Clinical and Electrophysiological Predictors of Isthmus Dependency in Atrial Flutter
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
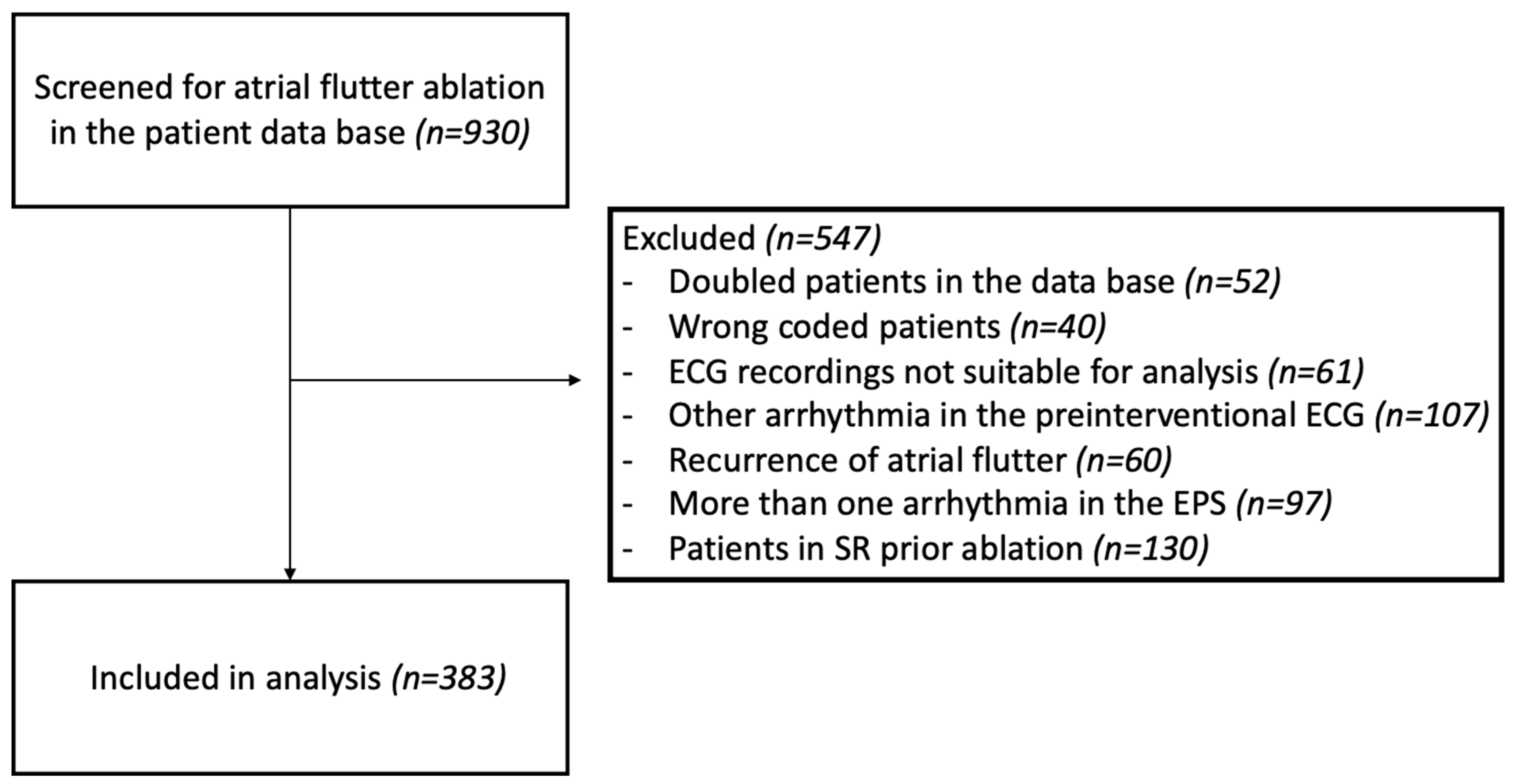
2.1. Study Population
2.2. EPS and Ablation
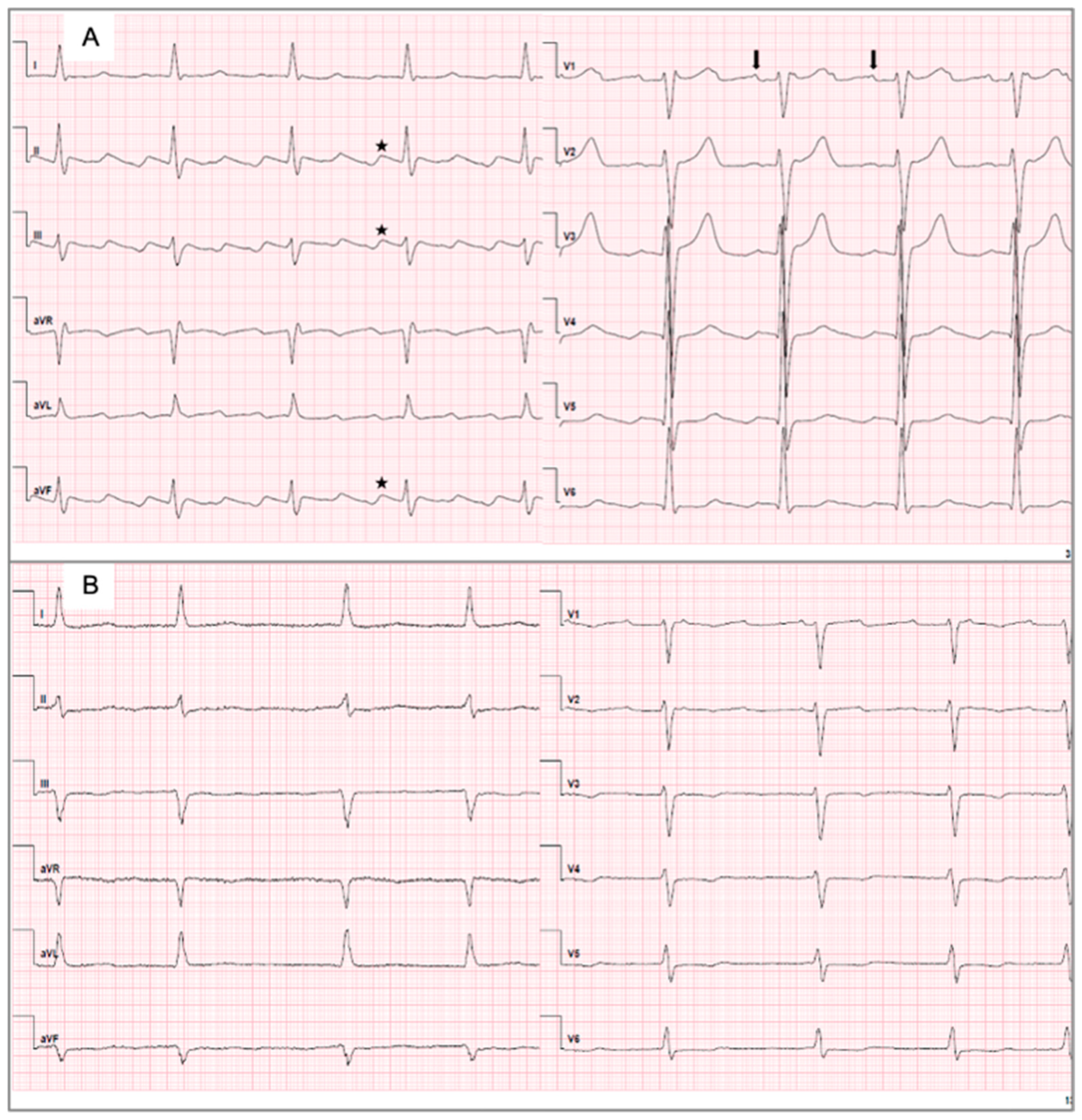
2.3. ECG Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.1.1. Baseline Characteristics of Patients with Type I ECGs and Type II ECGs
3.1.2. Baseline Characteristics of Patients with CTI-Dependent and Non-CTI-Dependent AFL
3.1.3. Baseline Characteristics of Subgroups Based on CTI Dependence and ECG Records
3.2. Characteristics of the ECG and Electrophysiological Parameters Between Subgroups
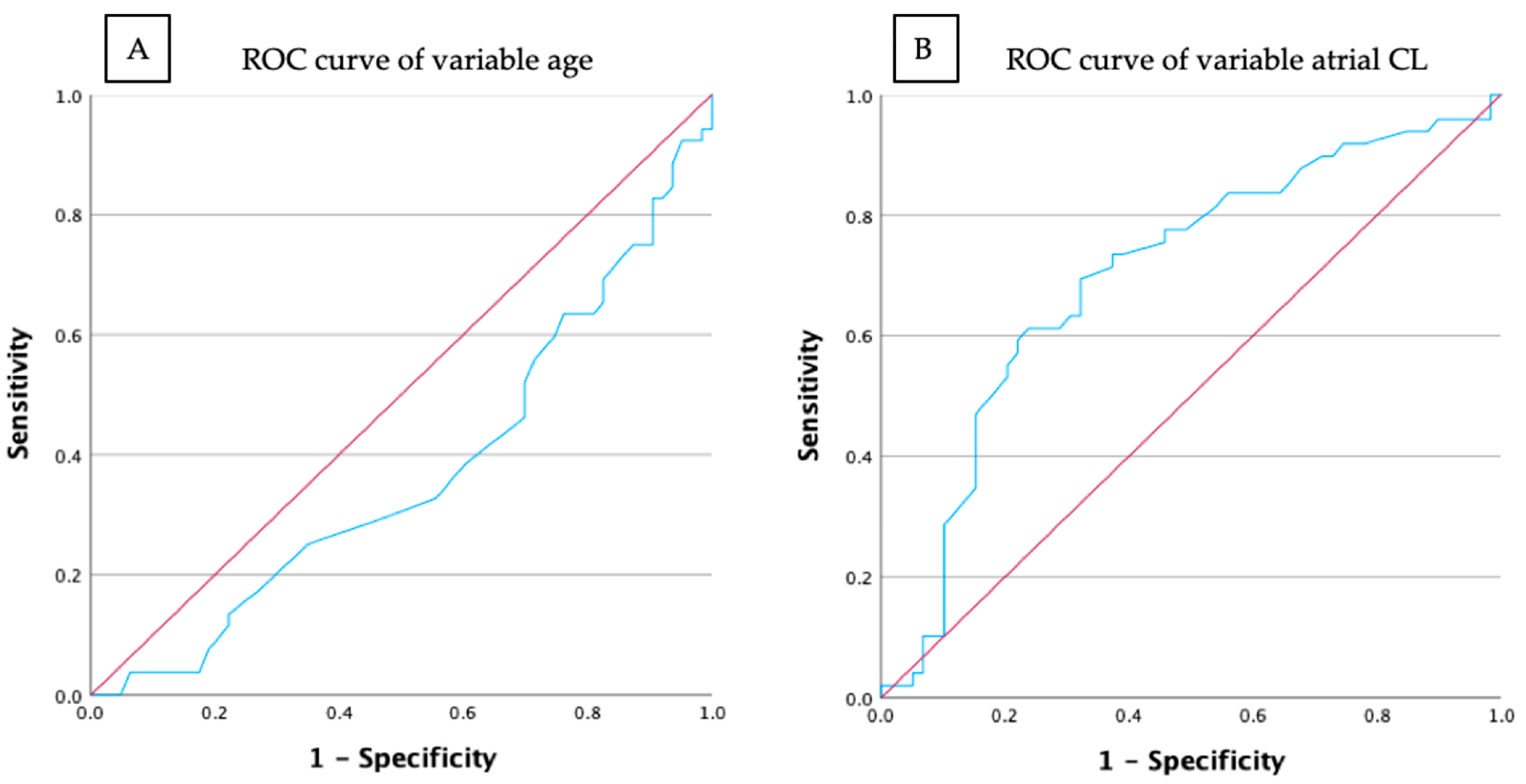
3.3. Prediction Models for CTI-Dependent AFL and Type I ECG
3.4. Prediction Models for CTI-Dependent AFL and Type II ECG
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAs | Antiarrhythmics |
| AAT | Antiarrhythmic therapy |
| AF | Atrial fibrillation |
| AFL | Atrial flutter |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| Bpm | Beats per minute |
| CCW | Counterclockwise |
| CL | Cycle length |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CS | Coronary sinus |
| CTI | Cavotricuspid isthmus |
| CW | Clockwise |
| Df | Degrees of freedom |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| EPS | Electrophysiological study |
| ICD | International classification of diseases |
| IVC | Inferior vena cava |
| LA | Left atrial |
| LAO | Left anterior oblique |
| LRA | Low right atrium |
| N/A | Not applicable |
| OAC | Oral anticoagulation |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| OSAS | Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome |
| PM | Pacemaker |
| PPI | Post-pacing interval |
| PVI | Pulmonary vein isolation |
| RA | Right atrial |
| ROC | Receiver operator characteristics |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| Sig. | Significance |
References
- Granada, J.; Uribe, W.; Chyou, P.-H.; Maassen, K.; Vierkant, R.; Smith, P.N.; Hayes, J.; Eaker, E.; Vidaillet, H. Incidence and Predictors of Atrial Flutter in the General Population. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 2242–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, B.; Grant, J.; Vincent, L.; Maning, J.; Olorunfemi, O.; Olarte, N.; Colombo, R.; Lambrakos, L.; Mendoza, I. Comparison of In-Hospital Outcomes of Patients Undergoing Catheter Ablation for Typical versus Atypical Atrial Flutter. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2022, 63, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bun, S.-S.; Latcu, D.G.; Marchlinski, F.; Saoudi, N. Atrial Flutter: More than Just One of a Kind. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 2356–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bun, S.-S.; Lațcu, D.G.; Wedn, A.M.; Squara, F.; Scarlatti, D.; Theodore, G.; Al Amoura, A.; Benaïch, F.A.; Hasni, K.; Saoudi, N.; et al. Cavotricuspid Isthmus Is Constantly a Zone of Slow Conduction: Data from Ultra-High-Resolution Mapping. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 2020, 43, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olgin, J.E.; Kalman, J.M.; Fitzpatrick, A.P.; Lesh, M.D. Role of Right Atrial Endocardial Structures as Barriers to Conduction during Human Type I Atrial Flutter. Activation and Entrainment Mapping Guided by Intracardiac Echocardiography. Circulation 1995, 92, 1839–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, P.A.; Luria, D.; Fenton, A.M.; Munger, T.M.; Jahangir, A.; Shen, W.K.; Rea, R.F.; Stanton, M.S.; Hammill, S.C.; Packer, D.L. Global Right Atrial Mapping of Human Atrial Flutter: The Presence of Posteromedial (Sinus Venosa Region) Functional Block and Double Potentials: A Study in Biplane Fluoroscopy and Intracardiac Echocardiography. Circulation 2000, 101, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doiny, D.; Merino, J.L. Atrial Flutter: Common and Main Atypical Forms. Available online: https://www.escardio.org/Journals/E-Journal-of-Cardiology-Practice/Volume-11/Atrial-flutter-common-and-main-atypical-forms (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- Puech, P.; Latour, H.; Grolleau, R. Flutter and his limits. Arch. Mal. Coeur Vaiss. 1970, 63, 116–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saoudi, N.; Cosío, F.; Waldo, A.; Chen, S.A.; Iesaka, Y.; Lesh, M.; Saksena, S.; Salerno, J.; Schoels, W.; Working Group of Arrhythmias of the European of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. A Classification of Atrial Flutter and Regular Atrial Tachycardia According to Electrophysiological Mechanisms and Anatomical Bases; a Statement from a Joint Expert Group from The Working Group of Arrhythmias of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Eur. Heart J. 2001, 22, 1162–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosio, F.G. Atrial Flutter, Typical and Atypical: A Review. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. Rev. 2017, 6, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Jiao, J.; Shen, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; Ju, W.; Gu, K.; Yang, G.; et al. A Simple Score to Predict New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation After Ablation of Typical Atrial Flutter. Can. J. Cardiol. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Giehm-Reese, M.; Kronborg, M.B.; Lukac, P.; Kristiansen, S.B.; Jensen, H.K.; Gerdes, C.; Kristensen, J.; Nielsen, J.M.; Nielsen, J.C. Recurrent Atrial Arrhythmia in a Randomised Controlled Trial Comparing Contact Force-Guided and Contact Force-Blinded Ablation for Typical Atrial Flutter. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2022, 63, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Xie, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Q.; Cao, Z.-J.; Tang, Q.-H.; Guo, X.-G.; Sun, Q.; Ma, J. Risk of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation Post-Cavotricuspid Isthmus Ablation in Typical Atrial Flutter Without History of Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 763478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maskoun, W.; Pino, M.I.; Ayoub, K.; Llanos, O.L.; Almomani, A.; Nairooz, R.; Hakeem, A.; Miller, J. Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation After Atrial Flutter Ablation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2016, 2, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, B.M.; Chen, J.; Hong, K.L.; Boveda, S.; Baranchuk, A.; Haugaa, K.H.; Dorian, P.; Potpara, T.S.; Crystal, E.; Mitchell, B.; et al. Catheter ablation for atrial flutter: A survey by the European Heart Rhythm Association and Canadian Heart Rhythm Society. EP Eur. 2016, 18, 1880–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugada, J.; Katritsis, D.G.; Arbelo, E.; Arribas, F.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Calkins, H.; Corrado, D.; Deftereos, S.G.; Diller, G.-P.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Supraventricular tachycardiaThe Task Force for the Management of Patients with Supraventricular Tachycardia of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC): Developed in Collaboration with the Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 655–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartzman, D.; Callans, D.J.; Gottlieb, C.D.; Dillon, S.M.; Movsowitz, C.; Marchlinski, F.E. Conduction Block in the Inferior Vena Caval-Tricuspid Valve Isthmus: Association with Outcome of Radiofrequency Ablation of Type I Atrial Flutter. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1996, 28, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, A.; Newby, K.H.; Pisanó, E.; Leonelli, F.; Fanelli, R.; Potenza, D.; Beheiry, S.; Tomassoni, G. Prospective Randomized Comparison of Antiarrhythmic Therapy versus First-Line Radiofrequency Ablation in Patients with Atrial Flutter. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 35, 1898–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Wang, T.J.; Leip, E.P.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Massaro, J.M.; Beiser, A.; Wolf, P.A.; et al. Lifetime Risk for Development of Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2004, 110, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Rienstra, M.; Bunting, K.V.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Caso, V.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; De Potter, T.J.R.; Dwight, J.; Guasti, L.; Hanke, T.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation Developed in Collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): Developed by the Task Force for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), with the Special Contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Endorsed by the European Stroke Organisation (ESO). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3314–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, B.P.; Michaud, G.F.; Strickberger, S.A.; Morady, F. Electrocardiographic Differentiation of Atrial Flutter from Atrial Fibrillation by Physicians. J. Electrocardiol. 1999, 32, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, F.; Wang, N.; Yin, X.; Ellinor, P.T.; Lubitz, S.A.; LeLorier, P.A.; McManus, D.D.; Sullivan, L.M.; Seshadri, S.; Vasan, R.S.; et al. Atrial Flutter: Clinical Risk Factors and Adverse Outcomes in the Framingham Heart Study. Heart Rhythm 2016, 13, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katov, L.; Teumer, Y.; Schlarb, A.; Reiländer, S.; Aktolga, D.; Diofano, F.; Bothner, C.; Rottbauer, W.; Weinmann-Emhardt, K. Comparative Efficacy of Cavotricuspid Isthmus Ablation in Sinus Rhythm Versus Typical Atrial Flutter. Hearts 2024, 5, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilek, C.; Gleirscher, L.; Strzelczyk, E.; Sepela, D.; Tiemann, K.; Lewalter, T. Rechtsatriales isthmusabhängiges Vorhofflattern. Herzschrittmachertherapie Elektrophysiol. 2023, 34, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinitz, J.S.; Gerstenfeld, E.P.; Marchlinski, F.E.; Callans, D.J. Atrial Fibrillation Is Common after Ablation of Isolated Atrial Flutter during Long-Term Follow-Up. Heart Rhythm 2007, 4, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, F.J.; Ibáñez Criado, J.L.; Quesada Dorador, A.; Collaborators of the Spanish Catheter Ablation Registry; REGISTRY COLLABORATORS. Spanish Catheter Ablation Registry. 17th Official Report of the Spanish Society of Cardiology Working Group on Electrophysiology and Arrhythmias (2017). Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Rozen, G.; Saleh, A.; Vaid, J.; Biton, Y.; Moazzami, K.; Heist, E.K.; Mansour, M.C.; Kaadan, M.I.; Vangel, M.; et al. Catheter Ablation for Cardiac Arrhythmias: Utilization and In-Hospital Complications, 2000 to 2013. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 3, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, F.; Kesek, M.; Englund, A.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Karlsson, L.O.; Kennebäck, G.; Poçi, D.; Samo-Ayou, R.; Sigurjónsdóttir, R.; Ringborn, M.; et al. A Decade of Catheter Ablation of Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sweden: Ablation Practices and Outcomes. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, G.; Carinci, V.; Tomasi, C.; Frassineti, V.; Margheri, M.; Di Pasquale, G. Is Electrocardiography a Reliable Tool for Identifying Patients with Isthmus-Dependent Atrial Flutter? EP Eur. 2009, 11, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Arora, P.; Avery, C.L.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Beaton, A.Z.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2023 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 147, e93–e621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiao, Y.A.; Rabinovitch, P.S. The Aging Heart. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a025148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havránek, S.; Simek, J.; Sťovíček, P.; Wichterle, D. Distribution of Mean Cycle Length in Cavo-Tricuspid Isthmus Dependent Atrial Flutter. Physiol. Res. 2012, 61, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-K.; Chen, Y.-A.; Lee, T.-I.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, S.-A.; Chen, Y.-J. Aging Modulates the Substrate and Triggers Remodeling in Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. J. 2018, 82, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.J.; Arora, R.; Jalife, J. Atrial Myopathy. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2019, 4, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, M.W.; Morton, M.; Fernando, R.; Elbracht-Leong, S.; Better, N.; Segan, L.; William, J.; Crowley, R.; Morton, J.B.; Sparks, P.B.; et al. Impact of Posterior Wall Isolation During AF Ablation on the Incidence of Left Atrial Flutter. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2024, 10, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pott, A.; Teumer, Y.; Weinmann, K.; Baumhardt, M.; Schweizer, C.; Buckert, D.; Bothner, C.; Rottbauer, W.; Dahme, T. Substrate-based ablation of atypical atrial flutter in patients with atrial cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2022, 40, 101018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, E.; Ripplinger, C.M. Antiarrhythmic Mechanisms of Beta Blocker Therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 146, 104274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Rienstra, M.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; Olshansky, B. Rate Control in Atrial Fibrillation. Lancet 2016, 388, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.-J.; Wang, B.-B.; Hou, F.-F.; Jiao, Y.; Li, H.-W.; Lv, S.-P.; Li, F.-H. Global Burden of Atrial Fibrillation/Atrial Flutter and Its Attributable Risk Factors from 1990 to 2019. EP Eur. 2023, 25, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmayer, K.S.; Yang, Y.; Joseph, S.; McCabe, J.M.; Bhave, P.; Hsu, J.; Ng, R.K.; Lee, B.K.; Badhwar, N.; Lee, R.J.; et al. Predictors of Unusual ECG Characteristics in Cavotricuspid Isthmus-Dependent Atrial Flutter Ablation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiology 2011, 34, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pap, R.; Kohári, M.; Makai, A.; Bencsik, G.; Traykov, V.B.; Gallardo, R.; Klausz, G.; Zsuzsanna, K.; Forster, T.; Sághy, L. Surgical Technique and the Mechanism of Atrial Tachycardia Late after Open Heart Surgery. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2012, 35, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhauser, H.K.; Adler, C.; Rosario, A.S.; Diederichs, C.; Ellert, U. Hypertension Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment and Control in Germany 1998 and 2008-11. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2015, 29, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Type I ECG | Type II ECG | Total Participants | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTI-dependent AFL | 242 (63.1) | 52 (13.6) | 294 (76.7) |
| Non-CTI-dependent AFL | 26 (6.8) | 63 (16.4) | 89 (23.2) |
| Total participants | 268 (70.0) | 115 (30.0) |
| Baseline Characteristics | All Patients (n = 383) |
|---|---|
| Age [years], mean ± SD | 69.3 ± 11.2 |
| Male, n (%) | 300 (78.3) |
| BMI [kg/m2], mean ± SD | 28.1 ± 5.7 |
| Coronary heart disease, n (%) | 149 (39.2) |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) | 275 (71.8) |
| Hyperlipoproteinemia, n (%) | 201 (52.5) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 89 (23.3) |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, n (%) | 45 (11.7) |
| Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, n (%) | 22 (5.7) |
| Pulmonary hypertension, n (%) | 27 (7.0) |
| Stroke, n (%) | 36 (9.4) |
| Oral anticoagulation prior to ablation, n (%) | 214 (58.0) |
| CHA2DS2-VASc score, mean ± SD | 3.0 ± 1.7 |
Antiarrhythmic drugs
| 31 (8.4) 281 (76.2) 24 (6.5) |
| Prior atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 145 (37.9) |
| Prior PVI, n (%) | 35 (9.1) |
| Prior LA/RA ablation (without PVI), n (%) | 13 (3.4) |
| Prior heart surgery, n (%) | 63 (16.4) |
| Type I ECG | Type II ECG | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total, n (%) | 268 (70.0) | 115 (30.0) | N/A |
| Age [years], mean ± SD | 67.8 ± 10.9 | 73.0 ± 11.1 | <0.001 |
| Male, n (%) | 220 (82.1) | 80 (69.6) | 0.006 |
| BMI [kg/m2], mean ± SD | 28.1 ± 5.7 | 28.1 ± 5.8 | 0.920 |
| Coronary heart disease, n (%) | 97 (36.5) | 52 (45.6) | 0.094 |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) | 185 (69.0) | 90 (78.3) | 0.066 |
| Hyperlipoproteinemia, n (%) | 136 (50.7) | 65 (56.5) | 0.300 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 51 (19.1) | 38 (33.0) | 0.003 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, n (%) | 33 (12.3) | 12 (10.4) | 0.601 |
| Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, n (%) | 15 (5.6) | 7 (6.1) | 0.850 |
| Pulmonary hypertension, n (%) | 17 (6.3) | 10 (8.7) | 0.410 |
| Stroke, n (%) | 18 (6.7) | 18 (15.7) | 0.006 |
| Oral anticoagulation prior to ablation, n (%) | 148 (56.5) | 66 (61.7) | 0.359 |
| CHA2DS2-VASc score, mean ± SD | 2.7 ± 1.6 | 3.8 ± 1.7 | <0.001 |
Antiarrhythmic drugs
| 25 (9.5) 193 (73.7) 17 (6.5) | 6 (5.6) 88 (82.2) 7 (6.5) | 0.216 0.079 0.985 |
| Prior atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 93 (34.7) | 52 (45.2) | 0.052 |
| Prior PVI, n (%) | 21 (7.8) | 14 (12.2) | 0.177 |
| Prior heart surgery, n (%) | 39 (14.6) | 24 (20.9) | 0.126 |
| CTI-dependent atrial flutter, n (%) | 242 (90.3) | 52 (45.2) | <0.001 |
| CTI | Non-CTI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total, n (%) | 294 (76.7) | 89 (23.2) | n/A |
| Age [years], mean ± SD | 67.9 ± 11.1 | 74.1 ± 10.1 | <0.001 |
| Male, n (%) | 247 (84.0) | 53 (59.6) | <0.001 |
| BMI [kg/m2], mean ± SD | 28.0 ± 5.3 | 28.5 ± 7.1 | 0.544 |
| Coronary heart disease, n (%) | 107 (36.6) | 42 (47.7) | 0.478 |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) | 201 (68.4) | 74 (83.1) | 0.007 |
| Hyperlipoproteinemia, n (%) | 147 (50.0) | 54 (60.7) | 0.077 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 65 (22.2) | 24 (27.0) | 0.350 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, n (%) | 38 (12.9) | 7 (7.9) | 0.194 |
| Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, n (%) | 18 (6.1) | 4 (4.5) | 0.563 |
| Pulmonary hypertension, n (%) | 21 (7.1) | 6 (6.7) | 0.897 |
| Stroke, n (%) | 23 (7.8) | 13 (14.6) | 0.055 |
| Oral anticoagulation prior to ablation, n (%) | 161 (55.9) | 53 (65.4) | 0.125 |
| CHA2DS2-VASc score, mean ± SD | 2.8 ± 1.7 | 3.9 ± 1.7 | <0.001 |
Antiarrhythmic drugs
| 25 (8.7) 210 (72.9) 18 (6.3) | 6 (7.4) 71 (87.7) 6 (7.4) | 0.751 0.006 0.709 |
| Prior atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 100 (34.0) | 45 (50.6) | 0.005 |
| Prior PVI, n (%) | 17 (5.8) | 18 (20.2) | <0.001 |
| Prior heart surgery, n (%) | 49 (16.7) | 14 (15.7) | 0.835 |
| ECG, type I, n (%) | 242 (82.3) | 26 (29.2) | <0.001 |
| CTI + Type I ECG | Non-CTI + Type I ECG | CTI + Type II ECG | Non-CTI + Type II ECG | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total, n (%) | 242 (63.1) | 26 (6.8) | 52 (13.6) | 63 (16.4) | N/A |
| Age [years], mean ± SD | 67.4 ± 10.7 *,*** | 71.1 ± 11.9 * | 70.1 ± 12.6 # | 75.4 ± 9.0 ***,# | 0.001 |
| Male, n (%) | 204 (84.3) **,*** | 16 (61.5) ** | 43 (82.7) * | 37 (58.7) ***,* | 0.001 |
| BMI [kg/m2], mean ± SD | 28.0 ± 5.4 | 29.6 ± 7.9 | 28.2 ± 4.4 | 28.0 ± 6.8 | 0.600 |
| Coronary heart disease, n (%) | 85 (35.1) | 14 (53.8) | 24 (46.2) | 28 (41.9) | 0.117 |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) | 165 (68.2) * | 20 (76.9) | 36 (69.2) | 54 (85.7) * | 0.044 |
| Hyperlipoproteinemia, n (%) | 119 (49.2) | 17 (65.4) | 28 (53.8) | 37 (58.7) | 0.259 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 49 (20.2) *,** | 2 (7.7) # | 16 (30.8) * | 22 (34.9) **,# | 0.013 |
| COPD, n (%) | 31 (12.8) | 2 (7.7) | 7 (13.5) | 5 (7.9) | 0.638 |
| OSAS, n (%) | 13 (5.4) | 2 (7.7) | 5 (9.6 | 2 (3.2) | 0.505 |
| Pulmonary hypertension, n (%) | 15 (6.2) | 2 (7.7) | 6 (11.5) | 4 (6.3) | 0.617 |
| Stroke, n (%) | 16 (6.7) * | 2 (7.7) | 7 (13.5) | 11 (17.5) * | 0.047 |
| OAC prior ablation, n (%) | 132 (55.5) | 16 (61.5) | 29 (55.8) | 37 (64.9) | 0.458 |
| CHA2DS2-VASc score, mean ± SD | 2.6 ± 1.6 *,***,### | 3.3 ± 1.5 * | 3.4 ± 1.8 ***,# | 4.2 ± 1.6 #,### | 0.001 |
Antiarrhythmic drugs
| 22 (9.2) 170 (70.2) *,# 16 (6.6) | 3 (12.5) 23 (95.8) * 1 (4.2) | 3 (5.8) 40 (76.9) 2 (3.8) | 3 (5.3) 48 (84.2) # 5 (8.8) | 0.591 0.013 0.734 |
| Prior atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 79 (32.6) *,# | 14 (53.8) * | 21 (40.4) | 31 (49.2) # | 0.029 |
| Prior PVI, n (%) | 12 (5.0) *,*** | 9 (34.6) *** | 5 (9.6) | 9 (14.3) * | 0.001 |
| Prior heart surgery, n (%) | 33 (13.6) *** | 6 (23.1) | 16 (30.8) *** | 8 (12.7) | 0.005 |
| Total | CTI + Type I ECG | Non-CTI + Type I ECG | CTI + Type II ECG | Non-CTI + Type II ECG | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECG characteristics | ||||||
| Heart rate [bpm], mean ± SD | 98.2 ± 31.3 | 96.6 ± 32.5 | 98.7 ± 33.3 | 98.8 ± 32.7 | 103.6 ± 29.4 | 0.461 |
| QRS [ms], mean ± SD | 113.0 ± 32.2 | 112.4 ± 32.5 | 110.5 ± 34.8 | 120.4 ± 32.4 | 110.4 ± 29.2 | 0.315 |
| Atrial CL [ms], mean ± SD | 234.3 ± 39.8 | 232.6 ± 36.0 | 224.6 ± 31.3 *,# | 250.6 ± 44.1 * | 231.1 ± 49.9 # | 0.023 |
| Atrial CL > 245 ms, n (%) | 121 (31.7) | 69 (28.5) *** | 6 (23.1) ** | 28 (53.8) ***,** | 18 (29.0) | <0.001 |
| Ventricular PM stimulation, n (%) | 23 (6.0) | 13 (5.4) | 2 (7.7) | 6 (11.5) | 2 (3.2) | 0.286 |
| EPS characteristics | ||||||
| Atrial CL [ms], mean ± SD | 244.8 ± 33.7 | 241.6 ± 32.2 ** | 238.0 ± 22.4 * | 264.7 ± 36.4 **,* | 243.1 ± 35.6 | 0.001 |
| Atrial CL > 245 ms, n (%) | 163 (45.2) | 97 (40.1) **,* | 9 (39.1) | 35 (71.4) **,* | 22 (37.3) | 0.001 |
| Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 0.965 | 0.924–1.007 | 0.100 |
| Age > 75 years | 0.600 | 0.259–1.389 | 0.233 |
| Male | 3.356 | 1.416–7.937 | 0.006 |
| Body mass index [kg/m2] | 0.960 | 0.906–1.019 | 0.180 |
| Arterial hypertension | 0.643 | 0.248–1.665 | 0.363 |
| Hyperlipoproteinemia | 0.512 | 0.220–1.194 | 0.121 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 3.062 | 0.700–13.402 | 0.137 |
| Coronary heart disease | 0.464 | 0.205–1.048 | 0.065 |
| CHA2DS2VASc score [points] | 0.793 | 0.621–1.013 | 0.063 |
| AAT with beta blockers | 0.109 | 0.014–0.821 | 0.031 |
| Prior atrial fibrillation | 0.415 | 0.184–0.940 | 0.035 |
| Prior PVI | 0.099 | 0.036–0.266 | <0.001 |
| Prior heart surgery | 0.526 | 0.197–1.407 | 0.201 |
| Atrial CL [ms] | 1.004 | 0.990–1.018 | 0.591 |
| Atrial CL > 245 ms | 1.135 | 0.472–2.728 | 0.778 |
| Regression Coefficient | Standard Error | Wald | df | Sig. | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 1.104 | 0.470 | 5.505 | 1 | 0.019 | 3.016 | 1.199–7.583 |
| AAT with beta blockers | −2.102 | 1.037 | 4.109 | 1 | 0.043 | 0.122 | 0.016–0.933 |
| Prior PVI | −0.754 | 0.444 | 2.880 | 1 | 0.090 | 0.470 | 0.197–1.124 |
| Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 0.954 | 0.918–0.991 | 0.016 |
| Age > 75 years | 0.370 | 0.172–0.796 | 0.011 |
| Male | 3.356 | 1.399–8.065 | 0.007 |
| Body mass index [kg/m2] | 1.003 | 0.937–1.074 | 0.926 |
| Arterial hypertension | 0.375 | 0.150–0.940 | 0.036 |
| Hyperlipoproteinemia | 0.820 | 0.391–1.720 | 0.599 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.828 | 0.378–1.815 | 0.638 |
| Coronary heart disease | 1.005 | 0.481–2.099 | 0.990 |
| CHA2DS2VASc score [points] | 0.758 | 0.604–0.951 | 0.017 |
| AAT with beta blockers | 0.433 | 0.080–2.339 | 0.331 |
| Prior atrial fibrillation | 0.699 | 0.333–1.469 | 0.345 |
| Prior PVI | 0.638 | 0.200–2.038 | 0.449 |
| Prior heart surgery | 3.056 | 1.185–7.877 | 0.021 |
| Atrial CL [ms] | 1.017 | 1.005–1.029 | 0.004 |
| Atrial CL > 245 ms | 4.205 | 1.863–9.489 | <0.001 |
| Regression Coefficient | Standard Error | Wald | df | Sig. | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | −0.032 | 0.022 | 2.073 | 1 | 0.150 | 0.969 | 0.927–1.012 |
| Male | 0.967 | 0.482 | 4.030 | 1 | 0.045 | 2.631 | 1.023–6.765 |
| Arterial hypertension | −0.524 | 0.536 | 0.955 | 1 | 0.328 | 0.592 | 0.207–1.693 |
| Prior heart surgery | 0.547 | 0.531 | 1.062 | 1 | 0.303 | 1.728 | 0.610–4.895 |
| Atrial CL > 245 ms | 0.902 | 0.428 | 4.451 | 1 | 0.035 | 2.465 | 1.066–5.701 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katov, L.; Reiländer, S.; Schlarb, A.; Diofano, F.; Aktolga, D.; Teumer, Y.; Bothner, C.; Rottbauer, W.; Weinmann-Emhardt, K. Clinical and Electrophysiological Predictors of Isthmus Dependency in Atrial Flutter. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091095
Katov L, Reiländer S, Schlarb A, Diofano F, Aktolga D, Teumer Y, Bothner C, Rottbauer W, Weinmann-Emhardt K. Clinical and Electrophysiological Predictors of Isthmus Dependency in Atrial Flutter. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(9):1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091095
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatov, Lyuboslav, Sonja Reiländer, Alyssa Schlarb, Federica Diofano, Deniz Aktolga, Yannick Teumer, Carlo Bothner, Wolfgang Rottbauer, and Karolina Weinmann-Emhardt. 2025. "Clinical and Electrophysiological Predictors of Isthmus Dependency in Atrial Flutter" Diagnostics 15, no. 9: 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091095
APA StyleKatov, L., Reiländer, S., Schlarb, A., Diofano, F., Aktolga, D., Teumer, Y., Bothner, C., Rottbauer, W., & Weinmann-Emhardt, K. (2025). Clinical and Electrophysiological Predictors of Isthmus Dependency in Atrial Flutter. Diagnostics, 15(9), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091095







