Ten Questions on Using Lung Ultrasonography to Diagnose and Manage Pneumonia in Hospital-at-Home Model: Part III—Synchronicity and Foresight
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Question 7: Do Initial Ultrasound Findings Associated with Pneumonia Hold Prognostic Value?
2.1. Red Flag Signs Related to ARDS
2.2. Red Flag Signs Related to Complicated Pneumonia
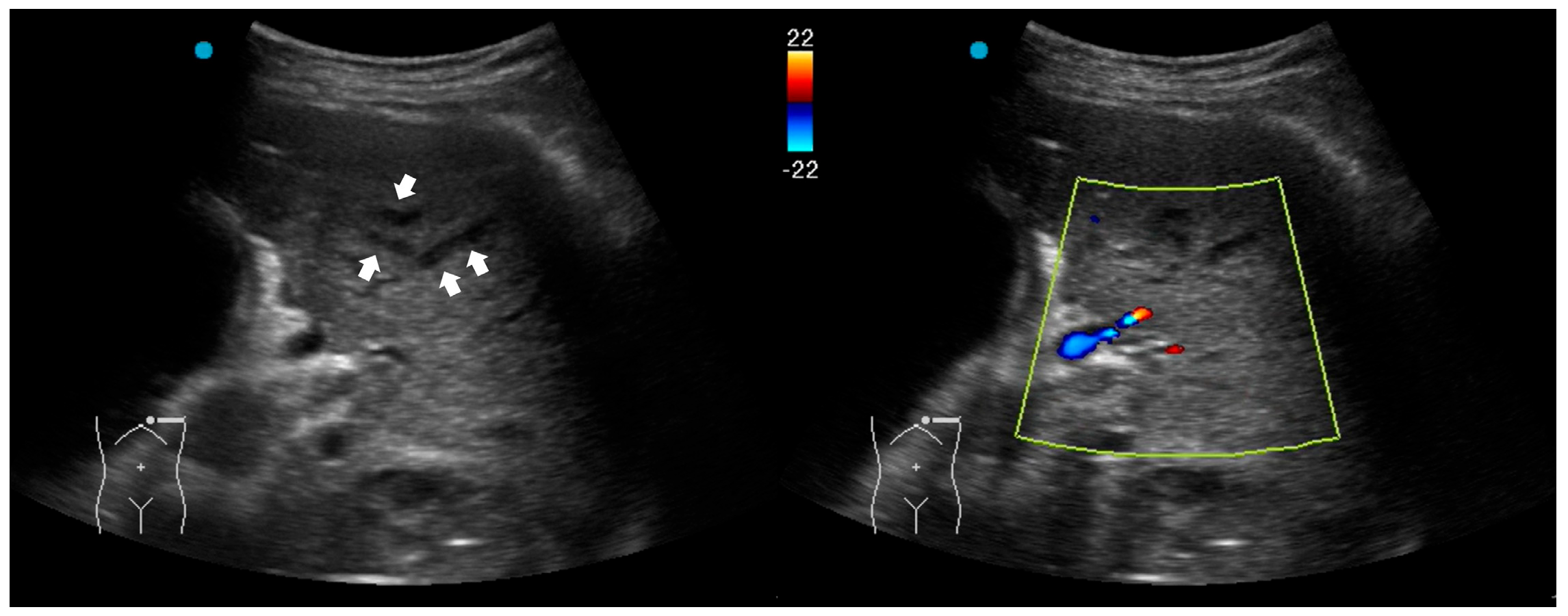
2.3. Red Flag Signs Related to Necrotizing Pneumonia
2.4. Other Red Flag Signs
3. Question 8: Do the Ultrasound Patterns Improve in Accordance with Pneumonia Recovery?
4. Question 9: Is Ultrasound Superior to Chest X-Ray for Diagnosing Pneumonia?
4.1. Pediatrics
4.2. Adults
4.3. Special Contexts
5. Question 10: Does Ultrasonography Lead to Overdiagnosis of Pneumonia?
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mirón-Rubio, M.; González-Ramallo, V.; Estrada-Cuxart, O.; Sanroma-Mendizábal, P.; Segado-Soriano, A.; Mujal-Martínez, A.; Del Río-Vizoso, M.; García-Lezcano, M.; Martín-Blanco, N.; Florit-Serra, L.; et al. Intravenous antimicrobial therapy in the hospital-at-home setting: Data from the Spanish Outpatient Parenteral Antimicrobial Therapy Registry. Future Microbiol. 2016, 11, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Goor, H.M.R.; de Hond, T.A.P.; van Loon, K.; Breteler, M.J.M.; Kalkman, C.J.; Kaasjager, K.A.H. Designing a Virtual Hospital-at-Home Intervention for Patients with Infectious Diseases: A Data-Driven Approach. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.Q.; Goh, J.; Tay, Y.K.; Nashi, N.; Hooi, B.M.Y.; Luo, N.; Kuan, W.S.; Soong, J.T.Y.; Chan, D.; Lai, Y.F.; et al. Treating acutely ill patients at home: Data from Singapore. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2022, 51, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkarainen, T.; Lahelma, M.; Rahkonen, T.; Lehtinen, V.; Shepelev, J.; Gram, T.; Heikkila, E. Cost comparison analysis of continuous versus intermittent antimicrobial therapy infusions in inpatient and outpatient care: Real-world data from Finland. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e085242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candel, F.J.; Salavert, M.; Basaras, M.; Borges, M.; Cantón, R.; Cercenado, E.; Cilloniz, C.; Estella, Á.; García-Lechuz, J.M.; Garnacho Montero, J.; et al. Ten Issues for Updating in Community-Acquired Pneumonia: An Expert Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouvenne, A.; Ticinesi, A.; Siniscalchi, C.; Rendo, M.; Cerundolo, N.; Parise, A.; Castaldo, G.; Chiussi, G.; Carrassi, R.; Guerra, A.; et al. The Multidisciplinary Mobile Unit (MMU) Program Bringing Hospital Specialist Geriatric Competencies at Home: A Feasible Alternative to Admission in Older Patients with Urgent Complaints. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zychlinski, N.; Fluss, R.; Goldberg, Y.; Zubli, D.; Barkai, G.; Zimlichman, E.; Segal, G. Tele-medicine controlled hospital at home is associated with better outcomes than hospital stay. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0309077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salton, F.; Kette, S.; Confalonieri, P.; Fonda, S.; Lerda, S.; Hughes, M.; Confalonieri, M.; Ruaro, B. Clinical Evaluation of the ButterfLife Device for Simultaneous Multiparameter Telemonitoring in Hospital and Home Settings. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, A.W.; McKee, J.L.; Couperus, K.; Colombo, C.J. Patient Self-Performed Point-of-Care Ultrasound: Using Communication Technologies to Empower Patient Self-Care. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xirouchaki, N.; Bolaki, M.; Psarologakis, C.; Pediaditis, E.; Proklou, A.; Papadakis, E.; Kondili, E.; Georgopoulos, D. Thoracic ultrasound use in hospitalized and ambulatory adult patients: A quantitative picture. Ultrasound J. 2024, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, N.M.; Jowkar, N.; Ma, I.W.Y.; Schulwolf, S.; Selame, L.A.; Fischetti, C.E.; Kapur, T.; Goldsmith, A.J. Novice-performed point-of-care ultrasound for home-based imaging. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Bellinger, R.; Shedd, A.; Wolfshohl, J.; Walker, J.; Healy, J.; Taylor, J.; Chao, K.; Yen, Y.H.; Tzeng, C.T.; et al. Point-of-Care Ultrasound in Airway Evaluation and Management: A Comprehensive Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganchi, F.A.; Hardcastle, T.C. Role of Point-of-Care Diagnostics in Lower- and Middle-Income Countries and Austere Environments. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Aquila, P.; Raimondo, P.; Racanelli, V.; De Luca, P.; De Matteis, S.; Pistone, A.; Melodia, R.; Crudele, L.; Lomazzo, D.; Solimando, A.G.; et al. Integrated lung ultrasound score for early clinical decision-making in patients with COVID-19: Results and implications. Ultrasound J. 2022, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabuel Ortega, P.; Almendros Lafuente, N.; Cánovas García, S.; Martínez Gálvez, L.; González-Vidal, A. The correlation between point-of-care ultrasound and digital tomosynthesis when used with suspected COVID-19 pneumonia patients in primary care. Ultrasound J. 2022, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, M.; MacGregor, H.; Ripoll, S.; Scoones, I.; Wilkinson, A. Rethinking Disease Preparedness: Incertitude and the Politics of Knowledge. Crit. Public Health 2022, 32, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajeepeta, S.; Bruzelius, E.; Ho, J.Z.; Prins, S.J. Policing the pandemic: Estimating spatial and racialized inequities in New York City police enforcement of COVID-19 mandates. Crit. Public Health 2022, 32, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, N.C.; Lin, Y.F.; Tsai, H.B.; Huang, T.Y.; Hsu, C.H. Ten Questions on Using Lung Ultrasonography to Diagnose and Manage Pneumonia in the Hospital-at-Home Model: Part I-Techniques and Patterns. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, N.C.; Lin, Y.F.; Tsai, H.B.; Liao, C.; Hsu, C.H. Ten Questions on Using Lung Ultrasonography to Diagnose and Manage Pneumonia in the Hospital-at-Home Model: Part II—Confounders and Mimickers. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, Y.E.; Berthier, F.; Baqué-Juston, M.; Perrin, C.; Faraggi, M.; Keita-Perse, O.; Duval, X. Early chest CT-scan in emergency patients affected by community-acquired pneumonia is associated with improved diagnosis consistency. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 29, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copetti, R.; Soldati, G.; Copetti, P. Chest sonography: A useful tool to differentiate acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema from acute respiratory distress syndrome. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2008, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli, G.; Elbarbary, M.; Blaivas, M.; Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mathis, G.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Melniker, L.; Gargani, L.; Noble, V.E.; Via, G.; et al. International Liaison Committee on Lung Ultrasound (ILC-LUS) for International Consensus Conference on Lung Ultrasound (ICC-LUS). International evidence-based recommendations for point-of-care lung ultrasound. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.S.; Ho, K.J. CT fluid bronchogram: Observation in postobstructive pulmonary consolidation. Clin. Imaging 1992, 16, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reissig, A.; Copetti, R. Lung ultrasound in community-acquired pneumonia and in interstitial lung diseases. Respiration 2014, 87, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedia, Y.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, R. Ultrasonographic view of fluid bronchogram secondary to endobronchial obstruction: A case report. Australas. J. Ultrasound Med. 2025, 28, e12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musolino, A.M.; Tomà, P.; Supino, M.C.; Scialanga, B.; Mesturino, A.; Scateni, S.; Battaglia, M.; Pirozzi, N.; Bock, C.; Buonsenso, D. Lung ultrasound features of children with complicated and noncomplicated community acquired pneumonia: A prospective study. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.C.; Lin, M.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Cheng, H.C.; Wu, J.R.; Hsu, J.H.; Dai, Z.K. The role of transthoracic ultrasonography in predicting the outcome of community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173343. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, S.H.; Wong, K.S.; Liao, S.L. Value of Lung Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis and Outcome Prediction of Pediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia with Necrotizing Change. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrard, J.; Bacher, S.; Rochat-Guignard, I.; Knebel, J.F.; Alamo, L.; Meuwly, J.Y.; Tenisch, E. Necrotizing pneumonia in children: Chest computed tomography vs. lung ultrasound. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 898402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.C.; Luh, K.T.; Chang, D.B.; Yu, C.J.; Kuo, S.H.; Wu, H.D. Ultrasonographic evaluation of pulmonary consolidation. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1992, 146, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, D.; Peyrouset, O. Is lung ultrasound superior to CT? The example of a CT occult necrotizing pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. 2006, 32, 334–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, M.J.; Auble, T.E.; Yealy, D.M.; Hanusa, B.H.; Weissfeld, L.A.; Singer, D.E.; Coley, C.M.; Marrie, T.J.; Kapoor, W.N. A prediction rule to identify low-risk patients with community-acquired pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.H.; Saha, B.K.; Conuel, E.; Chopra, A. The incidence of pleural effusion in COVID-19 pneumonia: State-of-the-art review. Heart Lung 2021, 50, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, S.; Casto, E.; Lomi, M.; Pagano, A.; Gabbrielli, L.; Pancani, R.; Aquilini, F.; Gemignani, G.; Carrozzi, L.; Celi, A. Pleural Effusion in COVID-19 Pneumonia: Clinical and Prognostic Implications-An Observational, Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Ni, R.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y. Analysis of clinical characteristics and risk factors of community-acquired pneumonia complicated by parapneumonic pleural effusion in elderly patients. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Niu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X.; Mei, Y.; Cai, G.; Chen, X.; et al. Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of non-malignant pleural effusions in hospitalised patients: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e077980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, H.A.; Albaroudi, B.; Shaban, E.E.; Shaban, A.; Elgassim, M.; Almarri, N.D.; Basharat, K.; Azad, A.M. Advancement in pleura effusion diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of point-of-care ultrasound versus radiographic thoracic imaging. Ultrasound J. 2024, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.C.; Grunkemeier, G.L.; Goldman, J.D.; Wang, M.; McKelvey, P.A.; Hadlock, J.; Wei, Q.; Diaz, G.A. A simplified pneumonia severity index (PSI) for clinical outcome prediction in COVID-19. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0303899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.S.; van der Eerden, M.M.; Laing, R.; Boersma, W.G.; Karalus, N.; Town, G.I.; Lewis, S.A.; Macfarlane, J.T. Defining community acquired pneumonia severity on presentation to hospital: An international derivation and validation study. Thorax 2003, 58, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.E.; Craddock, P.A.; Tayal, V.S.; Kline, J.A. Diagnostic accuracy of left ventricular function for identifying sepsis among emergency department patients with nontraumatic symptomatic undifferentiated hypotension. Shock 2005, 24, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieillard-Baron, A.; Prin, S.; Chergui, K.; Dubourg, O.; Jardin, F. Hemodynamic instability in sepsis: Bedside assessment by Doppler echocardiography. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotsman, I.; Leibowitz, D.; Keren, A.; Amir, O.; Zwas, D.R. Echocardiographic Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes of the Hyperdynamic Heart: A ‘Super-Normal’ Heart is not a Normal Heart. Am. J. Cardiol. 2023, 187, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.H.; Hsu, N.C. Elderly Man With Fall Incident. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2024, 83, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussuges, A.; Finance, J.; Chaumet, G.; Brégeon, F. Diaphragmatic motion recorded by M-mode ultrasonography: Limits of normality. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00714–02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, S.; Cardinael, C.; Tait, C.; Reid, M.; McCarthy, A. Exploring the adoption of diaphragm and lung ultrasound (DLUS) by physiotherapists, physical therapists, and respiratory therapists: An updated scoping review. Ultrasound J. 2025, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaarup, S.H.; Juhl-Olsen, P.; Grundahl, A.S.; Løgstrup, B.B. Replacement of fluoroscopy by ultrasonography in the evaluation of hemidiaphragm function, an exploratory prospective study. Ultrasound J. 2024, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto Silva, I.; Duarte, J.A.; Perret, A.; Dousse, N.; Wozniak, H.; Bollen Pinto, B.; Giraud, R.; Bendjelid, K. Diaphragm dysfunction and peripheral muscle wasting in septic shock patients: Exploring their relationship over time using ultrasound technology (the MUSiShock protocol). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartini, S.; Ferrari, L.; Cutuli, O.; Castellani, L.; Bagnasco, M.; Moisio Corsello, L.; Bracco, C.; Cristina, M.L.; Arboscello, E.; Sartini, M. The Role of Pocus in Acute Respiratory Failure: A Narrative Review on Airway and Breathing Assessment. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reissig, A.; Kroegel, C. Sonographic diagnosis and follow-up of pneumonia: A prospective study. Respiration 2007, 74, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkert, J.; Jarman, R.; Deol, P. Evolution of Lung Abnormalities on Lung Ultrasound in Recovery From COVID-19 Disease-A Prospective, Longitudinal Observational Cohort Study. J. Ultrasound Med. 2023, 42, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Píriz, A.; Tung-Chen, Y.; Jiménez-Virumbrales, D.; Ayala-Larrañaga, I.; Barba-Martín, R.; Canora-Lebrato, J.; Zapatero-Gaviria, A.; Casasola-Sánchez, G.G. Importance of Lung Ultrasound Follow-Up in Patients Who Had Recovered from Coronavirus Disease 2019: Results from a Prospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthy, A.; Faqihi, F.; Abuhamdah, M.; Noor, A.; Naseem, N.; Balhamar, A.; Al Saud, A.A.A.S.B.A.; Brindley, P.G.; Memish, Z.A.; Karakitsos, D.; et al. Prospective Longitudinal Evaluation of Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasound in Critically Ill Patients With Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia. J. Ultrasound Med. 2021, 40, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnikel, M.; Alig, A.H.S.; Anton, S.; Arenz, L.; Bendz, H.; Fraccaroli, A.; Götschke, J.; Vornhülz, M.; Plohmann, P.; Weiglein, T.; et al. Follow-up lung ultrasound to monitor lung failure in COVID-19 ICU patients. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Sun, Y.; Sheng, W.; Yao, Q. Diagnostic performance of lung ultrasound for transient tachypnea of the newborn: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, T.; Bulla, P.; Jödicke, L.; Klein, C.; Bott, S.M.; Keller, R.; Malek, N.; Fröhlich, E.; Göpel, S.; Blumenstock, G.; et al. Can follow up lung ultrasound in Coronavirus Disease-19 patients indicate clinical outcome? PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLario, D.J.; Sivitz, A.B. Point-of-Care Ultrasound in Pediatric Clinical Care. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafort, T.T.; Rufino, R.; da Costa, C.H.; da Cal, M.S.; Monnerat, L.B.; Litrento, P.F.; Parra, L.L.Z.; Marinho, A.S.E.S.; Lopes, A.J. One-month outcomes of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection and their relationships with lung ultrasound signs. Ultrasound J. 2021, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Yoshikawa, H.; Uchiyama, S.; Nagata, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Hiki, M.; Minamino, T.; Takahashi, K.; Daida, H.; et al. Artificial intelligence-based point-of-care lung ultrasound for screening COVID-19 pneumoniae: Comparison with CT scans. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, B.; Schuit, F.; Lieveld, A.; Azijli, K.; Nanayakkara, P.W.; Bosch, F. Comparing lung ultrasound: Extensive versus short in COVID-19 (CLUES): A multicentre, observational study at the emergency department. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e048795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenck, E.J.; Rajwani, K. Ultrasound in the diagnosis and management of pneumonia. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 29, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xirouchaki, N.; Kondili, E.; Prinianakis, G.; Malliotakis, P.; Georgopoulos, D. Impact of lung ultrasound on clinical decision making in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, M.; Isitt, C.E.; Vizcaychipi, M.P. Comment on Xirouchaki et al.: Impact of lung ultrasound on clinical decision making in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 1061–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.P.; Tunik, M.G.; Tsung, J.W. Prospective evaluation of point-of-care ultrasonography for the diagnosis of pneumonia in children and young adults. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buz Yaşar, A.; Tarhan, M.; Atalay, B.; Kabaalioğlu, A.; Girit, S. Investigation of Childhood Pneumonia With Thoracic Ultrasound: A Comparison Between X-ray and Ultrasound. Ultrasound Q. 2023, 39, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Xu, X.; Xu, Y. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the accuracy of lung ultrasound and chest radiography in diagnosing community acquired pneumonia in children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2024, 59, 3130–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balk, D.S.; Lee, C.; Schafer, J.; Welwarth, J.; Hardin, J.; Novack, V.; Yarza, S.; Hoffmann, B. Lung ultrasound compared to chest X-ray for diagnosis of pediatric pneumonia: A meta-analysis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2018, 53, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llamas-Álvarez, A.M.; Tenza-Lozano, E.M.; Latour-Pérez, J. Accuracy of Lung Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of Pneumonia in Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Chest 2017, 151, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padrao, E.M.H.; Caldeira Antonio, B.; Gardner, T.A.; Miyawaki, I.A.; Gomes, C.; Riceto Loyola Junior, J.E.; Daibes Rachid de Andrade, M.; Reis Marques, I.; Azevedo Ferreira de Souza, I.; Hellen Azevedo da Silva, C.; et al. Lung Ultrasound Findings and Algorithms to Detect Pneumonia: A Systematic Review and Diagnostic Testing Meta-Analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2025, 53, e2271–e2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darge, K.; Chen, A. Ultrasonography of the lungs and pleurae for the diagnosis of pneumonia in children: Prime time for routine use. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 187–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobson, D.J.; Cohen, O.; Cherniavsky, E.; Batumsky, M.; Fuchs, L.; Yellin, A. Ultrasonography can replace chest X-rays in the postoperative care of thoracic surgical patients. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaudin, F.; Marjanovic, N.; de Carvalho, H.; Gaborit, B.; Le Bastard, Q.; Boucher, E.; Haroche, D.; Montassier, E.; Le Conte, P. Contribution of lung ultrasound in diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia in the emergency department: A prospective multicentre study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e046849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strøm, J.J.; Haugen, P.S.; Hansen, M.P.; Graumann, O.; Jensen, M.B.B.; Aakjær Andersen, C. Accuracy of lung ultrasonography in the hands of non-imaging specialists to diagnose and assess the severity of community-acquired pneumonia in adults: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e036067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geis, D.; Canova, N.; Lhopitallier, L.; Kronenberg, A.; Meuwly, J.Y.; Senn, N.; Mueller, Y.; Fasseur, F.; Boillat-Blanco, N. Exploration of the Acceptance of the Use of Procalcitonin Point-of-Care Testing and Lung Ultrasonography by General Practitioners to Decide on Antibiotic Prescriptions for Lower Respiratory Infections: A Qualitative Study. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e063922. [Google Scholar]
- Tran-Le, Q.K.; Thai, T.T.; Tran-Ngoc, N.; Duong-Minh, N.; Nguyen-Ho, L.; Nguyen-Dang, K.; Nhat, P.T.H.; Pisani, L.; Vu-Hoai, N.; Le-Thuong, V. Lung ultrasound for the diagnosis and monitoring of pneumonia in a tuberculosis-endemic setting: A prospective study. BMJ Open 2025, 15, e094799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morello, R.; Camporesi, A.; De Rose, C.; Di Sarno, L.; Tagliaferri, L.; Orlandi, A.; Francavilla, M.; Supino, M.; Villani, A.; Musolino, A.C.; et al. Point-of-care lung ultrasound to differentiate bacterial and viral lower respiratory tract infections in pediatric age: A multicenter prospective observational study. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 35196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultrasound Guidelines: Emergency, Point-of-Care, and Clinical Ultrasound Guidelines in Medicine. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2023, 82, e115–e155. [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli, G.; Fraccalini, T.; Cardinale, L. Lung ultrasound: Are we diagnosing too much? Ultrasound J. 2023, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, R.E.; Mays, N.B.; Fraser, A. Do you see the problem? Visualising a generalised ‘complex local system’ of antibiotic prescribing across the United Kingdom using qualitative interview data. Crit. Public Health 2023, 33, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpicelli, G.; Rovida, S. Clinical research on point-of-care lung ultrasound: Misconceptions and limitations. Ultrasound J. 2024, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsegaw, T.K.; Alemu, E.A.; Arage, F.G.; Tadese, Z.B.; Taye, E.A.; Abate, T.G. Geographically weighted regression analysis of incomplete basic childhood vaccination in Sub-Saharan Africa: Evidence from DHS, 2019–2024. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0336498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyplosz, B.; Grenier, B.; Roche, N.; Roubille, F.; Loubet, P.; Sultan, A.; Fougère, B.; Fernandes, J.; Duhot, D.; Moulin, B.; et al. Pneumococcal vaccination at 65 years and vaccination coverage in at-risk adults: A retrospective population-based study in France. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0329703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuqbil, M.; Rabbani, S.I.; Alharbi, F.G.; Alharbi, M.H.; Gilkaramenthi, R.; Khormi, A.M.S.; Almalki, M.E.M.; Alsanie, W.F.; Alamri, A.S.; Alhomrani, M.; et al. Seasonal patterns of infectious diseases in Riyadh Province, Saudi Arabia: A retrospective analysis. Crit. Public Health 2025, 35, 2474686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puenpa, J.; Tantipraphat, L.; Aeemjinda, R.; Vichaiwattana, P.; Korkong, S.; Poovorawan, Y. Seasonal dynamics and genetic diversity of human adenoviruses in patients with acute respiratory infection in Thailand, 2024. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0338450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yu, K.; Zhang, H. Laboratory tests associated with clinical outcome in patients with severe/critical COVID-19: A retrospective study. Crit. Public Health 2025, 35, 2574958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, S.; Ulgen, A.; Sivgin, H.; Cetin, M.; Li, W. Osmolality as a strong predictor of COVID-19 mortality and its possible links to other biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0331344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Calpe, S.; Guitart, C.; Carrasco, J.L.; Salas, B.; Cambra, F.J.; Jordan, I.; Balaguer, M. Lung Elastance and Microvascularization as Quantitative Non-Invasive Biomarkers for the Aetiological Diagnosis of Lung Consolidations in Children (ELASMIC Study). Diagnostics 2025, 15, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartlehner, G.; Wagner, G.; Affengruber, L.; Chapman, A.; Dobrescu, A.; Klerings, I.; Kaminski-Hartenthaler, A.; Spiel, A.O. Point-of-Care Ultrasonography in Patients With Acute Dyspnea: An Evidence Report for a Clinical Practice Guideline by the American College of Physicians. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Irwig, L.; Craig, J.; Glasziou, P. Comparative accuracy: Assessing new tests against existing diagnostic pathways. BMJ 2006, 332, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Haken, I.; Ben Allouch, S.; van Harten, W.H. Quality and safety management of advanced medical technologies in home care organisations in the Netherlands: A qualitative survey at the tactical level. BMJ Open 2025, 15, e101968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.F.; Lynch, K.; Thorne, S.; Currie, L.M.; Arora, R.C.; McDermid, R.C.; Ahmad, O.; Crowe, S.; Hoiss, S.; David, A.; et al. From hospital to home: A heightened window of vulnerability post-critical illness. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0334092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Castellano, M.; Aguiar, D.; Aguilar-Rodríguez, F.; Cubo, P.; Flox, G.; Murcia, J.M.; Coloma, E.; Gracia, V.M.; Vicente, C.; Salamanca-Bautista, P. Practical management of heart failure in hospital at home: Recommendations from the Spanish Society of Internal Medicine and the Spanish Society of Hospital at Home. Rev. Clínica Española (Engl. Ed.) 2025, 225, 502399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prenner, S.B.; Dougherty, K.; Shofer, F.S.; Goldberg, L.R.; Panebianco, N. Home-operated ultrasound exam for detection of worsening heart failure (HOUSE-HF). ESC Heart Fail. 2025, 12, 3372–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaiodimos, L.; Kumar, S.S.; Gulani, P.; Maliha, M.; Mylonakis, A.; Lemberg, L.; Pranevicius, M.; Faillace, R.T.; Siembos, I.I.; Galen, B.; et al. Assessment of the Association Between Lung POCUS Findings During Preoperative Assessment and Cardiopulmonary Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Major Abdominal Surgery: A Pilot Study Protocol. POCUS J. 2025, 10, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guziak, M.; Walkiewicz, M.; Nowicka-Sauer, K.; Šantrić-Milićević, M. Future research directions on physicians in Polish primary healthcare: Workforce challenges and policy considerations. Crit. Public Health 2025, 35, 2495687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Red Flag Signs | Implications |
|---|---|
| Pleural line abnormality (thickened, irregular) | Possible ARDS |
| Absence or reduction of pleural sliding (gliding sign) | Possible ARDS |
| ‘Spared areas’ within confluent B-lines | Possible ARDS |
| Nonhomogeneous distribution of B-lines | Possible ARDS |
| Fluid (liquid) bronchogram | Post-obstructive pneumonia |
| Absence of color Doppler signals within consolidation (poor perfusion) | Necrotizing pneumonia |
| Hypoechoic lesions or microabscesses within consolidations | Necrotizing pneumonia |
| Pleural effusion | Possible complicated pneumonia |
| Hyperdynamic left ventricle | Sepsis |
| Suboptimal diaphragm excursion | Poor respiratory strength or endurance |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Hsu, N.-C.; Lin, Y.-F.; Tsai, H.-B.; Liao, C.; Hsu, C.-H. Ten Questions on Using Lung Ultrasonography to Diagnose and Manage Pneumonia in Hospital-at-Home Model: Part III—Synchronicity and Foresight. Diagnostics 2026, 16, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics16020192
Hsu N-C, Lin Y-F, Tsai H-B, Liao C, Hsu C-H. Ten Questions on Using Lung Ultrasonography to Diagnose and Manage Pneumonia in Hospital-at-Home Model: Part III—Synchronicity and Foresight. Diagnostics. 2026; 16(2):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics16020192
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Nin-Chieh, Yu-Feng Lin, Hung-Bin Tsai, Charles Liao, and Chia-Hao Hsu. 2026. "Ten Questions on Using Lung Ultrasonography to Diagnose and Manage Pneumonia in Hospital-at-Home Model: Part III—Synchronicity and Foresight" Diagnostics 16, no. 2: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics16020192
APA StyleHsu, N.-C., Lin, Y.-F., Tsai, H.-B., Liao, C., & Hsu, C.-H. (2026). Ten Questions on Using Lung Ultrasonography to Diagnose and Manage Pneumonia in Hospital-at-Home Model: Part III—Synchronicity and Foresight. Diagnostics, 16(2), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics16020192







