SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Associated with an Accelerated eGFR Decline in Kidney Transplant Recipients up to Four Years Post Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Selection and Demographics
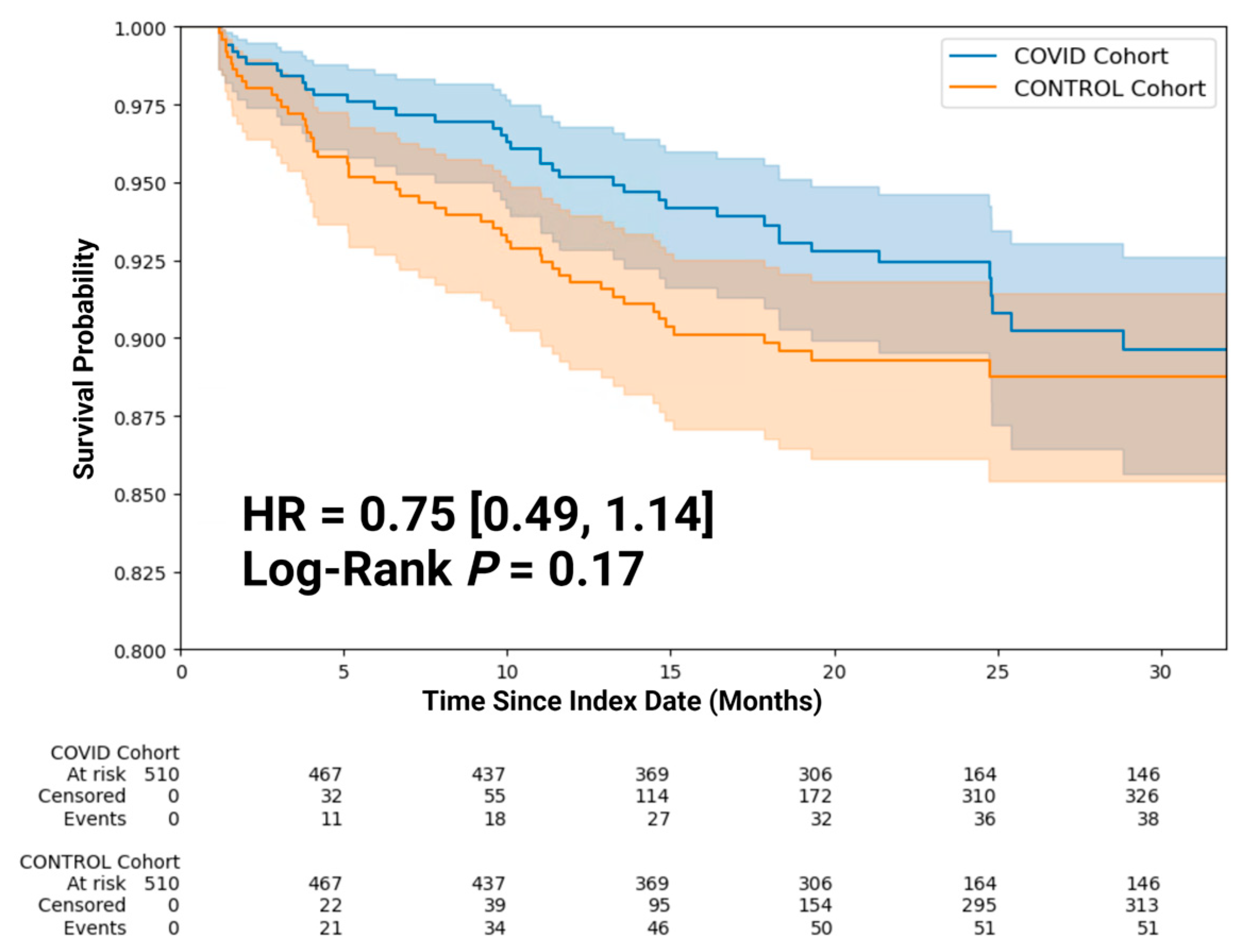
3.2. Clinical Outcomes
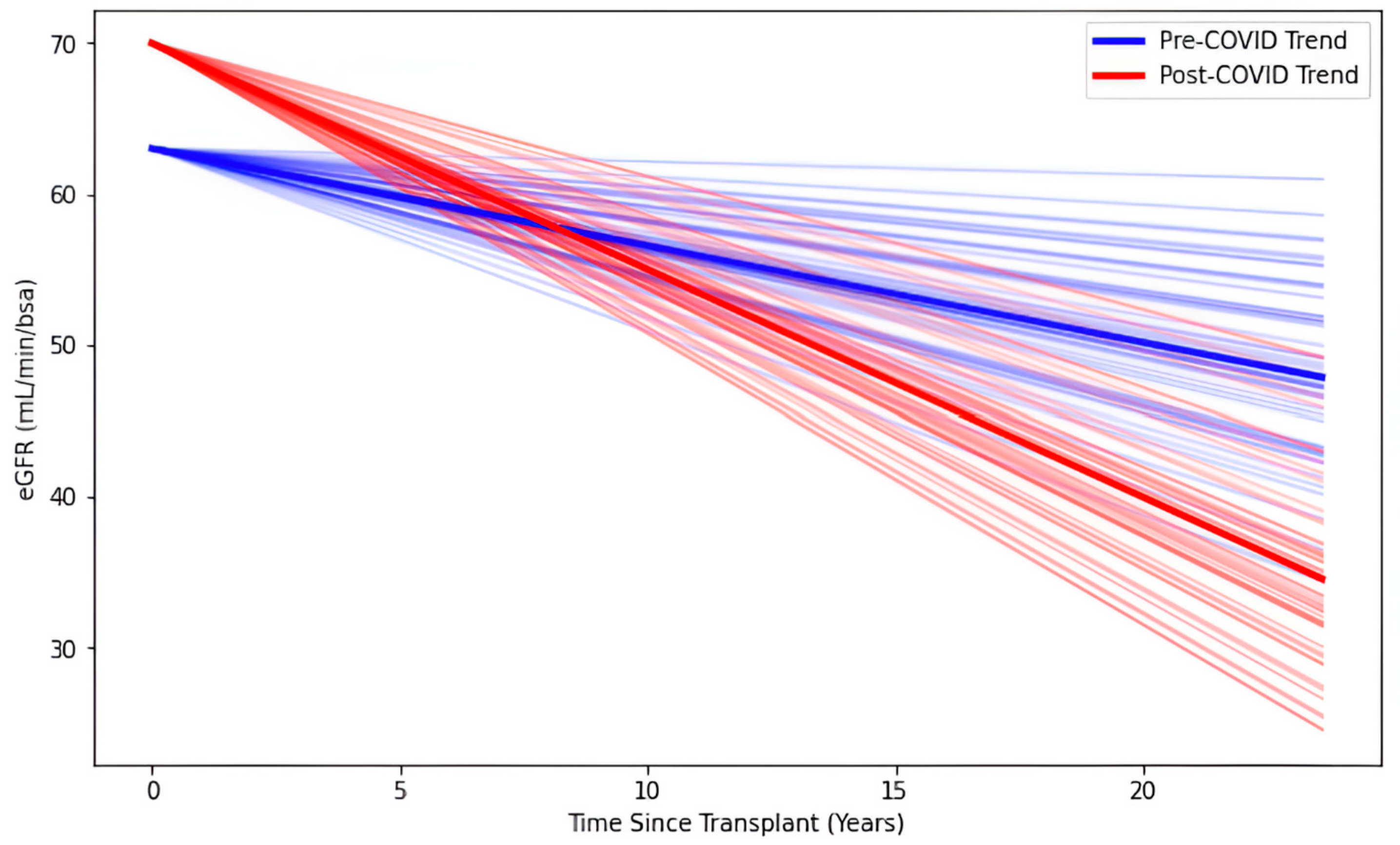
3.3. Biomarker Outcomes
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| KTR | Kidney transplant recipient |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| UPCR | Urine protein to creatinine ratio |
| aHR | Adjusted hazard ratio |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
References
- DeWolf, S.; Laracy, J.C.; Perales, M.A.; Kamboj, M.; van den Brink, M.R.M.; Vardhana, S. SARS-CoV-2 in immunocompromised individuals. Immunity 2022, 55, 1779–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.A.; Dube, S.; Lu, Y.; Yates, M.; Arnetorp, S.; Barnes, E.; Bell, S.; Carty, L.; Evans, K.; Graham, S.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 on immunocompromised populations during the Omicron era: Insights from the observational population-based INFORM study. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2023, 35, 100747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarelli, C.; Angeletti, A.; Perin, L.; Russo, L.S.; Sabiu, G.; Podestà, M.A.; Cravedi, P. Immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 in dialysis and kidney transplantation. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 1816–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devresse, A.; De Greef, J.; Yombi, J.C.; Belkhir, L.; Goffin, E.; Kanaan, N. Immunosuppression and SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplant. Direct 2022, 8, e1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumla, A.; Marais, B.J.; McHugh, T.D.; Maeurer, M.; Zumla, A.; Kapata, N.; Ntoumi, F.; Chanda-Kapata, P.; Mfinanga, S.; Centis, R.; et al. COVID-19 and tuberculosis-threats and opportunities. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2020, 24, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Fajgenbaum, D.C. Is severe COVID-19 a cytokine storm syndrome: A hyperinflammatory debate. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2021, 33, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, T.; Hassani, F.; Ghaffari, N.; Ebrahimi, B.; Yarahmadi, A.; Hassanzadeh, G. COVID-19 and multiorgan failure: A narrative review on potential mechanisms. J. Mol. Histol. 2020, 51, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.Y.; Komarasamy, T.V.; Rmt Balasubramaniam, V. Hyperinflammatory Immune Response and COVID-19: A Double Edged Sword. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 742941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Álvarez, J.E.; Pérez Fontán, M.; Jiménez Martín, C.; Blasco Pelícano, M.; Cabezas Reina, C.J.; Sevillano Prieto, Á.M.; Melilli, E.; Crespo Barrios, M.; Macía Heras, M.; Del Pino, Y.P.M.D. SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients on renal replacement therapy. Report of the COVID-19 Registry of the Spanish Society of Nephrology (SEN). Nefrología (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 40, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Xia, Q.X.; Zeng, X.P.; Peng, J.T.; Liu, J.; Xiao, X.Y.; Jiang, G.S.; Xiao, H.Y.; et al. Identification of Kidney Transplant Recipients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akalin, E.; Azzi, Y.; Bartash, R.; Seethamraju, H.; Parides, M.; Hemmige, V.; Ross, M.; Forest, S.; Goldstein, Y.D.; Ajaimy, M.; et al. Covid-19 and Kidney Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2475–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, Y.; Bartash, R.; Scalea, J.; Loarte-Campos, P.; Akalin, E. COVID-19 and Solid Organ Transplantation: A Review Article. Transplantation 2021, 105, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Q.Y.; Sultana, R.; Lee, T.L.; Thangaraju, S.; Kee, T.; Htay, H. Coronavirus disease 2019 in kidney transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Singap. Med. J. 2023, 64, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, V.; Fisher, M.; Hou, W.; Zhang, L.; Duong, T.Q. Incidence of New-Onset Hypertension Post-COVID-19: Comparison with Influenza. Hypertension 2023, 80, 2135–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.Y.; Ho, S.L.; Buczek, A.; Fleysher, R.; Hou, W.; Chacko, K.; Duong, T.Q. Clinical predictors of recovery of COVID-19 associated-abnormal liver function test 2 months after hospital discharge. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eligulashvili, A.; Gordon, M.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.; Mehrotra-Varma, S.; Mehrotra-Varma, J.; Hsu, K.; Hilliard, I.; Lee, K.; Li, A.; et al. Long-term outcomes of hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 with and without neurological involvement: 3-year follow-up assessment. PLoS Med. 2024, 21, e1004263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadidchi, R.; Wang, S.H.; Rezko, D.; Henry, S.; Coyle, P.K.; Duong, T.Q. SARS-CoV-2 infection increases long-term multiple sclerosis disease activity and all-cause mortality in an underserved inner-city population. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2024, 86, 105613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidchi, R.; Al-Ani, Y.; Piskun, H.; Pakan, R.; Duong, K.; Jamil, H.; Wang, S.; Henry, S.; Maurer, C.; Duong, T. Long-term outcomes of patients with Parkinson’s disease 3.5 years post SARS-CoV-2 infection in an inner-city population in the Bronx. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidchi, R.; Pakan, R.; Alamuri, T.; Cercizi, N.; Al-Ani, Y.; Wang, S.H.; Henry, S.; Duong, T.Q. Long COVID-19 outcomes of patients with pre-existing dementia. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2025, 103, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakan, R.; Hadidchi, R.; Al-Ani, Y.; Piskun, H.; Duong, K.S.; Henry, S.; Wang, S.; Maurer, C.W.; Duong, T.Q. Long-Term Outcomes of Patients with Pre-Existing Essential Tremor After SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidchi, R.; Al-Ani, Y.; Choi, S.; Renteria, S.; Duong, K.S.; Henry, S.; Wang, S.H.; Duong, T.Q. Long-term outcomes of patients with a pre-existing neurological condition after SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Neurol. Sci. 2025, 123477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.M. Best practice in statistics: The use of log transformation. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2022, 59, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colmenero, J.; Rodríguez-Perálvarez, M.; Salcedo, M.; Arias-Milla, A.; Muñoz-Serrano, A.; Graus, J.; Nuño, J.; Gastaca, M.; Bustamante-Schneider, J.; Cachero, A.; et al. Epidemiological pattern, incidence, and outcomes of COVID-19 in liver transplant patients. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, Y.; Parides, M.; Alani, O.; Loarte-Campos, P.; Bartash, R.; Forest, S.; Colovai, A.; Ajaimy, M.; Liriano-Ward, L.; Pynadath, C.; et al. COVID-19 infection in kidney transplant recipients at the epicenter of pandemics. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajibaratali, B.; Amini, H.; Dalili, N.; Ziaie, S.; Anvari, S.; Keykha, E.; Rezaee, M.; Samavat, S. Clinical outcomes of kidney recipients with COVID-19 (COVID-19 in kidney recipients). Transpl. Immunol. 2023, 76, 101772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Kuo, G.; Lee, T.H.; Yang, H.Y.; Wu, H.H.; Tu, K.H.; Tian, Y.C. Incidence of Mortality, Acute Kidney Injury and Graft Loss in Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basic-Jukic, N.; Juric, I.; Furic-Cunko, V.; Katalinic, L.; Radic, J.; Bosnjak, Z.; Jelakovic, B.; Kastelan, Z. Follow-up of renal transplant recipients after acute COVID-19-A prospective cohort single-center study. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2021, 9, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oto, O.A.; Ozturk, S.; Arici, M.; Velioglu, A.; Dursun, B.; Guller, N.; Sahin, I.; Eser, Z.E.; Paydas, S.; Trabulus, S.; et al. Middle-term outcomes in renal transplant recipients with COVID-19: A national, multicenter, controlled study. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Ucar, Z.A.; Dheir, H.; Danis, R.; Yelken, B.; Uyar, M.; Parmaksiz, E.; Artan, A.S.; Sinangil, A.; Merhametsiz, O.; et al. COVID-19 in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Multicenter Experience from the First Two Waves of Pandemic. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Meshram, H.S.; Kute, V.; Patel, H.; Desai, S.; Dave, R. Long-term follow-up of SARS-CoV-2 recovered renal transplant recipients: A single-center experience from India. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2021, 23, e13735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiekhani, M.; Abolghasemi, S.; Asgharpour, M.; Zare, Z.; Negahban, H.; Akbari, R.; Nikoupour, H.; Roozbeh, J.; Oliaie, F.; Yahyapour, Y.; et al. Post-COVID-19 complications in kidney transplant recipients. Russ. J. Infect. Immun. 2023, 13, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowska, A.; Ruszkowski, J.; Muchlado, M.; Ślizień, Z.; Heleniak, Z.; Parczewska, A.; Kanclerz, K.; Biedunkiewicz, B.; Tylicki, L.; Król, E.; et al. Effect of COVID-19 on Kidney Graft Function One Year after Onset. Medicina 2023, 60, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, R.N.; Low, R.J.; Akrami, A. A review of cytokine-based pathophysiology of Long COVID symptoms. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1011936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Ampudia, Y.; Monsalve, D.M.; Rojas, M.; Rodriguez, Y.; Zapata, E.; Ramirez-Santana, C.; Anaya, J.M. Persistent Autoimmune Activation and Proinflammatory State in Post-Coronavirus Disease 2019 Syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 2155–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, F.R.; Govender, M.; Svanberg, C.; Nordgren, J.; Waller, H.; Nilsdotter-Augustinsson, A.; Henningsson, A.J.; Hagbom, M.; Sjowall, J.; Nystrom, S.; et al. Major alterations to monocyte and dendritic cell subsets lasting more than 6 months after hospitalization for COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1082912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, K.; Peluso, M.J.; Luo, X.; Thomas, R.; Shin, M.G.; Neidleman, J.; Andrew, A.; Young, K.C.; Ma, T.; Hoh, R.; et al. Long COVID manifests with T cell dysregulation, inflammation and an uncoordinated adaptive immune response to SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameiro, J.; Marques, F.; Lopes, J.A. Long-term consequences of acute kidney injury: A narrative review. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, E.J.; Jayasinghe, K.; Glassford, N.; Bailey, M.; Johnson, D.W.; Polkinghorne, K.R.; Toussaint, N.D.; Bellomo, R. Long-term risk of adverse outcomes after acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies using consensus definitions of exposure. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malgaj Vrecko, M.; Ales Rigler, A.; Veceric-Haler, Z. Coronavirus Disease 2019-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy: Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.C.; Imig, J.D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Gupta, A. Kidney in the net of acute and long-haul coronavirus disease 2019: A potential role for lipid mediators in causing renal injury and fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2022, 31, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, A.; den Deurwaarder, E.S.G.; Bakker, S.J.L.; de Haas, R.J.; van Meurs, M.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Berger, S.P. Kidney Infarction in Patients with COVID-19. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Yang, M.; Wan, C.; Yi, L.X.; Tang, F.; Zhu, H.Y.; Yi, F.; Yang, H.C.; Fogo, A.B.; Nie, X.; et al. Renal histopathological analysis of 26 postmortem findings of patients with COVID-19 in China. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowe, B.; Xie, Y.; Xu, E.; Al-Aly, Z. Kidney Outcomes in Long COVID. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2851–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapkiewicz, A.V.; Mai, X.; Carsons, S.E.; Pittaluga, S.; Kleiner, D.E.; Berger, J.S.; Thomas, S.; Adler, N.M.; Charytan, D.M.; Gasmi, B.; et al. Megakaryocytes and platelet-fibrin thrombi characterize multi-organ thrombosis at autopsy in COVID-19: A case series. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 24, 100434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coca, S.G. Outcomes and renal function trajectory after acute kidney injury: The narrow road to perdition. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busana, M.; Rau, A.; Lazzari, S.; Gattarello, S.; Cressoni, M.; Biggemann, L.; Harnisch, L.O.; Giosa, L.; Vogt, A.; Saager, L.; et al. Causes of Hypoxemia in COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Combined Multiple Inert Gas Elimination Technique and Dual-energy Computed Tomography Study. Anesthesiology 2024, 140, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesp, A.C.; Schaub, J.A.; Prasad, P.V.; Vallon, V.; Laverman, G.D.; Bjornstad, P.; van Raalte, D.H. The role of renal hypoxia in the pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease: A promising target for newer renoprotective agents including SGLT2 inhibitors? Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, M.; Mik, E.G.; Johannes, T.; Payen, D.; Ince, C. Renal hypoxia and dysoxia after reperfusion of the ischemic kidney. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmon, M.; Schortgen, F.; Vargas, F.; Liazydi, A.; Schlemmer, B.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Brochard, L. Diagnostic accuracy of Doppler renal resistive index for reversibility of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2011, 37, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogagnolo, A.; Grasso, S.; Dres, M.; Gesualdo, L.; Murgolo, F.; Morelli, E.; Ottaviani, I.; Marangoni, E.; Volta, C.A.; Spadaro, S. Focus on renal blood flow in mechanically ventilated patients with SARS-CoV-2: A prospective pilot study. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2022, 36, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez-Bonilla, W.O.; Orozco, R.; Argueta, V.; Sierra, M.; Zambrano, L.I.; Muñoz-Lara, F.; López-Molina, D.S.; Arteaga-Livias, K.; Grimes, Z.; Bryce, C.; et al. A review of the main histopathological findings in coronavirus disease 2019. Hum. Pathol. 2020, 105, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Vecchio, L.; Balafa, O.; Dounousi, E.; Ekart, R.; Fernandez, B.F.; Mark, P.B.; Sarafidis, P.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Ferro, C.J.; Mallamaci, F. COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elec, A.D.; Oltean, M.; Goldis, P.; Cismaru, C.; Lupse, M.; Muntean, A.; Elec, F.I. COVID-19 after kidney transplantation: Early outcomes and renal function following antiviral treatment. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 104, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillard, S.; Chavarot, N.; Francois, H.; Matignon, M.; Greze, C.; Kamar, N.; Gatault, P.; Thaunat, O.; Legris, T.; Frimat, L.; et al. Is COVID-19 infection more severe in kidney transplant recipients? Am. J. Transplant. 2021, 21, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimnickaite, E.; Kucinaite, I.; Zablockiene, B.; Lisinskaite, A.; Zablockis, R.; Rimsevicius, L.; Miglinas, M.; Jancoriene, L. Characteristics of COVID-19 Disease in Renal Transplant Recipients. Medicina 2024, 60, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino-Pereira, P.; Ventura, V.; Pires, M.C.; Ponce, D.; do Carmo, G.A.L.; do Carmo, L.P.F.; de Paiva, B.B.M.; Schwarzbold, A.V.; Gomes, A.; de Castro, B.M.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes in COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients: A propensity score matched cohort study. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1350657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toapanta, N.; Torres, I.B.; Sellares, J.; Chamoun, B.; Seron, D.; Moreso, F. Kidney transplantation and COVID-19 renal and patient prognosis. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, i21–i29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Cubillo, B.; Moreno de la Higuera, M.A.; Pérez-Flores, I.; Calvo Romero, N.; Aiffil, A.S.; Arribi Vilela, A.; Peix, B.; Huertas, S.; Juez, A.; Sanchez-Fructuoso, A.I. Clinical Effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Renal Transplant Recipients. Antibody Levels Impact in Pneumonia and Death. Transplantation 2022, 106, e476–e487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.F.; Tsai, S.F.; Wu, M.J.; Yu, T.M.; Chuang, Y.W.; Chen, C.H. Outcomes and Effects of Vaccination on SARS-Cov-2 Omicron Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2023, 55, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Hsu, M.K.; Huang, Y.J.; Lai, M.J.; Wu, S.W.; Lin, M.H.; Hung, H.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Huang, Y.T.; Lee, Y.F.; et al. Protective Effect of Vaccine Doses and Antibody Titers Against SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transpl. Int. 2023, 36, 11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, S.R.; Rezahosseini, O.; Møller, D.L.; Loft, J.A.; Poulsen, J.R.; Knudsen, J.D.; Pedersen, M.S.; Schønning, K.; Harboe, Z.B.; Rasmussen, A.; et al. Incidence and severity of SARS-CoV-2 infections in liver and kidney transplant recipients in the post-vaccination era: Real-life data from Denmark. Am. J. Transplant. 2022, 22, 2637–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, S.; Campbell, J.; Lambourg, E.; Watters, C.; O’Neil, M.; Almond, A.; Buck, K.; Carr, E.J.; Clark, L.; Cousland, Z.; et al. The Impact of Vaccination on Incidence and Outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Patients with Kidney Failure in Scotland. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| COVID+ (n = 510) | COVID− (n = 510) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male, n (%) | 295 (57.84%) | 312 (61.18%) | 0.381 |
| Age at Index Date in Years, mean (SD) | 59 (24) | 59 (23) | 0.689 |
| Follow-Up Time in Months, mean (SD) | 23 (12) | 23 (12) | 0.955 |
| Transplant Date to Index Date in Years, median (IQR) | 4.61 (1.71, 9.67) | 6.48 (3.63, 11.48) | <0.001 |
| Race and Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| White | 52 (10.2%) | 56 (10.98%) | 0.710 |
| Black | 189 (37.06%) | 189 (37.06%) | 0.883 |
| Other Race | 269 (52.75%) | 265 (51.96%) | 0.715 |
| Hispanic | 212 (41.57%) | 191 (37.45%) | 0.092 |
| Pre-Existing Comorbidities, n (%) | |||
| Type 2 Diabetes | 366 (71.76%) | 309 (60.59%) | 0.045 |
| Hypertension | 506 (99.22%) | 492 (96.47%) | 0.675 |
| Asthma | 105 (20.59%) | 65 (12.75%) | 0.004 |
| COPD | 62 (12.16%) | 41 (8.04%) | 0.079 |
| Cardiovascular Diseases | 336 (65.88%) | 264 (51.76%) | 0.009 |
| Kidney Diseases Prior to Transplant, n (%) | |||
| Polycystic Kidney Disease | 23 (4.51%) | 15 (2.94%) | 0.25 |
| Glomerulonephritis | 37 (7.25%) | 34 (6.67%) | 0.81 |
| Acute COVID-19 Treatments, n (%) | |||
| Hospitalization Due to COVID-19 | 432 (83.68%) | N/A | N/A |
| Critical Illness Due to COVID-19 | 15 (2.94%) | N/A | N/A |
| Remdesivir | 190 (37.25%) | N/A | N/A |
| Baseline Biomarkers Pre-Index Date | |||
| eGFR (mL/min/BSA), median (IQR) | (n = 498) 46 (29, 60) | (n = 454) 48 (13, 60) | <0.001 |
| UPCR (mg/g), median (IQR) | (n = 440) 209 (117, 453) | (n = 431) 242 (131, 500) | 0.14 |
| Covariate | Mortality aHR [95% CI] | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| SARS-CoV-2 Infection | 0.66 [0.43, 1.01] | 0.057 |
| Age at Index Date (Years) | 1.05 [1.03, 1.07] | <0.001 |
| Transplant to Index Date (Years) | 0.99 [0.96, 1.03] | 0.75 |
| eGFR at Baseline (mL/min/BSA) | 0.98 [0.98, 0.99] | <0.001 |
| Male vs. Female Sex | 1.33 [0.86, 2.06] | 0.20 |
| Type 2 Diabetes | 1.39 [0.81, 2.40] | 0.23 |
| Cardiovascular Diseases | 1.54 [0.90, 2.63] | 0.11 |
| Predictor | eGFR β [95% CI] | p-Value | Standard Error | t-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Since Transplant (Years) | −0.98 [−1.50, −0.46] | <0.001 | 0.27 | −3.69 |
| Time Since Transplant (Years) × SARS-CoV-2 Infection | −0.82 [−1.19, −0.45] | <0.001 | 0.19 | −4.33 |
| Intercept | 63 [57, 70] | <0.001 | 3.23 | 19.73 |
| SARS-CoV-2 Infection | 7.12 [4.06, 10.18] | <0.001 | 1.56 | 4.57 |
| Age (Years) | −0.03 [−0.13, 0.08] | 0.637 | 0.055 | −0.47 |
| Male vs. Female Sex | 3.84 [0.90, 6.78] | 0.011 | 1.50 | 2.56 |
| Type 2 Diabetes | −0.22 [−3.63, 3.19] | 0.901 | 1.74 | −0.13 |
| Cardiovascular Diseases | −11.90 [−15.2, −8.60] | <0.001 | 1.69 | −7.06 |
| Predictor | UPCR eβ [95% CI] | p-Value | Standard Error | t-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Since Transplant (Years) | 1.05 [1.04, 1.07] | <0.001 | 0.009 | 6.068 |
| Time Since Transplant (Years) × SARS-CoV-2 Infection | 1.01 [0.99, 1.02] | 0.45 | 0.008 | 0.762 |
| Intercept | 121 [93, 158] | <0.001 | 0.134 | 35.901 |
| SARS-CoV-2 Infection | 1.15 [0.99, 1.33] | 0.076 | 0.077 | 1.777 |
| Age (Years) | 1.00 [1.00, 1.01] | 0.11 | 0.002 | 1.617 |
| Male vs. Female Sex | 1.06 [0.93, 1.21] | 0.38 | 0.068 | 0.883 |
| Type 2 Diabetes | 1.11 [0.96, 1.29] | 0.17 | 0.077 | 1.374 |
| Cardiovascular Diseases | 1.16 [1.00, 1.33] | 0.047 | 0.073 | 1.982 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, S.; Hadidchi, R.; Vichare, A.; Lu, J.Y.; Hou, W.; Henry, S.; Akalin, E.; Duong, T.Q. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Associated with an Accelerated eGFR Decline in Kidney Transplant Recipients up to Four Years Post Infection. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091091
Qiu S, Hadidchi R, Vichare A, Lu JY, Hou W, Henry S, Akalin E, Duong TQ. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Associated with an Accelerated eGFR Decline in Kidney Transplant Recipients up to Four Years Post Infection. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(9):1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091091
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Shawn, Roham Hadidchi, Aditi Vichare, Justin Y. Lu, Wei Hou, Sonya Henry, Enver Akalin, and Tim Q. Duong. 2025. "SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Associated with an Accelerated eGFR Decline in Kidney Transplant Recipients up to Four Years Post Infection" Diagnostics 15, no. 9: 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091091
APA StyleQiu, S., Hadidchi, R., Vichare, A., Lu, J. Y., Hou, W., Henry, S., Akalin, E., & Duong, T. Q. (2025). SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Associated with an Accelerated eGFR Decline in Kidney Transplant Recipients up to Four Years Post Infection. Diagnostics, 15(9), 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091091







