Management of Acetabular Fractures with Total Hip Replacement: A Narrative Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Indications and Surgical Options
3. Classification of Bone Defects
4. Surgical Technique
4.1. Delayed THA, Neglected, or Conservatively Treated Acetabular Fractures
Acetabular Exposure, Preparation, and Cup Fixation
4.2. Late THA, Failure of Previously Operated Acetabular Fractures
4.3. Acute THA in Acetabular Fractures
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Letournel, E. Acetabulum fractures: Classification and management. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1980, 5, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Shah, N.A.; Kershaw, S.A.; Clayson, A.D. Operative management of acetabular fractures: A review of 73 fractures. Injury 2005, 36, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, E.; Finless, A.; Adamczyk, A.; Dobransky, J.; Wilkin, G.; Gofton, W.T.; Beaulé, P.E.; Liew, A.; Papp, S.; Grammatopoulos, G. Outcome after Open Reduction Internal Fixation of Acetabular Fractures in the Elderly. J. Orthop. Trauma 2022, 36, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halvorson, J.J.; LaMothe, J.; Martin, C.R.; Grose, A.; Asprinio, D.E.; Wellman, D.; Helfet, D.L. Combined acetabulum and pelvic ring injuries. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2014, 22, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stibolt, R.D.; Patel, H.A.; Huntley, S.R.; Lehtonen, E.J.; Shah, A.B.; Naranje, S.M. Total hip arthroplasty for posttraumatic osteoarthritis following acetabular fracture: A systematic review of characteristics, outcomes, and complications. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2018, 21, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadura, E.; Truszczyńska-Baszak, A.; Szydłowski, D. Radiological and Functional Assessment of Treatment Outcomes in Patients after Open Reduction with Internal Fixation (ORIF) of Acetabular Fractures. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannoudis, P.V.; Grotz, M.R.W.; Papakostidis, C.; Dinopoulos, H. Operative treatment of displaced fractures of the acetabulum. A meta-analysis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Ser. B 2005, 87, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, R.V.; Hui, E.; Chandra, A.; Nascone, J.W. How often does open reduction and internal fixation of geriatric acetabular fractures lead to hip arthroplasty? J. Orthop. Trauma. 2014, 28, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigani, D.; Castiello, E.; Moghnie, A.; Comitini, S.; Ganci, M.; Consoli, A.; Berti, M.; Amendola, L. Dual mobility total hip arthroplasty in complex cases. Lo Scalpello Otodi Educ. 2021, 35, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, W.; Mousa, S.; Khalefa, A.; Sleem, A.; Kenawey, M.; Ravera, L.; Masse, A. Simultaneous open reduction and internal fixation and total hip arthroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic acetabular fractures. Int. Orthop. 2017, 41, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.; Peterson, D.F.; Yoo, J.; Working, Z.M.; Friess, D.; Kagan, R. Risk of Revision and Complications After Total Hip Arthroplasty for Acute Treatment of Acetabular Fracture. J. Arthroplast. 2023, 38, S270–S275.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, D.; Gupta, S.; Malhotra, R. Total hip arthroplasty in acetabular fractures. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herscovici, D.; Lindvall, E.; Bolhofner, B.; Scaduto, J.M. The combined hip procedure: Open reduction internal fixation combined with total hip arthroplasty for the management of acetabular fractures in the elderly. J. Orthop. Trauma 2010, 24, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hislop, S.; Alsousou, J.; Chou, D.; Rawal, J.; Hull, P.; Carrothers, A. Fix and replace: Simultaneous fracture fixation and hip replacement for acetabular fractures in older patients. Injury 2022, 53, 4067–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.G.; Carrothers, A.D. Fix and replace; an emerging paradigm for treating acetabular fractures. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2016, 13, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mears, D.C.; Velyvis, J.H. Acute total hip arthroplasty for selected displaced acetabular fractures: Two to twelve-year results. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2002, 84, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boraiah, S.; Ragsdale, M.; Achor, T.; Zelicof, S.; E Asprinio, D. Open reduction internal fixation and primary total hip arthroplasty of selected acetabular fractures. J. Orthop. Trauma 2009, 23, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannast, M.; Najibi, S.; Matta, J.M. Two to Twenty-Year Survivorship of the Hip in 810 Patients with Operatively Treated Acetabular Fractures. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2012, 94, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, G.M.; Sanders, E.B.; Kim, P.R.; Beaulé, P.E.; Gofton, W.T.; Grammatopoulos, G. Outcomes of Total Hip Arthroplasty After Acetabular Open Reduction and Internal Fixation in the Elderly—Acute vs Delayed Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, T.A.; Patel, R.; Bhandari, M.; Matta, J.M. Fractures of the acetabulum in patients aged 60 years and older: An epidemiological and radiological study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Ser. B 2010, 92, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoozabadi, R.; Cross, W.W.; Krieg, J.C.; Routt, M.L. Acetabular fractures in the senior population-epidemiology, mortality and treatments. Arch. Bone Jt. Surg. 2017, 5, 96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Caron, J.; Schmidt, A.H.; Torchia, M.; Templeman, D. Functional outcomes after total hip arthroplasty for the acute management of acetabular fractures: 1- to 14-year follow-up. J. Orthop. Trauma 2015, 29, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melhem, E.; Riouallon, G.; Habboubi, K.; Gabbas, M.; Jouffroy, P. Epidemiology of pelvic and acetabular fractures in France. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2020, 106, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trikha, V.; V, G.; Cabrera, D.; Bansal, H.; Mittal, S.; Sharma, V. Epidemiological assessment of acetabular fractures in a level one trauma centre: A 7-Year observational study. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, T.; Hernefalk, B.; Hailer, N.P. Acute total hip arthroplasty combined with internal fixation for displaced acetabular fractures in the elderly. Bone Jt. J. 2019, 101-B, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunet, B.; Tournier, C.; Billaud, A.; Lavoinne, N.; Fabre, T.; Durandeau, A. Acetabular fracture: Long-term follow-up and factors associated with secondary implantation of total hip arthroplasty. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2013, 99, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakos, N.; Pearce, R.; Bircher, M.D. Low energy fractures of the acetabulum. Ann. R Coll Surg. Engl. 2014, 96, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauregui, J.J.; Clayton, A.; Kapadia, B.H.; Cherian, J.J.; Issa, K.; A Mont, M. Total hip arthroplasty for acute acetabular fractures: A review of the literature. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2015, 12, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauregui, J.J.; Weir, T.B.; Chen, J.F.; Johnson, A.J.; Sardesai, N.R.; Maheshwari, A.V.; Manson, T.T. Acute total hip arthroplasty for older patients with acetabular fractures: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, R.; Gautam, D. Acute total hip arthroplasty in acetabular fractures using modern porous metal cup. J. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 27, 2309499019855438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelch, S.P.; Jordan, M.C.; Meffert, R.H.; Jansen, H. Comparison of open reduction and internal fixation and primary total hip replacement for osteoporotic acetabular fractures: A retrospective clinical study. Int. Orthop. 2017, 41, 1831–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, K.; Taha, W.; Powell, J.N. Non-union of acetabular fractures. Injury 2004, 35, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mears, D.C.; Velyvis, J.H. Primary total hip arthroplasty after acetabular fracture. Instr. Course Lect. 2001, 50, 335–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T Marmor, M.; Huang, A.; Knox, R.; Herfat, S.; Firoozabadi, R. Mapping of the Stable Articular Surface and Available Bone Corridors for Cup Fixation in Geriatric Acetabular Fractures. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 28, e573–e579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsemakers, W.-J.; Morgenstern, M.; Senneville, E.; Borens, O.; Govaert, G.A.M.; Onsea, J.; Depypere, M.; Richards, R.G.; Trampuz, A. General treatment principles for fracture-related infection: Recommendations from an international expert group. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2020, 140, 1013–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govaert, G.A.M.; Kuehl, R.; Atkins, B.L.; Trampuz, A.; Morgenstern, M.; Obremskey, W.T.; Verhofstad, M.H.J.; McNally, M.A.; Metsemakers, W.-J. Diagnosing Fracture-Related Infection: Current Concepts and Recommendations. J. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 34, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, A.A.; Blevins, K.; Kuo, F.-C.; Manrique, J.; Restrepo, C.; Parvizi, J. Total Hip Arthroplasty After Prior Acetabular Fracture: Infection Is a Real Concern. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 2619–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; O’TOole, R.V.; Castillo, R.; Reahl, B.; Montalvo, R.; Nascone, J.W.; Sciadini, M.F.; Carlini, A.R.; Manson, T.T. Risk factors for early reoperation after operative treatment of acetabular fractures. J. Orthop. Trauma 2018, 32, e251–e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antonio, J.A. Periprosthetic bone loss of the acetabulum: Classification and management. Orthop. Clin. North Am. 1992, 23, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paprosky, W.G.; Perona, P.G.; Lawrence, J.M. Acetabular defect classification and surgical reconstruction in revision arthroplasty. A 6-year follow-up evaluation. J. Arthroplast. 1994, 9, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, R.K.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Pattanshetti, V.; Saini, G.; Tripathy, S.K.; Sethy, S.S.; Sharma, S.K. A New Classification System for Acetabular Bone Defect Evaluation in Posttraumatic Acetabular Nonunion and Malunion. Indian J. Orthop 2022, 56, 1601–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, M.L.; Tile, M.; Schenk, R.S. Total hip replacement after acetabular fracture. Orthop. Clin. North Am. 1997, 28, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bircher, M.; Lewis, A.; Halder, S. Delays in definitive reconstruction of complex pelvic and acetabular fractures. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Ser. B 2006, 88, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel, M.P.; Trousdale, R.T.; Berry, D.J. Pelvic discontinuity associated with total hip arthroplasty: Evaluation and management. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2017, 25, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribes-Iborra, J.; Atienza, C.; La Torre, J.S.-D.; Pérez, A.G. Biomechanical study of pelvic discontinuity in failed total hip arthroplasty. Lessons learnt from the treatment of pelvic fractures. Injury 2017, 48, S34–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgadillo, C.A.; Pesantez, R. Fix and replace technique in elderly acetabular fractures. J. Musculoskelet. Surg. Res. 2023, 7, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, J.; Riouallon, G.; Martz, P.; de Dompsure, R.B.; Erivan, R.; Guignard, A.; Tiercelin, J.; Schmitz, A.; Belvisi, B.; Moreau, P.-E.; et al. Functional outcomes and center of rotation restoration in total hip arthroplasty after acetabular fracture: A review of 367 hips. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2024, 110, 103914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, K.; Wilson, M.J.; Whitehouse, S.L.; Timperley, A.J. Results using Trabecular MetalTM augments in combination with acetabular impaction bone grafting in deficient acetabula. Hip. Int. 2013, 23, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epinette, J.A.; Coulomb, R.; Pradel, S.; Kouyoumdjian, P. Do Modular Dual Mobility Cups Offer a Reliable Benefit? Minimum 5-Year Follow-Up of 102 Cups. J Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzkopf, R.; Chin, G.; Kim, K.; Murphy, D.; Chen, A.F. Do Conversion Total Hip Arthroplasty Yield Comparable Results to Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty? J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghoolizadeh, M.; Schwarzkopf, R. The Lawrence D. Dorr Surgical Techniques & Technologies Award: Conversion Total Hip Arthroplasty: Is it a Primary or Revision Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Durand-Hill, M.; Henckel, J.; Di Laura, A.; Hart, A.J. Can custom 3D printed implants successfully reconstruct massive acetabular defects? A 3D-CT assessment. J. Orthop. Res. 2020, 38, 2640–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhsine, E.; Garofalo, R.; Borens, O.; Blanc, C.-H.; Wettstein, M.; Leyvraz, P.F. Cable fixation and early total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of acetabular fractures in elderly patients. J. Arthroplast. 2004, 19, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulé, P.E.M.; Griffin, D.B.; Matta, J.M. The Levine Anterior Approach for Total Hip Replacement as the Treatment for an Acute Acetabular Fracture. J. Orthop. Trauma 2004, 18, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrektsson, M.; Möller, M.; Wolf, O.; Wennergren, D.; Sundfeldt, M. Acetabular fractures: Epidemiology and mortality based on 2,132 fractures from the Swedish Fracture Register. Bone Jt Open 2023, 4, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, C.; Caton, J.; Aslanian, T.; Samaha, C.; Yammine, K. The cross technique for the positioning of Kerboull plate in acetabular reconstruction surgery. Sicot J. 2018, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issack, P.S.; Nousiainen, M.; Beksac, B.; Helfet, D.L.; Sculco, T.P.; Buly, R.L. Acetabular component revision in total hip arthroplasty. Part II: Management of major bone loss and pelvic discontinuity. Am. J. Orthop. 2009, 38, 550–556. [Google Scholar]
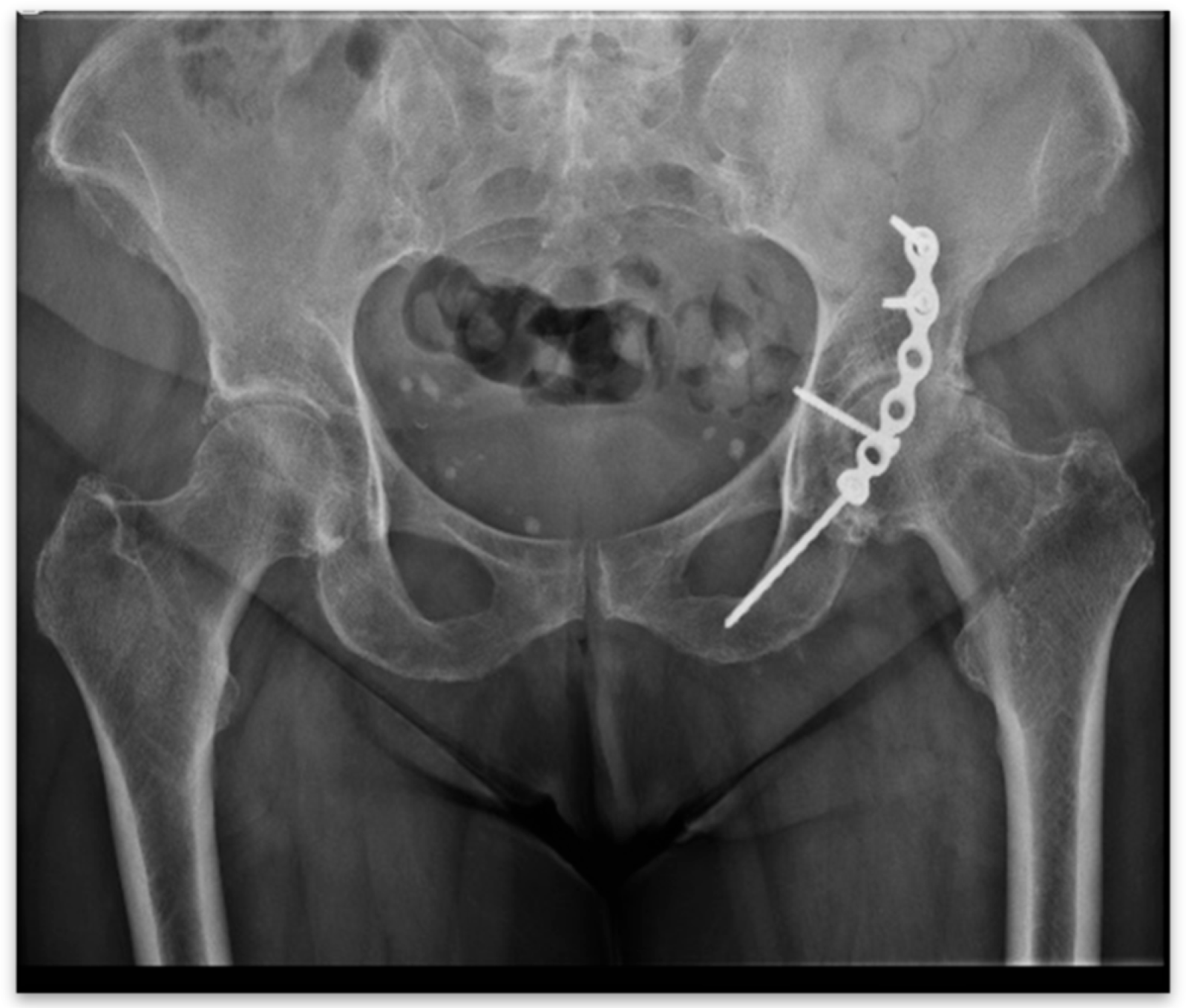

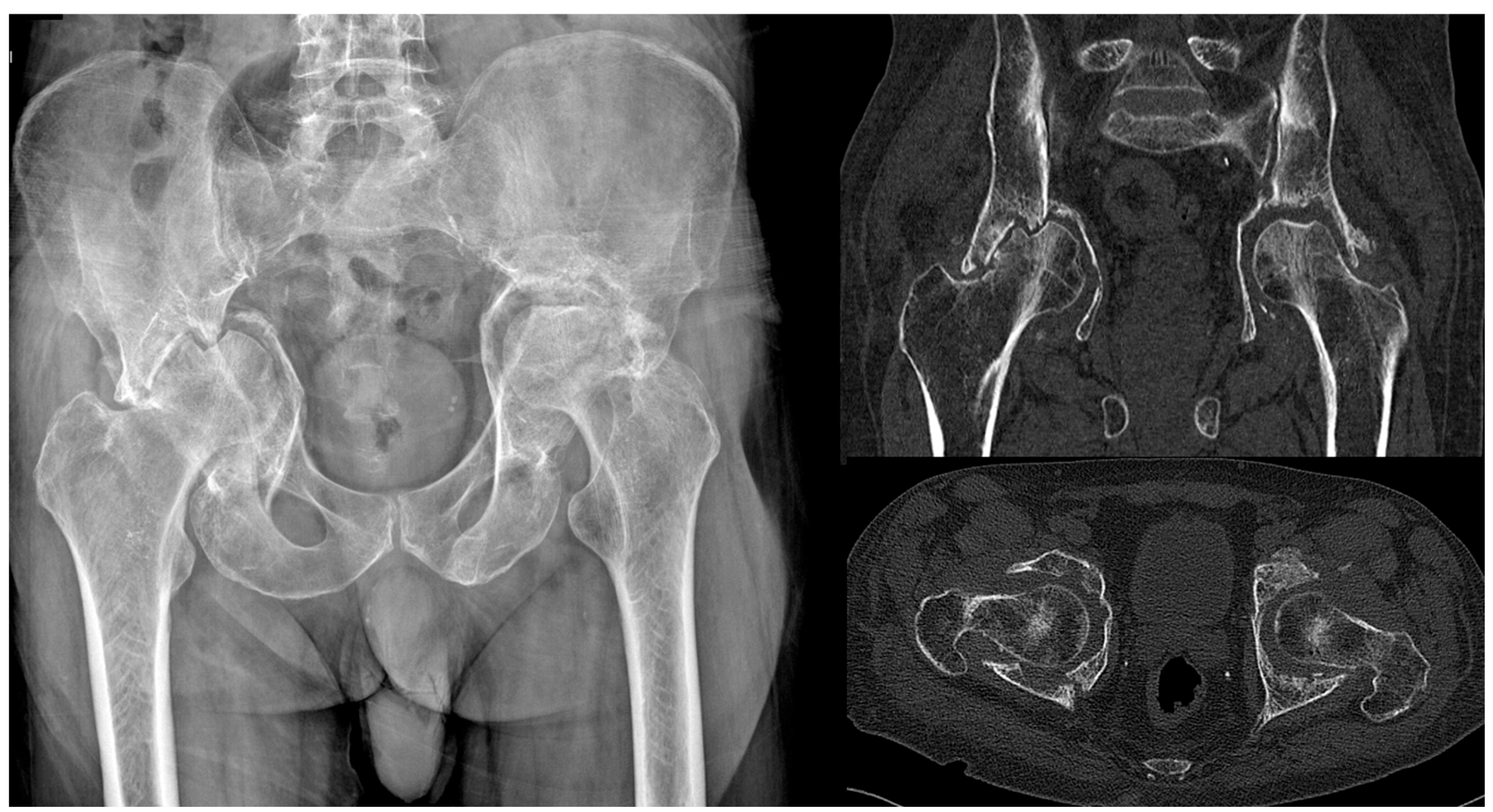
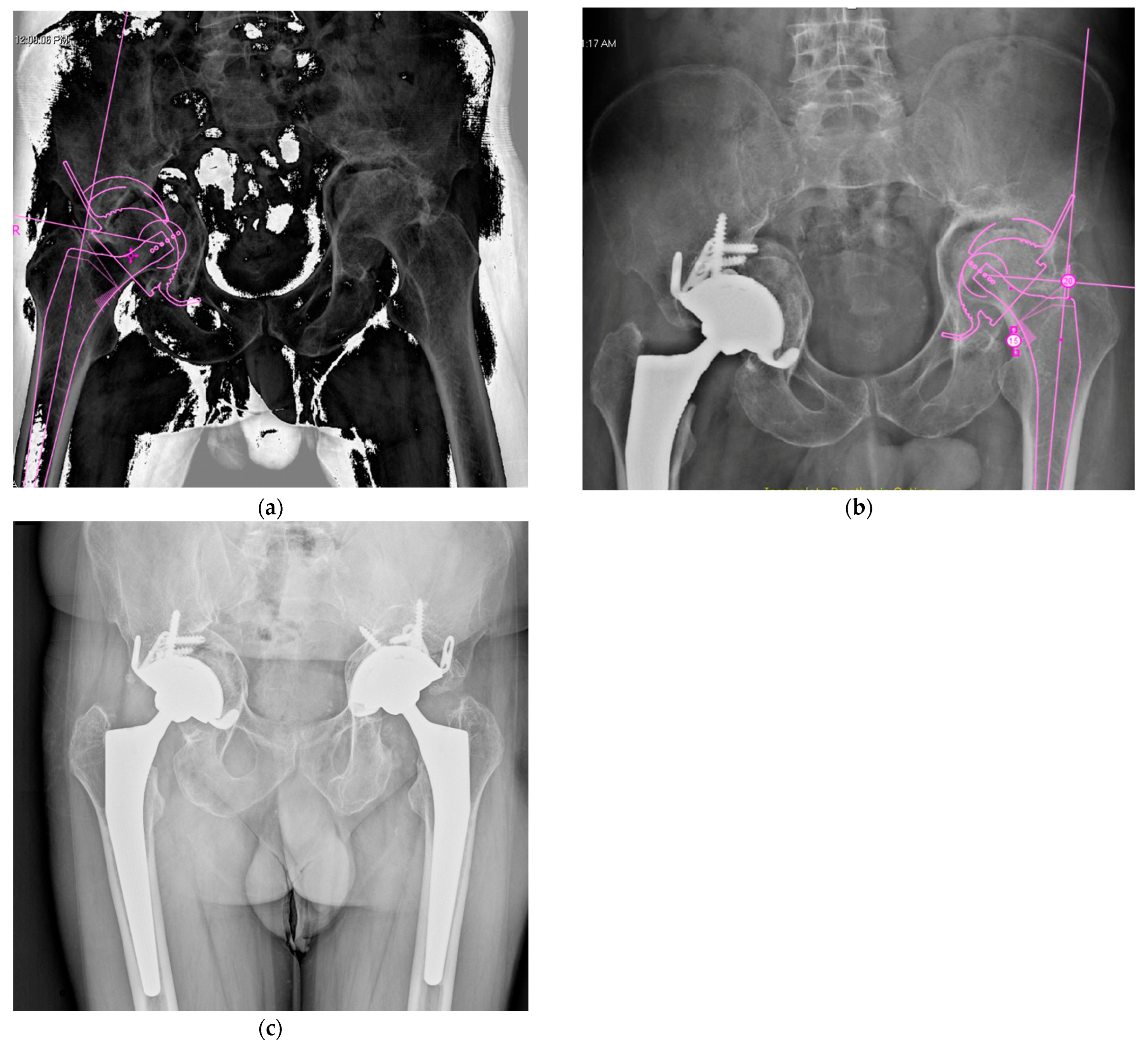

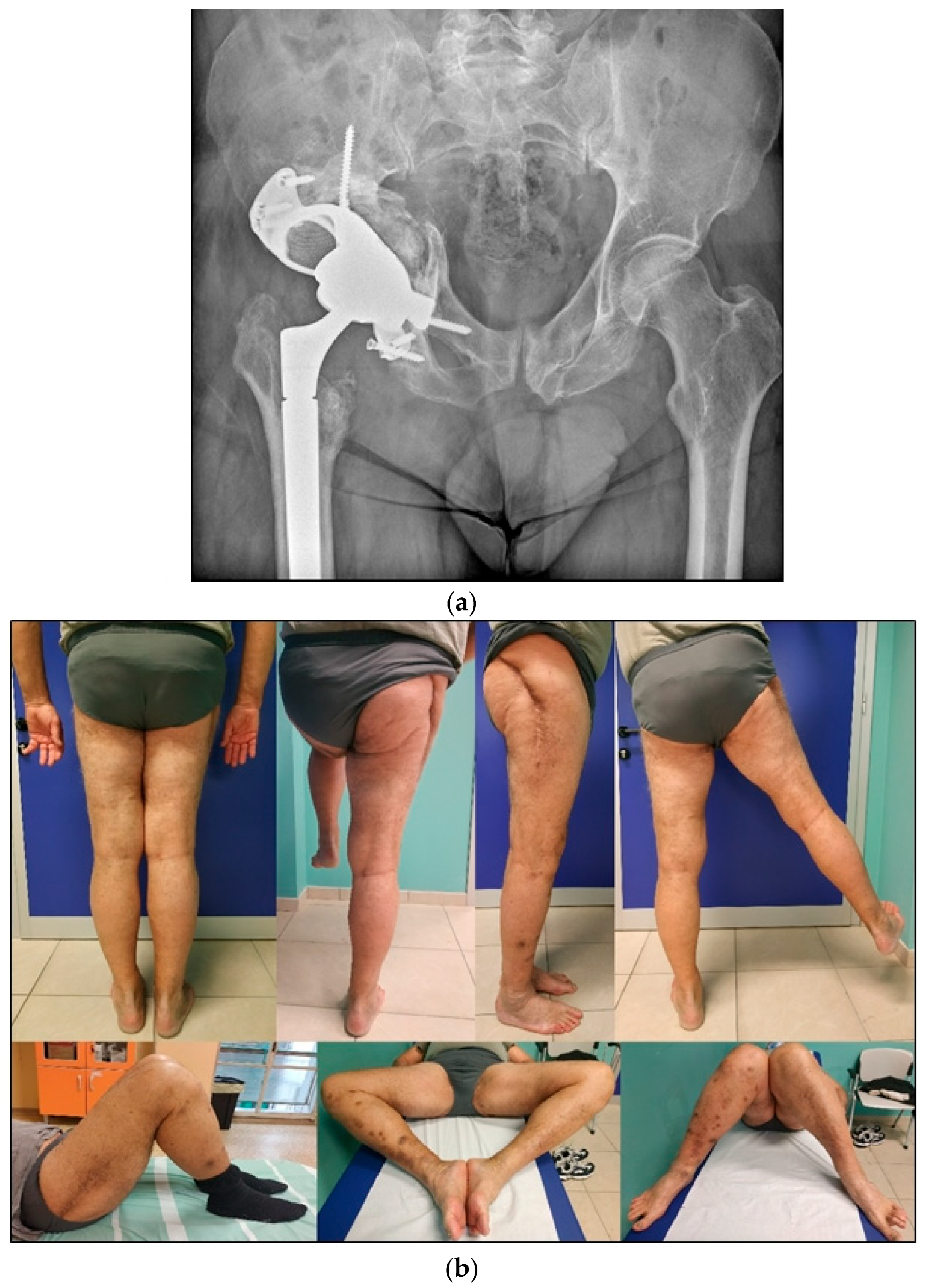
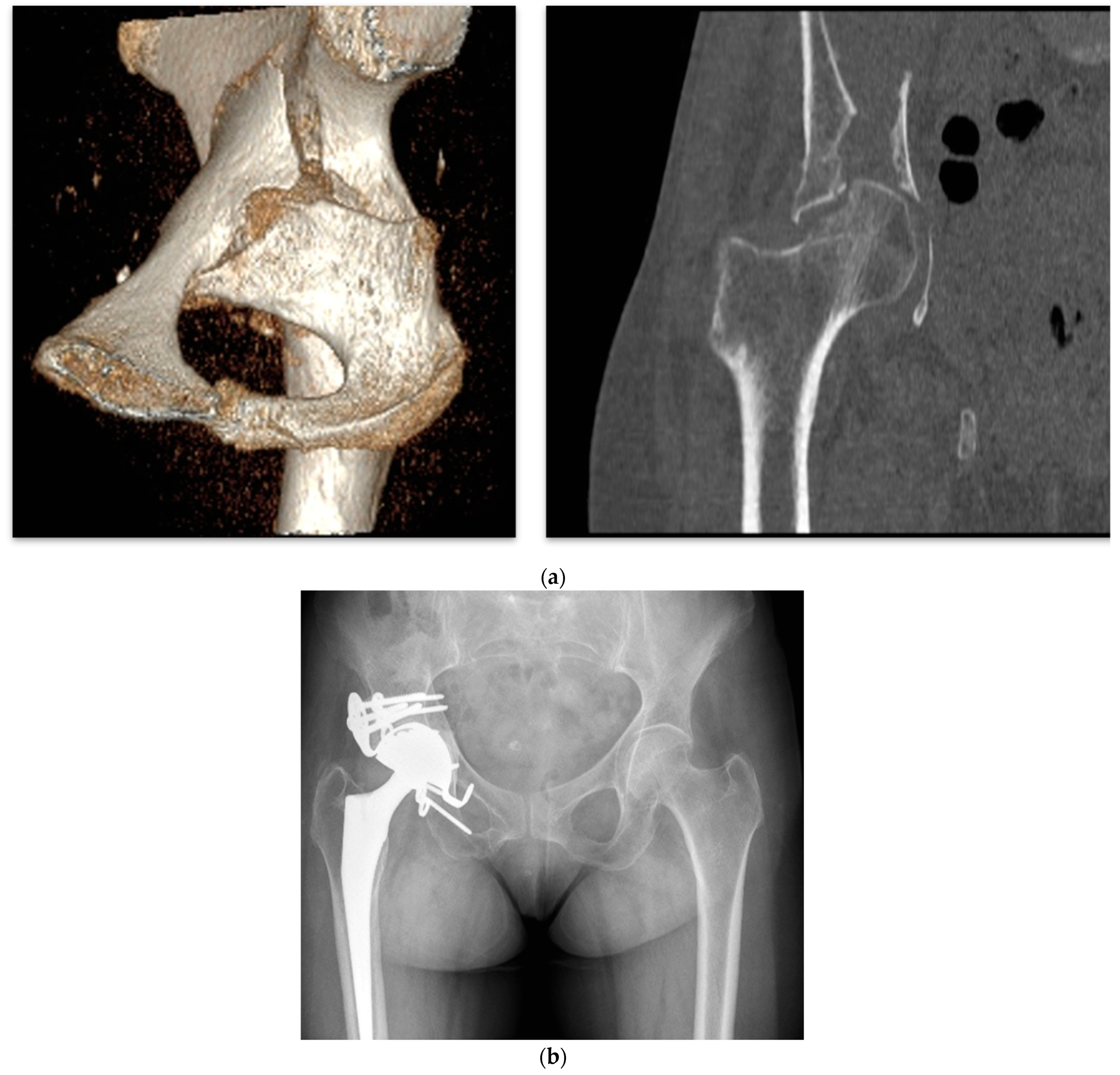
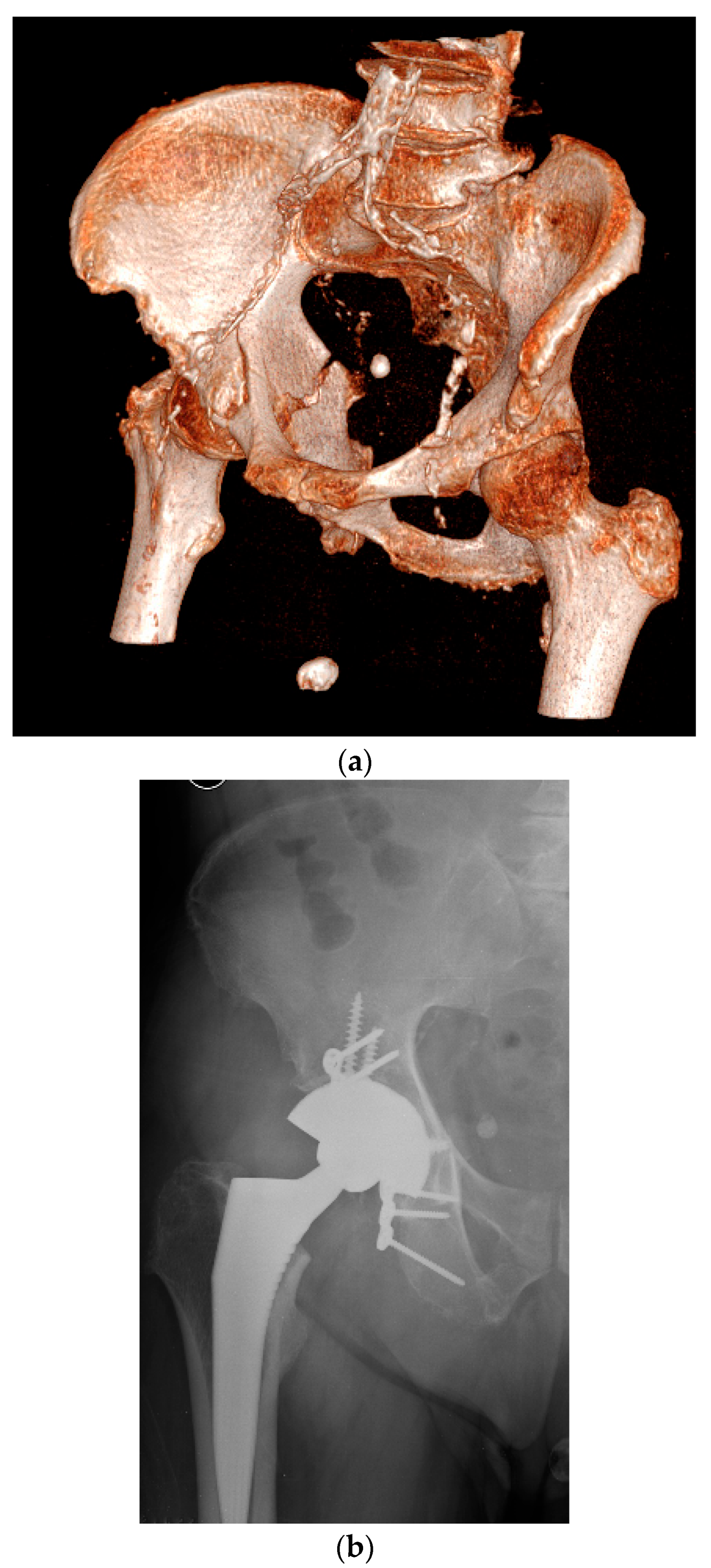
| I | Established post-traumatic arthritis or avascular necrosis of the femoral head following fixation or conservative treatment. | ||||
| II | Existing hip arthritis or associated fracture of the head and/or neck of the femur not amenable to a satisfactory outcome with fixation. | ||||
| III | Elderly patient with comminuted acetabular fractures and osteoporotic bone. | ||||
| IV | Expected undesirable outcome at an early follow-up period after fixation. | ||||
| (a) Associated severe articular cartilage injury and marginal impaction of the acetabulum. | (b) Persistently subluxated head or neglected fracture dislocation with risk of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. | (c) Thin and compromised posterior wall or column with risk of fixation failure. | |||
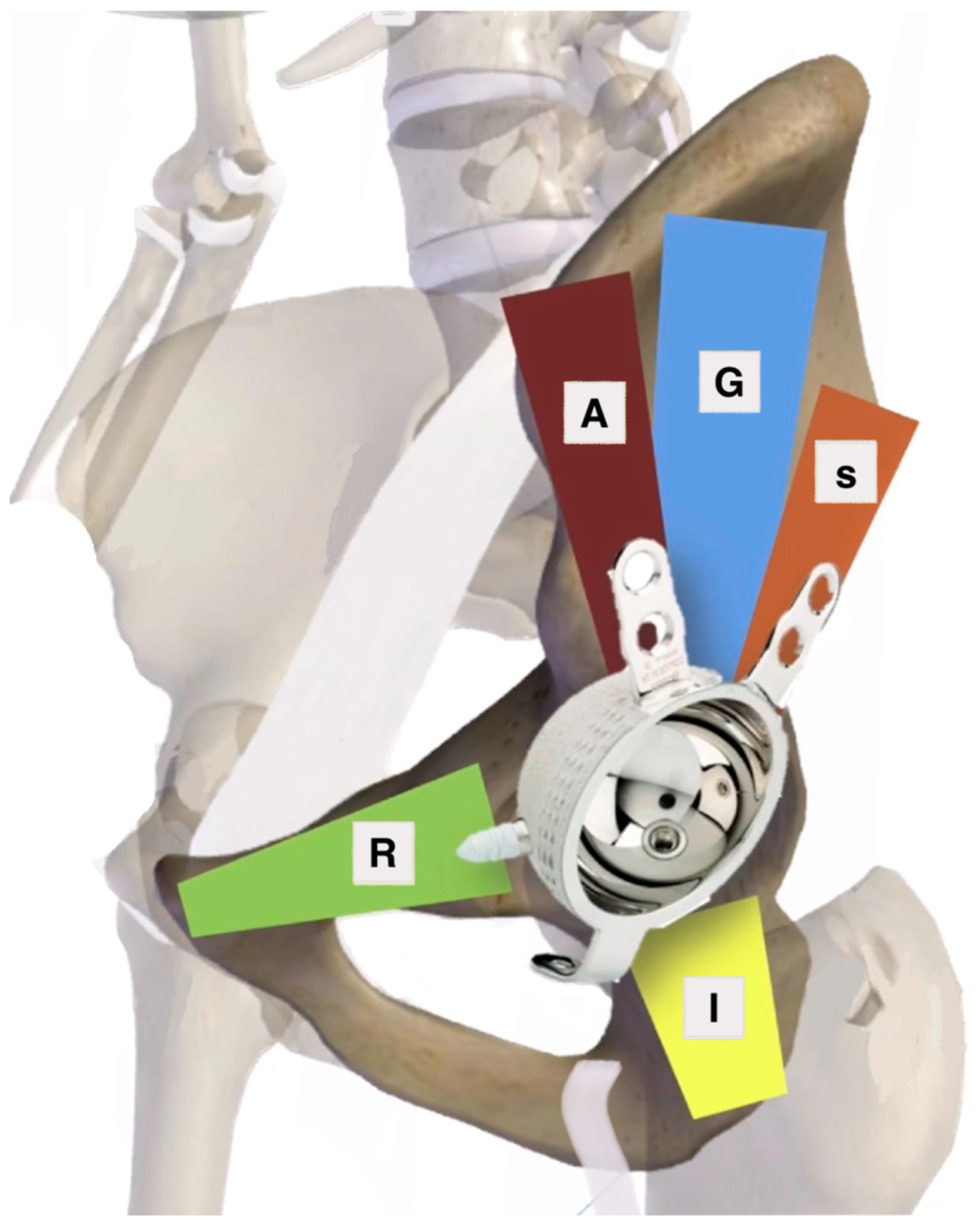
| 1. Zone of Articular Surface Fully or Partially Connected to Stable Bone | 2. Bone Stock Available for Screw Fixation |
|---|---|
| D—Dome zone only P—Posterior zone only A—Anterior zone only DP—Dome and posterior DA—Dome and anterior DAP—All zones | R—Superior ramus pubic corridor A—Anterior corridor G—Gluteal pillar corridor S—Sciatic buttress corridor I—Ischium corridor |
| New Classification Type | Posterior Wall | Illioischial Line | Illiopectineal Line | Femoral Head Position/Migration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 (circumferential widening) | Present | Undisplaced | Undisplaced | Minimal |
| Type 2 (posterior wall) | Absent/displaced | Undisplaced | Undisplaced | Posterior superior/superolateral/ dislocated |
| Type 3 (posterior column) | ||||
| 3A (malunion or fibrous union) | Present | Displaced but not broken | Undisplaced | Superomedial |
| 3B (frank nonunion) | Present | Displaced and broken | Undisplaced | Superomedial |
| Type 4 (transverse) | ||||
| 4A malunion or fibrous nonunion | Present | Displaced but not broken | Displaced but not broken | Superomedial |
| 4B frank nonunion (pelvic discontinuity) | Present | Displaced and broken | Displaced and broken | Superomedial |
| Type 5 (anterior column) | Present | Undisplaced | Displaced | Medial |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tigani, D.; Lamattina, L.; Assenza, A.; Melucci, G.; Pizzo, A.; Donadono, C. Management of Acetabular Fractures with Total Hip Replacement: A Narrative Literature Review. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070282
Tigani D, Lamattina L, Assenza A, Melucci G, Pizzo A, Donadono C. Management of Acetabular Fractures with Total Hip Replacement: A Narrative Literature Review. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(7):282. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070282
Chicago/Turabian StyleTigani, Domenico, Luigigiuseppe Lamattina, Andrea Assenza, Giuseppe Melucci, Alex Pizzo, and Cesare Donadono. 2025. "Management of Acetabular Fractures with Total Hip Replacement: A Narrative Literature Review" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 7: 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070282
APA StyleTigani, D., Lamattina, L., Assenza, A., Melucci, G., Pizzo, A., & Donadono, C. (2025). Management of Acetabular Fractures with Total Hip Replacement: A Narrative Literature Review. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(7), 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070282






