Lightweight Evolving U-Net for Next-Generation Biomedical Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Multi-scale feature extraction to improve the capture of nuclei with varying size and morphology.
- Depthwise separable convolutions to reduce parameter count and computational burden.
- Residual connections to facilitate deeper learning and stable convergence.
- Channel reduction and expansion blocks inspired by ShuffleNet for optimized memory usage.
- Spatial attention mechanisms to refine feature relevance and suppress background noise in cluttered histopathological scenes.
2. Related Works
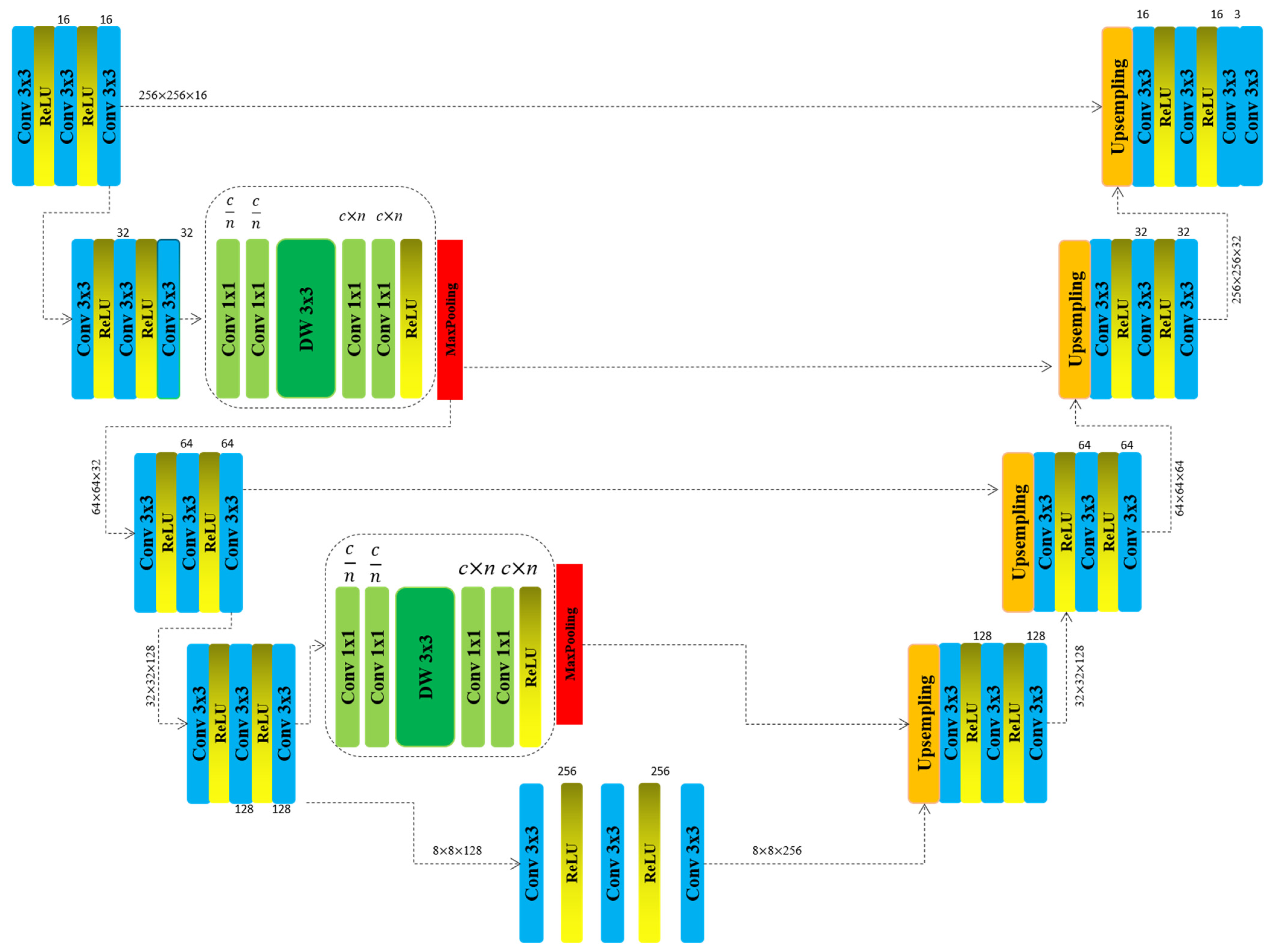
3. Materials and Methods
| Algorithm 1. Layer-wise architecture of the proposed Lightweight Evolving U-Net, including convolutional operations, activation functions, and spatial dimensions. | |
| Encoder (Downsampling ) | Decoder (Upsampling ) |
| Input {256 × 256 × c} | Block_5 {8 × 8 × 128} |
| Block_1 {256 × 256 × 16} | Block_6 {32 × 32 × 128} |
| -Conv3 × 3 -ReLU() -Conv3 × 3 -ReLU() -Conv3 × 3 | -Upsampling -Conv3 × 3 -ReLU() -Conv3 × 3 -ReLU() -Conv3 × 3 |
| Block_2 {256 × 256 × 32} | Block_7 {64 × 64 × 64} |
| -Conv3 × 3 -ReLU() -Conv3 × 3 -ReLU() -Conv3 × 3 | -Conv3 × 3 -ReLU() -Conv3 × 3 -ReLU() -Conv3 × 3 |
| NewBlock_1 {256 × 256 × 32} | Block_8 {128 × 128 × 32} |
| -Conv1 × 1 n/c -Conv1 × 1 n/c -DW3 × 3 -Conv1 × 1 n × c -Conv1 × 1 n × c -ReLU() | -Conv1 × 1 n/c -Conv1 × 1 n/c -DW3 × 3 -Conv1 × 1 n × c -Conv1 × 1 n × c -ReLU() |
| MaxPooling {128 × 128 × 16} | Block_9 {256 × 256 × 16} |
| Block_3 {64 × 64 × 16} | Block_4 {256 × 256 × c} |
| Block_4 {32 × 32 × 64} | |
| NewBlock_2 {32 × 32 × 128} | |
| Block_5 {8 × 8 × 128} | |
4. Results and Discussion
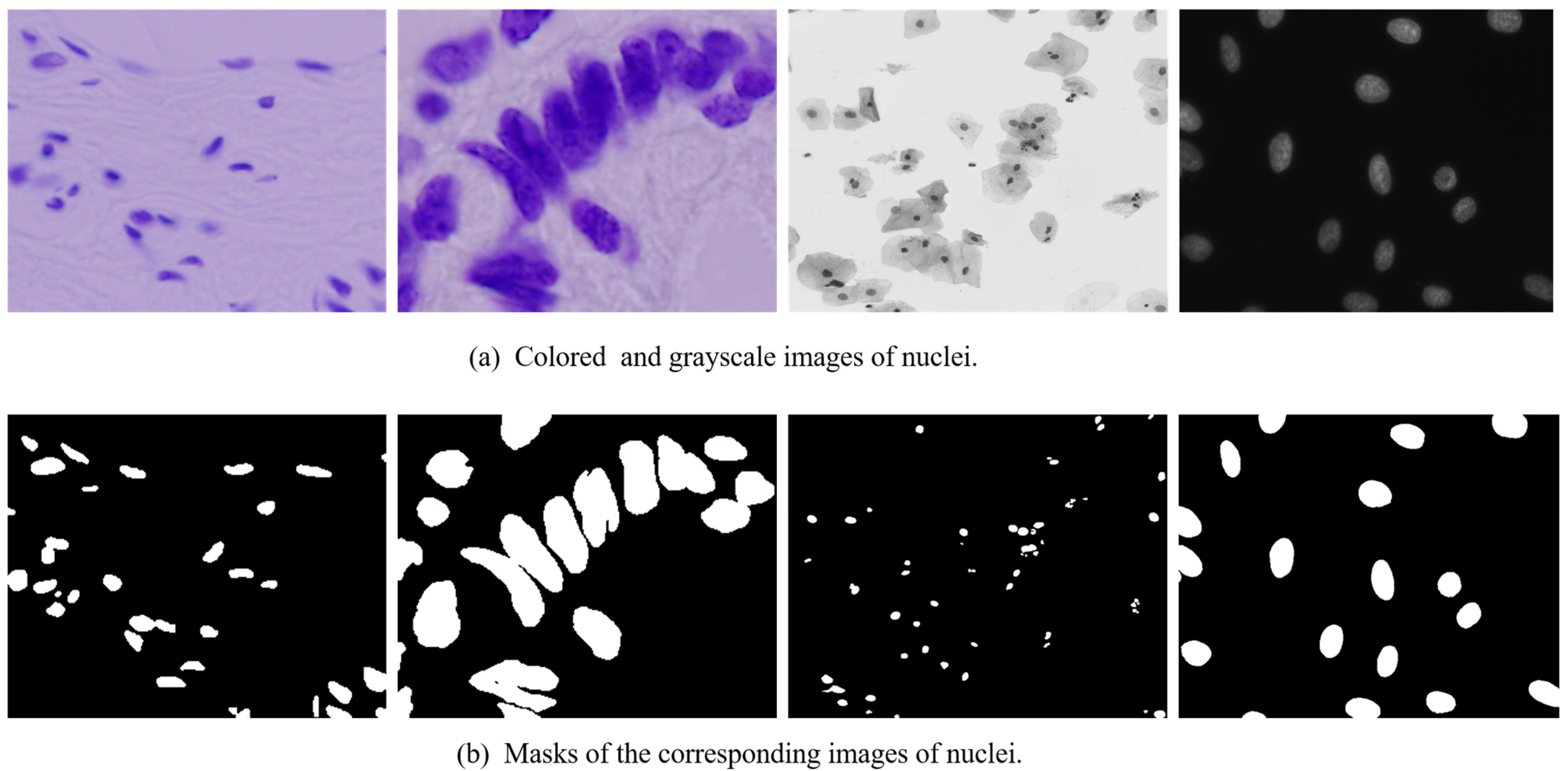
4.1. Dataset
4.2. The Data-Preprocessing
4.3. Comparative Analysis of Segmentation Models
4.4. Comparison with SOTA Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basu, A.; Senapati, P.; Deb, M.; Rai, R.; Dhal, K.G. A survey on recent trends in deep learning for nucleus segmentation from histopathology images. Evol. Syst. 2024, 15, 203–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.K.; Lim, C.C.; Hussain, F.A.; Oung, Q.W.; Yazid, A.I.; Azmi, S.M.; Yazid, H.; Chong, Y.F. The Current Challenges Review of Deep Learning-Based Nuclei Segmentation of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2025, 16, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z. Review of cervical cell segmentation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.; Efstathiou, C.; Yue, H.; Draviam, V.M. Opportunities and challenges for deep learning in cell dynamics research. Trends Cell Biol. 2024, 34, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riana, D.; Na’am, J.; Saputri, D.U.E.S.; Hadianti, S.; Aziz, F.; Liawatimena, S.P.; Hewiz, A.S.; Metalica, D.P.; Herwanto, T. Comparison of Segmentation Analysis in Nucleus Detection with GLCM Features using Otsu and Polynomial Methods. J. RESTI (Rekayasa Sist. Dan Teknol. Inf.) 2023, 7, 1422–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.N.; Fraz, M.M. Nuclei probability and centroid map network for nuclei instance segmentation in histology images. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 15447–15460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseva, T.; Omidali, B.; Hippeläinen, E.; Mäkelä, T.; Wilppu, U.; Sofiev, A.; Merivaara, A.; Yliperttula, M.; Savolainen, S.; Salli, E. Marker-controlled watershed with deep edge emphasis and optimized H-minima transform for automatic segmentation of densely cultivated 3D cell nuclei. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, C.G.; Nagaraj, P.; Muneeswaran, V.; Mokshagni, M.; Jaswanth, M. Astute Segmentation and Classification of leucocytes in blood microscopic smear images using titivated K-means clustering and robust SVM techniques. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 6–8 May 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 818–824. [Google Scholar]
- Win, K.Y.; Choomchuay, S.; Hamamoto, K.; Raveesunthornkiat, M. Detection and classification of overlapping cell nuclei in cytology effusion images using a double-strategy random forest. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Qiao, S.; Hao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G. Breast cancer histopathological images recognition based on two-stage nuclei segmentation strategy. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, T.; Prasath, V.S.; Kawanaka, H.; Aronow, B.J.; Tsuruoka, S. Computational nuclei segmentation methods in digital pathology: A survey. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos, O.; Hoque, M.Z.; Keskinarkaus, A.; Kemi, N.; Näpänkangas, J.; Eskuri, M.; Pohjanen, V.M.; Kauppila, J.H.; Seppänen, T. Optimized detection and segmentation of nuclei in gastric cancer images using stain normalization and blurred artifact removal. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2023, 248, 154694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncayo, R.; Martel, A.L.; Romero, E. Removing non-nuclei information from histopathological images: A preprocessing step towards improving nuclei segmentation methods. J. Pathol. Inform. 2023, 14, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.; Fu, C.; Tian, Y.; Song, W.; Sham, C.W. Gsn-hvnet: A lightweight, multi-task deep learning framework for nuclei segmentation and classification. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Lei, Y.; Shkolnikov, V.; Xin, D.; Auduong, A.; Barcelo, S.; Allebach, J.; Delp, E.J. An ensemble method with edge awareness for abnormally shaped nuclei segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 4315–4325. [Google Scholar]
- Senapati, P.; Basu, A.; Deb, M.; Dhal, K.G. Sharp dense u-net: An enhanced dense u-net architecture for nucleus segmentation. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2024, 15, 2079–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, B.; Digdarshi, D.; Paul, S.; Nayak, G.K.; Saxena, S. Effect of learning parameters on the performance of the U-Net architecture for cell nuclei segmentation from microscopic cell images. Microscopy 2023, 72, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, S.; Belalem, G.; Mahmoudi, S. An Automatic Nucleus Segmentation and Classification of White Blood Cell with ResUNet. Int. Inf. Eng. Technol. Assoc. 2025, 30, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Chen, L.; Tao, Q.; Wang, E.; Yu, Y. GA-UNeT: A lightweight ghost and attention u-net for medical image segmentation. J. Imaging Inform. Med. 2024, 37, 1874–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarov, F.; Khojamuratova, U.; Komoliddin, M.; Bolikulov, F.; Muksimova, S.; Cho, Y.-I. MBGPIN: Multi-Branch Generative Prior Integration Network for Super-Resolution Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traisuwan, A.; Limsiroratana, S.; Phukpattaranont, P.; Tandayya, P. Dynamic U-Net for multi-organ nucleus segmentation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; He, D.; Wang, K.; Wang, L. Lightweight multi-scale attention group fusion structure for nuclei segmentation. J. Supercomput. 2025, 81, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuiveling, M.; Liu, H.; Eek, D.; Breimer, G.E.; Suijkerbuijk, K.P.; Blokx, W.A.; Veta, M. A novel dataset for nuclei and tissue segmentation in melanoma with baseline nuclei segmentation and tissue segmentation benchmarks. GigaScience 2025, 14, giaf011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, M.Y.; Jeong, J.; Yang, S.; Kim, M.S.; Moon, I. Quantitative analysis of the dexamethasone side effect on human-derived young and aged skeletal muscle by myotube and nuclei segmentation using deep learning. Bioinformatics 2025, 41, btae658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, A.; Sharif, M.; Khan, M.A.; Nisar, W.; Alhaisoni, M. FF-UNet: A U-shaped deep convolutional neural network for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Cogn. Comput. 2022, 14, 1287–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ye, H.; Shu, X. DA-Net: Deep Attention Network for Biomedical Image Segmentation. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2025, 135, 117283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, R.; Sheng, H.; Jin, K.W.; Wu, F.; Luo, D.; Wen, Z.; Tang, C.; Yang, D.M.; Jia, L.; Amgad, M.; et al. A deep learning approach for histology-based nucleus segmentation and tumor microenvironment characterization. Mod. Pathol. 2023, 36, 100196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, S.; Wu, R.; Su, F.; Wang, G.; Guo, L.; Zhao, Z. NuSEA: Nuclei Segmentation with Ellipse Annotations. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2024, 28, 5996–6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addanki, S.; Sumathi, D. RLeU-Net: Segmentation of blood vessels in retinal fundus images for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 84, 6113–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Cheng, Y. SACU-Net: Shape-aware U-Net for Biomedical Image Segmentation with Attention Mechanism and Context Extraction. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 5719–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F. Microscopy cell nuclei segmentation with enhanced U-Net. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Bao, X.; Cheng, Q.; McCoy, S. CNN-Modified Encoders in U-Net for Nuclei Segmentation and Quantification of Fluorescent Images. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 107089–107097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goceri, E. Nuclei segmentation using attention aware and adversarial networks. Neurocomputing 2024, 579, 127445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavntaniti, K.; Plissiti, M.E.; Vrigkas, M.; Nikou, C. Accurate Cell Segmentation Based on Generative Adversarial Networks and Nuclei Guide Factors. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Athens, Greece, 27–30 May 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Lim, S.; Lu, Y.; Jung, S.W. Reversed domain adaptation for nuclei segmentation-based pathological image classification. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 168, 107726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budginaitė, E.; Morkūnas, M.; Laurinavičius, A.; Treigys, P. Deep learning model for cell nuclei segmentation and lymphocyte identification in whole slide histology images. Informatica 2021, 32, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wei, B.; Lai, M.; Shou, J.; Fan, Y.; Xu, Y. MSNSegNet: Attention-based multi-shape nuclei instance segmentation in histopathology images. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2024, 62, 1821–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, S.; Das, D.; Alabhya, K.; Kanfade, A.; Kumar, A.; Kini, J. NucleiSegNet: Robust deep learning architecture for the nuclei segmentation of liver cancer histopathology images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 128, 104075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Q.; Li, F. AFN-Net: Adaptive Fusion Nucleus Segmentation Network Based on Multi-Level U-Net. Sensors 2025, 25, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Deng, R.; Liu, Q.; Yao, T.; Bao, S.; Remedios, L.W.; Landman, B.A.; Tang, Y.; Huo, Y. All-in-sam: From weak annotation to pixel-wise nuclei segmentation with prompt-based finetuning. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2722, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

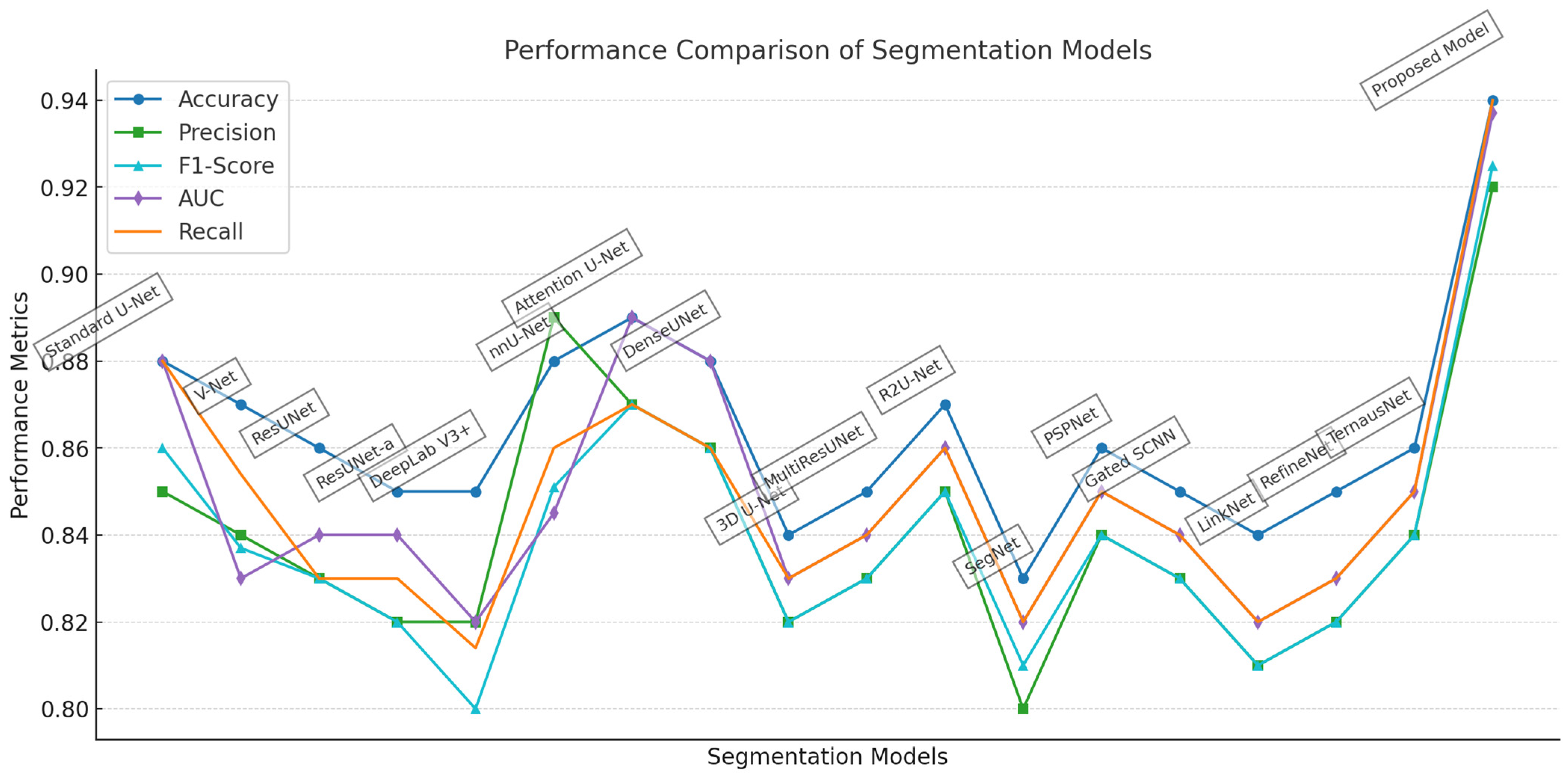
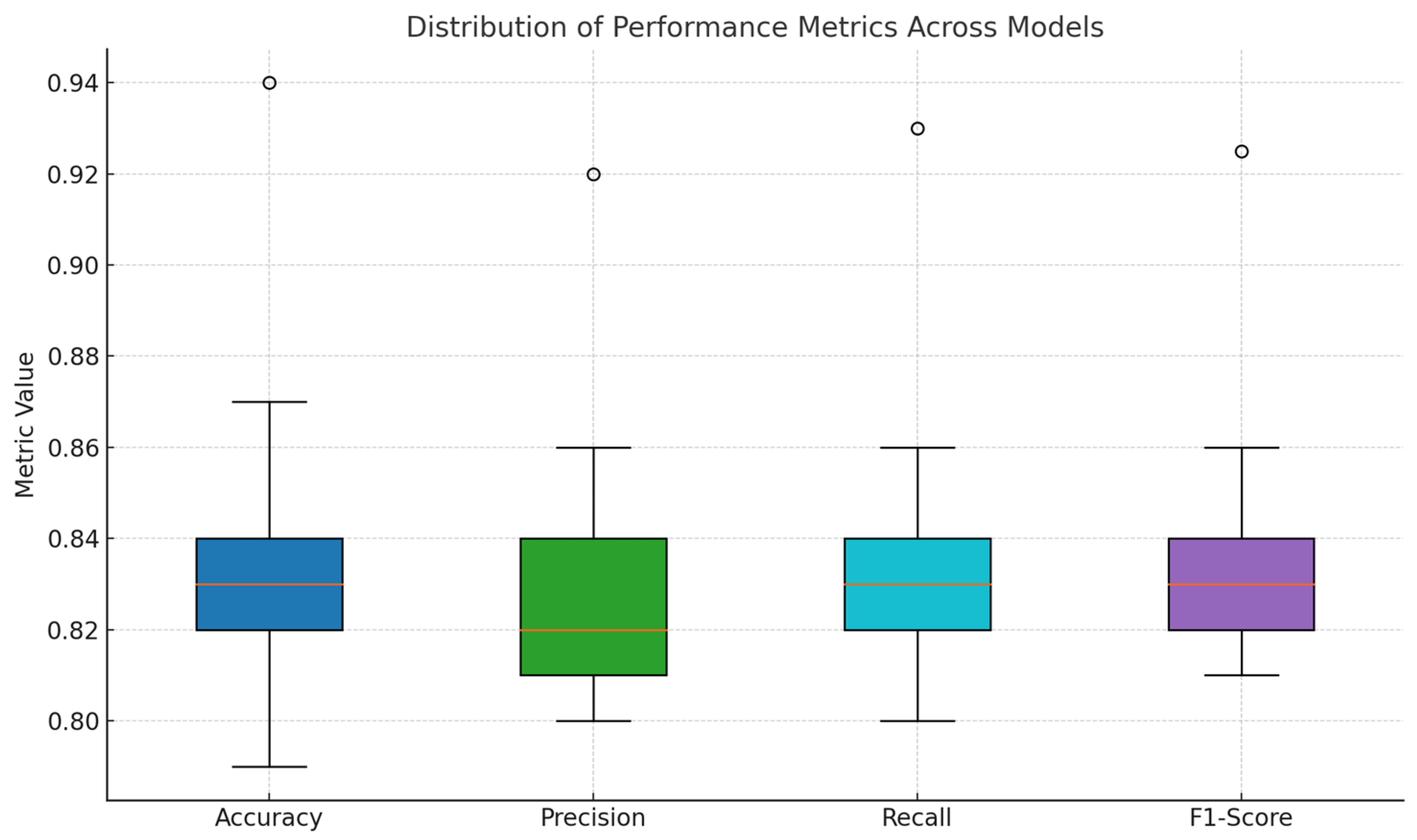
| Model | Architecture | Accuracy | Precision | F1-Score | Recall | DSC | IoU | FoM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard U-Net | Convolutional Network | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.754 | 0.762 |
| V-Net | Volumetric U-net | 0.87 | 0.84 | 0.837 | 0.854 | 0.85 | 0.739 | 0.735 |
| ResUNet | U-Net with Residual Connections | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.709 | 0.709 |
| ResUNet-a | Advanced ResUNet | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.695 | 0.702 |
| DeepLab V3+ | Atrous Convolutions | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.8 | 0.814 | 0.8 | 0.667 | 0.691 |
| nnU-Net | Self-adapting Framework based on U-Net | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.851 | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 0.777 |
| Attention U-Net | U-Net with Attention Mechanisms | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 0.77 |
| DenseUNet | Dense Connections in U-Net | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.754 | 0.754 |
| 3D U-Net | 3D Volumetric U-Net | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.695 | 0.702 |
| MultiResUNet | Multi-Resolution U-Net | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.709 | 0.717 |
| R2U-Net | Recurrent Residual U-Net | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.739 | 0.747 |
| SegNet | Encoder–Decoder Segmentation Network | 0.83 | 0.8 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.681 | 0.68 |
| PSPNet | Pyramid Scene Parsing Network | 0.86 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.724 | 0.732 |
| Gated SCNN | Gated Spatial CNN for Segmentation | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.709 | 0.717 |
| LinkNet | LinkNet Segmentation | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.681 | 0.688 |
| RefineNet | Multi-Path Refinement Network | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.695 | 0.702 |
| TernausNet | U-Net with VGG11 Encoder | 0.86 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.724 | 0.732 |
| Proposed Model | Modified U-Net | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.925 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.905 | 0.869 |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Computational Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NucleiSegNet [39] | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.85 | 0.85 | Low |
| Gsn-hvnet [15] | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.83 | Low |
| HER-CNN [16] | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.83 | Low |
| Sharp dense u-net [17] | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.83 | Moderate |
| Deep Unet [18] | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.82 | 0.81 | High |
| AFN-Net [40] | 0.80 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.82 | Moderate |
| CNN-Modified [33] | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 | Low |
| Dynamic U-Net [22] | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.83 | Moderate |
| NuSEA [29] | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.82 | Low |
| WCSegNe [19] | 0.80 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.82 | Moderate |
| Adversarial Networks [34] | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.84 | Low |
| MSNSegNet [38] | 0.79 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.81 | Moderate |
| GA-UNeT [20] | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.85 | Moderate |
| SACU-Net [31] | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.86 | High |
| RUDA [36] | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.82 | Low |
| All-in-sam [41] | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.82 | Low |
| Proposed Model | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.925 | High |
| Model Variant | DSC | Accuracy | Parameters (M) | Inference Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full Proposed Model (All Modules) | 0.950 | 0.940 | 2.3 | 48 |
| w/o Depthwise Separable Convs | 0.941 | 0.931 | 6.1 | 61 |
| w/o Residual Connections | 0.936 | 0.926 | 2.3 | 47 |
| w/o Spatial Attention | 0.931 | 0.922 | 2.1 | 44 |
| w/o Channel Reduction/Expansion | 0.938 | 0.929 | 3.6 | 52 |
| Baseline U-Net | 0.910 | 0.902 | 7.8 | 66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Safarov, F.; Khojamuratova, U.; Komoliddin, M.; Kurbanov, Z.; Tamara, A.; Nizamjon, I.; Muksimova, S.; Cho, Y.I. Lightweight Evolving U-Net for Next-Generation Biomedical Imaging. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091120
Safarov F, Khojamuratova U, Komoliddin M, Kurbanov Z, Tamara A, Nizamjon I, Muksimova S, Cho YI. Lightweight Evolving U-Net for Next-Generation Biomedical Imaging. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(9):1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091120
Chicago/Turabian StyleSafarov, Furkat, Ugiloy Khojamuratova, Misirov Komoliddin, Ziyat Kurbanov, Abdibayeva Tamara, Ishonkulov Nizamjon, Shakhnoza Muksimova, and Young Im Cho. 2025. "Lightweight Evolving U-Net for Next-Generation Biomedical Imaging" Diagnostics 15, no. 9: 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091120
APA StyleSafarov, F., Khojamuratova, U., Komoliddin, M., Kurbanov, Z., Tamara, A., Nizamjon, I., Muksimova, S., & Cho, Y. I. (2025). Lightweight Evolving U-Net for Next-Generation Biomedical Imaging. Diagnostics, 15(9), 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091120






