Quantitative Analysis of Early Retinal Changes and OCT Parameters in Diabetic Subjects with and Without Retinopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Correlation Between VD and FAZ and HbA1c, MAP, and Contrast Sensitivity
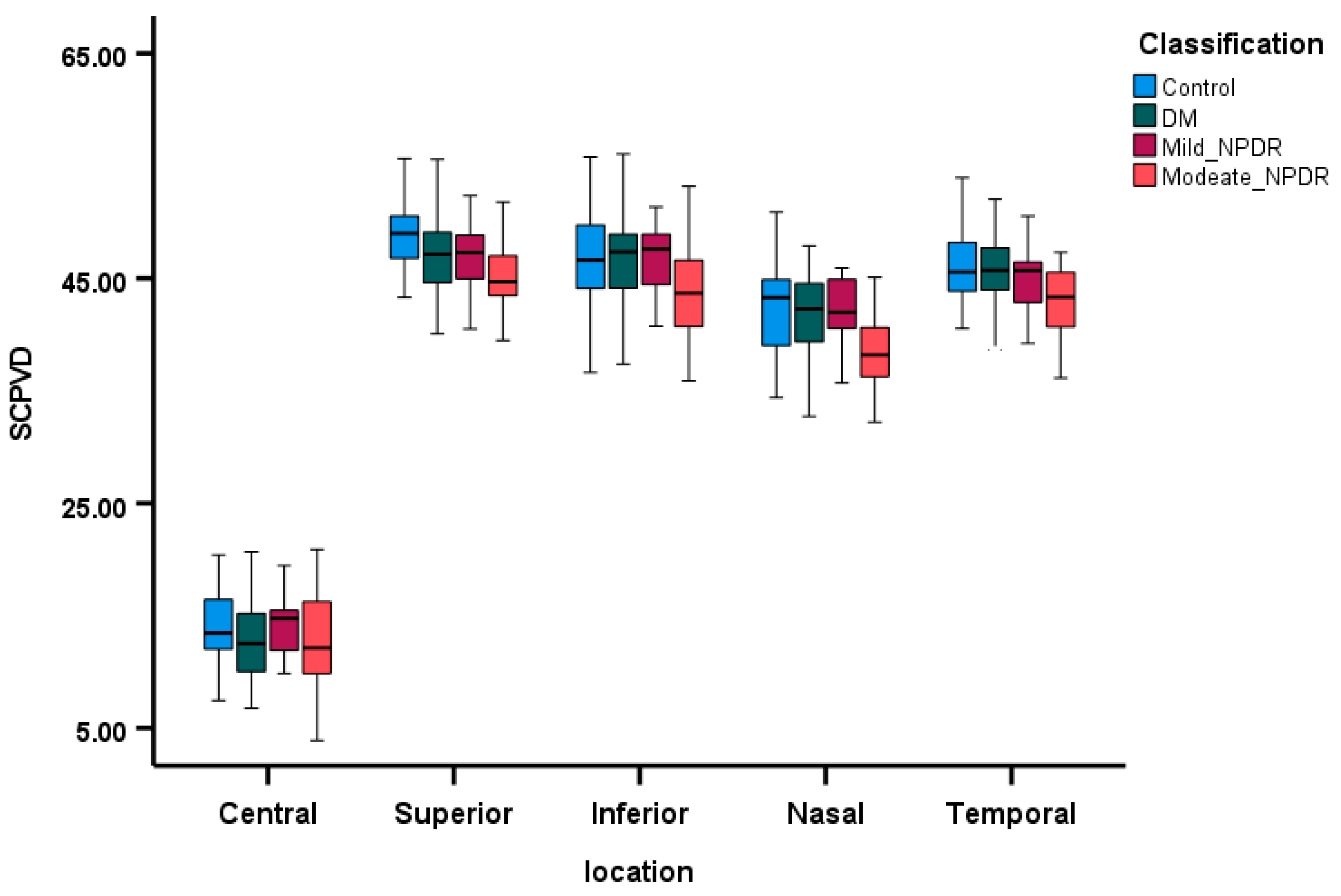
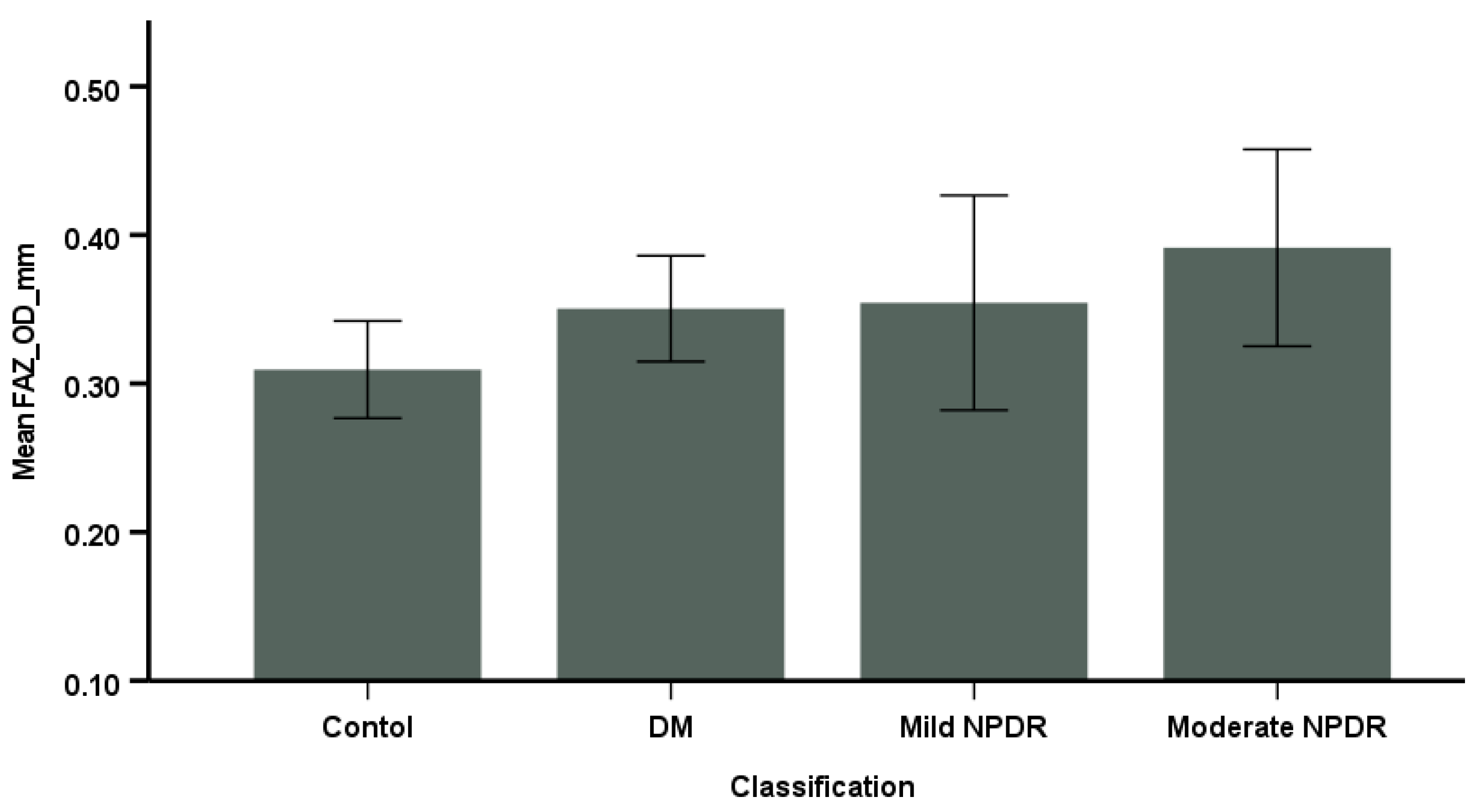
3.2. Comparison of OCTA Parameters Among the Groups
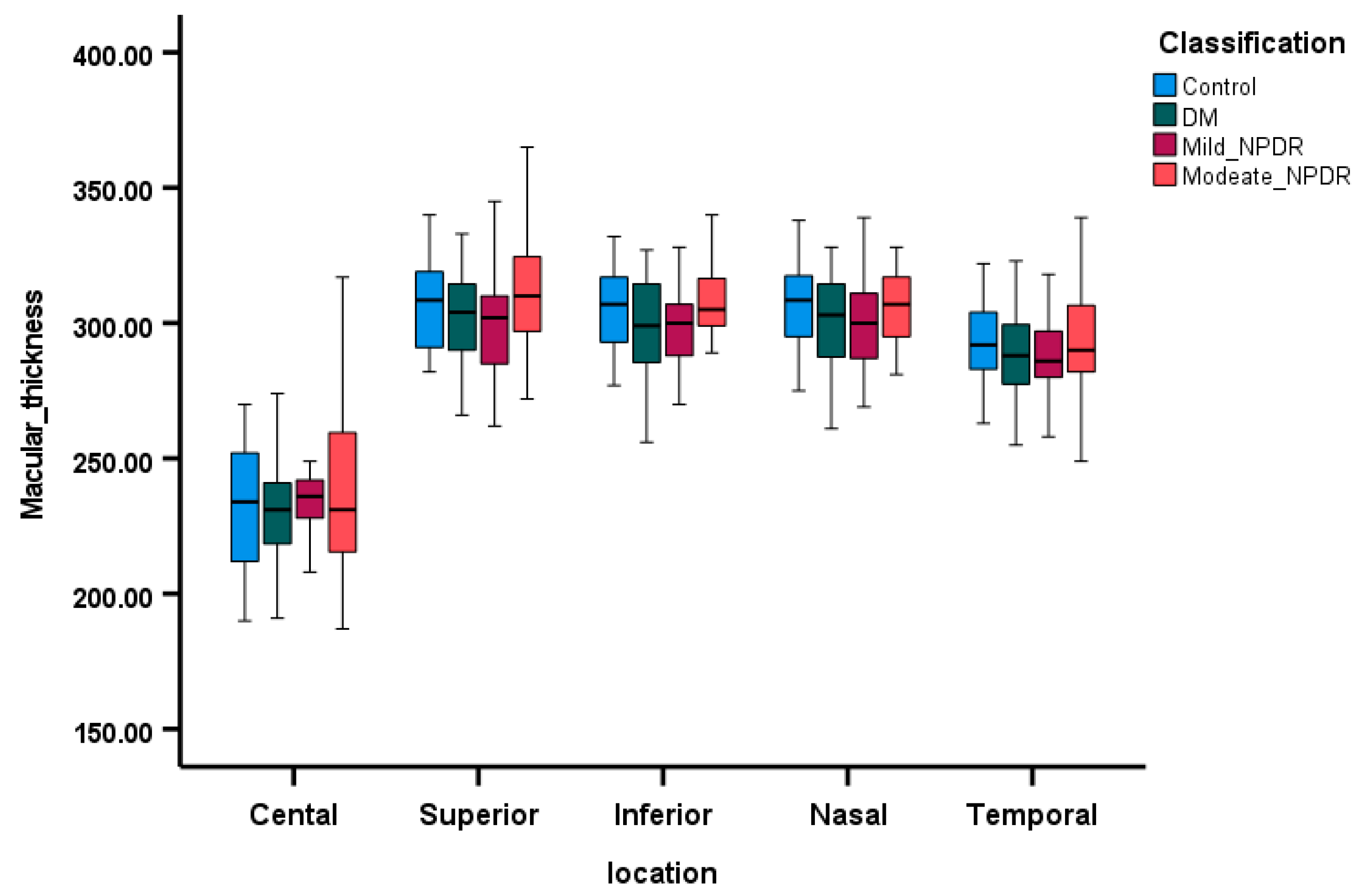
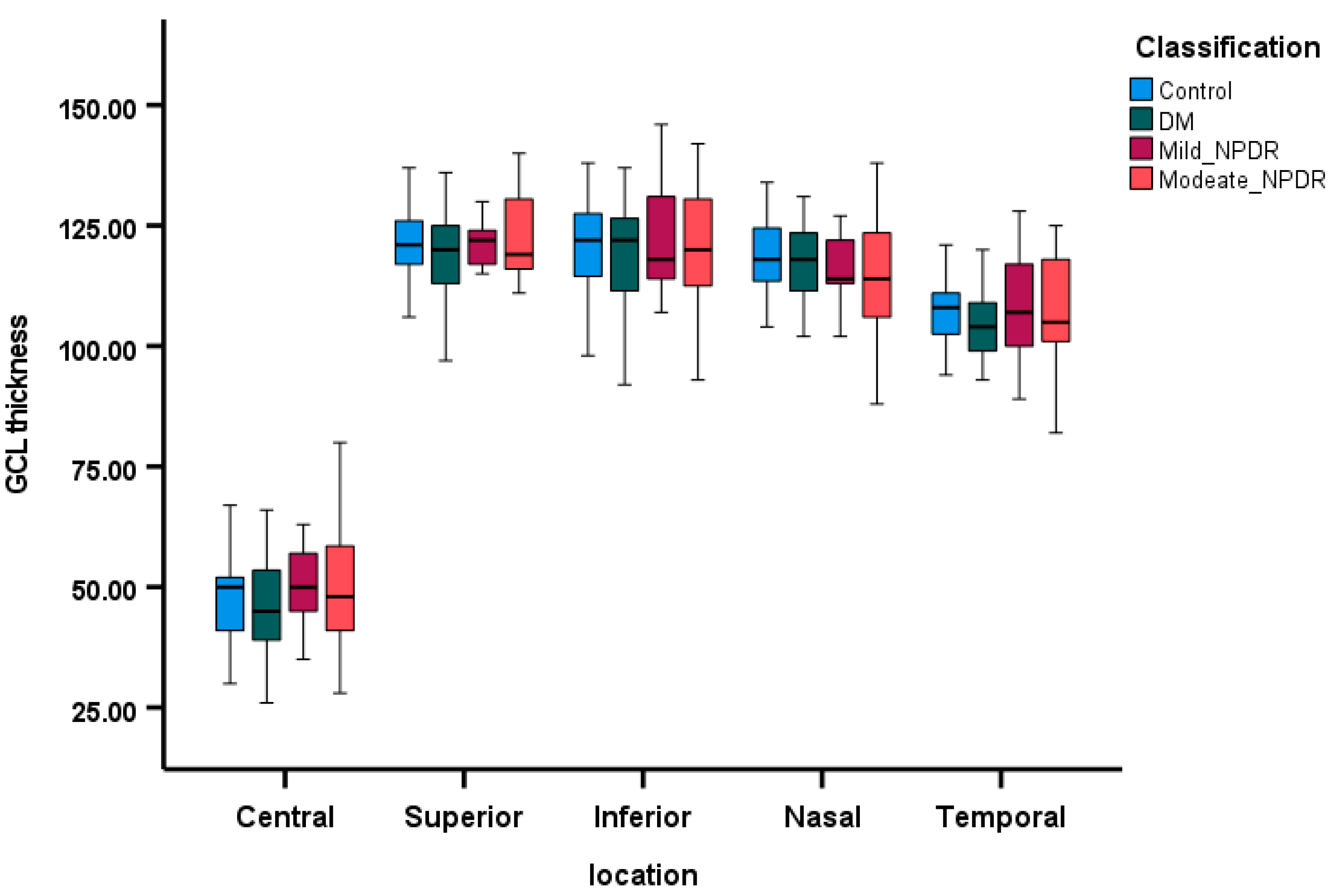
3.3. Comparison of OCT Parameters Among the Groups
3.4. Correlations Between SCP VD and Retinal Layers Thickness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fong, D.S.; Aiello, L.P.; Ferris, F.L.; Klein, R. Diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2540–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antcliff, R.J.; Marshall, J. The pathogenesis of edema in diabetic maculopathy. Semin. Ophthalmol. 1999, 14, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Benedetto, U.; Querques, G.; Lattanzio, R.; Borrelli, E.; Triolo, G.; Maestranzi, G.; Calori, G.; Querques, L.; Bandello, F. Macular dysfunction is common in both type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients without macular edema. Retina 2014, 34, 2171–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearse, M.A.; Ozawa, G.Y. Multifocal electroretinography in diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2014, 14, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonetti, D.A.; Barber, A.J.; Bronson, S.K.; Freeman, W.M.; Gardner, T.W.; Jefferson, L.S.; Kester, M.; Kimball, S.R.; Krady, J.K.; LaNoue, K.F.; et al. Diabetic retinopathy: Seeing beyond glucose-induced microvascular disease. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2401–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, G.R.; Barber, A.J. Visual dysfunction associated with diabetic retinopathy. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2010, 10, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, A.J. A new view of diabetic retinopathy: A neurodegenerative disease of the eye. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 27, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, A.J.; Gardner, T.W.; Abcouwer, S.F. The significance of vascular and neural apoptosis to the pathology of diabetic retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, T.W.; Abcouwer, S.F.; Barber, A.J.; Jackson, G.R. An integrated approach to diabetic retinopathy research. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2011, 129, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghirlanda, G.; Di Leo, M.A.; Caputo, S.; Cercone, S.; Greco, A.V. From functional to microvascular abnormalities in early diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Metab. Rev. 1997, 13, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biallosterski, C.; van Velthoven, M.E.J.; Michels, R.P.J.; Schlingemann, R.O.; DeVries, J.H.; Verbraak, F.D. Decreased optical coherence tomography-measured pericentral retinal thickness in patients with diabetes mellitus type 1 with minimal diabetic retinopathy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 91, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronson-Castain, K.W.; Bearse, M.A., Jr.; Neuville, J.; Jonasdottir, S.; King-Hooper, B.; Barez, S.; Schneck, M.E.; Adams, A.J. Adolescents with Type 2 diabetes: Early indications of focal retinal neuropathy, retinal thinning, and venular dilation. Retina 2009, 29, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.; von Wendt, G.; Wanger, P.; Martin, L. Early detection of macular changes in patients with diabetes using Rarebit Fovea Test and optical coherence tomography. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 91, 1596–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera DeBuc, D.; Somfai, G.M. Early detection of retinal thickness changes in diabetes using optical coherence tomography. Med. Sci. Monit. 2010, 16, MT15–MT21. [Google Scholar]
- Ghassemi, F.; Fadakar, K.; Berijani, S.; Babeli, A.; Gholizadeh, A.; Sabour, S. Quantitative assessment of vascular density in diabetic retinopathy subtypes with optical coherence tomography angiography. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021, 21, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Saif, P.S.; Salman, A.E.G.; Omran, N.A.H.; Farweez, Y.A.T. Assessment of Diabetic Retinopathy Vascular Density Maps. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 3941–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schmitt, J.M.; Knuttel, A.; Bonner, R.F. Measurement of optical properties of biological tissues by low-coherence reflectometry. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 6032–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvin, M.; Abramoff, M.; Wu, X.; Russell, S.; Burns, T.; Sonka, M. Automated 3-D intraretinal layer segmentation of macular spectral-domain optical coherence tomography images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2009, 50, 5778–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvin, M.K.; Abramoff, M.D.; Kardon, R.; Russell, S.R.; Wu, X.; Sonka, M. Intraretinal layer segmentation of macular optical. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2008, 27, 1495–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.Y.; Chu, Z.; Shahidzadeh, A.; Wang, R.K.; Puliafito, C.A.; Kashani, A.H. Quantifying Microvascular Density and Morphology in Diabetic Retinopathy Using Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, OCT362–OCT370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dimitrova, G.; Chihara, E.; Takahashi, H.; Amano, H.; Okazaki, K. Quantitative Retinal Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography in Patients With Diabetes Without Diabetic Retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agemy, S.A.; Scripsema, N.K.; Shah, C.M.; Chui, T.; Garcia, P.M.; Lee, J.G.; Gentile, R.C.; Hsiao, Y.S.; Zhou, Q.; Ko, T.; et al. Retinal Vascular Perfusion Density Mapping using Optical coherence Tomography Angiography in Normals and Diabetic retinopathy patients. Retina 2015, 35, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Dawish, M.A.; Robert, A.A.; Braham, R.; Al Hayek, A.A.; Al Saeed, A.; Ahmed, R.A.; Al Sabaan, F.S. Diabetes Mellitus in Saudi Arabia: A Review of the Recent Literature. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2016, 12, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, A.M.D.; Alhazmi, A.M.S. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Patient Awareness of Diabetic Retinopathy in Saudi Arabia: A Review of the Literature. Cureus 2020, 12, e11991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Al-Ghamdi, A.S. Adults visual impairment and blindness–An overview of prevalence and causes in Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 33, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rubeaan, K.; Abu El-Asrar, A.M.; Youssef, A.M.; Subhani, S.N.; Ahmad, N.A.; Al-Sharqawi, A.H.; Alguwaihes, A.; Alotaibi, M.S.; Al-Ghamdi, A.; Ibrahim, H.M. Diabetic retinopathy and its risk factors in a society with a type 2 diabetes epidemic: A Saudi National Diabetes Registry-based study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015, 93, e140–e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sheikh, M.; Akil, H.; Pfau, M.; Sadda, S.R. Swept-Source OCT Angiography Imaging of the Foveal Avascular Zone and Macular Capillary Network Density in Diabetic Retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 3907–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Shi, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhang, N.; Dong, L.; Zhou, S.; et al. Quantitative analysis of retinal vessel density and thickness changes in diabetes mellitus evaluated using optical coherence tomography angiography: A cross-sectional study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021, 21, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Yang, D.; Huang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L. Optical coherence tomography angiography discerns preclinical diabetic retinopathy in eyes of patients with type 2 diabetes without clinical diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupidi, M.; Coscas, G.; Coscas, F.; Fiore, T.; Spaccini, E.; Fruttini, D.; Cagini, C. Retinal Microvasculature in Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy: Automated Quantitative Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Assessment. Ophthalmic Res. 2017, 58, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulikov, A.N.; Maltsev, D.S.; Burnasheva, M.A. Improved analysis of foveal avascular zone area with optical coherence tomography angiography. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2018, 256, 2293–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelshafy, M.; Abdelshafy, A. Correlations Between Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Parameters and the Visual Acuity in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambhav, K.; Abu-Amero, K.K.; Chalam, K.V. Deep Capillary Macular Perfusion Indices Obtained with OCT Angiography Correlate with Degree of Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 27, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnevali, A.; Sacconi, R.; Corbelli, E.; Tomasso, L.; Querques, L.; Zerbini, G.; Scorcia, V.; Bandello, F.; Querques, G. Optical coherence tomography angiography analysis of retinal vascular plexuses and choriocapillaris in patients with type 1 diabetes without diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. 2017, 54, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinisik, M.; Kahraman, N.S.; Kurt, E.; Mayali, H.; Kayikcioglu, O. Quantitative analysis of early retinal vascular changes in type 2 diabetic patients without clinical retinopathy by optical coherence tomography angiography. Int. Ophthalmol. 2022, 42, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puro, D.G. Retinovascular physiology and pathophysiology: New experimental approach/new insights. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2012, 31, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carlo, T.E.; Chin, A.T.; Filho, M.A.B.; Adhi, M.; Branchini, L.; Salz, D.A.; Baumal, C.R.; Crawford, C.; Reichel, E.; Witkin, A.J.; et al. Detection of microvascular changes in eyes of patients with diabetes but not clinical diabetic retinopathy using optical coherence tomography angiography. Retina 2015, 35, 2364–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, G.; Weihong, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Zhikun, Y.; Xuan, Z.; Yi, Q.; Fangtian, D. A morphological study of the foveal avascular zone in patients with diabetes mellitus using optical coherence tomography angiography. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 254, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, M.; Chung, H.; Kim, H.C. Quantification of retinal vessel tortuosity in diabetic retinopathy using optical coherence tomography angiography. Retina 2018, 38, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durbin, M.K.; An, L.; Shemonski, N.D.; Soares, M.; Santos, T.; Lopes, M.; Neves, C.; Cunha-Vaz, J. Quantification of retinal microvascular density in optical coherence tomographic angiography images in diabetic retinopathy. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017, 135, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, E.H.; van Dijk, H.W.; Jiao, C.; Kok, P.H.B.; Jeong, W.; Demirkaya, N.; Garmager, A.; Wit, F.; Kucukevcilioglu, M.; van Velthoven, M.E.J.; et al. Retinal neurodegeneration may precede microvascular changes characteristic of diabetic retinopathy in diabetes mellitus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2655–E2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran, A.; Babu, M.; A Sudhakar, N.; Kudlu, K.P.; Shashidhara, B.C. Study of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in diabetic patients using optical coherence tomography. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 71, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpineto, P.; Toto, L.; Aloia, R.; Ciciarelli, V.; Borrelli, E.; Vitacolonna, E.; Di Nicola, M.; Di Antonio, L.; Mastropasqua, R. Neuroretinal alterations in the early stages of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eye 2016, 30, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehboob, M.A.; Amin, Z.A.; Islam, Q.U. Comparison of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness between normal population and patients with diabetes mellitus using optical coherence tomography. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Guo, Z.; Wang, F.; Li RZhao, L.; Lin, R. Alterations in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in early stages of diabetic retinopathy and potential risk factors. Curr. Eye Res. 2018, 43, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, M.; Oba, E.; Sensoz, H.; Ozdal, E. Retinal nerve fiber layer and ganglion cell complex thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 62, 719–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambiya, V.; Kumar, A.; Bhavaraj, V.R.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, N. Study of inner retinal neurodegeneration in Diabetes Mellitus using spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 32, 3074–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhablani, J.; Sharma, A.; Goud, A.; Peguda, H.K.; Rao, H.L.; Begum, V.U. Neurodegeneration in type 2 diabetes:.Evidence from spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 6333–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezhilvendhan, K.; Shenoy, A.; Rajeshkannan, R.; Balachandrachari, S.; Sathiyamoorthy, A. Evaluation of Macular Thickness, Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer and Ganglion Cell Layer Thickness in Patients among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Pharm. Bioallied. Sci. 2021, 13 (Suppl. 2), S1055–S1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van Dijk, H.W.; Verbraak, F.D.; Kok, P.H.B.; Stehouwer, M.; Garvin, M.K.; Sonka, M.; DeVries, J.H.; Schlingemann, R.O.; Abràmoff, M.D. Early neurodegeneration in the retina of type 2 diabetic patients. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 2715–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sng, C.C.; Cheung, C.Y.; Man, R.E.; Wong, W.; Lavanya, R.; Mitchell, P.; Aung, T.; Wong, T.Y. Influence of diabetes on macular thickness measured using optical coherence tomography: The Singapore Indian Eye Study. Eye 2012, 26, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- Wei, Q.; Qiu, W.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Y. Relationship Between Risk Factors and Macular Thickness in Patients with Early Diabetic Retinopathy. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 6021–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Jiang, H.; Liu, Y.; Rosa Gameiro, G.; Gregori, G.; Dong, C.; Rundek, T.; Wang, J. Age-Related Alterations in Retinal Tissue Perfusion and Volumetric Vessel Density. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| Parameter | Control | DM | Mild NPDR | Moderate NPDR | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numbers | 40 | 43 | 17 | 23 | |
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 15 (38%) | 11 (25%) | 9 (39%) | 7 (41%) | |
| Female | 25 (62%) | 32 (75%) | 14 (61%) | 10 (59%) | |
| Age | 43.67 ± 8.57 | 52.14 ± 6.13 | 51.65 ± 7.39 | 53.52 ± 5.66 | <0.01 |
| Contrast sensitivity (OU) | 2.58 ± 1.15 | 3.36 ± 1.58 | 3.32 ± 1.27 | 4.13 ± 1.55 | <0.01 |
| MAP in mm Hg | 87.88 ± 9.72 | 94.98 ± 9.62 | 86.74 ± 12.11 | 85.98 ± 10.74 | <0.05 |
| Duration of Diabetes (years) | - | 8.55 ± 5.53 | 15.64 ± 7.92 | 16.48 ± 8.92 | <0.01 |
| FBG | 5.17 ± 0.69 | 8.00 ± 3.20 | 9.80 ± 3.99 | 11.68 ± 5.18 | <0.01 |
| HBA1c | 5.39 ± 0.42 | 7.04 ± 1.32 | 8.00 ± 1.71 | 8.75 ± 1.52 | <0.01 |
| SCPVD_C | SCPVD_S | SCPVD_I | SCPVD_N | SCPVD_T | FAZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of DM | 0.01 | −0.17 | 0.15 | −0.36 ** | −0.25 * | −0.02 |
| MAP | −0.10 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.10 | −0.07 | 0.07 |
| Hb1Ac | −0.01 | −0.14 | −0.03 | −0.16 | −0.14 | 0.09 |
| Contrast sensitivity | −0.24 ** | −0.13 | −0.08 | −0.26 ** | −0.27 ** | 0.21 * |
| OCT Parameter | Regression Co-Efficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severity of DR | Reference = Control | |||
| No DR | Mild NPDR | Moderate NPDR | ||
| FAZ | 0.03 * | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.09 * |
| SCPVD_OD_VD_C | −0.21 | −1.37 | −0.37 | −1.38 |
| SCPVD_OD_VD_S | −0.91 * | −1.25 | −1.08 | −3.06 * |
| SCPVD_OD_VD_I | −0.95 * | −0.74 | 0.08 | −3.40 * |
| SCPVD_OD_VD_N | −0.92 * | −0.86 | 0.02 | −3.31 * |
| SCPVD_OD_VD_T | −0.96 * | −0.37 | −0.86 | −3.02 * |
| OCT Parameter | Regression Co-Efficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severity of DR | Reference = Control | |||
| No DR | Mild NPDR | Moderate NPDR | ||
| OD_MT_C | 1.46 | −7.24 | −6.70 | 4.46 |
| OD_MT_S | −0.95 | −1.70 | −4.34 | −2.35 |
| OD_MT_I | −2.29 | 0.58 | −5.15 | −5.75 |
| OD_MT_N | −2.35 | 1.17 | −7.80 | −4.89 |
| OD_MT_T | 2.02 | 0.30 | −3.54 | 7.89 |
| OD_RNFL_S | 0.17 | −1.62 | 0.40 | 0.14 |
| OD_RNFL_I | 0.40 | 0.30 | 1.29 | 1.00 |
| OD_RNFL_N | −0.51 * | −0.12 | −1.09 | −1.37 |
| OD_RNFL_T | 0.02 | −0.50 | 0.44 | −0.24 |
| OD_GCL_C | 0.21 | −2.46 | 0.85 | −0.41 |
| OD_GCL_S | −0.07 | −2.54 | −0.89 | −0.83 |
| OD_GCL-I | −1.23 | −0.67 | 0.64 | −4.48 |
| OD_GCL_N | −1.74 * | −0.91 | −2.74 | −5.17 |
| OD_GCL_T | −0.85 | −6.44 * | −1.86 | −4.39 |
| Group | Central SCP VD and MT | Central SCP VD and GCL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r Value | p-Value | r Value | p-Value | |
| Control | 0.63 | <0.01 | 0.72 | <0.01 |
| DM | 0.41 | 0.03 | 0.56 | <0.01 |
| Mild NPDR | 0.78 | <0.01 | 0.78 | <0.01 |
| Moderate NPDR | 0.84 | <0.01 | 0.76 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aldakhil, S.; Challa, N.; Alhoshan, S.A.; Abohaimed, F.; Alnasser, B.N.; Almuhawas, H.A.; AlObaisi, S.; Alrasheed, S.H. Quantitative Analysis of Early Retinal Changes and OCT Parameters in Diabetic Subjects with and Without Retinopathy. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15040451
Aldakhil S, Challa N, Alhoshan SA, Abohaimed F, Alnasser BN, Almuhawas HA, AlObaisi S, Alrasheed SH. Quantitative Analysis of Early Retinal Changes and OCT Parameters in Diabetic Subjects with and Without Retinopathy. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(4):451. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15040451
Chicago/Turabian StyleAldakhil, Sulaiman, Naveen Challa, Saja A. Alhoshan, Foziyah Abohaimed, Bashair N. Alnasser, Hana A. Almuhawas, Saif AlObaisi, and Saif H. Alrasheed. 2025. "Quantitative Analysis of Early Retinal Changes and OCT Parameters in Diabetic Subjects with and Without Retinopathy" Diagnostics 15, no. 4: 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15040451
APA StyleAldakhil, S., Challa, N., Alhoshan, S. A., Abohaimed, F., Alnasser, B. N., Almuhawas, H. A., AlObaisi, S., & Alrasheed, S. H. (2025). Quantitative Analysis of Early Retinal Changes and OCT Parameters in Diabetic Subjects with and Without Retinopathy. Diagnostics, 15(4), 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15040451






