PSI-Guided Mandible-First Orthognathic Surgery: Maxillo-Mandibular Position Accuracy and Vertical Dimension Adjustability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Planning and Surgery
2.2. Outcome Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Rigid Body Transformation Outcomes
3.2. Cephalometric Outcomes
3.3. Correlation Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borba, A.M.; Borges, A.H.; Cé, P.S.; Venturi, B.A.; Homem, M.G.; Miloro, M. Mandible-first sequence in bimaxillary orthognathic surgery: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badiali, G.; Bevini, M.; Ruggiero, F.; Cercenelli, L.; Lovero, E.; De Simone, E.; Rucci, P.; Bianchi, A.; Marchetti, C. Validation of a patient-specific system for mandible-first bimaxillary surgery: Ramus and implant positioning precision assessment and guide design comparison. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Shen, S.; Jiang, W.; Li, J.; Jiang, T.; Xia, J.; Wang, X. A new approach of splint-less orthognathic surgery using a personalized orthognathic surgical guide system: A preliminary study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suojanen, J.; Leikola, J.; Stoor, P. The use of patient-specific implants in orthognathic surgery: A series of 30 mandible sagittal split osteotomy patients. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tominaga, K.; Habu, M.; Tsurushima, H.; Takahashi, O.; Yoshioka, I. CAD/CAM splint based on soft tissue 3D simulation for treatment of facial asymmetry. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 38, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swennen, G.R.; Schutyser, F.; Hausamen, J.-E. Three-Dimensional Cephalometry. In Three-Dimensional Cephalometry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Baan, F.; Liebregts, J.; Xi, T.; Schreurs, R.; De Koning, M.; Bergé, S.; Maal, T. A New 3D Tool for Assessing the Accuracy of Bimaxillary Surgery: The OrthoGnathicAnalyser. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazzoni, S.; Bianchi, A.; Schiariti, G.; Badiali, G.; Marchetti, C. Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing Cutting Guides and Customized Titanium Plates Are Useful in Upper Maxilla Waferless Repositioning. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 73, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraeima, J.; Jansma, J.; Schepers, R. Splintless surgery: Does patient-specific CAD-CAM osteosynthesis improve accuracy of Le Fort I osteotomy? Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 54, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suojanen, J.; Leikola, J.; Stoor, P. The use of patient-specific implants in orthognathic surgery: A series of 32 maxillary osteotomy patients. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 1913–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, C.; Xu, H.; Tian, Y.; Yang, X.; Luo, E.; Bai, D. Precise control of maxillary multidirectional movement in Le Fort I osteotomy using a surgical guiding device. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoldelli, C.; Vandersteen, C.; Dassonville, O.; Santini, J. Dental occlusal-surface-supported titanium guide to assist cutting and drilling in mandibular bilateral sagittal split osteotomy. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 119, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunso, J.; Franco, M.; Constantinescu, T.; Barbier, L.; Santamaría, J.A.; Alvarez, J. Custom-Machined Miniplates and Bone-Supported Guides for Orthognathic Surgery: A New Surgical Procedure. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 74, 1061.e1–1061.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, J.; Murphy, C.; Ikeagwuani, O.; Adley, C.; Kearns, G. The fate of titanium miniplates and screws used in maxillofacial surgery: A 10 year retrospective study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 38, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhayer, A.; Piffkó, J.; Lippold, C.; Segatto, E. Accuracy of virtual planning in orthognathic surgery: A systematic review. Head Face Med. 2020, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokbro, K.; Liebregts, J.; Baan, F.; Bell, R.B.; Maal, T.; Thygesen, T.; Xi, T. Does Mandible-First Sequencing Increase Maxillary Surgical Accuracy in Bimaxillary Procedures? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 77, 1882–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tankersley, A.C.; Nimmich, M.C.; Battan, A.; Griggs, J.A.; Caloss, R. Comparison of the Planned Versus Actual Jaw Movement Using Splint-Based Virtual Surgical Planning: How Close Are We at Achieving the Planned Outcomes? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 77, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Riu, G.; Virdis, P.I.; Meloni, S.M.; Lumbau, A.; Vaira, L.A. Accuracy of computer-assisted orthognathic surgery. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokbro, K.; Aagaard, E.; Torkov, P.; Bell, R.; Thygesen, T. Surgical accuracy of three-dimensional virtual planning: A pilot study of bimaxillary orthognathic procedures including maxillary segmentation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
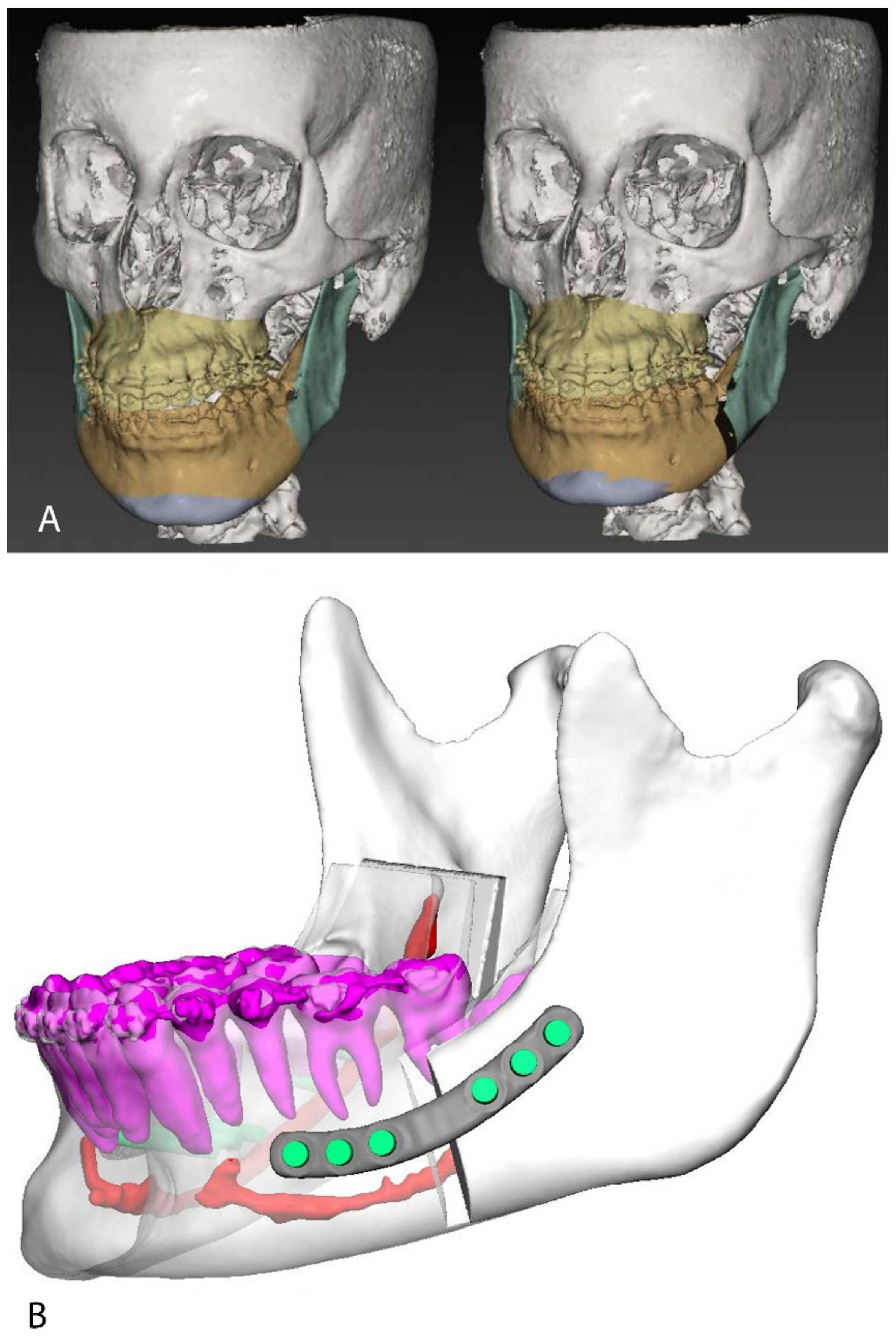


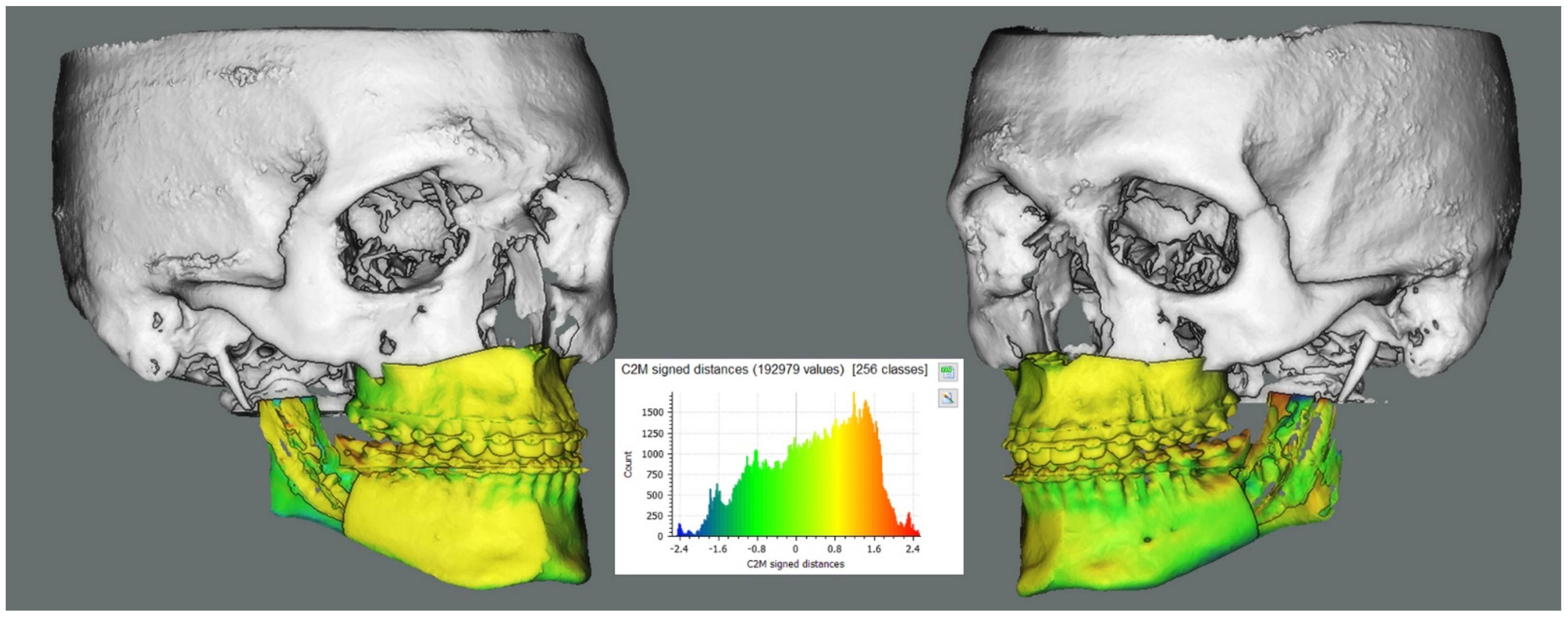
| Considered Cephalometric Measurements | |
|---|---|
| A/Sag | Distance of point A from the sagittal plane (maxillary deviation) |
| B/Sag | Distance of point B from the sagittal plane (mandibular deviation). |
| Pog/Sag | Distance of pogonion from the sagittal plane (mental deviation). |
| UIs/Sag | Distance from upper incisors midpoint to sagittal plane. |
| LIs/Sag | Distance in millimetres from Lower Incisors midpoint to Sagittal plane. |
| △Go/Sag | Difference between left and right gonion to sagittal plane distances in millimetres. |
| △U3/Sag | Difference between left and right upper canine to sagittal plane distances. |
| △U6/Sag | Difference between left and right first upper molars to sagittal plane distances. |
| A/McNamara | Distance of point A from McNamara plane. |
| Incisal Protrusion | Distance in millimetres of the upper incisors’ midpoint to plane A (plane parallel to McNamara plane passing though point A). |
| Pitch | Pitch Abs. | Roll | Roll Abs. | Yaw | Yaw Abs. | Tot. Ang. Displ. | Lateral | Lat. Abs. | Ant.-Post. | A-P Abs. | Vertical | Vert. Abs. | Total Trans | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maxilla | Average | −0.90 | 1.54 | −0.06 | 0.93 | −0.02 | 0.91 | 2.33 | −0.08 | 1.05 | −1.45 | 1.70 | −0.78 | 1.14 | 2.58 |
| St.Dev. | 1.65 | 1.06 | 1.21 | 0.75 | 1.20 | 0.76 | 0.91 | 1.28 | 0.70 | 1.87 | 1.64 | 1.37 | 1.08 | 1.70 | |
| Median | −0.92 | 1.52 | 0.00 | 0.78 | −0.28 | 0.72 | 2.31 | −0.23 | 0.99 | −1.27 | 1.39 | −0.78 | 0.93 | 2.03 | |
| IQR | 2.50 | 1.53 | 1.55 | 0.60 | 1.50 | 0.69 | 1.41 | 1.86 | 0.99 | 2.46 | 2.38 | 1.07 | 0.77 | 1.83 | |
| Mandible | Average | 0.83 | 1.53 | 0.39 | 0.96 | 0.73 | 1.13 | 2.55 | −0.32 | 1.14 | −1.26 | 1.49 | −0.61 | 1.05 | 2.51 |
| St.Dev. | 1.88 | 1.34 | 1.24 | 0.85 | 1.33 | 0.99 | 1.20 | 1.50 | 1.00 | 1.78 | 1.59 | 1.51 | 1.23 | 1.81 | |
| Median | 0.36 | 1.20 | 0.46 | 0.75 | 0.41 | 0.75 | 2.34 | −0.18 | 0.93 | −0.84 | 0.99 | −0.26 | 0.71 | 2.02 | |
| IQR | 2.59 | 1.52 | 1.04 | 0.72 | 2.00 | 1.38 | 1.30 | 1.54 | 0.91 | 1.41 | 1.18 | 1.05 | 1.20 | 1.35 |
| A/Sag | A/Sag Abs. | B/Sag | B/Sag Abs. | Pog/Sag | Pog/Sag Abs. | Δ Go/Sag | Δ Go/Sag Abs. | UIs/Sag | UIs/Sag Abs | LIs/Sag | LIs/Sag Abs | Δ U3/Sag | Δ U3/Sag Abs | Δ U6/Sag | Δ U6/Sag Abs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | 0.52 | 0.96 | 0.86 | 1.31 | 1.00 | 1.67 | −0.56 | 2.40 | 0.88 | 1.20 | 0.71 | 1.02 | 0.17 | 2.89 | −0.39 | 2.10 |
| St.Dev. | 1.17 | 0.83 | 1.36 | 0.91 | 1.91 | 1.33 | 3.26 | 2.23 | 1.30 | 0.99 | 1.29 | 1.04 | 3.55 | 1.97 | 2.70 | 1.68 |
| Median | 0.30 | 0.83 | 1.10 | 1.19 | 1.04 | 1.50 | −0.48 | 1.35 | 0.71 | 1.02 | 0.44 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 2.78 | −0.54 | 1.65 |
| IQR | 1.30 | 1.15 | 1.41 | 1.12 | 2.38 | 2.16 | 2.65 | 2.90 | 1.30 | 1.01 | 0.82 | 1.01 | 5.40 | 3.58 | 3.09 | 1.85 |
| Correlated Values | Correlated Values | Correlated Values | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mx pitch | corr. coeff. | −0.008 | Md pitch | corr. coeff. | −0.037 | Mx yaw | corr. coeff. | 0.613 |
| A/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.97 | B/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.871 | Md yaw | Sig.2-tail | 0.002 |
| Mx pitch | corr. coeff. | −0.221 | Md pitch | corr. coeff. | −0.167 | Mx lat | corr. coeff. | 0.581 |
| B/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.323 | Pog/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.459 | Md lat | Sig.2-tail | 0.005 |
| Mx pitch | corr. coeff. | −0.317 | Md pitch | corr. coeff. | 0.084 | Mx a-p | corr. coeff. | 0.819 |
| Pog/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.151 | Δ Go/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.71 | Md a-p | Sig.2-tail | 0 |
| Mx pitch | corr. coeff. | 0.018 | Md pitch | corr. coeff. | 0.169 | Mx vert | corr. coeff. | 0.648 |
| Δ Go/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.938 | UIs/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.453 | Md vert | Sig.2-tail | 0.001 |
| Mx pitch | corr. coeff. | 0.318 | Md pitch | corr. coeff. | −0.109 | Mx pitch | corr. coeff. | −0.461 |
| UIs/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.149 | Lis/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.629 | Md a-p | Sig.2-tail | 0.031 |
| Mx pitch | corr. coeff. | −0.053 | Md pitch | corr. coeff. | −0.012 | Mx pitch | corr. coeff. | −0.522 |
| Lis/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.816 | Δ U3/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.958 | Md vert | Sig.2-tail | 0.013 |
| Mx pitch | corr. coeff. | 0.22 | Md pitch | corr. coeff. | 0.047 | Md pitch | corr. coeff. | −0.542 |
| Δ U3/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.326 | Δ U6/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.836 | Mx A-P | Sig.2-tail | 0.009 |
| Mx pitch | corr. coeff. | 0.307 | Mx pitch | corr. coeff. | 0.523 | Md pitch | corr. coeff. | −0.612 |
| Δ U6/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.165 | Md pitch | Sig.2-tail | 0.012 | Mx vert | Sig.2-tail | 0.002 |
| Md pitch | corr. coeff. | 0.02 | Mx roll | corr. coeff. | 0.729 | A/McN | corr. coeff. | −0.519 |
| A/Sag | Sig.2-tail | 0.93 | Md roll | Sig.2-tail | 0 | Inc. Prot. | Sig.2-tail | 0.013 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Badiali, G.; Bevini, M.; Lunari, O.; Lovero, E.; Ruggiero, F.; Bolognesi, F.; Feraboli, L.; Bianchi, A.; Marchetti, C. PSI-Guided Mandible-First Orthognathic Surgery: Maxillo-Mandibular Position Accuracy and Vertical Dimension Adjustability. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111237
Badiali G, Bevini M, Lunari O, Lovero E, Ruggiero F, Bolognesi F, Feraboli L, Bianchi A, Marchetti C. PSI-Guided Mandible-First Orthognathic Surgery: Maxillo-Mandibular Position Accuracy and Vertical Dimension Adjustability. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(11):1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111237
Chicago/Turabian StyleBadiali, Giovanni, Mirko Bevini, Ottavia Lunari, Elisa Lovero, Federica Ruggiero, Federico Bolognesi, Liliana Feraboli, Alberto Bianchi, and Claudio Marchetti. 2021. "PSI-Guided Mandible-First Orthognathic Surgery: Maxillo-Mandibular Position Accuracy and Vertical Dimension Adjustability" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 11: 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111237
APA StyleBadiali, G., Bevini, M., Lunari, O., Lovero, E., Ruggiero, F., Bolognesi, F., Feraboli, L., Bianchi, A., & Marchetti, C. (2021). PSI-Guided Mandible-First Orthognathic Surgery: Maxillo-Mandibular Position Accuracy and Vertical Dimension Adjustability. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(11), 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111237








