Comparative Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Diagnosis of Helminth Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Deep Learning Models
3.2.1. ConvNeXt
3.2.2. EfficientNet
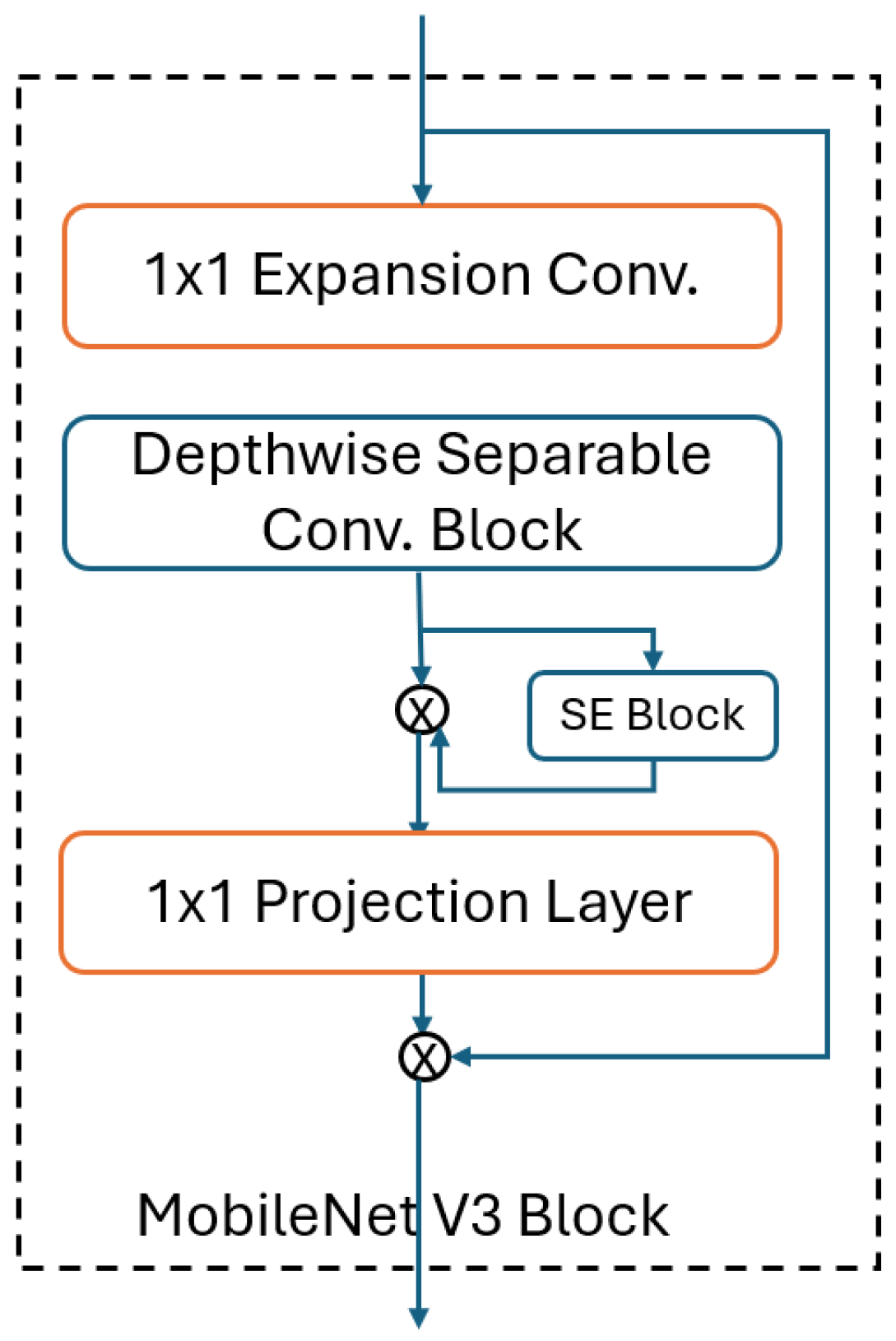
3.2.3. MobileNet
3.3. Experimental Design
3.4. Evaluation Metrics
4. Results
4.1. Experimental Results
4.2. Statistical Assessment with ANOVA
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martviset, P.; Phadungsil, W.; Na-Bangchang, K.; Sungkhabut, W.; Panupornpong, T.; Prathaphan, P.; Torungkitmangmi, N.; Chaimon, S.; Wangboon, C.; Jamklang, M.; et al. Current prevalence and geographic distribution of helminth infections in the parasitic endemic areas of rural Northeastern Thailand. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avcı, A.; Doğan, H.; Çiftçi, E.; Özüçelik, D.N.; Çukurova, Z.; Avcı, B.Ş.; Ay, M.O. The case of tapeworm uttered from Mouth. Med. J. Bakirkoy 2016, 12, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozan, E. Foodborne Helminths. Kocatepe Vet. J. 2016, 9, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/soil-transmitted-helminth-infections (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Alemu, Y.; Degefa, T.; Bajiro, M.; Teshome, G. Prevalence and intensity of soil-transmitted helminths infection among individuals in model and non-model households, South West Ethiopia: A comparative cross-sectional community based study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanksha, K.; Kumari, A.; Dutta, O.; Prasanth, A.; Deeba, F.; Salam, N. Prevalence of soil-transmitted helminth infections in HIV patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, E.; Süer, K. Epidemiology of intestinal parasites in a university hospital in Northern Cyprus: A 4-year retrospective experience. Epidemiology 2021, 45, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Parasites-Ascariasis. 2023. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/sth/about/ascariasis.html?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ascariasis/index.html (accessed on 21 August 2024).
- Butploy, N.; Kanarkard, W.; Maleewong Intapan, P. Deep learning approach for Ascaris lumbricoides parasite egg classification. J. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 2021, 6648038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurelli, M.P.; Alves, L.C.; Aggarwal, C.S.; Cociancic, P.; Levecke, B.; Cools, P.; Rinaldi, L.; Montresor, A.; Ianniello, D.; Gualdieri, L.; et al. Ascaris lumbricoides eggs or artefacts? A diagnostic conundrum. Parasitology 2021, 148, 1554–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Taeniasis FAQs. 2023. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/taeniasis/about/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/taeniasis/gen_info/faqs.html (accessed on 21 August 2024).
- Okello, A.L.; Thomas, L.F. Human taeniasis: Current insights into prevention and management strategies in endemic countries. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2017, 10, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Laboratory Identification of Parasites of Public Health Concern. Taeniasis, Image Gallery. 2023. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/taeniasis/index.html#:~:text=The%20eggs%20of%20Taenia%20spp,oncosphere%20contains%20six%20refractile%20hooks (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Sahin, A.R.; Ates, S.; Gunay, M. Basic Processing Models of Artificial Intelligence In Clinical Microbiology Laboratories. J. Biotechnol. Strateg. Health Res. 2019, 3, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Mustapha, M.T.; Ozsahin, D.U.; Ozsahin, I.; Uzun, B. Breast cancer screening based on supervised learning and multi-criteria decision-making. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbilge, E.; Güler, E.; Güvenir, M.; Sanlıdag, T.; Ozbilgin, A.; Suer, K. Automated malaria parasite detection using artificial neural network. In International Conference on Theory and Applications of Fuzzy Systems and Soft Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 631–640. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, A.U.; Guler, E.; Guvenir, M.; Suer, K.; Serte, S.; Ozsoz, M. Automated detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis using transfer learning. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2021, 15, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodswen, S.J.; Barratt, J.L.N.; Kennedy, P.J.; Kaufer, A.; Calarco, L.; Ellis, J.T. Machine learning and applications in microbiology. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 45, fuab015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Ye, T.; Juhas, M. Deep Learning for Imaging and Detection of Microorganisms. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhu, H.; Geng, J.; Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Wang, H.; Xie, L.; et al. Recognition of parasitic helminth eggs via a deep learning-based platform. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1485001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez Pastor, G.G.; Ancco Ruelas, C.R.; Castro-Gutierrez, E.; Vásquez Huerta, V.L. Automatic detection of Ascaris lumbricoides in microscopic images using convolutional neural networks (CNN). Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2024, 15, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthulakshm, M.; Venkatesan, K.; Rahayu, S.B.; Elangovan, K. A Squeeze-Excitation ResNet Approach for Effective Classification of Parasitic Eggs. In Proceedings of the Internationaş Visualization, Informatics and Technology Conference (IVIT), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 7–8 August 2024; pp. 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmula, A.M.; Mirzaei, O.; Güler, E.; Süer, K. Assessment of Deep Learning Models for Cutaneous Leishmania Parasite Diagnosis Using Microscopic Images. Diagnostics 2023, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A convnet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11976–11986. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnetv2: Smaller models and faster training. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 10096–10106. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Demsar, J. Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2006, 7, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, L.S.; Green, C.E. Analysis of variance: Is there a difference in means and what does it mean? J. Surg. Res. 2008, 144, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Disease | Number of Images | Spatial Dimensions |
|---|---|---|
| Ascaris lumbricoides | 884 | 3000 × 4000 |
| Taenia saginata | 440 | 3000 × 4000 |
| Uninfected | 1003 | 3000 × 4000 |
| Total | 2327 | - |
| Ascaris | Taenia | Uninfected | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
| ConvNeXt Tiny | 0.9793 | 0.9743 | 0.9767 | 0.9529 | 0.9744 | 0.963 | 0.9819 | 0.9759 | 0.9789 |
| EfficientNet V2 S | 0.9756 | 0.9846 | 0.9801 | 0.9863 | 0.981 | 0.9835 | 0.988 | 0.9818 | 0.9849 |
| MobileNet V3 S | 0.9469 | 0.9731 | 0.9596 | 0.9653 | 0.9465 | 0.9557 | 0.9816 | 0.9623 | 0.9716 |
| Model | Macro Precision | Macro Recall | Macro F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| ConvNeXt Tiny | 0.9714 | 0.9748 | 0.9729 |
| EfficientNet V2 S | 0.9833 | 0.9825 | 0.9828 |
| MobileNet V3 S | 0.9646 | 0.9606 | 0.9623 |
| Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0559 | 0.0101 | 0.0005 |
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Mean Difference | p-Adjusted | Lower Bound | Upper Bound |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ConvNext Tiny | EfficientNet V2 S | 0.0076 | 0.5198 | −0.0092 | 0.0244 |
| ConvNext Tiny | MobileNet V3 S | −0.0142 | 0.1113 | −0.031 | 0.0026 |
| EfficientNet V2 S | MobileNet V3 S | −0.0218 | 0.0081 | −0.0386 | −0.005 |
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Mean Difference | p-Adjusted | Lower Bound | Upper Bound |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ConvNext Tiny | EfficientNet V2 S | 0.0099 | 0.1089 | −0.0017 | 0.0216 |
| ConvNext Tiny | MobileNet V3 S | −0.0106 | 0.0826 | −0.0223 | 0.0011 |
| EfficientNet V2 S | MobileNet V3 S | −0.0205 | 0.0003 | −0.0322 | −0.0088 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mirzaei, O.; Ilhan, A.; Guler, E.; Suer, K.; Sekeroglu, B. Comparative Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Diagnosis of Helminth Infections. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15030121
Mirzaei O, Ilhan A, Guler E, Suer K, Sekeroglu B. Comparative Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Diagnosis of Helminth Infections. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(3):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15030121
Chicago/Turabian StyleMirzaei, Omid, Ahmet Ilhan, Emrah Guler, Kaya Suer, and Boran Sekeroglu. 2025. "Comparative Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Diagnosis of Helminth Infections" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 3: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15030121
APA StyleMirzaei, O., Ilhan, A., Guler, E., Suer, K., & Sekeroglu, B. (2025). Comparative Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Diagnosis of Helminth Infections. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(3), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15030121







