Management of COVID-19 Patients in the Emergency Department
Abstract
:1. Introduction
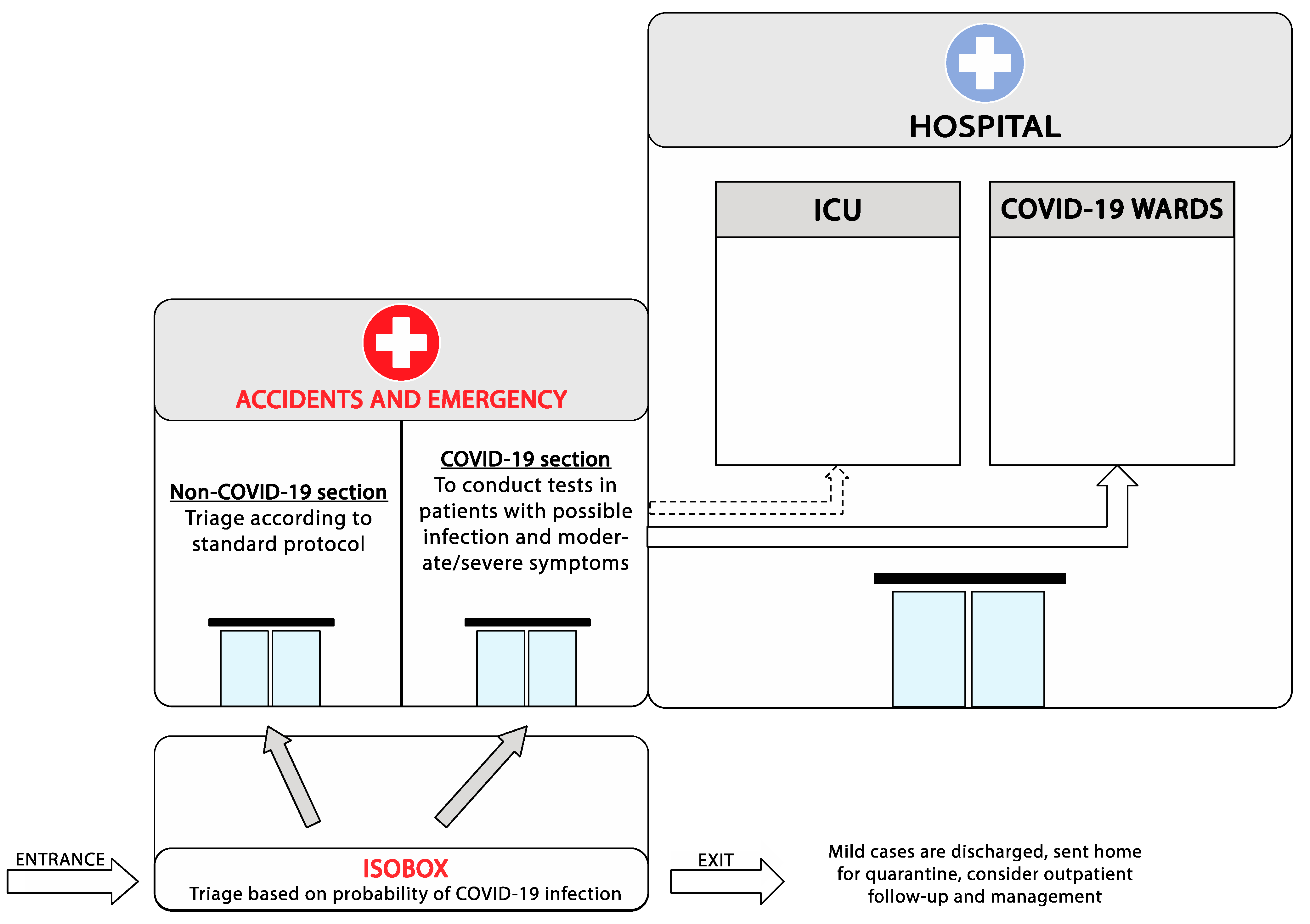
2. Triage of Suspected COVID-19 Patients
3. Severity of Illness at ED Presentation
4. Predicting Deterioration Risk
5. Correlation of Imaging Findings with Prognosis
6. Indications for Chest CT in the ED
7. The Role of Lung Ultrasound in COVID-19 Disease
8. Lab Tests Associated with Worse Prognosis
9. Confirmation of SARS-CoV-2 in the ED
10. Intubation of COVID-19 Patients in the ED
10.1. Time of Endotracheal Intubation
10.2. Indications for Endotracheal Intubation
11. Initial Ventilator Settings in the ED
12. Therapeutic Approaches in the ED
13. Monoclonal Antibody Infusion in the ED
14. Impact of Vaccination on ED Care
15. ED-Based COVID-19 Vaccination
16. Evidence Based Recommendations
17. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greece COVID: 593,668 Cases and 13,702 Deaths—Worldometer. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/country/greece/ (accessed on 3 September 2021).
- The Lancet Global Health. Publishing in the Time of COVID-19. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Deng, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Liu, E.; Zheng, X. Analysis and Suggestions for the Preview and Triage Screening of Children with Suspected COVID-19 Outside the Epidemic Area of Hubei Province. Transl. Pediatr. 2020, 9, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zowawi, H.M.; Alenazi, T.H.; AlOmaim, W.S.; Wazzan, A.; Alsufayan, A.; Hasanain, R.A.; Aldibasi, O.S.; Althawadi, S.; Altamimi, S.A.; Mutabagani, M.; et al. Portable RT-PCR System: A Rapid and Scalable Diagnostic Tool for COVID-19 Testing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e03004-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griswold, D.P.; Gempeler, A.; Kolias, A.G.; Hutchinson, P.J.; Rubiano, A.M. Personal Protective Equipment for Reducing the Risk of COVID-19 Infection among Healthcare Workers Involved in Emergency Trauma Surgery during the Pandemic: An Umbrella Review Protocol. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e045598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, Y.; Frenkel Nir, Y.; Ironi, A.; Englard, H.; Regev-Yochay, G.; Rahav, G.; Afek, A.; Grossman, E. Emergency Department Triage in the Era of COVID-19: The Sheba Medical Center Experience. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. IMAJ 2020, 22, 470–475. [Google Scholar]
- Soltan, A.A.S.; Kouchaki, S.; Zhu, T.; Kiyasseh, D.; Taylor, T.; Hussain, Z.B.; Peto, T.; Brent, A.J.; Eyre, D.W.; Clifton, D.A. Rapid Triage for COVID-19 Using Routine Clinical Data for Patients Attending Hospital: Development and Prospective Validation of an Artificial Intelligence Screening Test. Lancet Digit. Health 2021, 3, e78–e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, C.; Alsafi, Z.; O’Neill, N.; Khan, M.; Kerwan, A.; Al-Jabir, A.; Iosifidis, C.; Agha, R. World Health Organization Declares Global Emergency: A Review of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19). Int. J. Surg. 2020, 76, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Castrillo, L.; Petrino, R.; Leach, R.; Dodt, C.; Behringer, W.; Khoury, A.; Sabbe, M. European Society for Emergency Medicine Position Paper on Emergency Medical Systems’ Response to COVID-19. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Emerg. Med. 2020, 27, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.W.; Burleson, S.L.; Heimann, M.A.; Crosby, J.C.; Swanson, J.; Gibson, C.B.; Greene, C. An Adapted Emergency Department Triage Algorithm for the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Am. Coll. Emerg. Physicians Open 2020, 1, 1374–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical Spectrum. Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/overview/clinical-spectrum/ (accessed on 3 September 2021).
- Bouadma, L.; Lescure, F.-X.; Lucet, J.-C.; Yazdanpanah, Y.; Timsit, J.-F. Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infections: Practical Considerations and Management Strategy for Intensivists. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beals, J.; Barnes, J.J.; Durand, D.J.; Rimar, J.M.; Donohue, T.J.; Hoq, S.M.; Belk, K.W.; Amin, A.N.; Rothman, M.J. Stratifying Deterioration Risk by Acuity at Admission Offers Triage Insights for Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients. Crit. Care Explor. 2021, 3, e0400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Tu, G.-W.; Ju, M.-J.; Yu, S.-J.; Zheng, J.-L.; Ma, G.-G.; Liu, K.; Ma, J.-F.; Yu, K.-H.; Xue, Y.; et al. Comparison of CRB-65 and Quick Sepsis-Related Organ Failure Assessment for Predicting the Need for Intensive Respiratory or Vasopressor Support in Patients with COVID-19. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 647–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volff, M.; Tonon, D.; Bourenne, J.; Simeone, P.; Velly, L. No Added Value of the Modified NEWS Score to Predict Clinical Deterioration in COVID-19 Patients. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2020, 39, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, M.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Lv, T.; Li, S.; Liu, P.; et al. CURB-65 May Serve as a Useful Prognostic Marker in COVID-19 Patients within Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Yao, N.; Qiu, Y. The Comparison of REMS and MEWS for COVID-19 Patients Less Than 65 Years of Age. Acad. Emerg. Med. Off. J. Soc. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2020, 27, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucan, E.S.; Ozgen Alpaydin, A.; Ozuygur, S.S.; Ercan, S.; Unal, B.; Sayiner, A.A.; Ergan, B.; Gokmen, N.; Savran, Y.; Kilinc, O.; et al. Pneumonia Severity Indices Predict Prognosis in Coronavirus Disease-2019. Respir. Med. Res. 2021, 79, 100826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, S.R.; Ho, A.; Pius, R.; Buchan, I.; Carson, G.; Drake, T.M.; Dunning, J.; Fairfield, C.J.; Gamble, C.; Green, C.A.; et al. Risk Stratification of Patients Admitted to Hospital with COVID-19 Using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: Development and Validation of the 4C Mortality Score. BMJ 2020, 370, m3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.K.; Harrison, E.M.; Ho, A.; Docherty, A.B.; Knight, S.R.; van Smeden, M.; Abubakar, I.; Lipman, M.; Quartagno, M.; Pius, R.; et al. Development and Validation of the ISARIC 4C Deterioration Model for Adults Hospitalised with COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanne, J.P.; Bai, H.; Bernheim, A.; Chung, M.; Haramati, L.B.; Kallmes, D.F.; Little, B.P.; Rubin, G.D.; Sverzellati, N. COVID-19 Imaging: What We Know Now and What Remains Unknown. Radiology 2021, 299, E262–E279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempere-González, A.; Llaneras-Artigues, J.; Pinal-Fernández, I.; Cañas-Ruano, E.; Orozco-Gálvez, O.; Domingo-Baldrich, E.; Michelena, X.; Meza, B.; García-Vives, E.; Gil-Vila, A.; et al. Radiography-Based Triage for COVID-19 in the Emergency Department in a Spanish Cohort of Patients. Med. Clin. 2021, S0025-7753(21)00319–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo Marin, B.; Aghagoli, G.; Lavine, K.; Yang, L.; Siff, E.J.; Chiang, S.S.; Salazar-Mather, T.P.; Dumenco, L.; Savaria, M.C.; Aung, S.N.; et al. Predictors of COVID-19 Severity: A Literature Review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Abedi, A.; Balakrishnan, S.; Gholamrezanezhad, A. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Imaging Reporting and Data System (COVID-RADS) and Common Lexicon: A Proposal Based on the Imaging Data of 37 Studies. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4930–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, G.D.; Ryerson, C.J.; Haramati, L.B.; Sverzellati, N.; Kanne, J.P.; Raoof, S.; Schluger, N.W.; Volpi, A.; Yim, J.-J.; Martin, I.B.K.; et al. The Role of Chest Imaging in Patient Management during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Multinational Consensus Statement From the Fleischner Society. Chest 2020, 158, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, S.; Abedi, A.; Balakrishnan, S.; Gholamrezanezhad, A. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Systematic Review of Imaging Findings in 919 Patients. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revel, M.-P.; Parkar, A.P.; Prosch, H.; Silva, M.; Sverzellati, N.; Gleeson, F.; Brady, A.; European Society of Radiology (ESR) and the European Society of Thoracic Imaging (ESTI). COVID-19 Patients and the Radiology Department—Advice from the European Society of Radiology (ESR) and the European Society of Thoracic Imaging (ESTI). Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4903–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mouhat, B.; Besutti, M.; Bouiller, K.; Grillet, F.; Monnin, C.; Ecarnot, F.; Behr, J.; Capellier, G.; Soumagne, T.; Pili-Floury, S.; et al. Elevated D-Dimers and Lack of Anticoagulation Predict PE in Severe COVID-19 Patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2001811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, H.; Wang, M.; He, N.; Lv, Z.; Cui, L. Lung Ultrasound Findings in Patients with Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 216, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Li, Q.; Du, H.; Kang, W.; Lian, J.; Yuan, L. Lung Ultrasound Findings in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargani, L.; Soliman-Aboumarie, H.; Volpicelli, G.; Corradi, F.; Pastore, M.C.; Cameli, M. Why, When, and How to Use Lung Ultrasound during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Enthusiasm and Caution. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 21, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, A.O.; Costa, R.M.; Uzun, R.; Fraga, A.M.A.; Ribeiro, J.D.; Marson, F.A.L. Applicability of Lung Ultrasound in COVID-19 Diagnosis and Evaluation of the Disease Progression: A Systematic Review. Pulmonology 2021, S2531-0437(21)00050–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichter, Y.; Topilsky, Y.; Taieb, P.; Banai, A.; Hochstadt, A.; Merdler, I.; Gal Oz, A.; Vine, J.; Goren, O.; Cohen, B.; et al. Lung Ultrasound Predicts Clinical Course and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1873–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanforlin, A.; Strapazzon, G.; Falk, M.; Gallina, V.; Viteritti, A.; Valzolgher, L.; La Guardia, M.; Ferro, F.; Pagani, L.; Vezzali, N. Lung Ultrasound in the Emergency Department for Early Identification of COVID-19 Pneumonia. Respir. Int. Rev. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 100, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.; Butler, R.; Aujayeb, A. Lung Ultrasound in the COVID-19 Pandemic. Postgrad. Med. J. 2021, 97, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar, S.; Lecourtois, A.; Diouf, M.; Goldberg, E.; Bourbon, C.; Arnaud, E.; Domisse, L.; Dupont, H.; Gosset, P. The Association of Lung Ultrasound Images with COVID-19 Infection in an Emergency Room Cohort. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggiali, E.; Dacrema, A.; Bastoni, D.; Tinelli, V.; Demichele, E.; Mateo Ramos, P.; Marcianò, T.; Silva, M.; Vercelli, A.; Magnacavallo, A. Can Lung US Help Critical Care Clinicians in the Early Diagnosis of Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pneumonia? Radiology 2020, 295, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, C.; Daly, J.; Carley, S. Combatting COVID-19: Is Ultrasound an Important Piece in the Diagnostic Puzzle? Emerg. Med. J. EMJ 2020, 37, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagöz, A.; Sağlam, C.; Demirbaş, H.B.; Korkut, S.; Ünlüer, E.E. Accuracy of Bedside Lung Ultrasound as a Rapid Triage Tool for Suspected COVID-19 Cases. Ultrasound Q. 2020, 36, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonsenso, D.; Raffaelli, F.; Tamburrini, E.; Biasucci, D.G.; Salvi, S.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Scambia, G.; Lanzone, A.; Testa, A.C.; et al. Clinical Role of Lung Ultrasound for Diagnosis and Monitoring of COVID-19 Pneumonia in Pregnant Women. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 56, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porpora, M.G.; Merlino, L.; Masciullo, L.; D’Alisa, R.; Brandolino, G.; Galli, C.; De Luca, C.; Pecorini, F.; Fonsi, G.B.; Mingoli, A.; et al. Does Lung Ultrasound Have a Role in the Clinical Management of Pregnant Women with SARS CoV2 Infection? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yin, L.; Patel, J.; Tang, L.; Huang, Y. The Inflammatory Markers of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) and Adolescents Associated with COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 4358–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, I.; Pranata, R. Lymphopenia in Severe Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19): Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Intensive Care 2020, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.A.; Haridas, N.; Belgundi, P.; Jose, W.M. A Systematic Review of Clinical and Laboratory Parameters Associated with Increased Severity among COVID-19 Patients. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2021, 15, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Feng, X.; Jiang, C.; Mi, S.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. Correlation between White Blood Cell Count at Admission and Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, M.; Mansouritorghabeh, H. D-Dimer Level in COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2020, 13, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Ding, J.; Huang, Q.; Tang, Y.-Q.; Wang, Q.; Miao, H. Lymphopenia Predicts Disease Severity of COVID-19: A Descriptive and Predictive Study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, C.; Cheng, L.; Yan, S.; Li, H.; Li, Y. Diagnostic Value of D-Dimer in COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Off. J. Int. Acad. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2021, 27, 10760296211010976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.; Giannitsis, E.; Jaffe, A.S.; Huber, K.; Mair, J.; Cullen, L.; Hammarsten, O.; Mills, N.L.; Möckel, M.; Krychtiuk, K.; et al. Cardiovascular Biomarkers in Patients with COVID-19. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2021, 10, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydon, M.; Chevalier, K.; Al Tabaa, O.; Hamroun, S.; Delettre, A.-S.; Thomas, M.; Herrou, J.; Riviere, E.; Mariette, X. Myositis as a Manifestation of SARS-CoV-2. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, annrheumdis-2020-217573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalkias, A.; Mouzarou, A.; Samara, E.; Xanthos, T.; Ischaki, E.; Pantazopoulos, I. Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor: A Biomarker for Predicting Complications and Critical Care Admission of COVID-19 Patients. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 24, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovina, N.; Akinosoglou, K.; Eugen-Olsen, J.; Hayek, S.; Reiser, J.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J. Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor (SuPAR) as an Early Predictor of Severe Respiratory Failure in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, T.U.; Shadid, H.R.; Blakely, P.; O’Hayer, P.; Berlin, H.; Pan, M.; Zhao, P.; Zhao, L.; Pennathur, S.; Pop-Busui, R.; et al. Soluble Urokinase Receptor (SuPAR) in COVID-19-Related AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2020, 31, 2725–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Marca, A.; Capuzzo, M.; Paglia, T.; Roli, L.; Trenti, T.; Nelson, S.M. Testing for SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): A Systematic Review and Clinical Guide to Molecular and Serological in-Vitro Diagnostic Assays. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2020, 41, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardian, Y.; Kosasih, H.; Karyana, M.; Neal, A.; Lau, C.-Y. Review of Current COVID-19 Diagnostics and Opportunities for Further Development. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 615099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouliou, D.S.; Gourgoulianis, K.I. False-Positive and False-Negative COVID-19 Cases: Respiratory Prevention and Management Strategies, Vaccination, and Further Perspectives. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2021, 15, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Buitrago-Garcia, D.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Zambrano-Achig, P.; Del Campo, R.; Ciapponi, A.; Sued, O.; Martinez-García, L.; Rutjes, A.W.; Low, N.; et al. False-Negative Results of Initial RT-PCR Assays for COVID-19: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucirka, L.M.; Lauer, S.A.; Laeyendecker, O.; Boon, D.; Lessler, J. Variation in False-Negative Rate of Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction-Based SARS-CoV-2 Tests by Time Since Exposure. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, O.; Martiny, D.; Rochas, O.; van Belkum, A.; Kozlakidis, Z. Considerations for Diagnostic COVID-19 Tests. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmans, B.J.M.; Reusken, C.B.E.M.; van Oudheusden, A.J.G.; Godeke, G.-J.; Bonačić Marinović, A.A.; de Vries, E.; Kluiters-de Hingh, Y.C.M.; Vingerhoets, R.; Berrevoets, M.A.H.; Verweij, J.J.; et al. Test, Trace, Isolate: Evidence for Declining SARS-CoV-2 PCR Sensitivity in a Clinical Cohort. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 101, 115392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissleder, R.; Lee, H.; Ko, J.; Pittet, M.J. COVID-19 Diagnostics in Context. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eabc1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert-Niclot, S.; Cuffel, A.; Le Pape, S.; Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Morand-Joubert, L.; Roque-Afonso, A.-M.; Le Goff, J.; Delaugerre, C. Evaluation of a Rapid Diagnostic Assay for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen in Nasopharyngeal Swabs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00977-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegerlehner, S.; Suter-Riniker, F.; Jent, P.; Bittel, P.; Nagler, M. Diagnostic Accuracy of a SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test in Real-Life Clinical Settings. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2021, 109, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC Labs. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/resources/antibody-tests-guidelines.html (accessed on 3 September 2021).
- Alhazzani, W.; Møller, M.H.; Arabi, Y.M.; Loeb, M.; Gong, M.N.; Fan, E.; Oczkowski, S.; Levy, M.M.; Derde, L.; Dzierba, A.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: Guidelines on the Management of Critically Ill Adults with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 854–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, M.-Z.; Huang, Y.-G.; Ma, W.-H.; Xue, Z.-G.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Gong, Y.-H.; Che, L.; Chinese Society of Anesthesiology Task Force on Airway Management. Expert Recommendations for Tracheal Intubation in Critically Ill Patients with Noval Coronavirus Disease 2019. Chin. Med. Sci. J. 2020, 35, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cook, T.M.; El-Boghdadly, K.; McGuire, B.; McNarry, A.F.; Patel, A.; Higgs, A. Consensus Guidelines for Managing the Airway in Patients with COVID-19: Guidelines from the Difficult Airway Society, the Association of Anaesthetists the Intensive Care Society, the Faculty of Intensive Care Medicine and the Royal College of Anaesthetists. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.A.; Mosier, J.M.; Carlson, J.N.; Gibbs, M.A. Pragmatic Recommendations for Intubating Critically Ill Patients with Suspected COVID-19. J. Am. Coll. Emerg. Physicians Open 2020, 1, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewster, D.J.; Chrimes, N.; Do, T.B.; Fraser, K.; Groombridge, C.J.; Higgs, A.; Humar, M.J.; Leeuwenburg, T.J.; McGloughlin, S.; Newman, F.G.; et al. Consensus Statement: Safe Airway Society Principles of Airway Management and Tracheal Intubation Specific to the COVID-19 Adult Patient Group. Med. J. Aust. 2020, 212, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, J.J.; Gattinoni, L. Management of COVID-19 Respiratory Distress. JAMA 2020, 323, 2329–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, M.J.; Laghi, F.; Jubran, A. Caution about Early Intubation and Mechanical Ventilation in COVID-19. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papoutsi, E.; Giannakoulis, V.G.; Xourgia, E.; Routsi, C.; Kotanidou, A.; Siempos, I.I. Effect of Timing of Intubation on Clinical Outcomes of Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Non-Randomized Cohort Studies. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, A.; Yavorovskiy, A.; Verniero, L.; Landoni, G. Indications for Tracheal Intubation in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2021, 35, 1276–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasselli, G.; Cattaneo, E.; Florio, G.; Ippolito, M.; Zanella, A.; Cortegiani, A.; Huang, J.; Pesenti, A.; Einav, S. Mechanical Ventilation Parameters in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Scoping Review. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, B.M.; Ferguson, I.T.; Mohr, N.M.; Drewry, A.M.; Palmer, C.; Wessman, B.T.; Ablordeppey, E.; Keeperman, J.; Stephens, R.J.; Briscoe, C.C.; et al. Lung-Protective Ventilation Initiated in the Emergency Department (LOV-ED): A Quasi-Experimental, Before-After Trial. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2017, 70, 406–418.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattinoni, L.; Chiumello, D.; Caironi, P.; Busana, M.; Romitti, F.; Brazzi, L.; Camporota, L. COVID-19 Pneumonia: Different Respiratory Treatments for Different Phenotypes? Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhen, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wang, X.; Luo, H.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; et al. CT Imaging Features of Different Clinical Types of COVID-19 Calculated by AI System: A Chinese Multicenter Study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 5336–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; Beitler, J.R.; Brochard, L.; Calfee, C.S.; Ferguson, N.D.; Slutsky, A.S.; Brodie, D. COVID-19-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Is a Different Approach to Management Warranted? Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.C.; Ho, Y.-L.; Besen, B.A.M.P.; Malbouisson, L.M.S.; Taniguchi, L.U.; Mendes, P.V.; Costa, E.L.V.; Park, M.; Daltro-Oliveira, R.; Roepke, R.M.L.; et al. Protective Ventilation and Outcomes of Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: A Cohort Study. Ann. Intensive Care 2021, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.B.P.; Meade, M.O.; Slutsky, A.S.; Brochard, L.; Costa, E.L.V.; Schoenfeld, D.A.; Stewart, T.E.; Briel, M.; Talmor, D.; Mercat, A.; et al. Driving Pressure and Survival in the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haudebourg, A.-F.; Perier, F.; Tuffet, S.; de Prost, N.; Razazi, K.; Mekontso Dessap, A.; Carteaux, G. Respiratory Mechanics of COVID-19- versus Non-COVID-19-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, M.J.; Baldwin, M.R.; Abrams, D.; Jacobson, S.D.; Meyer, B.J.; Balough, E.M.; Aaron, J.G.; Claassen, J.; Rabbani, L.E.; Hastie, J.; et al. Epidemiology, Clinical Course, and Outcomes of Critically Ill Adults with COVID-19 in New York City: A Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenck, E.J.; Hoffman, K.; Goyal, P.; Choi, J.; Torres, L.; Rajwani, K.; Tam, C.W.; Ivascu, N.; Martinez, F.J.; Berlin, D.A. Respiratory Mechanics and Gas Exchange in COVID-19-Associated Respiratory Failure. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2020, 17, 1158–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; Del Sorbo, L.; Goligher, E.C.; Hodgson, C.L.; Munshi, L.; Walkey, A.J.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Amato, M.B.P.; Branson, R.; Brower, R.G.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society/European Society of Intensive Care Medicine/Society of Critical Care Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline: Mechanical Ventilation in Adult Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papazian, L.; Aubron, C.; Brochard, L.; Chiche, J.-D.; Combes, A.; Dreyfuss, D.; Forel, J.-M.; Guérin, C.; Jaber, S.; Mekontso-Dessap, A.; et al. Formal Guidelines: Management of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Del Sorbo, L.; Grieco, D.L.; Junhasavasdikul, D.; Rittayamai, N.; Soliman, I.; Sklar, M.C.; Rauseo, M.; Ferguson, N.D.; Fan, E.; et al. Potential for Lung Recruitment Estimated by the Recruitment-to-Inflation Ratio in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. A Clinical Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajjar, L.A.; da Silva Costa, I.B.S.; Rizk, S.I.; Biselli, B.; Gomes, B.R.; Bittar, C.S.; de Oliveira, G.Q.; de Almeida, J.P.; de Oliveira Bello, M.V.; Garzillo, C.; et al. Intensive Care Management of Patients with COVID-19: A Practical Approach. Ann. Intensive Care 2021, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepper, P.M.; Muellenbach, R.M. Mechanical Ventilation in Early COVID-19 ARDS. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 28, 100616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, S.; Long, B.; Koyfman, A.; Liang, S.Y. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): A Primer for Emergency Physicians. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 44, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yao, N.; Qiu, Y.; He, C. Predictive Performance of SOFA and QSOFA for In-Hospital Mortality in Severe Novel Coronavirus Disease. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 2074–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S.; et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19—Final Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remdesivir (Veklury) for COVID-19. Med. Lett. Drugs Ther. 2020, 62, 186–188.
- Chalmers, J.D.; Crichton, M.L.; Goeminne, P.C.; Cao, B.; Humbert, M.; Shteinberg, M.; Antoniou, K.M.; Ulrik, C.S.; Parks, H.; Wang, C.; et al. Management of Hospitalised Adults with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A European Respiratory Society Living Guideline. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2100048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RECOVERY Collaborative Group; Horby, P.; Lim, W.S.; Emberson, J.R.; Mafham, M.; Bell, J.L.; Linsell, L.; Staplin, N.; Brightling, C.; Ustianowski, A.; et al. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, L. Influence of Corticosteroid Dose on Viral Shedding Duration in Patients with COVID-19. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2021, 72, 1298–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RECOVERY Collaborative Group Tocilizumab in Patients Admitted to Hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): A Randomised, Controlled, Open-Label, Platform Trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 1637–1645. [CrossRef]
- REMAP-CAP Investigators; Gordon, A.C.; Mouncey, P.R.; Al-Beidh, F.; Rowan, K.M.; Nichol, A.D.; Arabi, Y.M.; Annane, D.; Beane, A.; van Bentum-Puijk, W.; et al. Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonists in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsburg, A.S.; Klugman, K.P. COVID-19 Pneumonia and the Appropriate Use of Antibiotics. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e1453–e1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulia, M.S.; Wolf, I.; Schulz, L.T.; Pop-Vicas, A.; Schwei, R.J.; Lindenauer, P.K. COVID-19: An Emerging Threat to Antibiotic Stewardship in the Emergency Department. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 21, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, A.; Kyriakoulis, K.G.; Dimakakos, E.; Poulakou, G.; Stergiou, G.S.; Syrigos, K. Thromboembolic Risk and Anticoagulant Therapy in COVID-19 Patients: Emerging Evidence and Call for Action. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 846–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moores, L.K.; Tritschler, T.; Brosnahan, S.; Carrier, M.; Collen, J.F.; Doerschug, K.; Holley, A.B.; Jimenez, D.; Le Gal, G.; Rali, P.; et al. Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of VTE in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 2020, 158, 1143–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spyropoulos, A.C.; Levy, J.H.; Ageno, W.; Connors, J.M.; Hunt, B.J.; Iba, T.; Levi, M.; Samama, C.M.; Thachil, J.; Giannis, D.; et al. Scientific and Standardization Committee Communication: Clinical Guidance on the Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2020, 18, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commissioner, O. Of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes Monoclonal Antibodies for Treatment of COVID-19. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-monoclonal-antibodies-treatment-covid-19 (accessed on 3 September 2021).
- Weinreich, D.M.; Sivapalasingam, S.; Norton, T.; Ali, S.; Gao, H.; Bhore, R.; Musser, B.J.; Soo, Y.; Rofail, D.; Im, J.; et al. REGN-COV2, a Neutralizing Antibody Cocktail, in Outpatients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, R.L.; Nirula, A.; Chen, P.; Boscia, J.; Heller, B.; Morris, J.; Huhn, G.; Cardona, J.; Mocherla, B.; Stosor, V.; et al. Effect of Bamlanivimab as Monotherapy or in Combination with Etesevimab on Viral Load in Patients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougan, M.; Nirula, A.; Azizad, M.; Mocherla, B.; Gottlieb, R.L.; Chen, P.; Hebert, C.; Perry, R.; Boscia, J.; Heller, B.; et al. Bamlanivimab plus Etesevimab in Mild or Moderate COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ash, J.; Leavitt, R.; Dietrich, T.; Schritter, S.; Wells, J.; Santarelli, A.; Ashurst, J. Real World Utilization of REGEN-COV2 at a Community Hospital. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 50, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, A.; Henley, S.J.; Mattocks, L.; Fernando, R.; Lansky, A.; Ahmad, F.B.; Adjemian, J.; Anderson, R.N.; Binder, A.M.; Carey, K.; et al. Decreases in COVID-19 Cases, Emergency Department Visits, Hospital Admissions, and Deaths Among Older Adults Following the Introduction of COVID-19 Vaccine—United States, September 6, 2020-May 1, 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, E.J.; Angulo, F.J.; McLaughlin, J.M.; Anis, E.; Singer, S.R.; Khan, F.; Brooks, N.; Smaja, M.; Mircus, G.; Pan, K.; et al. Impact and Effectiveness of MRNA BNT162b2 Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 Infections and COVID-19 Cases, Hospitalisations, and Deaths Following a Nationwide Vaccination Campaign in Israel: An Observational Study Using National Surveillance Data. Lancet 2021, 397, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantamneni, N. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Marginalized Populations in the United States: A Research Agenda. J. Vocat. Behav. 2020, 119, 103439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, M.A.; Moore, J.L.; Steege, L.M.; Koopman, R.J.; Belden, J.L.; Canfield, S.M.; Meadows, S.E.; Elliott, S.G.; Kim, M.S. Health Information Needs, Sources, and Barriers of Primary Care Patients to Achieve Patient-Centered Care: A Literature Review. Health Inform. J. 2016, 22, 992–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, M.J.; Moschella, P.; Duber, H.C.; Martin, D.R.; Benzoni, T.; Rothman, R.E.; Schechter-Perkins, E.M. Emergency Department-Based COVID-19 Vaccination: Where Do We Stand? Acad. Emerg. Med. Off. J. Soc. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2021, 28, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| First Author | Triaging Test | Population/Study Type | Outcome | Discriminatory Performance (ROC AUC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beals et al. [13] | Rothman index | 3499 COVID-19 patients (retrospective, multicenter study) | Identification of patients at admission with high risk for subsequent deterioration | 0.81–0.84 |
| Su et al. [14] | CRB-65, qSOFA | 116 COVID-19 patients (retrospective single center study) | Identification of patients who require intensive respiratory or vasopressor support | 0.81 ± 0.05 for CRB-65 0.70 ± 0.06 for qSOFA |
| Volff et al. [15] | NEWS, mNEWS | 363 COVID-19 patients (retrospective single center study) | Identification of patients at risk for clinical deterioration (ICU admission or death) | 0.74 for NEWS 0.72 for mNEWS |
| Guo et al. [16] | CURB-65 | 74 COVID-19 patients (retrospective single center study) | Identification of patients at risk for in-hospital death | 0.81 |
| Hu et al. [17] | MEWS, REMS | 105 COVID-19 patients (retrospective single center study) | Identification of patients at risk for in-hospital death | 0.677 for MEWS 0.833 for REMS |
| Ucan et al. [18] | PSI, CURB-65 A-DROP | 298 patients with probable or definitive COVID-19 (retrospective single center study) | Identification of patients at risk for in-hospital death and progression to severe disease | PSI: 0.873 for overall mortality & 0.697 for progression to severe COVID-19 CURB-65: 0.859 for overall mortality & 0.739 for progression to severe COVID-19 A-DROP: 0.875 for overall mortality & 0.660 for progression to severe COVID-19 |
| Triage |
|
| Illness severity |
|
| Deterioration risk prediction |
|
| Imaging |
|
| Laboratory tests |
|
| Intubation |
|
| Therapeutic approaches |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pantazopoulos, I.; Tsikrika, S.; Kolokytha, S.; Manos, E.; Porpodis, K. Management of COVID-19 Patients in the Emergency Department. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11100961
Pantazopoulos I, Tsikrika S, Kolokytha S, Manos E, Porpodis K. Management of COVID-19 Patients in the Emergency Department. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(10):961. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11100961
Chicago/Turabian StylePantazopoulos, Ioannis, Stamatoula Tsikrika, Stavroula Kolokytha, Emmanouil Manos, and Konstantinos Porpodis. 2021. "Management of COVID-19 Patients in the Emergency Department" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 10: 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11100961
APA StylePantazopoulos, I., Tsikrika, S., Kolokytha, S., Manos, E., & Porpodis, K. (2021). Management of COVID-19 Patients in the Emergency Department. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(10), 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11100961








