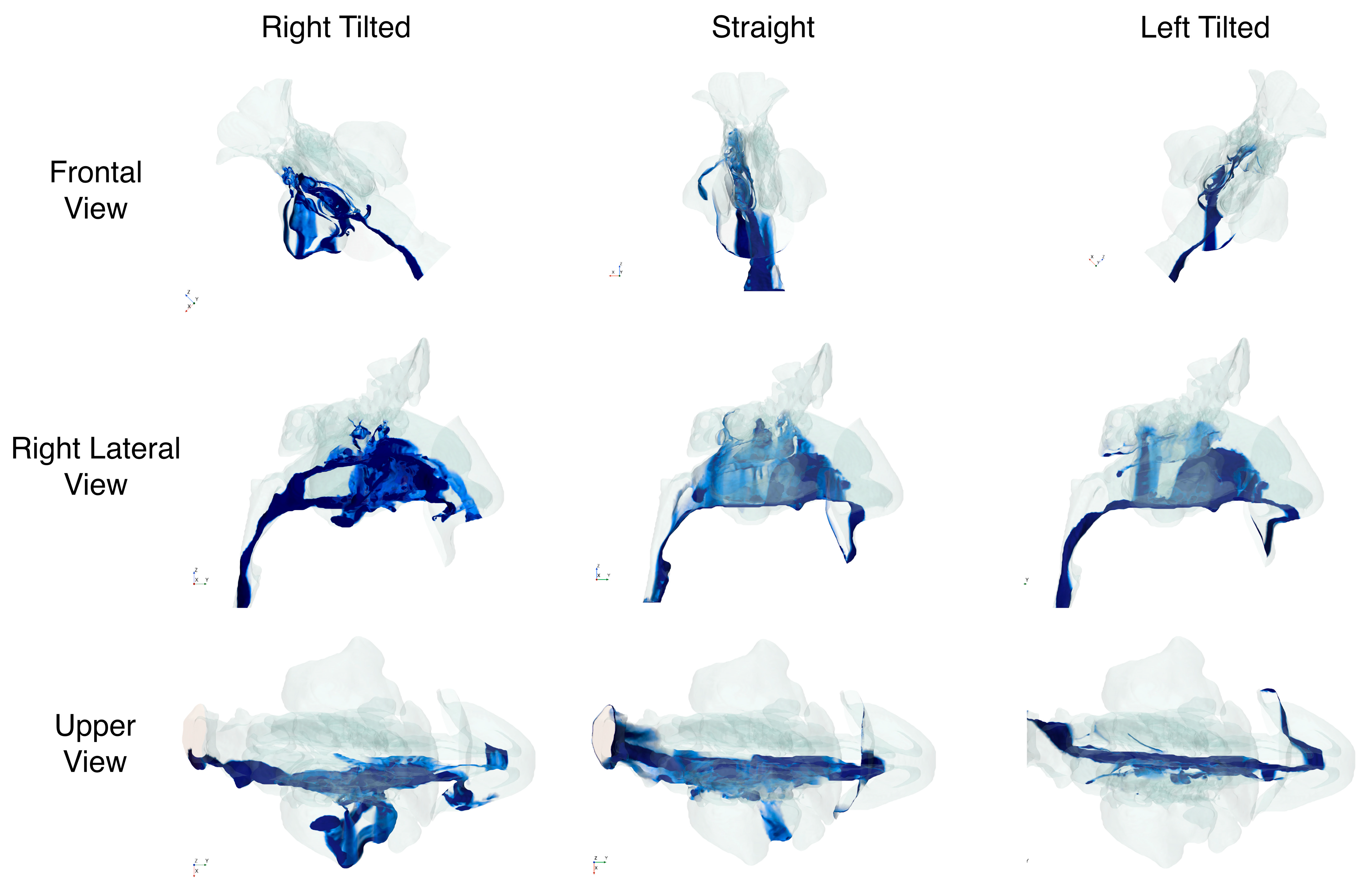
| Value | Head Position | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Upright 0° | Right-Tilted 45° | Left-Tilted 45° | |
| Volume reaching inferior third (mL) | 0.75 | 0.86 | 0.52 |
| Volume reaching middle third (mL) | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.09 |
| Volume reaching superior third (mL) | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Volume reaching right maxillary sinus (mL) | 0.02 | 0.28 | 0.00 |
| % of nasal mucosa irrigated (inferior third) | 87 | 50 | 29 |
| % of nasal mucosa irrigated (middle third) | 63 | 41 | 30 |
| % of nasal mucosa irrigated (upper third) | 18 | 6 | 9 |
| % of nasal mucosa irrigated (right maxillary sinus) | 16 | 35 | 0.2 |
| Total % of nasal mucosa irrigated | 57 | 32 | 22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radulesco, T.; Ebode, D.; Haddad, R.; Lechien, J.R.; Meister, L.; Gargula, S.; Michel, J. Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulations to Personalize Nasal Irrigations. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070288
Radulesco T, Ebode D, Haddad R, Lechien JR, Meister L, Gargula S, Michel J. Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulations to Personalize Nasal Irrigations. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(7):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070288
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadulesco, Thomas, Dario Ebode, Ralph Haddad, Jerome R. Lechien, Lionel Meister, Stephane Gargula, and Justin Michel. 2025. "Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulations to Personalize Nasal Irrigations" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 7: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070288
APA StyleRadulesco, T., Ebode, D., Haddad, R., Lechien, J. R., Meister, L., Gargula, S., & Michel, J. (2025). Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulations to Personalize Nasal Irrigations. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(7), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070288








