Beyond SOFA and APACHE II, Novel Risk Stratification Models Using Readily Available Biomarkers in Critical Care
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Definitions and Outcomes
2.3. Model Development and Validation Process
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
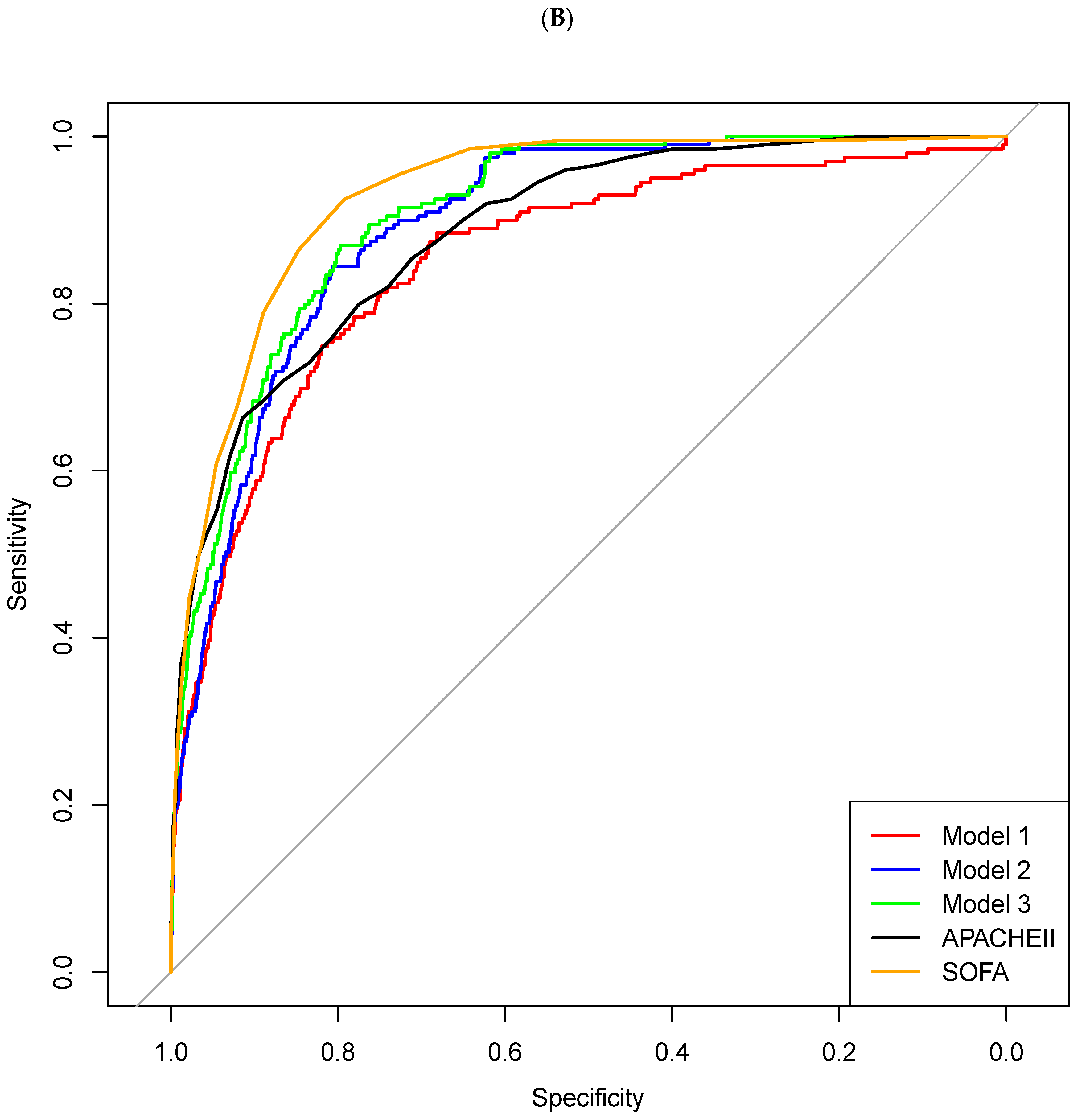
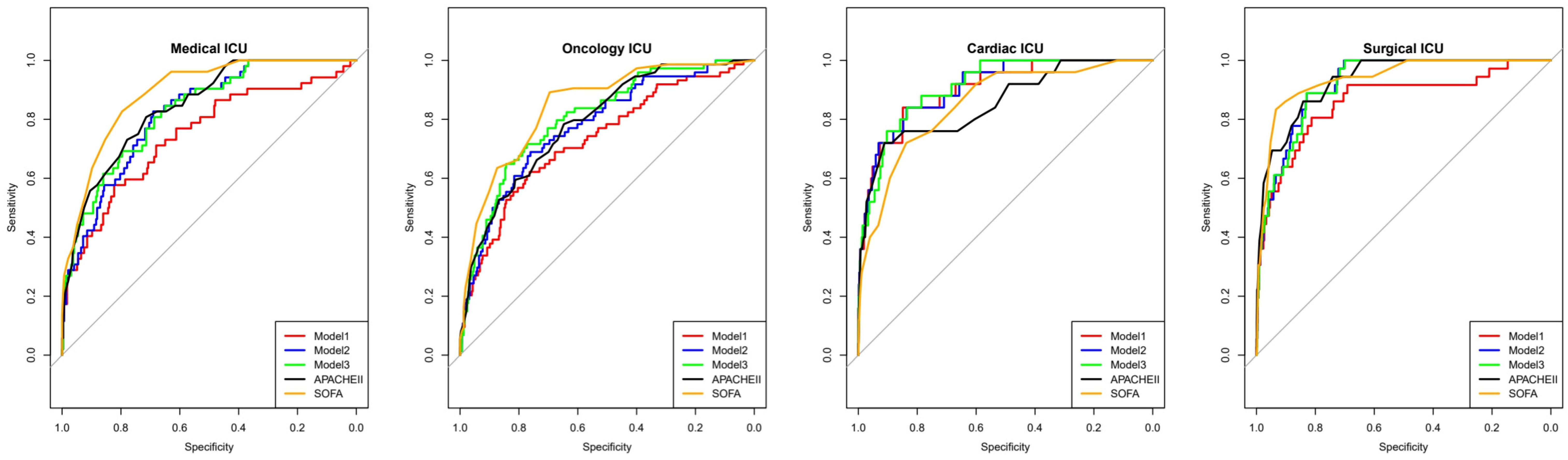
- Model 1: combining LAR and NPAR;
- Model 2: LAR, NPAR, and mechanical ventilation use;
- Model 3: LAR, NPAR, mechanical ventilation use, and CRRT use.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| SOFA | Sequential Organ Failure Assessment |
| APACHE II | Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II |
| LAR | Lactate-to-albumin ratio |
| NPAR | Neutrophil percent-to-albumin ratio |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| UCR | Urea-to-creatinine ratio |
| CAR | C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio |
| CRRT | Continuous renal replacement therapy |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| SHAP | SHapley Additive exPlanations |
| BUN | Blood Urea Nitrogen |
| Cr | Creatinine |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| p-value | Probability Value |
| GCS | Glasgow Coma Scale |
| WBC | White blood cell count |
| EMRs | Electronic Medical Records |
| ML | Machine learning |
| HR | Heart rate |
| RR | Respiratory rate |
| MAP | Mean arterial pressure |
| FiO₂ | Fraction of Inspired Oxygen |
| PaO₂ | Partial Pressure of Oxygen in Arterial Blood |
| PaCO₂ | Partial Pressure of Carbon Dioxide in Arterial Blood |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| Na | Sodium |
| K | Potassium |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| PLT | Platelet Count |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| DNR | Do not resuscitate |
| MV | Mechanical ventilation |
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| APTT | Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time |
| PT | Prothrombin Time |
| INR | International Normalized Ratio |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury |
| LOS | Length of Stay |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| PPV | Positive predictive value |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
| Se | Sensitivity |
| Sp | Specificity |
| CPR | Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation |
| ANC | Absolute neutrophil count |
| ALC | Absolute lymphocyte count |
| eGFR | Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| ACR | Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
References
- Marshall, J.C.; Bosco, L.; Adhikari, N.K.; Connolly, B.; Diaz, J.V.; Dorman, T.; Fowler, R.A.; Meyfroidt, G.; Nakagawa, S.; Pelosi, P.; et al. What is an intensive care unit? A report of the task force of the World Federation of Societies of Intensive and Critical Care Medicine. J. Crit. Care 2017, 37, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.L. The Intensive Care Unit. In Textbook of Critical Care; Vincent, J.L., Abraham, E., Moore, F.A., Kochanek, P.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, A.; Ferdinande, P.; Flaatten, H.; Guidet, B.; Metnitz, P.G.; Moreno, R.P. The variability of critical care bed numbers in Europe. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouch, D.C.; Thompson, J.P. Severity scoring systems in the critically ill. Contin. Educ. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain 2008, 8, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, W.A.; Draper, E.A.; Wagner, D.P.; Zimmerman, J.E. APACHE II: A severity of disease classification system. Crit. Care Med. 1985, 13, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.L.; Moreno, R.; Takala, J.; Willatts, S.; De Mendonca, A.; Bruining, H.; Reinhart, C.K.; Suter, P.M.; Thijs, L.G. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996, 22, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salluh, J.I.; Soares, M. ICU severity of illness scores: APACHE, SAPS and MPM. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2014, 20, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.L.; Moreno, R. Clinical review: Scoring systems in the critically ill. Crit. Care 2010, 14, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, H.; Ge, Q.; Fei, A.; Pan, S. Prognostic Significance of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Sepsis: A Prospective Observational Study. Mediators Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 8191254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Jo, I.J.; Kim, W.Y.; Ryoo, S.M.; Kang, G.H.; Kim, K.; Jo, Y.H.; Chung, S.P.; Joo, Y.S.; et al. Prognostic Value of The Lactate/Albumin Ratio for Predicting 28-Day Mortality in Critically ILL Sepsis Patients. Shock 2018, 50, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statlender, L.; Shochat, T.; Robinson, E.; Fishman, G.; Hellerman-Itzhaki, M.; Bendavid, I.; Singer, P.; Kagan, I. Urea to creatinine ratio as a predictor of persistent critical illness. J. Crit. Care 2024, 83, 154834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahorec, R. Ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte counts--rapid and simple parameter of systemic inflammation and stress in critically ill. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2001, 102, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Zhang, B.; Sun, T.; Zhao, F.; Ma, J.; Pei, X.; He, C.; Che, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y. Neutrophil Percentage to Albumin Ratio was Associated with Clinical Outcomes in Coronary Care Unit Patients. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.E.; Chung, K.S.; Song, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, E.Y.; Jung, J.Y.; Kang, Y.A.; Park, M.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Chang, J.; et al. The C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio as a Predictor of Mortality in Critically Ill Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA; pp. 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Kumrawat, A.; Gupta, S.; Dhillon, H.S.; Kumrawat, P. Prognostic Value of Admission Lactate Levels in Critically Ill Patients: A Comparative Study With Sequential Organ Failure Assessment and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II Scores. Cureus 2024, 16, e71372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Survivor (n = 19,054) | Non-Survivor (n = 666) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient demographics | |||
| Age, years | 63.0 ± 13.1 | 62.0 ± 14.2 | 0.066 |
| Sex, male | 12,037 (63.2) | 432 (64.9) | 0.396 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Malignancy | 11,856 (62.2) | 414 (62.2) | 1.000 |
| Hypertension | 4008 (21.0) | 126 (18.9) | 0.204 |
| Stroke | 2577 (13.5) | 86 (12.9) | 0.886 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 2395 (12.6) | 94 (14.1) | 0.263 |
| Chronic kidney disease a | 1493 (7.8) | 49 (7.4) | 0.705 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 1557 (8.2) | 44 (6.6) | 0.167 |
| Habitual risk factors | |||
| Alcohol intake | 2911 (15.3) | 98 (14.7) | 0.732 |
| Current smoker | 1318 (6.9) | 48 (7.2) | 0.832 |
| Causes of ICU admission | <0.001 | ||
| Perioperative management | 14,424 (75.7) | 65 (9.8) | |
| Cardiovascular disease | 1933 (10.1) | 90 (13.5) | |
| Respiratory distress | 1010 (5.3) | 257 (38.6) | |
| Abdominal disorder | 381 (2.0) | 40 (6.0) | |
| Neurological disorder | 277 (1.5) | 26 (3.9) | |
| Post-cardiac arrest syndrome | 144 (0.8) | 64 (9.6) | |
| Others | 703 (3.7) | 94 (14.1) | |
| Management in the ICU | |||
| Mechanical ventilation | 7089 (37.2) | 616 (92.5) | <0.001 |
| Continuous renal replacement therapy | 580 (3.0) | 229 (34.4) | <0.001 |
| Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation | 238 (1.2) | 75 (11.3) | <0.001 |
| Use of inotropic agent | 1288 (6.8) | 134 (20.1) | <0.001 |
| Use of vasopressor | 851 (4.5) | 75 (11.3) | <0.001 |
| Survivor (n = 19,054) | Non-Survivor (n = 666) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANC (×103/µL) | 9.7 ± 5.2 | 8.9 ± 13.1 | 0.138 |
| ALC (×103/µL) | 1.1 ± 1.3 | 0.8 ± 1.2 | <0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 2.7 ± 0.6 | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 4.7 ± 6.0 | 12.4 ± 11.1 | <0.001 |
| NPAR | 19.8 ± 5.3 | 26.2 ± 9.1 | <0.001 |
| LAR | 0.8 ± 0.9 | 3.0 ± 3.1 | <0.001 |
| UCR | 17.8 ± 8.6 | 24.3 ± 15.3 | <0.001 |
| CAR | 1.6 ± 2.3 | 4.9 ± 4.6 | <0.001 |
| APACHE II | 19.4 ± 8.2 | 35.5 ± 8.8 | <0.001 |
| SOFA score | 3.2 ± 3.2 | 11.3 ± 4.2 | <0.001 |
| Variable | Coefficient | SE | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPAR | 0.0482 | 0.0066 | 1.05 (1.04–1.06) | <0.0001 |
| LAR | 0.4056 | 0.0253 | 1.50 (1.43–1.58) | <0.0001 |
| Use of MV | 2.2578 | 0.1556 | 9.56 (7.05–12.97) | <0.0001 |
| Use of CRRT | 1.5638 | 0.1067 | 4.78 (3.87–5.89) | <0.0001 |
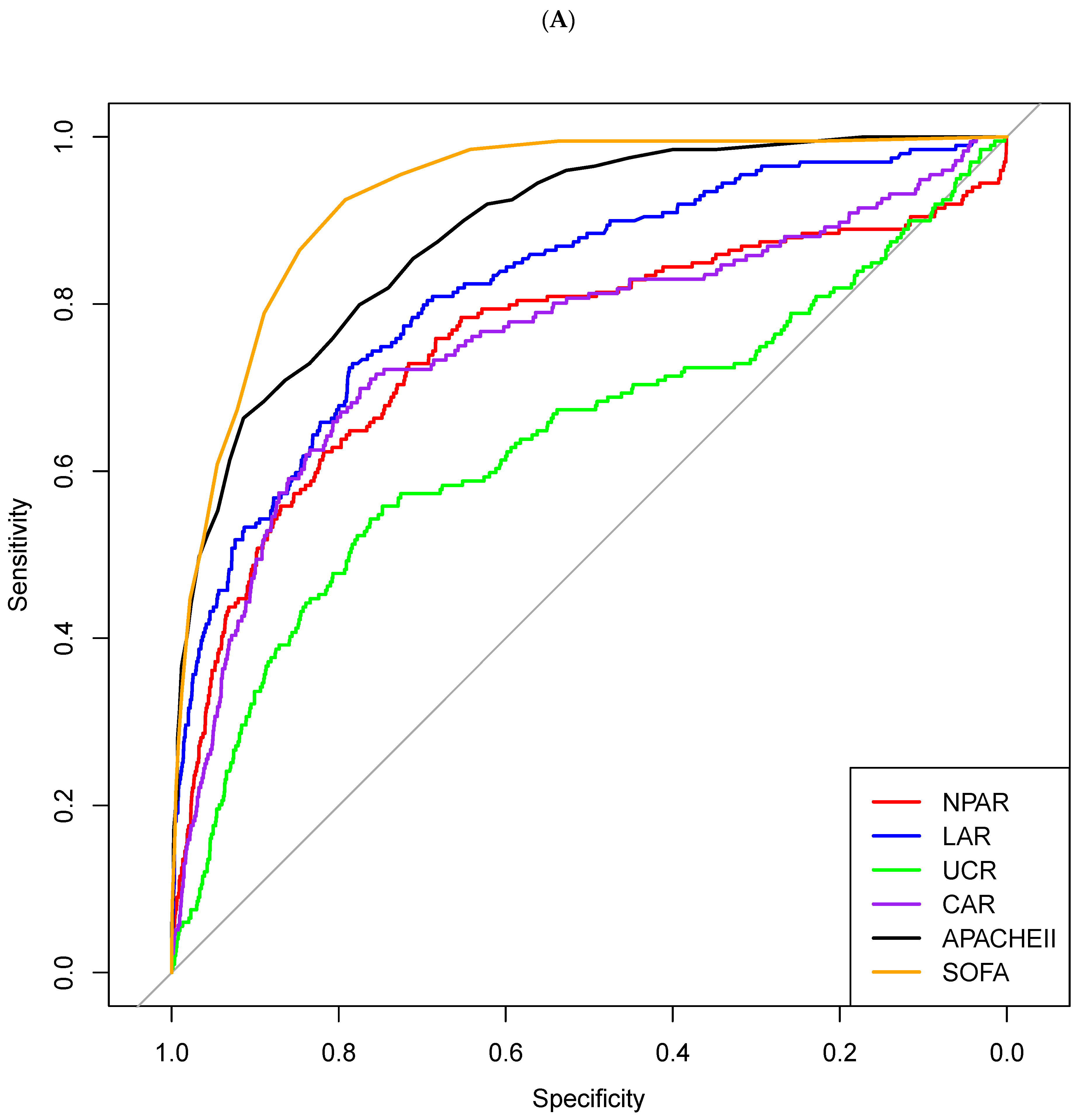
| AUC (95% CI) | Cut-Off | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPAR | 0.754 (0.712–0.796) | 22.7 | 0.678 | 0.754 | 0.086 | 0.986 | 0.751 |
| LAR | 0.823 (0.792–0.854) | 1.01 | 0.716 | 0.762 | 0.093 | 0.988 | 0.760 |
| UCR | 0.651 (0.606–0.696) | 21.1 | 0.510 | 0.744 | 0.064 | 0.978 | 0.737 |
| CAR | 0.759 (0.714–0.805) | 1.9 | 0.704 | 0.777 | 0.092 | 0.988 | 0.775 |
| APACHE II score | 0.903 (0.882–0.924) | 30 | 0.741 | 0.880 | 0.174 | 0.990 | 0.876 |
| SOFA score | 0.933 (0.919–0.947) | 6 | 0.895 | 0.806 | 0.137 | 0.996 | 0.809 |
| MV use | 0.777 (0.757–0.796) | Used | 0.925 | 0.628 | 0.078 | 0.996 | 0.638 |
| CRRT use | 0.657 (0.624–0.691) | Used | 0.345 | 0.970 | 0.278 | 0.978 | 0.949 |
| Model 1 | 0.853 (0.823–0.882) | 0.027 | 0.807 | 0.760 | 0.103 | 0.992 | 0.762 |
| Model 2 | 0.894 (0.875–0.912) | 0.046 | 0.827 | 0.810 | 0.128 | 0.993 | 0.810 |
| Model 3 | 0.908 (0.891–0.925) | 0.039 | 0.848 | 0.812 | 0.133 | 0.994 | 0.813 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, J.; Ahn, J.; Ryu, J.-A. Beyond SOFA and APACHE II, Novel Risk Stratification Models Using Readily Available Biomarkers in Critical Care. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091122
Chung J, Ahn J, Ryu J-A. Beyond SOFA and APACHE II, Novel Risk Stratification Models Using Readily Available Biomarkers in Critical Care. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(9):1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091122
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Jihyuk, Joonghyun Ahn, and Jeong-Am Ryu. 2025. "Beyond SOFA and APACHE II, Novel Risk Stratification Models Using Readily Available Biomarkers in Critical Care" Diagnostics 15, no. 9: 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091122
APA StyleChung, J., Ahn, J., & Ryu, J.-A. (2025). Beyond SOFA and APACHE II, Novel Risk Stratification Models Using Readily Available Biomarkers in Critical Care. Diagnostics, 15(9), 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091122





