The Risk Factors of Severe Hypoglycemia in Older Patients with Dementia and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Selection of Patients with AD and T2DM
2.3. Definition of Hypoglycemic Event
2.4. Definition and Measurement of Biochemical and Medical Data
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
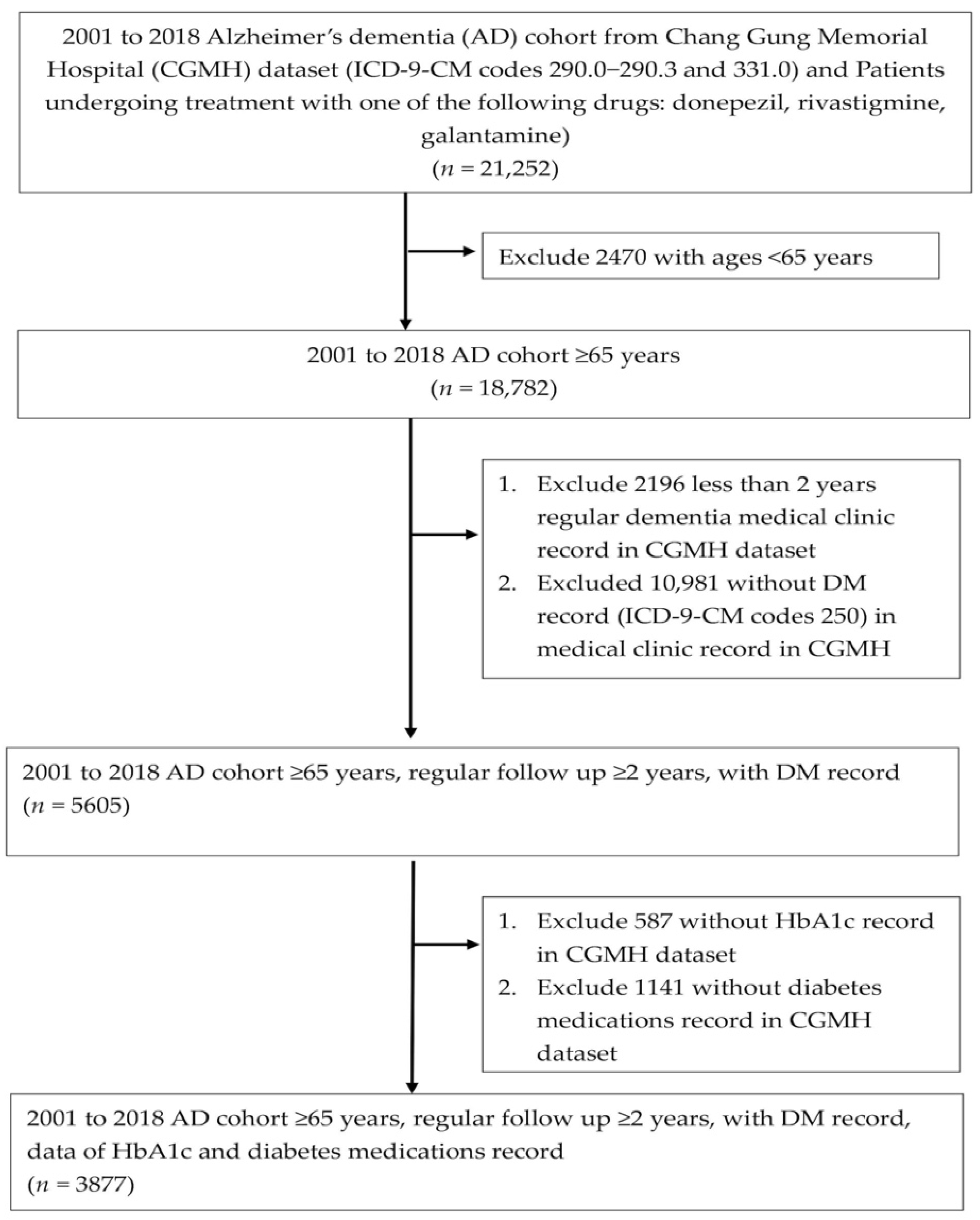
3.1. Study Process Flowchart
3.2. Patient Characteristics and Comorbidities
3.3. Different Characteristics and Comorbidities between Patients with and without Hypoglycemic Events
3.4. The Usage of Antidiabetic Medications in Patients with and without Hypoglycemic Event
3.5. Risk Factors Correlated with Hypoglycemic Events in Patients with AD and T2DM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Alzheimer Report 2015: The Global Impact of Dementia: An Analysis of Prevalence, Incidence, Cost and Trends; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2015.
- Wu, Y.T.; Ali, G.C.; Guerchet, M.; Prina, A.M.; Chan, K.Y.; Prince, M.; Brayne, C. Prevalence of dementia in mainland China, Hong Kong and Taiwan: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 47, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prince, M.; Bryce, R.; Albanese, E.; Wimo, A.; Ribeiro, W.; Ferri, C.P. The global prevalence of dementia: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2013, 9, 63–75.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.E.; Cooper, M.E.; Del Prato, S. Pathophysiology and treatment of type 2 diabetes: Perspectives on the past, present, and future. Lancet 2014, 383, 1068–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biessels, G.J.; Despa, F. Cognitive decline and dementia in diabetes mellitus: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, D.M.; Cleary, P.A.; Backlund, J.Y.; Genuth, S.M.; Lachin, J.M.; Orchard, T.J.; Raskin, P.; Zinman, B.; Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Study Research Group. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2643–2653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holman, R.R.; Paul, S.K.; Bethel, M.A.; Matthews, D.R.; Neil, H.A. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- American Diabetes Association. 6. Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44 (Suppl. S1), S73–S84. [Google Scholar]
- American Diabetes Association. 12. Older Adults: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44 (Suppl. S1), S169–S179. [Google Scholar]
- Kalra, S.; Mukherjee, J.J.; Venkataraman, S.; Bantwal, G.; Shaikh, S.; Saboo, B.; Das, A.K.; Ramachandran, A. Hypoglycemia: The neglected complication. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 17, 819–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipska, K.J.; Yao, X.; Herrin, J.; McCoy, R.G.; Ross, J.S.; Steinman, M.A.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Gill, T.M.; Krumholz, H.M.; Shah, N.D. Trends in Drug Utilization, Glycemic Control, and Rates of Severe Hypoglycemia, 2006–2013. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beard, H.A.; Markides, K.S.; Al Ghatrif, M.; Kuo, Y.F.; Raji, M.A. Trends in diabetes medication use and prevalence of geriatric syndromes in older Mexican Americans from 1993/1994 to 2004/2005. Ann. Pharmacother. 2010, 44, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, D.H.; Rungby, J.; Thomsen, R.W. Nationwide trends in glucose-lowering drug use, Denmark, 1999–2014. Clin. Epidemiol. 2016, 8, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, G.C.; Sehgal, N.L.; Moloney, R.M.; Stafford, R.S. National trends in treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, 1994–2007. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 2088–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, S.C.; Chan, Y.Y.; Kao Yang, Y.H.; Lin, S.J.; Hung, M.J.; Chien, R.N.; Lai, C.C.; Lai, E.C. The Chang Gung Research Database—A multi-institutional electronic medical records database for real-world epidemiological studies in Taiwan. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2019, 28, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.L.; Liang, C.K.; Yin, C.H.; Lin, Y.T.; Lee, C.C.; Chen, N.C. Corrigendum to ‘Effects of Socioeconomic Status on Alzheimer Disease Mortality in Taiwan’ [The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 28 (2020) 205–216]. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2020, 28, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundararajan, V.; Henderson, T.; Perry, C.; Muggivan, A.; Quan, H.; Ghali, W.A. New ICD-10 version of the Charlson comorbidity index predicted in-hospital mortality. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2004, 57, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasheen, W.P.; Cordier, T.; Gumpina, R.; Haugh, G.; Davis, J.; Renda, A. Charlson Comorbidity Index: ICD-9 Update and ICD-10 Translation. Am. Health Drug Benefits 2019, 12, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaewput, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Varothai, N.; Sirirungreung, A.; Rangsin, R.; Bathini, T.; Mao, M.A.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Prevalence and associated factors of hospitalization for dysglycemia among elderly type 2 diabetes patients: A nationwide study. World J. Diabetes 2019, 10, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, P.P.; Strachan, M.W.; Frier, B.M.; Butcher, I.; Deary, I.J.; Price, J.F.; Edinburgh Type 2 Diabetes Study Investigators. Severe hypoglycaemia and late-life cognitive ability in older people with Type 2 diabetes: The Edinburgh Type 2 Diabetes Study. Diabet. Med. 2012, 29, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Seong, J.M.; Kim, J. Risk of hospitalization for hypoglycemia among older Korean people with diabetes mellitus: Interactions between treatment modalities and comorbidities. Medicine 2016, 95, e5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattishent, K.; Loke, Y.K. Bi-directional interaction between hypoglycaemia and cognitive impairment in elderly patients treated with glucose-lowering agents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Araki, A.; Ito, H. Diabetes mellitus and geriatric syndromes. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2009, 9, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, S.V.; Taylor, P.J.; Shields, B.M.; Hattersley, A.T.; Hamilton, W. Are we missing hypoglycaemia? Elderly patients with insulin-treated diabetes present to primary care frequently with non-specific symptoms associated with hypoglycaemia. Prim. Care Diabetes 2018, 12, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.E.; Kim, K.A.; Son, K.J.; Song, S.O.; Park, K.H.; Park, S.H.; Nam, J.Y. Trends and risk factors in severe hypoglycemia among individuals with type 2 diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 178, 108946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, J.V.; Roseberry, S.; Rivas, J.A.; Cauthon, K.A.B. Hypoglycemia in Older People with Type 2 Diabetes: Prevention and Treatment Strategies for Outpatient and Long-Term Care Facility Settings. Sr. Care Pharm. 2021, 36, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeRoith, D.; Biessels, G.J.; Braithwaite, S.S.; Casanueva, F.F.; Draznin, B.; Halter, J.B.; Hirsch, I.B.; McDonnell, M.E.; Molitch, M.E.; Murad, M.H.; et al. Treatment of Diabetes in Older Adults: An Endocrine Society* Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 1520–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zammitt, N.N.; Frier, B.M. Hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes: Pathophysiology, frequency, and effects of different treatment modalities. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2948–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsiki, N.; Kotsa, K.; Stoian, A.P.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Hypoglycaemia and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Patients with Diabetes. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 5637–5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, C.T.; Gellad, W.F.; Good, C.B.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.; Mor, M.; Fine, M.J. Tight glycemic control and use of hypoglycemic medications in older veterans with type 2 diabetes and comorbid dementia. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbatecola, A.M.; Bo, M.; Barbagallo, M.; Incalzi, R.A.; Pilotto, A.; Bellelli, G.; Maggi, S.; Paolisso, G.; Italian Society of Gerontology and Geriatrics (SIGG), Florence, Italy. Severe hypoglycemia is associated with antidiabetic oral treatment compared with insulin analogs in nursing home patients with type 2 diabetes and dementia: Results from the DIMORA study. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 349.e7–349.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, E.; Wongrakpanich, S.; Munshi, M.N. Diabetes Management in the Elderly. Diabetes Spectr. 2018, 31, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Variables | n, (%) |
|---|---|
| Patients, number | 3877 |
| Gender | |
| Male | 1454 (37.5%) |
| Female | 2423 (62.5%) |
| Age (years) | 77.5 (8.9) |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | |
| 0 | 664 (17.1%) |
| 1 | 893 (23.0%) |
| ≥2 | 2320 (59.9%) |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.04 ± 1.36 |
| HbA1c (%) | |
| value ≤ 7 | 2350 (60.6%) |
| 7 < value ≤ 9 | 1235 (31.9%) |
| value > 9 | 292 (7.5%) |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 90.14 ± 30.70 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | |
| Not available | 889 (22.9%) |
| <70 | 748 (19.3%) |
| 70–100 | 1276 (32.9%) |
| ≥100 | 964 (24.9%) |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 156.99 ± 34.23 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | |
| Not available | 836 (21.6%) |
| <200 | 2625 (67.7%) |
| ≥200 | 416 (10.7%) |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.42 ± 1.41 |
| Creatinine (normal range men: 0.57–1.02, women: 0.68–1.19) (mg/dL) | |
| Not available | 486 (12.5%) |
| Within range | 1462 (37.7%) |
| Above range | 1510 (38.9%) |
| Under range | 419 (10.8%) |
| e-GFR (mL/min/1,73 m2) | 66.64 ± 39.18 |
| e-GFR (mL/min/1,73 m2) | |
| Not available | 486 (12.5%) |
| ≤60 | 1432 (36.9%) |
| >60 | 1959 (50.5%) |
| Systemic disease | n (%) |
| Acute myocardial infarction | 199 (5.1%) |
| Congestive heart failure | 410 (10.6%) |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 90 (2.3%) |
| Cerebral vascular accident | 1352 (34.9%) |
| Pulmonary disease | 642 (16.6%) |
| Peptic ulcer | 931 (24.0%) |
| Liver disease | 416 (10.7%) |
| Paraplegia | 79 (2.0%) |
| Renal disease | 1432 (36.9%) |
| Cancer | 489 (12.6%) |
| Antidiabetic medication | n (%) |
| Metformin | 1474 (38.0%) |
| Insulin | 1205 (31.1%) |
| Sulfonylureas | 1250 (32.2%) |
| α-glucosidases inhibitors | 525 (13.5%) |
| Thiazolidinediones | 198 (5.1%) |
| DPP-4 inhibitors | 1081 (27.9%) |
| GLP-1 receptor agonists | 19 (0.5%) |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | 67 (1.7%) |
| Meglitinides | 304 (7.8%) |
| Combinations of oral blood glucose lowering drugs | 1105 (28.5%) |
| Variables | Hypoglycemia | No Hypoglycemia | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, number | 494 | 3383 | |
| Female | 319 (64.6%) | 2104 (62.2%) | 0.307 |
| Age (years) | 77.1 (8.8) | 77.6 (8.9) | 0.122 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | <0.001 | ||
| 0 | 21 (4.3%) | 643 (19%) | |
| 1 | 62 (12.6%) | 831 (24.6%) | |
| ≥2 | 441 (83.2%) | 1909 (56.4%) | |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.96 ± 1.35 | 7.06 ± 1.36 | 0.140 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 83.86 ± 30.82 | 91.42 ± 30.62 | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 151.06 ± 38.10 | 162.47 ± 37.13 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.94 ± 1.89 | 1.33 ± 1.31 | <0.001 |
| Metformin | 120 (24.3%) | 1354 (40.0%) | <0.001 |
| Insulin | 310 (62.8%) | 895 (26.5%) | <0.001 |
| Sulfonylureas | 180 (36.4%) | 1070 (31.6%) | 0.033 |
| α-glucosidases inhibitors | 85 (17.2%) | 440 (13.0%) | 0.011 |
| Thiazolidinediones | 42 (8.5%) | 156 (4.6%) | <0.001 |
| DPP-4 inhibitors | 142 (28.7%) | 939 (27.8%) | 0.647 |
| GLP-1 receptor agonists | 1 (0.2%) | 18 (0.5%) | 0.327 |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | 6 (1.2%) | 61 (1.8%) | 0.348 |
| Meglitinides | 51 (10.3%) | 253 (7.5%) | 0.028 |
| Combinations of oral blood glucose lowering drugs | 159 (32.2%) | 946 (28.0%) | 0.052 |
| Acute myocardial infarction | 48 (9.7%) | 151 (4.5%) | <0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 92 (18.6%) | 318 (9.4%) | <0.001 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 18 (3.6%) | 72 (2.1%) | 0.037 |
| Cerebral vascular accident | 225 (45.6%) | 1127 (33.3%) | <0.001 |
| Pulmonary disease | 118 (23.9%)) | 524 (15.5%) | <0.001 |
| Peptic ulcer | 203 (41.1%) | 728 (21.5%) | <0.001 |
| Liver disease | 74 (15.0%) | 342 (10.1%) | 0.001 |
| Paraplegia | 9 (1.8%) | 70 (2.1%) | 0.716 |
| Renal disease | 281 (56.9%) | 1151 (34.0%) | <0.001 |
| Cancer | 87 (17.6%) | 402 (11.9%) | <0.001 |
| Factors | Crude Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Male | Ref. | ||
| Female | 1.11 | 0.91–1.35 | 0.307 |
| Age (years) | 0.99 | 0.97–1.00 | 0.142 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | |||
| 0 | Ref. | ||
| 1 | 2.28 | 1.38–3.79 | 0.001 |
| ≥2 | 6.59 | 4.21–10.31 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 0.95 | 0.88–1.02 | 0.140 |
| HbA1c (%) | |||
| value ≤ 7 | Ref. | ||
| 7 < value ≤ 9 | 0.92 | 0.75–1.14 | 0.454 |
| 9 < value | 0.90 | 0.63–1.31 | 0.591 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | |||
| NA | Ref. | ||
| <70 | 1.25 | 0.97–1.61 | 0.089 |
| 70–100 | 0.82 | 0.65–1.05 | 0.113 |
| >100 | 0.50 | 0.37–0.67 | <0.0001 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | |||
| NA | Ref. | ||
| <200 | 0.92 | 0.75–1.11 | 0.377 |
| ≥200 | 0.49 | 0.31–0.77 | 0.002 |
| Creatinine (normal range men: 0.57–1.02, women: 0.68–1.19) (mg/dL) | |||
| NA | Ref. | ||
| Within range | 0.50 | 0.38–0.65 | <0.0001 |
| Above range | 1.05 | 0.84–1.32 | 0.665 |
| Under range | 0.49 | 0.33–0.73 | 0.0004 |
| e-GFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | |||
| NA | Ref. | ||
| ≤60 | 1.07 | 0.86–1.34 | 0.549 |
| >60 | 0.46 | 0.36–0.60 | <0.0001 |
| Metformin | 0.48 | 0.39–0.60 | <0.0001 |
| Insulin | 4.68 | 3.84–5.71 | <0.0001 |
| Sulfonylurea | 1.24 | 1.02–1.51 | 0.033 |
| α-glucosidases inhibitor | 1.39 | 1.08–1.79 | 0.011 |
| Thiazolidinedione | 1.92 | 1.35–2.74 | 0.0003 |
| DPP-4 inhibitors | 1.05 | 0.85–1.29 | 0.647 |
| GLP-1 receptor agonist | 0.38 | 0.05–2.85 | 0.346 |
| SGLT2 inhibitor | 0.67 | 0.29–1.56 | 0.353 |
| Meglitinide | 1.43 | 1.04–1.96 | 0.028 |
| Combinations of oral blood glucose lowering drugs | 1.22 | 1.00–1.50 | 0.052 |
| Acute myocardial infarction | 2.30 | 1.64–3.23 | <0.0001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 2.21 | 1.71–2.84 | <0.0001 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 1.74 | 1.03–2.94 | 0.039 |
| Cerebral vascular accident | 1.67 | 1.38–2.03 | <0.0001 |
| Pulmonary disease | 1.71 | 1.36–2.15 | <0.0001 |
| Peptic ulcer | 2.54 | 2.09–3.10 | <0.0001 |
| Liver disease | 1.57 | 1.19–2.05 | 0.0012 |
| Paraplegia | 0.88 | 0.44–1.77 | 0.717 |
| Renal disease | 2.98 | 2.46–3.62 | <0.0001 |
| Cancer | 1.59 | 1.23–2.04 | 0.0004 |
| Factors | Adjusted Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | |||
| 0 | Ref. | ||
| 1 | 2.21 | 1.32–3.71 | 0.0027 |
| ≥2 | 4.76 | 2.99–7.56 | <0.0001 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | |||
| NA | Ref. | ||
| <70 | 1.12 | 0.76–1.67 | 0.561 |
| 70–100 | 0.84 | 0.57–1.22 | 0.353 |
| >100 | 0.60 | 0.38–0.95 | 0.030 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | |||
| NA | Ref. | ||
| <200 | 1.28 | 0.91–1.80 | 0.161 |
| ≥200 | 0.99 | 0.54–1.81 | 0.984 |
| Creatinine (normal range men: 0.57–1.02, women: 0.68–1.19) (mg/dL) | |||
| NA | Ref. | ||
| Within range | 0.63 | 0.46–0.85 | 0.0023 |
| Above range | 0.91 | 0.69–1.18 | 0.462 |
| Under range | 0.60 | 0.39–0.91 | 0.018 |
| Metformin | 0.75 | 0.59–0.96 | 0.023 |
| Insulin | 4.64 | 3.73–5.78 | <0.001 |
| Sulfonylureas | 1.46 | 1.17–1.82 | 0.0007 |
| α-glucosidases inhibitors | 1.24 | 0.94–1.64 | 0.132 |
| Thiazolidinediones | 2.04 | 1.37–3.05 | 0.0004 |
| Meglitinides | 1.24 | 0.88–1.76 | 0.219 |
| Combinations of oral blood glucose lowering drugs | 1.92 | 1.51–2.45 | <0.0001 |
| HbA1c | Events | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤5 | 5 (0.12%) | Ref | ||
| 5 < value ≤ 6 | 112 (2.89%) | 1.15 | 0.44–3.00 | 0.777 |
| 6 < value ≤ 7 | 191 (4.93%) | 0.97 | 0.37–2.50 | 0.942 |
| 7 < value ≤ 8 | 106 (2.73%) | 0.94 | 0.36–2.45 | 0.893 |
| 8 < value ≤ 9 | 45 (1.16%) | 0.97 | 0.36–2.62 | 0.959 |
| 9 < value ≤ 10 | 19 (0.49%) | 1.05 | 0.37–3.02 | 0.927 |
| >10 | 16 (0.41%) | 0.96 | 0.30–3.02 | 0.941 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, N.-C.; Chen, C.-L.; Shen, F.-C. The Risk Factors of Severe Hypoglycemia in Older Patients with Dementia and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12010067
Chen N-C, Chen C-L, Shen F-C. The Risk Factors of Severe Hypoglycemia in Older Patients with Dementia and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(1):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12010067
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Nai-Ching, Chien-Liang Chen, and Feng-Chih Shen. 2022. "The Risk Factors of Severe Hypoglycemia in Older Patients with Dementia and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 1: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12010067
APA StyleChen, N.-C., Chen, C.-L., & Shen, F.-C. (2022). The Risk Factors of Severe Hypoglycemia in Older Patients with Dementia and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(1), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12010067






