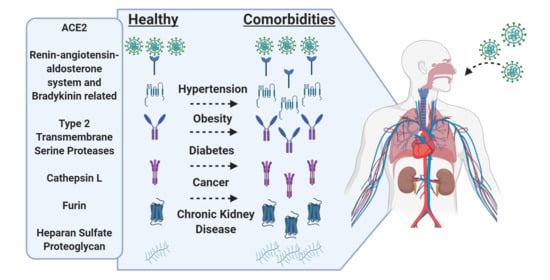
Impact of Comorbidities on SARS-CoV-2 Viral Entry-Related Genes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
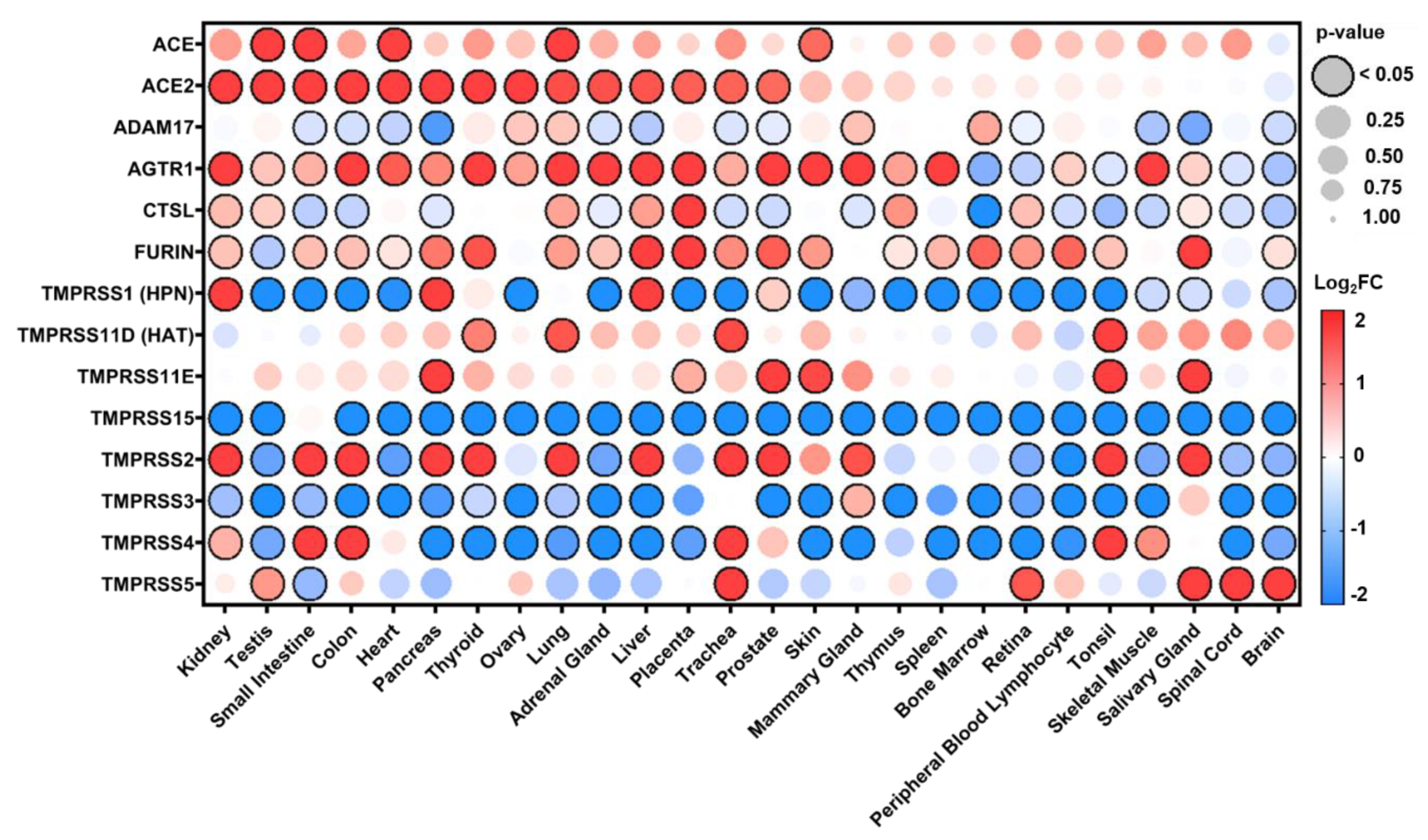
3.1. Distribution of Expression in Healthy Tissues
3.2. Expression in Common Comorbidities
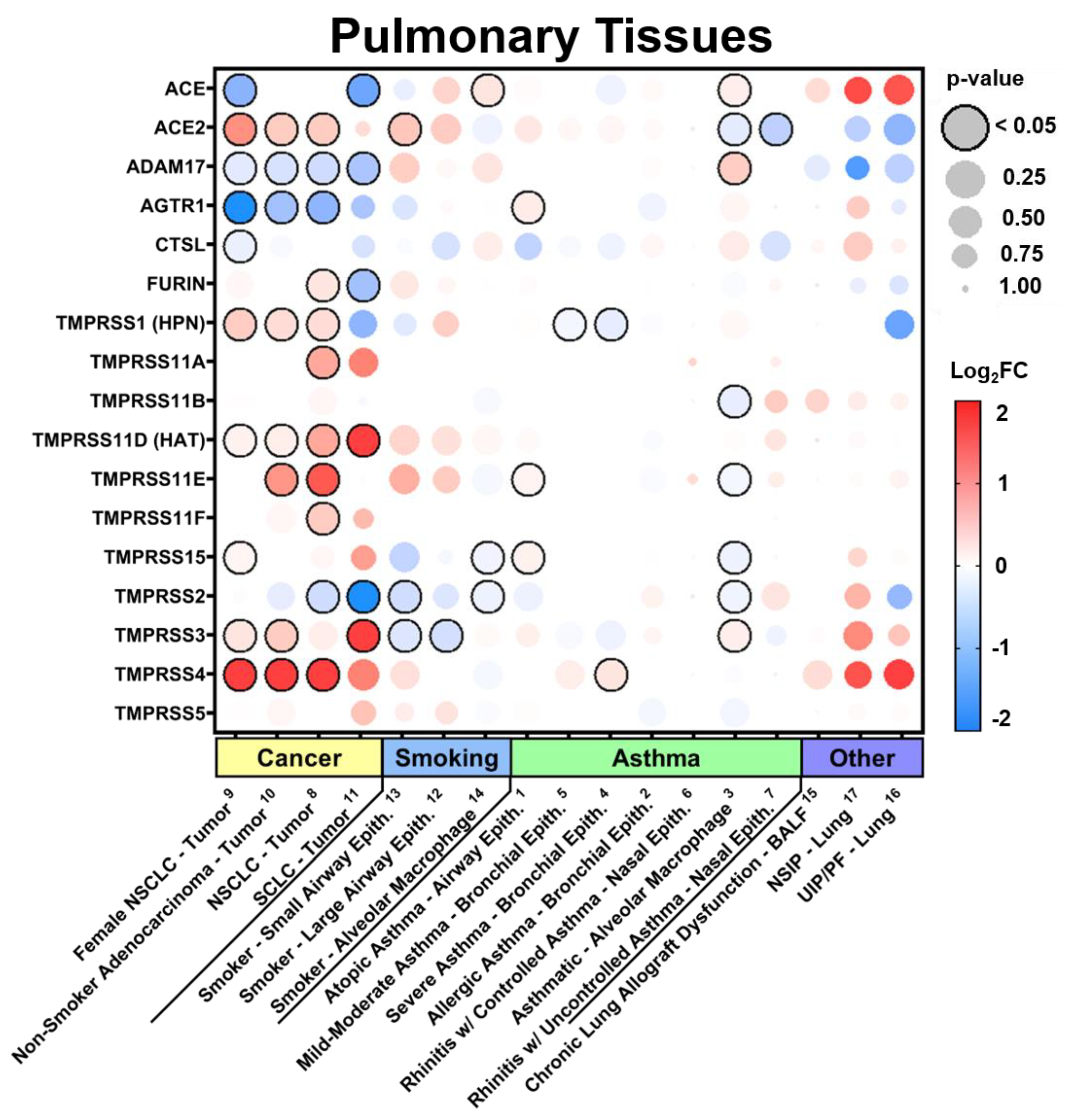
3.2.1. Expression in Pulmonary Tissues in Comorbid States
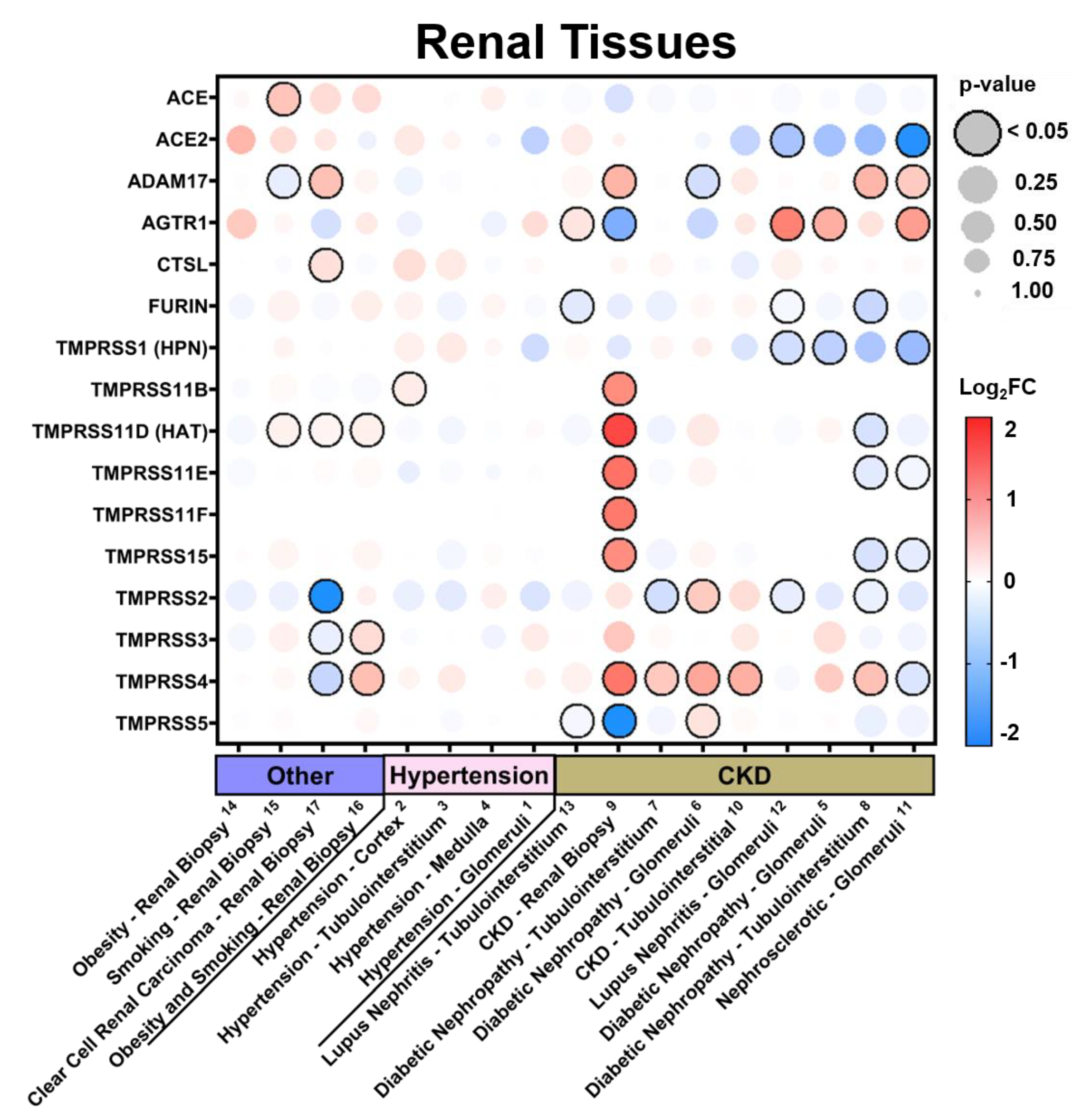
3.2.2. Expression in Renal Tissues in Comorbid States
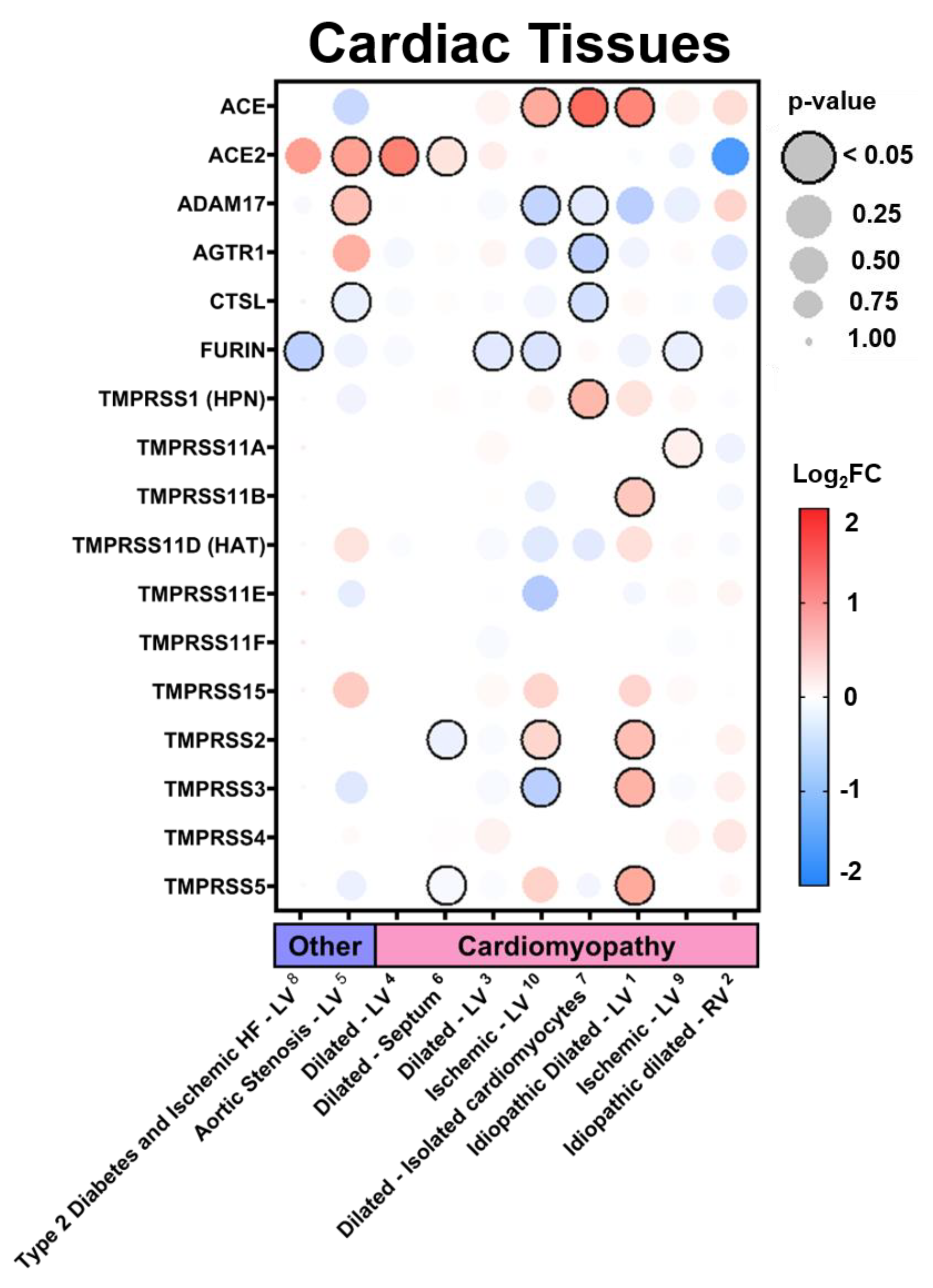
3.2.3. Expression in Cardiac Tissues in Comorbid States
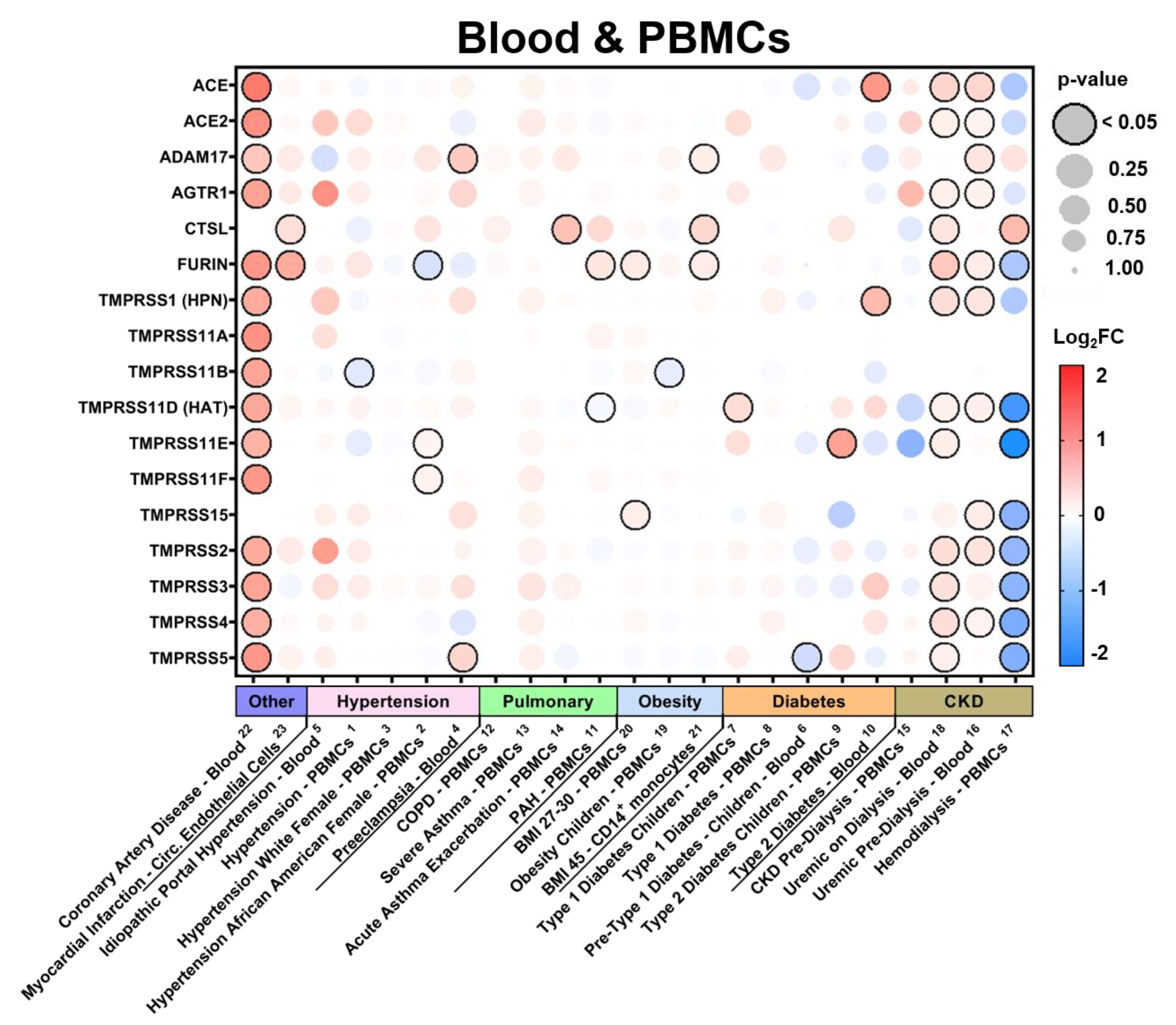
3.2.4. Expression in Blood Tissues in Comorbid States
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Team, C.C.-R. Preliminary Estimates of the Prevalence of Selected Underlying Health Conditions among Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019—United States, 12 February–28 March 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Vardeny, O.; Michel, T.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Solomon, S.D. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puelles, V.G.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Sperhake, J.P.; Wong, M.N.; Allweiss, L.; Chilla, S.; Heinemann, A.; Wanner, N.; Liu, S.; et al. Multiorgan and Renal Tropism of SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Gao, R.; Lu, R.; Han, K.; Wu, G.; Tan, W. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Different Types of Clinical Specimens. JAMA 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Kruger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Jin, W.; Sood, A.; Montgomery, D.W.; Grant, O.C.; Fuster, M.M.; Fu, L.; Dordick, J.S.; Woods, R.J.; Zhang, F.; et al. Characterization of heparin and severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike glycoprotein binding interactions. Antivir. Res. 2020, 181, 104873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Haan, C.A.; Haijema, B.J.; Schellen, P.; Wichgers Schreur, P.; te Lintelo, E.; Vennema, H.; Rottier, P.J. Cleavage of group 1 coronavirus spike proteins: How furin cleavage is traded off against heparan sulfate binding upon cell culture adaptation. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6078–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarrazin, S.; Lamanna, W.C.; Esko, J.D. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garvin, M.R.; Alvarez, C.; Miller, J.I.; Prates, E.T.; Walker, A.M.; Amos, B.K.; Mast, A.E.; Justice, A.; Aronow, B.; Jacobson, D. A mechanistic model and therapeutic interventions for COVID-19 involving a RAS-mediated bradykinin storm. Elife 2020, 9, e59177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heurich, A.; Hofmann-Winkler, H.; Gierer, S.; Liepold, T.; Jahn, O.; Pohlmann, S. TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 cleave ACE2 differentially and only proteolysis by TMPRSS2 augments entry driven by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ou, X.; Liu, Y.; Lei, X.; Li, P.; Mi, D.; Ren, L.; Guo, L.; Guo, R.; Chen, T.; Hu, J.; et al. Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webb, S.L.; Sanders, A.J.; Mason, M.D.; Jiang, W.G. Type II transmembrane serine protease (TTSP) deregulation in cancer. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2011, 16, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shang, J.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Ye, G.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11727–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Pohlmann, S. A Multibasic Cleavage Site in the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Is Essential for Infection of Human Lung Cells. Mol. Cell. 2020, 78, 779–784.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Smyth, G.K. limma: Linear Models for Microarray Data. In Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions Using R and Bioconductor; Gentleman, R., Carey, V.J., Huber, W., Irizarry, R.A., Dudoit, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 397–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sungnak, W.; Huang, N.; Becavin, C.; Berg, M.; Queen, R.; Litvinukova, M.; Talavera-Lopez, C.; Maatz, H.; Reichart, D.; Sampaziotis, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leung, J.M.; Yang, C.X.; Tam, A.; Shaipanich, T.; Hackett, T.L.; Singhera, G.K.; Dorscheid, D.R.; Sin, D.D. ACE-2 expression in the small airway epithelia of smokers and COPD patients: Implications for COVID-19. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Breidenbach, J.D.; Dube, P.; Ghosh, S.; Abdullah, B.N.; Modyanov, N.N.; Malhotra, D.; Dworkin, L.D.; Haller, S.T.; Kennedy, D.J. Impact of Comorbidities on SARS-CoV-2 Viral Entry-Related Genes. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040146
Breidenbach JD, Dube P, Ghosh S, Abdullah BN, Modyanov NN, Malhotra D, Dworkin LD, Haller ST, Kennedy DJ. Impact of Comorbidities on SARS-CoV-2 Viral Entry-Related Genes. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2020; 10(4):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040146
Chicago/Turabian StyleBreidenbach, Joshua D., Prabhatchandra Dube, Subhanwita Ghosh, Belal N. Abdullah, Nikolai N. Modyanov, Deepak Malhotra, Lance D. Dworkin, Steven T. Haller, and David J. Kennedy. 2020. "Impact of Comorbidities on SARS-CoV-2 Viral Entry-Related Genes" Journal of Personalized Medicine 10, no. 4: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040146
APA StyleBreidenbach, J. D., Dube, P., Ghosh, S., Abdullah, B. N., Modyanov, N. N., Malhotra, D., Dworkin, L. D., Haller, S. T., & Kennedy, D. J. (2020). Impact of Comorbidities on SARS-CoV-2 Viral Entry-Related Genes. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 10(4), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040146