Hybrid Faster R-CNN for Tooth Numbering in Periapical Radiographs Based on Fédération Dentaire Internationale System
Abstract
1. Introduction
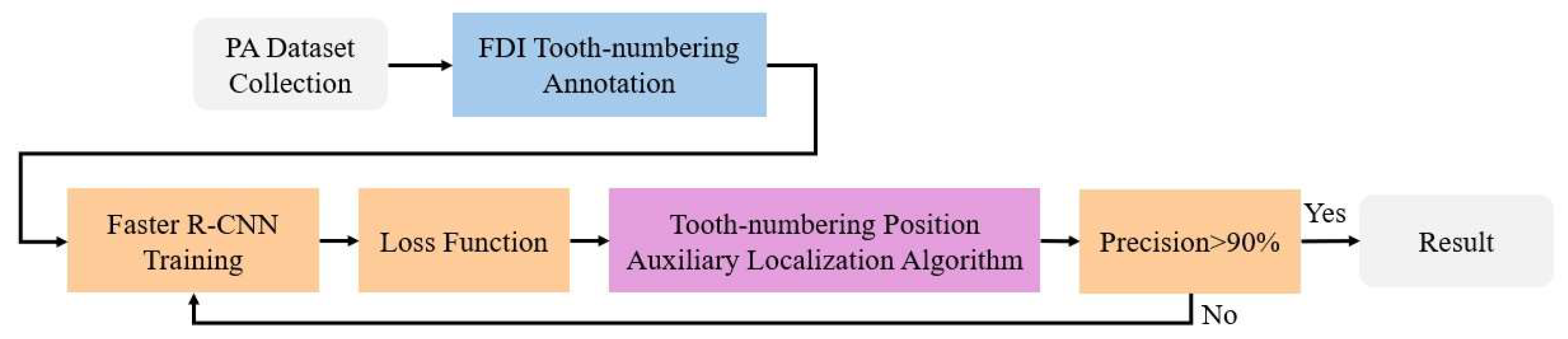
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PA Dataset Collection and FDI Tooth-Numbering Annotation
2.1.1. PA Dataset Collection
| The Number of Datasets | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set | Validation Set | Test Set | |
| Quantity | 254 | 70 | 98 |
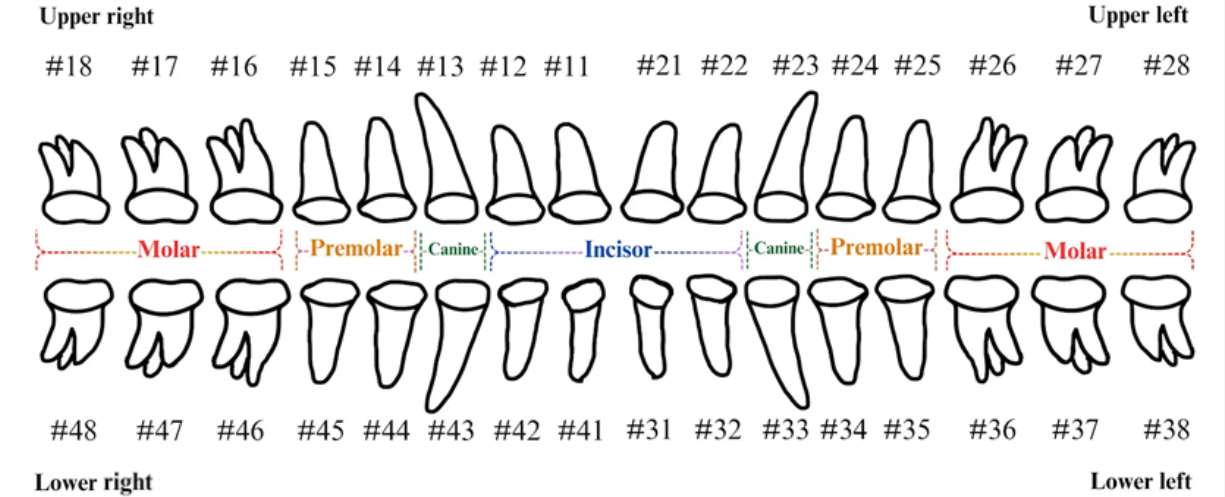
2.1.2. FDI Tooth-Numbering System
2.1.3. Tooth-Numbering Annotation
2.2. Tooth-Numbering Position Loss Function
2.2.1. Hard Label and Soft Label
2.2.2. Kullback–Leibler Divergence Loss Function
2.3. Tooth-Numbering Position Deep Learning and Parameter Settings
2.3.1. PA Tooth-Numbering Deep Learning Model
2.3.2. Parameter Setting and Experiment Platform
2.3.3. Model Training and Validation
2.4. Tooth-Number Position Auxiliary Localization Algorithm
| Algorithm 1. Tooth-numbering position auxiliary localization algorithm. |
| Input:
Output: |
| 1:
L
2: 3: ) 4: )) 5: 6: |
3. Results
3.1. Faster R-CNN Training Results
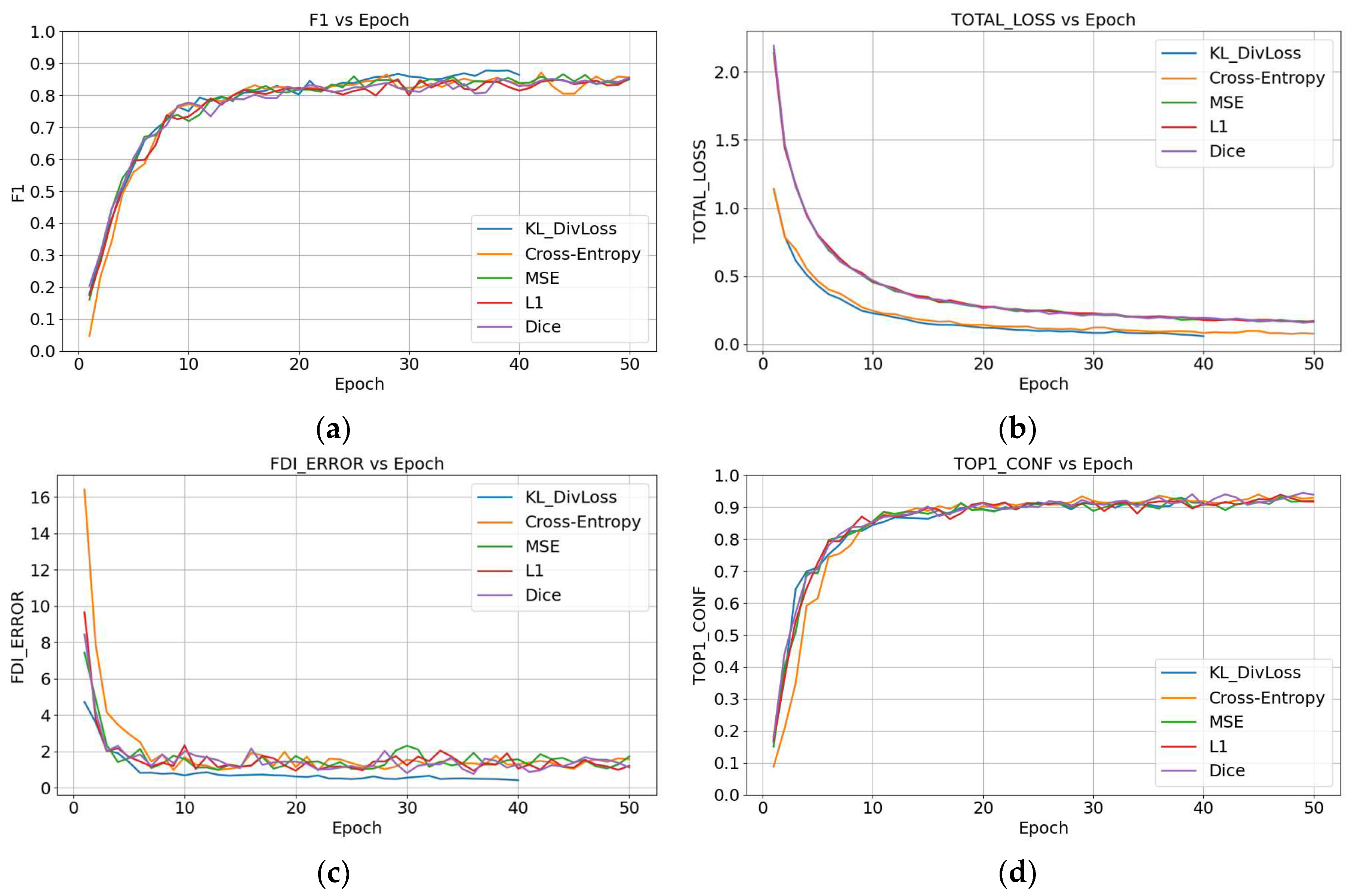
3.2. DivLoss Function and Tooth-Numbering Position Auxiliary Localization Algorithm Training Results
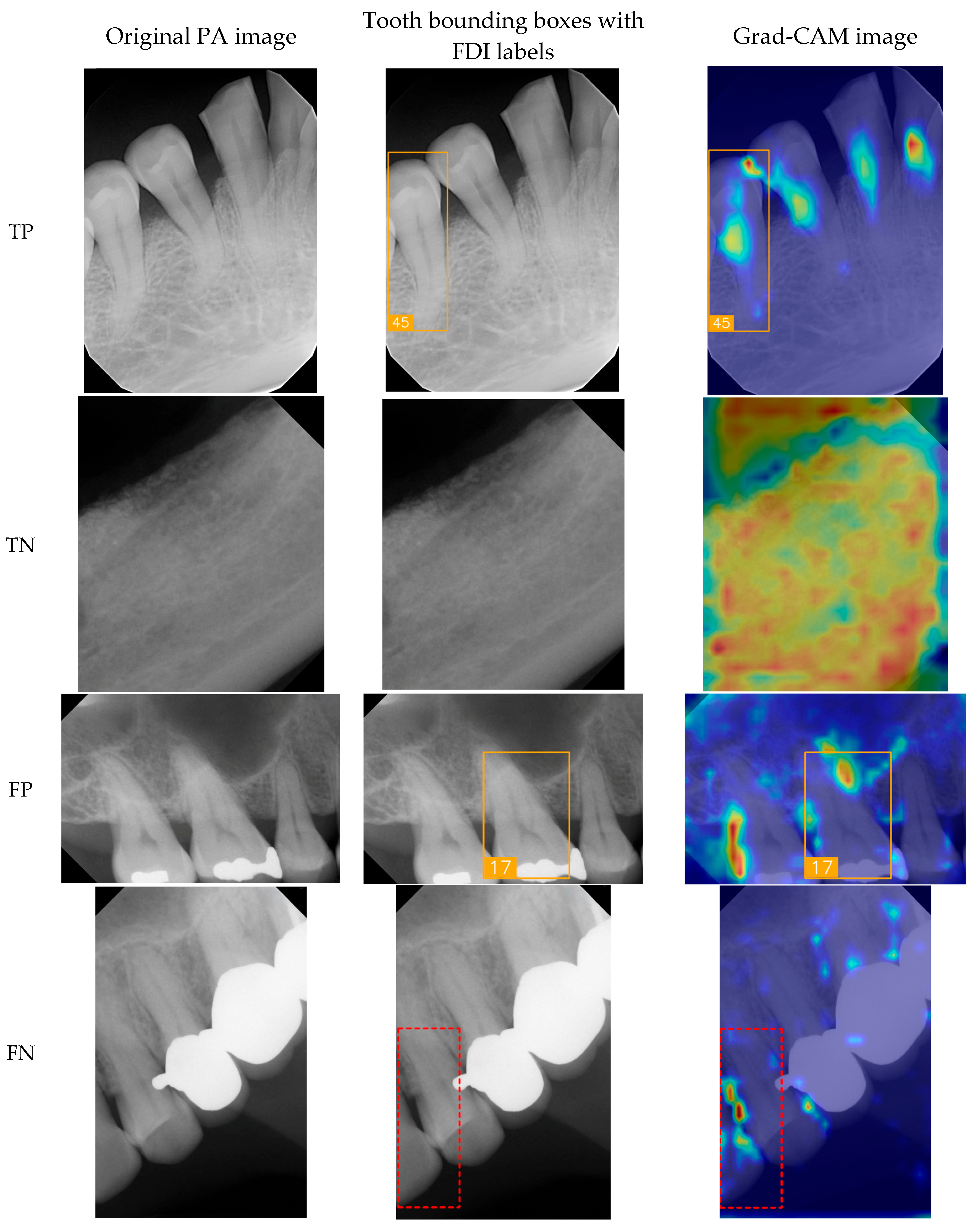
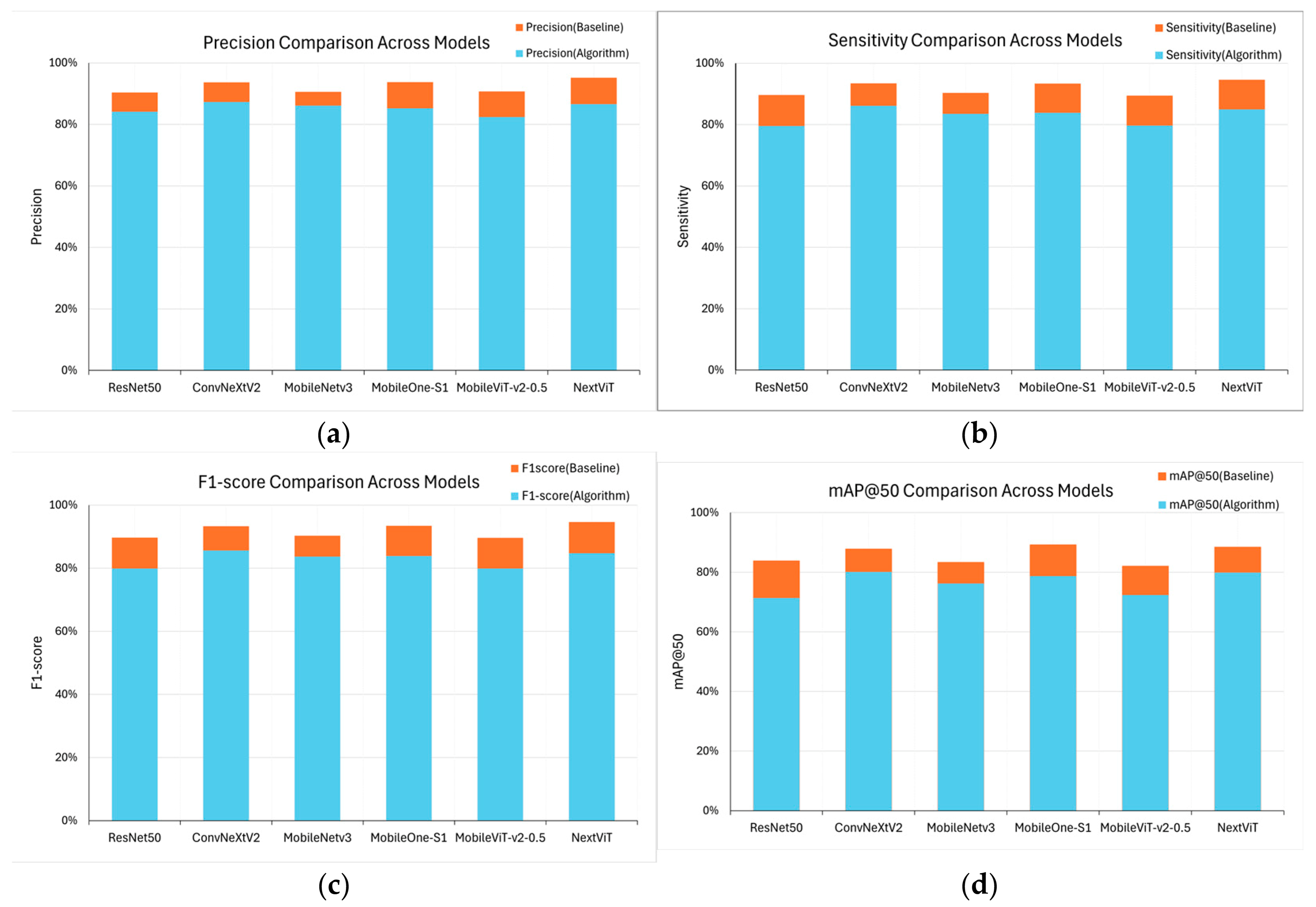
3.3. Clinical FDI Tooth-Number Detection Results
4. Discussion
- We proposed a Hybrid Faster R-CNN method to address challenges in dental position identification. Unlike other studies, the dataset used in this study includes common clinical scenarios, such as dental implants, incomplete crowns, and missing teeth. The proposed method achieved a maximum accuracy exceeding 95%, demonstrating its effectiveness in handling complex dental cases.
- During the model-training process, integrating the KL DivLoss function significantly accelerated model convergence, addressing the challenge posed by the increasing size of PA tooth position datasets, which makes it difficult for models to reach optimal convergence points. Compared to models without KL DivLoss, this approach reduces training time by 19.8%.
- After we incorporated the tooth-number position auxiliary localization algorithm, the accuracy of tooth-numbering localization improved by approximately 8.5%. The NextViT-Faster R-CNN hybrid model achieved the highest accuracy, reaching 95.16%, indicating its superior performance in dental position recognition.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zardak, N.; Amini-Rarani, M.; Abdollahpour, I.; Eslamipour, F.; Tahani, B. Utilization of dental care among adult populations: A scoping review of applied models. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, T.; Ida, Y.; Miura, H. A nationwide survey on working hours and working environment among hospital dentists in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, N.B.; Zero, D.T.; Marsh, P.D.; Ekstrand, K.; Weintraub, J.A.; Ramos-Gomez, F.; Tagami, J.; Twetman, S.; Tsakos, G.; Ismail, A. Dental caries. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y. Orthodontic treatment planning based on artificial neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-K.; Huang, J.-Y.; Wu, Y.-T.; Chang, Y.-C. Dental scaling decreases the risk of Parkinson’s disease: A nationwide population-based nested case-control study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel, J.; Villarroel, M.; Tran, D.; Kee, E.; Bruggers, K. The utilization of snap-on provisionals for dental veneers: From an analog to a digital approach. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2020, 32, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akintoye, S.O.; Greenberg, M.S. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 58, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Gallagher, J.E. Healthy ageing and oral health: Priority, policy and public health. BDJ Open 2024, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, M.A.; Ali, Z.; Maqbool, M.S.; Aziz, M. X-ray image analysis for dental disease: A deep learning approach using EfficientNets. VFAST Trans. Softw. Eng. 2024, 12, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turosz, N.; Chęcińska, K.; Chęciński, M.; Rutański, I.; Sielski, M.; Sikora, M. Oral health status and treatment needs based on artificial intelligence (AI) dental panoramic radiograph (DPR) analysis: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meusburger, T.; Wülk, A.; Kessler, A.; Heck, K.; Hickel, R.; Dujic, H.; Kühnisch, J. The detection of dental pathologies on periapical radiographs—Results from a reliability study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehabeldin, R.R.; Hamama, H.H. Introduction of ‘qpdb’ teeth numbering system. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendra Santosh, A.B.; Jones, T. Enhancing precision: Proposed revision of FDI’s 2-digit dental numbering system. Int. Dent. J. 2024, 74, 359–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-J.; Mao, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-J.; Liang, C.-H.; He, Y.-Q.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Chen, S.-L.; Chen, T.-Y.; Chen, C.-A.; Li, K.-C.; et al. Evaluation of the alveolar crest and cemento-enamel junction in periodontitis using object detection on periapical radiographs. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.-Y.; Chen, S.-L.; Lin, Y.-J.; Wang, L.-H.; Chang, Y.-C. Precision medicine for apical lesions and peri-endo combined lesions based on transfer learning using periapical radiographs. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-H.; Xie, C.-X.; Yang, T.; Tan, H.-X.; Fan, M.-H.; Kuo, I.-C.; Lee, Z.-J.; Chen, T.-Y.; Huang, P.-C.; Chen, S.-L.; et al. Paper-recorded ECG digitization method with automatic reference voltage selection for telemonitoring and diagnosis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-L.; Chen, T.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-A.; Chou, H.-S.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Lin, W.-C.; Li, T.-C.; Yuan, J.-J.; Abu, P.A.R.; et al. Missing teeth and restoration detection using dental panoramic radiography based on transfer learning with CNNs. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 118654–118664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-J.; Chen, S.-L.; Mao, Y.-C.; Chen, T.-Y.; Peng, C.-H.; Tsai, T.-H.; Li, K.-C.; Chen, C.-A.; Tu, W.-C.; Abu, P.A.R. Precision oral medicine: A DPR segmentation and transfer learning approach for detecting third molar compress inferior alveolar nerve. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2025, 2025, 3568922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-L.; Chen, T.-Y.; Mao, Y.-C.; Lin, S.-Y.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Chen, C.-A.; Lin, Y.-J.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Li, C.-A.; Chiang, W.-Y.; et al. Automated detection system based on convolution neural networks for retained root, endodontic treated teeth, and implant recognition on dental panoramic images. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 23293–23306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-J.; Chen, S.-L.; Lu, Y.-C.; Lin, X.-M.; Mao, Y.-C.; Chen, M.-Y.; Yang, C.-S.; Chen, T.-Y.; Li, K.-C.; Tu, W.-C.; et al. Deep learning-assisted diagnostic system: Implant brand detection using improved IB-YOLOv10 in periapical radiographs. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Lee, M.-K.; Chen, T.-E.; Lan, T.-H.; Chang, C.-M.; Tseng, T.-Y.; Wang, T.; Du, J.-K. Convolutional-neural-network-based radiographs evaluation assisting in early diagnosis of the periodontal bone loss via periapical radiograph. J. Dent. Sci. 2024, 19, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, N.; Bin Khalid, W.; Umer, F. An artificial intelligence model for instance segmentation and tooth numbering on orthopantomograms. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2023, 26, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayhan, B.; Ayan, E.; Bayraktar, Y. A novel deep learning-based perspective for tooth numbering and caries detection. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Fujita, D.; Kobashi, S. Teeth and prostheses detection in dental panoramic X-rays using CNN-based object detector and a priori knowledge-based algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarsam, W.; Davies, J.; Al-Salehi, S.K. The role of imaging in endodontics. Br. Dent. J. 2025, 238, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görürgöz, C.; Orhan, K.; Bayrakdar, I.S.; Çelik, Ö.; Bilgir, E.; Odabaş, A.; Aslan, A.F.; Jagtap, R. Performance of a convolutional neural network algorithm for tooth detection and numbering on periapical radiographs. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2022, 51, 20210246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Wu, Y.-F.; Aung, L.M.; Lin, J.C.-Y.; Ngo, S.T.; Su, J.-N.; Lin, Y.-M.; Chang, W.-J. Automatic recognition of teeth and periodontal bone loss measurement in digital radiographs using deep-learning artificial intelligence. J. Dent. Sci. 2023, 18, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-T.; Lee, J.-B. Identification of dental implant systems from low-quality and distorted dental radiographs using AI trained on a large multi-center dataset. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, M. What is YOLOv8: An in-depth exploration of the internal features of the next-generation object detector. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.15857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. YOLOv11: An overview of the key architectural enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-based Localization. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 336–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Block Number | Type | Kernel Size | Stride | Filters | Feature Map Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Conv2D | 4 × 4 | 4 | 96 | 56 × 56 × 96 |
| 1 | Depthwise Conv + MLP | 3 × 3 | 1 | 96 | 56 × 56 × 96 |
| 2 | Depthwise Conv + MLP | 3 × 3 | 1 | 96 | 56 × 56 × 96 |
| 3 | Depthwise Conv + MLP | 3 × 3 | 1 | 96 | 56 × 56 × 96 |
| 4 | Downsampling Conv | 2 × 2 | 2 | 192 | 28 × 28 × 192 |
| 5 | Depthwise Conv + MLP | 3 × 3 | 1 | 192 | 28 × 28 × 192 |
| 6 | Depthwise Conv + MLP | 3 × 3 | 1 | 192 | 28 × 28 × 192 |
| 7 | Depthwise Conv + MLP | 3 × 3 | 1 | 192 | 28 × 28 × 192 |
| 8 | Downsampling Conv | 2 × 2 | 2 | 384 | 14 × 14 × 384 |
| 9 | Stage 3 Block (4 layers) | 3 × 3 | 1 | 384 | 14 × 14 × 384 |
| 10 | Stage 3 Block (4 layers) | 3 × 3 | 1 | 384 | 14 × 14 × 384 |
| 11 | Stage 3 Block (4 layers) | 3 × 3 | 1 | 384 | 14 × 14 × 384 |
| 12 | Stage 3 Block (4 layers) | 3 × 3 | 1 | 384 | 14 × 14 × 384 |
| 13 | Stage 3 Block (4 layers) | 3 × 3 | 1 | 384 | 14 × 14 × 384 |
| 14 | Downsampling Conv | 2 × 2 | 2 | 768 | 7 × 7 × 768 |
| 15 | Depthwise Conv + MLP | 3 × 3 | 1 | 768 | 7 × 7 × 768 |
| 16 | Depthwise Conv + MLP | 3 × 3 | 1 | 768 | 7 × 7 × 768 |
| 17 | Depthwise Conv + MLP | 3 × 3 | 1 | 768 | 7 × 7 × 768 |
| 18 | Global Average Pool | - | - | - | 7 × 7 × 768 |
| 19 | Fully Connected (FC) | - | - | 32 | 1 × 1 × 32 |
| Hardware Platform | Version |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel Core i9-12900H |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3070 Ti |
| DRAM | 32 GB DDR5 |
| Software platform | Version |
| Python | 3.10.13 |
| PyTorch | 2.2.0 |
| CUDA | 12.1 |
| Precision | Sensitivity | Specificity | F1-Score | mAP50 | mAP @0.5:0.95 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 87.29 | 86.16 | 99.44 | 86.72 | 80.11 | 50.80 |
| [85.1–89.5] | [83.9–88.4] | [98.9–99.9] | [84.5–88.9] | [77.5–82.7] | [46.8–54.8] | |
| YOLOv8 | 49.38 | 57.90 | NaN | 53.27 | 38.56 | 22.54 |
| [45.6–53.1] | [54.1–61.7] | [49.4–57.1] | [35.1–42.1] | [20.6–24.5] | ||
| YOLOv11 | 54.02 | 58.82 | NaN | 56.30 | 60.57 | 36.54 |
| [50.2–57.8] | [55.0–62.5] | [52.6–60.0] | [57.2–63.9] | [33.3–39.7] |
| α | Precision | Sensitivity | F1-Score | FDIerror | TOP1conf | Epoch | Training Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 88.48% | 86.49% | 87.47% | 1.373 | 91.00% | 42 | 5193.79 s |
| 0.2 | 87.06% | 86.41% | 86.73% | 0.5073 | 89.19% | 39 | 4129.63 s |
| 0.5 | 88.23% | 87.08% | 87.66% | 0.4557 | 90.55% | 38 | 4203.73 s |
| 0.7 | 88.25% | 85.90% | 87.06% | 0.3942 | 87.98% | 32 | 4162.60 s |
| 1.0 | 86.80% | 84.41% | 85.59% | 0.3155 | 88.70% | 38 | 4390.91 s |
| Algorithm | Precision | Sensitivity | Specificity | F1-Score | mAP50 | mAP @0.5:0.95 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet50 | 90.35 | 89.66 | 99.55 | 90.00 | 83.85 | 48.29 | 0.0967 |
| ConvNext_v2 | 93.66 | 93.45 | 99.72 | 93.55 | 87.77 | 55.68 | 0.5867 |
| MobileNet_v3 | 90.59 | 90.31 | 99.62 | 90.45 | 83.32 | 49.44 | 0.1358 |
| Mobileone_s1 | 93.75 | 93.37 | 99.76 | 93.56 | 89.18 | 54.25 | 0.6092 |
| MobileViT_v2-0.5 | 90.72 | 89.43 | 99.61 | 90.07 | 82.04 | 47.85 | 0.1222 |
| NextViT | 95.16 | 94.60 | 99.82 | 94.88 | 88.42 | 54.81 | - |
| Precision | Sensitivity | Specificity | F1-Score | mAP50 | mAP @0.5:0.95 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resnet50 | 84.09 | 79.59 | 99.19 | 81.77 | 71.35 | 41.13 |
| [81.7–86.5] | [76.9–82.3] | [98.6–99.7] | [79.2–84.3] | [68.4–74.3] | [37.9–44.4] | |
| ConvNext_v2 | 87.29 | 86.16 | 99.44 | 86.72 | 80.11 | 50.80 |
| [85.1–89.5] | [83.9–88.4] | [98.9–99.9] | [84.5–88.9] | [77.5–82.7] | [46.8–54.8] | |
| MobileNet_v3 | 86.13 | 83.48 | 99.29 | 84.78 | 76.21 | 45.13 |
| [83.8–88.4] | [81.0–85.9] | [98.8–99.8] | [82.4–87.1] | [73.4–79.0] | [41.6–48.6] | |
| Mobileone_s1 | 85.23 | 83.86 | 99.35 | 84.54 | 78.71 | 47.89 |
| [82.9–87.6] | [81.5–86.2] | [98.8–99.8] | [82.2–86.9] | [75.9–81.5] | [44.1–51.7] | |
| MobileViT_v2-0.5 | 82.36 | 79.71 | 99.25 | 81.01 | 72.34 | 42.26 |
| [79.9–84.9] | [77.0–82.4] | [98.7–99.8] | [78.4–83.6] | [69.4–75.3] | [38.9–45.6] | |
| NextViT | 86.61 | 84.94 | 99.32 | 85.77 | 79.89 | 49.61 |
| [84.3–88.9] | [82.5–87.3] | [98.8–99.8] | [83.5–88.0] | [77.2–82.6] | [45.7–53.6] |
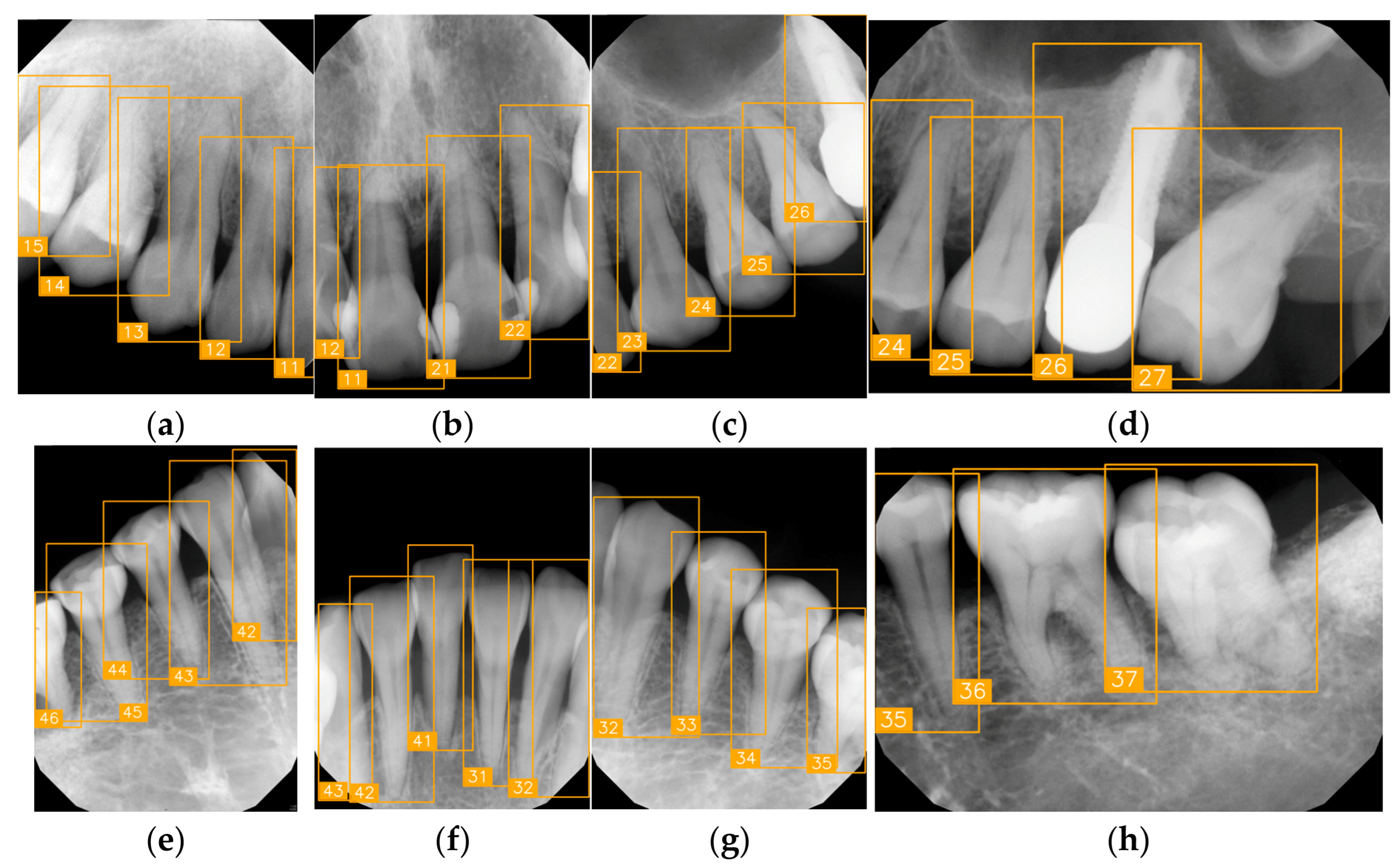
| Number | (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| Condition | Fractured tooth; Implant | Overlaapping | Missing Tooth | Incomplete crown |
| PA | 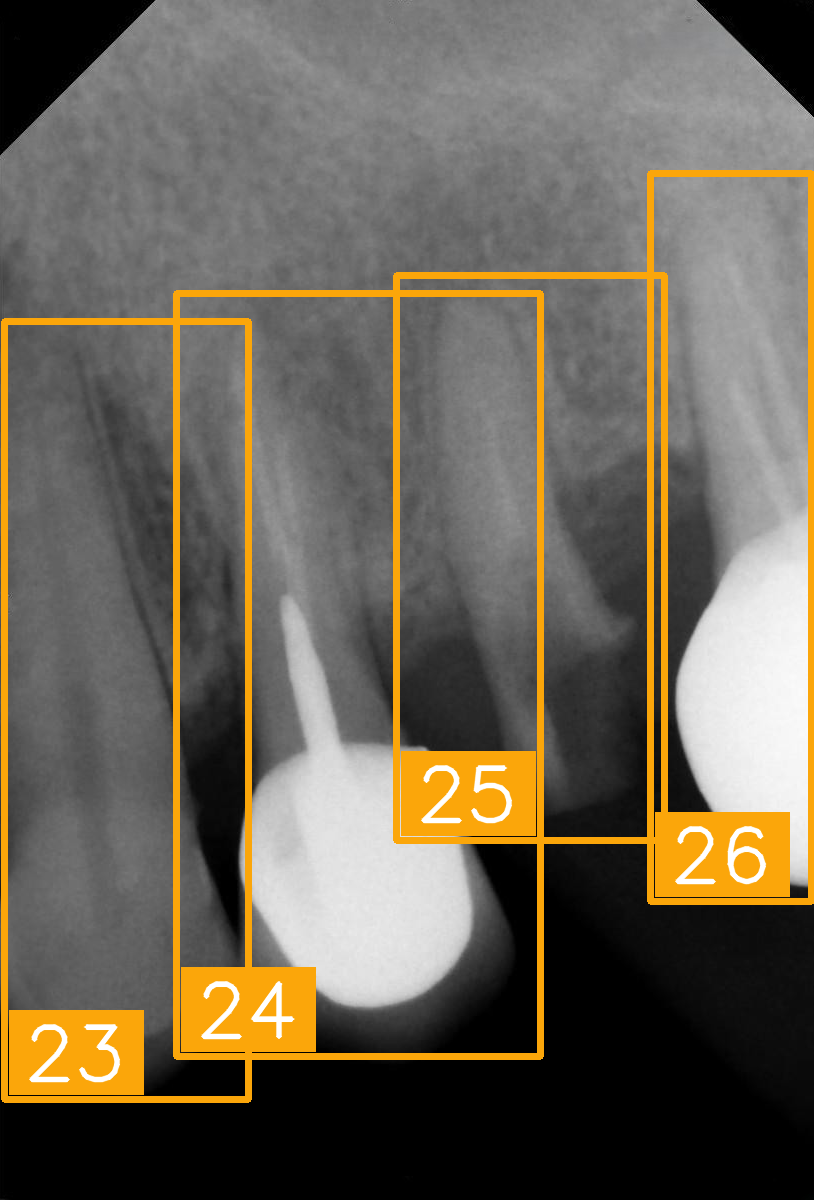 | 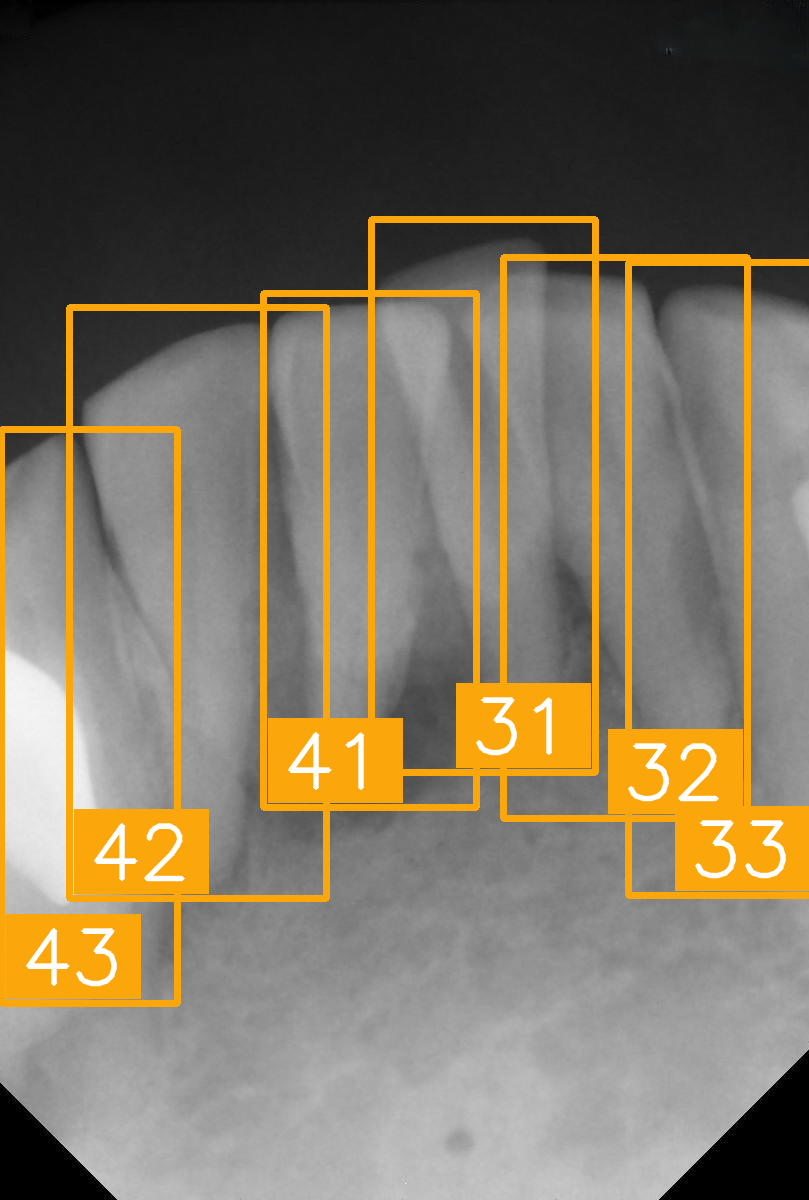 | 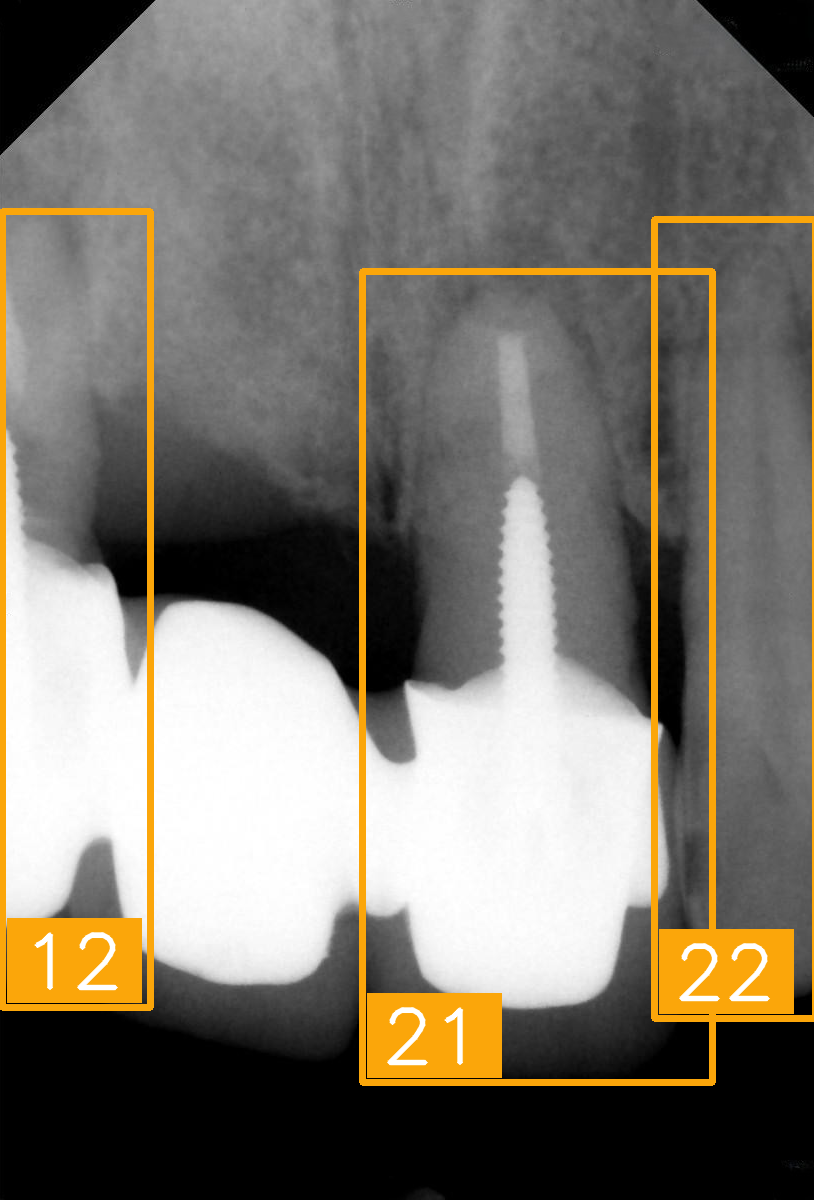 | 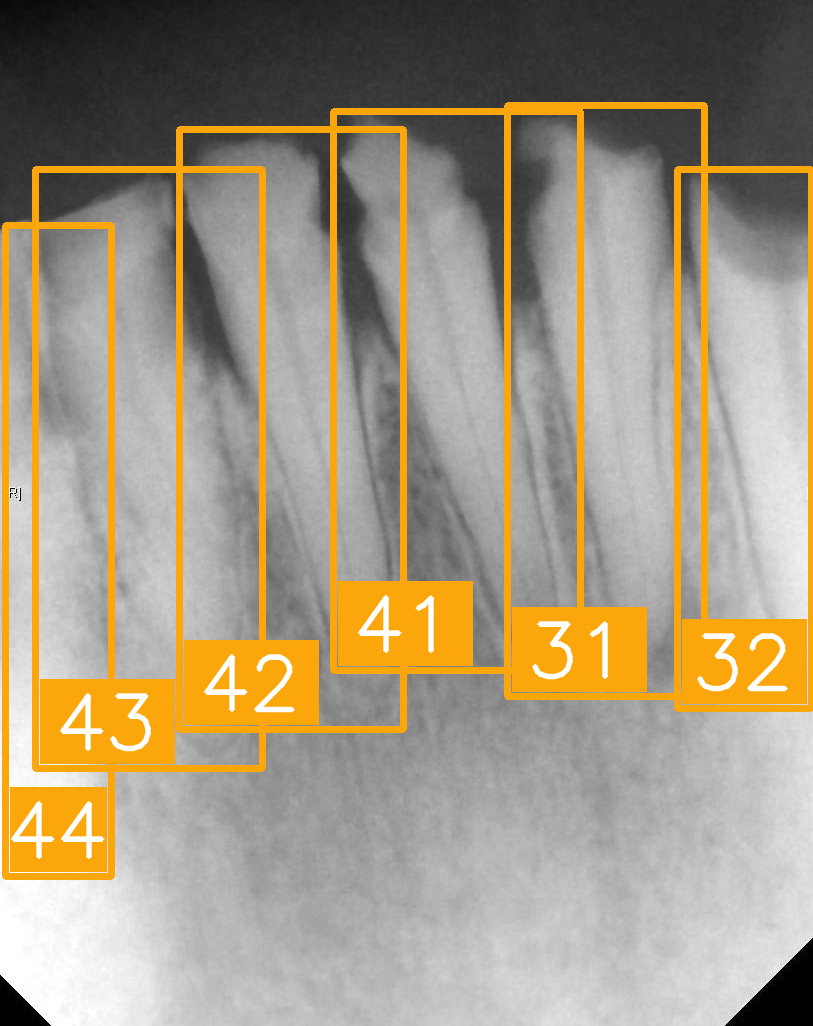 |
| FDI ground truth number | 23, 24, 25, 26 | 43, 42, 41, 31, 32, 33 | 12, 11, 21, 22 | 44, 43, 42, 41, 31, 32 |
| Inference Time | 75.9 ms | 73.3 ms | 76.1 ms | 69.9 ms |
| Number | (e) | (f) | (g) | (h) |
| Condition | Fractured tooth; lower brightness | Overlapping | Implant | Implant |
| PA | 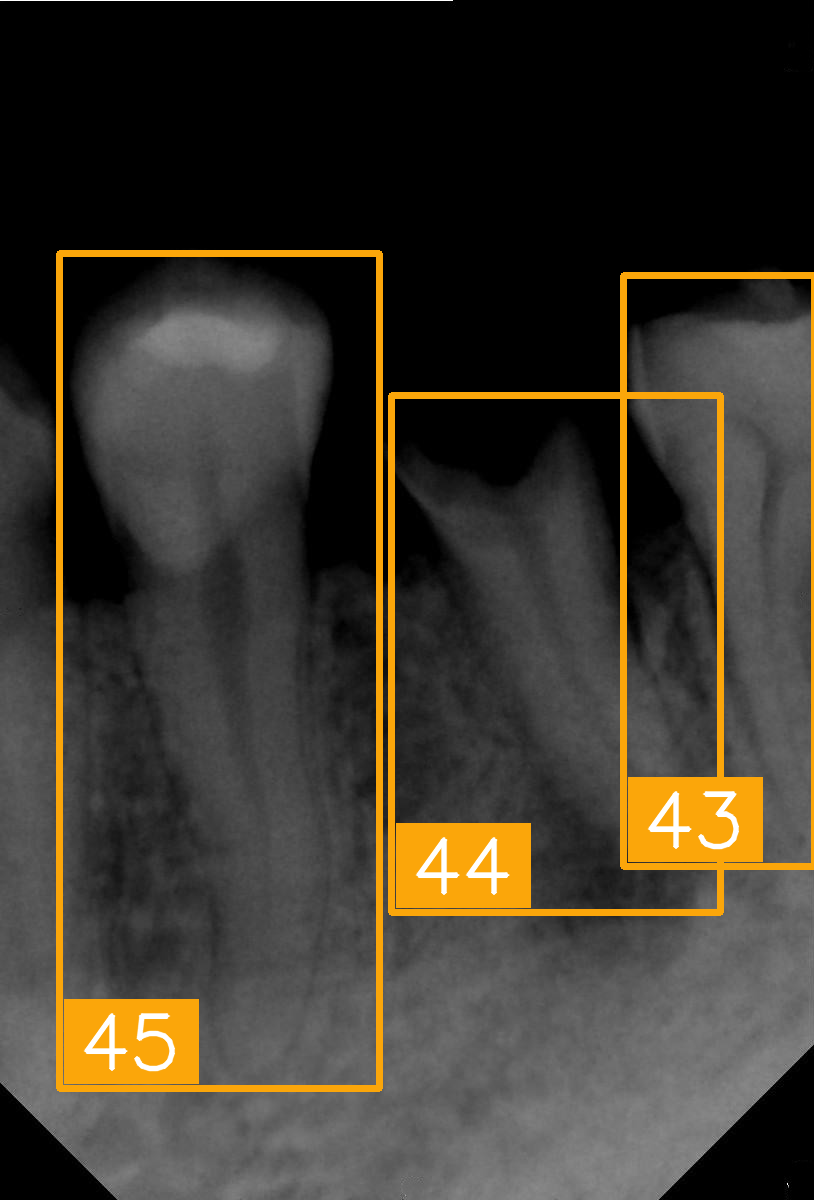 | 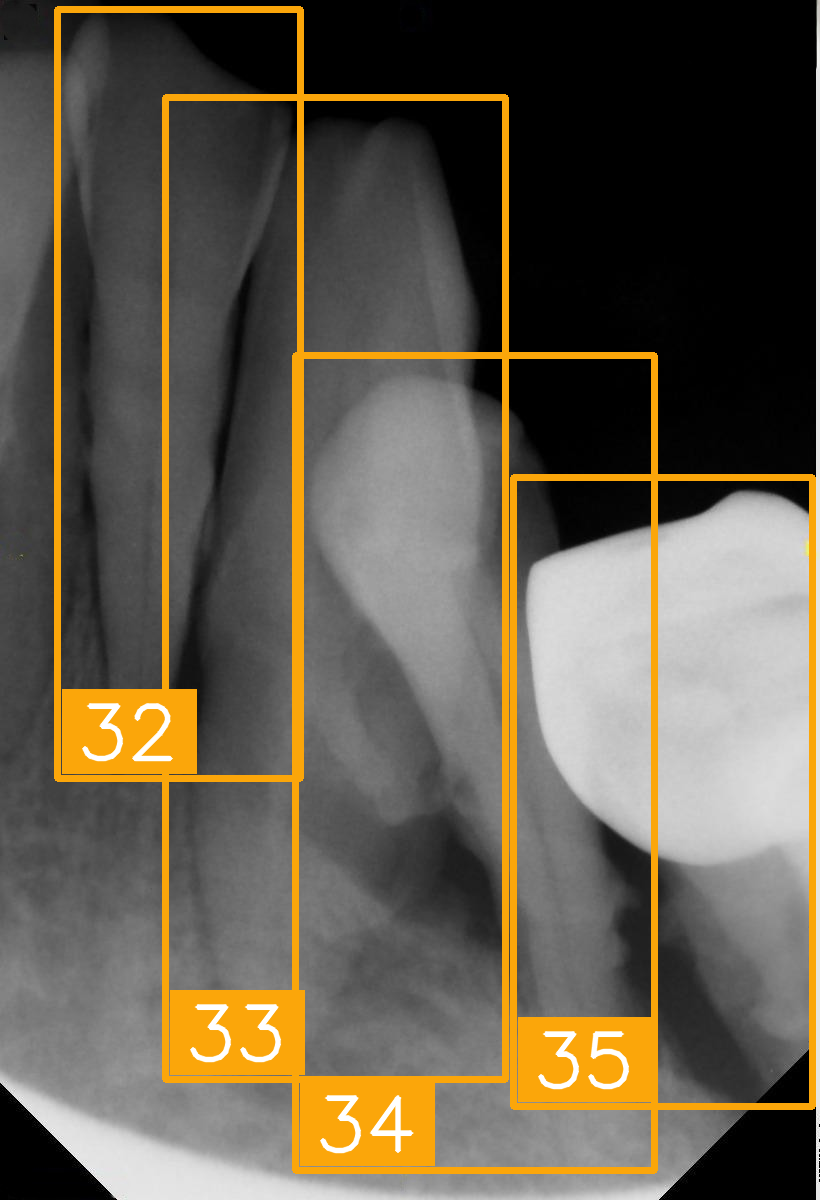 | 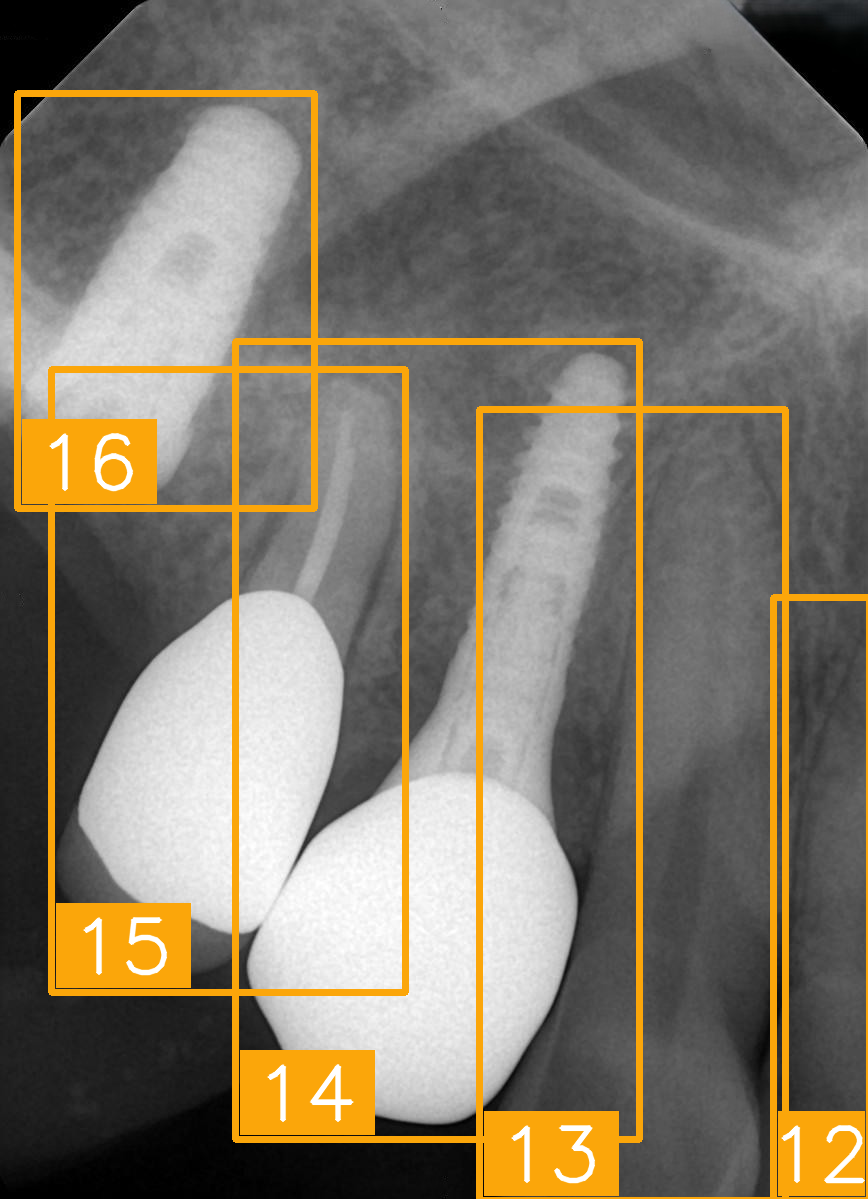 | 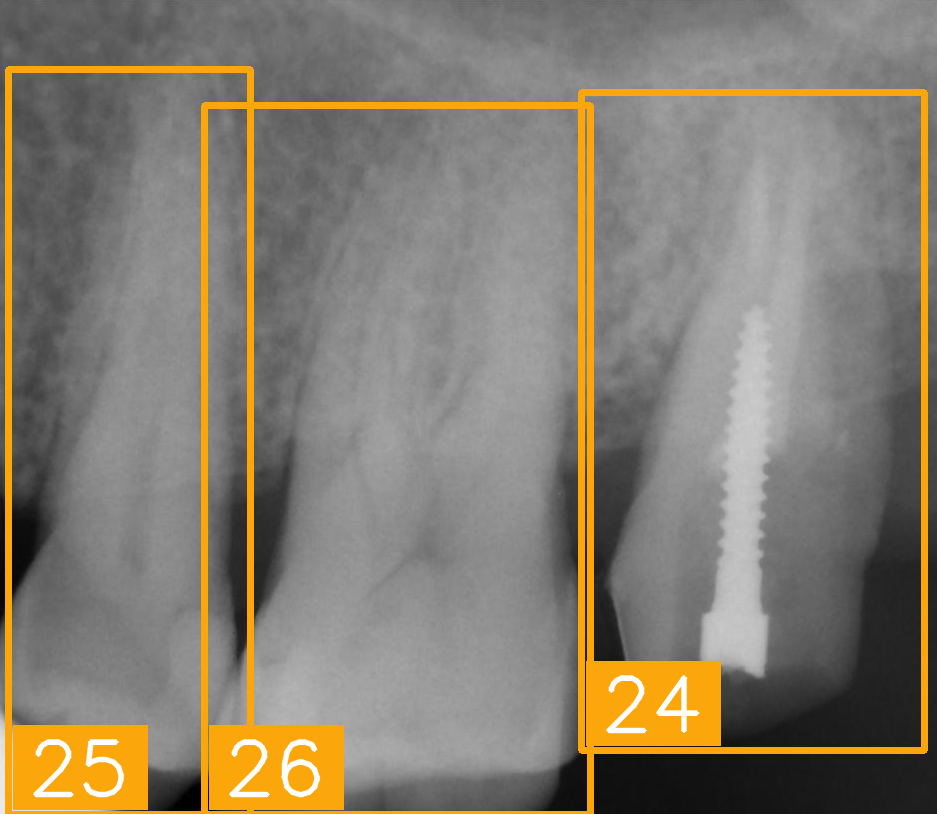 |
| FDI ground truth number | 45, 44, 43 | 32, 33, 34, 35 | 16, 15, 14, 13, 12 | 24, 25, 26 |
| Inference Time | 72.8 ms | 77.2 ms | 70.6 ms | 72.4 ms |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Y.-S.; Cha, I.E.; Mao, Y.-C.; Chang, L.-H.; Kao, Z.-C.; Tien, S.-Y.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chen, S.-L.; Li, K.-C.; Abu, P.A.R. Hybrid Faster R-CNN for Tooth Numbering in Periapical Radiographs Based on Fédération Dentaire Internationale System. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222900
Su Y-S, Cha IE, Mao Y-C, Chang L-H, Kao Z-C, Tien S-Y, Lin Y-J, Chen S-L, Li K-C, Abu PAR. Hybrid Faster R-CNN for Tooth Numbering in Periapical Radiographs Based on Fédération Dentaire Internationale System. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(22):2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222900
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Yong-Shao, I Elizabeth Cha, Yi-Cheng Mao, Li-Hsin Chang, Zi-Chun Kao, Shun-Yuan Tien, Yuan-Jin Lin, Shih-Lun Chen, Kuo-Chen Li, and Patricia Angela R. Abu. 2025. "Hybrid Faster R-CNN for Tooth Numbering in Periapical Radiographs Based on Fédération Dentaire Internationale System" Diagnostics 15, no. 22: 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222900
APA StyleSu, Y.-S., Cha, I. E., Mao, Y.-C., Chang, L.-H., Kao, Z.-C., Tien, S.-Y., Lin, Y.-J., Chen, S.-L., Li, K.-C., & Abu, P. A. R. (2025). Hybrid Faster R-CNN for Tooth Numbering in Periapical Radiographs Based on Fédération Dentaire Internationale System. Diagnostics, 15(22), 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222900






