Artificial Intelligence-Based Algorithm for Stent Coverage Assessments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Description
2.2. Data Preprocessing, Model Architecture, and Training
2.3. Statistic Analysis
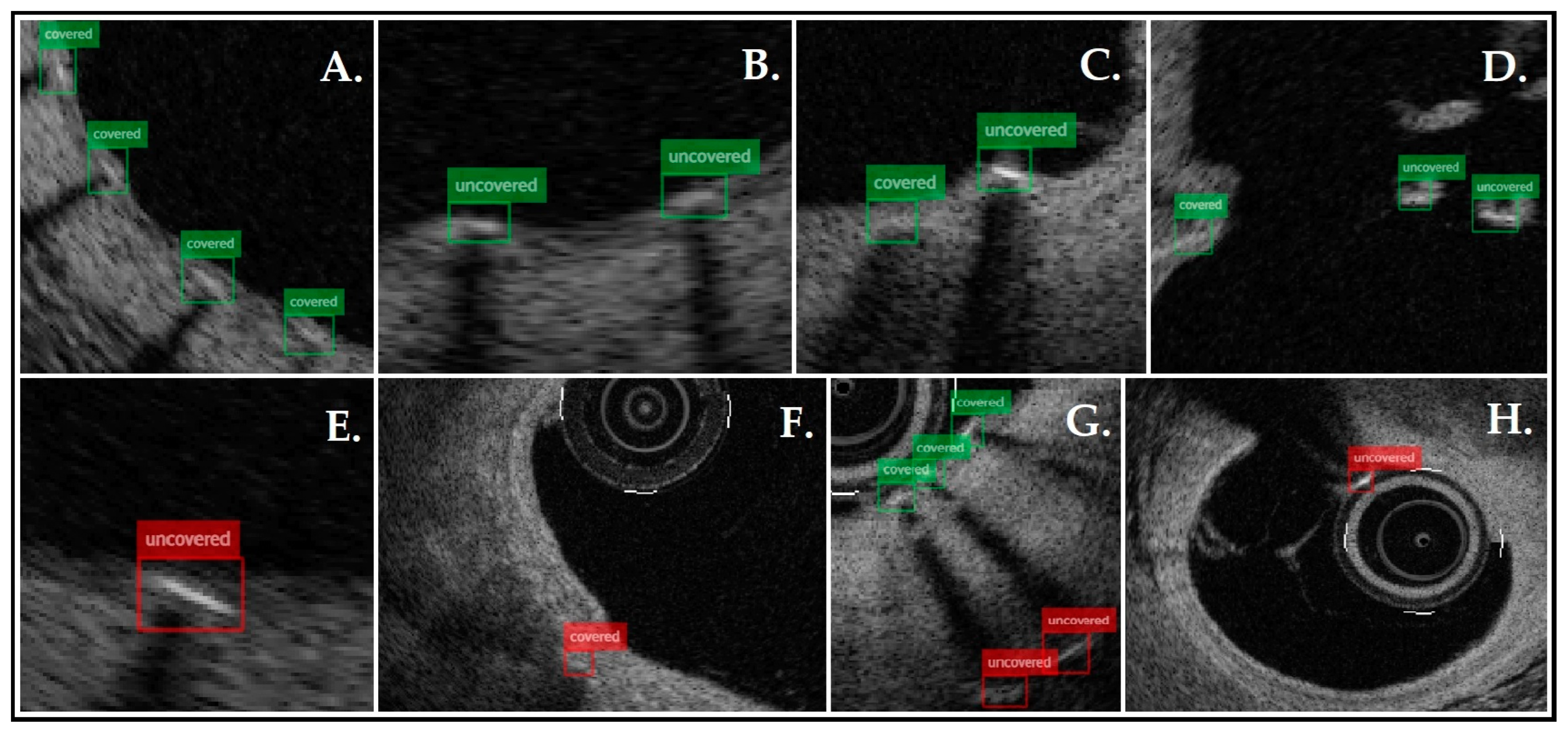
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alfonso, F.; Coughlan, J.C.; Giacoppo, D.; Kastrati, A.; Byrne, R.B. Management of In-Stent Restenosis. EuroIntervention 2022, 18, e103–e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joner, M.; Finn, A.V.; Farb, A.; Mont, E.K.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Ladich, E.; Kutys, R.; Skorija, K.; Gold, H.K.; Virmani, R. Pathology of Drug-Eluting Stents in Humans. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, A.V.; Joner, M.; Nakazawa, G.; Kolodgie, F.; Newell, J.; John, M.C.; Gold, H.K.; Virmani, R. Pathological Correlates of Late Drug-Eluting Stent Thrombosis: Strut Coverage as a Marker of Endothelialization. Circulation 2007, 115, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenaweser, P.; Daemen, J.; Zwahlen, M.; Van Domburg, R.; Jüni, P.; Vaina, S.; Hellige, G.; Tsuchida, K.; Morger, C.; Boersma, E.; et al. Incidence and Correlates of Drug-Eluting Stent Thrombosis in Routine Clinical Practice. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tearney, G.J.; Waxman, S.; Shishkov, M.; Vakoc, B.J.; Suter, M.J.; Freilich, M.I.; Desjardins, A.E.; Oh, W.-Y.; Bartlett, L.A.; Rosenberg, M.; et al. Three-Dimensional Coronary Artery Microscopy by Intracoronary Optical Frequency Domain Imaging. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2008, 1, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, M.W.; Yoo, H. Diagnostic Fiber-Based Optical Imaging Catheters. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2014, 4, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tearney, G.J.; Brezinski, M.E.; Bouma, B.E.; Boppart, S.A.; Pitris, C.; Southern, J.F.; Fujimoto, J.G. In Vivo Endoscopic Optical Biopsy with Optical Coherence Tomography. Science 1997, 276, 2037–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attizzani, G.F.; Bezerra, H.G. Contemporary Assessment of Stent Strut Coverage by OCT. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 29, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R. A Survey: Comparison between Convolutional Neural Network and YOLO in Image Identification. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1453, 012139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluder-Wlodarczyk, J.; Schneider, Z.; Pawłowski, T.; Wojakowski, W.; Gasior, P.; Pociask, E. Assessment of Effectiveness of the Algorithm for Automated Quantitative Analysis of Metallic Strut Tissue Short-Term Coverage with Intravascular Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CVAT.ai: Computer Vision Annotation Tool. Available online: https://cvat.ai (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Ultralytics. YOLO11—State-of-the-Art Object Detection Model. Available online: https://ultralytics.com (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- Wang, A.; Eggermont, J.; Dekker, N.; Garcia-Garcia, H.M.; Pawar, R.; Reiber, J.H.C.; Dijkstra, J. Automatic Stent Strut Detection in Intravascular Optical Coherence Tomographic Pullback Runs. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 29, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ughi, G.J.; Adriaenssens, T.; Onsea, K.; Kayaert, P.; Dubois, C.; Sinnaeve, P.; Coosemans, M.; Desmet, W.; D’hooge, J. Automatic Segmentation of In-Vivo Intra-Coronary Optical Coherence Tomography Images to Assess Stent Strut Apposition and Coverage. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 28, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, H.S.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.J.; Song, J.W.; Kim, J.W.; Yoo, H. Automated Detection of Vessel Lumen and Stent Struts in Intravascular Optical Coherence Tomography to Evaluate Stent Apposition and Neointimal Coverage. Med. Phys. 2016, 43, 1662–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Lee, J.; Ray, S.; Tanaka, K.; Bezerra, H.G.; Rollins, A.M.; Wilson, D.L. Automated Stent Coverage Analysis in Intravascular OCT (IVOCT) Image Volumes Using a Support Vector Machine and Mesh Growing. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Lee, J.; Jakl, M.; Wang, Z.; Cervinka, P.; Bezerra, H.G.; Wilson, D.L. Application and Evaluation of Highly Automated Software for Comprehensive Stent Analysis in Intravascular Optical Coherence Tomography. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugaletta, S.; Garcia-Garcia, H.M.; Gomez-Lara, J.; Radu, M.D.; Pawar, R.; Khachabi, J.; Bruining, N.; Sabaté, M.; Serruys, P.W. Reproducibility of Qualitative Assessment of Stent Struts Coverage by Optical Coherence Tomography. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 29, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Antonsen, L.; Thayssen, P.; Junker, A.; Veien, K.T.; Hansen, H.S.; Hansen, K.N.; Hougaard, M.; Jensen, L.O. Intra- and Interobserver Reliability and Intra-Catheter Reproducibility Using Frequency Domain Optical Coherence Tomography for the Evaluation of Morphometric Stent Parameters and Qualitative Assessment of Stent Strut Coverage. Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. 2015, 16, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, D.; Shite, J.; Shinke, T.; Otake, H.; Tanino, Y.; Ogasawara, D.; Sawada, T.; Paredes, O.L.; Hirata, K.-i.; Yokoyama, M. Neointimal Coverage of Sirolimus-Eluting Stents at 6-Month Follow-up: Evaluated by Optical Coherence Tomography. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliescu, C.A.; Cilingiroglu, M.; Giza, D.E.; Rosales, O.; Lebeau, J.; Guerrero-Mantilla, I.; Lopez-Mattei, J.; Song, J.; Silva, G.; Loyalka, P.; et al. “Bringing on the Light” in a Complex Clinical Scenario: Optical Coherence Tomography–Guided Discontinuation of Antiplatelet Therapy in Cancer Patients with Coronary Artery Disease (PROTECT-OCT Registry). Am. Heart J. 2017, 194, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Yoon, H.-J.; Hur, S.-H.; Lee, S.-G.; Kim, J.W.; Hong, Y.J.; Kim, K.-S.; Choi, S.-Y.; Shin, D.-H.; et al. Early Strut Coverage in Patients Receiving Drug-Eluting Stents and Its Implications for Dual Antiplatelet Therapy. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, H.; Shin, D.-H.; Kim, B.-K.; Mintz, G.S.; Kim, J.-S.; Ko, Y.-G.; Choi, D.; Jang, Y.; Hong, M.-K. Optical Coherence Tomography Derived Cut-off Value of Uncovered Stent Struts to Predict Adverse Clinical Outcomes after Drug-Eluting Stent Implantation. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 29, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guagliumi, G.; Sirbu, V.; Musumeci, G.; Gerber, R.; Biondi-Zoccai, G.; Ikejima, H.; Ladich, E.; Lortkipanidze, N.; Matiashvili, A.; Valsecchi, O.; et al. Examination of the In Vivo Mechanisms of Late Drug-Eluting Stent Thrombosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2012, 5, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutter, C.; Mori, H.; Yahagi, K.; Ladich, E.; Joner, M.; Kutys, R.; Fowler, D.; Romero, M.; Narula, J.; Virmani, R.; et al. Histopathological Differential Diagnosis of Optical Coherence Tomographic Image Interpretation After Stenting. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2016, 9, 2511–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guagliumi, G.; Shimamura, K.; Sirbu, V.; Garbo, R.; Boccuzzi, G.; Vassileva, A.; Valsecchi, O.; Fiocca, L.; Canova, P.; Colombo, F.; et al. Temporal Course of Vascular Healing and Neoatherosclerosis after Implantation of Durable- or Biodegradable-Polymer Drug-Eluting Stents. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 2448–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, G.; AlKhalfan, F.; Lee, J.J.; Montazerin, S.M.; Fitzgerald, C.; Korjian, S.; Omar, W.; Barnathan, E.; Plotnikov, A.; Gibson, C.M. Factors Associated with Early, Late, and Very Late Stent Thrombosis among Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome Undergoing Coronary Stent Placement: Analysis from the ATLAS ACS 2-TIMI 51 Trial. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 10, 1269011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovou, I.; Schmidt, T.; Bonizzoni, E.; Ge, L.; Sangiorgi, G.M.; Stankovic, G.; Airoldi, F.; Chieffo, A.; Montorfano, M.; Carlino, M.; et al. Incidence, Predictors, and Outcome of Thrombosis After Successful Implantation of Drug-Eluting Stents. JAMA 2005, 293, 2126–2130. [Google Scholar]
- Mehanna, E.A.; Attizzani, G.F.; Kyono, H.; Hake, M.; Bezerra, H.G. Assessment of Coronary Stent by Optical Coherence Tomography, Methodology and Definitions. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2011, 27, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, G.; Finn, A.V.; Joner, M.; Ladich, E.; Kutys, R.; Mont, E.K.; Gold, H.K.; Burke, A.P.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Virmani, R. Delayed Arterial Healing and Increased Late Stent Thrombosis at Culprit Sites After Drug-Eluting Stent Placement for Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients: An Autopsy Study. Circulation 2008, 118, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, K.; Torii, S.; Nakamura, N.; Hozumi, H.; Shiozaki, M.; Sato, Y.; Yoshikawa, M.; Kamioka, N.; Ijichi, T.; Natsumeda, M.; et al. Pathological Evaluation of Predictors for Delayed Endothelial Coverage after Currently Available Drug-Eluting Stent Implantation in Coronary Arteries: Impact of Lesions with Acute and Chronic Coronary Syndromes. Am. Heart J. 2024, 277, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| All Pullbacks (n = 22) | The Testing Set (n = 2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (average) | 68 | 63 |
| Male | 14 | 1 |
| Indication for PCI | ||
| ACS | 3 | 1 |
| UA | 10 | 0 |
| CCS | 9 | 1 |
| Risk factors | ||
| Hypertension | 18 | 2 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 4 | 0 |
| Dyslipidemia | 6 | 0 |
| Smoking | 5 | 2 |
| Coronary artery | ||
| LAD | 8 | 2 |
| Cx | 8 | 0 |
| IM | 1 | 0 |
| RCA | 5 | 0 |
| Stent type (strut thickness) | ||
| Alex Plus (71 µm) | 9 | 0 |
| Resolute Onyx (81 μm) | 8 | 0 |
| Supraflex Cruz (60 μm) | 2 | 1 |
| Resolute Integrity (90 μm) | 1 | 0 |
| Orsiro (60 μm) | 2 | 1 |
| GT | Algorithm | GT vs. Algorithm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPV (%) | TPR (%) | |||
| Total strut | 3539 | 3439 | 92 | 90 |
| Covered | 2324 | 2440 | 81 | 85 |
| Uncovered | 1215 | 999 | 73 | 60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fluder-Wlodarczyk, J.; Darakhovich, M.; Schneider, Z.; Roleder-Dylewska, M.; Dobrolińska, M.; Pawłowski, T.; Wojakowski, W.; Gasior, P.; Pociask, E. Artificial Intelligence-Based Algorithm for Stent Coverage Assessments. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15040151
Fluder-Wlodarczyk J, Darakhovich M, Schneider Z, Roleder-Dylewska M, Dobrolińska M, Pawłowski T, Wojakowski W, Gasior P, Pociask E. Artificial Intelligence-Based Algorithm for Stent Coverage Assessments. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(4):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15040151
Chicago/Turabian StyleFluder-Wlodarczyk, Joanna, Mikhail Darakhovich, Zofia Schneider, Magda Roleder-Dylewska, Magdalena Dobrolińska, Tomasz Pawłowski, Wojciech Wojakowski, Pawel Gasior, and Elżbieta Pociask. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence-Based Algorithm for Stent Coverage Assessments" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 4: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15040151
APA StyleFluder-Wlodarczyk, J., Darakhovich, M., Schneider, Z., Roleder-Dylewska, M., Dobrolińska, M., Pawłowski, T., Wojakowski, W., Gasior, P., & Pociask, E. (2025). Artificial Intelligence-Based Algorithm for Stent Coverage Assessments. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(4), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15040151





