Lipid, Metabolomic and Gut Microbiome Profiles in Long-Term-Hospitalized Cardiac Patients—An Observational and Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Confirmed cardiovascular diagnosis (including heart failure, ischaemic heart disease, arrhythmias, or valvular disease);
- Hospitalisation of at least three days;
- Availability of complete clinical, laboratory, and follow-up data during the admission period;
- Written informed consent for participation and use of anonymised biological samples.
- Active oncological disease under treatment;
- Advanced chronic kidney disease requiring dialysis;
- Chronic inflammatory or autoimmune disorders with immunosuppressive therapy;
- Active systemic infection at the time of enrolment;
- Prior solid-organ transplantation;
- Refusal or withdrawal of informed consent.
2.1. Study Protocol
2.2. Lipid Profiling
2.3. Metabolomic Assessment
2.4. Gut Microbiome Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Supplementary Methods
3. Results
3.1. Results of the Lipidic Profile Study
- Total cholesterol levels were broadly similar in the two groups, with mean values of 137.6 ± 7.3 mg/dL in the control group and 142.7 ± 14.4 mg/dL in the long-term group.
- LDL cholesterol appeared lower in patients with prolonged hospitalisation (66.4 ± 25.2 mg/dL, n = 2) compared with controls (113.3 ± 8.6 mg/dL, n = 3).
- HDL cholesterol values, available in a limited number of patients, were slightly higher in the long-term group (61.6 mg/dL) compared with the control group (57.1 mg/dL).
- Triglyceride levels showed a tendency to be lower in the long-term group (62.8 mg/dL) compared to controls (158.6 ± 113.0 mg/dL).
3.2. Results of the Study of the Metabolomic Profile
3.3. Results of the Study of Gut Microbiome
3.4. Results—Integrative Statistical Analyses
- ATP and phosphocreatine ratio were inversely associated with clinical severity scores (ρ = –0.44, p < 0.01).
- Ketone body utilisation correlated positively with hospital stay (ρ = 0.47, p < 0.01).
- Dysbiosis index correlated with both length of stay (ρ = 0.53, p < 0.001) and comorbidity burden (ρ = 0.46, p < 0.01).
- Reduced Shannon diversity correlated negatively with ATP levels (ρ = –0.39, p < 0.05).
3.5. Temporal Dynamics Within Groups
4. Discussion
4.1. Lipid Profile in Prolonged Hospitalisation
4.2. Metabolomic Reprogramming
4.3. Gut Microbiome Disruption
4.4. Integrative Perspective and Multi-Omics Relevance
4.5. Clinical Implications
4.6. Strengths and Limitations
4.7. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lv, J.; Pan, C.; Cai, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Pang, J.; Xu, F.; Wu, S.; Kou, T.; et al. Plasma metabolomics reveals the shared and distinct metabolic disturbances associated with cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.S.; Saraiva, F.; Ferreira, R.; Leite-Moreira, A.; Barros, A.S.; Diaz, S.O. Metabolomics and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, V.S.; Petucci, C.; Kim, M.S.; Bedi, K.C., Jr.; Wang, H.; Mishra, S.; Koleini, N.; Yoo, E.J.; Margulies, K.B.; Arany, Z.; et al. Myocardial Metabolomics of Human Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Circulation 2023, 147, 1147–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, V.S.; Selvaraj, S.; Sharma, K.; Shah, S.H. Towards Metabolomic-Based Precision Approaches for Classifying and Treating Heart Failure. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2024, 9, 1144–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Meenatchi, R.; Ahmed, Z.T.; Thacharodi, A.; M, R.; Kumar, R.R.; Varthan M K, H.; Hassan, S. Implications of the gut microbiome in cardiovascular diseases: Association of gut microbiome with cardiovascular diseases, therapeutic interventions and multi-omics approach for precision medicine. Med. Microecol. 2024, 19, 100096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z. Gut microbiome and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2020, 35, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trøseid, M.; Holter, J.C.; Holm, K.; Vestad, B.; Sazonova, T.; Granerud, B.K.; Dyrhol-Riise, A.M.; Holten, A.R.; Tonby, K.; Kildal, A.B.; et al. Gut microbiota composition during hospitalization is associated with 60-day mortality after severe COVID-19. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, F.; Mora, S.; Stroes, E.S.G. Consensus and guidelines on lipoprotein(a)—Seeing the forest through the trees. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2022, 33, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alebna, P.; Mehta, A. An Update on Lipoprotein (a): The Latest on Testing, Treatment, and Guideline Recommendations; Expert Analysis; American College of Cardiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Mach, F.; Koskinas, K.C.; Roeters van Lennep, J.E.; Tokgözoğlu, L.; Badimon, L.; Baigent, C.; Benn, M.; Binder, C.J.; Catapano, A.L.; De Backer, G.G.; et al. Focused Update of the 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias. Atherosclerosis 2025, 409, 120479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, M.L.; Rosenson, R.S.; López, J.A.G.; Lepor, N.E.; Baum, S.J.; Stout, E.; Gaudet, D.; Knusel, B.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. The Off-Treatment Effects of Olpasiran on Lipoprotein(a) Lowering: OCEAN(a)-DOSE Extension Period Results. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 84, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.S.; Maron, B.A.; Loscalzo, J. Multiomics Network Medicine Approaches to Precision Medicine and Therapeutics in Cardiovascular Diseases. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2023, 43, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboktakin Rizi, S.; Stamenkovic, A.; Ravandi, A. Integrative Omics Approaches in Cardiovascular Disease Research: Current Trends and Future Directions. Can. J. Cardiol. 2025, 41, 1642–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordestgaard, L.T.; Wolford, B.N.; de Gonzalo-Calvo, D.; Sopić, M.; Devaux, Y.; Matic, L.; Wettinger, S.B.; Schmid, J.A.; Amigó, N.; Masana, L.; et al. Multiomics in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 2025, 408, 120414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, L.; Bernhard, J.; Schrutka, L.; Haider, P.; Distelmaier, K.; Hengstenberg, C.; Krychtiuk, K.A.; Speidl, W.S. Effects of the 2019 guideline update on lipid-lowering therapy in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, J.; Su, Q.; Fan, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, J.; Hong, J. Evaluation of Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis and Arterial Stiffness in Cardiovascular Disease Risk: An Ongoing Prospective Study From the Kailuan Cohort. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 812652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Yin, G.; Gong, Z.; Lv, X.; Feng, C.; Liu, L.; Abdu, F.A.; Shi, T.; Zhang, W.; Alifu, J.; et al. IL-22 Attenuates Pressure Overload-Induced Heart Failure and Inflammation. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2025, 18, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhevnikova, M.V.; Belenkov, Y.N.; Shestakova, K.M.; Ageev, A.A.; Markin, P.A.; Kakotkina, A.V.; Korobkova, E.O.; Moskaleva, N.E.; Kuznetsov, I.V.; Khabarova, N.V.; et al. Metabolomic profiling in heart failure as a new tool for diagnosis and phenotyping. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Islam, F.; Or-Rashid, M.H.; Mamun, A.A.; Rahaman, M.S.; Islam, M.M.; Meem, A.F.K.; Sutradhar, P.R.; Mitra, S.; Mimi, A.A.; et al. The Gut Microbiota (Microbiome) in Cardiovascular Disease and Its Therapeutic Regulation. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 903570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrignani, V.; Salvo, A.; Pacinella, G.; Tuttolomondo, A. The Mediterranean Diet, Its Microbiome Connections, and Cardiovascular Health: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hînganu, M.V.; Hînganu, D.; Cozma, S.R.; Asimionoaiei-Simionescu, C.; Scutariu, I.A.; Ionesi, D.S.; Haba, D. Morphofunctional evaluation of buccopharyngeal space using three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography (3D-CBCT). Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. 2018, 220, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarchi, A.; Al-Qadami, G.; Tran, C.D.; Conlon, M. Understanding dysbiosis and resilience in the human gut microbiome: Biomarkers, interventions, and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1559521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigore, I.; Ciobotaru, O.R.; Hînganu, D.; Gurau, G.; Tutunaru, D.; Hînganu, M.V. A Systemic Perspective of the Link Between Microbiota and Cardiac Health: A Literature Review. Life 2025, 15, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruden, D.M. The emerging role of multiomics in aging research. Epigenomics 2025, 17, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuciureanu, D.I.; Statescu, C.; Sascau, R.A.; Cuciureanu, T.; Constantinescu, V.A.; Hinganu, D.; Preda, C.; Hinganu, M.V.; Turliuc, M.D. Particularities of Using Contrast Agents in Diagnosis of Stroke. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekhael, M.; Bidaoui, G.; Falloon, A.; Pandey, A.C. Personalization of primary prevention: Exploring the role of coronary artery calcium and polygenic risk score in cardiovascular diseases. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 35, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima-Cozma, L.C.; Cozma, S.; Hinganu, D.; Ghiciuc, C.M.; Mitu, F. Targeting Matrix Metalloproteinases in Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Dysfunction. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 718–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallidis, L.S. The changing landscape of lipid-lowering therapy after the new ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Launching the era of triple hypolipidaemic therapy in very high risk patients. Atherosclerosis 2020, 292, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
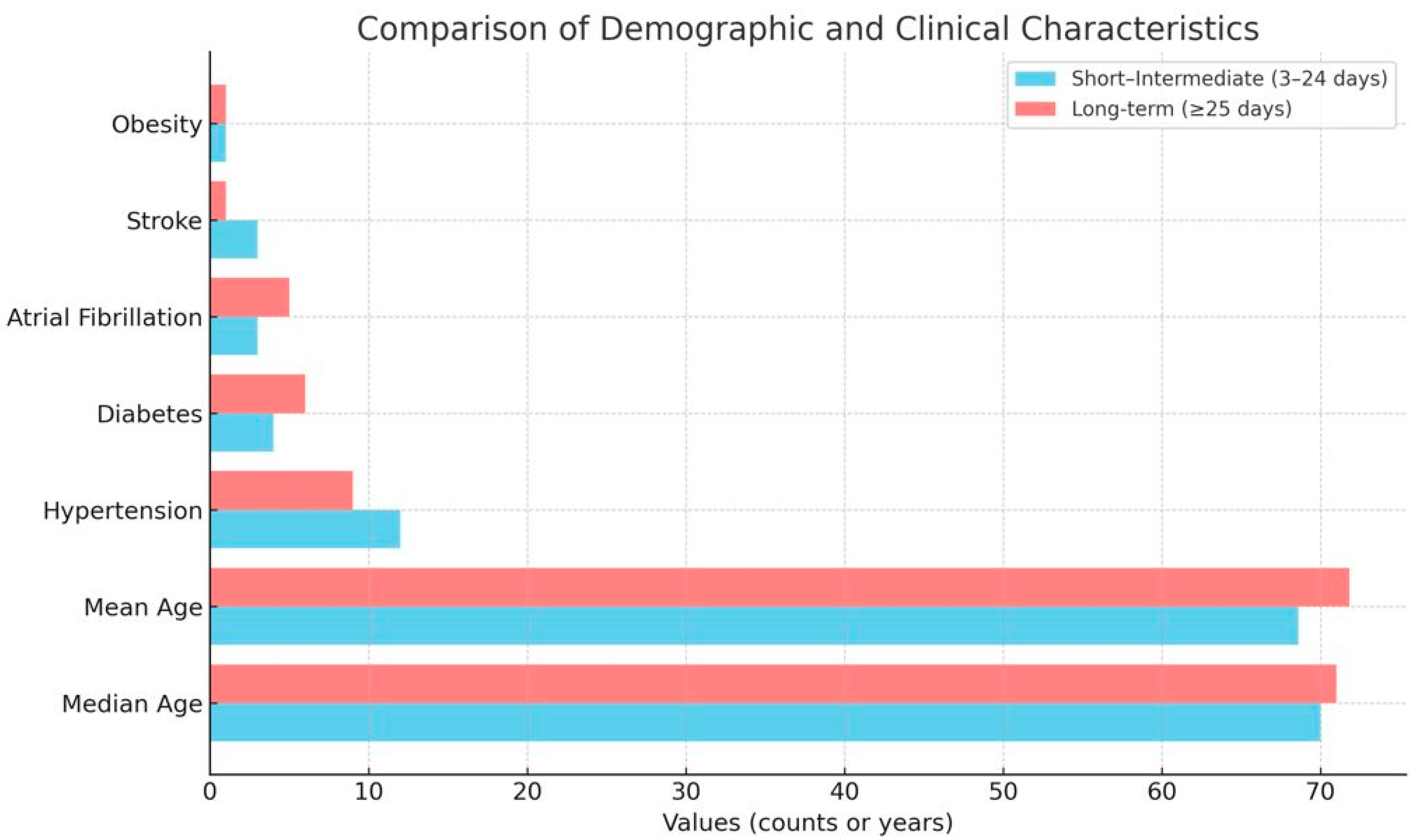
| Characteristic | Short–Intermediate Stay (3–24 Days, n = 41) | Long-Term Stay (≥25 Days, n = 51) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years, range) | 49–90 | 45–93 |
| Age (median) | 70 | 71 |
| Age (mean) | 68.6 | 71.8 |
| Insufficiency heart failure (mentions) | 33 | 48 |
| Ischaemic heart disease (mentions) | 10 | 6 |
| Hypertension (mentions) | 12 | 9 |
| Diabetes mellitus (mentions) | 4 | 6 |
| Atrial fibrillation (mentions) | 3 | 5 |
| Stroke (mentions) | 3 | 1 |
| Obesity (mentions) | 1 | 1 |
| Variable | Control (3–24 Days) | Long-Term (≥25 Days) |
|---|---|---|
| Total cholesterol | 137.6 ± 7.3 mg/dL (n = 3) | 142.7 ± 14.4 mg/dL (n = 3) |
| LDL cholesterol | 113.3 ± 8.6 mg/dL (n = 3) | 66.4 ± 25.2 mg/dL (n = 2) |
| HDL cholesterol | 57.1 mg/dL (n = 1) | 61.6 mg/dL (n = 1) |
| Triglycerides | 158.6 ± 113.0 mg/dL (n = 3) | 62.8 mg/dL (n = 1) |
| Metabolite Category | Control (3–24 Days) | Long-Term (≥25 Days) | Direction of Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATP | Reference range | ↓ Reduced | ↓ |
| Phosphocreatine ratio | Reference range | ↓ Reduced | ↓ |
| Lactate | Normal | ↑ Elevated | ↑ |
| Ketone bodies | Low | ↑ Increased | ↑ |
| BCAA (Val, Leu, Ile) | Normal | ↓ Reduced | ↓ |
| Aromatic AA (Phe, Tyr, Trp) | Normal | ↑ Increased | ↑ |
| Acylcarnitines | Normal | ↑ Altered | ↑ |
| Phospholipids | Normal | ↓ Altered | ± |
| Parameter | Control (3–24 Days) | Long-Term (≥25 Days) | Direction of Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon diversity index | Reference/normal | ↓ Reduced | ↓ |
| Simpson index | Reference/normal | ↓ Reduced | ↓ |
| β-diversity (Bray–Curtis) | Within normal variation | Distinct clustering | — |
| Dysbiosis index | Low–moderate | ↑ Increased | ↑ |
| Firmicutes (%) | Normal abundance | ↓ Reduced | ↓ |
| Bacteroidetes (%) | Normal abundance | ↓ Reduced | ↓ |
| Proteobacteria (%) | Low abundance | ↑ Increased | ↑ |
| Enterococcus spp. | Absent/rare | ↑ Present | ↑ |
| Candida spp. | Rare | ↑ Overrepresented | ↑ |
| Variable | Test Applied | Association with Hospital Stay | Association with Severity Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDL cholesterol | t-test | ↓ p < 0.05 | ns |
| Triglycerides | t-test | ↓ p < 0.05 | ns |
| HDL cholesterol | t-test | ns | trend ↑ (ns) |
| ATP, phosphocreatine | RM-ANOVA/Spearman | ↓ p < 0.01 | ρ = –0.44, p < 0.01 |
| Ketone bodies | RM-ANOVA/Spearman | ↑ p < 0.05 | ρ = 0.40, p < 0.05 |
| BCAA (Val, Leu, Ile) | Mann–Whitney U | ↓ p < 0.05 | ns |
| Aromatic AA (Phe, Tyr, Trp) | Mann–Whitney U | ↑ p < 0.05 | ρ = 0.35, p < 0.05 |
| Dysbiosis index | Mann–Whitney U | ↑ p < 0.01 | ρ = 0.46, p < 0.01 |
| Shannon diversity | Mann–Whitney U | ↓ p < 0.01 | ρ = –0.37, p < 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grigore, I.; Ciobotaru, O.R.; Hînganu, D.; Gurau, G.; Stamate, E.; Tutunaru, D.; Gavril, R.S.; Ciobotaru, O.C.; Hînganu, M.V. Lipid, Metabolomic and Gut Microbiome Profiles in Long-Term-Hospitalized Cardiac Patients—An Observational and Retrospective Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222874
Grigore I, Ciobotaru OR, Hînganu D, Gurau G, Stamate E, Tutunaru D, Gavril RS, Ciobotaru OC, Hînganu MV. Lipid, Metabolomic and Gut Microbiome Profiles in Long-Term-Hospitalized Cardiac Patients—An Observational and Retrospective Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(22):2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222874
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrigore, Ionica, Oana Roxana Ciobotaru, Delia Hînganu, Gabriela Gurau, Elena Stamate, Dana Tutunaru, Radu Sebastian Gavril, Octavian Catalin Ciobotaru, and Marius Valeriu Hînganu. 2025. "Lipid, Metabolomic and Gut Microbiome Profiles in Long-Term-Hospitalized Cardiac Patients—An Observational and Retrospective Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 22: 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222874
APA StyleGrigore, I., Ciobotaru, O. R., Hînganu, D., Gurau, G., Stamate, E., Tutunaru, D., Gavril, R. S., Ciobotaru, O. C., & Hînganu, M. V. (2025). Lipid, Metabolomic and Gut Microbiome Profiles in Long-Term-Hospitalized Cardiac Patients—An Observational and Retrospective Study. Diagnostics, 15(22), 2874. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222874







