Quantitative Three-Dimensional Color Power Angiography Parameters Predict Response to Locally Injected Bleomycin in Infantile Hemangioma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
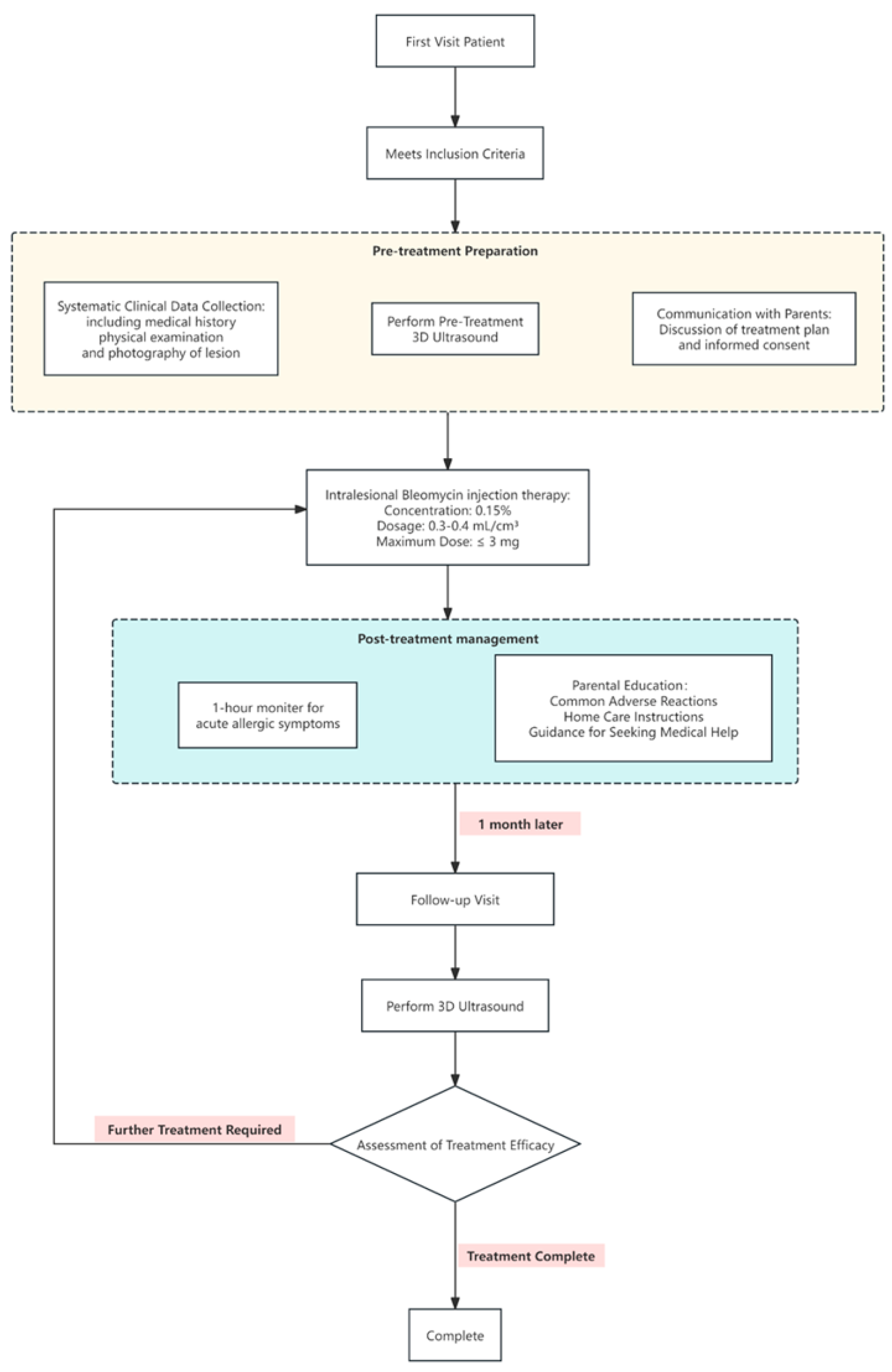
2.2. Patient Management
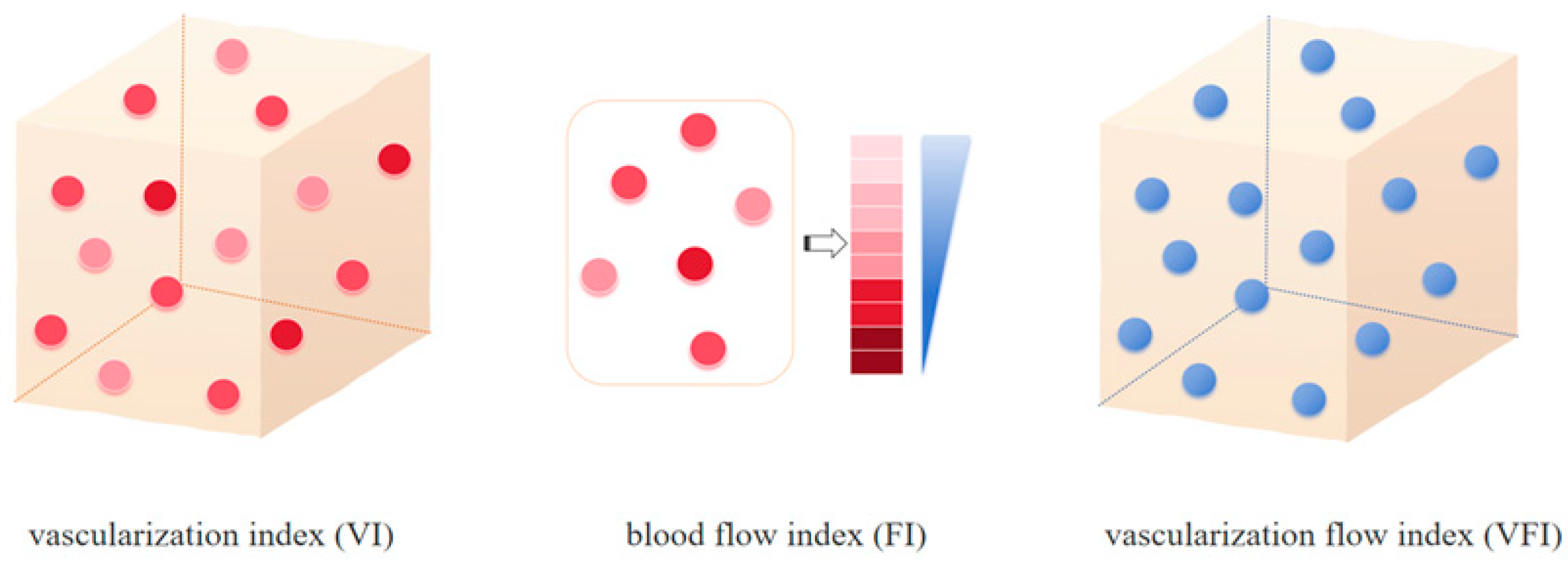
2.3. D-CPA
2.4. Assessment of Treatment Effect
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Features of All Patients of IH
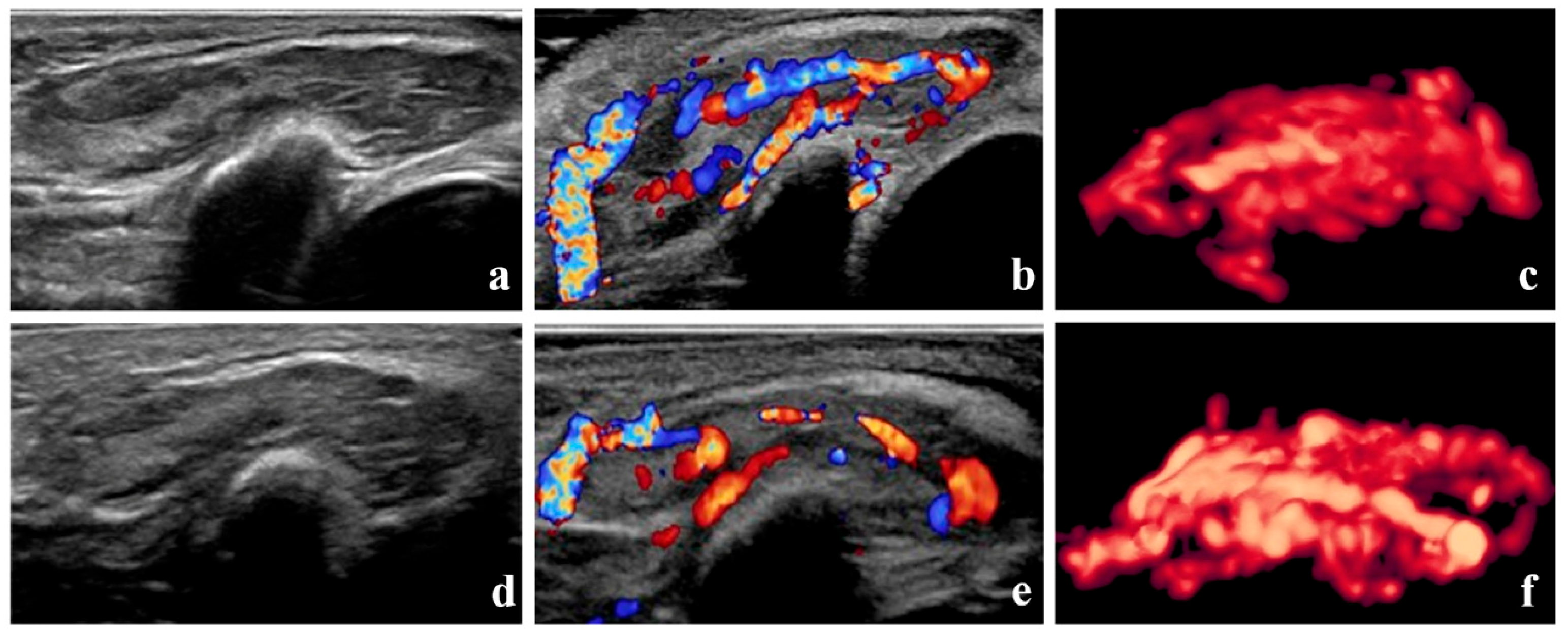
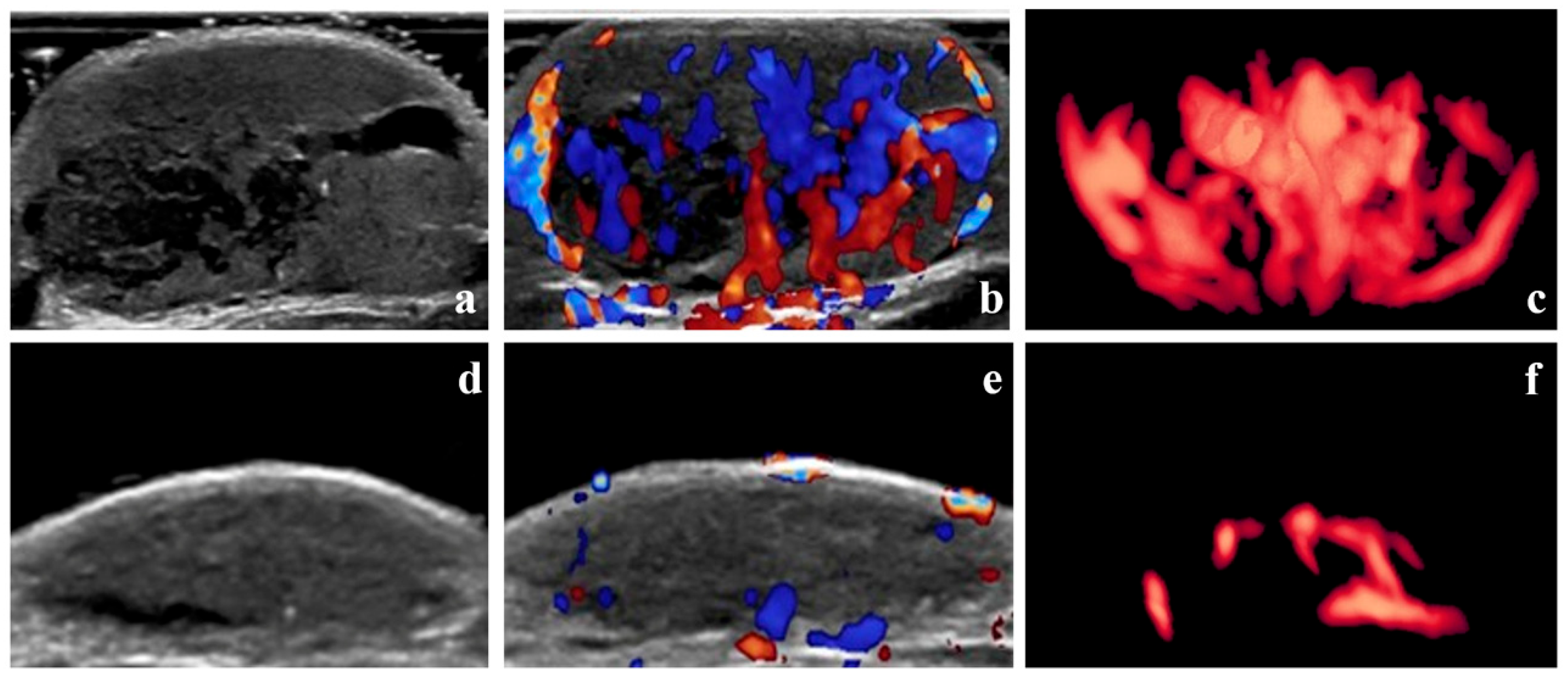
3.2. Assessment of Treatment Efficacy
3.3. Baseline Lesion Characteristics According to Treatment Efficacy
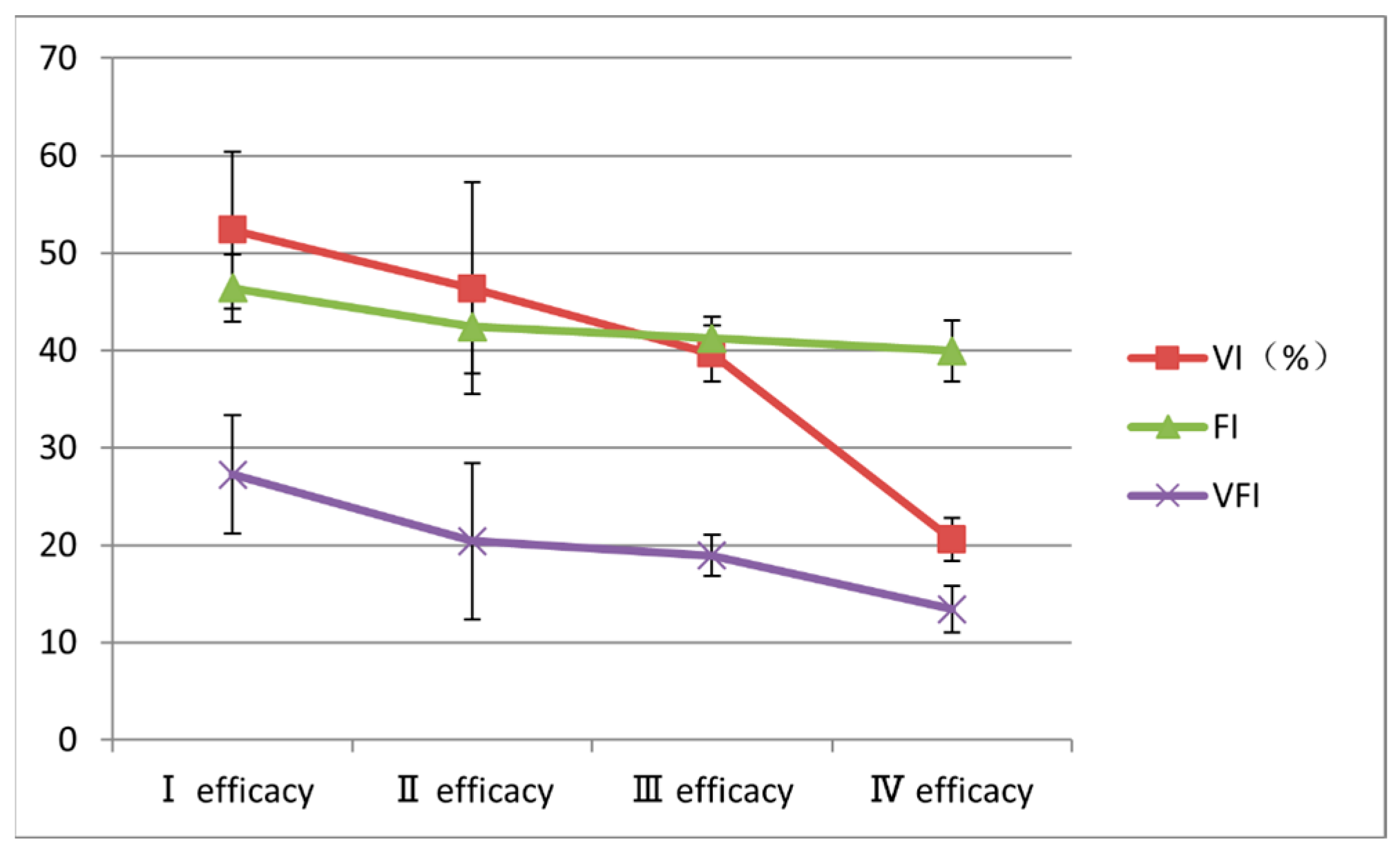
3.4. Baseline 3D-CPA Parameters of Lesions According to Treatment Efficacy
3.5. Predictors of Treatment Response
3.6. Optimal VFI Cutoff Value
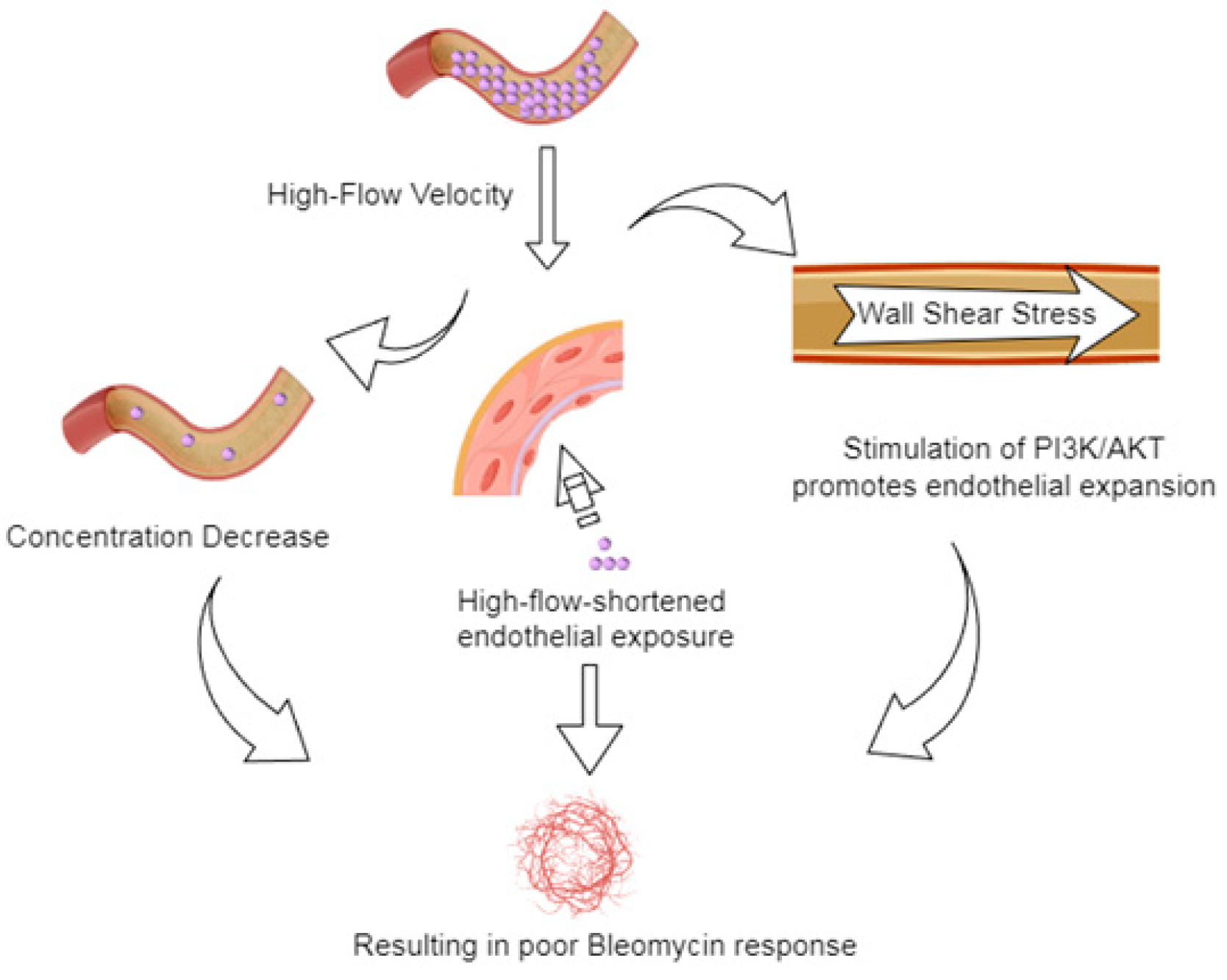
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FI | flow index |
| IH | infantile hemangioma |
| 3D | three-dimensional |
| 3D-CPA | three-dimensional color power angiography |
| VFI | Vascularization–flow index |
| VI | vascularization index |
References
- Colmant, C.; Powell, J. Medical management of infantile hemangiomas: An update. Paediatr. Drugs 2022, 24, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Cui, J.; Shi, X.; Wang, T.; Liu, S. Itraconazole inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and reduces angiogenesis of hemangioma endothelial cells by downregulating the hedgehog signaling pathway. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemann, L.; Hein, S. Infantile hemangioma: A review of current pharmacotherapy treatment and practice pearls. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 25, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, A.A.; Daboos, M.A. Five years’ experience of combined intralesional therapy in infantile hemangioma. Ann. Pediatr. Surg. 2019, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, Q.; Tan, S.T.; Gush, J.; Peters, S.G.; Davis, P.F. Steroid therapy of a proliferating hemangioma: Histochemical and molecular changes. Pediatrics 2000, 105, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, T.; Kirsten, M.; Fourie, P.; Dippenaar; Ionescu, G.O. Intralesional bleomycin injection (ibi) treatment for haemangiomas and congenital vascular malformations. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2004, 19, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Yin, S.Y.; Zhou, D.K.; Wen, J.X.; Gao, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.X. Quantitative evaluation of percutaneous local drug perfusion against refractory infantile hemangioma via 3-d power doppler angiography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, D.P.; Meyer, D. Intralesional bleomycin for the treatment of periocular capillary hemangiomas. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 60, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidvari, S.; Nezakatgoo, N.; Ahmadloo, N.; Mohammadianpanah, M.; Mosalaei, A. Role of intralesional bleomycin in the treatment of complicated hemangiomas: Prospective clinical study. Dermatol. Surg. 2005, 31, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeHart, A.; Richter, G. Hemangioma: Recent advances. F1000Research 2019, 8, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Rho, M.H.; Jung, H.L. Ultrasound and mri findings as predictors of propranolol therapy response in patients with infantile hemangioma. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.; Bera, R.N.; Diwedi, A.N.D.; Singh, O.P.; Tiwari, P. Color doppler ultrasound indices as predictors of propranolol response in infantile hemangioma: A prospective study. Indian Pediatr. 2024, 61, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pairleitner, H.; Steiner, H.; Hasenoehrl, G.; Staudach, A. Three-dimensional power doppler sonography: Imaging and quantifying blood flow and vascularization. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 1999, 14, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krowchuk, D.P.; Frieden, I.J.; Mancini, A.J.; Darrow, D.H.; Blei, F.; Greene, A.K.; Annam, A.; Baker, C.N.; Frommelt, P.C.; Hodak, A.; et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of infantile hemangiomas. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20183475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Y.; Osman, A.K.; Altyeb, A. Noninvasive management of hemangioma and vascular malformation using intralesional bleomycin injection. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2013, 70, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achauer, B.M.; Chang, C.J.; Kam, V.M.V. Management of hemangioma of infancy: Review of 245 patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1997, 99, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.K.C.; Lam, J.M.; Leong, K.F.; Hon, K.L. Infantile hemangioma: An updated review. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2021, 17, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, H.; Hao, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, F.; Chen, Y. Therapeutic efficacy of propranolol for infantile hemangiomas. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. 2019, 128, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, Q.; Lin, Y.; Chen, X. Treatments for infantile hemangioma: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. eClinicalMedicine 2020, 26, 100506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zheng, J.; Bian, Q. Cell fate regulation during the development of infantile hemangioma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2025, 145, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, G.M.; Reinisch, J.F.; Nichter, L.S.; Saber, W.L.; Lew, K.; Morwood, D.T. Intralesional corticosteroid therapy for infantile hemangiomas. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1989, 83, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.T.; Yeong, E.K.; Horng, S.Y. Intralesional corticosteroid therapy in proliferating head and neck hemangiomas: A review of 155 cases. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2000, 35, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Duan, H.; Zhou, K.; Hu, F. Comparison of efficacy and safety between oral propranolol combined with and without intralesional injection of lauromacrogol for infantile hemangioma. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1361105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Guo, J.; Hu, K.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Kong, L.; Liu, G.; Lei, D. A clinical study of ultrasound-guided intralesional injection of bleomycin a5 on venous malformation in cervical-facial region in china. J. Vasc. Surg. 2010, 51, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.B.; Li, Q.Y.; Jiang, F.; Hu, X.Y.; Ma, R.Z.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Pattar, P.; Li, S.X. Pingyangmycin stimulates apoptosis in human hemangioma-derived endothelial cells through activation of the p53 pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabeta, P. Decreased secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with increased apoptosis in vascular tumor derived endothelial cells. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 64, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pienaar, C.; Graham, R.; Geldenhuys, S.; Hudson, D.A. Intralesional bleomycin for the treatment of hemangiomas. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, Y.J.; Gyon, Y.H.; Yang, S.; Lee, Y.K.; Park, J.; Park, M. A prospective study to assess the efficacy and safety of oral propranolol as first-line treatment for infantile superficial hemangioma. Korean J. Pediatr. 2015, 58, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Ma, G.; Lin, X. Intralesional bleomycin injection for propranolol-resistant hemangiomas. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2018, 29, e128–e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushner, B.J. The treatment of periorbital infantile hemangioma with intralesional corticosteroid. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1985, 76, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberger, S.; Bischoff, J. Pathogenesis of infantile haemangioma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansfield, S.A.; Williams, R.F.; Iacobas, I. Vascular tumors. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 29, 150975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, D.; Xu, C.; Wang, K.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y. Roxarsone induces angiogenesis via pi3k/akt signaling. Cell Biosci. 2016, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Jiang, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Kang, Y. Mechanical stress regulates osteogenesis and adipogenesis of rat mesenchymal stem cells through pi3k/akt/gsk-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6027402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, M.; Dębek, W.; Matuszczak, E. Infantile hemangiomas: An update on pathogenesis and treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Evaluation Index | Therapeutic Grade | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (Poor) | II (Fair) | III (Good) | IV (Excellent) | |
| Tumor volume reduction | 0–25% | 26–50% | 51–75% | 76–100% |
| Color change | Lightened | Markedly lightened | Markedly lightened | Resolved |
| Characteristic | Treatment Efficacy Grade | χ2/Z-Value | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (n = 13) | II (n = 16) | III (n = 8) | IV (n = 3) | |||
| Lesion type | ||||||
| Superficial | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.76 | 1 * |
| Mixed | 10 (76.92%) | 12 (75%) | 6 (75%) | 3 (100%) | ||
| Deep | 3 (23.08%) | 4 (25%) | 2 (25%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| Age (months) | ||||||
| 0–3 | 6 (46.15%) | 6 (37.5%) | 3 (37.5%) | 1 (33.3%) | 6.45 | 0.736 * |
| 4 –6 | 2 (15.38%) | 7 (43.75%) | 3 (37.5%) | 1 (33.3%) | ||
| 7–9 | 1 (7.69%) | 1 (6.25%) | 1 (12.5%) | 1 (33.3%) | ||
| 10–12 | 4 (30.77%) | 2 (12.5%) | 1 (12.5%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| Lesion location | ||||||
| Face | 3 (23.08%) | 3 (18.75%) | 3 (37.5%) | 0 (0%) | 4.94 | 0.905 * |
| Head and neck | 2 (15.38%) | 3 (18.75%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (33.3%) | ||
| Trunk | 7 (53.85%) | 9 (56.25%) | 4 (50%) | 2 (66.7%) | ||
| Limbs | 1 (7.69%) | 1 (6.25%) | 1 (12.5%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| Parameter | Treatment Efficacy Grade | F-Value | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (n = 13) | II (n = 16) | III (n = 8) | IV (n = 3) | |||
| Volume (mL) | 7.86 ± 7.0 | 7.25 ± 12.12 | 5.45 ± 2.33 | 29.45 ± 41.82 | 2.692 | 0.061 * |
| Vascularization index (%) | 52.35 ± 8.06 | 46.36 ± 10.86 | 39.66 ± 2.93 | 20.57 ± 2.22 | 12.472 | <0.001 * |
| Flow index | 46.38 ± 3.43 | 42.41 ± 4.75 | 41.21 ± 2.17 | 39.93 ± 3.16 | 4.618 | 0.008 * |
| Vascularization–flow index | 27.23 ± 6.09 | 20.4 ± 8.02 | 18.93 ± 2.15 | 13.4 ± 2.42 | 5.746 | 0.003 * |
| Parameter | B | SE | Wald | p-Value * | OR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vascularization index | −0.121 | 0.053 | 5.143 | 0.023 | 0.886 | 0.798–0.984 |
| Flow index | −0.332 | 0.118 | 7.873 | 0.005 | 0.717 | 0.569–0.905 |
| Vascularization-flow index | −0.201 | 0.076 | 7.11 | 0.008 | 0.818 | 0.705–0.948 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, K.; Zhong, Y.; Wen, J.; Wang, Z. Quantitative Three-Dimensional Color Power Angiography Parameters Predict Response to Locally Injected Bleomycin in Infantile Hemangioma. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222903
Gu K, Zhong Y, Wen J, Wang Z. Quantitative Three-Dimensional Color Power Angiography Parameters Predict Response to Locally Injected Bleomycin in Infantile Hemangioma. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(22):2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222903
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Kai, Yi Zhong, Jiexin Wen, and Zhaoxia Wang. 2025. "Quantitative Three-Dimensional Color Power Angiography Parameters Predict Response to Locally Injected Bleomycin in Infantile Hemangioma" Diagnostics 15, no. 22: 2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222903
APA StyleGu, K., Zhong, Y., Wen, J., & Wang, Z. (2025). Quantitative Three-Dimensional Color Power Angiography Parameters Predict Response to Locally Injected Bleomycin in Infantile Hemangioma. Diagnostics, 15(22), 2903. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222903




