Evaluation of the Relationship Between Neurologic Manifestations and Genetic Mutations in Wilson’s Disease with Next-Generation Sequencing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Isolation
2.3. Library Preparation and WES
2.4. Analysis of WES Raw Data and Variant Interpretation
2.5. Detection of CNVs Using Control Data from WES
2.6. Pathogenicity Prediction of Identified Variants
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Variants and CNVs
3.2. Prediction of the Pathogenicity of Variants and Genotype-Phenotype Correlations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mulligan, C.; Bronstein, J.M. Wilson Disease: An Overview and Approach to Management. Neurol. Clin. 2020, 38, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Monteagudo, A.; Ripollés, E.; Berenguer, M.; Espinós, C. Wilson’s Disease: Facing the Challenge of Diagnosing a Rare Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.J.; Hahn, S.H. Chapter 3—The genetics of Wilson disease. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Członkowska, A., Schilsky, M.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 142, pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Członkowska, A.; Litwin, T.; Dusek, P.; Ferenci, P.; Lutsenko, S.; Medici, V.; Rybakowski, J.K.; Weiss, K.H.; Schilsky, M.L. Wilson disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena-Valera, A.; Ruz-Zafra, P.; Ampuero, J. Wilson’s disease: Overview. Med. Clin. 2023, 160, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shribman, S.; Poujois, A.; Bandmann, O.; Czlonkowska, A.; Warner, T.T. Wilson’s disease: Update on pathogenesis, biomarkers and treatments. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitter, R.M.; Oh, S.; Deng, Z.; Rahman, S.; Hite, R.K.; Yuan, P. Structure of the Wilson disease copper transporter ATP7B. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, J.; Aizenman, E. The physiological and pathophysiological roles of copper in the nervous system. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2024, 60, 3505–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Strader, C.; Costantino, H.; Weiss, K.H.; Hedera, P. Wilson disease in the USA: Epidemiology and real-world patient characteristics based on a retrospective observational health claims study. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e089032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedera, P. Wilson’s disease: A master of disguise. Park. Relat. Disord. 2019, 59, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Ghaffar, T.Y.; Elsayed, S.M.; Elnaghy, S.; Shadeed, A.; Elsobky, E.S.; Schmidt, H. Phenotypic and genetic characterization of a cohort of pediatric Wilson disease patients. BMC Pediatr. 2011, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovchinnikova, E.V.; Garbuz, M.M.; Ovchinnikova, A.A.; Kumeiko, V.V. Epidemiology of Wilson’s Disease and Pathogenic Variants of the ATP7B Gene Leading to Diversified Protein Disfunctions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, T.; Guan, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Assessment and factors affecting quality of life among patients with Wilson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jopowicz, A.; Tarnacka, B. Neurological Wilson’s Disease Signs-Hepatic Encephalopathy or Copper Toxicosis? Diagnostics 2023, 13, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Cave, V.; Di Dato, F.; Iorio, R. Wilson’s Disease with Acute Hepatic Onset: How to Diagnose and Treat It. Children 2024, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL-ERN Clinical Practice Guidelines on Wilson’s disease. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 690–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, S.M.; Matsukuma, K.E.; Medici, V. Wilson disease and the differential diagnosis of its hepatic manifestations: A narrative review of clinical, laboratory, and liver histological features. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medici, V.; LaSalle, J.M. Genetics and epigenetic factors of Wilson disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromadzka, G.; Bendykowska, M.; Przybyłkowski, A. Wilson’s Disease-Genetic Puzzles with Diagnostic Implications. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenci, P. Chapter 14—Diagnosis of Wilson disease. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Członkowska, A., Schilsky, M.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 142, pp. 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, H.M.; Amin, M.; Syed, J.; Sarfraz, Z.; Sarfraz, A.; Sarfraz, M.; Farfán Bajaña, M.J.; Felix, M.; Cherrez-Ojeda, I. Biochemical testing for the diagnosis of Wilson’s disease: A systematic review. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wungjiranirun, M.; Sharzehi, K. Wilson’s Disease. Semin. Neurol. 2023, 43, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenci, P.; Caca, K.; Loudianos, G.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Tanner, S.; Sternlieb, I.; Schilsky, M.; Cox, D.; Berr, F. Diagnosis and phenotypic classification of Wilson disease. Liver Int. 2003, 23, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QIAGEN Digital Insights. QIAGEN Bioinformatics Software. Available online: https://digitalinsights.qiagen.com/ (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Ioannidis, N.M.; Rothstein, J.H.; Pejaver, V.; Middha, S.; McDonnell, S.K.; Baheti, S.; Musolf, A.; Li, Q.; Holzinger, E.; Karyadi, D.; et al. REVEL: An Ensemble Method for Predicting the Pathogenicity of Rare Missense Variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircher, M.; Witten, D.M.; Jain, P.; O’Roak, B.J.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J. A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V.E.; Gerasimova, A.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A.S.; Sunyaev, S.R. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.C.; Henikoff, S. SIFT: Predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3812–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Cooper, D.N.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster2: Mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loudianos, G.; Dessi, V.; Lovicu, M.; Angius, A.; Altuntas, B.; Giacchino, R.; Marazzi, M.; Marcellini, M.; Sartorelli, M.R.; Sturniolo, G.C.; et al. Mutation analysis in patients of Mediterranean descent with Wilson disease: Identification of 19 novel mutations. J. Med. Genet. 1999, 36, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schushan, M.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Ben-Tal, N.; Lutsenko, S. A structural model of the copper ATPase ATP7B to facilitate analysis of Wilson disease-causing mutations and studies of the transport mechanism. Metallomics 2012, 4, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capalbo, A.; Valero, R.A.; Jimenez-Almazan, J.; Pardo, P.M.; Fabiani, M.; Jiménez, D.; Simon, C.; Rodriguez, J.M. Optimizing clinical exome design and parallel gene-testing for recessive genetic conditions in preconception carrier screening: Translational research genomic data from 14,125 exomes. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Villarreal, L.; Hernández-Ortega, A.; Sánchez-Monteagudo, A.; Peña-Quintana, L.; Ramírez-Lorenzo, T.; Riaño, M.; Moreno-Pérez, R.; Monescillo, A.; González-Santana, D.; Quiñones, I.; et al. Wilson disease: Revision of diagnostic criteria in a clinical series with great genetic homogeneity. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Monteagudo, A.; Álvarez-Sauco, M.; Sastre, I.; Martínez-Torres, I.; Lupo, V.; Berenguer, M.; Espinós, C. Genetics of Wilson disease and Wilson-like phenotype in a clinical series from eastern Spain. Clin. Genet. 2020, 97, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.B.; Chernov, I.; Zhang, H.T.; Ross, B.M.; Das, K.; Lutsenko, S.; Parano, E.; Pavone, L.; Evgrafov, O.; Ivanova-Smolenskaya, I.A.; et al. Identification and analysis of mutations in the Wilson disease gene (ATP7B): Population frequencies, genotype-phenotype correlation, and functional analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1997, 61, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squitti, R.; Siotto, M.; Bucossi, S.; Polimanti, R. In silico investigation of the ATP7B gene: Insights from functional prediction of non-synonymous substitution to protein structure. Biometals 2014, 27, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stranneheim, H.; Lagerstedt-Robinson, K.; Magnusson, M.; Kvarnung, M.; Nilsson, D.; Lesko, N.; Engvall, M.; Anderlid, B.M.; Arnell, H.; Johansson, C.B.; et al. Integration of whole genome sequencing into a healthcare setting: High diagnostic rates across multiple clinical entities in 3219 rare disease patients. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Xiang, J.; Fan, C.; Asan; Shang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, B.; Cai, W.; Chen, S.; et al. Pilot study of expanded carrier screening for 11 recessive diseases in China: Results from 10,476 ethnically diverse couples. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 27, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caca, K.; Ferenci, P.; Kühn, H.J.; Polli, C.; Willgerodt, H.; Kunath, B.; Hermann, W.; Mössner, J.; Berr, F. High prevalence of the H1069Q mutation in East German patients with Wilson disease: Rapid detection of mutations by limited sequencing and phenotype-genotype analysis. J. Hepatol. 2001, 35, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bie, P.; van de Sluis, B.; Burstein, E.; van de Berghe, P.V.; Muller, P.; Berger, R.; Gitlin, J.D.; Wijmenga, C.; Klomp, L.W. Distinct Wilson’s disease mutations in ATP7B are associated with enhanced binding to COMMD1 and reduced stability of ATP7B. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huster, D.; Kühne, A.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Raines, L.; Jantsch, V.; Noe, J.; Schirrmeister, W.; Sommerer, I.; Sabri, O.; Berr, F.; et al. Diverse functional properties of Wilson disease ATP7B variants. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 947–956.e945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kars, M.E.; Başak, A.N.; Onat, O.E.; Bilguvar, K.; Choi, J.; Itan, Y.; Çağlar, C.; Palvadeau, R.; Casanova, J.L.; Cooper, D.N.; et al. The genetic structure of the Turkish population reveals high levels of variation and admixture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2026076118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.J.; Yan, J.; Cao, L.; Wang, P.; et al. The utility of hierarchical genetic testing in paediatric liver disease. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuduxikuer, K.; Li, L.T.; Qiu, Y.L.; Wang, N.L.; Wang, J.S. Wilson disease with hepatic presentation in an eight-month-old boy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8981–8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amendola, L.M.; Dorschner, M.O.; Robertson, P.D.; Salama, J.S.; Hart, R.; Shirts, B.H.; Murray, M.L.; Tokita, M.J.; Gallego, C.J.; Kim, D.S.; et al. Actionable exomic incidental findings in 6503 participants: Challenges of variant classification. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balashova, M.S.; Tuluzanovskaya, I.G.; Glotov, O.S.; Glotov, A.S.; Barbitoff, Y.A.; Fedyakov, M.A.; Alaverdian, D.A.; Ivashchenko, T.E.; Romanova, O.V.; Sarana, A.M.; et al. The spectrum of pathogenic variants of the ATP7B gene in Wilson disease in the Russian Federation. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 59, 126420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barada, K.; El-Atrache, M.; El, H., II; Rida, K.; El-Hajjar, J.; Mahfoud, Z.; Usta, J. Homozygous mutations in the conserved ATP hinge region of the Wilson disease gene: Association with liver disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, J.F.T.; Yu, M.H.C.; Chui, M.M.C.; Yeung, C.C.W.; Kwok, A.W.C.; Zhuang, X.; Lee, R.; Fung, J.L.F.; Lee, M.; Mak, C.C.Y.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of recessive carrier status using exome and genome sequencing data in 1543 Southern Chinese. npj Genom. Med. 2022, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Yu, H.; Wang, R.M.; Xie, J.J.; Ni, W.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wu, Z.Y. Contribution of intragenic deletions to mutation spectrum in Chinese patients with Wilson’s disease and possible mechanism underlying ATP7B gross deletions. Park. Relat. Disord. 2019, 62, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couchonnal, E.; Bouchard, S.; Sandahl, T.D.; Pagan, C.; Lion-François, L.; Guillaud, O.; Habes, D.; Debray, D.; Lamireau, T.; Broué, P.; et al. ATP7B variant spectrum in a French pediatric Wilson disease cohort. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 64, 104305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshjoo, O.; Garshasbi, M. Novel compound heterozygote mutations in the ATP7B gene in an Iranian family with Wilson disease: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2018, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggilla, S.R.; Senagari, J.R.; Rao, P.N.; Madireddi, S. Spectrum of mutations in the ATP binding domain of ATP7B gene of Wilson Disease in a regional Indian cohort. Gene 2015, 569, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, R.; Hua, F.; Jiao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yang, X.; Peng, S.; Niu, J. Mutational analysis of ATP7B in Chinese Wilson disease patients. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 2851–2861. [Google Scholar]
- Iida, M.; Terada, K.; Sambongi, Y.; Wakabayashi, T.; Miura, N.; Koyama, K.; Futai, M.; Sugiyama, T. Analysis of functional domains of Wilson disease protein (ATP7B) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 1998, 428, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Che, F.; Shu, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Analysis of clinical phenotypes and ATP7B gene variants in 75 children patients with Wilson’s disease. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 2022, 39, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penon-Portmann, M.; Lotz-Esquivel, S.; Chavez Carrera, A.; Jiménez-Hernández, M.; Alvarado-Romero, D.; Segura-Cordero, S.; Rimolo-Donadio, F.; Hevia-Urrutia, F.; Mora-Guevara, A.; Saborío-Rocafort, M.; et al. Wilson disease in Costa Rica: Pediatric phenotype and genotype characterization. JIMD Rep. 2020, 52, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Ge, J.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; Hu, S.; Li, W.; Li, T. Pathogenic gene variation spectrum and carrier screening for Wilson’s disease in Qingdao area. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2021, 9, e1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Shu, S.; Han, Y.Z.; Chiu, Y.J.; Han, Y.S. A case report: Co-occurrence of Wilson disease and oculocutaneous albinism in a Chinese patient. Medicine 2018, 97, e13744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzi, R.E.; Petrukhin, K.; Chernov, I.; Pellequer, J.L.; Wasco, W.; Ross, B.; Romano, D.M.; Parano, E.; Pavone, L.; Brzustowicz, L.M.; et al. The Wilson disease gene is a copper transporting ATPase with homology to the Menkes disease gene. Nat. Genet. 1993, 5, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, N.; Murong, S.; Lin, M. Missense mutations of exons 14 and 18 of Wilson’s disease gene in Chinese patients. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 1999, 16, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Tang, H.; Liu, L.; Tang, J.; Shi, X. Molecular analysis of 53 Chinese families with Wilson’s disease: Six novel mutations identified. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2021, 9, e1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Jia, S.; Yi, L.; Wu, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, A.; Li, X.; et al. Identification of potential modifier genes in Chinese patients with Wilson disease. Metallomics 2022, 14, mfac024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battisti, C.; Loudianos, G.; Rufa, A.; Dotti, M.T.; Sangiorgi, S.; Dessì, V.; Lovicu, M.; Pirastu, M.; Federico, A. Detection of a rare Wilson disease mutation associated with arylsulfatase A pseudodeficiency. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1999, 85, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceyhan-Birsoy, O.; Murry, J.B.; Machini, K.; Lebo, M.S.; Yu, T.W.; Fayer, S.; Genetti, C.A.; Schwartz, T.S.; Agrawal, P.B.; Parad, R.B.; et al. Interpretation of Genomic Sequencing Results in Healthy and Ill Newborns: Results from the BabySeq Project. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 104, 76–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocoş, R.; Şendroiu, A.; Schipor, S.; Bohîlţea, L.C.; Şendroiu, I.; Raicu, F. Genotype-phenotype correlations in a mountain population community with high prevalence of Wilson’s disease: Genetic and clinical homogeneity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Członkowska, A.; Gromadzka, G.; Chabik, G. Monozygotic female twins discordant for phenotype of Wilson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1066–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Członkowska, A.; Rodo, M.; Gromadzka, G. Late onset Wilson’s disease: Therapeutic implications. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 896–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mohammed, A.; Mandal, T.; Maji, S.; Verma, J.; Ruturaj; Gupta, A. Polarized trafficking and copper transport activity of ATP7B: A mutational approach to establish genotype-phenotype correlation in Wilson disease. Hum. Mutat. 2022, 43, 1408–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despotov, K.; Klivényi, P.; Nagy, I.; Pálvölgyi, A.; Vécsei, L.; Rajda, C. Rare co-occurrence of multiple sclerosis and Wilson’s disease—Case report. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, J.; Fonseca, A.G.; Arboleda, R.; Frade, A.; Gennaro, M.P.; Jayakar, P.; Schleifer, P.; Hernandez, E. Case Report: The Association of Wilson Disease in a Patient with Ataxia and GLUT-1 Deficiency. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 750593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, O.Y.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Nokhrin, S.; Uhlemann, E.M.; Lutsenko, S. Difference in stability of the N-domain underlies distinct intracellular properties of the E1064A and H1069Q mutants of copper-transporting ATPase ATP7B. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 16355–16362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, H.H.; Hefter, H.; Stremmel, W.; Castañeda-Guillot, C.; Hernández Hernández, A.; Cox, D.W.; Auburger, G. His1069Gln and six novel Wilson disease mutations: Analysis of relevance for early diagnosis and phenotype. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 1998, 6, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzinovic, I.; Boesch, S.; Škorvánek, M.; Necpál, J.; Švantnerová, J.; Pavelekova, P.; Havránková, P.; Tsoma, E.; Indelicato, E.; Runkel, E.; et al. Genetic overlap between dystonia and other neurologic disorders: A study of 1,100 exomes. Park. Relat. Disord. 2022, 102, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firneisz, G.; Lakatos, P.L.; Szalay, F.; Polli, C.; Glant, T.T.; Ferenci, P. Common mutations of ATP7B in Wilson disease patients from Hungary. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 108, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenberg-Hua, Y.; Freudenberg, J.; Vacic, V.; Abhyankar, A.; Emde, A.K.; Ben-Avraham, D.; Barzilai, N.; Oschwald, D.; Christen, E.; Koppel, J.; et al. Disease variants in genomes of 44 centenarians. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2014, 2, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucev, Z.S.; Pop-Jordanova, N.; Calovska, V.; Tasic, V.; Slavevska, N.; Laban, N.; Noli, M.C.; Lepori, M.B.; Loudianos, G. Acute Gallbladder Hydrops and Arthritis: Unusual initial manifestations of Wilson’s Disease (WD): Case Report. Prilozi 2011, 32, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.C.; Yu, H.C.; Martin, R.; Cirulli, E.T.; Schenker-Ahmed, N.M.; Hicks, M.; Cohen, I.V.; Jönsson, T.J.; Heister, R.; Napier, L.; et al. Precision medicine integrating whole-genome sequencing, comprehensive metabolomics, and advanced imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3053–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwin, T.; Gromadzka, G.; Członkowska, A. Apolipoprotein E gene (APOE) genotype in Wilson’s disease: Impact on clinical presentation. Park. Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier-Dobersberger, T.; Ferenci, P.; Polli, C.; Balać, P.; Dienes, H.P.; Kaserer, K.; Datz, C.; Vogel, W.; Gangl, A. Detection of the His1069Gln mutation in Wilson disease by rapid polymerase chain reaction. Ann. Intern. Med. 1997, 127, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marazzi, M.G.; Giardino, S.; Dufour, C.; Serafino, M.; Sperlì, D.; Giacchino, R. Good response with zinc acetate monotherapy in an adolescent affected by severe Wilson disease. Pediatr. Med. Chir. 2012, 34, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCreary, D.; Omoyinmi, E.; Hong, Y.; Mulhern, C.; Papadopoulou, C.; Casimir, M.; Hacohen, Y.; Nyanhete, R.; Ahlfors, H.; Cullup, T.; et al. Development and Validation of a Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Gene Panel for Children with Neuroinflammation. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1914274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, S.W.; Wang, J.; Burke, R. In Vivo Modeling of the Pathogenic Effect of Copper Transporter Mutations That Cause Menkes and Wilson Diseases, Motor Neuropathy, and Susceptibility to Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4113–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.T.; Tsivkovskii, R.; Kosinsky, Y.A.; Efremov, R.G.; Lutsenko, S. The distinct functional properties of the nucleotide-binding domain of ATP7B, the human copper-transporting ATPase: Analysis of the Wilson disease mutations E1064A, H1069Q, R1151H, and C1104F. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 36363–36371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzer, M.; Viveiros, A.; Schaefer, B.; Baumgartner, N.; Seppi, K.; Djamshidian, A.; Todorov, T.; Griffiths, W.J.H.; Schott, E.; Schuelke, M.; et al. Synonymous mutation in adenosine triphosphatase copper-transporting beta causes enhanced exon skipping in Wilson disease. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, S.; Polishchuk, E.V.; Allocca, S.; Ciano, M.; Musto, A.; Gallo, M.; Perone, L.; Ranucci, G.; Iorio, R.; Polishchuk, R.S.; et al. Characterization of the most frequent ATP7B mutation causing Wilson disease in hepatocytes from patient induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petters, J.; Völkner, C.; Krohn, S.; Murua Escobar, H.; Bullerdiek, J.; Reuner, U.; Frech, M.J.; Hermann, A.; Lukas, J. Generation of two induced pluripotent stem cell lines from a female adult homozygous for the Wilson disease associated ATP7B variant p.H1069Q (AKOSi008-A) and a healthy control (AKOSi009-A). Stem Cell Res. 2020, 49, 102079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polishchuk, E.V.; Concilli, M.; Iacobacci, S.; Chesi, G.; Pastore, N.; Piccolo, P.; Paladino, S.; Baldantoni, D.; van, I.S.C.; Chan, J.; et al. Wilson disease protein ATP7B utilizes lysosomal exocytosis to maintain copper homeostasis. Dev. Cell 2014, 29, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Granillo, A.; Sedlak, E.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Stability and ATP binding of the nucleotide-binding domain of the Wilson disease protein: Effect of the common H1069Q mutation. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 383, 1097–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadzadeh, S.; Kruschel, T.; Novak, M.; Kallenbach, M.; Hefter, H. Different Response Behavior to Therapeutic Approaches in Homozygotic Wilson’s Disease Twins with Clinical Phenotypic Variability: Case Report and Literature Review. Genes 2022, 13, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapuppo, A.; Pavone, P.; Praticò, A.D.; Ruggieri, M.; Bertino, G.; Fiumara, A. Genotype-phenotype variable correlation in Wilson disease: Clinical history of two sisters with the similar genotype. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowronska, M.; Litwin, T.; Kurkowska-Jastrzębska, I.; Członkowska, A. Transcranial sonography changes in heterozygotic carriers of the ATP7B gene. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usta, J.; Abu Daya, H.; Halawi, H.; Al-Shareef, I.; El-Rifai, O.; Malli, A.H.; Sharara, A.I.; Habib, R.H.; Barada, K. Homozygosity for Non-H1069Q Missense Mutations in ATP7B Gene and Early Severe Liver Disease: Report of Two Families and a Meta-analysis. JIMD Rep. 2012, 4, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berghe, P.V.; Stapelbroek, J.M.; Krieger, E.; de Bie, P.; van de Graaf, S.F.; de Groot, R.E.; van Beurden, E.; Spijker, E.; Houwen, R.H.; Berger, R.; et al. Reduced expression of ATP7B affected by Wilson disease-causing mutations is rescued by pharmacological folding chaperones 4-phenylbutyrate and curcumin. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1783–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walshe, J.M. Wilson disease: A most unusual patient. QJM Int. J. Med. 2016, 109, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zech, M.; Jech, R.; Boesch, S.; Škorvánek, M.; Weber, S.; Wagner, M.; Zhao, C.; Jochim, A.; Necpál, J.; Dincer, Y.; et al. Monogenic variants in dystonia: An exome-wide sequencing study. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chai, H.; Zhou, Q.; Wen, J.; Reddy, U.M.; Kastury, R.; Jiang, Y.; Mak, W.; Bale, A.E.; Zhang, H.; et al. Exome sequencing analysis on products of conception: A cohort study to evaluate clinical utility and genetic etiology for pregnancy loss. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousova, O.B.; Okishev, D.N.; Ignatova, T.M.; Balashova, M.S.; Boulygina, E.S. Hereditary Multiple Cerebral Cavernous Malformations Associated with Wilson Disease and Multiple Lipomatosis. World Neurosurg. 2017, 105, 1034.e1–1034.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, D.; Durkie, M.; Balac, P.; Sheard, D.; Goodeve, A.; Peake, I.; Quarrell, O.; Tanner, S. A study of Wilson disease mutations in Britain. Hum. Mutat. 1999, 14, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.Y.; Alipanahi, B.; Lee, L.J.; Bretschneider, H.; Merico, D.; Yuen, R.K.; Hua, Y.; Gueroussov, S.; Najafabadi, H.S.; Hughes, T.R.; et al. RNA splicing. The human splicing code reveals new insights into the genetic determinants of disease. Science 2015, 347, 1254806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Quiroga, S.A.; Rosales, J.; Arakaki, T.; Cordoba, M.; González-Morón, D.; Medina, N.; Garretto, N.S.; Kauffman, M.A. Timely diagnosis of Wilson’s disease using whole exome sequencing. Park. Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 1375–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barada, K.; Nemer, G.; ElHajj, II; Touma, J.; Cortas, N.; Boustany, R.M.; Usta, J. Early and severe liver disease associated with homozygosity for an exon 7 mutation, G691R, in Wilson’s disease. Clin. Genet. 2007, 72, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denoyer, Y.; Woimant, F.; Bost, M.; Edan, G.; Drapier, S. Neurological Wilson’s disease lethal for the son, asymptomatic in the father. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 402–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loudianos, G.; Dessì, V.; Lovicu, M.; Angius, A.; Nurchi, A.; Sturniolo, G.C.; Marcellini, M.; Zancan, L.; Bragetti, P.; Akar, N.; et al. Further delineation of the molecular pathology of Wilson disease in the Mediterranean population. Hum. Mutat. 1998, 12, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, H.; Bertoli-Avella, A.M.; Skrahina, V.; Anjum, M.N.; Waheed, N.; Saeed, A.; Beetz, C.; Perez-Lopez, J.; Rocha, M.E.; Alawbathani, S.; et al. Genomic testing in 1019 individuals from 349 Pakistani families results in high diagnostic yield and clinical utility. npj Genom. Med. 2020, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; McCann, C.J.; Ralle, M.; Ray, K.; Ray, J.; Lutsenko, S.; Jayakanthan, S. Analysis of Wilson disease mutations revealed that interactions between different ATP7B mutants modify their properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figus, A.; Angius, A.; Loudianos, G.; Bertini, C.; Dessi, V.; Loi, A.; Deiana, M.; Lovicu, M.; Olla, N.; Sole, G.; et al. Molecular pathology and haplotype analysis of Wilson disease in Mediterranean populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1995, 57, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, E.; Aguilar-Cevallos, J.; Silva-Garcia, R.; Ibarra, A. Cytokine and Growth Factor Activation In Vivo and In Vitro after Spinal Cord Injury. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 9476020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Li, H.Y.; Wu, J.F.; Wu, S.H.; Chen, H.L.; Yang, Y.H.; Hsu, Y.H.; Liou, B.Y.; Chang, M.H.; Ni, Y.H. Panel-Based Next-Generation Sequencing for the Diagnosis of Cholestatic Genetic Liver Diseases: Clinical Utility and Challenges. J. Pediatr. 2019, 205, 153–159.e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Liu, B.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Wu, B.; Liu, R.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Yu, S.; Chen, B.; et al. Clinical exome sequencing as the first-tier test for diagnosing developmental disorders covering both CNV and SNV: A Chinese cohort. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 57, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Yu, J.; Lou, J.; Peng, K.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J. Clinical and Genetic Spectra of Inherited Liver Disease in Children in China. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 631620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haer-Wigman, L.; van der Schoot, V.; Feenstra, I.; Vulto-van Silfhout, A.T.; Gilissen, C.; Brunner, H.G.; Vissers, L.; Yntema, H.G. 1 in 38 individuals at risk of a dominant medically actionable disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 27, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrand, M.S.; Jackson, V.E.; Scerri, T.S.; Van Reyk, O.; Coleman, M.; Braden, R.O.; Turner, S.; Rigbye, K.A.; Boys, A.; Barton, S.; et al. Severe childhood speech disorder: Gene discovery highlights transcriptional dysregulation. Neurology 2020, 94, e2148–e2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Fang, M.; Xiao, X.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, C. Genetic studies discover novel coding and non-coding mutations in patients with Wilson’s disease in China. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.R.; Forbes, J.R.; Roberts, E.A.; Walshe, J.M.; Cox, D.W. The Wilson disease gene: Spectrum of mutations and their consequences. Nat. Genet. 1995, 9, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, M.; Takaki, R.; Kobayashi, F.; Nagasaka, T.; Shindo, K.; Takiyama, Y. Multiple pseudofractures due to Fanconi’s syndrome associated with Wilson’s disease. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 2017, 57, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usta, J.; Wehbeh, A.; Rida, K.; El-Rifai, O.; Estiphan, T.A.; Majarian, T.; Barada, K. Phenotype-genotype correlation in Wilson disease in a large Lebanese family: Association of c.2299insC with hepatic and of p. Ala1003Thr with neurologic phenotype. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Xie, J.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Dong, Q.Y.; Dong, Y.; Ni, W.; Wu, Z.Y. Clinical features and outcome in patients with osseomuscular type of Wilson’s disease. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loudianos, G.; Dessì, V.; Angius, A.; Lovicu, M.; Loi, A.; Deiana, M.; Akar, N.; Vajro, P.; Figus, A.; Cao, A.; et al. Wilson disease mutations associated with uncommon haplotypes in Mediterranean patients. Hum. Genet. 1996, 98, 640–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margarit, E.; Bach, V.; Gómez, D.; Bruguera, M.; Jara, P.; Queralt, R.; Ballesta, F. Mutation analysis of Wilson disease in the Spanish population—Identification of a prevalent substitution and eight novel mutations in the ATP7B gene. Clin. Genet. 2005, 68, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, R.G.; Al-Musawi, B.M. Spectrum and classification of ATP7B variants with clinical correlation in children with Wilson disease. Saudi Med. J. 2025, 46, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindamo, M.C.; Judice, C.C.; Valladares, M.A.B.; da Rocha, B.P.R.; do Vale, E.A.; Pereira, A.M.F.; Santos, U.C.; Evangelista, A.S.; Calçado, F.L.V.; Rotman, V.; et al. Frequency of ATP7B Gene Mutations in a Brazilian Cohort of Patients with Wilson’s Disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Das, S.; De, S.; Dutta, T.; Roy, S.; Biswas, A.; Sengupta, M. An Effort to Identify Genetic Determinants in Siblings with Wilson Disease Manifesting Striking Clinical Heterogeneity: An Exome Profiling Study of Two Indian Families. Pediatr. Neurol. 2024, 155, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, A.; Topcu, V.; Cavdarli, B. Wilson Disease in a Turkish Population: Molecular Insights into an Old Disease with Reported and Novel Variants. Gazi Med. J. 2024, 35, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsek Papur, O.; Akman, S.A.; Cakmur, R.; Terzioglu, O. Mutation analysis of ATP7B gene in Turkish Wilson disease patients: Identification of five novel mutations. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2013, 56, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simsek Papur, Ö.; Asik Akman, S.; Terzioglu, O. Clinical and genetic analysis of pediatric patients with Wilson disease. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 26, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

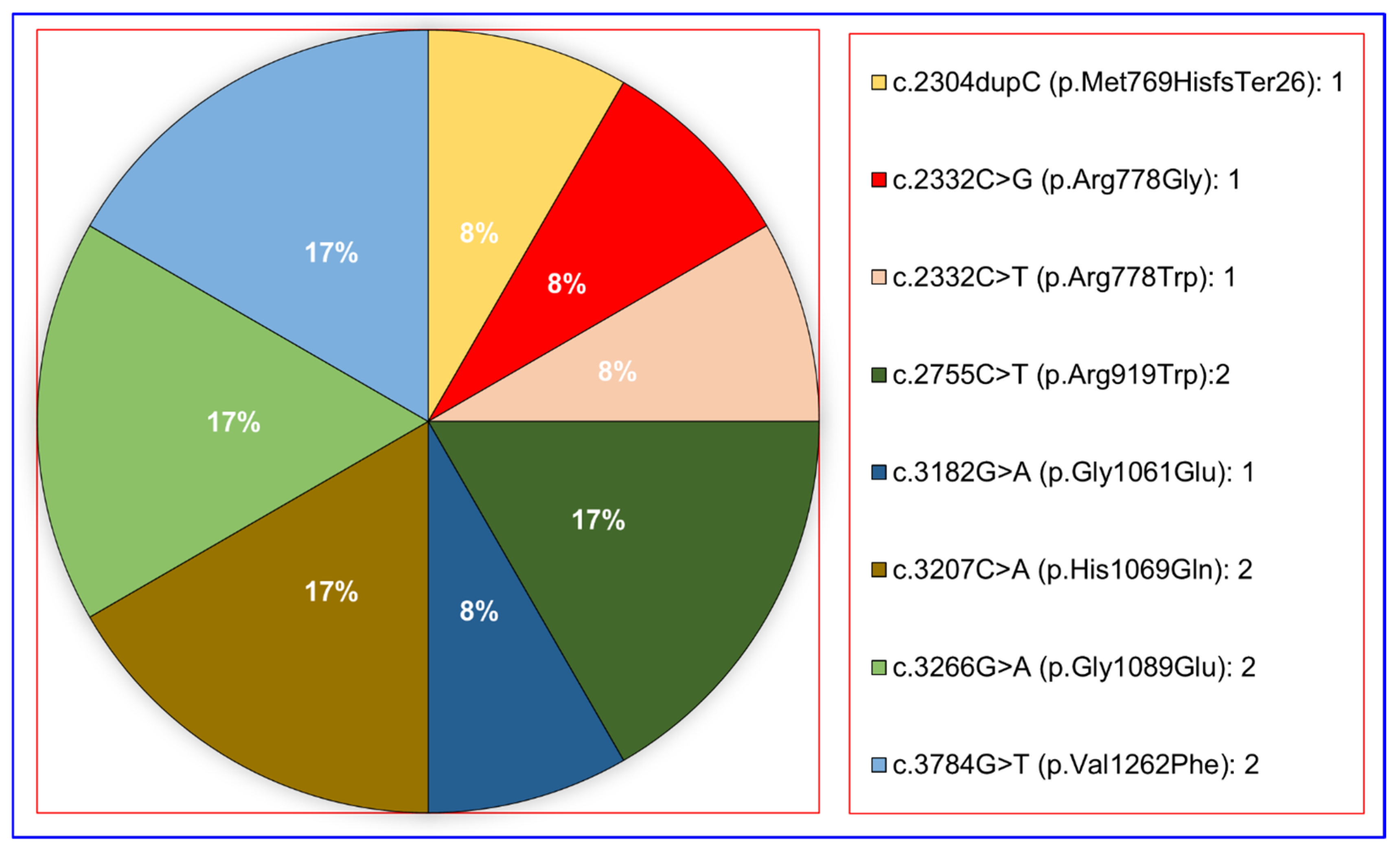
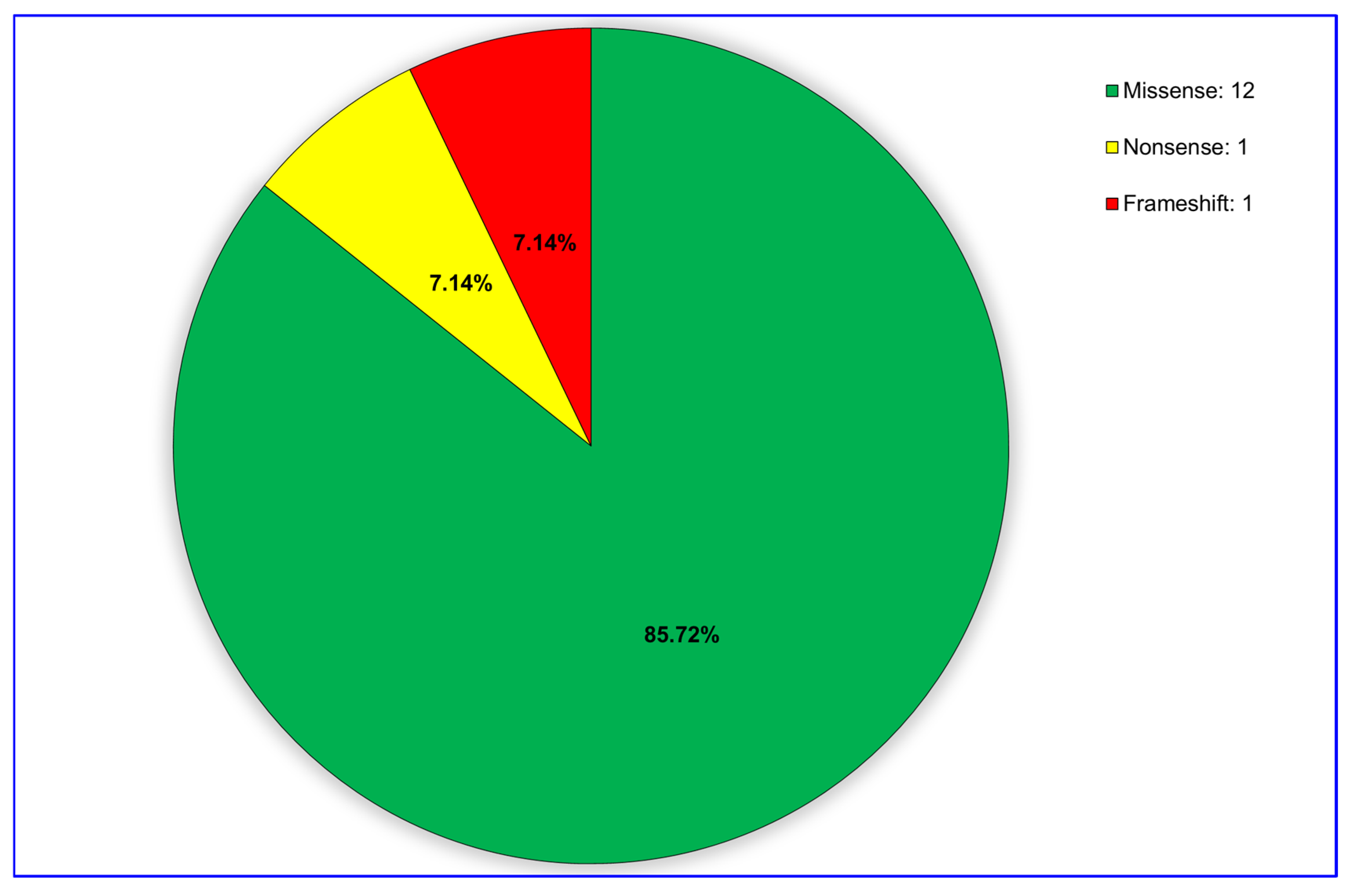
| Phenotype | Case ID | Mutation (cDNA) | Mutation (Protein) | Zygosity | Mutation Type | Protein Domain | Description | HGMD Accession ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WD with Hepatic Symptoms | H1 | c.3979C > G | p.Leu1327Val | Homozygous | Missense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM993113 (DM) |
| H2 | c.2332C > T | p.Arg778Trp | Homozygous | Missense | Transmembrane | Helical | CM970140 (DM) | |
| H3 | c.1846C > T | p.Arg616Trp | Heterozygous | Missense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM014320 (DM) | |
| c.3809A > G | p.Asn1270Ser | Heterozygous | Missense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM930060 (DM) | ||
| H4 | c.3207C > A | p.His1069Gln | Homozygous | Missense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM930059 (DM) | |
| H5 | c.1369C > T | p.Gln457Ter | Heterozygous | Nonsense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM992591 (DM) | |
| c.3704G > A | p.Gly1235Asp | Heterozygous | Missense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM1510476 (DM) | ||
| H6 | c.2071G > A | p.Gly691Arg | Homozygous | Missense | Transmembrane | Helical | CM980170 (DM) | |
| H7 | c.2071G > A | p.Gly691Arg | Homozygous | Missense | Transmembrane | Helical | CM980170 (DM) | |
| WD with Neurological Symptoms | N1 | c.3207C > A | p.His1069Gln | Homozygous | Missense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM930059 (DM) |
| N2 | c.3182G > A | p.Gly1061Glu | Homozygous | Missense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM992600 (DM) | |
| N3 | c.2332C > T | p.Arg778Trp | Homozygous | Missense | Transmembrane | Helical | CM970140 (DM) | |
| N4 | c.3207C > A | p.His1069Gln | Homozygous | Missense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM930059 (DM) | |
| N5 | c.2332C > G | p.Arg778Gly | Homozygous | Missense | Transmembrane | Helical | CM950112 (DM) | |
| N6 | c.2755C > T | p.Arg919Trp | Homozygous | Missense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM980176 (DM) | |
| N7 | c.2755C > T | p.Arg919Trp | Homozygous | Missense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM980176 (DM) | |
| N8 | c.2304dupC | p.Met769HisfsTer26 | Homozygous | Frameshift | Transmembrane | Helical | CI951903 (DM) | |
| N9 | c.3266G > A | p.Gly1089Glu | Heterozygous | Missense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM960130 (DM) | |
| c.3784G > T | p.Val1262Phe | Heterozygous | Missense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM992828 (DM) | ||
| N10 | c.3266G > A | p.Gly1089Glu | Heterozygous | Missense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM960130 (DM) | |
| c.3784G > T | p.Val1262Phe | Heterozygous | Missense | Topological | Cytoplasmic | CM992828 (DM) |
| ATP7B Variant | REVEL | CADD | PolyPhen | SIFT | Mutation Taster |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.3979C > G; p.Leu1327Val | Deleterious (Score: 0.793) | Deleterious (Score: 24.9) | Possibly Damaging | Damaging | Disease Causing |
| c.2332C > T; p.Arg778Trp | Deleterious (Score: 0.877) | Deleterious (Score: 25.4) | Probably Damaging | Damaging | Disease Causing |
| c.1846C > T; p.Arg616Trp | Deleterious (Score: 0.813) | Deleterious (Score: 25.8) | Probably Damaging | Damaging | Disease Causing |
| c.3809A > G; p.Asn1270Ser | Deleterious (Score: 0.896) | Deleterious (Score: 23.3) | Probably Damaging | Damaging | Disease Causing |
| c.3207C > A; p.His1069Gln | Deleterious (Score: 0.909) | Deleterious (Score: 23.0) | Probably Damaging | Damaging | Disease Causing |
| c.2071G > A; p.Gly691Arg | Deleterious (Score: 0.977) | Deleterious (Score: 29.4) | Probably Damaging | Damaging | Disease Causing |
| c.3704G > A; p.Gly1235Asp | Deleterious (Score: 0.949) | Deleterious (Score: 26.6) | Probably Damaging | Damaging | Disease Causing |
| c.3182G > A; p.Gly1061Glu | Deleterious (Score: 0.928) | Deleterious (Score: 28.3) | Probably Damaging | Damaging | Disease Causing |
| c.2332C > G; p.Arg778Gly | Deleterious (Score: 0.872) | Deleterious (Score: 24.6) | Probably Damaging | Damaging | Disease Causing |
| c.2755C > T; p.Arg919Trp | Deleterious (Score: 0.75) | Deleterious (Score: 32.0) | Probably Damaging | Damaging | Disease Causing |
| c.3266G > A; p.Gly1089Glu | Deleterious (Score: 0.933) | Deleterious (Score: 28.0) | Probably Damaging | Tolerated | Disease Causing |
| c.3784G > T; p.Val1262Phe | Deleterious (Score: 0.975) | Deleterious (Score: 24.4) | Probably Damaging | Damaging | Disease Causing |
| Phenotype | Case ID | Gene Variant | Exon Location | Allele Frequency (%) | Functional Consequence According to | Reported in | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleotide Change | Protein Change | gnomAD v4.1 | HGMD | |||||
| WD with Hepatic Symptoms | H1 | c.3979C > G | p.Leu1327Val | 19 | NO | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [30,31] |
| H2 | c.2332C > T | p.Arg778Trp | 19 | 0.007125 | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38] | |
| H3 | c.1846C > T | p.Arg616Trp | 8 | 0.001673 | Compound Heterozygous Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [38,39,40,41,42,43] | |
| c.3809A > G | p.Asn1270Ser | 18 | 0.01431 | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [31,32,36,38,41,42,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,107] | ||
| H4 | c.3207C > A | p.His1069Gln | 11 | 0.1019 | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [31,32,34,36,41,42,46,50,54,59,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97] | |
| H5 | c.1369C > T | p.Gln457Ter | 5 | NO | Compound Heterozygous Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [50,98,99] | |
| c.3704G > A | p.Gly1235Asp | 12 | NO | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [42,100] | ||
| H6 | c.2071G > A | p.Gly691Arg | 8 | NO | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [31,32,50,101,102,103] | |
| H7 | c.2071G > A | p.Gly691Arg | 8 | NO | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [31,32,50,101,102,103] | |
| WD with Neurological Symptoms | N1 | c.3207C > A | p.His1069Gln | 11 | 0.1019 | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [31,32,34,36,41,42,46,50,54,59,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97] |
| N2 | c.3182G > A | p.Gly1061Glu | 14 | NO | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [31,32,52,98,104,105] | |
| N3 | c.2332C > T | p.Arg778Trp | 19 | 0.007125 | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38] | |
| N4 | c.3207C > A | p.His1069Gln | 11 | 0.1019 | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [31,32,34,36,41,42,46,50,54,59,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97] | |
| N5 | c.2332C > G | p.Arg778Gly | 19 | 0.001177 | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [31,34,36,42,46,50,73,95,106,107] | |
| N6 | c.2755C > T | p.Arg919Trp | 12 | 0.003222 | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [31,38,48,77,103] | |
| N7 | c.2755C > T | p.Arg919Trp | 12 | 0.003222 | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [31,38,48,77,103] | |
| N8 | c.2304dupC | p.Met769HisfsTer26 | 8 | 0.009789 | Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [32,33,38,42,43,46,48,49,50,53,57,65,77,89,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117] | |
| N9 | c.3266G > A | p.Gly1089Glu | 13 | NO | Compound Heterozygous Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [30,42,93] | |
| c.3784G > T | p.Val1262Phe | 13 | 0.0005576 | Compound Heterozygous Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [30,36,93] | ||
| N10 | c.3266G > A | p.Gly1089Glu | 13 | NO | Compound Heterozygous Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [30,42,93] | |
| c.3784G > T | p.Val1262Phe | 13 | 0.0005576 | Compound Heterozygous Loss of Function | Disease Mutation | [30,36,93] | ||
| Case ID | Age (Year) | Gender | AST | ALT | ALP | GGT | TBil | DBil | CRE | PLT | CP | 24 h U-Cu | PC | RelWD | KFR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 13 | M | 7 | 17 | 78 | 9 | 0.46 | 0.12 | 0.5 | 175 | 0.08 | 323 | Cousins | – | NA |
| H2 | 16 | M | 64 | 55 | 173 | 97 | 1.04 | 0.21 | 0.8 | 345 | NA | 343 | – | – | Pos |
| H3 | 16 | F | 33 | 33 | 200 | 47 | 0.4 | 0.09 | 0.6 | 150 | 0.12 | 438 | – | 2 Siblings, 3 Maternal Relatives | Neg |
| H4 | 11 | M | 93 | 102 | 198 | 175 | 0.43 | 0.09 | 0.9 | 202 | 11.8 | 403 | Cousins | Paternal Uncle | Pos |
| H5 | 13 | M | 54 | 62 | 863 | 43 | 0.48 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 283 | 32.02 | 992 | Cousins | – | Neg |
| H6 | 9 | F | 19 | 15 | 155 | 10 | 0.9 | 0.19 | 0.6 | 265 | NA | NA | Cousins | Sibling | Neg |
| H7 | 8 | F | 32 | 25 | 277 | 19 | 0.6 | 0.09 | 0.5 | 248 | 0.33 | 402 | Cousins | Sibling | Neg |
| N1 | 24 | M | 58 | 69 | 238 | 349 | 0.86 | 0.27 | 0.8 | 203 | NA | 1066 | Cousins | Sibling | Pos |
| N2 | 15 | F | 492 | 457 | 96 | 83 | 1.2 | 0.46 | 1.6 | 153 | 0.08 | 137 | – | – | Pos |
| N3 | 6 | M | 33 | 27 | 339 | 17 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 312 | 0.28 | 410 | NA | – | Pos |
| N4 | 23 | F | 21 | 10 | 49 | 10 | 0.34 | 0.08 | 0.9 | 262 | 15.7 | 405 | Cousins | – | Pos |
| N5 | 20 | F | 99 | 104 | 351 | 280 | 6.7 | 3.54 | 0.7 | 23 | 10 | 25 | Cousins | – | Pos |
| N6 | 24 | F | 22 | 23 | 100 | 7 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 194 | 0.07 | 190 | Cousins | – | Pos |
| N7 | 20 | F | 36 | 41 | 125 | 8 | 1.7 | 0.27 | 0.6 | 321 | 0.06 | 29 | Cousins | Sibling | Neg |
| N8 | 10 | M | 25 | 24 | 500 | 24 | 1.9 | 0.39 | 0.7 | 31 | 0.08 | 3062 | Cousins | – | Neg |
| N9 | 18 | M | 20 | 26 | 136 | 86 | 0.46 | 0.12 | 0.8 | 250 | 0.09 | 2467 | Cousins | Sibling | Neg |
| N10 | 21 | M | 22 | 22 | 95 | 20 | 1.86 | 0.35 | 0.8 | 259 | NA | 1152 | Cousins | Sibling | Pos |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akbulut, S.; Is, S.; Koprulu, T.K.; Varol, F.I.; Kucukakcali, Z.; Colak, C.; Koc, A.; Tekin, S.; Yilmaz, S. Evaluation of the Relationship Between Neurologic Manifestations and Genetic Mutations in Wilson’s Disease with Next-Generation Sequencing. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212689
Akbulut S, Is S, Koprulu TK, Varol FI, Kucukakcali Z, Colak C, Koc A, Tekin S, Yilmaz S. Evaluation of the Relationship Between Neurologic Manifestations and Genetic Mutations in Wilson’s Disease with Next-Generation Sequencing. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(21):2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212689
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkbulut, Sami, Seyma Is, Tugba Kul Koprulu, Fatma Ilknur Varol, Zeynep Kucukakcali, Cemil Colak, Ahmet Koc, Saban Tekin, and Sezai Yilmaz. 2025. "Evaluation of the Relationship Between Neurologic Manifestations and Genetic Mutations in Wilson’s Disease with Next-Generation Sequencing" Diagnostics 15, no. 21: 2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212689
APA StyleAkbulut, S., Is, S., Koprulu, T. K., Varol, F. I., Kucukakcali, Z., Colak, C., Koc, A., Tekin, S., & Yilmaz, S. (2025). Evaluation of the Relationship Between Neurologic Manifestations and Genetic Mutations in Wilson’s Disease with Next-Generation Sequencing. Diagnostics, 15(21), 2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212689








