Unsupervised Phenotyping of Asthma: Integrating Serum Periostin with Clinical and Inflammatory Profiles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
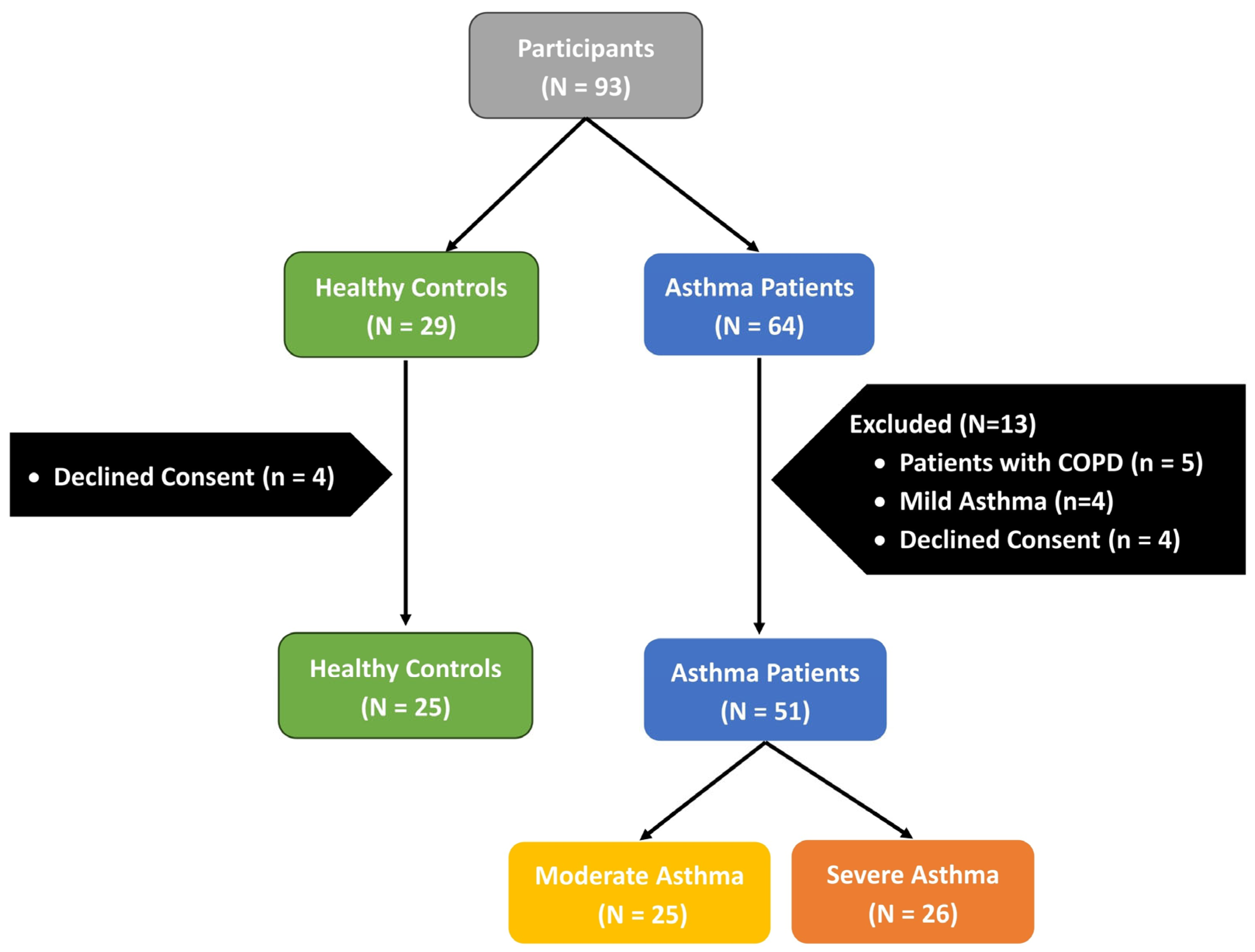
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Detection of Serum Periostin
2.3. Statistical Analysis
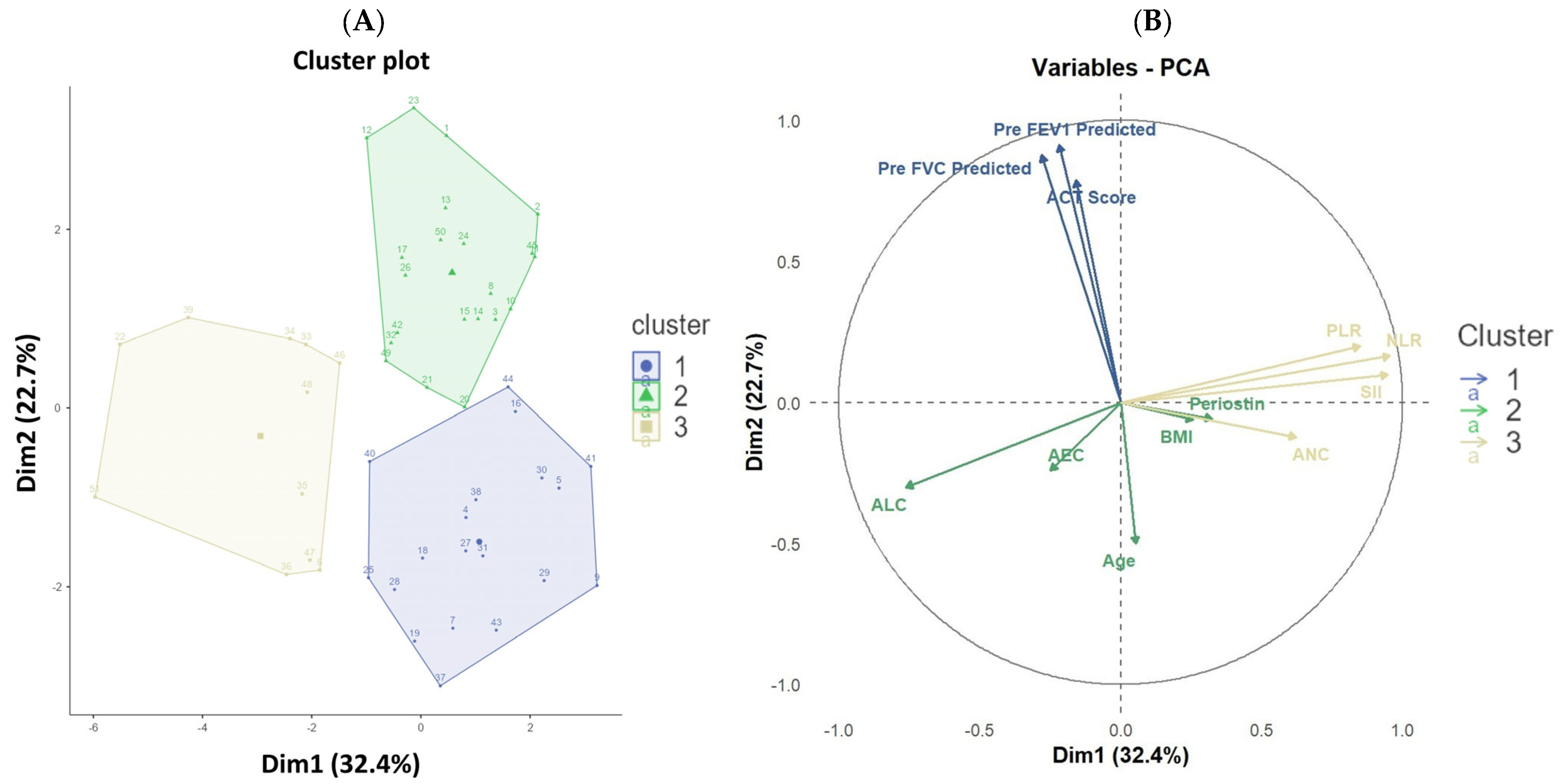
3. Results
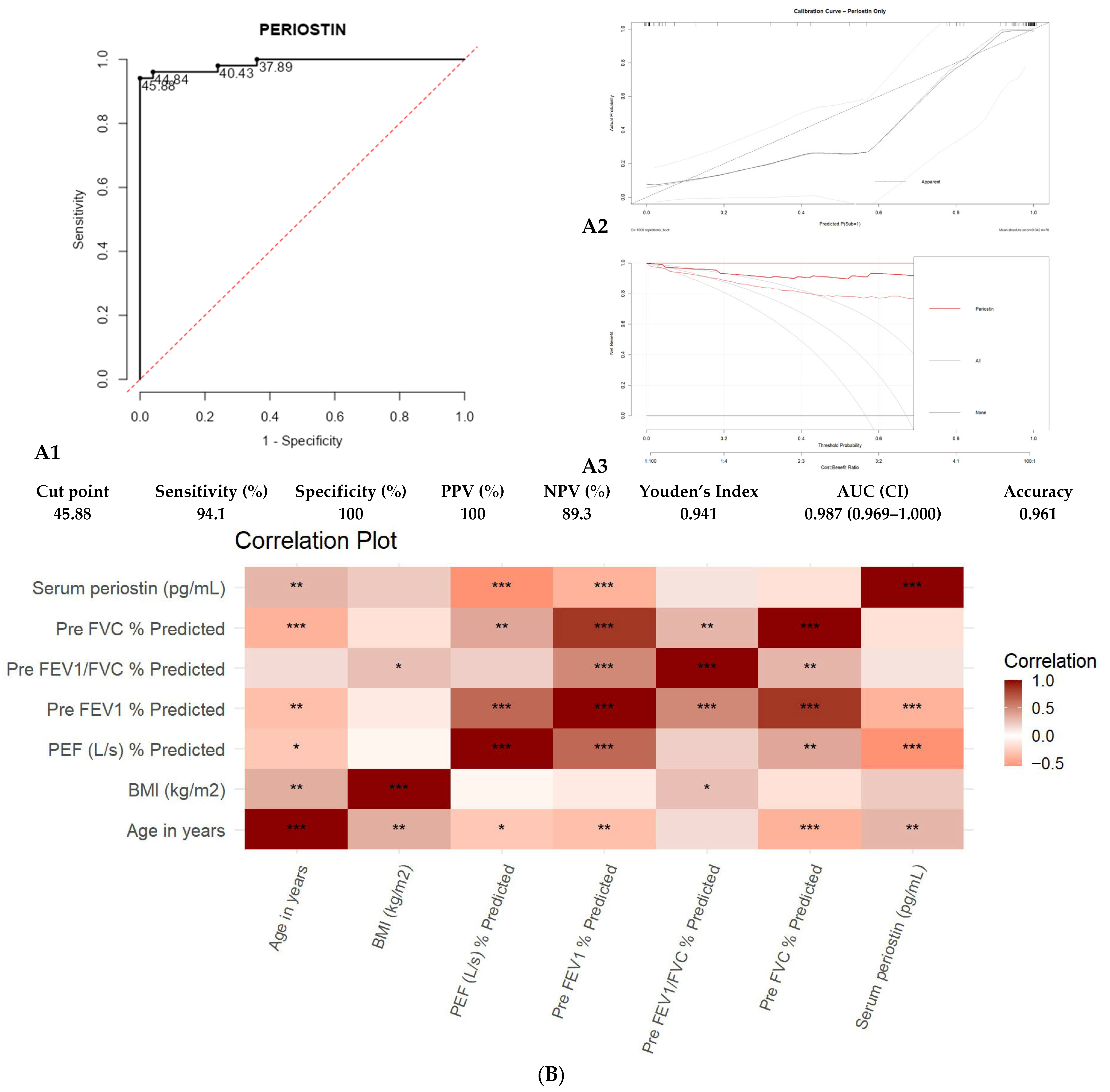
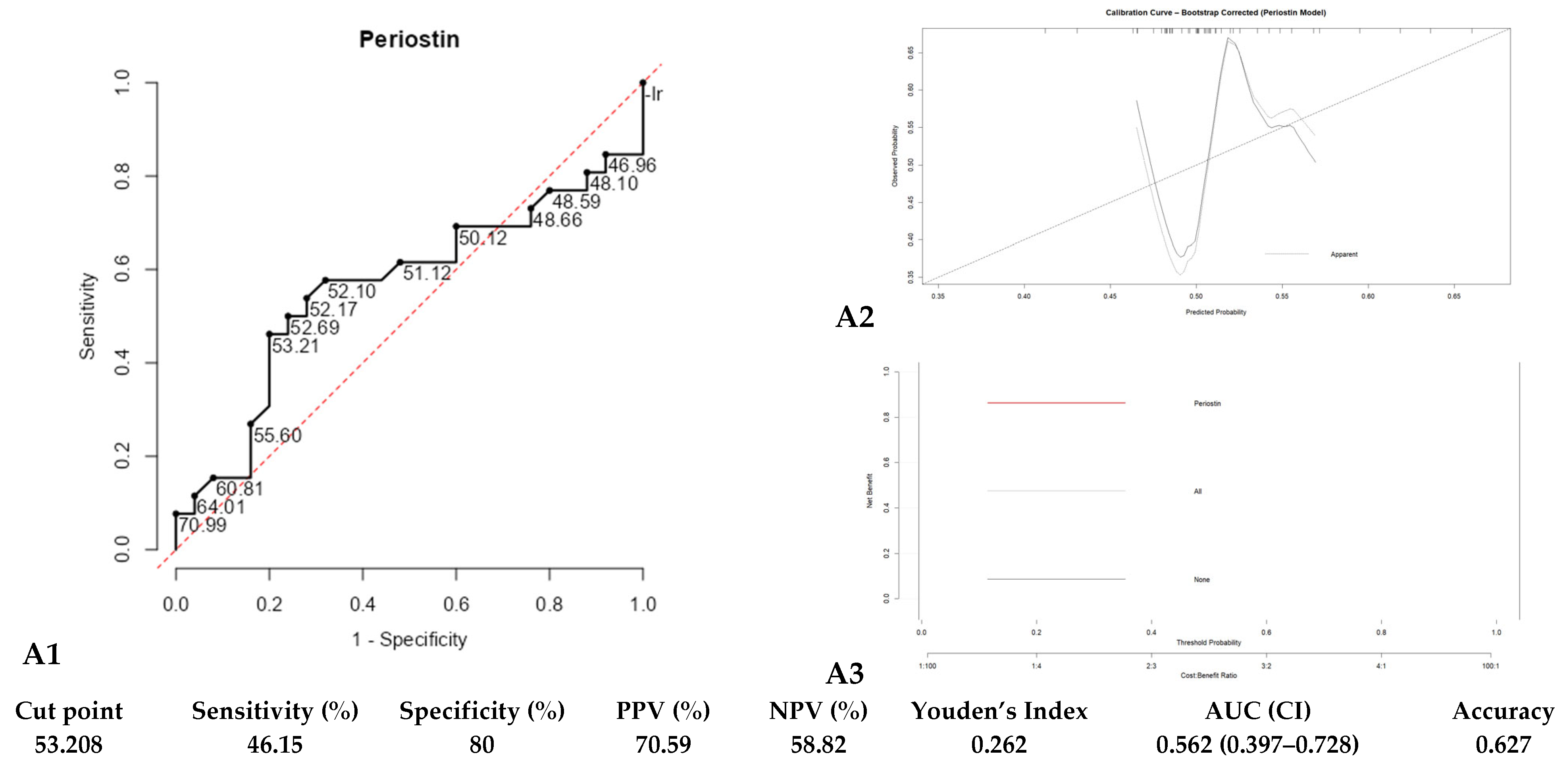
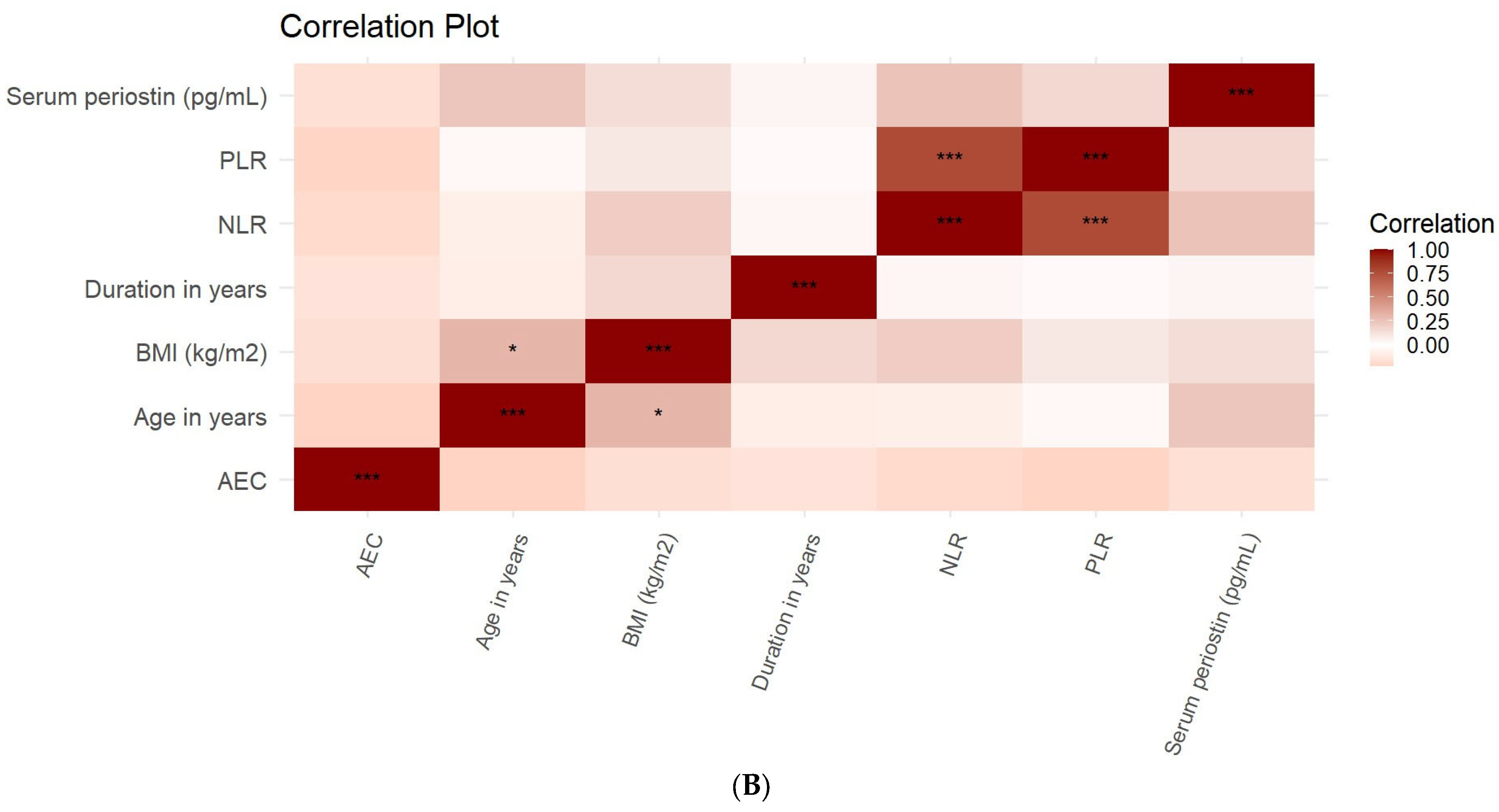
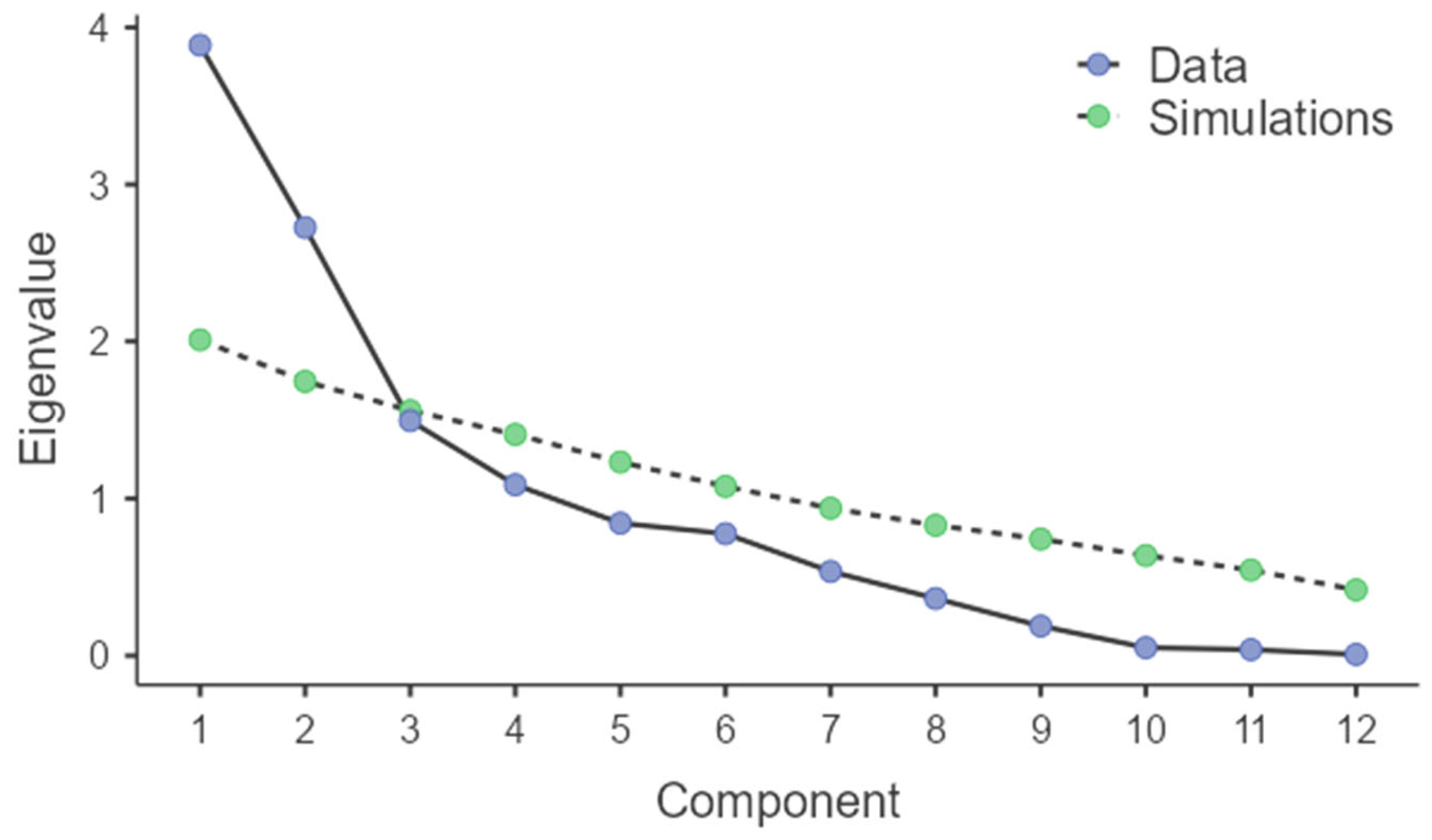
| Component | Eigenvalue | % of Variance | Cumulative % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.887 | 32.395 | 32.395 |
| 2 | 2.725 | 22.712 | 55.107 |
| 3 | 1.495 | 12.454 | 67.561 |
| 4 | 1.087 | 9.061 | 76.623 |
| 5 | 0.843 | 7.024 | 83.647 |
| 6 | 0.776 | 6.466 | 90.113 |
| 7 | 0.536 | 4.467 | 94.580 |
| 8 | 0.364 | 3.031 | 97.611 |
| 9 | 0.189 | 1.574 | 99.185 |
| 10 | 0.051 | 0.427 | 99.611 |
| 11 | 0.038 | 0.320 | 99.932 |
| 12 | 0.008 | 0.068 | 100.000 |
| Cluster 1 (N = 19) | Cluster 2 (N = 21) | Cluster 3 (N = 11) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age in years | 27.0 (23.0–44.0) | 47.0 (35.7–57.0) | 40.0 (25.3–47.0) | 0.001 1 |
| Gender | 0.527 2 | |||
| Female (n, %) | 7.0 (36.8%) | 11.0 (52.4%) | 6.0 (54.5%) | |
| Male (n, %) | 12.0 (63.2%) | 10.0 (47.6%) | 5.0 (45.5%) | |
| Severity | <0.001 2 | |||
| Moderate | 19.0 (100.0%) | 1.0 (4.8%) | 5.0 (45.5%) | |
| Severe | 0.0 (0.0%) | 20.0 (95.2%) | 6.0 (54.5%) | |
| Periostin(pg/mL) | 50.9 (49.0–52.5) | 51.2 (48.0–53.9) | 53.1 (52.1–58.6) | 0.210 1 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.1 (19.5–30.7) | 24.1 (20.4–26.8) | 24.2 (22.0–28.4) | 0.720 1 |
| Smoking | 0.374 2 | |||
| No | 16.0 (84.2%) | 19.0 (90.5%) | 11.0 (100.0%) | |
| Yes | 3.0 (15.8%) | 2.0 (9.5%) | 0.0 (0.0%) | |
| Duration in years | 3.0 (1.0–6.0) | 2.0 (0.8–3.0) | 3.0 (1.0–5.7) | 0.210 1 |
| ACT Score | 17.0 (16.0–18.8) | 13.0 (12.0–14.0) | 13.0 (14.0–16.8) | <0.001 1 |
| NLR | 2.3 (1.4–3.1) | 2.0 (1.6–2.9) | 5.1 (4.8–6.5) | <0.001 1 |
| PLR | 107.9 (75.4–129.9) | 100.0 (82.9–141.1) | 200.0 (173.2–225.8) | <0.001 1 |
| SII | 518.3 (393.7–631.3) | 516.4 (428.1–697.8) | 1247.5 (1131.2–1784.5) | <0.001 1 |
| Eosinophilia | 0.260 2 | |||
| No | 7.0 (36.8%) | 3.0 (14.3%) | 3.0 (27.3%) | |
| Yes | 12.0 (63.2%) | 18.0 (85.7%) | 8.0 (72.7%) | |
| Pre-FVC predicted | 92.0 (87.0–98.8) | 72.0 (63.7–75.3) | 79.0 (68.2–83.8) | <0.001 1 |
| Pre-FEV1 predicted | 81.0 (72.7–85.8) | 56.0 (45.0–60.3) | 65.0 (56.2–73.7) | <0.001 1 |
| Post-FVC predicted | 98.0 (91.2–105.8) | 80.0 (73.0–89.7) | 87.0 (84.2–90.8) | <0.001 1 |
| Post-FEV1 predicted | 94.0 (85.3–102.2) | 68.0 (63.3–77.3) | 83.0 (70.3–87.2) | <0.001 1 |
| Pre-FEV1/FVC predicted | 88.0 (82.0–90.0) | 79.0 (71.7–84.0) | 85.0 (78.0–89.7) | <0.001 1 |
| Post-FEV1/FVC predicted | 95.0 (91.0–98.7) | 88.0 (83.0–91.0) | 92.0 (86.3–96.8) | <0.001 1 |
| AEC | 490.0 (241.7–735.0) | 560.0 (400.0–820.0) | 500.0 (216.7–641.7) | 0.400 1 |
| ANC | 4790.0 (3755.0–5818.3) | 5160.0 (4366.7–5656.7) | 6780 (5888.3–7816.7) | <0.001 1 |
| ALC | 2260.0 (1468.3–3156.7) | 2400.0 (1813.3–3100.0) | 1280.0 (1196.7–1320.0) | <0.001 1 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LMICs | Low- and Middle-Income Countries |
| DALYs | Disability-Adjusted Life Years |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| IL | Interleukin |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| GINA | Global Initiative for Asthma |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| NAEPP | National Asthma Education and Prevention Program |
| ATS | American Thoracic Society |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| PLR | Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| OR | Odds Ratios |
| CI | Confidence Intervals |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| ACT | Asthma Control Test |
| FVC | Forced Vital Capacity |
| FEV1 | Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 Sec |
| AEC | Absolute Eosinophil Count |
| ANC | Absolute Neutrophil Count |
| ALC | Absolute Lymphocyte Count |
| FeNO | Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide |
| SII | Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index |
| DCA | Decision Curve Analysis |
| GBM | Gradient Boosting Machine |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
References
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. p. 225. 2020. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/ (accessed on 26 November 2020).
- Miller, R.L.; Peden, D.B. Environmental Effects on Immune Responses in Patients with Atopy and Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, G.; Cecchi, L.; D’Amato, M.; Liccardi, G. Urban Air Pollution and Climate Change as Environmental Risk Factors of Respiratory Allergy: An Update. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 20, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jackson, D.J.; Johnston, S.L. The Role of Viruses in Acute Exacerbations of Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Salvi, S.; Mangal, D.K.; Singh, M.; Awasthi, S.; Mahesh, P.A.; Kabra, S.K.; Mohammed, S.; Sukumaran, T.U.; Ghoshal, A.G.; et al. Prevalence, Time Trends and Treatment Practices of Asthma in India: The Global Asthma Network Study. ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8, 00528–02021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safiri, S.; Carson-Chahhoud, K.; Karamzad, N.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Taghizadieh, A.; Bell, A.W.; Kolahi, A.-A.; Ansarin, K.; Mansournia, M.A.; et al. Prevalence, Deaths, and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years Due to Asthma and Its Attributable Risk Factors in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019. Chest 2022, 161, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.Y.; Zheng, H.; Ouyang, G. Periostin, a Multifunctional Matricellular Protein in Inflammatory and Tumor Microenvironments. Matrix Biol. 2014, 37, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, G.; Arima, K.; Kanaji, T.; Toda, S.; Tanaka, H.; Shoji, S.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Nagai, H.; Hotokebuchi, T.; Izuhara, K. Periostin: A Novel Component of Subepithelial Fibrosis of Bronchial Asthma Downstream of IL-4 and IL-13 Signals. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izuhara, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Ohta, S.; Ono, J.; Arima, K.; Ogawa, M. Recent Developments Regarding Periostin in Bronchial Asthma. Allergol. Int. 2015, 64, S3–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Meguro, K.; Kawashima, H.; Kashiwakuma, D.; Kagami, S.-I.; Ohta, S.; Ono, J.; Izuhara, K.; Iwamoto, I. Serum Periostin Levels Serve as a Biomarker for Both Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation and Fixed Airflow Limitation in Well-Controlled Asthmatics. J. Asthma Off. J. Assoc. Care Asthma 2019, 56, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, M.; Ohtawa, J.; Akitsu, K. Effect of Treatment with Inhaled Corticosteroid on Serum Periostin Levels in Asthma. Respirol. Carlton Vic. 2016, 21, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemitsu, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Izuhara, K.; Tohda, Y.; Kita, H.; Horiguchi, T.; Kuwabara, K.; Tomii, K.; Otsuka, K.; Fujimura, M.; et al. Increased Periostin Associates with Greater Airflow Limitation in Patients Receiving Inhaled Corticosteroids. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 305–312.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaron, S.D.; Boulet, L.P.; Reddel, H.K.; Gershon, A.S. Underdiagnosis and Overdiagnosis of Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luks, V.P.; Vandemheen, K.L.; Aaron, S.D. Confirmation of Asthma in an Era of Overdiagnosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaron, S.D.; Vandemheen, K.L.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Ainslie, M.; Gupta, S.; Lemière, C.; Field, S.K.; McIvor, R.A.; Hernandez, P.; Mayers, I.; et al. Reevaluation of Diagnosis in Adults with Physician-Diagnosed Asthma. JAMA 2017, 317, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polu, P.R.; Bikki, V.K. Asthma Endotypes in Flux: Integrating Type 1 and Type 2 Inflammation for Biological Therapy Advancement. J. Asthma 2025, 62, 2030–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izuhara, K.; Ohta, S.; Ono, J. Using Periostin as a Biomarker in the Treatment of Asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2016, 8, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parulekar, A.D.; Atik, M.A.; Hanania, N.A. Periostin, a Novel Biomarker of TH2-Driven Asthma. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2014, 20, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaia, C.; Heffler, E.; Crimi, C.; Maglio, A.; Vatrella, A.; Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W. Interleukins 4 and 13 in Asthma: Key Pathophysiologic Cytokines and Druggable Molecular Targets. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 851940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scichilone, N.; Crimi, C.; Benfante, A.; Battaglia, S.; Iemmolo, M.; Spatafora, M.; Crimi, N. Higher Serum Levels of Periostin and the Risk of Exacerbations in Moderate Asthmatics. Asthma Res. Pract. 2016, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.L.; Steenbruggen, I.; Miller, M.R.; Barjaktarevic, I.Z.; Cooper, B.G.; Hall, G.L.; Hallstrand, T.S.; Kaminsky, D.A.; McCarthy, K.; McCormack, M.C.; et al. Standardization of Spirometry 2019 Update. An Official American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society Technical Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, e70–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajotia, R. Classifying Asthma Severity and Treatment Determinants: National Guidelines Revisited. Malays. Fam. Physician Off. J. Acad. Fam. Physicians Malays. 2008, 3, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Hanania, N.A.; King, M.J.; Braman, S.S.; Saltoun, C.; Wise, R.A.; Enright, P.; Falsey, A.R.; Mathur, S.K.; Ramsdell, J.W.; Rogers, L.; et al. Asthma in the Elderly: Current Understanding and Future Research Needs—A Report of a National Institute on Aging (NIA) Workshop. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, S4–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.S.; Gossiel, F.; Scott, J.R.; Paggiosi, M.A.; Eastell, R. Effect of Age and Gender on Serum Periostin: Relationship to Cortical Measures, Bone Turnover and Hormones. Bone 2017, 99, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuseini, H.; Newcomb, D.C. Mechanisms Driving Gender Differences in Asthma. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2017, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raviv, S.; Dixon, A.E.; Kalhan, R.; Shade, D.; Smith, L.J. Effect of Obesity on Asthma Phenotype Is Dependent upon Asthma Severity. J. Asthma 2011, 48, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Konno, S.; Makita, H.; Taniguchi, N.; Kimura, H.; Goudarzi, H.; Shimizu, K.; Suzuki, M.; Shijubo, N.; Shigehara, K.; et al. Serum Periostin Is Associated with Body Mass Index and Allergic Rhinitis in Healthy and Asthmatic Subjects. Allergol. Int. 2018, 67, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Guo, J.; Deng, K.; Yao, Y. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Biomarker for Asthma Identification and Severity Stratification: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1620695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahseen, R.; Parvez, M.; Kumar, G.S.; Jahan, P. A Correlational Study on Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Bronchial Asthma. Adv. Hum. Biol. 2023, 13, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, L.; Brightling, C.E. Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation: Role in Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2016, 7, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Gao, D.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, T. The Hidden Connection: Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and Its Role in Asthma. Clinics 2025, 80, 100779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S. The Role of Serum Periostin in the Diagnosis of Asthma: A Meta-Analysis. In Allergy & Asthma Proceedings; OceanSide Publications, Inc.: Providence, RI, USA, 2020; Volume 41. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Li, S.; Xu, T.; Ji, N.; Huang, M. Diagnostic Accuracy of Periostin in Predicting Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Asthma 2021, 58, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izuhara, K.; Nunomura, S.; Nanri, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Ono, J.; Mitamura, Y.; Yoshihara, T. Periostin in Inflammation and Allergy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2017, 74, 4293–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dwyer, D.N.; Moore, B.B. The Role of Periostin in Lung Fibrosis and Airway Remodeling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2017, 74, 4305–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izuhara, K.; Conway, S.J.; Moore, B.B.; Matsumoto, H.; Holweg, C.T.J.; Matthews, J.G.; Arron, J.R. Roles of Periostin in Respiratory Disorders. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsusaka, M.; Kabata, H.; Fukunaga, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Masaki, K.; Mochimaru, T.; Sakamaki, F.; Oyamada, Y.; Inoue, T.; Oguma, T.; et al. Phenotype of Asthma Related with High Serum Periostin Levels. Allergol. Int. 2015, 64, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata, H.; Matsusaka, M.; Fukunaga, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Miyata, J.; Tanaka, K.; Masaki, K.; Mochimaru, T.; Ono, J.; Ohta, S. Relationship between Serum Periostin Levels and Severity/Phenotype of Asthma. In B14. Asthma Phenotyping: Understanding of Pathogenesis and Rationale for New Therapies; American Thoracic Society: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. A2330. ISBN 1073-449X. [Google Scholar]
- Yavuz, S.T.; Bagci, S.; Bolat, A.; Akin, O.; Ganschow, R. Association of Serum Periostin Levels with Clinical Features in Children with Asthma. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 32, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.L.; Yang, I.A.; Upham, J.W.; Reynolds, P.N.; Hodge, S.; James, A.L.; Jenkins, C.; Peters, M.J.; Jia, G.; Holweg, C.T.J.; et al. Periostin Levels and Eosinophilic Inflammation in Poorly-Controlled Asthma. BMC Pulm. Med. 2016, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yon, D.K.; An, J.; Ha, E.K.; Jee, H.M.; Izuhara, K.; Ono, J.; Jung, Y.H.; Lee, K.S.; Sheen, Y.H.; Baek, H.; et al. Serum Periostin Is Negatively Correlated With Exposure to Formaldehyde and Volatile Organic Compounds in Children. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, N.C.; Chaudhuri, R.; Spears, M.; Haughney, J.; McSharry, C. Serum Periostin in Smokers and Never Smokers with Asthma. Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graja, A.; Garcia-Carrizo, F.; Jank, A.-M.; Gohlke, S.; Ambrosi, T.H.; Jonas, W.; Ussar, S.; Kern, M.; Schürmann, A.; Aleksandrova, K.; et al. Loss of Periostin Occurs in Aging Adipose Tissue of Mice and Its Genetic Ablation Impairs Adipose Tissue Lipid Metabolism. Aging Cell 2018, 17, e12810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, S.; Castro, M.; Corren, J.; Maspero, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Pirozzi, G.; Sutherland, E.R.; Evans, R.R.; Joish, V.N.; et al. Dupilumab Efficacy and Safety in Adults with Uncontrolled Persistent Asthma despite Use of Medium-to-High-Dose Inhaled Corticosteroids plus a Long-Acting Β2 Agonist: A Randomised Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Pivotal Phase 2b Dose-Ranging Trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J.; Lemanske, R.F.; Hanania, N.A.; Korenblat, P.E.; Parsey, M.V.; Arron, J.R.; Harris, J.M.; Scheerens, H.; Wu, L.C.; Su, Z.; et al. Lebrikizumab Treatment in Adults with Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, J.; Takai, M.; Kamei, A.; Azuma, Y.; Izuhara, K. Pathological Roles and Clinical Usefulness of Periostin in Type 2 Inflammation and Pulmonary Fibrosis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansur, A.H.; Srivastava, S.; Sahal, A. Disconnect of Type 2 Biomarkers in Severe Asthma; Dominated by FeNO as a Predictor of Exacerbations and Periostin as Predictor of Reduced Lung Function. Respir. Med. 2018, 143, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custovic, A.; Siddiqui, S.; Saglani, S. Considering Biomarkers in Asthma Disease Severity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, M.; Pastore, D.; Lupia, C.; Candia, C.; Bruni, A.; Garofalo, E.; Longhini, F.; Maglio, A.; Petrone, A.; Vatrella, A.; et al. Biologic Therapy in Severe Asthma: A Phenotype-Driven and Targeted Approach. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Akashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Ashizuka, S.; Motoki, T.; Suzuki, R.; Sagara, N.; Yanagida, N.; Sato, S.; et al. Periostin as a Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Pediatric Asthma. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 27, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yooma, P.; Manuyakorn, W.; Sawatchai, A.; Jotikasthira, W.; Kiewngam, P.; Kanchongkittiphon, W. Serum Periostin Predicts Wheezing Exacerbation: A Prospective Study in Preschool Children with Recurrent Wheezing. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 183, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türk, M.; Yilmaz, I.; Gökahmetoğlu, S.; Koç, A.N. Stable and Exacerbation Period Serum Cytokine and Periostin Levels of the Five Distinct Phenotypes of Severe Asthma. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 52, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H. Serum Periostin: A Novel Biomarker for Asthma Management. Allergol. Int. 2014, 63, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, D.; Abdelnaby, A.; El Zamran, E.; Ibrahim, I. Role of Serum Periostin as a Biomarker in Diagnosis of Bronchial Asthma. Egypt. J. Chest Dis. Tuberc. 2018, 67, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, D.C.; Romaldini, J.G.; Pizzichini, M.M.M.; Cançado, J.E.D.; Dellavance, A.; Stirbulov, R. Periostin as an Important Biomarker of Inflammatory Phenotype T2 in Brazilian Asthma Patients. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2023, 49, e20220040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, H. Role of Serum Periostin in the Management of Asthma and Its Comorbidities. Respir. Investig. 2020, 58, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.A.; Shin, S.W.; Park, J.S.; Uh, S.T.; Chang, H.S.; Bae, D.J.; Cho, Y.S.; Park, H.S.; Yoon, H.J.; Choi, B.W.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Exacerbation-Prone Adult Asthmatics Identified by Cluster Analysis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2017, 9, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; Jia, X.; Chen, W.; Liu, C. Distinct Phenotype and Risk Factor Analysis of Persistent Airflow Limitation among Asthmatic Children: A Case-Control Study. BMC Pediatr. 2024, 24, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
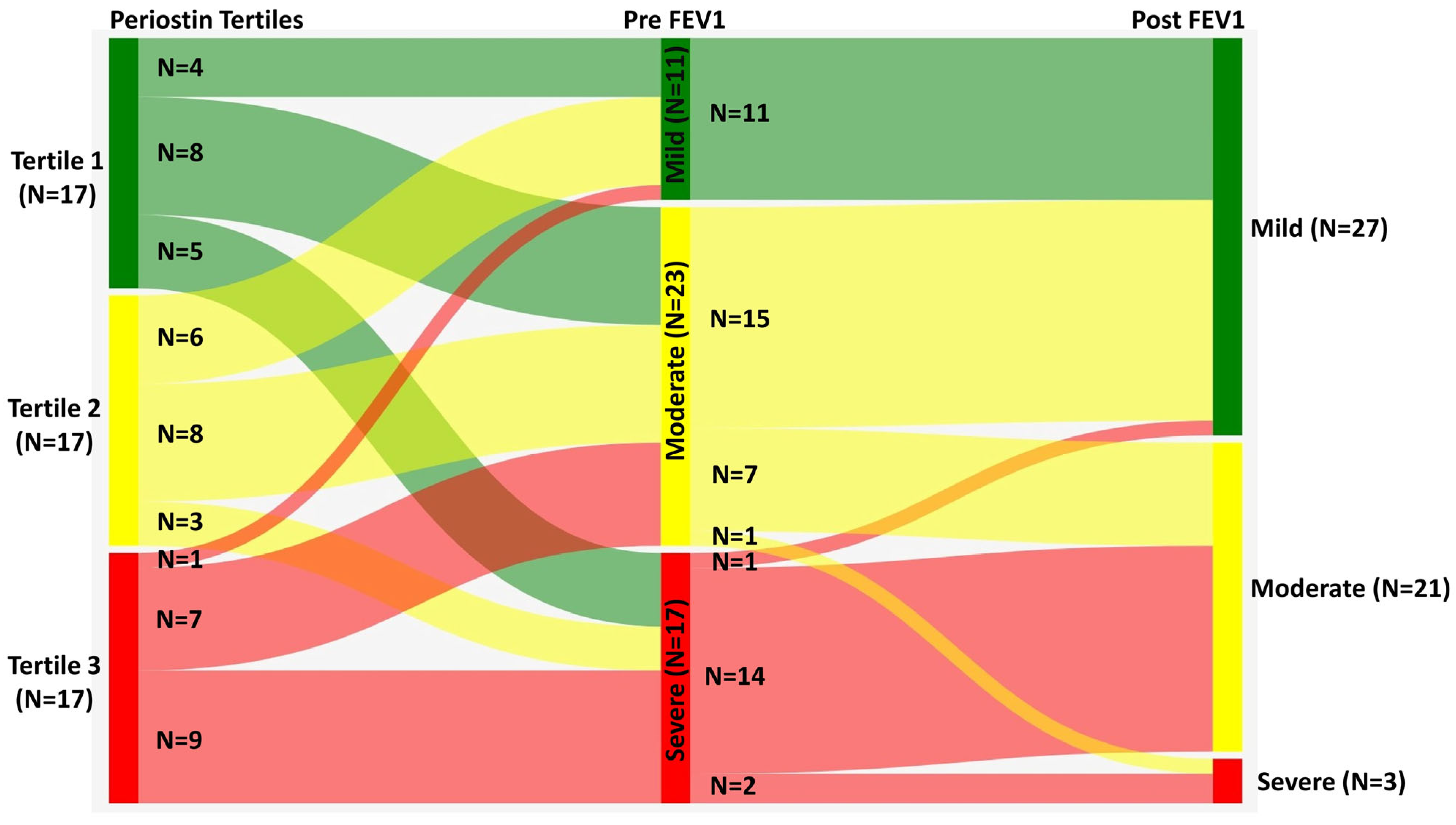
| Moderate (N = 25) | Severe (N = 26) | Healthy Control (N = 25) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age in years | 30.5 (23.0–46.0) | 45.5 (34.8–56.1) | 36.0 (26.3–45.0) | <0.001 1 |
| Gender | 0.880 2 | |||
| Female (n, %) | 11.0 (44.0%) | 13.0 (50.0%) | 14 (56%) | |
| Male (n, %) | 14.0 (56.0%) | 13.0 (50.0%) | 11 (44%) | |
| Periostin (pg/mL) | 51.1 (48.8–52.8) | 52.5 (48.6–56.4) | 35.5 (25.1–40.8) | <0.001 1 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.2 (20.0–30.2) | 24.8 (20.6–27.3) | 24.2 (21.5–24.5) | 0.560 1 |
| Smoking | 0.605 2 | |||
| No | 22.0 (88.0%) | 24.0 (92.3%) | - | |
| Yes | 3.0 (12.0%) | 2.0 (7.7%) | - | |
| Duration in years | 3.0 (1.0–4.7) | 2.0 (1.0–4.1) | - | 0.330 1 |
| ACT Score | 17.0 (16.0–18.0) | 13.0 (12.0–14.0) | - | <0.001 1 |
| NLR | 2.6 (1.8–3.9) | 2.5 (1.8–3.6) | - | 0.830 1 |
| PLR | 112.7 (86.8–171.6) | 104.7 (90.0–165.9) | - | 0.763 1 |
| SII | 541.1 (412.2–829.1) | 660.1 (430.4–830.9) | - | 0.520 1 |
| Eosinophil % | 0.296 2 | |||
| No | 8.0 (32.0%) | 5.0 (19.2%) | - | |
| Yes | 17.0 (68.0%) | 21.0 (80.8%) | - | |
| Pre-FVC predicted | 90.0 (84.3–97.3) | 69.5 (62.8–75.1) | 81.0 (65.7–92.3) | <0.001 1 |
| Pre-FEV1 predicted | 80.0 (71.7–83.0) | 56.0 (45.0–60.1) | 80.0 (66.3–94.0) | <0.001 1 |
| Post-FVC predicted | 97.0 (89.7–105.3) | 81.0 (73.8–89.5) | - | <0.001 1 |
| Post-FEV1 predicted | 91.0 (83.7–97.3) | 68.5 (64.9–77.4) | - | <0.001 1 |
| Pre-FEV1/FVC predicted | 88.0 (82.0–90.0) | 79.0 (72.9–84.0) | 81.6 (79.3–83.3) | <0.001 1 |
| Post-FEV1/FVC predicted | 96.0 (91.0–97.7) | 87.5 (83.0–91.0) | - | <0.001 1 |
| AEC | 420.0 (246.7–650.0) | 590.0 (407.5–812.5) | - | 0.170 1 |
| ANC | 5100.0 (4293.3–6156.7) | 5265.0 (4634.2–6500.4) | - | 0.570 1 |
| ALC | 1830.0 (1333.3–3113.3) | 2100.0 (1662.5–2944.2) | - | 0.510 1 |
| 95% CI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | β (Coefficient) | SE (β) | OR | Lower | Upper | χ2 | p-Value |
| Periostin (pg/mL) | 0.387 | 0.101 | 1.473 | 1.233 | 2.085 | 45.724 | <0.0001 |
| Age (years) | −0.033 | 0.038 | 0.968 | 0.870 | 1.056 | 0.524 | 0.469 |
| Gender (Female vs. Male) | −0.334 | 0.963 | 0.716 | 0.060 | 6.538 | 0.092 | 0.761 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.010 | 0.119 | 1.010 | 0.729 | 1.341 | 0.005 | 0.945 |
| Smoker (Yes vs. No) | 0.030 | 1.733 | 1.030 | 0.005 | 42.450 | 0.0002 | 0.988 |
| Pre-FEV1 % predicted | −0.031 | 0.028 | 0.970 | 0.903 | 1.033 | 0.922 | 0.337 |
| 95% CI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | β (Coefficient) | SE (β) | OR | Lower | Upper | χ2 | p-Value |
| Periostin (pg/mL) | 0.030 | 0.054 | 1.030 | 0.930 | 1.176 | 0.281 | 0.5963 |
| Age (years) | 0.067 | 0.027 | 1.069 | 1.017 | 1.138 | 7.031 | 0.0080 |
| Gender (Female vs. Male) | −0.060 | 0.619 | 0.942 | 0.267 | 3.315 | 0.009 | 0.9249 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | −0.080 | 0.066 | 0.923 | 0.800 | 1.051 | 1.442 | 0.2298 |
| NLR | −1.035 | 0.696 | 0.355 | 0.071 | 1.347 | 2.265 | 0.1323 |
| PLR | 0.001 | 0.010 | 1.001 | 0.981 | 1.021 | 0.003 | 0.9547 |
| SII | 0.004 | 0.003 | 1.004 | 0.999 | 1.010 | 2.166 | 0.1410 |
| Eosinophilia (Yes) | 1.328 | 0.759 | 3.775 | 0.881 | 21.080 | 3.175 | 0.0748 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ravindran, S.; Kaleem Ullah, M.; Karnik, M.; Greeshma, M.V.; Bansal, N.; Kulkarni, S.; ShankaraSetty, R.V.; Madhunapantula, S.V.; Siddaiah, J.B.; Chaya, S.K.; et al. Unsupervised Phenotyping of Asthma: Integrating Serum Periostin with Clinical and Inflammatory Profiles. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 3028. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15233028
Ravindran S, Kaleem Ullah M, Karnik M, Greeshma MV, Bansal N, Kulkarni S, ShankaraSetty RV, Madhunapantula SV, Siddaiah JB, Chaya SK, et al. Unsupervised Phenotyping of Asthma: Integrating Serum Periostin with Clinical and Inflammatory Profiles. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(23):3028. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15233028
Chicago/Turabian StyleRavindran, Sukanya, Mohammed Kaleem Ullah, Medha Karnik, Mandya Venkateshmurthy Greeshma, Nidhi Bansal, Shreedhar Kulkarni, Rekha Vaddarahalli ShankaraSetty, SubbaRao V. Madhunapantula, Jayaraj Biligere Siddaiah, Sindaghatta Krishnarao Chaya, and et al. 2025. "Unsupervised Phenotyping of Asthma: Integrating Serum Periostin with Clinical and Inflammatory Profiles" Diagnostics 15, no. 23: 3028. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15233028
APA StyleRavindran, S., Kaleem Ullah, M., Karnik, M., Greeshma, M. V., Bansal, N., Kulkarni, S., ShankaraSetty, R. V., Madhunapantula, S. V., Siddaiah, J. B., Chaya, S. K., Lokesh, K. S., Ramaiah, S., Srinivas, S., Padmakaran, V., Shankar, M., Parthasarathi, A., & Mahesh, P. A. (2025). Unsupervised Phenotyping of Asthma: Integrating Serum Periostin with Clinical and Inflammatory Profiles. Diagnostics, 15(23), 3028. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15233028







