Multi-Omics Reveals the Role of Osteopontin/Secreted Phosphoprotein 1 in Regulating Ovarian Aging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
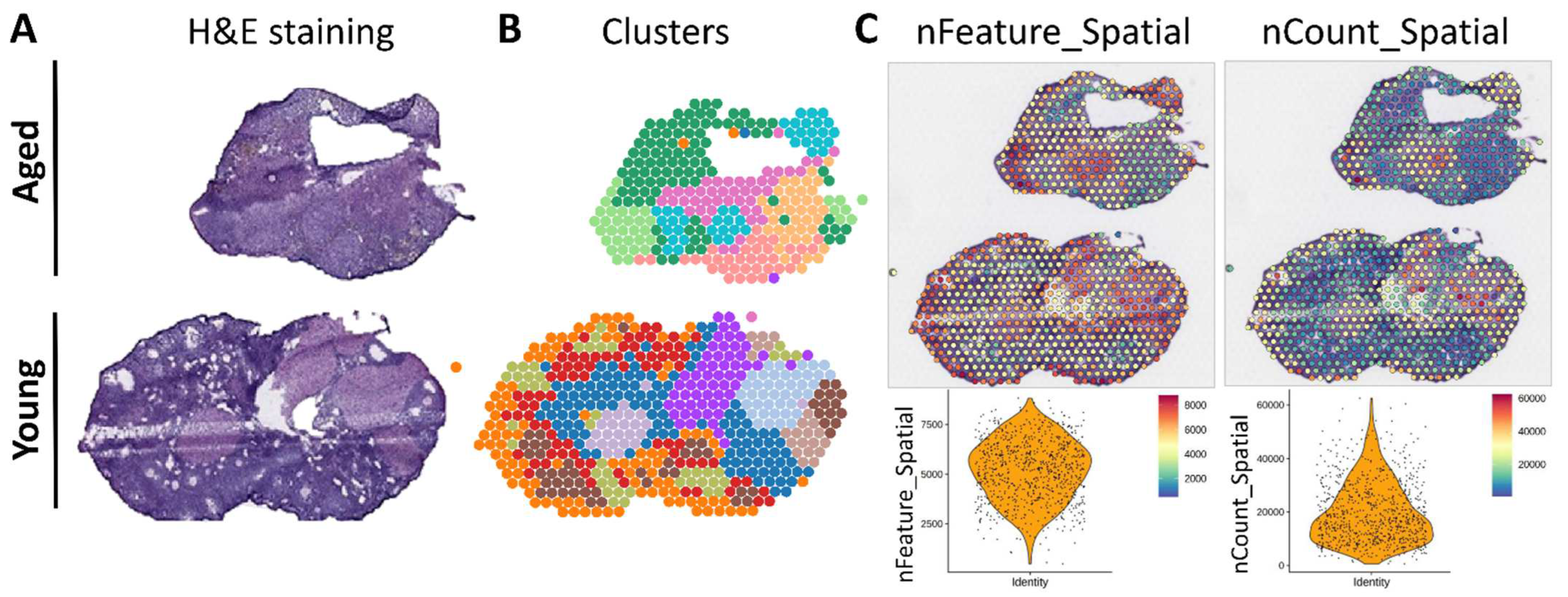
2.1. Analysis of Spatial Transcriptomics Data
2.2. Analysis of Single-Cell RNA-Seq Data
2.3. Analysis of SPP1 Expression in the Human Tissue Atlas
2.4. Protein–Protein Interaction
2.5. Statistical Evaluation
3. Results
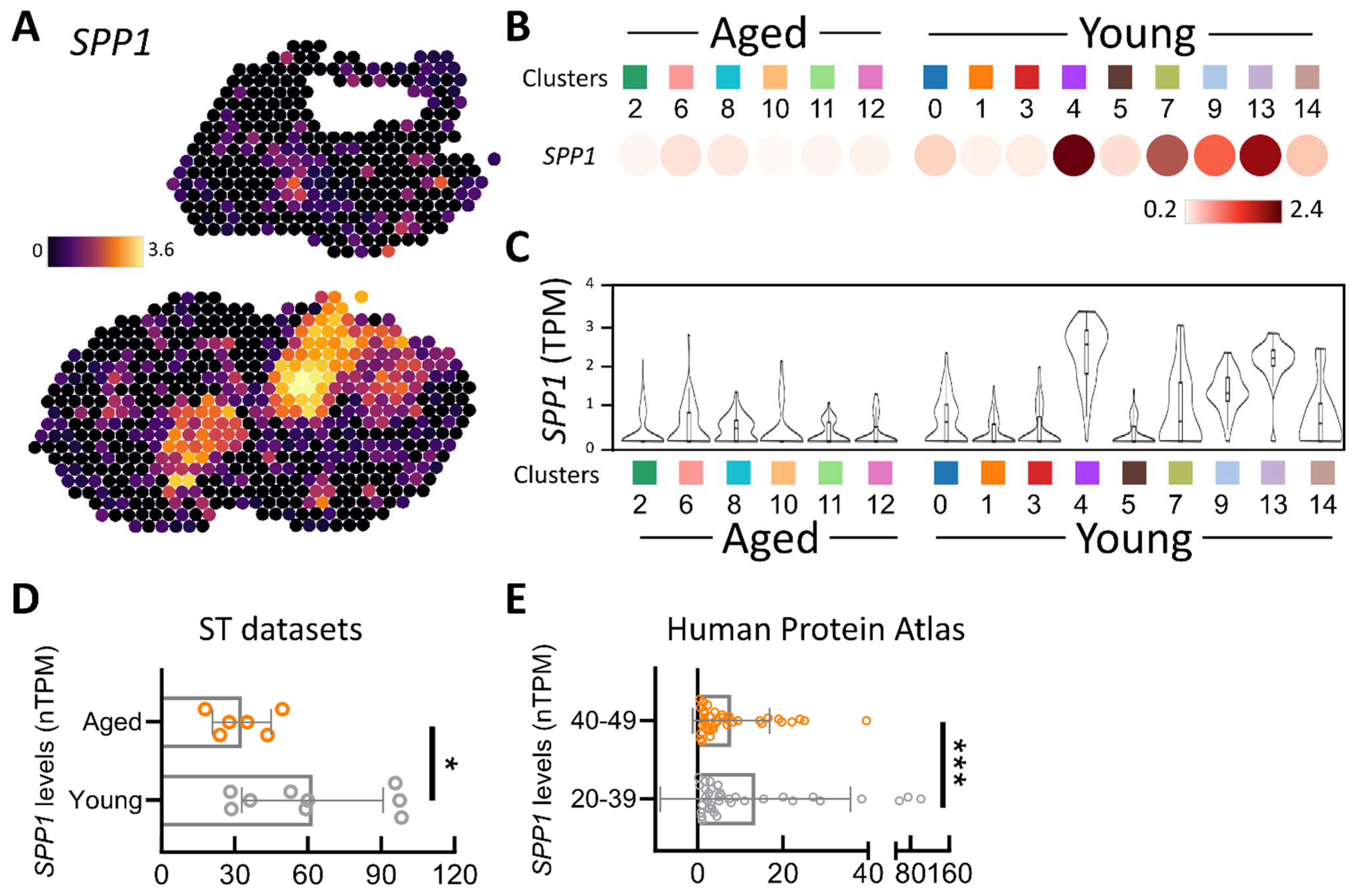
3.1. Spatial Transcriptomic Assessment of SPP1
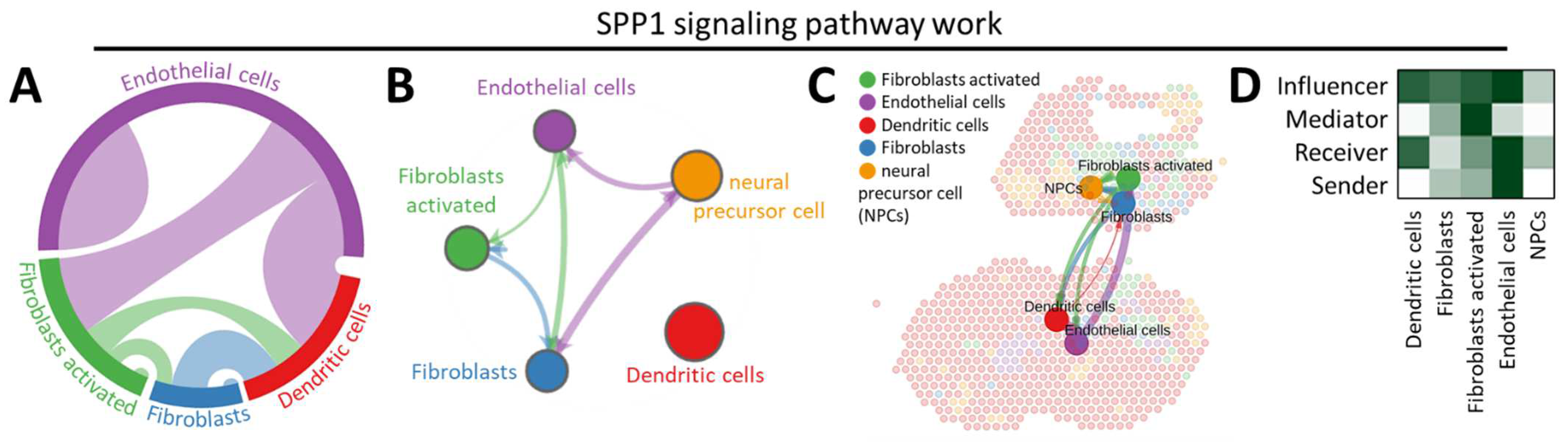
3.2. CellChat Reveals the Continuum of Cell Lineage SPP1-Related Signaling Events
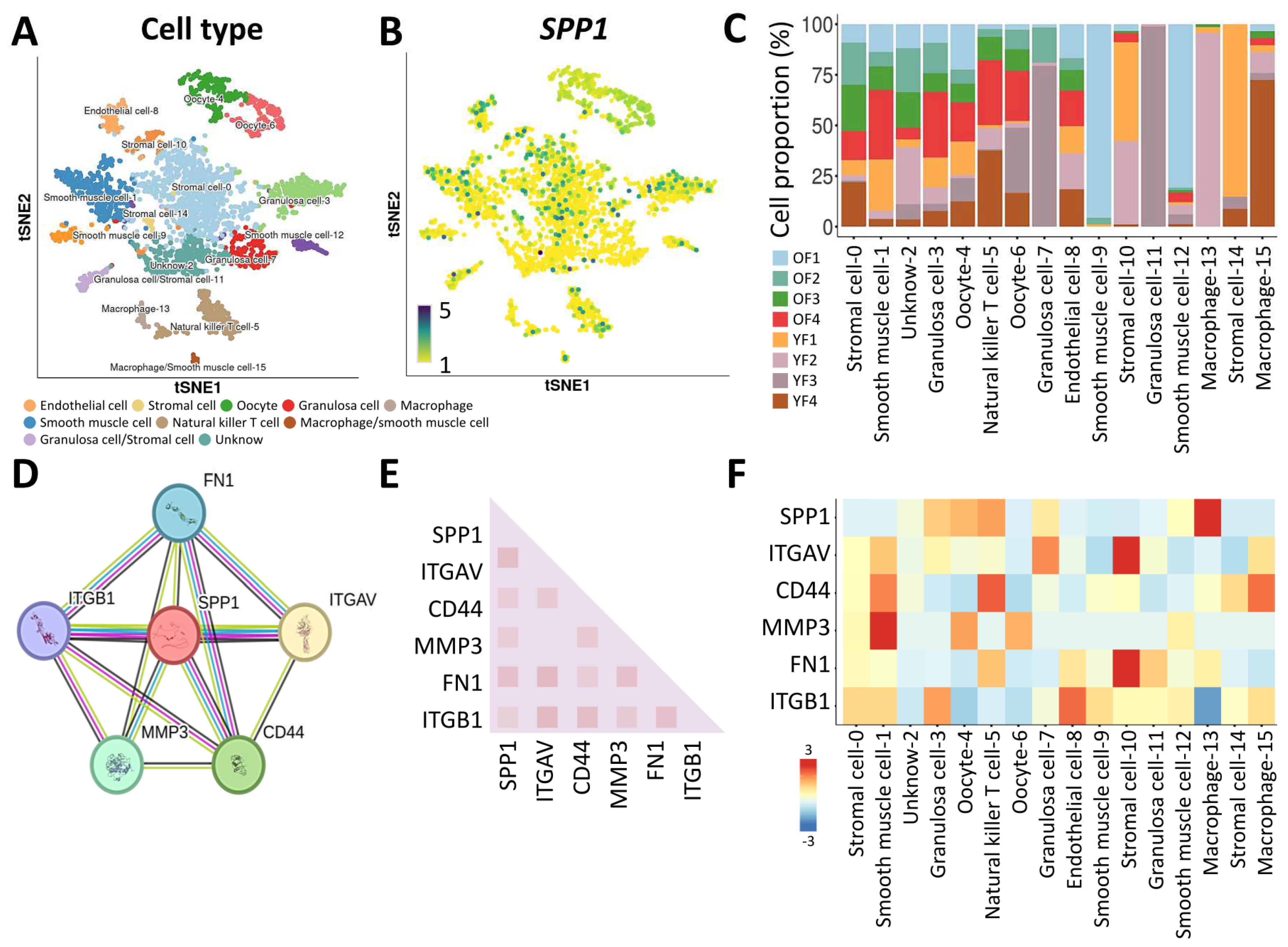
3.3. Characterization of the SPP1 Gene in Ovarian Tissue by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.J.; Lin, L.T.; Tsai, H.W.; Chern, C.U.; Wen, Z.H.; Wang, P.H.; Tsui, K.H. The Molecular Regulation in the Pathophysiology in Ovarian Aging. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 934–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Zhou, M.; Wu, H.; Xiong, Z. SPP1 promotes ovarian cancer progression via Integrin beta1/FAK/AKT signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.Q.; Zheng, Z.Q.; Liao, J.; Li, Y.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Wang, T.Y.; Yuan, G.Q.; Wang, Z.; Xue, Q. SPP1/AnxA1/TIMP1 as Essential Genes Regulate the Inflammatory Response in the Acute Phase of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion in Rats. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 4873–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Chen, J.; Han, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, F. Upregulation of SPP1 Is a Marker for Poor Lung Cancer Prognosis and Contributes to Cancer Progression and Cisplatin Resistance. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 646390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, M.L.; Lee, J.C.; Cheng, S.Y.; Lawal, B.; Ho, C.L.; Wu, C.C.; Tzeng, D.T.W.; Chen, J.H.; Wu, A.T.H. Transcriptomic discovery of a theranostic signature (SERPINE1/MMP3/COL1A1/SPP1) for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas and identification of antrocinol as a candidate drug. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 150, 106185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ma, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, M.; Zhuang, G.; Jing, Y. Divergent tumor and immune cell reprogramming underlying immunotherapy response and immune-related adverse events in lung squamous cell carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e007305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ren, L.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, Y. Immunobiological signatures and the emerging role of SPP1 in predicting tumor heterogeneity, malignancy, and clinical outcomes in stomach adenocarcinoma. Aging 2023, 15, 11588–11610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.F.; Fan, Z.B.; Wu, C.W.; Qi, G.X.; Cao, Q.Y.; Xu, F. Sacubitril Valsartan Enhances Cardiac Function and Alleviates Myocardial Infarction in Rats through a SUV39H1/SPP1 Axis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 5009289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jakobs, T.C. Secreted phosphoprotein 1 slows neurodegeneration and rescues visual function in mouse models of aging and glaucoma. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, W.; Chen, L. Secreted phosphoprotein 1 exacerbates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Tissue Cell 2023, 83, 102154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.Y.; Hsiao, J.H.; Tzeng, Y.T.; Chang, R.; Tsang, Y.L.; Kuo, C.H.; Li, C.J. Single-cell landscape and spatial transcriptomic analysis reveals macrophage infiltration and glycolytic metabolism in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. Aging 2023, 15, 11298–11312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, Y.L.; Kao, C.L.; Lin, S.A.; Li, C.J. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Aging and Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.H.; Lin, L.T.; Li, C.J.; Kao, P.G.; Tsai, H.W.; Chen, S.N.; Wen, Z.H.; Wang, P.H.; Tsui, K.H. Combining Bioinformatics and Experiments to Identify CREB1 as a Key Regulator in Senescent Granulosa Cells. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y. microRNA-944 inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation and promotes cell apoptosis by reducing SPP1 through inactivating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Apoptosis 2023, 28, 1546–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Tan, M.; Wang, C.; Liang, L. Decreased miR-127 promotes the occurrence of breast cancer via increasing the expression of SPP1. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 32, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Jin, L.; Li, S. Role of SPP1 in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2023, 26, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, K.P.; Yu, L.; Shen, X.; Qiu, Y.; Tasaki, S.; Iatrou, A.; Beeri, M.S.; Seyfried, N.T.; Menon, V.; Wang, Y.; et al. Associations of cortical SPP1 and ITGAX with cognition and common neuropathologies in older adults. Alzheimers Dement. 2023. submitted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.A.; Simitsidellis, I.; Kelepouri, O.; Critchley, H.O.D.; Saunders, P.T.K. Dehydroepiandrosterone enhances decidualization in women of advanced reproductive age. Fertil. Steril. 2018, 109, 728–734.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, A.; Gangi, L.M.; Zegers-Hochschild, F.; Balmaceda, J.; Pommer, R.; Trejo, L.; Pacheco, I.M.; Salvatierra, A.M.; Henriquez, S.; Quezada, M.; et al. Differences in the endometrial transcript profile during the receptive period between women who were refractory to implantation and those who achieved pregnancy. Hum. Reprod. 2008, 23, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaki, D.; Zhang, Y.; Mohamadi, A.; Pini, M.; Mezdari, Z.; Lipskaia, L.; Naushad, S.; Lamendour, L.; Altintas, D.M.; Breau, M.; et al. Osteopontin promotes age-related adipose tissue remodeling through senescence-associated macrophage dysfunction. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e145811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Chen, M.; Rao, M.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, R.; Hu, X.; Chen, R.; Chai, W.; Huang, X.; et al. Deciphering Immune Landscape Remodeling Unravels the Underlying Mechanism for Synchronized Muscle and Bone Aging. Adv. Sci. 2023, e2304084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ng, Y.E.; Chini, L.C.S.; Heeren, A.A.; White, T.A.; Li, H.; Huang, H.; Doolittle, M.L.; Khosla, S.; LeBrasseur, N.K. Senescent skeletal muscle fibroadipogenic progenitors recruit and promote M2 polarization of macrophages. Aging Cell 2023, e14069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, F.; Tian, X.; Tian, Z.; Chen, D.; Miao, Q. Machine learning algorithm integrates bulk and single-cell transcriptome sequencing to reveal immune-related personalized therapy prediction features for pancreatic cancer. Aging 2023, 15, 14109–14140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, K.H.; Li, C.J. Mitoquinone shifts energy metabolism to reduce ROS-induced oxeiptosis in female granulosa cells and mouse oocytes. Aging 2023, 15, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.P.; Li, C.J.; Lin, L.T.; Lin, P.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Sheu, J.J.; Tsui, K.H. Boosting mitochondrial function and metabolism in aging female germ cells with dual ROCK/ROS inhibition. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.H.; Su, W.P.; Li, C.J.; Lin, L.T.; Sheu, J.J.; Wen, Z.H.; Cheng, J.T.; Tsui, K.H. Investigating the Role of Ferroptosis-Related Genes in Ovarian Aging and the Potential for Nutritional Intervention. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Lin, L.T.; Tsai, H.W.; Wen, Z.H.; Tsui, K.H. Phosphoglycerate mutase family member 5 maintains oocyte quality via mitochondrial dynamic rearrangement during aging. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, K.H.; Wang, P.H.; Lin, L.T.; Li, C.J. DHEA protects mitochondria against dual modes of apoptosis and necroptosis in human granulosa HO23 cells. Reproduction 2017, 154, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, L.-C.; Li, C.-J.; Lin, L.-T.; Pan, L.-F.; Wen, Z.-H.; Sheu, J.J.-C.; Tsui, K.-H. Multi-Omics Reveals the Role of Osteopontin/Secreted Phosphoprotein 1 in Regulating Ovarian Aging. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010078
Hsu L-C, Li C-J, Lin L-T, Pan L-F, Wen Z-H, Sheu JJ-C, Tsui K-H. Multi-Omics Reveals the Role of Osteopontin/Secreted Phosphoprotein 1 in Regulating Ovarian Aging. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(1):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010078
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Li-Chuan, Chia-Jung Li, Li-Te Lin, Li-Fei Pan, Zhi-Hong Wen, Jim Jinn-Chyuan Sheu, and Kuan-Hao Tsui. 2024. "Multi-Omics Reveals the Role of Osteopontin/Secreted Phosphoprotein 1 in Regulating Ovarian Aging" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 1: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010078
APA StyleHsu, L.-C., Li, C.-J., Lin, L.-T., Pan, L.-F., Wen, Z.-H., Sheu, J. J.-C., & Tsui, K.-H. (2024). Multi-Omics Reveals the Role of Osteopontin/Secreted Phosphoprotein 1 in Regulating Ovarian Aging. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(1), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010078










