Neonatal Sepsis as Organ Dysfunction: Prognostic Accuracy and Clinical Utility of the nSOFA in the NICU—A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Information Sources and Search Strategy
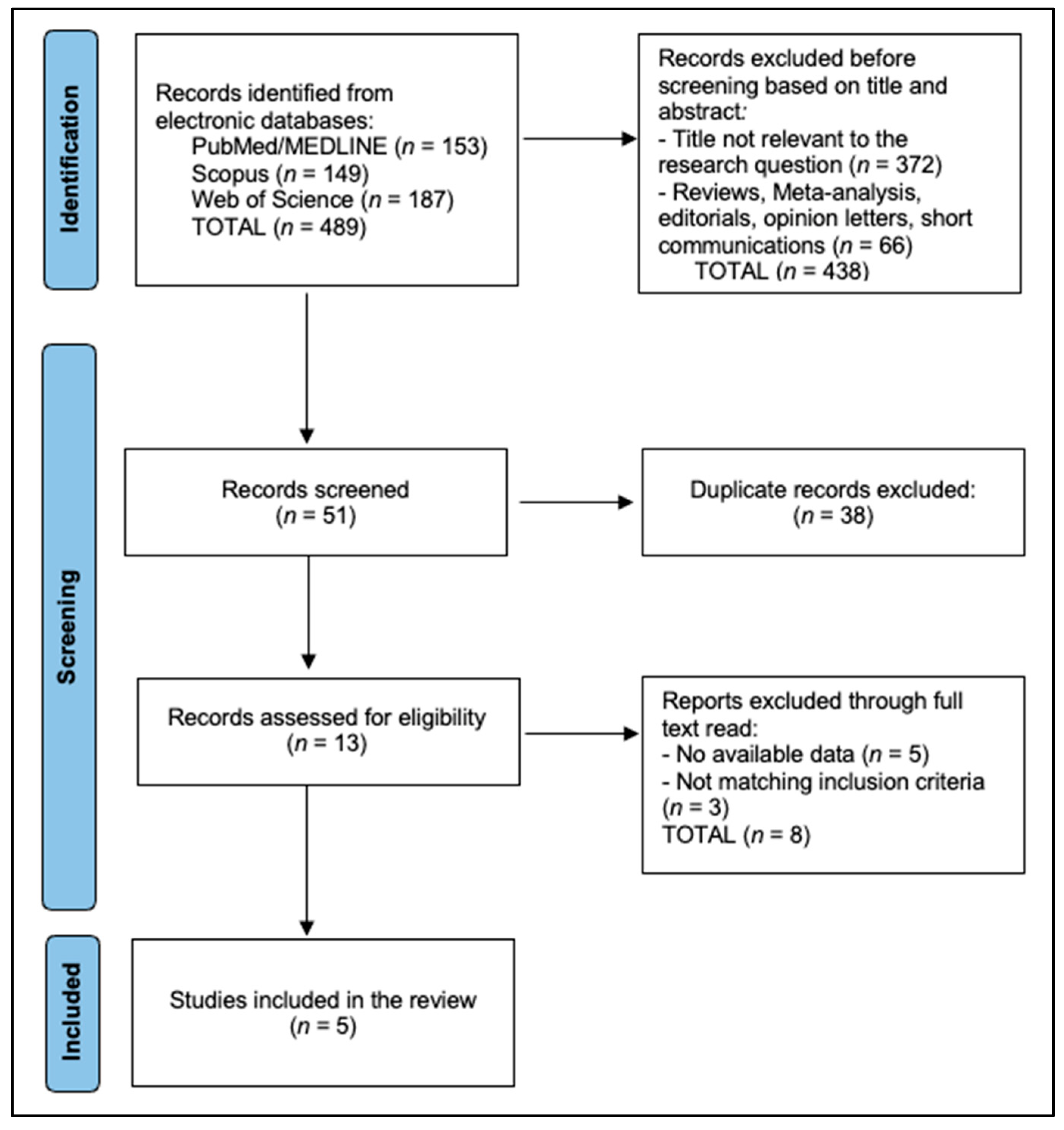
2.4. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.5. Risk of Bias
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Evidence
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Matics, T.J.; Sanchez-Pinto, L.N. Adaptation and Validation of a Pediatric Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score and Evaluation of the Sepsis-3 Definitions in Critically Ill Children. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, e172352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sanchez-Pinto, L.N.; Bennett, T.D.; DeWitt, P.E.; Russell, S.; Rebull, M.N.; Martin, B.; Akech, S.; Albers, D.J.; Alpern, E.R.; Balamuth, F.; et al. Development and Validation of the Phoenix Criteria for Pediatric Sepsis and Septic Shock. JAMA 2024, 331, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fleischmann-Struzek, C.; Goldfarb, D.M.; Schlattmann, P.; Schlapbach, L.J.; Reinhart, K.; Kissoon, N. The global burden of paediatric and neonatal sepsis: A systematic review. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariniotaki, C.; Thomou, C.; Gkentzi, D.; Panteris, E.; Dimitriou, G.; Hatzidaki, E. Neonatal Sepsis: A Comprehensive Review. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Glaser, K.; Speer, C.P. Late-Onset Sepsis Caused by Gram-Negative Bacteria in Very Low Birth Weight Infants: A Systematic Review. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2019, 17, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, M.; Rosa-Mangeret, F.; Agyeman, P.K.A.; McDougall, J.; Berger, C.; Giannoni, E. Management of Neonates at Risk of Early Onset Sepsis: A Probability-Based Approach and Recent Literature Appraisal: Update of the Swiss National Guideline of the Swiss Society of Neonatology and the Pediatric Infectious Disease Group Switzerland. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2024, 183, 5517–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, K.B.; Saxonhouse, M.; Mahesh, D.; Wheeler, K.E.; Wynn, J.L. The Frequency and Timing of Sepsis-Associated Coagulopathy in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1364725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadogeorgou, P.; Boutsikou, T.; Boutsikou, M.; Pergantou, E.; Mantzou, A.; Papassotiriou, I.; Iliodromiti, Z.; Sokou, R.; Bouza, E.; Politou, M.; et al. A Global Assessment of Coagulation Profile and a Novel Insight into ADAMTS-13 Implication in Neonatal Sepsis. Biology 2023, 12, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, B.; Giroir, B.; Randolph, A.; International Consensus Conference on Pediatric Sepsis. International Pediatric Sepsis Consensus Conference: Definitions for Sepsis and Organ Dysfunction in Pediatrics. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 6, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavilla, O.C.; Aziz, K.B.; Lure, A.C.; Gipson, D.; de la Cruz, D.; Wynn, J.L. Hourly Kinetics of Critical Organ Dysfunction in Extremely Preterm Infants. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dathe, A.K.; Stein, A.; Bruns, N.; Craciun, E.D.; Tuda, L.; Bialas, J.; Brasseler, M.; Felderhoff-Mueser, U.; Huening, B.M. Early Prediction of Mortality after Birth Asphyxia with the nSOFA. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raith, E.P.; Udy, A.A.; Bailey, M.; McGloughlin, S.; MacIsaac, C.; Bellomo, R.; Pilcher, D.V.; Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Society (ANZICS) Centre for Outcomes and Resource Evaluation (CORE). Prognostic Accuracy of the SOFA Score, SIRS Criteria, and qSOFA Score for In-Hospital Mortality Among Adults with Suspected Infection Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit. JAMA 2017, 317, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Lu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhou, W.; Cui, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, W.; Hua, T.; Zhu, H.; et al. Interpretable Machine Learning Model for Early Prediction of 28-Day Mortality in ICU Patients with Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy: Development and Validation. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Malik, A.; Taksande, A.; Meshram, R. Pediatric Sequential Organ Assessment Score: A Comprehensive Review of the Prognostic Marker in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit. Cureus 2024, 16, e60034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleiss, N.; Coggins, S.A.; Lewis, A.N.; Zeigler, A.; Cooksey, K.E.; Walker, L.A.; Husain, A.N.; de Jong, B.S.; Wallman-Stokes, A.; Alrifai, M.W.; et al. Evaluation of the Neonatal Sequential Organ Failure Assessment and Mortality Risk in Preterm Infants With Late-Onset Infection. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2036518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, D.; Dong, Z.; Yin, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Neonatal sequential organ failure assessment score within 72 h after delivery reliably predicts bronchopulmonary dysplasia in very preterm infants. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1233189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shi, S.; Guo, J.; Fu, M.; Liao, L.; Tu, J.; Xiong, J.; Liao, Q.; Chen, W.; Chen, K.; Liao, Y. Evaluation of the neonatal sequential organ failure assessment and mortality risk in neonates with respiratory distress syndrome: A retrospective cohort study. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 911444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kurul, Ş.; Reijnierse, J.J.; Koppens, H.J.; Onland, W.; Simons, S.H.P.; Reiss, I.K.M.; Taal, H.R.; Visser, D.H. Assessing neonatal Sequential Organ Failure (nSOFA) scores in suspected late-onset neonatal sepsis among preterm infants: Implications for morbidity and mortality. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2024, 8, e002884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zeigler, A.C.; Ainsworth, J.E.; Fairchild, K.D.; Wynn, J.L.; Sullivan, B.A. Sepsis and Mortality Prediction in Very Low Birth Weight Infants: Analysis of HeRO and nSOFA. Am. J. Perinatol. 2023, 40, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wynn, J.L.; Mayampurath, A.; Carey, K.; Slattery, S.; Andrews, B.; Sanchez-Pinto, L.N. Multicenter Validation of the Neonatal Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score for Prognosis in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J. Pediatr. 2021, 236, 297–300.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wynn, J.L.; Polin, R.A. A neonatal sequential organ failure assessment score predicts mortality to late-onset sepsis in preterm very low birth weight infants. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 88, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Poggi, C.; Ciarcià, M.; Miselli, F.; Dani, C. Prognostic accuracy of Neonatal SOFA score versus SIRS criteria in preterm infants with late-onset sepsis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 4731–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Al Gharaibeh, F.N.; Liu, S.; Wynn, J.L.; Aziz, K.B. The utility of neonatal sequential organ failure assessment in mortality risk in all neonates with suspected late-onset infection. J. Perinatol. 2025, 45, 1438–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kraja, E.; Demirtas, F.; Kostekci, Y.E.; Turker, N.; Okulu, E.; Erdeve, Ö.; Atasay, B.; Arsan, S. Evaluation of the “Neonatal Sequential Organ Failure Assessment” to Predict Mortality in Late-Onset Sepsis in Very Preterm Infants. Z. Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 2024, 228, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, K.T.; Goh, G.L.; Park, W.Y.; Wynn, J.L.; Aziz, K.B. Evaluation of the Neonatal Sequential Organ Failure Assessment and Mortality Risk in Neonates with Early-Onset Infection. Neonatology 2023, 120, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, B.B.P.; Marba, S.T.M.; Machado, H.C.; Caldas, J.P.S. Neonatal Sequential Organ Failure Assessment as a late-onset sepsis mortality predictor in very low birth weight newborns: A Brazilian cohort study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 3767–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggi, C.; Sarcina, D.; Miselli, F.; Ciarcià, M.; Dani, C. Neonatal Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score Predicts Respiratory Outcomes in Preterm Newborns with Late-Onset Sepsis: A Retrospective Study. Neonatology 2025, 122, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berka, I.; Korček, P.; Janota, J.; Straňák, Z. Neonatal Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (nSOFA) Score within 72 Hours after Birth Reliably Predicts Mortality and Serious Morbidity in Very Preterm Infants. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lewis, A.N.; de la Cruz, D.; Wynn, J.L.; Frazer, L.C.; Yakah, W.; Martin, C.R.; Yang, H.; Itriago, E.; Unger, J.; Hair, A.B.; et al. Evaluation of the Neonatal Sequential Organ Failure Assessment and Mortality Risk in Preterm Infants with Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Neonatology 2022, 119, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hao, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Du, Y.; Cheng, X. Comparing nSOFA, CRIB-II, and SNAPPE-II for predicting mortality and short-term morbidities in preterm infants ≤32 weeks gestation. Ann. Med. 2024, 56, 2426752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Parry, G.; Tucker, J.; Tarnow-Mordi, W.; UK Neonatal Staffing Study Collaborative Group. CRIB II: An update of the clinical risk index for babies score. Lancet 2003, 361, 1789–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, D.K.; Corcoran, J.D.; Escobar, G.J.; Lee, S.K. SNAP-II and SNAPPE-II: Simplified newborn illness severity and mortality risk scores. J. Pediatr. 2001, 138, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janota, J.; Stranák, Z.; Statecná, B.; Dohnalová, A.; Sípek, A.; Simák, J. Characterization of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in very low birthweight infants: A new sequential scoring system. Shock 2001, 15, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetinkaya, M.; Köksal, N.; Özkan, H. A new scoring system for evaluation of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in premature infants. Am. J. Crit. Care 2012, 21, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, L.; Wynn, J.L.; de la Cruz, D. Utility of the neonatal and pediatric sequential organ failure assessment scores in critically ill term neonates. Front. Pediatr. 2025, 13, 1546408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moorman, J.R.; Carlo, W.A.; Kattwinkel, J.; Schelonka, R.L.; Porcelli, P.J.; Navarrete, C.T.; Bancalari, E.; Aschner, J.L.; Whit Walker, M.; Perez, J.A.; et al. Mortality reduction by heart rate characteristic monitoring in very low birth weight neonates: A randomized trial. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 900–906.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Curley, A.; Stanworth, S.J.; Willoughby, K.; Fustolo-Gunnink, S.F.; Venkatesh, V.; Hudson, C.; Deary, A.; Hodge, R.; Hopkins, V.; Santamaria, B.L.; et al. PlaNeT2 MATISSE Collaborators. Randomized Trial of Platelet-Transfusion Thresholds in Neonates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fustolo-Gunnink, S.F.; Fijnvandraat, K.; van Klaveren, D.; Stanworth, S.J.; Curley, A.; Onland, W.; Steyerberg, E.W.; de Kort, E.; d’Haens, E.J.; Hulzebos, C.V.; et al. Preterm neonates benefit from low prophylactic platelet transfusion threshold despite varying risk of bleeding or death. Blood 2019, 134, 2354–2360, Erratum in Blood 2020, 135, 2199. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2020006498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hayes, R.; Hartnett, J.; Semova, G.; Murray, C.; Murphy, K.; Carroll, L.; Plapp, H.; Hession, L.; O’tOole, J.; McCollum, D.; et al. Neonatal sepsis definitions from randomised clinical trials. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, 1141–1148, Erratum in Pediatr. Res. 2024, 96, 1882. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-024-03416-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Husain, A.N.; Eiden, E.; Vesoulis, Z.A. Use of an electronic medical record to optimize a neonatal sepsis score for mortality prediction. J. Perinatol. 2023, 43, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sodero, G.; Gentili, C.; Mariani, F.; Pulcinelli, V.; Valentini, P.; Buonsenso, D. Procalcitonin and Presepsin as Markers of Infectious Respiratory Diseases in Children: A Scoping Review of the Literature. Children 2024, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| First Author (Year) | Country/Region | Setting/Design | Population/Phenotype | N (Infants/Episodes) | Time Window/Context |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fleiss (2021) [18] | US multicenter | Multicenter cohort | Preterm infants with late-onset infection | 259 | Evaluation; serial (+6, +12 h) |
| Xu (2023) [19] | China | Single-center, retrospective | Very preterm (≤32 wk) within 72 h after birth; BPD outcome | 238 | Early postnatal (≤72 h) |
| Shi (2022) [20] | China | Retrospective cohort | Neonates with RDS in NICU | 1281 | Admission; whole stay |
| Kurul (2024) [21] | Netherlands | Preterm with suspected LOI | Morbidity and mortality | 706 | T0, +6, +12 h (serial) |
| Zeigler (2023) [22] | US | VLBW; HeRO vs. nSOFA | Sepsis/mortality prediction | 956 | Evaluation; +12 h |
| Wynn (2021) [23] | US multicenter | Validation study | All NICU admissions (prognosis) | 20,152 | Admission and serial windows |
| Wynn (2020) [24] | US single-center | Bacteremic VLBW with LOS | Mortality discrimination | 60 | T0, +6, +12 h |
| Poggi (2023) [25] | Italy | Retrospective | ≤32 wk with LONS | 112 | T0, +6, +12, +24 h; vs. SIRS |
| Al Gharaibeh (2025) [26] | US | Single-center, retrospective | All neonates with LOI evaluations | 1481 | T0 and +6 h; eval-specific mortality |
| Kraja (2024) [27] | Turkey | Single-center, retrospective | Very preterm with culture-proven LOS | 106 | 9 time points incl. pre-/post-eval up to 48 h |
| Yeo (2023) [28] | Multicenter | Prospective cohort | Early-onset infection | 104 | Evaluation; serial; mortality |
| Lobo (2022) [29] | Brazil | Retrospective | VLBW with LONS | 1574 | Evaluation; mortality predictor |
| Poggi (2025) [30] | Italy | Retrospective | Preterm with LONS; respiratory outcomes | NR | T0/+6/+12/+24; respiratory endpoints |
| Berka (2022) [31] | Czech Republic | Single-center | <32 wk within 72 h after birth | 423 | Peak nSOFA (first 72 h) vs. outcomes |
| Lewis (2022) [32] | US multicenter | Retrospective | Preterm with NEC (≥IIA) | 259 | Evaluation; death and surgery/death |
| Hao (2024) [33] | China | Retrospective | ≤32 wk; compare nSOFA vs. CRIB-II vs. SNAPPE-II | 759 | Admission; mortality; and short-term morbidities |
| First Author (Year) | Timing Assessed | AUROC/AUC (95% CI) | Reported Threshold/Operating Points or Key Performance Note |
|---|---|---|---|
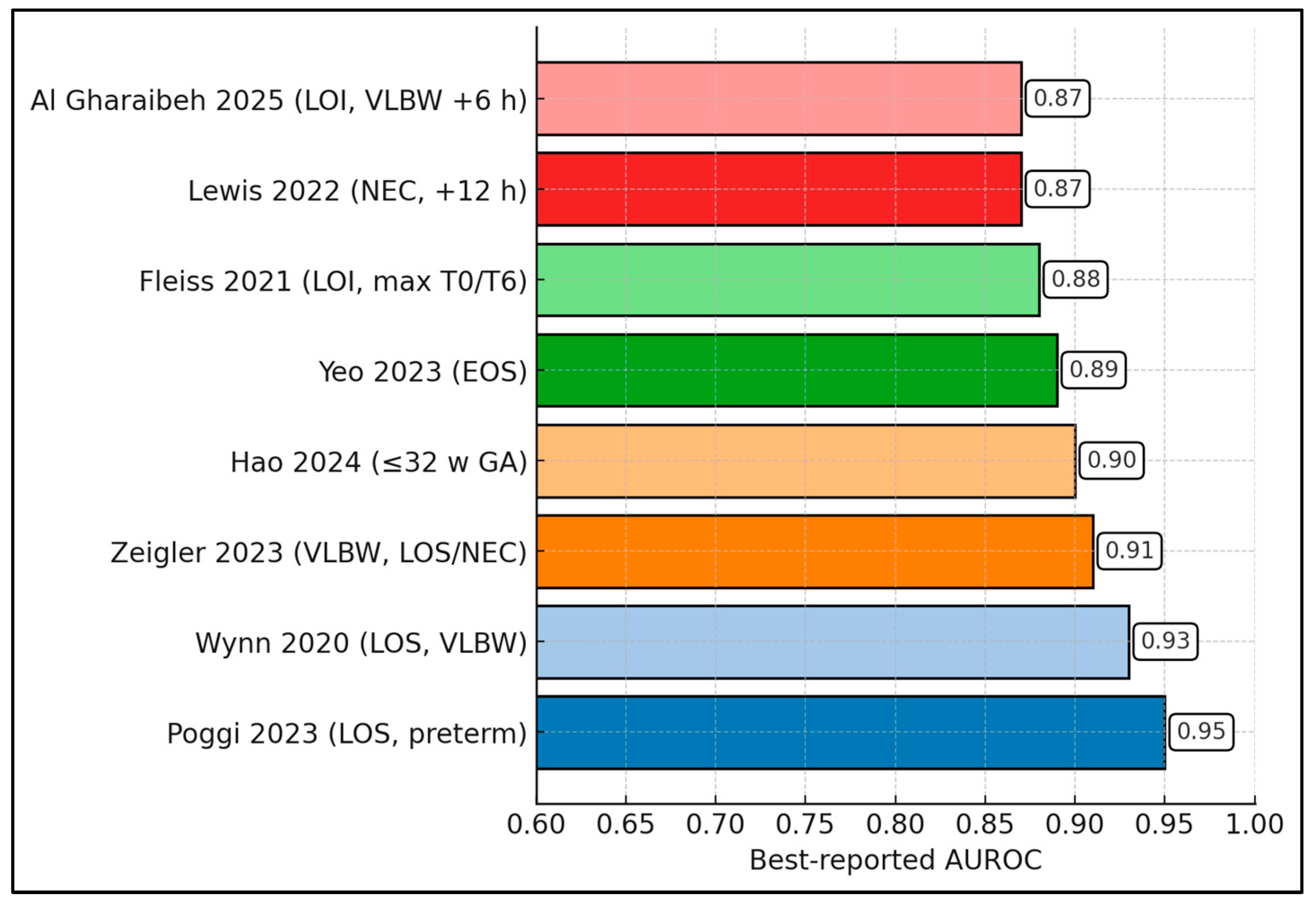
| Wynn (2020) [24] | T0; +6; +12 h | T0 0.77 (0.62–0.92); +6 0.79; +12 0.93 (0.86–0.997) | ≥4 associated with much higher mortality at each window (e.g., +12 h 71% vs. 7%). |
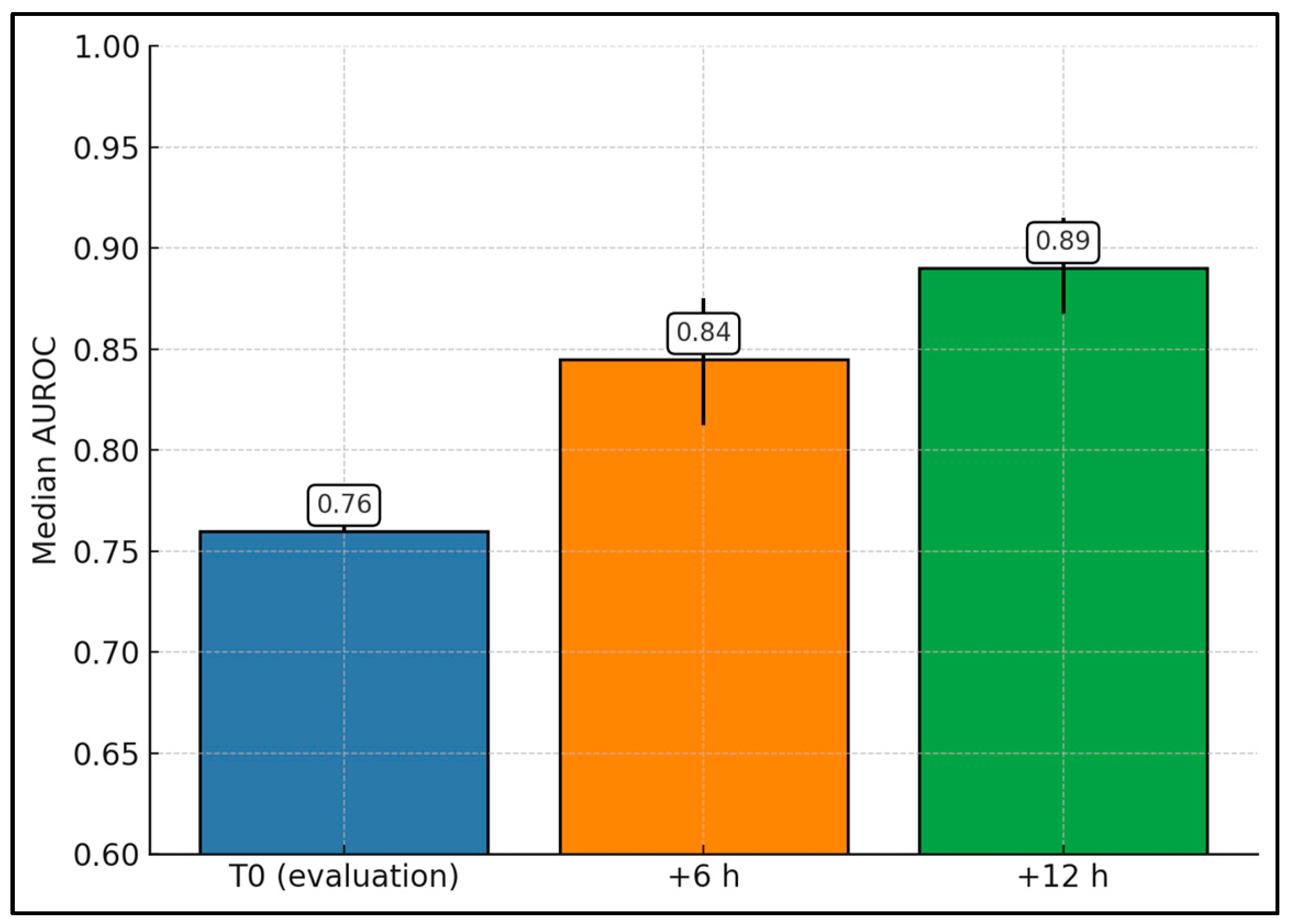
| Fleiss (2021) [18] | Eval; +6; +12 h | Max(T0/T6) 0.88 (0.84–0.91); center ranges T0 0.71–0.95, T6 0.77–0.96, T12 0.78–0.96 | Discrimination improved at +6 versus T0 across centers. |
| Poggi (2023) [25] | T0; +6; +12; +24 h | At T0, nSOFA 0.950 vs. SIRS 0.569 (p = 0.0002) | Best cut-off at T0 = 4; T0 and +6 were independent predictors. |
| Al Gharaibeh (2025) [26] | T0; +6 h | T0 0.76 (0.71–0.81); +6 0.82 (0.78–0.87) | Cut-off ≥ 2: Se 87%, Sp 66%, NPV 99% (all LOI evals). |
| Zeigler (2023) [22] | +12 h | 0.91 (+12 h) | Compared with HeRO analysis in VLBW infants. |
| Yeo (2023) * [28] | T0; +6 h; T0–6 max | T0 0.76; +6 0.89; T0–6 max 0.87 | EOS cohort; +6 h outperformed T0. |
| Lewis (2022) * [32] | Eval/serial (NEC) | Death 0.87; Surgery/death 0.84 | Discrimination for death and for surgery/death composite. |
| Hao (2024) [33] | Admission | nSOFA 0.90 vs. SNAPPE-II 0.82 vs. CRIB-II 0.79 | nSOFA significantly higher than CRIB-II/SNAPPE-II. |
| Kurul (2024) [21] | T0; +6; +12 h | NR | At +6 h, aOR per 1-point = 1.31 for 10-day mortality; also associations with BPD/ROP |
| Wynn (2021) [23] | Admission/serial | “Good-to-excellent” across centers/BW/time | Multicenter validation across 20,152 NICU admissions. |
| Kraja (2024) [27] | Multiple (−6 to +48 h) | NR | nSOFA > 4 at assessment associated with ~7–16× mortality risk (adj. ~9–18×). |
| Lobo (2022) [29] | Early after LONS onset | 0.92 | Brazilian VLBW LONS cohort; strong performance reported. |
| Berka (2022) * [31] | ≤72 h after birth | NR | Early nSOFA predicted mortality/serious morbidity in very preterms. |
| Shi (2022) * [20] | NICU stay (RDS) | NR | Mortality risk increased per point |
| Poggi (2025) * [30] | T0; +6; +12; +24 h | NR | Study focused on respiratory outcomes |
| Xu (2023) * [19] | ≤72 h after birth | NR | Study focused on BPD prediction. |
| Lavilla (2022) * [12] | Hourly kinetics | NR | Organ dysfunction trajectories in extremely preterm infants. |
| First Author (Year) | Primary Outcome(s) | Adjusted Per-Point Effect (OR/HR, 95% CI) | Other Non-Overlapping Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wynn (2020) [24] | Mortality (LOS VLBW) | NR | Marked risk separation at ≥4 across T0/+6/+12; +12 h performed best with large mortality gap (71% vs. 7%). |
| Fleiss (2021) [18] | Mortality (LOI) | NR | Improvement from T0 → +6 observed across centers; center-specific performance broad but consistently “good.” |
| Poggi (2023) [25] | LONS mortality vs. SIRS | NR | nSOFA at T0 and +6 independently predicted death in multivariate models, outperforming SIRS at T0. |
| Al Gharaibeh (2025) [26] | LOI-specific mortality | NR | Cut-off ≥ 2 yielded high NPV (99%); effect persisted in VLBW subgroup. |
| Zeigler (2023) [22] | Sepsis/mortality prediction | NR | Joint analysis with HeRO monitoring; nSOFA retained strong discrimination at +12 h. |
| Yeo (2023) [28] | EOS mortality | NR | +6 h outperformed T0; early serial assessment was key (T0–6 max better than T0). |
| Lewis (2022) [32] | NEC death; surgery/death | NR | nSOFA discriminated both death and surgery/death; supports use beyond bacteremia. |
| Hao (2024) [33] | Mortality ≤ 32 wk | NR | nSOFA outperformed CRIB-II/SNAPPE-II in the same cohort at admission. |
| Kurul (2024) [21] | 10-day mortality; BPD; ROP | aOR 1.31 per point at +6 h (1.22–1.40) mortality; BPD aOR 1.30 (1.13–1.50); ROP aOR 1.24 (1.09–1.41) for nSOFA burden | Burden metric (count of timepoints with nSOFA ≥ 4 from −6 to +48 h) tracked severe morbidity risk. |
| Shi (2022) [20] | RDS mortality (NICU) | aHR 1.48 per point (1.32–1.67); high vs. low group aHR 19.35 (4.41–84.95) | Mortality rose steeply with increasing nSOFA; results robust after PS-matching. |
| Xu (2023) [19] | BPD (≤72 h post-birth) | NR (independent association) | Early nSOFA associated with later BPD; broadened use beyond infection episodes. |
| Poggi (2025) [30] | Respiratory outcomes (LONS) | OR 1.68 (1.34–2.10) for increased respiratory support at +24 h; OR 1.56 (1.21–2.01) for invasive ventilation; OR 1.39 (1.10–1.77) for failure to return to baseline support (all per-point) | nSOFA also associated with severe ROP (OR 1.30, 1.02–1.66). |
| Berka (2022) [31] | Mortality; serious morbidity (≤72 h) | NR | Early nSOFA within 72 h after birth predicted adverse outcomes in very preterms. |
| Lobo (2022) [29] | LONS mortality (VLBW) | NR | Strong association between early post-onset nSOFA and sepsis-attributable death in Brazilian cohort. |
| Kraja (2024) [27] | LOS mortality (very preterm) | NR | Scores > 4 linked to ~7–16× crude and ~9–18× adjusted mortality odds across windows. |
| Wynn (2021) [23] | All-cause NICU mortality | NR | Good–excellent discrimination across BW strata and time after admission in 20k+ infants. |
| Lavilla (2022) [12] | Adverse outcomes in extremely preterm | NR | Hourly organ dysfunction trajectories (nSOFA components) linked with adverse outcomes; supports serial monitoring. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Cerbu, B.; Boia, M.; Pantea, M.; Ignat, T.; Dima, M.; Enatescu, I.; Rotea, B.; Rotea, A.; David, V.; Iacob, D. Neonatal Sepsis as Organ Dysfunction: Prognostic Accuracy and Clinical Utility of the nSOFA in the NICU—A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2026, 16, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics16020349
Cerbu B, Boia M, Pantea M, Ignat T, Dima M, Enatescu I, Rotea B, Rotea A, David V, Iacob D. Neonatal Sepsis as Organ Dysfunction: Prognostic Accuracy and Clinical Utility of the nSOFA in the NICU—A Systematic Review. Diagnostics. 2026; 16(2):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics16020349
Chicago/Turabian StyleCerbu, Bogdan, Marioara Boia, Manuela Pantea, Teodora Ignat, Mirabela Dima, Ileana Enatescu, Bogdan Rotea, Andra Rotea, Vlad David, and Daniela Iacob. 2026. "Neonatal Sepsis as Organ Dysfunction: Prognostic Accuracy and Clinical Utility of the nSOFA in the NICU—A Systematic Review" Diagnostics 16, no. 2: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics16020349
APA StyleCerbu, B., Boia, M., Pantea, M., Ignat, T., Dima, M., Enatescu, I., Rotea, B., Rotea, A., David, V., & Iacob, D. (2026). Neonatal Sepsis as Organ Dysfunction: Prognostic Accuracy and Clinical Utility of the nSOFA in the NICU—A Systematic Review. Diagnostics, 16(2), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics16020349