Optimizing Radiation Dose in High-Resolution Chest CT: The Impact of Patient-Specific Factors and Size-Specific Dose Estimates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection
2.2. CT Equipment and Techniques
2.3. Effective Dose
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Demographics and Protocol Description
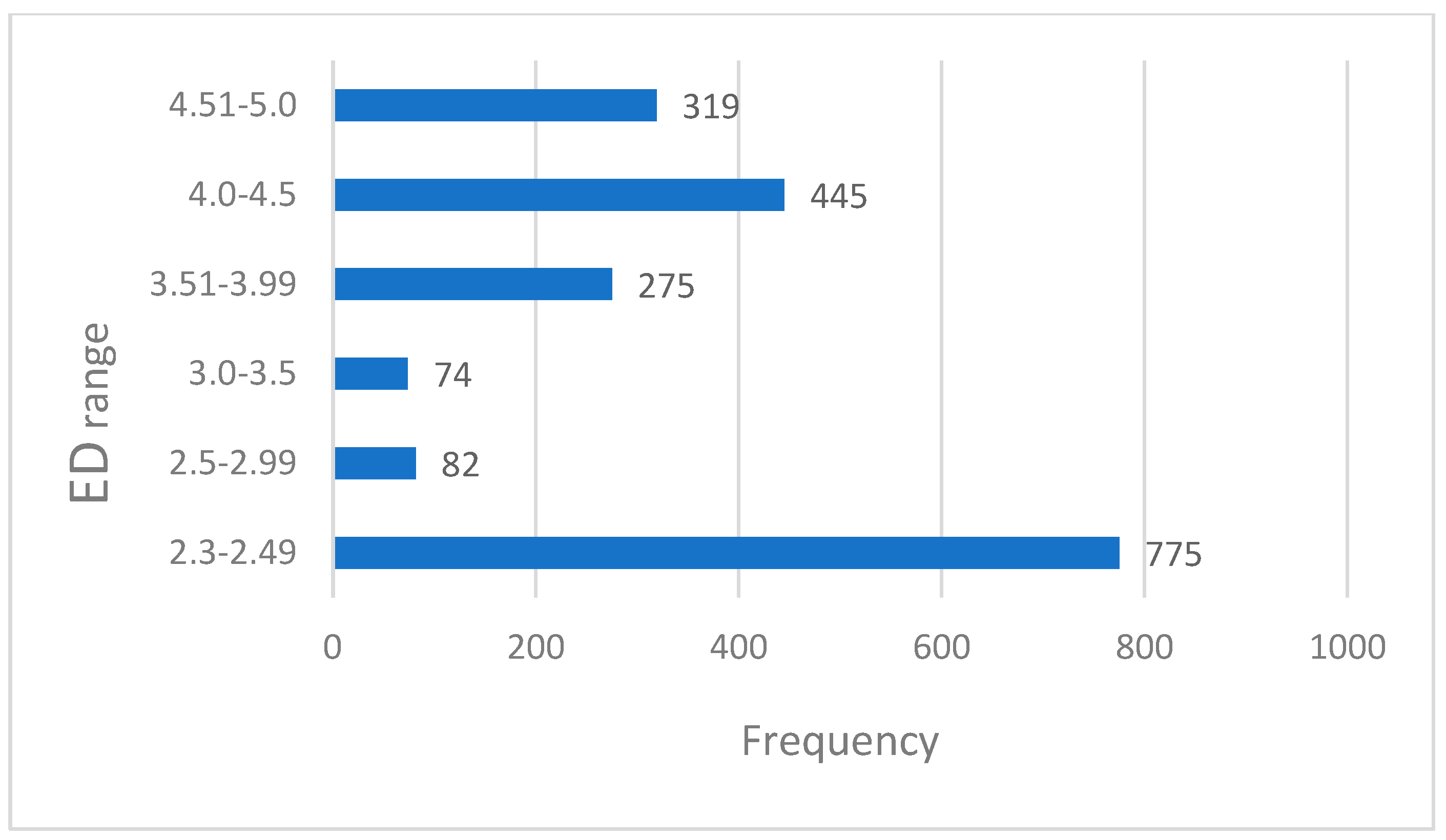
3.2. Dosimetric Analysis of HRCT Chest Scans
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Patient Factors and Radiation Dose Parameters
4. Discussion
Limitation
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HRCT | High-Resolution Computed Tomography |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| CTDIvol | Volume Computed Tomography Dose Index |
| DLP | Dose-Length Product |
| SSDE | Size-Specific Dose Estimate |
| AEC | Automatic Exposure Control |
| kVp | Automatic Exposure Control |
| DRLs | Diagnostic Reference Levels |
| AAPM | American Association of Physicists in Medicine |
| ACR | American College of Radiology |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| ICRP | International Commission on Radiological Protection |
| RIS | Radiology Information System |
| PACS | Picture Archiving and Communication System |
| ED | Effective Dose |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
References
- Kumar, N.; Pradhan, A.; Kadavigere, R.; Sukumar, S. Low dose protocol for high resolution CT thorax: Influence of matrix size and tube voltage on image quality and radiation dose. F1000Research 2022, 11, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, J.R.; Jackson, S.A.; Muller, N.L. High-resolution CT of the chest: Radiation dose. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1993, 160, 479–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, S.L.; Mirro, A.E.; Moore, B.M.; Kaufman, R.A. How to appropriately calculate effective dose for CT using either size-specific dose estimates or dose-length product. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujiguchi, T.; Obara, H.; Ono, S.; Saito, Y.; Kashiwakura, I. Consideration of the usefulness of a size-specific dose estimate in pediatric CT examination. J. Radiat. Res. 2018, 59, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCollough, C.; Bakalyar, D.M.; Bostani, M.; Brady, S.; Boedeker, K.; Boone, J.M.; Wang, J. Use of Water Equivalent Diameter for Calculating Patient Size and Size-Specific Dose Estimates (SSDE) in CT: The Report of AAPM Task Group 220. AAPM Rep. 2014, 2014, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Israel, G.M.; Cicchiello, L.; Brink, J.; Huda, W. Patient size and radiation exposure in thoracic, pelvic, and abdominal CT examinations performed with automatic exposure control. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 1342–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, M.K.; Dang, P.; Singh, S.; Saini, S.; Shepard, J.A.O. In-Plane Shielding for CT: Effect of Off-Centering, Automatic Exposure Control and Shield-to-Surface Distance. Korean J. Radiol. 2009, 10, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulieman, A.; Adam, H.; Elnour, A.; Tamam, N.; Alhaili, A.; Alkhorayef, M.; Alghamdi, S.; Khandaker, M.U.; Bradley, D.A. Patient radiation dose reduction using a commercial iterative reconstruction technique package. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 178, 108996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, A.; Koehler, T.; Brendel, B.; Aichele, J.; Neumann, J.; Noël, P.B.; Muenzel, D. CT pulmonary angiography: Dose reduction via a next generation iterative reconstruction algorithm. Acta Radiol. 2019, 60, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, S.; Shiung, M.; Duan, X.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; McCollough, C.H. Size-specific Dose Estimates for Chest, Abdominal, and Pelvic CT: Effect of Intrapatient Variability in Water-equivalent Diameter. Radiology 2015, 276, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puiggrós, I.V.; Moreno, E.G.; Dotu, C.O.; Agustí, M.Q.I.; Díaz, F.L. Diagnostic Efficacy of High-Resolution Computed Tomography Densitometry for Diagnosing Otosclerosis. Otol. Neurotol. 2023, 44, e697–e701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Fan, H.; Cai, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, B.; Hou, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Y.; Xuan, W.; et al. High-resolution computed tomography manifestations of COVID-19 infections in patients of different ages. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 126, 108972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report of AAPM Task Group 204. Size-Specific Dose Esitmates (SSDE) in Pediatric and Adult Body CT Examinations 2011. Available online: https://www.aapm.org/pubs/reports/rpt_204.pdf (accessed on 29 February 2025).
- Vañó, E.; Miller, D.L.; Martin, C.J.; Rehani, M.M.; Kang, K.; Rosenstein, M.; Ortiz-López, P.; Mattsson, S.; Padovani, R.R.A. ICRP Publication 135: Diagnostic Reference Levels in Medical Imaging. Ann. ICRP 2017, 46, 1–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Gao, Y.; Liu, H.; Caracappa, P.F.; Long, D.J.; Bolch, W.E.; Xu, X.G. VirtualDose: A software for reporting organ doses from CT for adult and pediatric patients. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 5601–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Quinn, B.; Pandit-Taskar, N.; Behr, G.; Mahmood, U.; Long, D.; Xu, X.G.; Germain, J.S.; Dauer, L.T. Patient-specific organ and effective dose estimates in pediatric oncology computed tomography. Phys. Medica 2018, 45, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShurbaji, M.; El Haout, S.; Chanchal, A.; Dhou, S.; Dalah, E. Investigating the Effect of Patient-Related Factors on Computed Tomography Radiation Dose Using Regression and Correlation Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X. Body size and tube voltage-dependent guiding equations for optimal selection of image acquisition parameters in clinical X-ray imaging. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2018, 11, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C. Managing radiation dose from chest CT in patients with COVID-19. Radiology 2021, 298, E158–E159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almohammed, H.I.; Elshami, W.; Hamd, Z.Y.; Abuzaid, M. Optimizing CT Abdomen–Pelvis Scan Radiation Dose: Examining the Role of Body Metrics (Waist Circumference, Hip Circumference, Abdominal Fat, and Body Mass Index) in Dose Efficiency. Tomography 2024, 10, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghetti, C.; Ortenzia, O.; Maddalo, M.; Altabella, L.; Sverzellati, N. Dosimetric and radiation cancer risk evaluation of high resolution thorax CT during COVID-19 outbreak. Phys. Medica 2020, 80, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brat, H.; Zanca, F.; Rizk, B.; Montandon, S.; Racine, D. Influence of BMI on clinical DRLs for CT examinations: A prospective multicenter study after protocol harmonization and optimization. EuroSafe Imaging 2019, 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzaid, M.M.; Yuvali, M.; Ozsahin, D.U. Machine Learning Classification of Patients Undergoing Abdominal CT Scans: Factors Affecting Imaging Quality and Radiation Exposure. In Proceedings of the Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 3–5 June 2024; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, Y.; Itoh, H.; Nagahara, K.; Hata, H.; Mitsui, K. Relationships of Radiation Dose Indices with Body Size Indices in Adult Body Computed Tomography. Tomography 2023, 9, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, P.D.; Chawke, L.; Twomey, M.; Murphy, K.P.; O’neill, S.B.; McWilliams, S.R.; James, K.; Kavanagh, R.G.; Sullivan, C.; Chan, F.E.; et al. Body composition determinants of radiation dose during abdominopelvic CT. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltybaeva, N.; Martini, K.; Frauenfelder, T.; Alkadhi, H. Organ Dose and Attributable Cancer Risk in Lung Cancer Screening with Low-Dose Computed Tomography. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.; Heiss, R.; Koehnen, J.; Wetzl, M.; Wiesmueller, M.; Treutlein, C.; Braeuer, L.; Uder, M.; Kopp, M. Personalized Chest Computed Tomography: Minimum Diagnostic Radiation Dose Levels for the Detection of Fibrosis, Nodules, and Pneumonia. Investig. Radiol. 2021, 57, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Mean ± SD | Min–Max |
|---|---|---|
| Images per series | 65.4 ± 7.4 | 44–93 |
| Scanning length (mm) | 399.1 ± 34.3 | 302.1–499.6 |
| Exposure time (ms) | 3263.1 ± 304.8 | 2019.9–7199.9 |
| Tube voltage (kVp) | 112.5 ± 10.1 | 100–140 |
| Tube current (mA) | 162.1 ± 53.2 | 72.2–300 |
| Pitch factor | 1.5 ± 0.0001 | 1.5–1.5 |
| Exposure time per rotation (s/rot) | 0.5 (constant) | 0.5–0.5 |
| n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 971 (49.28) |
| Male | 999 (50.71) | |
| BMI Range | Underweight | 2 (0.1) |
| Healthy Weight | 524 (26.59) | |
| Overweight | 946 (48.02) | |
| Obesity | 498 (25.27) | |
| Study Protocol | First Time | 858 (43.55) |
| Thorax FU | 1112 (56.44) | |
| Indications | Consolidation | 184 (9.34) |
| Dyspnea | 608 (30.86) | |
| Dyspnea and Expectoration | 203 (10.3) | |
| Pneumonia | 478 (24.26) | |
| Pulmonary Thromboembolism | 497 (25.22) |
| Percentile | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Min–Max | 25 | 50 | 75 | |
| DLP (mGy·cm) | 161.14 ± 80.92 | 48.9–486.9 | 83.8 | 150.4 | 231 |
| CTDIvol (mGy) | 4.01 ± 2.03 | 1.2–12.1 | 2.0 | 3.8 | 5.9 |
| SSDE (mGy) | 5.56 ± 1.33 | 2.7–12.4 | 5.0 | 5.6 | 6.0 |
| E103 (mSv) | 3.24 ± 1.2 | 2.3–4.9 | 3.09 | 3.1 | 3.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abuzaid, M. Optimizing Radiation Dose in High-Resolution Chest CT: The Impact of Patient-Specific Factors and Size-Specific Dose Estimates. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060740
Abuzaid M. Optimizing Radiation Dose in High-Resolution Chest CT: The Impact of Patient-Specific Factors and Size-Specific Dose Estimates. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(6):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060740
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbuzaid, Mohamed. 2025. "Optimizing Radiation Dose in High-Resolution Chest CT: The Impact of Patient-Specific Factors and Size-Specific Dose Estimates" Diagnostics 15, no. 6: 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060740
APA StyleAbuzaid, M. (2025). Optimizing Radiation Dose in High-Resolution Chest CT: The Impact of Patient-Specific Factors and Size-Specific Dose Estimates. Diagnostics, 15(6), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060740






