Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Serum Adhesion Molecules, and Serum Oxidative Stress in Patients with Acute Traumatic Brain Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
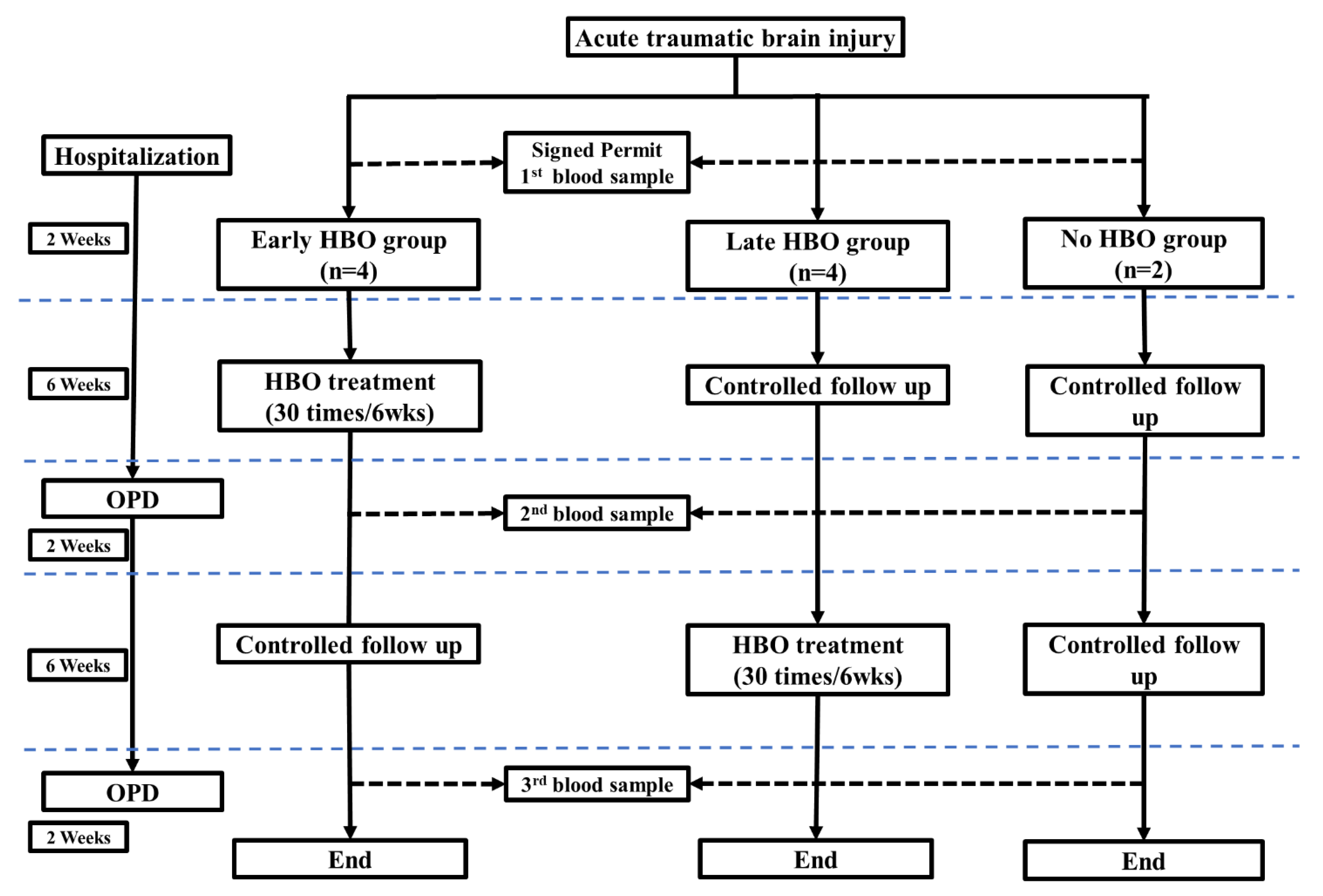
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
2.3. Blood Sampling, Assessment of Oxidative Stress and Adhesion Molecules
2.3.1. Serum Glutathione (GSH) Levels
2.3.2. Serum Thiobarbituric Acid-Reactive Substances (TBARS) Levels
2.3.3. Serum Soluble Intercellular Cell Adhesion-Molecule-1 (sICAM-1) Levels, and Serum Soluble Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (sVCAM-1) Levels
2.4. Clinical Manifestations
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Patients
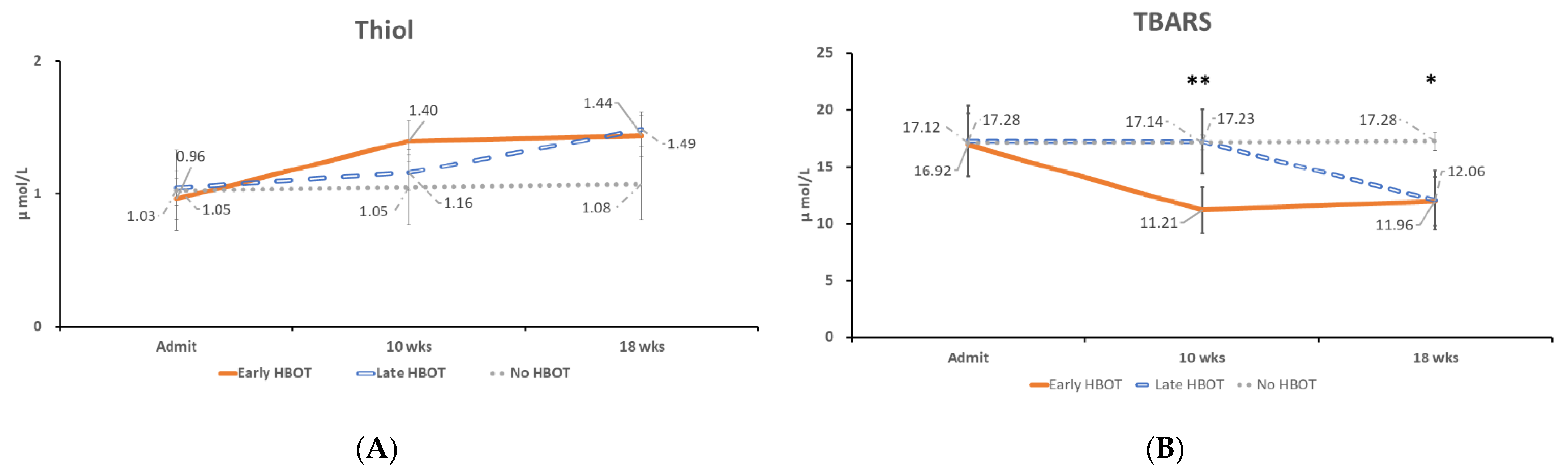
3.2. The Time Course of Oxidative Stress and Serum Adhesion Molecules Concentration Changes
4. Discussion
4.1. Oxidative Stress in TBI Patients
4.2. Adhesion Molecules in TBI Patients
4.3. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lenzlinger, P.M.; Morganti-Kossmann, M.C.; Laurer, H.L.; McIntosh, T.K. The duality of the inflammatory response to traumatic brain injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2001, 24, 169–181. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Jenkins, L.W.; Kochanek, P.M.; Clark, R.S. Bench-to-bedside review: Apoptosis/programmed cell death triggered by traumatic brain injury. Crit. Care 2005, 9, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, Z.Z.; Li, F.; Maiese, K. Oxidative stress in the brain: Novel cellular targets that govern survival during neurodegenerative disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2005, 75, 207–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Xue, W.; Dong, L.; Hu, X.; Huang, D.; Wang, K. Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside suppresses napdh oxidative stress to mitigate apoptosis and autophagy induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 3913981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandravanshi, L.P.; Gupta, R.; Shukla, R.K. Developmental neurotoxicity of arsenic: Involvement of oxidative stress and mitochondrial functions. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 186, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, V.; Shaw, S.; Jayatilleke, E.; Stopler-Kasdan, T. Most free-radical injury is iron-related: It is promoted by iron, hemin, holoferritin and vitamin c, and inhibited by desferoxamine and apoferritin. Stem Cells 1994, 12, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floyd, R.A.; Carney, J.M. Free radical damage to protein and DNA: Mechanisms involved and relevant observations on brain undergoing oxidative stress. Ann. Neurol. 1992, 32, S22–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontos, H.A.; Wei, E.P. Superoxide production in experimental brain injury. J. Neurosurg. 1986, 64, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, E.D.; Andrus, P.K.; Yonkers, P.A. Brain hydroxyl radical generation in acute experimental head injury. J. Neurochem. 1993, 60, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.L.; Andrus, P.K.; Zhang, J.R.; Hall, E.D. Direct measurement of hydroxyl radicals, lipid peroxidation, and blood-brain barrier disruption following unilateral cortical impact head injury in the rat. J. Neurotrauma 1994, 11, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.M.; Geng, L.; Cahill-Smith, S.; Liu, F.; Douglas, G.; McKenzie, C.A.; Smith, C.; Brooks, G.; Channon, K.M.; Li, J.M. Nox2 contributes to age-related oxidative damage to neurons and the cerebral vasculature. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3374–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, L.; Du, Y.; He, J.; Liao, L.; Xiong, K.; Yi, C.X.; et al. The main molecular mechanisms underlying methamphetamine- induced neurotoxicity and implications for pharmacological treatment. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.J.; Tran, H.Q.; Nguyen, P.T.; Jeong, J.H.; Nah, S.Y.; Jang, C.G.; Nabeshima, T.; Kim, H.C. Role of mitochondria in methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity: Involvement in oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and pro-apoptosis-a review. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, D.J.; Capela, J.P.; Feio-Azevedo, R.; Teixeira-Gomes, A.; Bastos Mde, L.; Carvalho, F. Mitochondria: Key players in the neurotoxic effects of amphetamines. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1695–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Liang, J.; Yan, J.X.; Ye, Y.C.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, C.; Sun, H.T.; Chen, F.; Tu, Y.; Li, X.H. Tbhq improved neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury by inhibiting the overactivation of astrocytes. Brain Res. 2020, 1739, 146818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Goh, S.J.; Tng, P.Y.; Deng, Y.Y.; Ling, E.A.; Moochhala, S. Systemic inflammatory response following acute traumatic brain injury. Front. Biosc. 2009, 14, 3795–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, S.C.; Smith, D.H. Coagulopathy in traumatic brain injury. Neurocrit. Care 2004, 1, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnardt, S. Innate immunity and neuroinflammation in the cns: The role of microglia in toll-like receptor-mediated neuronal injury. Glia 2010, 58, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhind, S.G.; Crnko, N.T.; Baker, A.J.; Morrison, L.J.; Shek, P.N.; Scarpelini, S.; Rizoli, S.B. Prehospital resuscitation with hypertonic saline-dextran modulates inflammatory, coagulation and endothelial activation marker profiles in severe traumatic brain injured patients. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bednar, M.M.; Gross, C.E.; Howard, D.B.; Lynn, M. Neutrophil activation in acute human central nervous system injury. Neurol. Res. 1997, 19, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, M.J.; Thrash, J.C.; Walter, B. The cellular response in neuroinflammation: The role of leukocytes, microglia and astrocytes in neuronal death and survival. Clin. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 6, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadhim, H.J.; Duchateau, J.; Sebire, G. Cytokines and brain injury: Invited review. J. Intensive Care Med. 2008, 23, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Benveniste, E.N. Adhesion molecule expression and regulation on cells of the central nervous system. J. Neuroimmunol. 1999, 98, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, S.G.; Piva, S. Central nervous system inflammation. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. Suppl. 2008, 42, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balabanov, R.; Goldman, H.; Murphy, S.; Pellizon, G.; Owen, C.; Rafols, J.; Dore-Duffy, P. Endothelial cell activation following moderate traumatic brain injury. Neurol. Res. 2001, 23, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, H.F.; Chavakis, T. Leukocyte-endothelial interactions in inflammation. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Wang, P.M.; Lin, Y.J.; Kwan, A.L.; Lin, W.C.; Tsai, N.W.; Cheng, B.C.; Chang, W.N.; Su, B.Y.; Kung, C.T.; et al. Serum adhesion molecules, outcome and neuro-psychological function in acute traumatic brain injury patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 423, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeating, E.G.; Andrews, P.J.; Mascia, L. The relationship of soluble adhesion molecule concentrations in systemic and jugular venous serum to injury severity and outcome after traumatic brain injury. Anesth. Analg. 1998, 86, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.C.; Liu, L.J.; Liu, B. Neuroprotection of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in sub-acute traumatic brain injury: Not by immediately improving cerebral oxygen saturation and oxygen partial pressure. Neural. Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chazalviel, L.; Haelewyn, B.; Degoulet, M.; Blatteau, J.E.; Vallee, N.; Risso, J.J.; Besnard, S.; Abraini, J.H. Hyperbaric oxygen increases tissue-plasminogen activator-induced thrombolysis in vitro, and reduces ischemic brain damage and edema in rats subjected to thromboembolic brain ischemia. Med. Gas. Res. 2016, 6, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Rockswold, S.B.; Rockswold, G.L.; Zaun, D.A.; Zhang, X.; Cerra, C.E.; Bergman, T.A.; Liu, J. A prospective, randomized clinical trial to compare the effect of hyperbaric to normobaric hyperoxia on cerebral metabolism, intracranial pressure, and oxygen toxicity in severe traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 112, 1080–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, G.; Cifu, D.; Baugh, L.; Carne, W.; Profenna, L. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen on symptoms after mild traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 2606–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussi-Gross, R.; Golan, H.; Fishlev, G.; Bechor, Y.; Volkov, O.; Bergan, J.; Friedman, M.; Hoofien, D.; Shlamkovitch, N.; Ben-Jacob, E.; et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can improve post concussion syndrome years after mild traumatic brain injury—randomized prospective trial. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, W.C.; Franke, L.M.; Cifu, D.X.; Hart, B.B. Randomized, sham-controlled, feasibility trial of hyperbaric oxygen for service members with postconcussion syndrome: Cognitive and psychomotor outcomes 1 week postintervention. Neurorehabil. Neural. Repair. 2014, 28, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daugherty, W.P.; Levasseur, J.E.; Sun, D.; Rockswold, G.L.; Bullock, M.R. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on cerebral oxygenation and mitochondrial function following moderate lateral fluid-percussion injury in rats. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 101, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palzur, E.; Zaaroor, M.; Vlodavsky, E.; Milman, F.; Soustiel, J.F. Neuroprotective effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in brain injury is mediated by preservation of mitochondrial membrane properties. Brain Res. 2008, 1221, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palzur, E.; Vlodavsky, E.; Mulla, H.; Arieli, R.; Feinsod, M.; Soustiel, J.F. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for reduction of secondary brain damage in head injury: An animal model of brain contusion. J. Neurotrauma. 2004, 21, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harch, P.G.; Kriedt, C.; Van Meter, K.W.; Sutherland, R.J. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves spatial learning and memory in a rat model of chronic traumatic brain injury. Brain Res. 2007, 1174, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.P.; O’Neill, B.; Haddon, W., Jr.; Long, W.B. The injury severity score: A method for describing patients with multiple injuries and evaluating emergency care. J. Trauma. 1974, 14, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Sakakima, H.; Dhammu, T.S.; Shunmugavel, A.; Im, Y.B.; Gilg, A.G.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, I. S-nitrosoglutathione reduces oxidative injury and promotes mechanisms of neurorepair following traumatic brain injury in rats. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyurin, V.A.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Borisenko, G.G.; Sokolova, T.V.; Ritov, V.B.; Quinn, P.J.; Rose, M.; Kochanek, P.; Graham, S.H.; Kagan, V.E. Oxidative stress following traumatic brain injury in rats: Quantitation of biomarkers and detection of free radical intermediates. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 2178–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bayir, H.; Kagan, V.E.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Tyurin, V.; Ruppel, R.A.; Adelson, P.D.; Graham, S.H.; Janesko, K.; Clark, R.S.; Kochanek, P.M. Assessment of antioxidant reserves and oxidative stress in cerebrospinal fluid after severe traumatic brain injury in infants and children. Pediatr. Res. 2002, 51, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayir, H.; Adelson, P.D.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Shore, P.; Lai, Y.; Brown, D.; Janesko-Feldman, K.L.; Kagan, V.E.; Kochanek, P.M. Therapeutic hypothermia preserves antioxidant defenses after severe traumatic brain injury in infants and children. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, H.A.; Wozniak, A.; Drewa, G.; Wozniak, B. Enhanced lipid peroxidation processes in patients after brain contusion. J. Neurotrauma 2001, 18, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giddings, J.C. Soluble adhesion molecules in inflammatory and vascular diseases. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 406–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, B. Immune cell entry into the central nervous system: Involvement of adhesion molecules and chemokines. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 274, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeating, E.G.; Andrews, P.J. Cytokines and adhesion molecules in acute brain injury. Br. J. Anaesth. 1998, 80, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.M.; Cryer, H.G.; Abraham, E. Elevated levels of soluble icam-1 correlate with the development of multiple organ failure in severely injured trauma patients. J. Trauma 1994, 37, 100–109, discussion 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, M.J.; Carlos, T.M.; Dixon, C.E.; Schiding, J.K.; Clark, R.S.; Baum, E.; Yan, H.Q.; Marion, D.W.; Kochanek, P.M. Effect of traumatic brain injury in mice deficient in intercellular adhesion molecule-1: Assessment of histopathologic and functional outcome. J. Neurotrauma 1999, 16, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Early HBOT (N = 4) | Late HBOT (N = 4) | No HBOT (N = 2) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 53 ± 10.3 | 41 ± 10.9 | 44 ± 4 | 0.708 |
| BMI | 26.4 ± 1.8 | 25.2 ± 1.1 | 22.6 ± 1.2 | 0.346 |
| Male | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0.223 |
| Underlying diseases | ||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.153 |
| Hypertension | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0.435 |
| Coronary artery disease | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Alcoholism | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Smoking | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Clinical feature at presentation | ||||
| Brief unconsciousness | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0.368 |
| Motor deficits | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0.153 |
| Posttraumatic amnesia | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0.153 |
| GCS at presentation | 15 ± 0 | 8.5 ± 0.9 | 15 ± 0 | ≤0.001 |
| Injury Severity Score at presentation | 19.3 ± 2.1 | 19.8 ± 3.7 | 22.5 ± 11.5 | 0.9 |
| Laboratory data at presentation | ||||
| WBC (×103/mL) | 11.4 ± 1.9 | 17.3 ± 2.6 | 15.1 ± 1.8 | 0.223 |
| Hemoglobin (gm/dl) | 12.8 ± 1.0 | 12.1 ± 1.2 | 13.9 ± 0.1 | 0.611 |
| Hematocrit | 38.9 ± 3.1 | 36.9 ± 3.7 | 42.0 ± 0.5 | 0.655 |
| Platelet counts (×103/mL) | 230.2 ± 14.9 | 303.8 ± 37.5 | 228.5 ± 10.5 | 0.167 |
| Prothrombin Time (PT) | 10.5 ± 0.38 | 10.8 ± 0.43 | 11.1 ± 0.15 | 0.701 |
| Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) | 23.7 ± 0.5 | 25.7 ± 1.9 | 26.4 ± 0.7 | 0.432 |
| Brain Imagies Findings at presentation | ||||
| Parenchymal contusion hemorrhage | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0.223 |
| Epidural hemorrhage | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0.732 |
| Subdural hemorrhage | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0.435 |
| Traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0.153 |
| Depressed skull fracture | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Pneumocranium | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Neurosurgical intervention | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.732 |
| Oxidative Stress at presentation | ||||
| Glutathione (μmol/L) | 0.96 ± 0.15 | 1.05 ± 0.16 | 1.03 ± 0.17 | 0.916 |
| TBARS (μmol/L) | 16.92 ± 1.40 | 17.28 ± 1.55 | 17.12 ± 0.19 | 0.98 |
| Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule at presentation | ||||
| sICAM-1 (ng/mL) | 216 ± 15 | 246 ± 17 | 201 ± 13 | 0.306 |
| sVCAM-1 (ng/mL) | 696 ± 33 | 690 ± 16 | 732 ± 34 | 0.548 |
| Acute neurosurgical complications | ||||
| Newly onset of neurological deficit | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Deterioration of consciousness | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Posttraumatic seizure | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| GOS at 10 wks follow-up | 5 ± 0 | 4.5 ± 0.29 | 5 ± 0 | 0.193 |
| GOS at 18 wks follow-up | 5 ± 0 | 4.5 ± 0.29 | 5 ± 0 | 0.193 |
| Days of ICU stay | 2.8 ± 1.4 | 3.8 ± 1.3 | 3 ± 0 | 0.848 |
| Days of Hospitalization | 11.8 ± 1.3 | 25 ± 5 | 9 ± 4 | 0.134 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.-C.; Wang, P.-M.; Lin, Y.-T.; Tsai, N.-W.; Lai, Y.-R.; Kung, C.-T.; Su, C.-M.; Lu, C.-H. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Serum Adhesion Molecules, and Serum Oxidative Stress in Patients with Acute Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11100985
Wang H-C, Wang P-M, Lin Y-T, Tsai N-W, Lai Y-R, Kung C-T, Su C-M, Lu C-H. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Serum Adhesion Molecules, and Serum Oxidative Stress in Patients with Acute Traumatic Brain Injury. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(10):985. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11100985
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hung-Chen, Pei-Ming Wang, Yu-Tsai Lin, Nai-Wen Tsai, Yun-Ru Lai, Chia-Te Kung, Chih-Min Su, and Cheng-Hsien Lu. 2021. "Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Serum Adhesion Molecules, and Serum Oxidative Stress in Patients with Acute Traumatic Brain Injury" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 10: 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11100985
APA StyleWang, H.-C., Wang, P.-M., Lin, Y.-T., Tsai, N.-W., Lai, Y.-R., Kung, C.-T., Su, C.-M., & Lu, C.-H. (2021). Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Serum Adhesion Molecules, and Serum Oxidative Stress in Patients with Acute Traumatic Brain Injury. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(10), 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11100985







